Submitted:
25 May 2023
Posted:
26 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Results
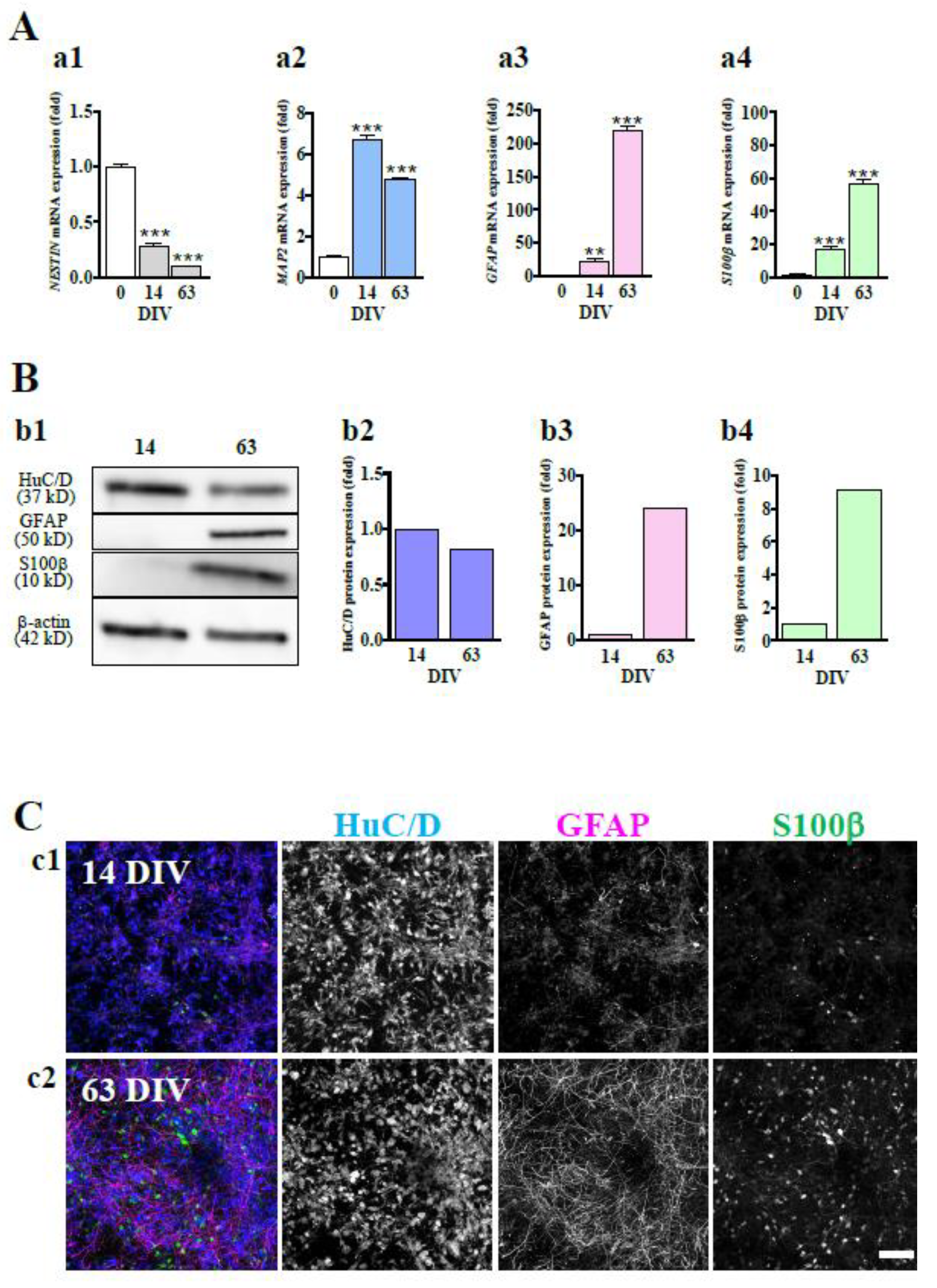
Astrocytes Are Differentiated in hiPSC-Derived Neural Cultures.
