1. Introduction
On December 31, 2019, the first case of a novel infectious disease with unknown origin (causative agent), features, duration of human transmission, and epidemiological parameters was confirmed in a designated hospital in Wuhan, a major city of China [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. The studies on this new infectious disease revealed that a new generation of coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2), is its causative agent [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Coronaviruses are a group of Coronaviridae families with a broad distribution in mammals which are known as the non-segmented positive-sense RNA viruses [
5]. This novel disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 was called Coronavirus disease 2019 and termed as COVID-19 by WHO on 11 Fed 2020 [
20]. Although the human infections resulted from coronavirus are mild in the most cases [
5], shortly after the first report of COVID-19, the novel COVID-19 exhibited a high potential for the outbreaks and becoming an epidemic disease and even a pandemics, as now we see in the world [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28].
The most common symptoms of this novel disease are only including shortness of breath, fever, and cough [
5,
6,
7,
8]. The incubation period of the COVID-19 is variable from 5 to 14 days [
31]. This too-long incubation period causes the rapid outbreaks of the COVID-19 as a scary global epidemic disease because the disease may be speared during the communal period which the peoples think that they are healthy. Consequently, after the outbreaks in China, the COVID-19 has rapidly spread around the world due to its unique epidemiologic properties and long communal period (variable from 5 to 14 days) and has now become a scary global epidemic, resulting in the ongoing 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28]. The COVID-19 has declared as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) on 30 January 2020 by WHO (World Health Organization), however, the WHO declared this novel global outbreaks as a pandemic on 11 March 2020 [
29,
30].
The aim of this article is the quick review of the recent studies on the novel coronavirus disease 2019, for instance, researches on the epidemiological parameters, mechanism of action, diagnosis, and treatment of the novel coronavirus disease, as well as clinical features of patients infected with COVID-19. Moreover, the COVID-19 has comprised of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), influenza A (H1N1), and the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS).
2. Clinical features of COVID-19
In regard to investigation of the clinical feature of COVID-19, recently, C. Huang et al. [
5] described epidemiological, clinical, laboratory, and radiological characteristics, treatment, and outcomes of 41 patients confirmed to have the 2019-nCoV infection (Jan 2, 2020), moreover, they also obtained a comparison between the clinical features of the serve COVID-19 patients (intensive care unit (ICU)) and not-serve cases (non-ICU). They reported that 73% of the infected patients with COVID-19 were men and 32% of patients infected with 2019-nCoV had underlying diseases, including diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease. They found that 98% of patients of COVID-19 had a fever, 63% of patients had lymphopenia, and 76% coughed at the onset of illness. While the less common symptoms were sputum production (28%), headache (8%), hemoptysis (5%), and diarrhea (3%). They reported that Dyspnoea developed in 55 patients after 5 -13 days (median: 8 days) from the onset of COVID-19.
They also reported that all patients had pneumonia with abnormal findings on chest CT and 98% had bilateral involvement. They also found that the blood counts of 25% of COVID-1 patients show leucopenia while 63% had lymphopenia for 63%. Also, for 37% of COID-19 patients, the level of aspartate Aminotransferase was increased in their blood. Moreover, they noted that the concentrations of VEGF, TNFα, IL7, IL8, IL9, IL10, basic FGF, GMCSF, IFNγ, IP10, MCP1, PDGF, MIP1B, MIP1A, GCSF, IL1B, and IL1RA in the plasma samples of patients with COVID-19 were found to be higher than those in healthy adults [
5].
Besides R. Li et al. [
8] reported the clinical characteristics of 225 patients with COVID-19 (between January 20 and February 14, 2020). They noted that fever, cough, and conspicuous ground-grass opacity lesions in the lungs apparent in CT images combined with a normal or decreased count of WBCs are highly suspected clinical features of COVID-19 pneumonia. Moreover, they reported that hypertension was present in 20.89% of patients. However, 16.5% of patients showed severe COVID-19. They found that the major clinical symptoms of the COVID-19 were fever (84.44 % of patients), cough (56.44 % of patients). In addition, they reported that dyspnea, expectoration, fatigue, chills, headache, chest pain, and pharyngalgia were observed for some patients infected with COVID-19. It should be noted that the emerging data particularly from China, reveals that the patients with diabetes and hypertension are at high risk for COVID-19 infection [
32,
33,
34,
35]. Also, M. A. Hill et al. reported that the diabetic patients with COVID-19 are at higher risk for morbidity and mortality than the patient without diabetes [
28]. T. Xu et al [
36] reported that the fever is the most common symptom of COVID-19 at the onset of illness, 50% COVID-19 patients show a low-grade temperature with a duration of fever <7 days and the bilateral pneumonia observe in the CT scans of the most patients infected with COVID-19. Moreover, they noted that the viral loads in the patients with COVID-19 are not detectable after 14 days from the onset of illness.
