1. Tumor angiogenesis and alternative mode of tumor vascularization
Vasculogenesis, or the creation of capillaries from endothelial cells differentiating in situ from mesodermal cells, causes the first blood vessels to arise throughout embryonic life. In this manner, the primitive vascular plexus and the primitive heart are created. The creation of capillaries from pre-existing vessels, such as capillaries and post-capillary venules, is referred to as angiogenesis. This process is based on endothelial sprouting microvascular growth. The first step in angiogenesis is the local breakdown of the basement membrane enclosing the capillaries. Next, the underlying endothelial cells invade the surrounding stroma in the path of the angiogenic stimulation. A network of new blood vessels is formed as a result of endothelial cell migration, which is accompanied by the proliferation of endothelial cells and their arrangement into three-dimensional structures. Physiological angiogenesis only happens during certain distinct processes in adults, including female reproductive cycle, tissue repair, and wound healing.
Folkman first suggested the idea that angiogenesis, which is closely related to tumor growth, is correlated with microvascular density, or the number of microvessels that can be counted in a sample tumor area using antibodies that are specific for endothelial cell markers (e.g. CD31, CD34, or factor VIII related antigen). Intra-tumoral microvessel density and prognosis have been found to be positively correlated in solid tumors, according to the greater part of research literature. Numerous studies have found associations between intratumoral microvascular density, expression of angiogenic growth factors, tumour growth, and the occurrence of metastases. These findings indicate that intratumoral microvascular density provides crucial information on the extent and role of tumor vasculature [
1].
An avascular phase precedes a vascular phase in the process of tumor growth. The majority of tumors develop and persist in situ, devoid of angiogenesis, for a considerable amount of time before starting angiogenic process [
2]. The histopathological image characterized by a small colony of neoplastic cells that reaches a stable state before becoming invasive, represents the avascular phase. In this situation, metabolites and catabolites are distributed through the surrounding tissue by simple diffusion. While cells in the deeper part of the tumor degenerate, those on the tumor's periphery continue to grow. The production and release of angiogenic factors or a decrease in the level of endogenous angiogenic inhibitors have both been linked to the activation of the angiogenic switch.
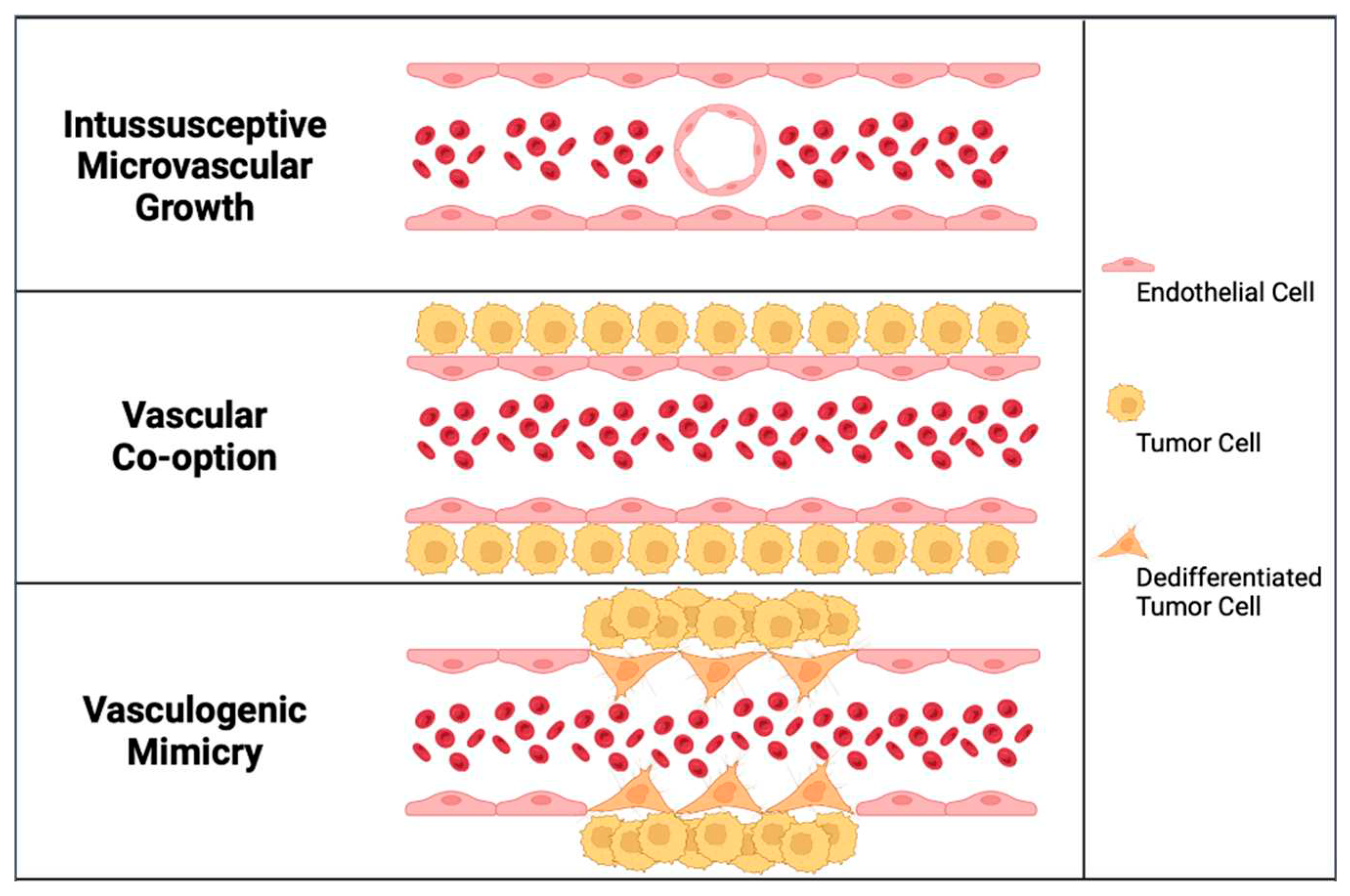
In the last thirty years, alternative modes of vascularization of tumor growth have been described. These techniques include intussusceptive microvascular growth (IMG), vascular co-option, and vasculogenic mimicry (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2) [
3,
4,
5].