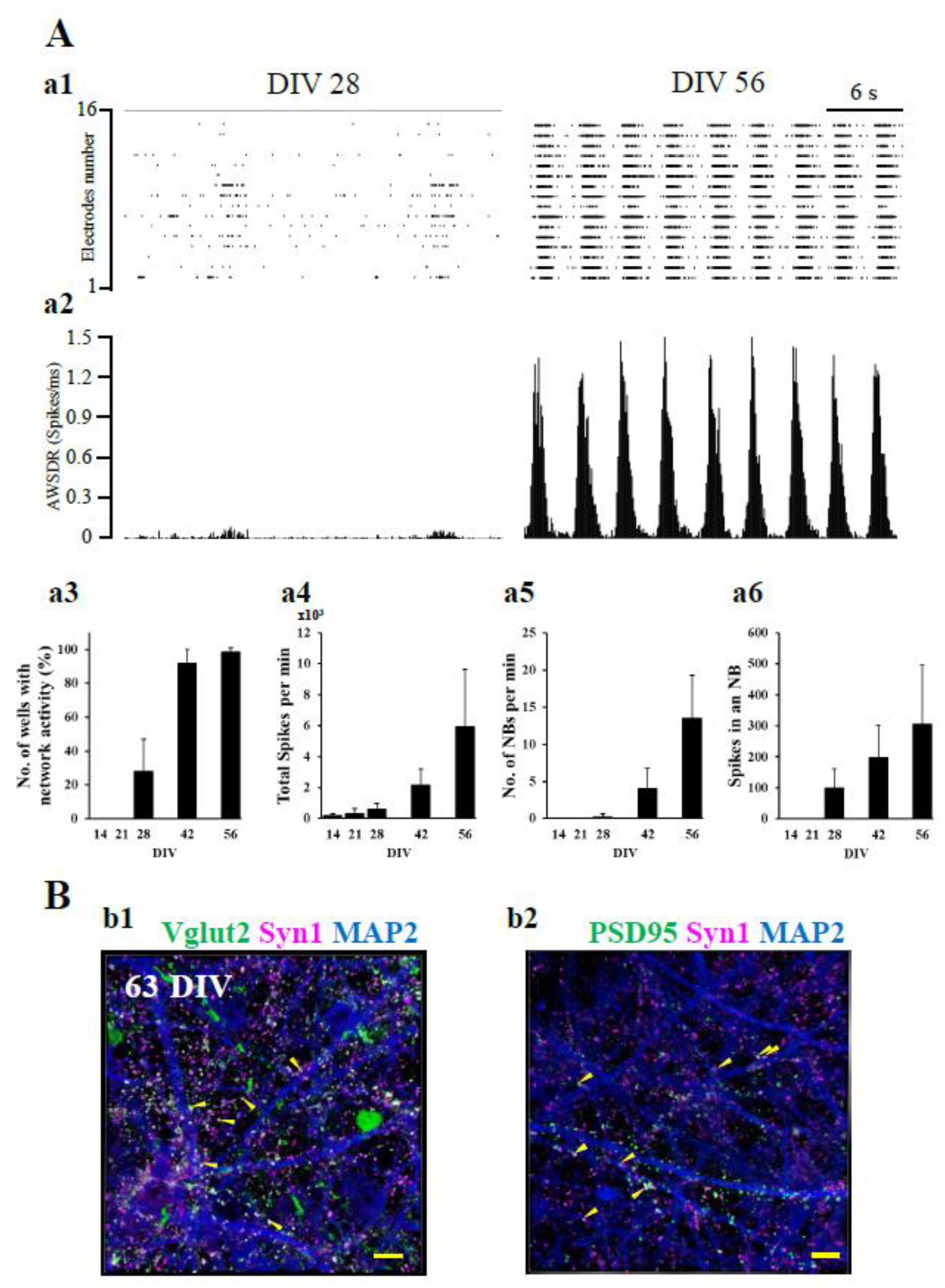
Functional Maturation of hiPSC-Derived Neural Networks