W. Guan et al [
37] reported that the average age of the COVID-19 patients is around 47 years. However, about 60% of patients are male and only 40% are female. Fever (89%) and cough (68%) are the most common symptoms while diarrhea is uncommon. The ground-glass commonly has observed in the CT images of COVID-19 patients. Moreover, they noted that the incubation period of COVID-19 is in the range of 2-7 days with a median of 4 days. However, T. Singha [
38] reported that the incubation period of COVID-19 is in the range of 2-14 days with a median of 5 days. J. Wu et al [
39] noted that the mean age of the peoples infected with COVID-19 is about 46 years and the most common symptoms of the disease are cough and fever and 68% of patients with COVID-19 have abnormal density shadows in the parenchyma of both lungs. D. Wang et al [
40] investigated the clinical features of 138 COVID-19 patients, found that the age of the CoVID-19 patients is around 42-68, 98.6% of patients have fever, 70% show fatigue, and 60% have the dry cough. Moreover, bilateral patchy shadows or ground-glass opacity present in the CT images of all patients with COVID-19. P. I. Lee et al. [
41] reported that children are less susceptible to COVID-19 infections. However, H. Qiu et al [
42] investigated the epidemiological and clinical features of 36 children infected with COVID-19. They reported that 53% of children infected with COVID-19 showed moderate clinical type with pneumonia and 47% revealed mild clinical type. The common symptoms of the disease in children infected with COVID-19 are fever and dry.
Abstractly, the common clinical feature of COVID-19 are including fever, cough, normal or decreased white blood cells (WBCs), and multiple patchy glassy shadows on CT images of the peripheral and posterior lungs. The median of the age of peoples infected with COVID-19 is above 40 years. Children are less susceptible to COVID-19 infections and the incubation period of COVID-19 is variable from 2 to 14 days [
5,
6,
7,
8,
28,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42].
3. Epidemiological parameters
Epidemiological parameters of COVID-19 including basic reproduction number (R
0), transmission rate (β), the average ascertainment rate, and infectious period have been investigated in recent months after reporting the first case of COVID-19 at the end of 2019. In this regard, several high impact types of research have been reported in the literature. The WHO reported the R
0 of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) ranged from 1.4 to 2.5 (mean =1.95) for the direct (human-to-human) transmission [
43]. It should be noted that the transmissibility of a virus has defined in term of R
0, on the other hand, the R
0 represents the average number of new infections generated by an infectious person which R
0 >1 indicated the high potential of virus for outbreaks and R
0 <1, revealed the low potential of outbreaks.
J. Riou and C.L. Althaus [
44], N. Imai et al. [
45], and M. Shen et al. [
46] estimated the mean R
0 of the 2019-nCoV over 2-5 which is larger than the reported range by WHO. In addition, M. Majumder and K.D. Mandl [
47] reported the R
0 of the 2019-nCoV in the rage of 2.0–3.3. Moreover, Ying Liu et al. reported that the mean R
0 of COVID-19 is around 3.28 (median: 2.79). They also noted that this value is within the range of the mean R
0 of the SARS-CoV [
4]. Also, S. Zhao et al. [
2] reported that the R
0 of the 2019-nCoV is variable from 2.24-3.58 which is significantly larger than one. It should be noted that sources of discrepancies may be due to model differences and differences in the contribution of specific types of data to our estimates. They also reported that the mean R
0 of 2019-nCoV is largely in the range of those of SARS (R
0= 2-5) and MERS (2.7-3.9).They noted that the coronavirus disease 2019 reveals a high potential for the outbreaks due to its very large R
0.
J. M. Read et al. [
3] reported that the R
0 of the infection is in the range of 2.39–4.13 with an average of 3.11. They noted that the R
0 of the COVID-19 is comparable to the range for SARS estimated from outbreaks during the 2003 epidemic. They evaluated the transmission rate and the infectious period of COVID-19 within Wuhan over the range of 1.25-6.71 d
-1 and 0.35-3.23 days, respectively. The average transmission rate and the infectious period were found to be 1.94 d
-1 and 1.61 days, respectively, with a 95% confidence level. They. also estimated the average ascertainment rate of COVID-19 in Wuhan “between” 1-22 January 2020. They reported that the average ascertainment rate of COVID-19 is over the range of 3.6-7.6% with a mean value of 5.0%. They pointed out that this value of the average ascertainment rate reflects the difficulty in identifying cases of a novel pathogen [
3]. As a consequence, based on the recent reports on the epidemiological parameters, it can be concluded that the COVID-19 reveals a high potential for causing a global pandemics, as now we see around the world.
4. Mechanism of 2019-nCoV action
We know that the common coronavirus infections such as SARS damage the cells through the binding of the SARS-CoV to the target cells via ACE2. J. R. Delanghe [
9] pointed out that the epidemiological findings in 2019-nCoV infections can be explained by the host’s angiotensin-converting enzyme polymorphism. Additionally, some other researchers also believe that the novel pathogenic coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, acts via binding to the ACE2 enzyme. More precisely, they believe that the novel coronavirus accesses host cells through affecting the ACE2 enzyme (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) via connecting to the peplomer (a special surface glycoprotein) of the enzyme. The ACE2 is the most abundant enzyme in the type II alveolar cells of the lungs, hence, the 2019-nCoV has entered to the host cells through the peplomer and destroyed the lungs [
48,
49,
50,
51]. In regard to this hypothesis, Zhang et al. [
52] reported that 30% of COVID-19 patients have hypertension while Huang et al. [
53] noted that hypertension was observed in 15% of COVID-19 patients. In addition, R. Li et al. [
8] found that the incidence of hypertension was 45.95% in the severe COVID-19 patients and 15.96% in the non-severe patients of COVID-19. They noted that hypertension is a high risk for COVID-19 patients, however, the mechanism underlying this link is unknown. They emphasized that the high blood pressure in the COVID-19 patients may damage the ACE2 receptor-expressing endothelial or alveolar epithelial cells in the lung. Also, T. Singha [
38] pointed out that the studies on the mechanism of action of 2019-nCoV have proved that the ACE2 is the receptor of this novel virus.