In IMG, the expansion of the vascular network is achieved by inserting tissue columns into the vascular lumen of pre-existing vessels [
3]. IMG occurs in various tumors, including colon and breast carcinomas, melanoma, and gliomas [
6,
7,
8,
9]. IMG has several advantages over sprouting angiogenesis, including faster blood vessel formation, metabolic cost savings due to the lack of extensive endothelial cell proliferation, basement membrane degradation, and surrounding tissue invasion during sprouting angiogenesis, and less leaky capillaries as a result.
The second pathway involves cancer cells invading and occupying normal tissues to utilize pre-existing vessels, which is referred to as vascular or vessel co-option. The field of vessel co-option was introduced by Pezzella and coworkers in 1997 [
10]. They demonstrated that tumor growth in non-small cell lung carcinomas occurs without angiogenesis, and that, in this context, cancer cells survive by using pre-existing vessels as a source of oxygen and metabolites. An example of vascular co-option is represented in
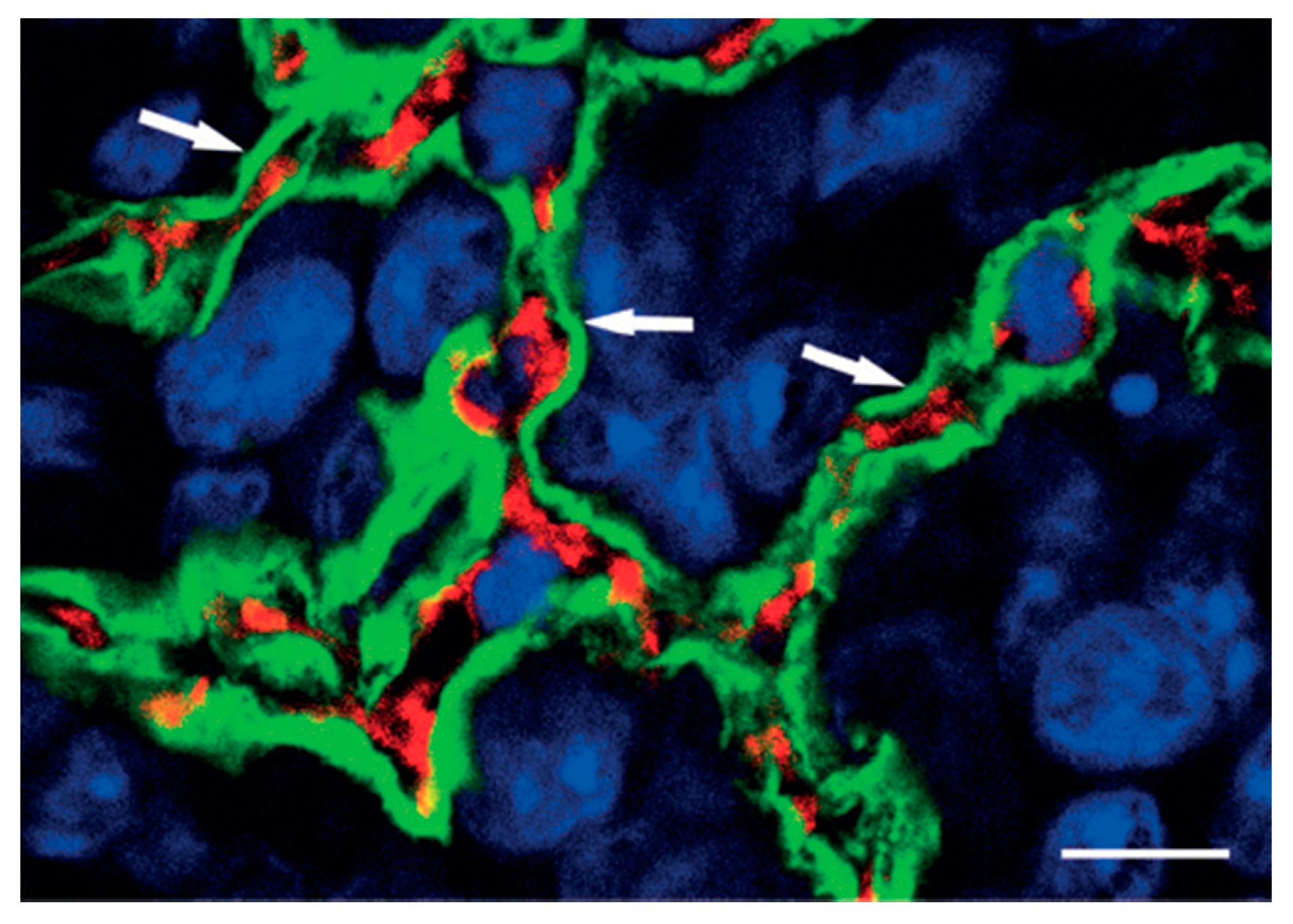
Figure 1, that shows, in the outer parts of lung metastases, the conservation of the alveolar architecture. SCID mice were injected with HT1080 tumor cells to produce experimental metastases. Tumor cells penetrate the alveolar air space after extravasation and the formation of tiny interstitial colonies. Type I alveolar epithelial cells were identified by immunostaining with anti-podoplanin antibodies (green fluorescence), blood vessels were identified by immunostaining with anti-CD31 antibodies to mark endothelial cells (red fluorescence), and nuclear staining was obtained by immunostaining with TOTO-3 (blue fluorescence).
