Submitted:
26 May 2023
Posted:
29 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
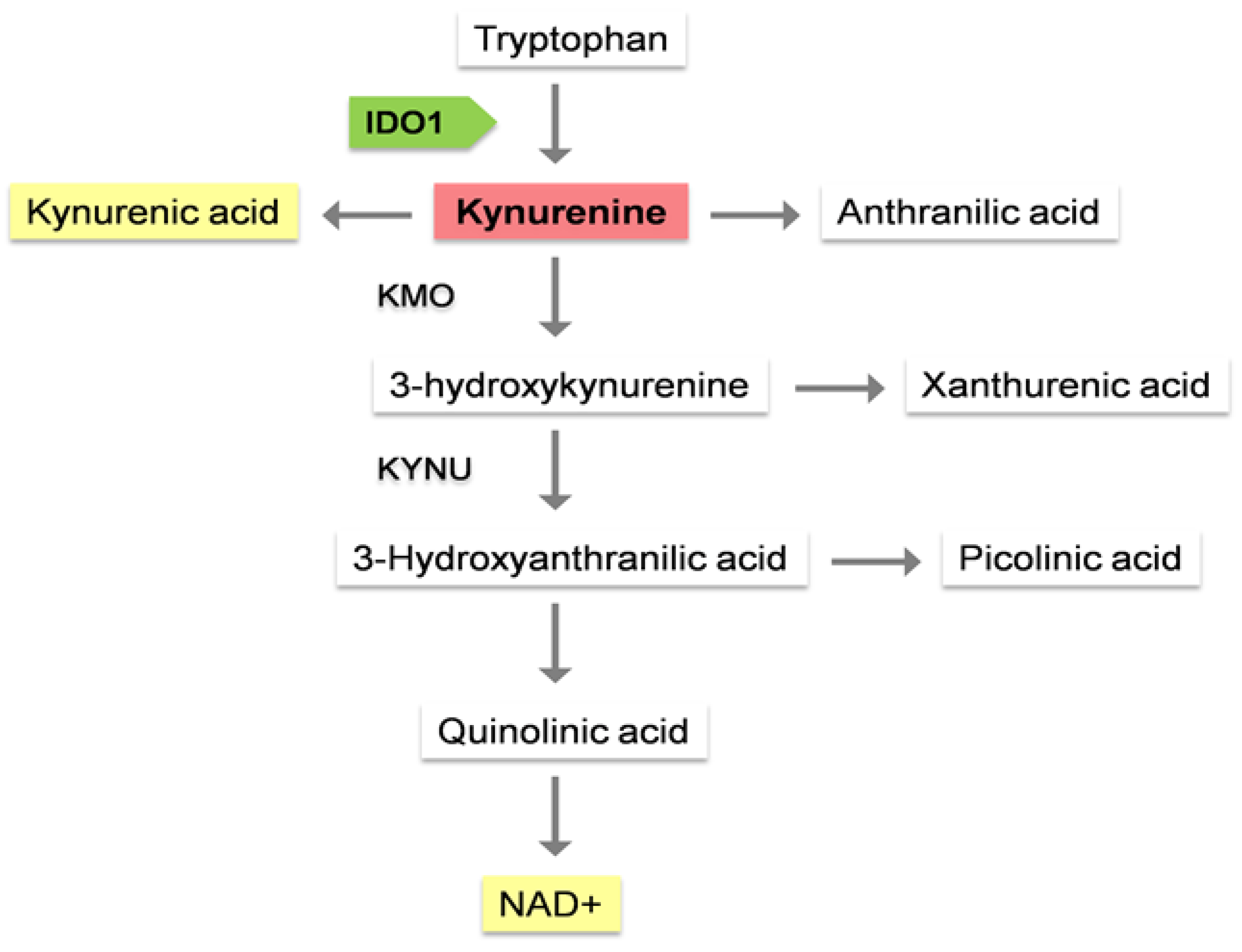
1.1. Kynurenine pathway, the main route for tryptophan metabolism
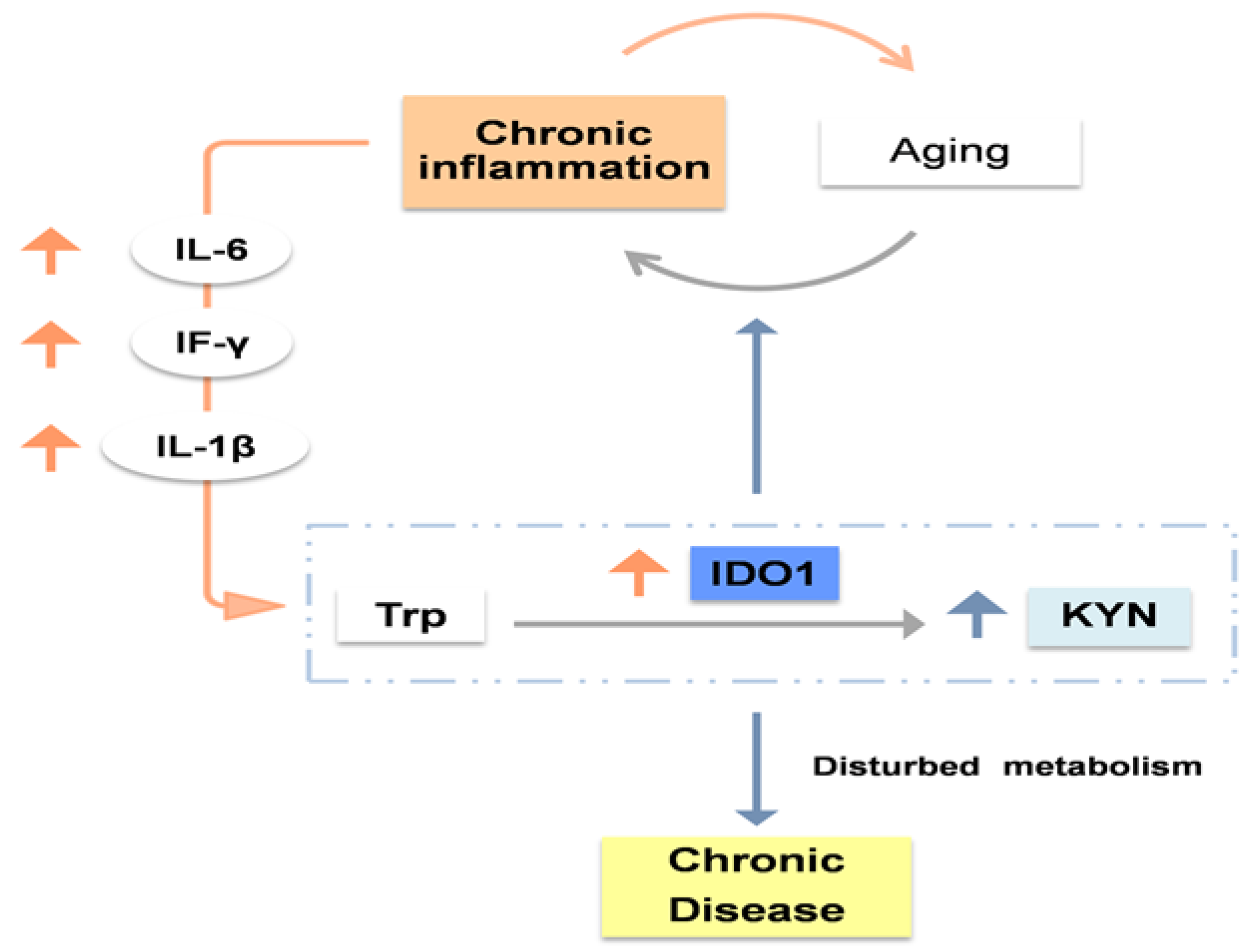
1.2. Does aging modulate the kynurenine pathway? IDO1, the key to this interplay
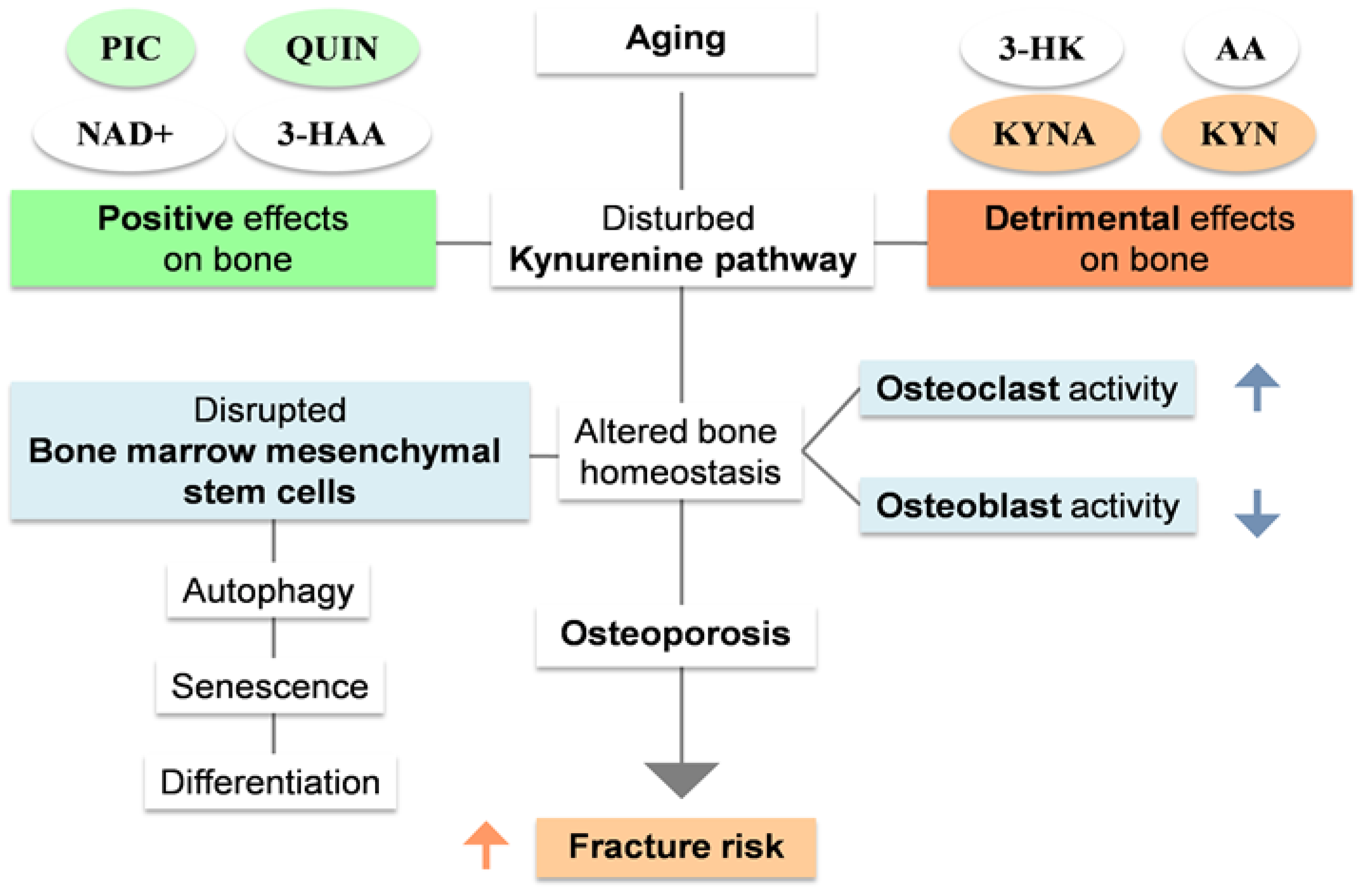
2. Kynurenine pathway: an unexplored mechanism for osteoporosis
2.1. The link between aging and osteoporosis.
2.2. Kynurenine pathway as a regulator of bone metabolism
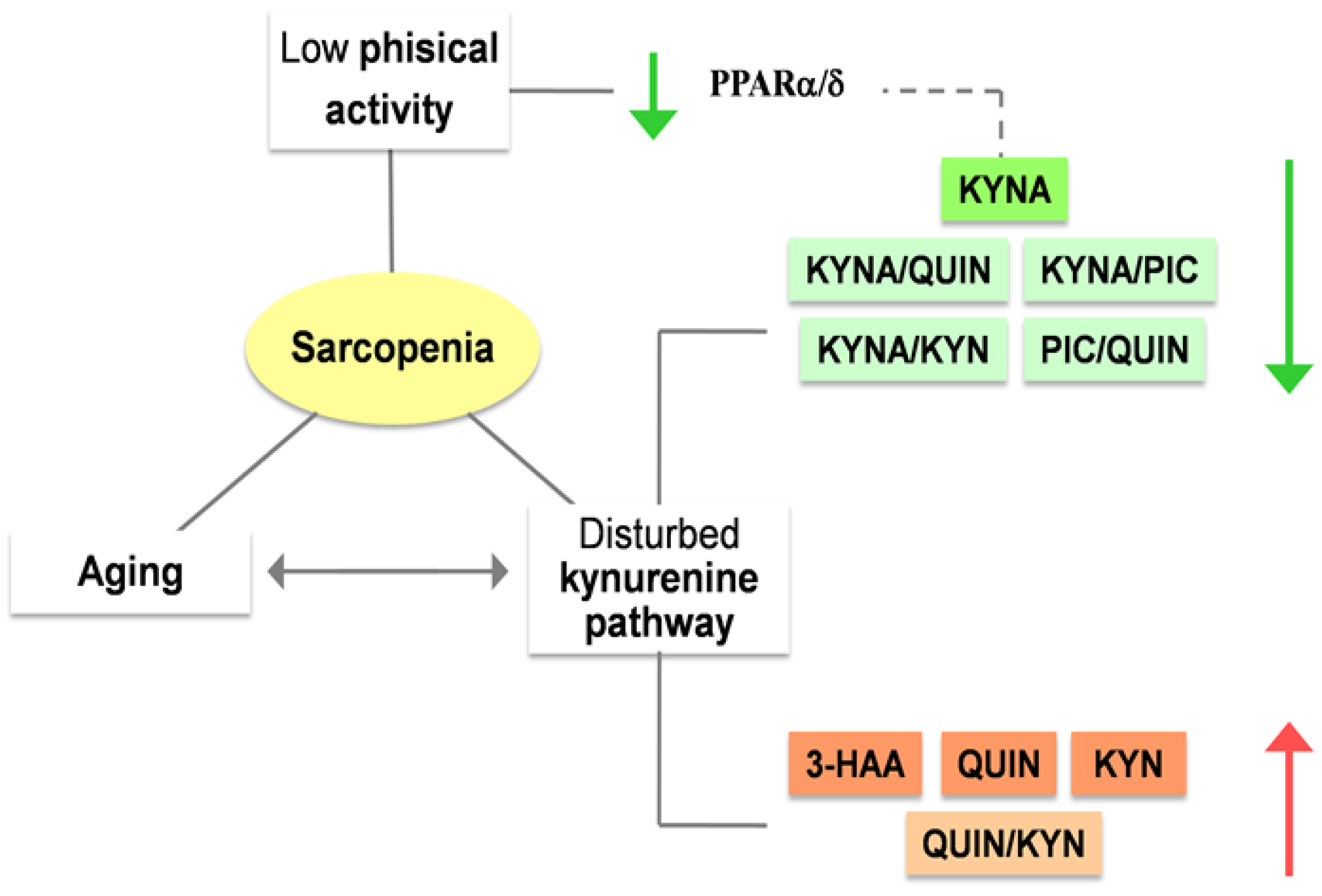
3. Kynurenines can modulate the risk of sarcopenia
3.1. The link between aging and sarcopenia.
3.1. The role of kynurenines in sarcopenia: a promising interplay
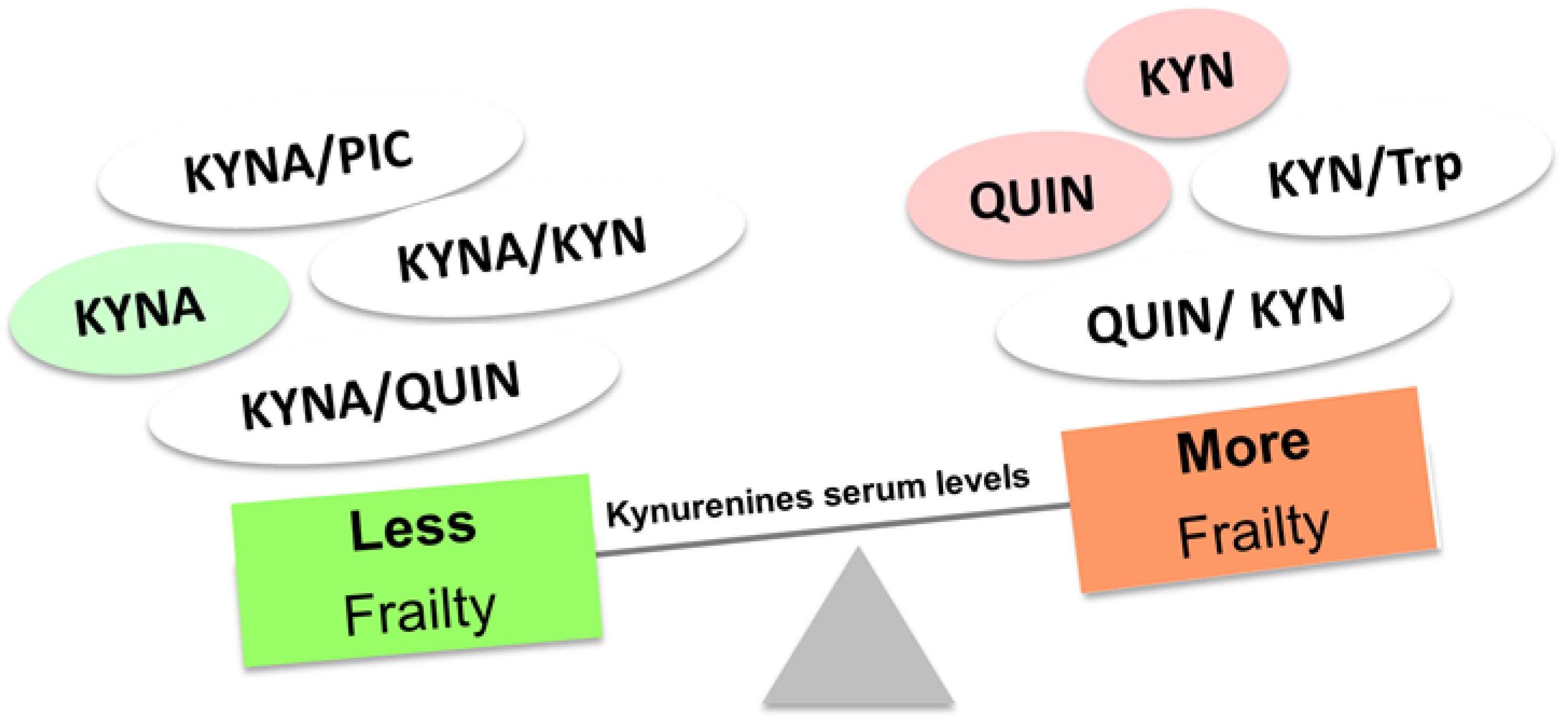
4. Frailty, an expression of aging and poor physical activity: ¿Have the kynurenines something to tell?
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.-J.; Movassat, J.; Portha, B. Emerging Role for Kynurenines in Metabolic Pathologies. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, D.A. Effects of a Dietary Excess of Leucine on the Metabolism of Tryptophan in the Rat: A Mechanism for the Pellagragenic Action of Leucine. Br. J. Nutr. 1983, 50, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boado, R.J.; Li, J.Y.; Nagaya, M.; Zhang, C.; Pardridge, W.M. Selective Expression of the Large Neutral Amino Acid Transporter at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1999, 96, 12079–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.S.; Davies, S.S. Microbial Metabolism of Dietary Components to Bioactive Metabolites: Opportunities for New Therapeutic Interventions. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takikawa, O.; Yoshida, R.; Kido, R.; Hayaishi, O. Tryptophan Degradation in Mice Initiated by Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 3648–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canli, T.; Lesch, K.-P. Long Story Short: The Serotonin Transporter in Emotion Regulation and Social Cognition. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, C.A.; Herbert, J. Differential Circadian Rhythms in Pineal and Hypothalamic 5-HT Induced by Artificial Photoperiods or Melatonin. Nature 1976, 262, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W.; Stoy, N.; Darlington, L.G. An Expanding Range of Targets for Kynurenine Metabolites of Tryptophan. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-J.; Hamrick, M.W.; Yoo, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Koh, J.-M.; Isales, C.M. The Detrimental Effects of Kynurenine, a Tryptophan Metabolite, on Human Bone Metabolism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgdrager, F.J.H.; Vermeiren, Y.; Van Faassen, M.; van der Ley, C.; Nollen, E.A.A.; Kema, I.P.; De Deyn, P.P. Age- and Disease-Specific Changes of the Kynurenine Pathway in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2019, 151, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.; Forteza, M.J.; Ketelhuth, D.F.J. The Interplay between Cytokines and the Kynurenine Pathway in Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. Cytokine 2019, 122, 154148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytton, S.D.; Osiecki, M.; MałgorzataWoźniak; Cukrowska, B.; Wierzbicka, A.; Goliszek, M.; Socha, P.; Janczyk, W.; Dayanakli, D.; Abendroth, D.; et al. Tryptophan-Kynurenine Profile in Pediatric Autoimmune Hepatitis. Immunol. Res. 2019, 67, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Ramprasath, T.; Wang, H.; Zou, M.-H. Abnormal Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Catabolism in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2017, 74, 2899–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantó, C.; Menzies, K.J.; Auwerx, J. NAD(+) Metabolism and the Control of Energy Homeostasis: A Balancing Act between Mitochondria and the Nucleus. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelp, M.T.; Kates, P.A.; Hunt, J.T.; Newitt, J.A.; Balog, A.; Maley, D.; Zhu, X.; Abell, L.; Allentoff, A.; Borzilleri, R.; et al. Immune-Modulating Enzyme Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Is Effectively Inhibited by Targeting Its Apo-Form. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2018, 115, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, M.; Funakoshi, H.; Takahashi, H.; Hayakawa, T.; Mizuno, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Tryptophan 2,3-Dioxygenase Is a Key Modulator of Physiological Neurogenesis and Anxiety-Related Behavior in Mice. Mol. Brain 2009, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civen, M.; Knox, W.E. The Independence of Hydrocortisone and Tryptophan Inductions of Tryptophan Pyrrolase. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 1787–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greengard, O.; Feigelson, P. A Difference between the Modes of Action of Substrate and Hormonal Inducers of Rat Liver Tryptophan Pyrrolase. Nature 1961, 190, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.-B. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism: Regulatory and Functional Aspects. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. IJTR 2017, 10, 1178646917691938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, M.T.; Rossini, S.; Suvieri, C.; Coletti, A.; Orabona, C.; Macchiarulo, A.; Volpi, C.; Grohmann, U. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO1): An up-to-Date Overview of an Eclectic Immunoregulatory Enzyme. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 6099–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Lee, H.B.; Shin, D.-M.; Kang, M.J.; Yi, E.C.; Noh, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Min, C.-K.; Choi, E.Y. Heme-Binding-Mediated Negative Regulation of the Tryptophan Metabolic Enzyme Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) by IDO2. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarcz, R.; Bruno, J.P.; Muchowski, P.J.; Wu, H.-Q. Kynurenines in the Mammalian Brain: When Physiology Meets Pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizuka, Y.; Hayaishi, O. Enzymic Synthesis of Niacin Nucleotides from 3-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid in Mammalian Liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, A.; Orjalo, A.V.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Campisi, J. Inflammatory Networks during Cellular Senescence: Causes and Consequences. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Valensin, S.; Bonafè, M.; Paolisso, G.; Yashin, A.I.; Monti, D.; De Benedictis, G. The Network and the Remodeling Theories of Aging: Historical Background and New Perspectives. Exp. Gerontol. 2000, 35, 879–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benayoun, B.A.; Pollina, E.A.; Singh, P.P.; Mahmoudi, S.; Harel, I.; Casey, K.M.; Dulken, B.W.; Kundaje, A.; Brunet, A. Remodeling of Epigenome and Transcriptome Landscapes with Aging in Mice Reveals Widespread Induction of Inflammatory Responses. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, F.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Yan, C.; Yan, F.; Ren, X. Noncanonical NF-ΚB Activation Mediates STAT3-Stimulated IDO Upregulation in Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Breast Cancer. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2014, 193, 2574–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailankot, M.; Nagaraj, R.H. Induction of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase by Interferon-Gamma in Human Lens Epithelial Cells: Apoptosis through the Formation of 3-Hydroxykynurenine. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.V.; Schultze, J.L. New Insights into IDO Biology in Bacterial and Viral Infections. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Wang, H.-S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, K.-F.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, G.; Cai, S.