As a consequence, the 2019-nCoV (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel betacoronavirus and the present data about the mechanism action of 2019-nCoV is unclear. On the other hand, in the current situation, the mechanism in which the 2019-nCoV enters and damages its host cells is not established completely but some useful hypothesizes are reported in the literature about the mechanism of this novel betacoronavirus.
5. Diagnosis of COVID-19
The WHO has published several testing methods for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Up to now, different testing methods have been utilized for the diagnosis of COVID-19 including;
✓ Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR)
✓ Hematology examination
✓ Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
✓ Diagnostic guidelines based on clinical features
✓ Chest CT scans
5.1. rRT-PCR
RT-PCR is a laboratory testing method that works via reverse transcription of RNA into DNA, following by amplification of specific DNA of virus utilizing the PCR analysis and usually employed for measuring the amount of a specific RNA by real-time PCR testing method via a fluorescence detection system [
54]. During the last decades several important rRT-PCR laboratory tests have been developed for the rapid and reliable detection of pandemics for instance, (H1N1) 2009 influenza virus, European swine influenza A virus, SARS-associated coronavirus, and MERS [
55,
56]. After the first report of outbreaks of the novel COVID-19, the WHO has published several testing methods for its diagnosis. Among these techniques, the rRT-PCR has introduced as the standard testing method for the detection of 2019-nCoV by WHO [
57]. Typically, the rRT-PCR test for the detection of COVID-19 is performed on respiratory samples provided by a nasopharyngeal swab [
5,
16,
21]. The testing method is rapid and the results are usually available maximally after 2 days. It should be noted that however, the RT-PCR testing method shows significant advantages for the diagnosis of COVID-19, its accuracy is only 70% [
58]. However, concerning the rapid detection of COVID-19 utilizing the rRT-PCR test, several high impact types of research have reported in the literature after the first report of this novel epidemic. For instance, G. Ye et al. [
21] reported significant research on the differences between the results of the lingual swab and throat swab respiratory tract sampling strategies for the detection of COVID-19 using an RT-PCR assay. They found that the positive rate (for testing 91 patients) of throat swabs for the detection of 2019-nCoV was about 44.0% while it was estimated at 36.3% for the lingual swabs sampling. Besides, they tested the effect of the experience of the nurse on the sensitivity of the diagnostic process, they found that when the sampling was performed by an experienced nurse, the positive rates of throat swabs for the detection of 2019-nCoV was increased to 54.3% while that of the lingual swabs showed no any significant change (36.9%). According to these findings, they concluded that the positive rate of throat swabs is higher than that of lingual swabs for the detection of COVID-19, however, the sensitivity of the diagnostic process has improved by sampling from both sites (i.e., throat swabs and lingual swabs). In another report, C. Huang et al [
5] studied the clinical features of the COVID-19 based on the detection of 2019-nCoV in the plasma samples of 41 hospital patients with 2019-nCoV infection using a standard detection method based on the rRT-PCR and next-generation sequencing. It should be noted that they used the RNAaemia as a positive response to the rRT-PCR test in the plasma sample. Besides, N. Zhu et al [
16] reported the use of the rRT-PCR assay for the detection of viral RNA of 2019-nCoV by targeting a consensus RdRp region of β-CoV.
5.2. Hematology examination
Blood tests can be utilized for the detection of COVID-19 but this method needs two blood samples obtained two weeks apart. However, the results of hematology examination are not so reliable and show no significant clinical diagnostic value for COVID-19 detection. In this regard, Y. H. Jin et al [
1] reported that hematology examination may be a useful method for the detection of COVID-19 because, in the early stages of the COVID-19, the total numbers of the leukocytes and lymphocyte were decreased in the blood while the counts of the monocytes were increased (or normal). However, they noted that this test should be repeated after 3 days for rechecking the blood routine changes. Besides, R. Li et al [
8] used the blood tests including the procalcitonin (PCT), blood cell differential count, C-reactive protein (CRP), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), serum creatinine (Cr), and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) total bilirubin (TBil) as a primary test for the COVID-19 detection. They found that TBil, Cr, AST, ALT, and BUN were in their normal ranges in all COVID-19 patients (225 cases) while the count of WBCs was decreased in 86.67% and the lymphocytes counts were normal or decreased in 99.11% of patients. Moreover, the ESR level showed an increase of 90.22% of patients from its normal range (0-15 mm/h) to 55.8 ± 25.3mm/h. Besides, the CRP level showed a significant increase from 0-10 mg/L to about 60.4± 57 mg/L in 86.22% of COVID-19 patients. Also, the PCT concentration was increased by 10.67% of COVID-19 patients from its normal range to 0.87 ± 0.560–0.5 mg/L. Based on the reported results by R. Li et al [
8], it can be concluded that the test of the CRP, ESR, WBCs, and lymphocytes counts can be useful for the diagnosis of COVID-19 as the primary diagnostic test at the early stages of the disease. Also, C. Huang et al. [
5] reported that the initial plasma IL1RA, IL1B, GCSF, IL7, IL8, IL9, IL10, GMCSF, basic FGF, IP10, IFNγ, MIP1A, MCP1, MIP1B, TNFα, PDGF, and VEGF concentrations were higher in the plasma of the COVID-19 patients than that in the plasma of healthy peoples. Consequently, based on the above-mentioned reports, t can be deduced that the hematology examination can be useful for the detection of the COVID-19 at its early stages but these tests are not a specific test for this purpose.