In 1999, Holash et al. reported that tumor cells co-opt pre-existing vessels and grow around them as cuffs [
11]. These Authors evaluated the possibility that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and angiopoietins (Angs) interact during tumor angiogenesis is a rat glioma experimental model. They demonstrated that early after tumor cells implantation, tumor vascularization was attributable to the co-option of existing blood vessels by tumor cells. By 4 weeks after tumor cells implantation, blood vessels within the core of the tumors regressed because of the destabilizing action of Ang-2 on the vessel wall. The coopted vasculature trigger an apoptotic cascade, likely by autocrine production of Ang-2, which exterminates most of the dependant tumor and causes widespread tumor death. This is the outcome of a host defensive mechanism that has been engaged. When the ratio of VEGF to Ang-2 is high, the new tumor vessels continue to grow; when it is low, the new tumor vessels contract. The interaction of VEGF and Ang-2 at the edge of the expanding tumor mass results in angiogenesis.
In human melanoma cells, Maniotis and colleagues (1999) initially identified the third alternative route of tumor vascularization, which they named vasculogenic mimicry to underline the development of new blood vessels independently of angiogenesis [
12]. ''Vasculogenic'' was chosen to denote the pathway’s de novo formation, and ‘’mimicry'' was chosen since the paths employed by tumor cells to convey fluid to tissues were obviously not blood vessels. Laminin 5 and matrix metalloproteinases-1, -2, and -9 (MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-9) were significantly more expressed in highly aggressive human cutaneous melanoma cell lines when compared to less aggressive cell lines, according to a microarray gene chip analysis. Vasculogenic mimicry describes the highly aggressive cancers' capacity to produce blood arteries made of tumor cells rather than endothelial cells. Accordingly, the development of blood vessels in tumors may be directly influenced by cancer cells.
Another theory is that tumor cells take the place of the endothelial cell lining, creating what are known as mosaic vasculature, in which both endothelium and tumor cells help to construct vascular tubes [
13]. This study used endogenous green fluorescent protein (GFP) to label tumor cells and CD105 to identify endothelial cells. It showed that 15% of the colon carcinoma xenografts' perfused vasculature were made up of mosaic vessels.
2. Angiogenesis and microvascular density in Hodgkin’s lymphomas
Lymphomas constitute a large group of lymphoproliferative disorders. Hodgkin Lymphomas (HL), a type of lymphoma, are characterized by the presence of Hodgkin–Reed–Stenberg (HRS) cells, which can be either mono- or multi-nucleated. HL can be further classified into classical HL (cHL) and nodular lymphocyte-predominant HL (NLPHL). cHL, which is the more common subtype (making up about 95% of HL cases), includes mixed cellularity, nodular sclerosis, and lymphocyte-rich subtypes. In contrast, NLPHL is a rare subtype, accounting for only 5% of HL cases, and is characterized by lymphocyte-predominant (LP) cells [
14].
Inflammatory cells like T and B cells, tumor associated macrophages (TAMs), mast cells, plasma cells, eosinophils, myeloid derived suppressor cells, and NK cells are present in the HL tumor microenvironment and secrete cytokines and chemokines that control tumor angiogenesis, progression, and metastasis.
The key mediator of tumor angiogenesis is the VEGF. In HL, both HRS cells and TAMs secrete VEGF [
15,
16]. However, the lack of a connection between VEGF expression and microvascular density suggests that other pro- and anti-angiogenic molecules, such as fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), MMP-2, MMP-9, and hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1), may also play a role in regulating angiogenesis in HL [
17]. At least two different angiogenic processes appear to be involved in the promotion of lymphoma development and progression: paracrine effects of the proangiogenic tumor microenvironment and autocrine stimulation of tumor cells via production of VEGF and VEGFR by lymphoma cells. When compared to data from other solid tumors, there is little information available regarding the role of the HGF/c-MET signaling pathway in lymphomas. In B cell lymphoma cell lines and patient samples, however, there was no evidence of MET gene amplification.