-H.; Du, J. The Role of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO) in Immune Tolerance: Focus on Macrophage Polarization of THP-1 Cells. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 289, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, D.H.; Mellor, A.L. IDO in the Tumor Microenvironment: Inflammation, Counter-Regulation, and Tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezrich, J.D.; Fechner, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, B.P.; Burlingham, W.J.; Bradfield, C.A. An Interaction between Kynurenine and the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Can Generate Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2010, 185, 3190–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothhammer, V.; Quintana, F.J. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor: An Environmental Sensor Integrating Immune Responses in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNatale, B.C.; Murray, I.A.; Schroeder, J.C.; Flaveny, C.A.; Lahoti, T.S.; Laurenzana, E.M.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Perdew, G.H. Kynurenic Acid Is a Potent Endogenous Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligand That Synergistically Induces Interleukin-6 in the Presence of Inflammatory Signaling. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2010, 115, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, A.; Somarribas Patterson, L.F.; Öztürk, S.; Mohapatra, S.R.; Panitz, V.; Secker, P.F.; Pfänder, P.; Loth, S.; Salem, H.; Prentzell, M.T.; et al. IL4I1 Is a Metabolic Immune Checkpoint That Activates the AHR and Promotes Tumor Progression. Cell 2020, 182, 1252–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Luo, L.; Tian, L.; Yin, S.; Ma, X.; Cheng, S.; Tang, W.; Yu, J.; Ma, W.; Zhou, X.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Promotes IL-10 Expression in Inflammatory Macrophages Through Src-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torti, M.F.; Giovannoni, F.; Quintana, F.J.; García, C.C. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor as a Modulator of Anti-Viral Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 624293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, C.J.M.; Rosser, E.C.; Oleinika, K.; Nistala, K.; Krausgruber, T.; Rendeiro, A.F.; Banos, A.; Drozdov, I.; Villa, M.; Thomson, S.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Contributes to the Transcriptional Program of IL-10-Producing Regulatory B Cells. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1878–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, R.; Kumar, D.; Burns, E.J.; Nadeau, M.; Dake, B.; Laroni, A.; Kozoriz, D.; Weiner, H.L.; Quintana, F.J. Activation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Induces Human Type 1 Regulatory T Cell-like and Foxp3(+) Regulatory T Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.D.; Cross, B.L.; Grosicki, G.J. Evidence for the Contribution of Gut Microbiota to Age-Related Anabolic Resistance. Nutrients 2021, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolagas, S.C.; Parfitt, A.M. What Old Means to Bone. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2010, 21, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönherr, E.; Hausser, H.J. Extracellular Matrix and Cytokines: A Functional Unit. Dev. Immunol. 2000, 7, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolagas, S.C. Birth and Death of Bone Cells: Basic Regulatory Mechanisms and Implications for the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Lu, Y.; Williams, E.A.; Lai, F.; Lee, J.Y.; Enishi, T.; Balani, D.H.; Ominsky, M.S.; Ke, H.Z.; Kronenberg, H.M.; et al. Sclerostin Antibody Administration Converts Bone Lining Cells Into Active Osteoblasts. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffler, M.B.; Cheung, W.