5.3. PCR based methods
Regarding the COVID-19 detection through utilizing PCR methods, Y. H. Jin et al [
1] strongly recommended the accurate detection of RNA of 2019-nCoV in respiratory tracts (e.g., throat swab) using the fluorescence quantitative PCR method. Besides, R. Li et al [
8] reported the use of one-step real-time PCR for the detection of 2019-nCoV via identification of RNA of the virus in the samples obtained from the nasal cavity or the pharynx with sputum or throat swabs. Moreover, N. Zhu et al [
16] used both PCR (using a RespiFinderSmart22kit) and Light Cycler 480 real-time PCR systems for the detection of COVID-19 in 22 patients.
5.4. Diagnosis of COVID-19 using clinical features
Y. H. Jin et al (Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University recommended Diagnostic guidelines) [
1] reported that the clinical features especially fever can be used as a primary step in the diagnosis of COVID-19. Moreover, R. Li et al. [
8] reported that the major clinical symptoms of the COVID-19 were fever (84.44 %), and cough (56.44 %) which may be useful for the early detection of COVID-19. Besides, C. Huang et al. [
5] reported that 98% of patients of COVID-19 had a fever, and 76% coughed at the onset of illness. Based on these reports, the diagnosis based on the clinical features of patients may be a rapid way for the detection of COVID-19 but it is not a specific diagnostic way.
5.5. Chest CT scans
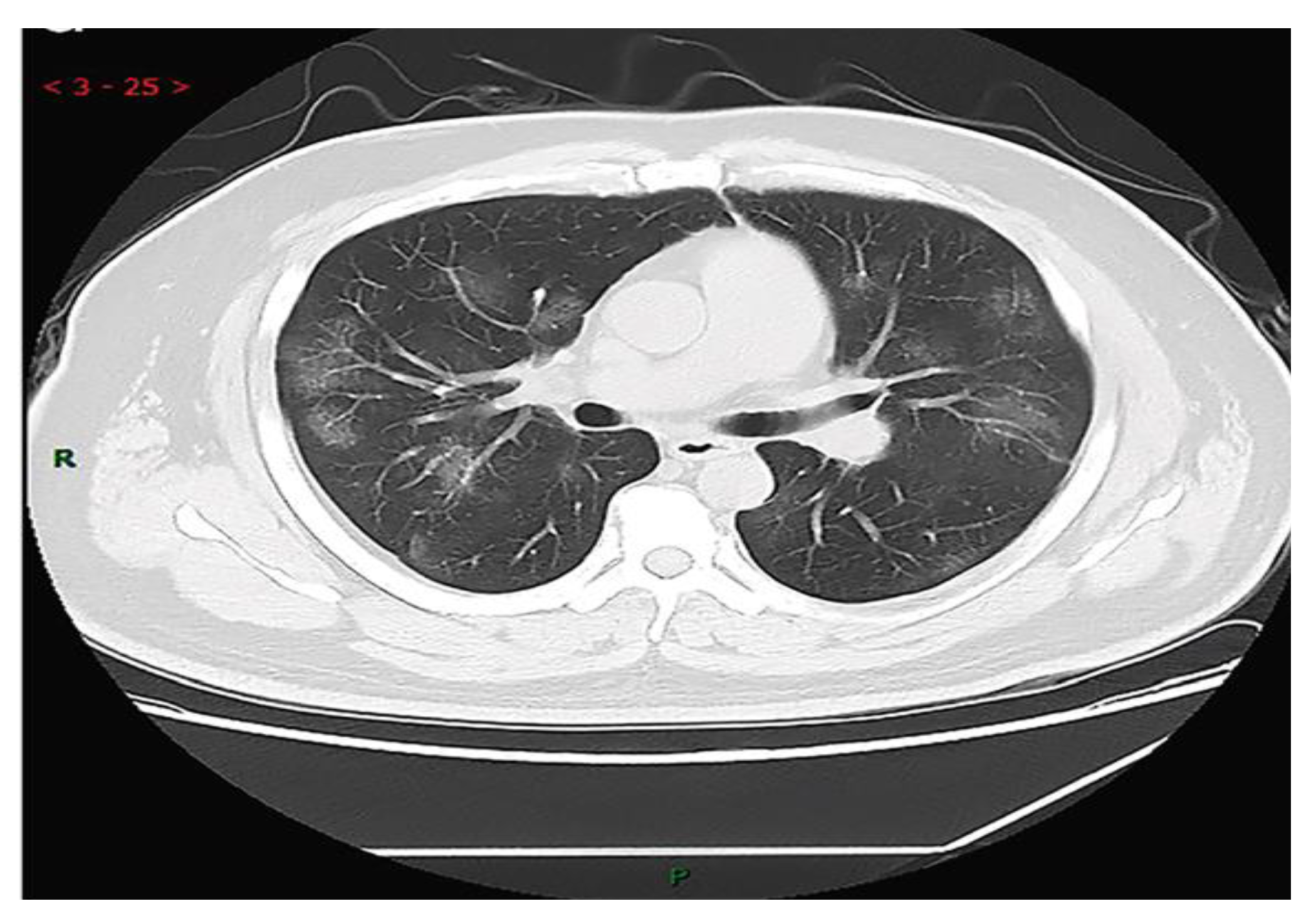
The chest CT scans testing method is one of the most useful methods for the detection of COID-19 along with laboratory testing methods such as PCR, hematology tests, and rRT-PCR. In this regard, Y. H. Jin et al [
1] strongly suggested CT imaging for the diagnosis of COIVD-19. They reported that in the CT images of 54.2% COVID-19 patients, multiple, patchy, sub-segmental or segmental ground-glass density shadows in both lungs were observed (
Figure 1). They also noted that the CT scans of 31.3% of severe patients infected with COVID-19 showed the patchy, multiple, and/or large patches of consolidation in lungs along with a honeycomb-shaped interlobular septal thickening or little grid-like in the lower and middle lobes.