Furthermore, it is unclear whether aggressive lymphomas are linked to high microvessel density. According to a group of scientists, microvascular density is greater in aggressive than indolent lymphomas as well as lymphomas compared to reactive nodes. However, it has been discovered that the microvascular density in reactive nodes is more or on par with that seen in lymphomas, particularly large cell lymphomas.
Korkolopoulou et al. demonstrated that in HL microvascular density is reduced with stage progression according to Ann Arbor stages I-IV [
18]. Further research investigated the expression of HIF-1α in HL and found that it was present in HRS cells but did not correlate with increased microvascular density [
19]. Another study focused on FGF cytokines and their receptors in HRS cells but did not find a direct correlation between their expression and the formation of new blood vessels [
20]. In patients with HL, pre-treatment levels of VEGF and HGF were elevated but significantly reduced after therapy, and both pre- and post-treatment VEGF levels were found to be predictive of survival [
21]. Furthermore, elevated serum VEGF levels in pre-treatment HL patients were reduced in cases of prolonged complete remission, but still remained higher compared to healthy individuals [
22]. Dimtsas et al. evaluated the expression pattern of VEGF-A and VEGF receptor-1 and -2 (VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2) in cHL and NLPHL and found that they were expressed in the HRS and lymphocytic and histiocytic cells [
23].
3. Angiogenesis and microvascular density in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas
B-cell lymphomas, including diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs), follicular lymphomas (FLs), extranodal marginal zone lymphomas, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and mantle cell lymphomas (MCLs), represent the 88% of all non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (NHLs), while T and natural killer (NK) cell lymphomas the 12%. T-cell lymphomas are more aggressive than B-cell lymphomas [
24].
In Burkitt's lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL), microvascular density tends to be higher, while tends to intermediate values in DLBCL, and is lower FL [
25]. In DLBCL, an increased vascular density (determined by the vascular maturation index, calculated as the ratio of LH39/CD34
+ to all CD34
+ vessels.) has been demonstrated compared to that in FL [
26]. Ultrastructurally, the stroma of B cell-NHLs contains immature vessels. These capillaries are made up of two endothelial cells that are parallel to one another and have thicker cytoplasm, creating a lumen that resembles a slit [
25]. The distinguishing feature of follicular intermediate- and low-grade B-cell NHLs is the continuous basement membrane enclosing differentiated fenestrated capillaries. The blood vessels lumen in low-grade B-cell NHLs can develop in two different ways: either by curving the endothelial cell body or, more frequently, by the fusion of intracellular vacuoles in undifferentiated endothelial cells. High-grade B-cell NHLs, on the other hand, frequently have a distinct pattern of blood vessel growth that is defined by the creation of a slit-like lumen through neo-angiogenesis [
27]. There is no known relationship between the microvascular density and the histologic subtype of NHLs [
28].
Other studies on NHLs and DLBCL have found a correlation [
29,
30] or no correlation between microvascular density and VEGF expression [
31,
32,
33]. Gratzinger et al. reported that the average microvascular densities significantly correlates with the intensity of VEGF staining [
29]. Studies have shown that in both cutaneous T-cell and B-cell lymphomas, the microvascular density is higher compared to skin with a benign cutaneous lymphoid infiltrate [
34,
35,
36]. Studies have shown that in both cutaneous T-cell and B-cell lymphomas, the microvascular density is higher compared to skin with a benign cutaneous lymphoid infiltrate [
37,
38]. According to research, aggressive T cell lymphomas exhibit high levels of expression of VEGF-A compared to indolent B cell lymphomas [
39]. This suggests that VEGF-A may play a role in the progression and aggressiveness of certain types of lymphoma. It is worth noting that while a minority of indolent follicular lymphomas (FLs) do show variable expression of VEGF-A, it is not a consistent feature across all indolent B cell lymphomas [
31,
40]. VEGFRs expression levels are correlated with the level of VEGF expression in DLBCL [
29]. CLL also expresses VEGFRs [
41]. VEGF prevents apoptosis and increase the phosphorylation of VEGFRs. Immunocytochemical methods demonstrated the expression of VEGFRs, suggesting that VEGF transduction pathway is active in CLL [
41].
HIF-1 and -2 and VEGF have a lower expression in indolent compared to aggressive lymphomas [
42]. Indolent lymphomas transforming into aggressive lymphoma, express VEGF-A [
43]. Angiogenesis is also correlated with mast cell density in B-NHL, according to the capacity of mast cells to release angiogenic factors [
27].
4. Vasculogenic mimicry and IMG in lymphomas
Crivellato et al. demonstrated that in B-cell NHLs at the ultrastructural level, tumor cells are closely intermingled with endothelial cells and that this relationship can be recognized in the early stages of vessel formation, as an expression of vasculogenic mimicry [
27]. Lymphoid tumor cells are indeed closely intermingled with vacuolated endothelial cells and that this relationship can be recognized in the early stages of vessel formation when immature endothelial cells have not yet formed a vascular lumen. Moreover, the tumor cells appeared to be completely enveloped by the cytoplasmic expansions of one or more endothelial cells, while vascular spaces were occasionally lined by lymphoid tumor cells. Moreover, Crivellato et al. showed that both low- and high-grade B-NHLs develop transluminal bridges in larger vessels, causing the parent vessel to split into two or more sections, suggesting that an intussusceptive modality of vascular growth also takes place in B-NHLs. This vascular pattern was more frequent in the center than on the margins of the lymphomas. [
27].
