Submitted:
25 May 2023
Posted:
26 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To the best of our knowledge, for the first time, a general machine-learning model is developed for predicting heat transfer in heat exchangers based on coating thickness over a wide range of domains.
- This work proposes a new way to combine input features without losing any sensitive information about the original feature space.
- The proposed method cures the curse of dimensionality of the K-Nearest Neighbors algorithm and as a result, the model accuracy is significantly improved.
- Feature engineering and feature combination methods used in this work make it possible to train machine-learning models over a smaller dataset with acceptable accuracy over unseen data from new domains.
2. Heat transfer analysis and feature extraction
3. Proposed method
3.1. Training model
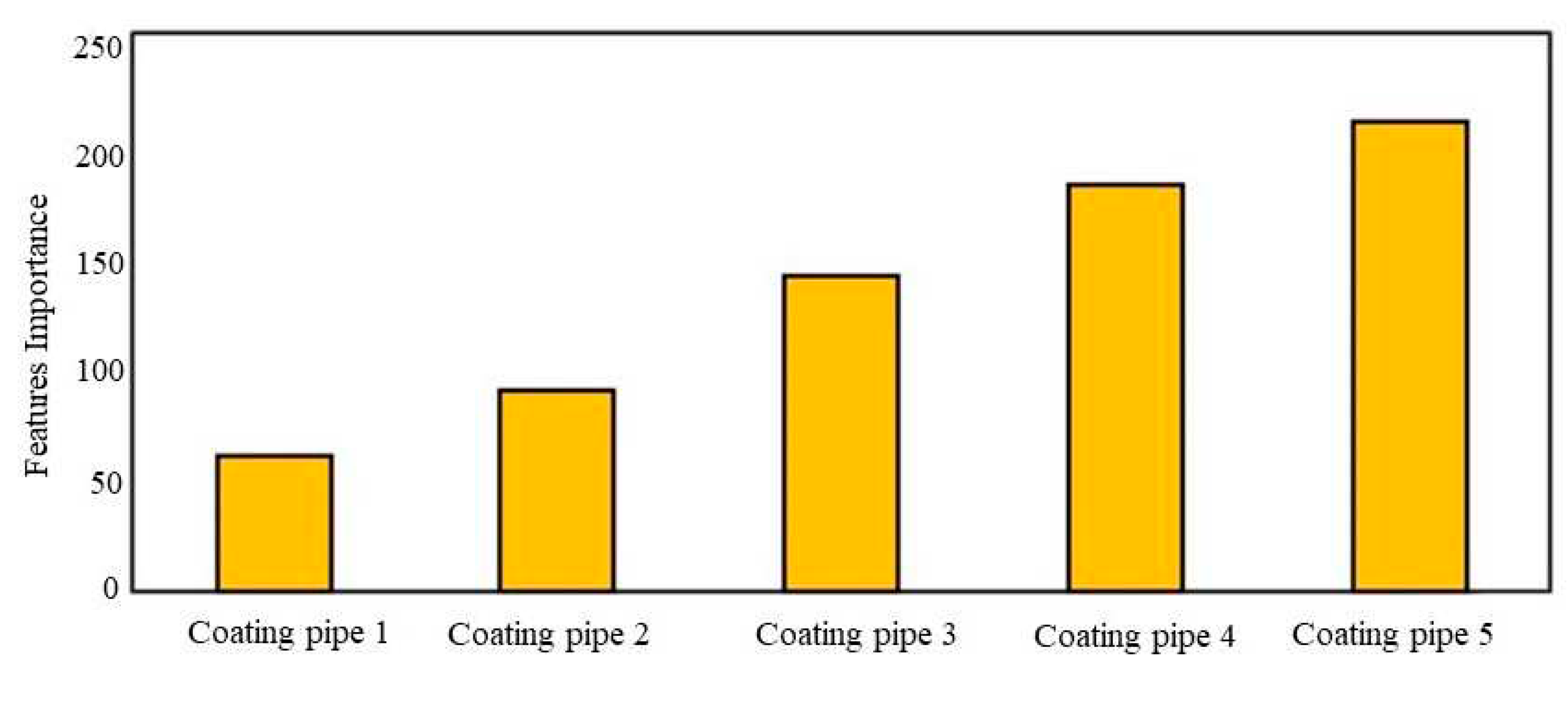
3.2. Features combination and expanding model domain
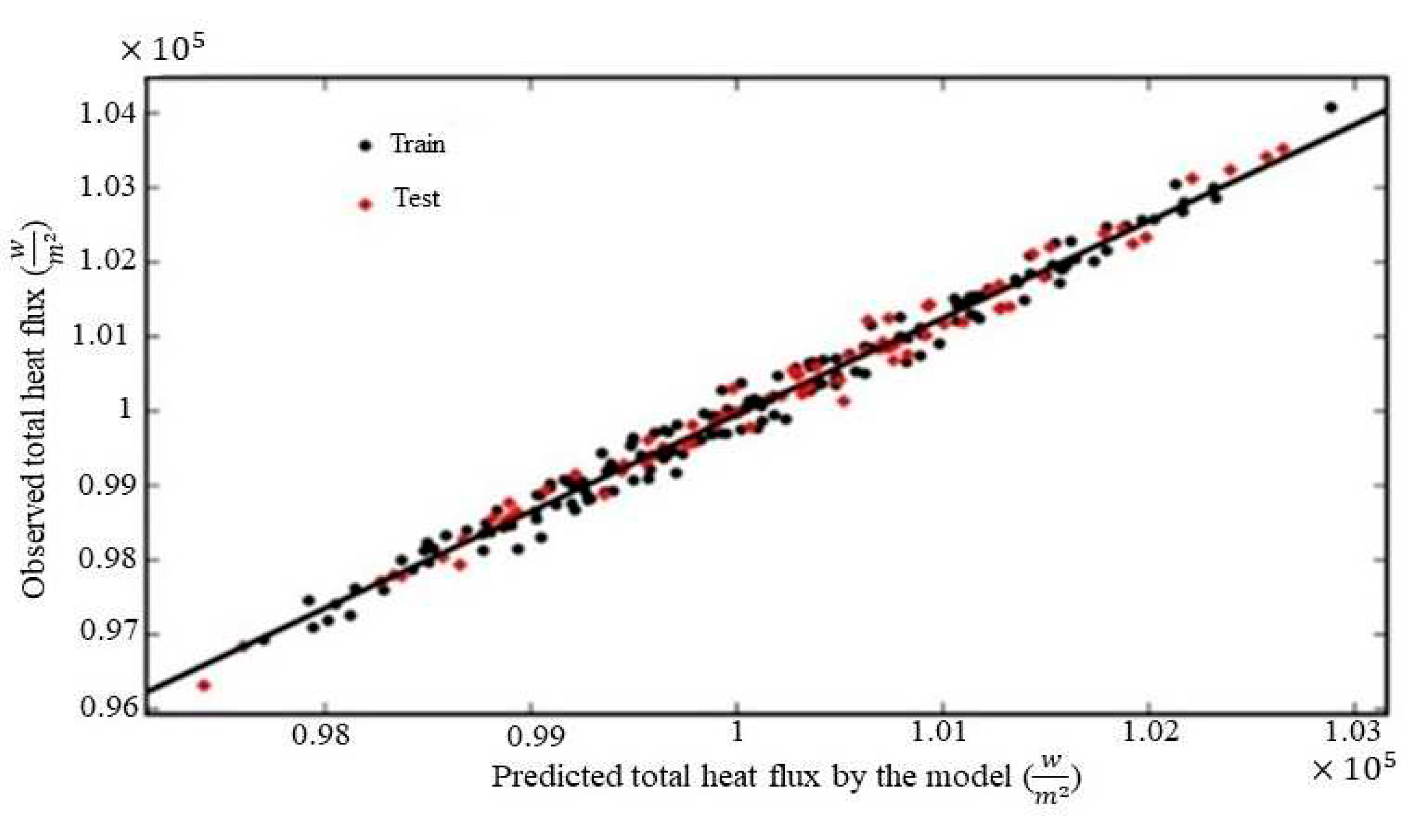
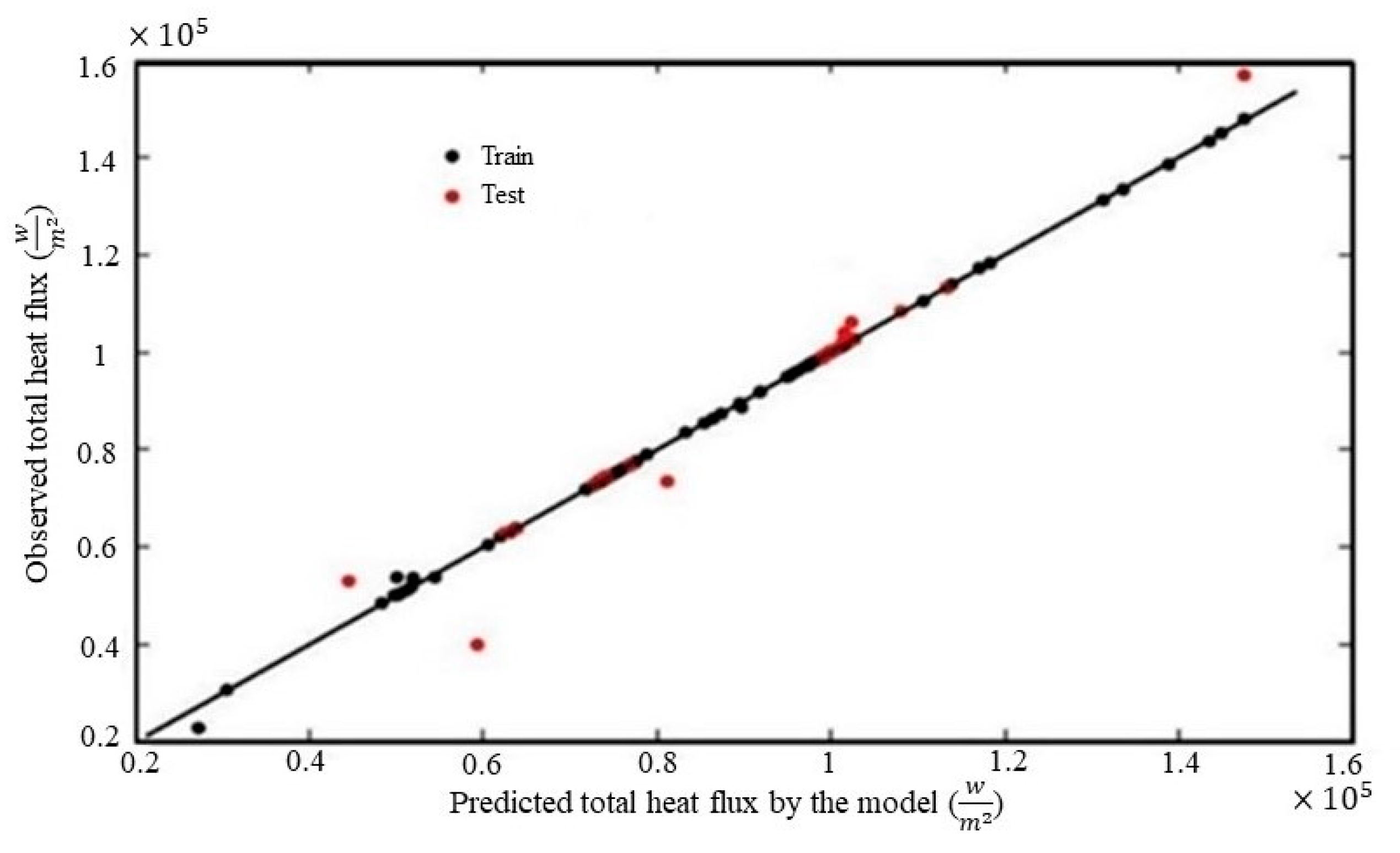
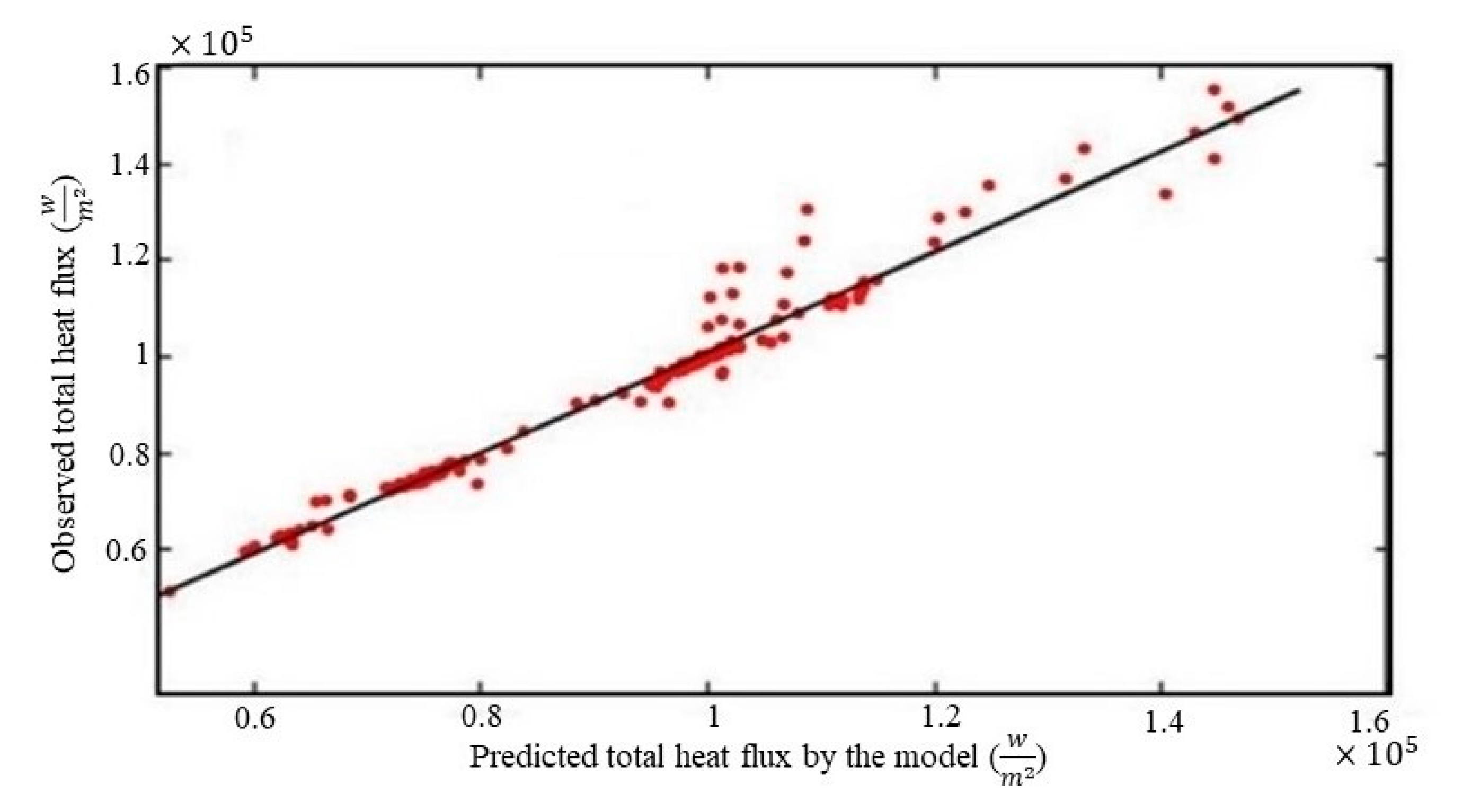
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isa, “Usman, M. A., S. O. Adeosun, and G. O. Osifeso. ‘Optimum Calcium Carbonate Filler Concentration for Flexible Polyurethane Foam Composite.’ Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering 11.03 (2012):311–320. Web.” 2018, [Online].
- J. Lefebvre, B. J. Lefebvre, B. Bastin, M. Le Bras, S. Duquesne, R. Paleja, and R. Delobel, “Thermal stability and fire properties of conventional flexible polyurethane foam formulations,”Polym. Degrad. Stab., vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 28–34, Apr. 2005. [CrossRef]