Moreover, W. Hao and M. Li [
6] published a high impact article about the clinical diagnostic value of CT imaging for detection of COVID-19 with multiple negative RT-PCR results, he noted that however, the RT-PCR testing method shows significant advantages for the diagnosis of COVID-19, its accuracy is only 70% while the accuracy of CT imaging for the detection of COVID-19 is about 98%. He recommended that if the RT-PCR test of a patient was negative, the CT scans should be recorded and if the chest CT image of the patient showed characteristics of viral pneumonia, the isolation, and treatment of the patient should be considered. Also, F. Yicheng et al [
58] reported that the CT scan is a more suitable test for the clinical diagnosis of CVID-19 than the routine rRT-PCR method.
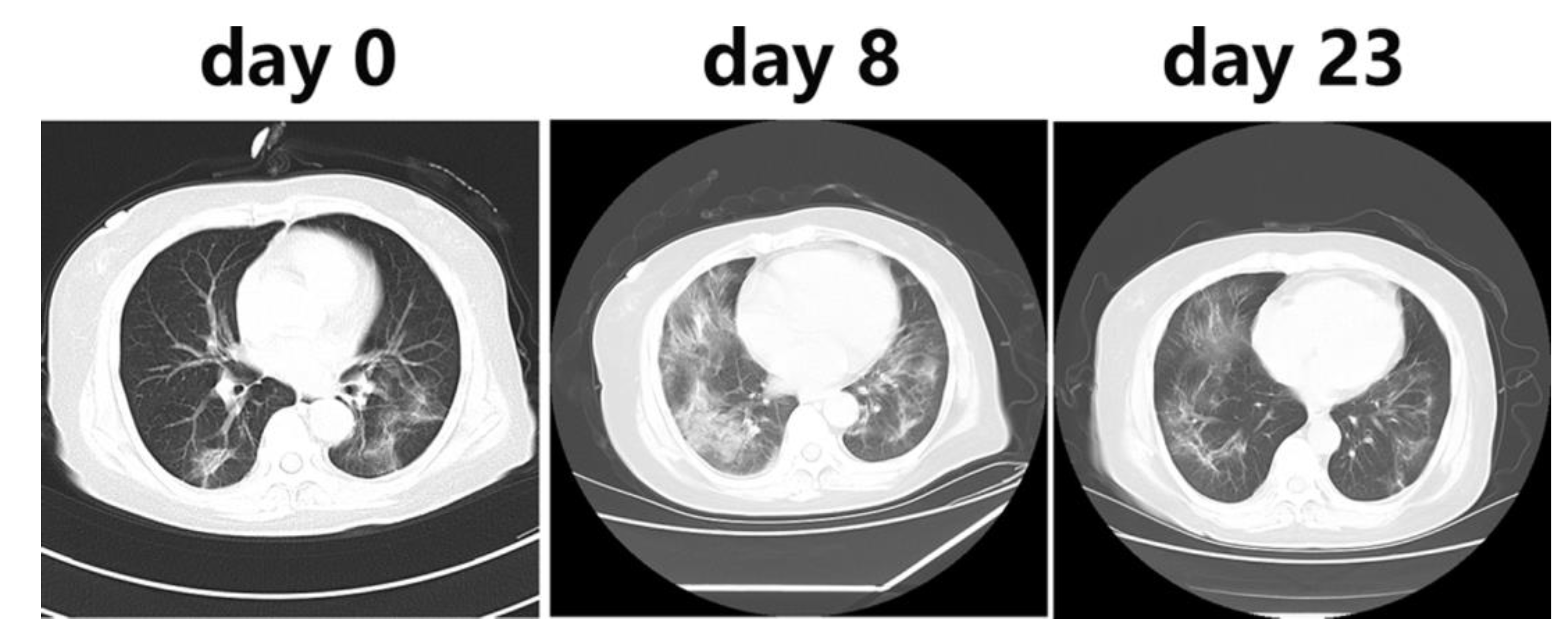
Besides, R. Li et al [
8] used the CT imaging for the detection of COVID-19, they reported that the CT scans of all COVID-19 patients showed lung infiltrates and for 86.22%, multiple patchy glassy shadows were observed in the CT images of their both lungs. They also noted that the lesions increased by the progression of the disease and their scope in size or number expanded (
Figure 2). In addition, N. Zhu et al [
16] reported that the bilateral fluffy opacities were observed in the CT images of the lungs of a COVID-19 patient after 8 days of onset of symptoms but density, profusion, and the confluence of these bilateral fluffy opacities were increased by the progression of COVID-19 (after 14 days). Also, C. Huang et al. [
5] noted that chest CT images of a 40-year-old man with COVID-19 recorded on day 15 after symptom onset showed sub-segmental areas of consolidation and bilateral multiple lobular while the images of a woman (53-year-old) recorded on 8
th day after symptom onset showed sub-segmental areas of consolidation and bilateral ground-glass opacity and her CT image recorded after 12 days from symptom onset showed only bilateral ground-glass opacity. Based on the above-mentioned reports, the CT imaging method can be used as a highly accurate method for the clinical diagnosis of the COIVD-19 along with the rRT-PCR.