Using immunocytochemistry and confocal laser imaging, more proof of vasculogenic mimicry has been found in primary diffuse central nerve system lymphomas (PCNSL). Studies have demonstrated that a variety of cells, including CD20+ tumor cells, factor CD31+ endothelial cells, aquaporin-4 (AQP4)+ tumor cells, CD31+ endothelial cells, and CD20+ and AQP4+ tumor cells, engage in vessel formation [
44]. PCNS B-cell lymphoma tumor cells show positivity with an anti-CD20 antibody. Blood-brain barrier stability and activity are associated with AQP4 expression, and this expression shifts in neurological conditions that disrupt the BBB. Peritumoral edema is linked with AQP4 expression, and AQP4 is significantly increased and redistributed over the borders of tumor cells in glioblastoma.
In 2003, Passalidou et al. showed that microvascular density was significantly greater in the paracortex than in the follicles in reactive lymph nodes and in FL. Interestingly, both reactive and neoplastic follicles did not significantly differ in microvascular density. In addition, the paracortex of reactive nodes showed higher microvascular density compared to FL and DLFL paracortex, demonstrating that tumor-induced angiogenesis is less effective than normal angiogenesis in responsive nodes [
26]. Taken together, these findings suggest that vasculogenic mimicry and alternative modes of vascularization may play a significant role in the progression and survival of lymphomas and may contribute to the development of new therapeutic strategies targeting tumor angiogenesis.
5. Prognostic and therapeutic implications of angiogenesis in lymphomas and alternative mode of vascular growth as a mechanism of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies
Due to the variability of illnesses, various classifications, and research techniques, the prognostic and predictive significance of microvascular density and angiogenic variables in lymphomas is still debatable (immunohistochemistry, serum levels of angiogenic markers, mRNA extraction). Estimating microvascular density and VEGF are important for the development of NHL. Numerous investigations have investigated the connection between microvascular density, VEGF expression, and NHL prognosis; however, these studies have produced contradictory findings. Chemo resistant DLBCL and those with chemo sensitive lymphomas have different patterns of microvascular densities [
41]. Progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) are higher in FL patients treated with chemotherapy in conjunction with anti-angiogenic interferon-alpha2b, when the microvascular density is high before the treatment [
40]. However, there was no association between elevated microvascular density and VEGF expression in individuals with DBLC after anthracycline treatment [
45]. High serum VEGF levels before treatment have been proven to be prognostic indicators for survival in NHL [
46]. However, it has been found that the pre-treatment serum level of VEGF is negatively correlated with both OS rate and disease-free survival in T and B cell lymphomas [
47]. High serum VEGF levels have also been linked to unfavorable outcomes in DLBCL patients [
48].
Furthermore, FGFR-1 expression correlates with lower frequencies of full remission in NHL patients, whereas FGF-2 expression is related with poor OS and PFS [
49]. Moreover, Additionally, blood FGF-2 levels did not change following chemotherapy, nor a connection was established between microvascular density and the histological grade or prognosis [
49]. High levels of FGF-2 before therapy have been found to independently predict survival, irrespective of other risk factors [
46]. Soluble levels of VEGF, FGF-2, and PDGF-β declined after radiotherapy in NHL patients [
50]. Blocking the VEGF-VEGFR pathway with neutralizing antibodies or tyrosine kinase inhibitors reduced p-STAT-3 levels and induce apoptosis in CLL [
51]. High expression of both VEGF and VEGFR-1 in DBLC patients has been linked to increased OS and PFS following anthracycline therapy [
45]. However, higher tissue expression of VEGF has been associated with unfavorable outcomes [
52]. When compared to reactive lymph nodes, VEGF-A has been discovered to be overexpressed in tumor and endothelial cells in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, and this overexpression is linked to a short survival time [
53]. Increased VEGF expression is linked to aggressive DLBCL and subgroups of DLBCL with poor prognosis, as well as the transition from indolent B cell lymphoma [
54]. VEGF expression in PCNSLs correlates with microvascular density, is linked to longer survival, and changes to the blood-brain barrier [
55].
An adaptive response to conventional use of antitumor and antiangiogenic drugs to reestablish the normal characteristics of the vasculature, improving drug delivery and treatment efficacy, is represented by a transition from angiogenesis to IMG [
56]. Sprouting angiogenesis is common in untreated tumors, but IMG is common following short-term therapy, restoring a vasculature with a modest rate of endothelial proliferation. A major path of acquired resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy is non-angiogenic growth. Using the existing vasculature and increasing the fraction of co-opted vessels, tumor cells may be able to resist anti-VEGF treatments [
57]. One way of acquiring resistance to anti-VEGF treatments is vascular co-option [
58,
59,
60].