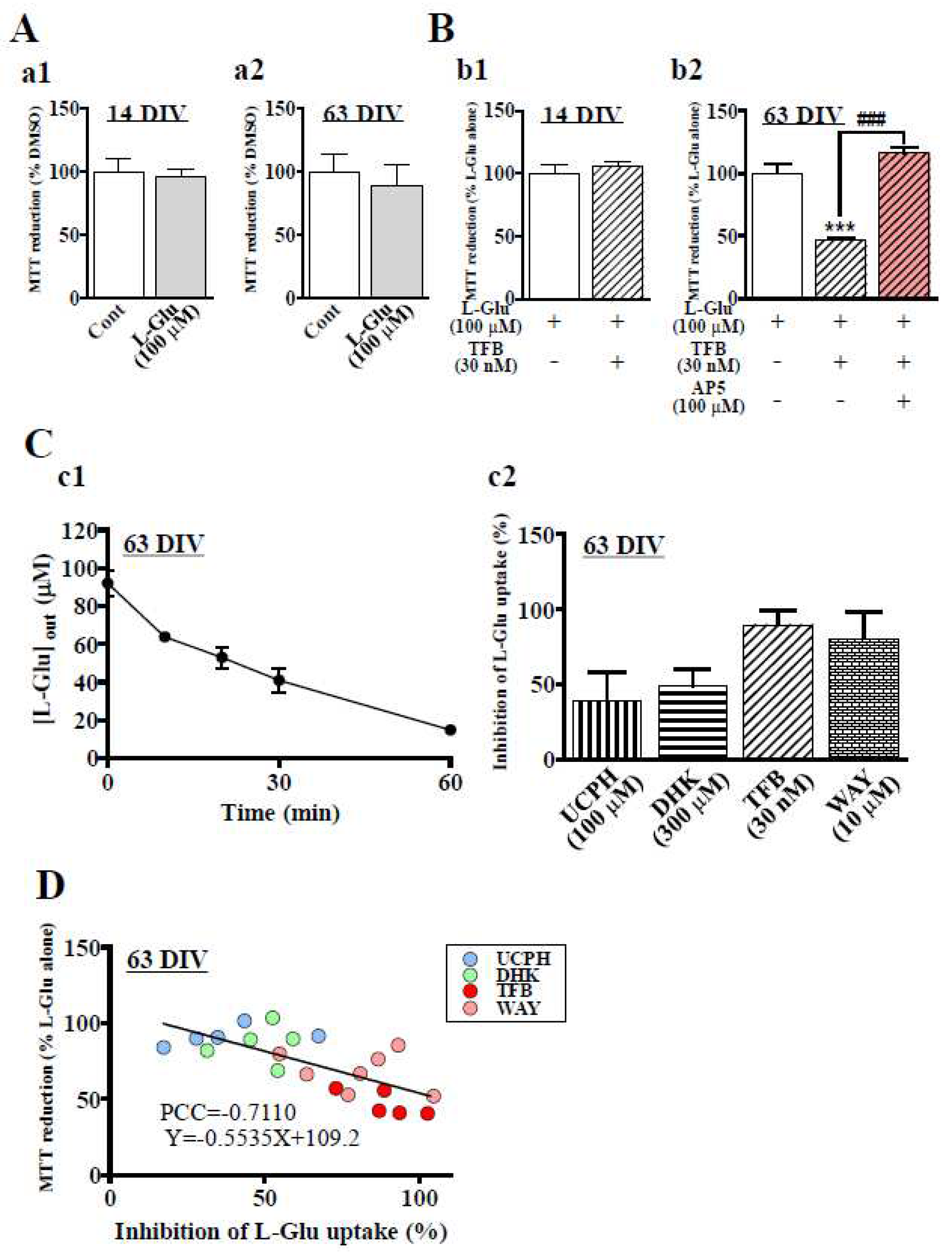
The Roles of EAATs in the Sensitivity of hiPSC-Derived Neurons to Excitotoxicity.