6. Comparison with SARS and MERS
S. Zhao et al. [
2] reported that the mean R
0 of 2019-nCoV is closely in the range of the R
0 of SARS (R
0= 2-5) and MERS (R
0= 2.7-3.9). However, J. A. Al-Tawfiq [
59] noted that the recent studies showed that the 2019-nCoV reveals the higher potential for outbreaks than both MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV. Moreover, C. Huang et al [
5] noted that the clinical features of the 2019-nCoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV are similar to each other. They noted that commonly, the COVID-19 patients have a fever, bilateral ground-glass opacities on chest CT scans and dyspnoea, and dry cough which is closed to the clinical features of patients with SARS and MERS. They emphasized that in some cases of COVID-19, the few patients showed sneezing, sore throat, and/or rhinorrhea which are not common in SARS MERS. Besides, only about 20–25% of SARS or MERS patients show diarrhea while the COVID-19 patients rarely developed diarrhea. Moreover, the levels of IL6, IFNγ, IL1B, IL12, MCP1, and IP10 have increased in the plasma of patients with SARS associated with pulmonary inflammation, and extensive lung damage, also, in the case of MERS, the concentrations of IL17, IFNγ, IL15, and TNFα have increased in the plasma. Similarly, COVID-19 patients show high levels of IFNγ, MCP1, IL1B, and IP10. They emphasized that the level of T-helper-2 cytokines such as IL4 and IL10 have increased in the plasma of patients with COVID-19 while the levels of these cytokines are at their normal levels in the case of SARS [
5]. Moreover, N. Petrosillo et al [
60] published a narrative review in the comparison between the differences SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 in terms of pathogenesis, clinical, and epidemiology feature. They reported that the COVID-19 exhibited the same clinical features with SARS and MERS while the fatality rate of COVID-19 (2.3%) is lower than MERS (34.5%) and SARS (9.5%), hence, the COVID-19 shows higher potential for easier outbreaks than the SRAS or MERS. They also pointed out that both COVID-19 and SARS share the ACE2 as receptor while MERS-CoV access cell via dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4). Abstractly, SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 show the same clinical features while the COVID-19 reveals the higher potential for outbreaks and consequently for causing global pandemics than both MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV. However, the mechanism of action of COVID-19 seems to be similar to SARS.
7. Comparison with H1N1
The influenza viruses show common etiologies with 2019-nCoV, also, both H1N1 and COVID-19 occur in the same season. Previously reported researches in the literature pointed out that fever and productive cough are the common symptoms of H1N1 while nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea (GI symptoms) are less common in patients with H1N1. Moreover, the ground-glass opacities commonly are not observed in the chest CT scans of H1N1 patients [
61]. The similarity between the etiologies of COVID-19 and H1N1 cause difficulty for the accurate distinguishing of the COVID-19 patients from the H1N1 patients while the treatments and prognoses of these diseases are not the same, therefore, the accurate identification of H1N1 and COVID-19 through their differential clinical manifestations is important. In this regard, a few months after the outbreaks of 2019-nCoV in China, X. Tang et al published a comparison between the COVID-19 and H1NI patients [
7]. They reported that the age of H1N1patients is usually lower than the median age of COVID-19 patients while the proportion of male subjects is higher among the COVID-19 patients than the H1N1. Fever, dyspnea, and cough are common symptoms of both COVID-19 and H1N1 and hemoptysis is their less common symptom. Productive cough in COVID-19 significantly less than the H1N1 while the proportions of myalgia, fatigue, and GI symptoms in COVID-19 is commonly higher than the H1N1. Moreover, they noted that although, the impairments in cellular immune function is another property of both H1N1 and COVID-19, the level of CD
3+ T lymphocyte in COVID-19 patients is characteristically lower than that in H1N1 patients. They also pointed out that the levels of lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate transaminase, and troponin I in H1N1 patients is significantly higher than those in COVID-19 patients while the ground-glass opacity on chest CT scans is more common in COVID-19 patients than in H1N1 patients, however, the consolidation is more common in H1N1 patients. Moreover, in the comparison between H1N1 and COVID-19, T. Singha [
38] pointed out that the R
0 of COVID-19 is over the range of 2-6.47 which is higher than that for pandemic flu H1N1 2009 (1.30). Abstractly, the influenza viruses show common etiologies with 2019-nCoV, also, both H1N1 and COVID-19 occur in the same season. The R
0 of COVID-19 is higher than that for H1N1, indicating higher potential of COVID-19 for outbreaks than H1N1. Fever, dyspnea, and cough are common symptoms of both COVID-19 and H1N1. Productive cough in COVID-19 significantly less than the H1N1 and the ground-glass opacity on chest CT scans is more common in COVID-19 patients than in H1N1 patients,
8. Conclusions
The COVID-19 is a global pandemics infectious disease which caused by 2019-nCoV or SARS-CoV-2. The common clinical feature of COVID-19 are including fever, cough, normal or decreased white blood cells (WBCs), and multiple patchy glassy shadows on CT images of the peripheral and posterior lungs. The median of the age of peoples infected with COVID-19 is above 40 years and children are less susceptible to COVID-19 infections. Studies on the epidemiological parameters of COVID-19 reveal its high potential for outbreaks, as now we see around the world. Regarding the mechanism action of 2019-nCoV, some researchers suggested that the ACE2 is the receptor of this novel virus. Concerning the clinical diagnosis, CT scans can be used as a highly accurate method for the clinical diagnosis of the COIVD-19 along with the rRT-PCR. In comparison with SARS, MERS, and H1N1, although the novel COVID-19 shows the same clinical features with these diseases, it reveals the higher potential for outbreaks and consequently for causing global pandemics than MERS, H1N1, and SARS.