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
The last literature evidence has clearly demonstrated that angiogenesis is not a hallmark of cancer, but that tumors may have both angiogenic and non-angiogenic areas. This different mechanism of tumor vascularization is influenced by the interactions of tumor cells with their microenvironment. Non-angiogenic growth is a critical mechanism through which tumor cells acquire resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. After taking over an artery, the cancer cell can travel along the abluminal vascular surface or develop surrounding the vessels. A potential tactical move to stop perivascular spread and local growth is to target the molecular machinery that causes co-option. To prevent an angiogenic neoplasm treated with anti-angiogenic medications from "escape" by becoming non-angiogenic while a non-angiogenic tumor could "escape" anti-co-option medications, one developing treatment strategy combines anti-angiogenic chemicals with blocking of vascular co-option.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.R; validation, D.R., R.T., T.A., G.I., G.S.; D.R., writing—original draft preparation, D.R.; writing—review and editing, D.R., A. D.; funding acquisition, D.R, G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This work was supported by Associazione “Il Sorriso di Antonio,” Corato, Italy, and Associazione Italiana Contro le Leucemie, Linfomi e Mielomi (AIL), Bari, Italy.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Folkman, J. Tumor Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Nico, B.; Crivellato, E.; Roccaro, A.M.; Vacca, A. The History of the Angiogenic Switch Concept. Leukemia 2007, 21, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Djonov, V. Intussusceptive Microvascular Growth in Tumors. Cancer Lett. 2012, 316, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Pezzella, F. Overview on the Different Patterns of Tumor Vascularization. Cells 2021, 10, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugassy, C.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Ribatti, D.; Pezzella, F.; Barnhill, R.L. Vessel Co-Option and Angiotropic Extravascular Migratory Metastasis: A Continuum of Tumour Growth and Spread. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djonov V; Hogger K; Sedlacek R; Laissue J; Draeger A MMP-19: Cellular Localization of a Novel Metalloproteinase within Normal Breast Tissue and Mammary Gland Tumours. J Pathol 2001, 195, 147–55. [CrossRef]
- Nico, B.; Crivellato, E.; Guidolin, D.; Annese, T.; Longo, V.; Finato, N.; Vacca, A.; Ribatti, D. Intussusceptive Microvascular Growth in Human Glioma. Clin. Exp. Med. 2010, 10, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patan, S.; Munn, L.L.; Jain, R.K. Intussusceptive Microvascular Growth in a Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Xenograft: A Novel Mechanism of Tumor Angiogenesis. Microvasc. Res. 1996, 51, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Nico, B.; Floris, C.; Mangieri, D.; Piras, F.; Ennas, M.G.; Vacca, A.; Sirigu, P. Microvascular Density, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Immunoreactivity in Tumor Cells, Vessel Diameter and Intussusceptive Microvascular Growth in Primary Melanoma. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 14, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella, F.; Pastorino, U.; Tagliabue, E.; Andreola, S.; Sozzi, G.; Gasparini, G.; Menard, S.; Gatter, K.C.; Harris, A.L.; Fox, S.; et al. Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma Tumor Growth without Morphological Evidence of Neo-Angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Holash, J.; Maisonpierre, P.C.; Compton, D.; Boland, P.; Alexander, C.R.; Zagzag, D.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Wiegand, S.J. Vessel Cooption, Regression, and Growth in Tumors Mediated by Angiopoietins and VEGF. Science 1999, 284, 1994–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniotis, A.J.; Folberg, R.; Hess, A.; Seftor, E.A.; Gardner, L.M.G.; Pe’er, J.; Trent, J.M.; Meltzer, P.S.; Hendrix, M.J.C. Vascular Channel Formation by Human Melanoma Cells in Vivo and in Vitro: Vasculogenic Mimicry. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.S.; di Tomaso, E.; McDonald, D.M.; Jones, R.; Jain, R.K.; Munn, L.L. Mosaic Blood Vessels in Tumors: Frequency of Cancer Cells in Contact with Flowing Blood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2000, 97, 14608–14613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 Revision of the World Health Organization Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doussis-Anagnostopoulou, I.A.; Talks, K.L.; Turley, H.; Debnam, P.; Tan, D.C.; Mariatos, G.; Gorgoulis, V.; Kittas, C.; Gatter, K.C. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Is Expressed by Neoplastic Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg Cells in Hodgkin’s Disease. J. Pathol. 2002, 197, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, B.; Naresh, K.N. Re: Doussis-Anagnostopoulou et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Is Expressed by Neoplastic Hodgkin–Reed–Sternberg Cells in Hodgkin’s Disease. J Pathol 2002; 197: 677–683. J. Pathol. 2003, 201, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citak, E.C.; Oguz, A.; Karadeniz, C.; Akyurek, N. Immunohistochemical Expression of Angiogenic Cytokines in Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma. Pathol. - Res. Pract. 2008, 204, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkolopoulou, P.; Thymara, I.; Kavantzas, N.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Angelopoulou, M.K.; Kokoris, S.I.; Dimitriadou, E.M.; Siakantaris, M.P.; Anargyrou, K.; Panayiotidis, P.; et al. Angiogenesis in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: A Morphometric Approach in 286 Patients with Prognostic Implications. Leukemia 2005, 19, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passam, F.H.; Alexandrakis, M.G.; Kafousi, M.; Fotinou, M.; Darivianaki, K.; Tsirakis, G.; Roussou, P.A.; Stathopoulos, E.N.; Siafakas, N.M. Histological Expression of Angiogenic Factors: VEGF, PDGFRalpha, and HIF-1alpha in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2009, 205, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khnykin, D.; Troen, G.; Berner, J.