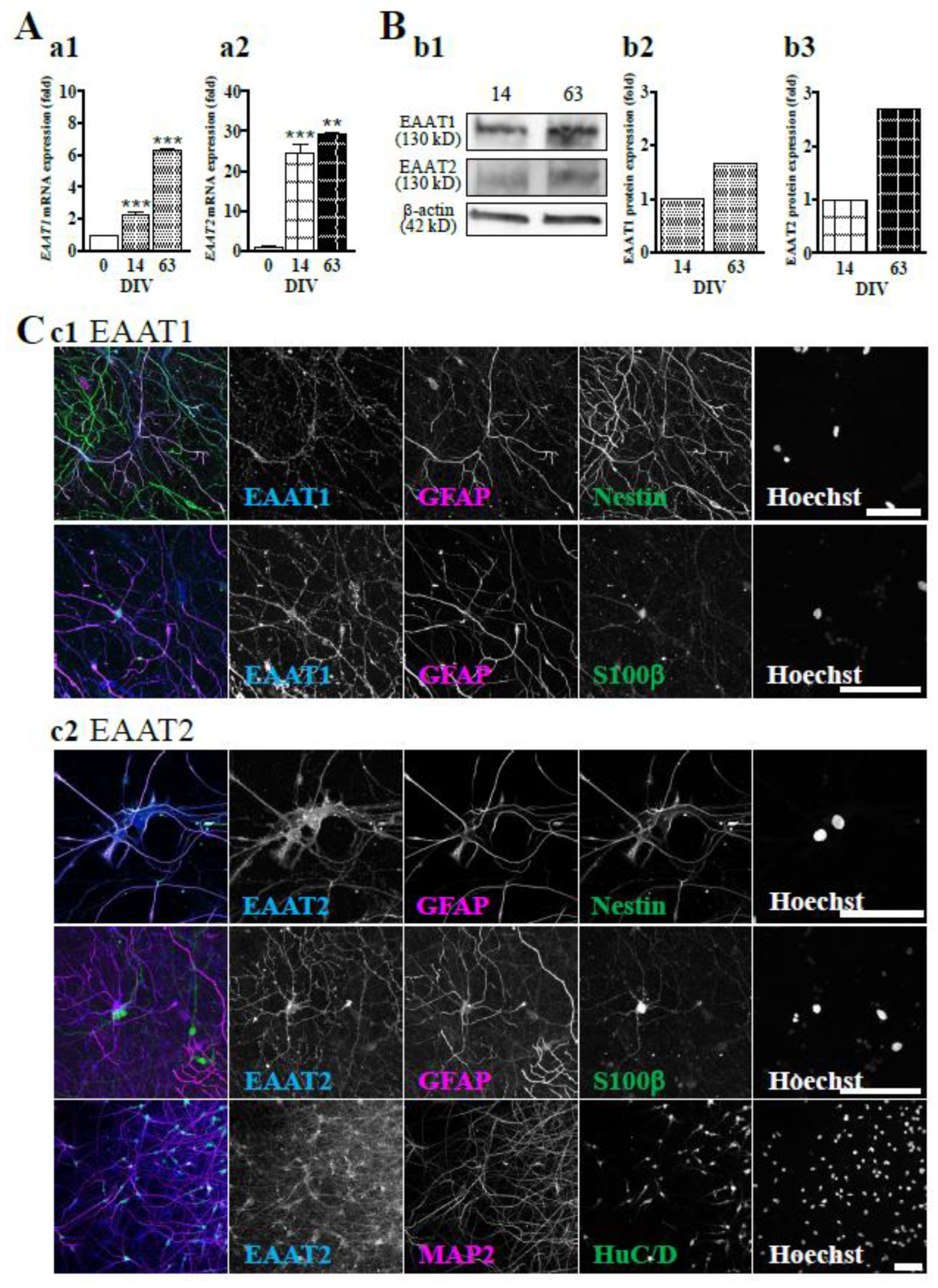
The Expression of EAAT1 and EAAT2 in hiPSC-Derived Neural Cells.