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to acknowledge the support of this work by Hormozi Laboratory of Chemistry and Biochemistry.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing for financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Y. H. Jin, L. Cai, Z. S. Cheng, H. Cheng, T. Deng, Y. P. Fan, C. Fang et al, A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version), Military Medical Research 7 (2020) 4. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhao, Q. Lin, J. Ran, S. S. Musa, G. Yang, W. Wang, Y. Lou et al, Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China, from 2019 to 2020: A data-driven analysis in the early phase of the outbreak, International journal of infectious diseases 92 (2020) 214-217. [CrossRef]
- J.M. Read, J.R.E. Bridgen, D.A.T. Cummings, A. Ho, C.P. Jewell, Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: early estimation of epidemiological parameters and epidemic predictions, MedRxiv (2020).
- Y. Liu, A.A. Gayle, A. Wilder-Smith, J. Rocklöv, The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus, Journal of travel medicine (2020). [CrossRef]
- C. Huang, Y. Wang, X. Li, L. Ren, J. Zhao, Y.Hu, L. Zhang et al, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, The Lancet 395 (2020) 497-506. [CrossRef]
- W. Hao, M. Li, Clinical diagnostic value of CT imaging in COVID-19 with multiple negative RT-PCR testing, Travel medicine and infectious disease (2020) 101627. [CrossRef]
- X. Tang, R. Du, R. Wang, T. Cao, L. Guan, C. Yang, Q. Zhu et al, Comparison of Hospitalized Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Caused by COVID-19 and H1N1, Chest (2020). [CrossRef]
- R. Li, J. Tian, F. Yang, L. Lv, J. Yu, G. Sun, Y. Ma, X. Yang, J. Ding, Clinical Characteristics of 225 Patients with COVID-19 in a Tertiary Hospital near Wuhan, China, Journal of Clinical Virology (2020) 104363. [CrossRef]
- J.R. Delanghe, M.M. Speeckaert, M.L. De Buyzere, The host’s angiotensin-converting enzyme polymorphism may explain epidemiological findings in COVID-19 infections, Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry 505 (2020) 192-193. [CrossRef]
- . [CrossRef]
- K.M. Ha, Emergency response to the outbreak of COVID-19: the Korean case, Microbes and Infection (2020). [CrossRef]
- B. Moazzami, N. Razavi-Khorasani, A.D. Moghadam, E. Farokhi, N. Rezaei, COVID-19 and Telemedicine: Immediate action required for maintaining healthcare providers well-being, Journal of Clinical Virology (2020) 104345. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Backer, D. Klinkenberg, J. Wallinga, Incubation period of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections among travellers from Wuhan, China, 20–28 January 2020." Eurosurveillance 25 (2020) 2000062. [CrossRef]
- Gherghel, M. Bulai, Is Romania ready to face the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak? The role of incoming travelers and that of Romanian diaspora, Travel medicine and infectious disease (2020) 101628. [CrossRef]
- D.S. Hui, E.I. Azhar, T.A.M Madani, F. Ntoumi, R. Kock, O. Dar, G. Ippolito et al, The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health—The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China, International Journal of Infectious Diseases 91 (2020) 264-266. [CrossRef]
- N. Zhu, D. Zhang, W. Wang, X. Li, B. Yang, J. Song, X. Zhao et al, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, New England Journal of Medicine (2020). [CrossRef]
- V.J. Munster, M. Koopmans, N. van Doremalen, D. van Riel, E. de Wit, A novel coronavirus emerging in China—key questions for impact assessment, New England Journal of Medicine 382 (2020) 692-694. [CrossRef]
- V. Surveillances, The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19)—China, 2020, China CDC Weekly 2 (2020) 113-122. [CrossRef]
- D. Jiménez-Pavón, A. Carbonell-Baeza, C.J. Lavie, Physical exercise as therapy to fight against the mental and physical consequences of COVID-19 quarantine: Special focus in older people, Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases (2020). [CrossRef]
- https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novelcoronavirus-2019.
- G. Ye, Y. Li, M. Lu, S. Chen, Y. Luo, S. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Wang, Experience of different upper respiratory tract sampling strategies for detection of COVID-19, Journal of Hospital Infection 105 (2020) 1-2. [CrossRef]
- H. Lau, V. Khosrawipour, P. Kocbach, A. Mikolajczyk, H. Ichii, M. Zacharksi, J. Bania, T. Khosrawipour, The association between international and domestic air traffic and the coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak, Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection (2020). [CrossRef]
- Saglietto, F. D’Ascenzo, G.B. Zoccai, G.M. De Ferrari, COVID-19 in Europe: the Italian lesson, The Lancet (2020). [CrossRef]
- K.O. Kwok, F. Lai, W.I. Wei, S.Y.S. Wong, J.W.T. Tang, Herd immunity–estimating the level required to halt the COVID-19 epidemics in affected countries, The Journal of Infection (2020). [CrossRef]
- Z. Wu, J.M. McGoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Jama (2020).
- P.N. Newton, K.C. Bond, M. Adeyeye, M. Antignac, A. Ashenef, G.R. Awab, W.J. Bannenberg et al, COVID-19 and risks to the supply and quality of tests, drugs, and vaccines, The Lancet Global Health (2020). [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Zhou, F. Liu, Reasons for healthcare workers becoming infected with novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China. The Journal of Hospital Infection (2020). [CrossRef]
- M.A. Hill, C. Mantzoros, J.R. Sowers, Commentary: COVID-19 in patients with diabetes, Metabolism 107 (2020) 154217. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, COVID 19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC), Global research and innovation forum: towards a research roadmap (2020).