-M.; Delabie, J. The Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factors and Their Receptors in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, F.J.; Vose, J.M.; Do, K.-A.; Johnson, M.M.; Manshouri, T.; Bociek, G.; Bierman, P.J.; O’Brien, S.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Armitage, J.O.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Circulating Angiogenic Factors in Patients with Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma or Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2004, 28, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, A.; Olmos, D.; Villareal, V.; Torres, E.; Pajares, B.I.; Alba, E. Elevated Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Pretreatment Levels Are Correlated with the Tumor Burden in Hodgkin Lymphoma and Continue to Be Elevated in Prolonged Complete Remission. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2007, 7, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimtsas, G.S.; Georgiadi, E.C.; Karakitsos, P.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Thymara, I.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Patsouris, E.; Kittas, C.; Doussis-Anagnostopoulou, I.A. Prognostic Significance of Immunohistochemical Expression of the Angiogenic Molecules Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2 in Patients with Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.I.; Miller, T.P.; Grogan, T.M. New REAL Clinical Entities. Cancer J. Sci. Am. 1998, 4 Suppl 2, S5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ribatti, D.; Vacca, A.; Nico, B.; Fanelli, M.; Roncali, L.; Dammacco, F. Angiogenesis Spectrum in the Stroma of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas. An Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Study. Eur. J. Haematol. 1996, 56, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passalidou, E.; Stewart, M.; Trivella, M.; Steers, G.; Pillai, G.; Dogan, A.; Leigh, I.; Hatton, C.; Harris, A.; Gatter, K.; et al. Vascular Patterns in Reactive Lymphoid Tissue and in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivellato, E.; Nico, B.; Vacca, A.; Ribatti, D. B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas Express Heterogeneous Patterns of Neovascularization. Haematologica 2003, 88, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Hazar, B.; Paydas, S.; Zorludemir, S.; Sahin, B.; Tuncer, I. Prognostic Significance of Microvessel Density and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Expression in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzinger, D.; Zhao, S.; Marinelli, R.J.; Kapp, A.V.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Hammer, A.S.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Natkunam, Y. Microvessel Density and Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Its Receptors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Subtypes. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshenawy, H.A. Prognostic Significance of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, Basic Fibroblastic Growth Factor, and Microvessel Density and Their Relation to Cell Proliferation in B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2010, 14, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.M.; Sørensen, F.B.; Bendix, K.; Nielsen, J.L.; Olsen, M.L.; Funder, A.M.D.; d’Amore, F. Angiogenesis in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: Clinico-Pathological Correlations and Prognostic Significance in Specific Subtypes. Leuk. Lymphoma 2007, 48, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjoo, K.N.; An, C.S.; Robertson, M.J.; Gordon, L.I.; Sen, J.A.; Weisenbach, J.; Li, S.; Weller, E.A.; Orazi, A.; Horning, S.J. Rituximab, Bevacizumab and CHOP (RA-CHOP) in Untreated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Safety, Biomarker and Pharmacokinetic Analysis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Hyjek, E.; Kermani, P.; Christos, P.J.; Hooper, A.T.; Coleman, M.; Hempstead, B.; Leonard, J.P.; Chadburn, A.; Rafii, S. Magnitude of Stromal Hemangiogenesis Correlates with Histologic Subtype of Non–Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5622–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, A.; Moretti, S.; Ribatti, D.; Pellegrino, A.; Pimpinelli, N.; Bianchi, B.; Bonifazi, E.; Ria, R.; Serio, G.; Dammacco, F. Progression of Mycosis Fungoides Is Associated with Changes in Angiogenesis and Expression of the Matrix Metalloproteinases 2 and 9. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaerer, L.; Schmid, M.H.; Mueller, B.; Dummer, R.G.; Burg, G.; Kempf, W. Angiogenesis in Cutaneous Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Microvessel Density Discriminates between Cutaneous B-Cell Lymphomas and B-Cell Pseudolymphomas. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2000, 22, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G, M.; Z, W.; T, W.; J, M.; K, K. Increased Angiogenesis in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas. Pathol. Oncol. Res. POR 2004, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Treweeke, A.T.; West, D.C.; Till, K.J.; Cawley, J.C.; Zuzel, M.; Toh, C.H. In Vitro and in Vivo Production of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. Blood 2000, 96, 3181–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, N.E.; Bone, N.D.; Tschumper, R.C.; Howell, K.H.; Geyer, S.M.; Dewald, G.W.; Hanson, C.A.; Jelinek, D.F. B-CLL Cells Are Capable of Synthesis and Secretion of Both pro- and Anti-Angiogenic Molecules. Leukemia 2002, 16, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foss, H.D.; Araujo, I.; Demel, G.; Klotzbach, H.; Hummel, M.; Stein, H. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Lymphomas and Castleman’s Disease. J. Pathol. 1997, 183, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, A.; van Krieken, J.H.J.M.; Mackenzie, M.A.; Schraders, M.; Borm, G.F.