Discussion
Patterns of the Expression of Developmental Markers and L-Glu Transporters
EAAT Subtypes Contribute to Tolerance to Excitotoxicity in hiPSC-Derived Neurons
The Significance of Our Data for Preclinical St udies
- Further utilization of hiPSC-derived neural cells in drug development
Materials and Methods
Materials and Methods
Culture of hiPSC-Derived Neurons
Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real-Time PCR)
Western Blotting
Immunocytochemistry Scale
MEA Recording and Data Analysis (Extracellular Recording, Burst Analysis)
MTT Reduction Assays
Measurement of the Extracellular L-Glu Concentration (L-Glu Uptake Assay)
Drug Treatment
Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonaventura, G.; Iemmolo, R.; Attaguile, G.A.; La Cognata, V.; Pistone, B.S.; Raudino, G.; D'Agata, V.; Cantarella, G.; Barcellona, M.L.; Cavallaro, S. iPSCs: A Preclinical Drug Research Tool for Neurological Disorders. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663-676. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Inoue, H.; Wu, J.C.; Yamanaka, S. Induced pluripotent stem cell technology: a decade of progress. Nature reviews. Drug discovery 2017, 16, 115-130. [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Brown, D.; Alexander, R.; March, R.; Morgan, P.; Satterthwaite, G.; Pangalos, M.N. Lessons learned from the fate of AstraZeneca's drug pipeline: a five-dimensional framework. Nature reviews. Drug discovery 2014, 13, 419-431. [CrossRef]
- Onakpoya, I.J.; Heneghan, C.J.; Aronson, J.K. Post-marketing withdrawal of 462 medicinal products because of adverse drug reactions: a systematic review of the world literature. BMC medicine 2016, 14, 10. [CrossRef]
- Arrowsmith, J.; Miller, P. Trial watch: phase II and phase III attrition rates 2011-2012. Nature reviews. Drug discovery 2013, 12, 569. [CrossRef]
- Oberheim, N.A.; Takano, T.; Han, X.; He, W.; Lin, J.H.; Wang, F.; Xu, Q.; Wyatt, J.D.; Pilcher, W.; Ojemann, J.G.; et al. Uniquely hominid features of adult human astrocytes. J Neurosci 2009, 29, 3276-3287. [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, E.K. Molecular biology of glutamate receptors in the central nervous system and their role in excitotoxicity, oxidative stress and aging. Progress in neurobiology 1998, 54, 369-415. [CrossRef]
- Kritis, A.A.; Stamoula, E.G.; Paniskaki, K.A.; Vavilis, T.D. Researching glutamate - induced cytotoxicity in different cell lines: a comparative/collective analysis/study. Front Cell Neurosci 2015, 9, 91. [CrossRef]
- Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate uptake. Progress in neurobiology 2001, 65, 1-105.
- Zerangue, N.; Kavanaugh, M.P. Flux coupling in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Nature 1996, 383, 634-637. [CrossRef]
- Gilyarov, A.V. Nestin in central nervous system cells. Neurosci Behav Physiol 2008, 38, 165-169. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C.; Díaz-Nido, J.; Avila, J. Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) and its relevance for the regulation of the neuronal cytoskeleton function. Progress in neurobiology 2000, 61, 133-168. [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, D.B.; Cornwall, E.H.; Landar, A.; Song, W. The S100 protein family: history, function, and expression. Brain research bulletin 1995, 37, 417-429. [CrossRef]
- Eng, L.F.; Ghirnikar, R.S.; Lee, Y.L. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969-2000). Neurochemical research 2000, 25, 1439-1451. [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, W.; Okano, H.J.; Osumi, N.; Inoue, T.; Nakamura, S.; Sakakibara, S.; Miura, M.; Matsuo, N.; Darnell, R.B.; Okano, H. Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1999, 96, 9885-9890.
- Lucas, D.R.; Newhouse, J.P. The toxic effect of sodium L-glutamate on the inner layers of the retina. AMA Arch Ophthalmol 1957, 58, 193-201. [CrossRef]
- Olney, J.W.; Ho, O.L.; Rhee, V. Cytotoxic effects of acidic and sulphur containing amino acids on the infant mouse central nervous system. Exp Brain Res 1971, 14, 61-76. [CrossRef]
- Olney, J.W.; Sharpe, L.G. Brain lesions in an infant rhesus monkey treated with monsodium glutamate. Science 1969, 166, 386-388. [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1988, 1, 623-634. [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.; Tymianski, M. Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology 2010, 460, 525-542. [CrossRef]
- Maragakis, N.J.; Rothstein, J.D. Glutamate transporters in neurologic disease. Archives of neurology 2001, 58, 365-370. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.A.; Amin, S.; Leitner, M. Glutamate uptake disguises neurotoxic potency of glutamate agonists in cerebral cortex in dissociated cell culture. J Neurosci 1992, 12, 56-61. [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.W.; Maulucci-Gedde, M.; Kriegstein, A.R. Glutamate neurotoxicity in cortical cell culture. J Neurosci 1987, 7, 357-368. [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Matsuki, N. Measurement of cellular 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction activity and lactate dehydrogenase release using MTT. Neurosci Res 2000, 38, 325-329.