- https://www.who.int/diagnostics_laboratory/EUL/en.
- World Health Organization (19 February 2020), Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): situation report, 29, World Health Organization (WHO), hdl:10665/331118.
- B. Li, et al, Prevalence and impact of cardiovascularmetabolic diseases on COVID-19 in China, Clin Res Cardiol 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-020-01626-9 Mar 11. [CrossRef]
- X. Yang Y. Yu, J. Xu, et al, Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir Med 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20) 30079-5 Feb 24. pii: S2213-2600(20)30079-5. [CrossRef]
- J.J. Zhang, X. Dong, Y.Y. Cao, et al, Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected by SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy 2020, https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14238. [CrossRef]
- W. Guan, Z. Ni, Y. Hu, et al, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med 2020. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 Feb 28. [CrossRef]
- T. Xu, C. Chen, Z. Zhu, M. Cui, C. Chen, H. Dai,Y. Xue, Clinical features and dynamics of viral load in imported and non-imported patients with COVID-19, International Journal of Infectious Diseases (2020). [CrossRef]
- W. Guan, Z. Ni, Y. Hu, W. Liang, C. Ou, J. He, L. Liu et al, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, New England Journal of Medicine (2020). [CrossRef]
- . [CrossRef]
- J. Wu, J. Liu, X. Zhao, C. Liu, W. Wang, D. Wang, W. Xu et al, Clinical Characteristics of Imported Cases of COVID-19 in Jiangsu Province: A Multicenter Descriptive Study, Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (2020).
- D. Wang, B. Hu, C. Hu, F. Zhu, X. Liu, J. Zhang, B. Wang et al, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, Jama 323 (2020) 1061-1069. [CrossRef]
- P.I. Lee, Y.L. Hu, P.Y. Chen, Y.C. Huang, P.R. Hsueh, Are children less susceptible to COVID-19?, Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection (2020). [CrossRef]
- H. Qiu, J. Wu, L. Hong, Y. Luo, Q. Song, Dong Chen, Clinical and epidemiological features of 36 children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China: an observational cohort study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases (2020). [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019- nCoV) in suspected human cases, World Health Organization (WHO). 2020. https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus/laboratory-diagnostics-for-novel coronavirus.
- J. Riou, C.L. Althaus, Pattern of early human-to-human transmission of Wuhan 2019-nCoV. bioRxiv 2020; 2020.2001.2023.917351.
- N. Imai, I. Dorigatti, A. Cori, S. Riley, N.M. Ferguson, Estimating the potential total number of novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) cases in Wuhan City. China: Preprint published by the Imperial College London; 2020. https://www.imperial.ac.uk/mrc-global-infectious-disease-analysis/news–wuhan-coronavirus/.
- M. Shen Z. Peng, Y. Xiao L. Zhang, Modelling the epidemic trend of the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in China. bioRxiv 2020;2020: 2001.2023.916726.
- M. Majumder, K.D. Mandl, Early Transmissibility Assessment of a Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China, (2020) Available at: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=3524675 (Accessed: 27 January 2020).
- R. Yan, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Xia, Y. Guo, Q. Zhou, Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science (2020) pii: eabb2762.
- G. Lippi, M. Plebani, B. Michael Henry, Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A meta-analysis, Clin. Chim. Acta (2020), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.022. [CrossRef]
- K. Kuba, Y. Imai, J.M. Penninger, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in lung diseases, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 6 (2006) 271–276. [CrossRef]
- G. Lippi, M. Plebani, Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis, Clin. Chim. Acta 505 (2020) 190–191. [CrossRef]
- J.J. Zhang, X. Dong, Y.Y. Cao, Y.D. Yuan, Y.B. Yang, Y.Q. Yan, et al., Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected by SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy (2020), https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14238. [CrossRef]
- S.Q. Deng, H.J. Peng, Characteristics of and Public Health Responses to the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak in China, J. Clin. Med. 9 (2020) E575. [CrossRef]
- W.M. Freeman, S.J. Walker, K.E. Vrana, Quantitative RT-PCR: pitfalls and potential, Biotechniques 26 (1999) 112-125. [CrossRef]
- M.J. Slomka, A.L.E. Densham, V.J. Coward, S. Essen, S.M. Brookes, R.M. Irvine, E. Spackman et al, Real time reverse transcription (RRT)-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods for detection of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 influenza virus and European swine influenza A virus infections in pigs, Influenza and other respiratory viruses 4 (2010) 277-293. [CrossRef]
- S.L. Emery, Shannon, D.D. Erdman, M.D. Bowen, B.R. Newton, J.M. Winchell, R.F. Meyer, S. Tong et al, Real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction assay for SARS-associated coronavirus, Emerging infectious diseases 10 (2004) 311. [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Interim Guidelines for Collecting, Handling, and Testing Clinical Specimens from Persons for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), (2020).
- Y. Fang, Z. Huangqi, X. Jicheng, et al, Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR, J Radiol (2020). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020200432. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Al-Tawfiq, Viral loads of SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 in respiratory specimens: What have we learned?, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease (2020).
- N. Petrosillo, G. Viceconte, O. Ergonul, G. Ippolito, E. Petersen, COVID-19, SARS and MERS: are they closely related?, Clinical Microbiology and Infection (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.03.026. [CrossRef]
- B. Cao, X.W. Li, Y. Mao et al, Clinical features of the initial cases of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus infection in China, N Engl J Med. 361(2009) 2507-2517. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).