-Y.; Majeska, R.; Kennedy, O. Osteocytes: Master Orchestrators of Bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2014, 94, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matic, I.; Matthews, B.G.; Wang, X.; Dyment, N.A.; Worthley, D.L.; Rowe, D.W.; Grcevic, D.; Kalajzic, I. Quiescent Bone Lining Cells Are a Major Source of Osteoblasts During Adulthood. Stem Cells Dayt. Ohio 2016, 34, 2930–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, Y.-S.; Chung, N.-C.; Chen, Y.-R.; Huang, H.-Y.; Chuang, W.-P.; Lai, D.-M. Imbalanced Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis in Mice Deficient in the Chemokine Cxcl12/Sdf1 in the Bone Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2018, 33, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll, C.B.; Bunnell, B.A. Comparative Characterization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from EGFP Transgenic and Non-Transgenic Mice. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashi, F.; Modarressi, A.; Pepper, M.S. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation: A Review. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Wong, N.-K.; Xiao, J.; So, K.-F. Oxidative Stress in Stem Cell Aging. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coipeau, P.; Rosset, P.; Langonne, A.; Gaillard, J.; Delorme, B.; Rico, A.; Domenech, J.; Charbord, P.; Sensebe, L. Impaired Differentiation Potential of Human Trabecular Bone Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Elderly Patients. Cytotherapy 2009, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, A.; Rodríguez, C.I. Osteogenesis and Aging: Lessons from Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonafede, M.; Espindle, D.; Bower, A.G. The Direct and Indirect Costs of Long Bone Fractures in a Working Age US Population. J. Med. Econ. 2013, 16, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, N.C.; Looker, A.C.; Saag, K.G.; Curtis, J.R.; Delzell, E.S.; Randall, S.; Dawson-Hughes, B. The Recent Prevalence of Osteoporosis and Low Bone Mass in the United States Based on Bone Mineral Density at the Femoral Neck or Lumbar Spine. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 2520–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sözen, T.; Özışık, L.; Başaran, N.Ç. An Overview and Management of Osteoporosis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 4, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmansi, A.M.; Hussein, K.A.; Herrero, S.M.; Periyasamy-Thandavan, S.; Aguilar-Pérez, A.; Kondrikova, G.; Kondrikov, D.; Eisa, N.H.; Pierce, J.L.; Kaiser, H.; et al. Age-Related Increase of Kynurenine Enhances MiR29b-1-5p to Decrease Both CXCL12 Signaling and the Epigenetic Enzyme Hdac3 in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Bone Rep. 2020, 12, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.-L.; Simon, A.K.; Prescott, M.; Menendez, J.A.; Liu, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Wolvetang, E.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Zhang, J. Autophagy in Stem Cells. Autophagy 2013, 9, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Shuai, Y.; Li, L.; Luo, K.; Liu, W.; Jin, Y. Autophagy Maintains the Function of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Prevent Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4498–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, G.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, L. Autophagy Activation Facilitates Mechanical Stimulation-Promoted Osteoblast Differentiation and Ameliorates Hindlimb Unloading-Induced Bone Loss. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, R.; Zou, Z.; Luo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, B. Mechanically Induced Autophagy Is Associated with ATP Metabolism and Cellular Viability in Osteocytes in Vitro. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrikov, D.; Elmansi, A.; Bragg, R.T.; Mobley, T.; Barrett, T.; Eisa, N.; Kondrikova, G.; Schoeinlein, P.; Aguilar-Perez, A.; Shi, X.-M.; et al. Kynurenine Inhibits Autophagy and Promotes Senescence in Aged Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells through the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Pathway. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 130, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, G.P.; Lee, X.; Basile, G.; Acosta, M.; Scott, G.; Roskelley, C.; Medrano, E.E.; Linskens, M.; Rubelj, I.; Pereira-Smith, O. A Biomarker That Identifies Senescent Human Cells in Culture and in Aging Skin in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1995, 92, 9363–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilosi, M.; Carloni, A.; Rossi, A.; Poletti, V. Premature Lung Aging and Cellular Senescence in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and COPD/Emphysema. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2013, 162, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignolo, R.J.; Samsonraj, R.M.; Law, S.F.; Wang, H.; Chandra, A. Targeting Cell Senescence for the Treatment of Age-Related Bone Loss. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2019, 17, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.Y.; Jee, H.J.; Um, J.-H.; Kim, Y.M.; Bae, S.S.; Yun, J. Cooperation between P21 and Akt Is Required for P53-Dependent Cellular Senescence. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee-Lawrence, M.E.; Carpio, L.R.; Schulze, R.J.; Pierce, J.L.; McNiven, M.A.; Farr, J.N.; Khosla, S.; Oursler, M.J.; Westendorf, J.J. Hdac3 Deficiency Increases Marrow Adiposity and Induces Lipid Storage and Glucocorticoid Metabolism in Osteochondroprogenitor Cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtinger, X.; Muschitz, C.; Heimel, P.; Baierl, A.; Fahrleitner-Pammer, A.; Redl, H.; Resch, H.; Geiger, E.; Skalicky, S.; Dormann, R.; et al. Bone-Related Circulating MicroRNAs MiR-29b-3p, MiR-550a-3p, and MiR-324-3p and Their Association to Bone Microstructure and Histomorphometry. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razidlo, D.F.; Whitney, T.J.; Casper, M.E.; McGee-Lawrence, M.E.; Stensgard, B.A.; Li, X.; Secreto, F.J.; Knutson, S.K.; Hiebert, S.W.; Westendorf, J.J. Histone Deacetylase 3 Depletion in Osteo/Chondroprogenitor Cells Decreases Bone Density and Increases Marrow Fat. PloS One 2010, 5, e11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaey, M.E.; McGee-Lawrence, M.E.; Fulzele, S.; Kennedy, E.J.; Bollag, W.B.; Elsalanty, M.; Zhong, Q.; Ding, K.-H.; Bendzunas, N.G.; Shi, X.-M.; et al. Kynurenine, a Tryptophan Metabolite That Accumulates With Age, Induces Bone Loss. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.A.R.; Stein, J.L.; Westendorf, J.J.; van Wijnen, A.J. Chromatin Modifiers and Histone Modifications in Bone Formation, Regeneration, and Therapeutic Intervention for Bone-Related Disease. Bone 2015, 81, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenson, M.; Shull, L.C.; Taylor, E.L.; Camilleri, E.T.; Riester, S.M.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Bradley, E.W.; Westendorf, J.J. Histone Deacetylase 3 Deletion in Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells Hinders Long Bone Development. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, L.R.; Bradley, E.W.; McGee-Lawrence, M.E.; Weivoda, M.M.; Poston, D.D.; Dudakovic, A.; Xu, M.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L.; van Wijnen, A.J.; et al. Histone Deacetylase 3 Supports Endochondral Bone Formation by Controlling Cytokine Signaling and Matrix Remodeling. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya, J.M.; Bollag, W.B.; Hamrick, M.W.; Isales, C.M. The Role of Tryptophan Metabolites in Musculoskeletal Stem Cell Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darlington, L.G.; Forrest, C.M.; Mackay, G.M.; Smith, R.A.; Smith, A.J.; Stoy, N.; Stone, T.W. On the Biological Importance of the 3-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid: Anthranilic Acid Ratio. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. IJTR 2010, 3, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isales, C.; Ding, K.; Bollag, W.; McGee-Lawrence, M.; Hill, W.; Shi, X.; Elsalanty, M.; Hamrick, M. KYNURENIC ACID A TRYPTOPHAN METABOLITE INDUCES BONE LOSS IN MICE. Innov. Aging 2018, 2, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. Hydrogen Peroxide-Mediated Neuronal Cell Death Induced by an Endogenous Neurotoxin, 3-Hydroxykynurenine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996, 93, 12553–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Tao, J.; Fang, E. Therapeutic Potential of Boosting NAD+ in Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Transl. Med. Aging 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; McGee-Lawrence, M.E.; Kaiser, H.; Sharma, A.K.; Pierce, J.L.; Irsik, D.L.; Bollag, W.B.; Xu, J.; Zhong, Q.; Hill, W.; et al. Picolinic Acid, a Tryptophan Oxidation Product, Does Not Impact Bone Mineral Density but Increases Marrow Adiposity. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 133, 110885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.; Li, W.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Lim, C.K.; Guillemin, G.J.; Ball, H.J.; Hunt, N.H.; Nanan, R.; Duque, G. The Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Degradation Is Activated during Osteoblastogenesis. Stem Cells Dayt. Ohio 2015, 33, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, C.M.; Mackay, G.M.; Oxford, L.; Stoy, N.; Stone, T.W.; Darlington, L.G. Kynurenine Pathway Metabolism in Patients with Osteoporosis after 2 Years of Drug Treatment. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalset, E.M.; Gjesdal, C.G.; Ueland, P.M.; Midttun, Ø.; Ulvik, A.; Eide, G.E.; Meyer, K.; Tell, G.S. Interferon (IFN)-γ-Mediated Inflammation and the Kynurenine Pathway in Relation to Bone Mineral Density: The Hordaland Health Study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 176, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duque, G.; Vidal, C.; Li, W.; Al Saedi, A.; Khalil, M.; Lim, C.K.; Myers, D.E.; Guillemin, G.J. Picolinic Acid, a Catabolite of Tryptophan, Has an Anabolic Effect on Bone In Vivo. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 2275–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Wang, Z.M.; Ross, R. Skeletal Muscle Mass and Distribution in 468 Men and Women Aged 18-88 Yr. J. Appl. Physiol. Bethesda Md 1985 2000, 89, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jin, P.; Duan, R.; Chen, E.H. Mechanisms of Myoblast Fusion during Muscle Development. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2015, 32, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavlakadze, T.; McGeachie, J.; Grounds, M.D. Delayed but Excellent Myogenic Stem Cell Response of Regenerating Geriatric Skeletal Muscles in Mice. Biogerontology 2010, 11, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, C.S.; Lee, J.D.; Mula, J.; Kirby, T.J.; Jackson, J.R.; Liu, F.; Yang, L.; Mendias, C.L.; Dupont-Versteegden, E.E.; McCarthy, J.J.; et al. Inducible Depletion of Satellite Cells in Adult, Sedentary Mice Impairs Muscle Regenerative Capacity without Affecting Sarcopenia. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Victor, P.; Gutarra, S.; García-Prat, L.; Rodriguez-Ubreva, J.; Ortet, L.; Ruiz-Bonilla, V.; Jardí, M.; Ballestar, E.; González, S.; Serrano, A.L.; et al. Geriatric Muscle Stem Cells Switch Reversible Quiescence into Senescence. Nature 2014, 506, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.E.; Hsu, M.; Conboy, I.M. Imbalance between PSmad3 and Notch Induces CDK Inhibitors in Old Muscle Stem Cells. Nature 2008, 454, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conboy, I.M.; Conboy, M.J.; Smythe, G.M.; Rando, T.A. Notch-Mediated Restoration of Regenerative Potential to Aged Muscle. Science 2003, 302, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, A.S.; Conboy, M.J.; Roy, S.; Lee, M.; Kuo, C.J.; Keller, C.; Rando, T.A. Increased Wnt Signaling during Aging Alters Muscle Stem Cell Fate and Increases Fibrosis. Science 2007, 317, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, J.D.; Doles, J.D.; Hall, J.K.; Kelly Tanaka, K.; Carter, T.A.; Olwin, B.B. P38 MAPK Signaling Underlies a Cell-Autonomous Loss of Stem Cell Self-Renewal in Skeletal Muscle of Aged Mice. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakkalakal, J.V.; Jones, K.M.; Basson, M.A.; Brack, A.S. The Aged Niche Disrupts Muscle Stem Cell Quiescence. Nature 2012, 490, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, M.T.; Aydogdu, T.; Sala, D.; Malecova, B.; Gatto, S.; Puri, P.L.; Latella, L.; Sacco, A. STAT3 Signaling Controls Satellite Cell Expansion and Skeletal Muscle Repair. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, F.D.; von Maltzahn, J.; Bentzinger, C.F.; Dumont, N.A.; Yin, H.; Chang, N.C.; Wilson, D.H.; Frenette, J.; Rudnicki, M.A. Inhibition of JAK-STAT Signaling Stimulates Adult Satellite Cell Function. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, B.D.; Gilbert, P.M.; Porpiglia, E.; Mourkioti, F.; Lee, S.P.; Corbel, S.Y.; Llewellyn, M.E.; Delp, S.L.; Blau, H.M. Rejuvenation of the Muscle Stem Cell Population Restores Strength to Injured Aged Muscles. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Victor, P.; Perdiguero, E.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Geroconversion of Aged Muscle Stem Cells under Regenerative Pressure. Cell Cycle Georget. Tex 2014, 13, 3183–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segalés, J.; Perdiguero, E.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Regulation of Muscle Stem Cell Functions: A Focus on the P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, E.M.; Sayer, A.A.; Cooper, C. Epidemiology of Sarcopenia and Insight into Possible Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyère, O.; Beaudart, C.; Ethgen, O.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Locquet, M. The Health Economics Burden of Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Maturitas 2019, 119, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, S.X.; Holloway-Kew, K.L.; Hyde, N.K.; Williams, L.J.; Tembo, M.C.; Leach, S.; Pasco, J.A. Prevalence of Sarcopenia Employing Population-Specific Cut-Points: Cross-Sectional Data from the Geelong Osteoporosis Study, Australia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.Q.; Yu, S.; Tucker, G.R.; Adams, R.J.; Cesari, M.; Theou, O.; Visvanathan, R. Frailty and Sarcopenia in Combination Are More Predictive of Mortality than Either Condition Alone. Maturitas 2021, 144, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, S.K.; Tsintavis, P.; Potsaki, P.; Papandreou, D. Differences in the Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling, Nursing Home and Hospitalized Individuals. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifico, J.; Geerlings, M.A.J.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Phassouliotis, C.; Lim, W.K.; Maier, A.B. Prevalence of Sarcopenia as a Comorbid Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 131, 110801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wan, C.S.; Ktoris, K.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Maier, A.B. Sarcopenia Is Associated with Mortality in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gerontology 2022, 68, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.; Yu, K.; Pandya, C.; Mendhe, B.; Isales, C.M.; McGee-Lawrence, M.E.; Johnson, M.; Fulzele, S.; Hamrick, M.W. Kynurenine, a Tryptophan Metabolite That Increases with Age, Induces Muscle Atrophy and Lipid Peroxidation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9894238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukes, A.; Davis, C.; El Refaey, M.; Upadhyay, S.; Mork, S.; Arounleut, P.; Johnson, M.H.; Hill, W.D.; Isales, C.M.; Hamrick, M.W. The Aromatic Amino Acid Tryptophan Stimulates Skeletal Muscle IGF1/P70s6k/MTor Signaling in Vivo and the Expression of Myogenic Genes in Vitro. Nutr. Burbank Los Angel. Cty. Calif 2015, 31, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanti, F.; Romano, A.D.; Lo Buglio, A.; Castriotta, V.; Guglielmi, G.; Greco, A.; Serviddio, G.; Vendemiale, G. Oxidative Stress Is Increased in Sarcopenia and Associated with Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Sarcopenic Obesity. Maturitas 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto Montes, A.; Boga, J.A.; Bermejo Millo, C.; Rubio González, A.; Potes Ochoa, Y.; Vega Naredo, I.; Martínez Reig, M.; Romero Rizos, L.; Sánchez Jurado, P.M.; Solano, J.J.; et al. Potential Early Biomarkers of Sarcopenia among Independent Older Adults. Maturitas 2017, 104, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, J.C.; Ferreira, D.M.S.; Ruas, J.L. Intercellular: Local and Systemic Actions of Skeletal Muscle PGC-1s. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2015, 26, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudelo, L.Z.; Femenía, T.; Orhan, F.; Porsmyr-Palmertz, M.; Goiny, M.; Martinez-Redondo, V.; Correia, J.C.; Izadi, M.; Bhat, M.; Schuppe-Koistinen, I.; et al. Skeletal Muscle PGC-1α1 Modulates Kynurenine Metabolism and Mediates Resilience to Stress-Induced Depression. Cell 2014, 159, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlittler, M.; Goiny, M.; Agudelo, L.Z.; Venckunas, T.; Brazaitis, M.; Skurvydas, A.; Kamandulis, S.; Ruas, J.L.; Erhardt, S.; Westerblad, H.; et al. Endurance Exercise Increases Skeletal Muscle Kynurenine Aminotransferases and Plasma Kynurenic Acid in Humans. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Saedi, A.; Chow, S.; Vogrin, S.; Guillemin, G.J.; Duque, G. Association Between Tryptophan Metabolites, Physical Performance, and Frailty in Older Persons. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. IJTR 2022, 15, 11786469211069952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Mandel, R.; Fain, M.J. Frailty: An Emerging Geriatric Syndrome. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walston, J.; Hadley, E.C.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Newman, A.B.; Studenski, S.A.; Ershler, W.B.; Harris, T.; Fried, L.P. Research Agenda for Frailty in Older Adults: Toward a Better Understanding of Physiology and Etiology: Summary from the American Geriatrics Society/National Institute on Aging Research Conference on Frailty in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, K.; Mitnitski, A. Frailty in Relation to the Accumulation of Deficits. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2007, 62, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Vellas, B.; van Kan, G.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bauer, J.M.; Bernabei, R.; Cesari, M.; Chumlea, W.C.; Doehner, W.; Evans, J.; et al. Frailty Consensus: A Call to Action. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in Older Adults: Evidence for a Phenotype. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in Elderly People. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2013, 381, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Marcos-Pérez, D.; Lorenzi, M.; Onder, G.; Gostner, J.M.; Strasser, B.; Fuchs, D.; Bonassi, S. Immunological Alterations in Frail Older Adults: A Cross Sectional Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 112, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos-Pérez, D.; Sánchez-Flores, M.; Maseda, A.; Lorenzo-López, L.; Millán-Calenti, J.C.; Strasser, B.; Gostner, J.M.; Fuchs, D.; Pásaro, E.; Valdiglesias, V.; et al. Frailty Status in Older Adults Is Related to Alterations in Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 and Guanosine Triphosphate Cyclohydrolase I Enzymatic Pathways. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, I.-Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, S.J.; Kim, D.A.; Hamrick, M.W.; Kim, B.-J. The Association of Circulating Kynurenine, a Tryptophan Metabolite, with Frailty in Older Adults. Aging 2020, 12, 22253–22265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