- G. Woods, in: D.C. Allport (Ed.), The ICI polyurethanes book, 2nd ed., 1990, p. 1.
- F. Valipour, S. F. F. Valipour, S. F. Dehghan, and R. Hajizadeh, “The effect of nano- and microfillers on thermal properties of Polyurethane foam,” Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 541–552, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Al-Homoud, “Performance characteristics and practical applications of common building thermal insulation materials,” Build. Environ., vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 353–366, Mar. 2005. [CrossRef]
- Y. Cheng, D. Y. Cheng, D. Miao, L. Kong, J. Jiang, and Z. Guo, “Preparation and Performance Test of the Super-Hydrophobic Polyurethane Coating Based on Waste Cooking Oil,” Coatings, vol. 9, no. 12. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, Anna, and Aleksey Bychkov. 2022. "How to Train an Artificial Neural Network to Predict Higher Heating Values of Biofuel" Energies 15, no. 19: 7083. [CrossRef]
- Góra, Krystian, Paweł Smyczyński, Mateusz Kujawiński, and Grzegorz Granosik. 2022. "Machine Learning in Creating Energy Consumption Model for UAV" Energies 15, no. 18: 6810. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Amira, Hatem Ibrahem, Rui Yang, and Kibum Kim. 2022. "Optimization of Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer Cell Design Using Machine Learning" Energies 15, no. 18: 6657. [CrossRef]
- K. Runchal and M. M. Rao, “CFD of the Future: Year 2025 and Beyond BT - 50 Years of CFD in Engineering Sciences: Commemorative Volume in Memory of D. Brian Spalding,” A. Runchal, Ed. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2020, pp. 779–795.