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; Leenders, W.; Hebeda, K.; Raemaekers, J.M.M. Increased Vascularization Predicts Favorable Outcome in Follicular Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairey, O.; Boycov, O.; Kaganovsky, E.; Zimra, Y.; Shaklai, M.; Rabizadeh, E. All Three Receptors for Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Are Expressed on B-Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Cells. Leuk. Res. 2004, 28, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.; Talks, K.; Leek, R.; Turley, H.; Pezzella, F.; Harris, A.; Gatter, K. Expression of Angiogenic Factors and Hypoxia Inducible Factors HIF 1, HIF 2 and CA IX in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Histopathology 2002, 40, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-L.; Sheu, L.-F.; Li, C.-Y. Immunohistochemical Expression of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, and Their Receptors in Stage IV Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. AIMM 2002, 10, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, B.; Annese, T.; Tamma, R.; Longo, V.; Ruggieri, S.; Senetta, R.; Cassoni, P.; Specchia, G.; Vacca, A.; Ribatti, D. Aquaporin-4 Expression in Primary Human Central Nervous System Lymphomas Correlates with Tumour Cell Proliferation and Phenotypic Heterogeneity of the Vessel Wall. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzinger, D.; Zhao, S.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Hsi, E.D.; Hans, C.P.; Pohlman, B.; Bast, M.; Avigdor, A.; Schiby, G.; Nagler, A.; et al. Prognostic Significance of VEGF, VEGF Receptors, and Microvessel Density in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Treated with Anthracycline-Based Chemotherapy. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2008, 88, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salven, P.; Orpana, A.; Teerenhovi, L.; Joensuu, H. Simultaneous Elevation in the Serum Concentrations of the Angiogenic Growth Factors VEGF and BFGF Is an Independent Predictor of Poor Prognosis in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Single-Institution Study of 200 Patients. Blood 2000, 96, 3712–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niitsu, N.; Okamato, M.; Nakamine, H.; Yoshino, T.; Tamaru, J.; Nakamura, S.; Higashihara, M.; Hirano, M. Simultaneous Elevation of the Serum Concentrations of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Interleukin-6 as Independent Predictors of Prognosis in Aggressive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2002, 68, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, S.; Mabed, M.; Zalata, K.; Sakrana, M.; El Askalany, H. The Interplay between C-Myc Oncogene Expression and Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (SVEGF), Its Antagonist Receptor, Soluble Flt-1 in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Relationship to Patient Outcome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazgal, I.; Zimra, Y.; Tzabar, C.; Okon, E.; Rabizadeh, E.; Shaklai, M.; Bairey, O. Expression of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Is Associated with Poor Outcome in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 1770–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ria, R.; Cirulli, T.; Giannini, T.; Bambace, S.; Serio, G.; Portaluri, M.; Ribatti, D.; Vacca, A.; Dammacco, F. Serum Levels of Angiogenic Cytokines Decrease after Radiotherapy in Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Clin. Exp. Med. 2008, 8, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Bone, N.D.; Strege, A.K.; Jelinek, D.F.; Kay, N.E. VEGF Receptors on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) B Cells Interact with STAT 1 and 3: Implication for Apoptosis Resistance. Leukemia 2005, 19, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramoto, K.; Sakai, A.; Shigemasa, K.; Takimoto, Y.; Asaoku, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Oda, K.; Kimura, A.; Uesaka, T.; Watanabe, H.; et al. High Expression of MCL1 Gene Related to Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Is Associated with Poor Outcome in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 116, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-L.; Mourah, S.; Mounier, N.; Leboeuf, C.; Daneshpouy, M.E.; Legrès, L.; Meignin, V.; Oksenhendler, E.; Maignin, C.L.; Calvo, F.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Is Expressed Both on Lymphoma Cells and Endothelial Cells in Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma and Related to Lymphoma Progression. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2004, 84, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, M.A.; Ross, K.N.; Tamayo, P.; Weng, A.P.; Kutok, J.L.; Aguiar, R.C.T.; Gaasenbeek, M.; Angelo, M.; Reich, M.; Pinkus, G.S.; et al. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Outcome Prediction by Gene-Expression Profiling and Supervised Machine Learning. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Matsuda, K.; Kitai, R.; Sato, K.; Kubota, T. Angiogenesis in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL). J. Neurooncol. 2007, 84, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlushchuk, R.; Riesterer, O.; Baum, O.; Wood, J.; Gruber, G.; Pruschy, M.; Djonov, V. Tumor Recovery by Angiogenic Switch from Sprouting to Intussusceptive Angiogenesis after Treatment with PTK787/ZK222584 or Ionizing Radiation. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Dudley, A.C. Models and Molecular Mechanisms of Blood Vessel Co-Option by Cancer Cells. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, V.L.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Foo, S.; Bilecz, A.; Daley, F.; Kostaras, E.; Nathan, M.R.; Wan, E.; Frentzas, S.; Schweiger, T.; et al. Vessel Co-Option Is Common in Human Lung Metastases and Mediates Resistance to Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Preclinical Lung Metastasis Models. J. Pathol. 2017, 241, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frentzas, S.; Simoneau, E.; Bridgeman, V.L.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Foo, S.; Kostaras, E.; Nathan, M.; Wotherspoon, A.; Gao, Z.-H.; Shi, Y.; et al. Vessel Co-Option Mediates Resistance to Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Liver Metastases. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, E.A.; Yin, M.; Bar-Zion, A.; Lee, C.R.; Butz, H.; Man, S.; Daley, F.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Yousef, G.M.; Foster, F.S.; et al. Co-Option of Liver Vessels and Not Sprouting Angiogenesis Drives Acquired Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djw030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).