- Alexiou K, Pariotis EG, Leligou HC, Zannis TC. Towards Data-Driven Models in the Prediction of Ship Performance (Speed—Power) in Actual Seas: A Comparative Study between Modern Approaches. Energies. 2022; 15(16):6094. [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Pérez, E. Data Mining and Machine Learning Techniques for Aerodynamic Databases: Introduction, Methodology and Potential Benefits. Energies. 2020; 13(21):5807. [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, S. Shamshirband, E. Salwana, K. Chau, and J. H. M. Tah, “Prediction of multi-inputs bubble column reactor using a novel hybrid model of computational fluid dynamics and machine learning,” Eng. Appl. Comput.Fluid Mech., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 482–492, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Gaurav Krishnayatra, Sulekh Tokas, Rajesh Kumar,Numerical heat transfer analysis & predicting thermal performance of fins for a novel heat exchanger using machine learning,Case Studies in Thermal Engineering,Volume 21,2020,100706,ISSN 2214-157X. [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, K.; Wilson, Z.T.; Næss, E.; Sahinidis, N.V. A Machine Learning Approach to Correlation Development Applied to Fin-Tube Bundle Heat Exchangers. Energies 2018, 11, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beomjin Kwon, Faizan Ejaz, Leslie K. Hwang,Machine learning for heat transfer correlations,International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer,Volume 116,2020,104694,ISSN 0735-1933. [CrossRef]
- T. Vu, S. T. Vu, S. Gulati, P. A. Vogel, T. Grunwald, and T. Bergs, “Machine learning-based predictive modeling of contact heat transfer,”Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., vol. 174, p. 121300, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. K. M. Nasution, M. M. K. M. Nasution, M. Elveny, R. Syah, I. Behroyan, and M. Babanezhad, “Numerical investigation of water forced convection inside a copper metal foam tube: Genetic algorithm (GA) based fuzzy inference system (GAFIS) contribution with CFD modeling,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., vol. 182, p. 122016, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Jamei, I. A. M. Jamei, I. A. Olumegbon, M. Karbasi, I. Ahmadianfar, A. Asadi, and M. Mosharaf-Dehkordi, “On the Thermal Conductivity Assessment of Oil-Based Hybrid Nanofluids using Extended Kalman Filter integrated with feed-forward neural network,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., vol. 172, p. 121159, 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Wu, J. W. Wu, J. Wang, Y. Huang, H. Zhao, and X. Wang, “A novel way to determine transient heat flux based on GBDT machine learning algorithm,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., vol. 179, p. 121746, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Aref Eskandari, Jafar Milimonfared, Mohammadreza Aghaei,Line-line fault detection and classification for photovoltaic systems using ensemble learning model based on I-V characteristics,Solar Energy,Volume 211,2020,Pages 354-365,ISSN 0038092X. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, F. Ejaz, and L. K. Hwang, “Machine learning for heat transfer correlations,” Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., vol. 116, p. 104694, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Swartz, L. Wu, Q. Zhou, and Q. Hao, “Machine learning predictions of critical heat fluxes for pillar-modified surfaces,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., vol. 180, p. 121744, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Genuer, J.-M. R. Genuer, J.-M. Poggi, C. Tuleau-Malot, and N. Villa-Vialaneix, “Random Forests for Big Data,” Big Data Res., vol. 9, pp. 28–46, 2017. [CrossRef]
- K. J. Archer and R. V Kimes, “Empirical characterization of random forest variable importance measures,” Comput. Stat. Data Anal., vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 2249–2260, 2008. [CrossRef]
- L. Ladla and T. Deepa, “ Feature Selection Methods And Algorithms”, International Journal on Computer Science and Engineering (IJCSE), vol.3(5), pp. 1787-1797, 2011.
- Strobl, A.-L. Boulesteix, A. Zeileis, and T. Hothorn, “Bias in random forest variable importance measures: Illustrations, sources and a solution,” BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 25, 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. Wu, X.-Y. J. Wu, X.-Y. Chen, H. Zhang, L.-D. Xiong, H. Lei, and S.-H. Deng, “Hyperparameter Optimization for Machine Learning Models Based on Bayesian Optimizationb,” J. Electron. Sci. Technol., vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 26–40, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Indyk, Nearest neighbours in high-dimensional spaces, in: J.E. Goodman, J. O’Rourke (Eds.), Handbook of Discrete and Computational Geometry, Chapman and Hall, CRC, Boca Raton, London, New York, Washington, DC, 2004, pp. 877–892.
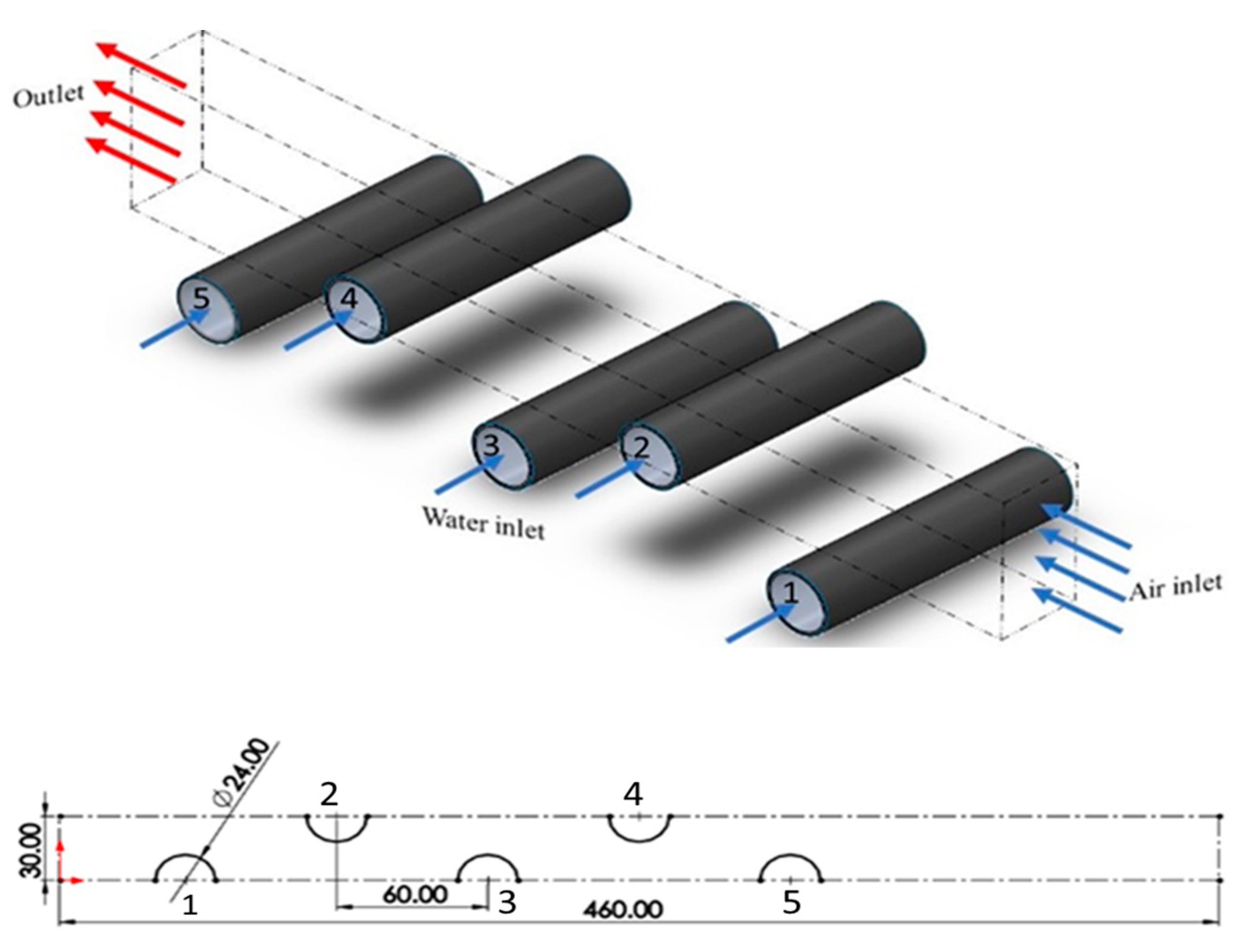
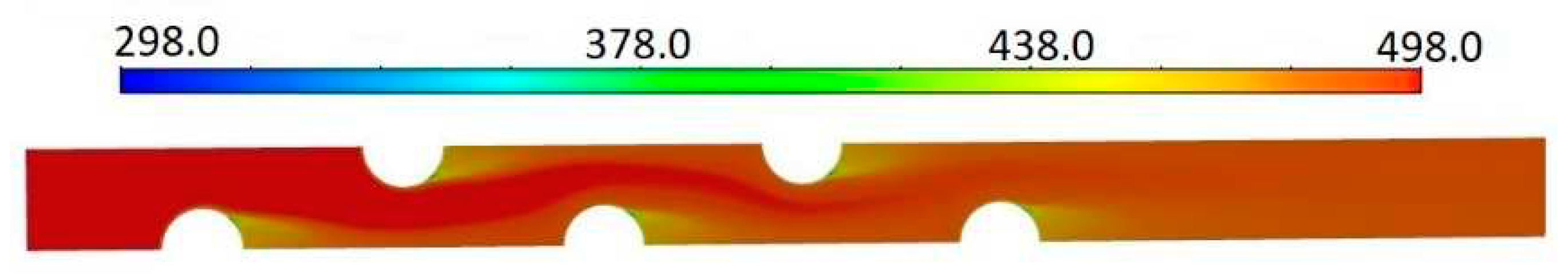
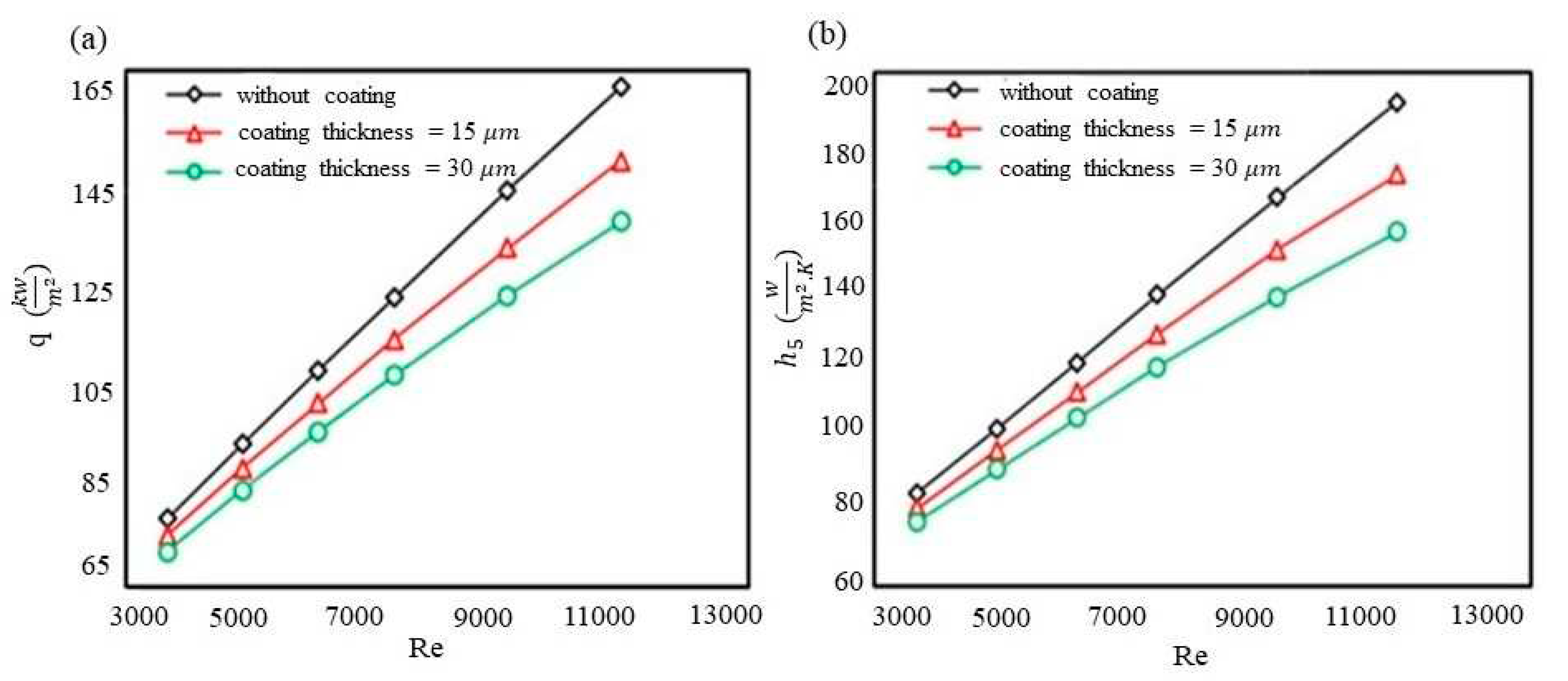
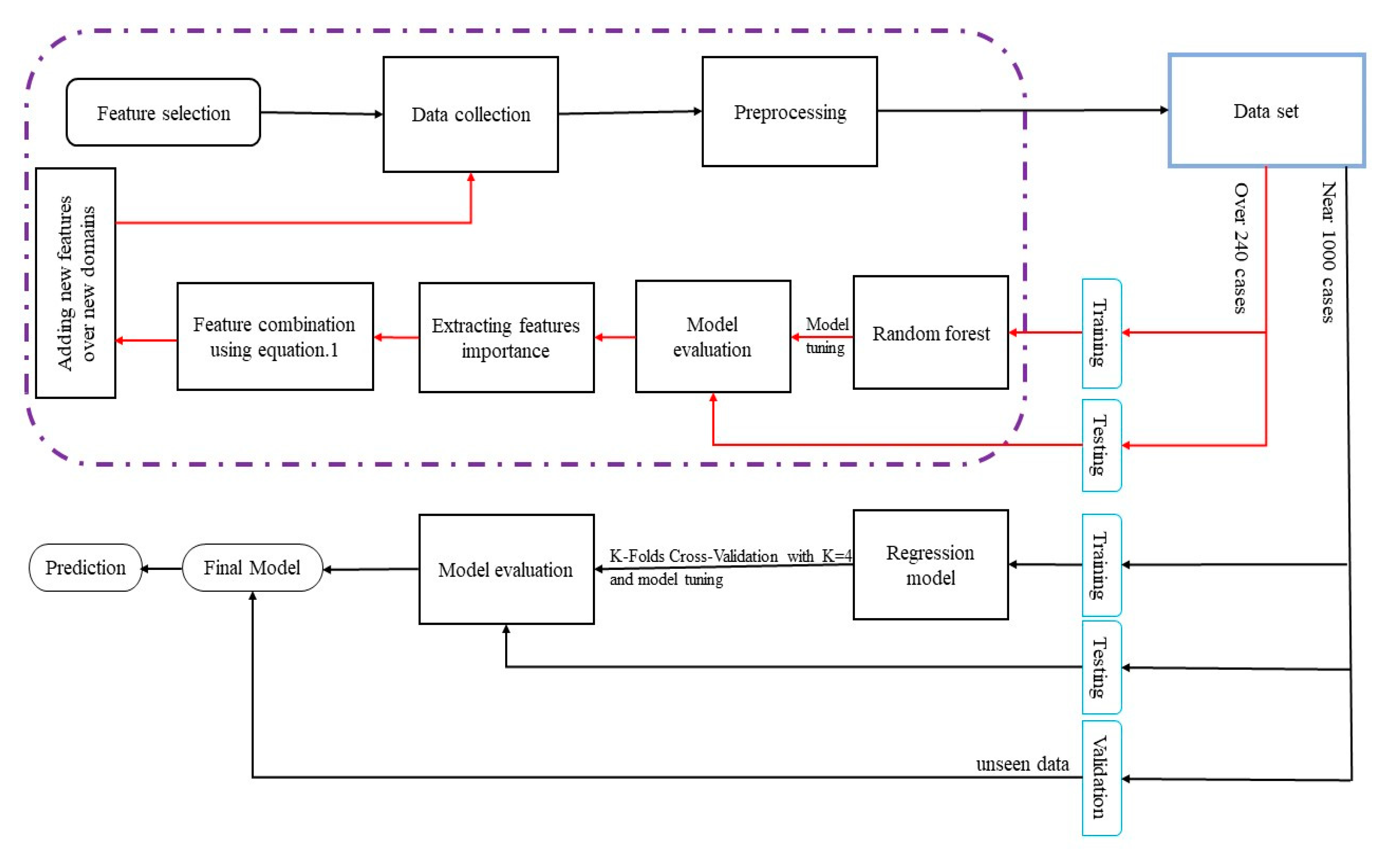
| Case | t (μm) | Tin(K) | ∆Td(K) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | --- | 10 | 498 | 200 | 108599 |
| 2 | --- | 10 | 508 | 200 | 108599 |
| 3 | --- | 15 | 498 | 200 | 144887 |
| 4 | 30 | 10 | 498 | 200 | 96316 |
| Tuning hyperparameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Total trees | Learn rate | Min. Leaf size |
| L.S.Boost | 409 | 0.49 | 2 |
| Tuning hyperparameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Total trees | Learn rate | Min. Leaf size | Max. Num. Splits |
Num. Variables to sample |
| L.S.Boost | 202 | 0.132 | 4 | 18 | 3 |
| [t1 , t2 , t3 , t4 , t5] | taverage | |
|---|---|---|
| [20,20,20,20,20] | 20 | 100020 |
| [100,0,0,0,0] | 20 | 104066 |
| [0,0,0,0,100] | 20 | 100685 |
| [30,30,20,10,10] | 20 | 100940 |
| Methods | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature combination with equation1 | Without feature combination | |
| Models | ||
| Random forest | (0.9994, 0.9810) | (0.9979,0.9732) |
| K-Nearest Neighbors | (1.0, 0.9037) | (1.0, 0.5390) |
| Support Vector Regression | (0.9995, 0.9754) | (0.9995, 0.9489) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