- Shimamoto, K.; Sakai, R.; Takaoka, K.; Yumoto, N.; Nakajima, T.; Amara, S.G.; Shigeri, Y. Characterization of novel L-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate derivatives, potent blockers of the glutamate transporters. Mol Pharmacol 2004, 65, 1008-1015. [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsen, B.; Schneider, N.; Erichsen, M.N.; Huynh, T.H.; Fahlke, C.; Bunch, L.; Jensen, A.A. Allosteric modulation of an excitatory amino acid transporter: the subtype-selective inhibitor UCPH-101 exerts sustained inhibition of EAAT1 through an intramonomeric site in the trimerization domain. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 1068-1087. [CrossRef]
- Arriza, J.L.; Fairman, W.A.; Wadiche, J.I.; Murdoch, G.H.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Amara, S.G. Functional comparisons of three glutamate transporter subtypes cloned from human motor cortex. J Neurosci 1994, 14, 5559-5569.
- Dunlop, J.; McIlvain, H.B.; Carrick, T.A.; Jow, B.; Lu, Q.; Kowal, D.; Lin, S.; Greenfield, A.; Grosanu, C.; Fan, K.; et al. Characterization of novel aryl-ether, biaryl, and fluorene aspartic acid and diaminopropionic acid analogs as potent inhibitors of the high-affinity glutamate transporter EAAT2. Mol Pharmacol 2005, 68, 974-982. [CrossRef]
- Marín-Padilla, M. Prenatal development of fibrous (white matter), protoplasmic (gray matter), and layer I astrocytes in the human cerebral cortex: a Golgi study. J Comp Neurol 1995, 357, 554-572. [CrossRef]
- Noctor, S.C.; Flint, A.C.; Weissman, T.A.; Dammerman, R.S.; Kriegstein, A.R. Neurons derived from radial glial cells establish radial units in neocortex. Nature 2001, 409, 714-720. [CrossRef]
- Malatesta, P.; Hartfuss, E.; Götz, M. Isolation of radial glial cells by fluorescent-activated cell sorting reveals a neuronal lineage. Development (Cambridge, England) 2000, 127, 5253-5263. [CrossRef]
- Bar-Peled, O.; Ben-Hur, H.; Biegon, A.; Groner, Y.; Dewhurst, S.; Furuta, A.; Rothstein, J.D. Distribution of glutamate transporter subtypes during human brain development. J Neurochem 1997, 69, 2571-2580. [CrossRef]
- DeSilva, T.M.; Borenstein, N.S.; Volpe, J.J.; Kinney, H.C.; Rosenberg, P.A. Expression of EAAT2 in neurons and protoplasmic astrocytes during human cortical development. The Journal of comparative neurology 2012, 520, 3912-3932. [CrossRef]
- Lundin, A.; Delsing, L.; Clausen, M.; Ricchiuto, P.; Sanchez, J.; Sabirsh, A.; Ding, M.; Synnergren, J.; Zetterberg, H.; Brolen, G.; et al. Human iPS-Derived Astroglia from a Stable Neural Precursor State Show Improved Functionality Compared with Conventional Astrocytic Models. Stem cell reports 2018, 10, 1030-1045. [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Vadodaria, K.C.; Jaeger, B.N.; Mei, A.; Lefcochilos-Fogelquist, S.; Mendes, A.P.D.; Erikson, G.; Shokhirev, M.; Randolph-Moore, L.; Fredlender, C.; et al. Differentiation of Inflammation-Responsive Astrocytes from Glial Progenitors Generated from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem cell reports 2017, 8, 1757-1769. [CrossRef]
- Krencik, R.; Weick, J.P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, S.C. Specification of transplantable astroglial subtypes from human pluripotent stem cells. Nature biotechnology 2011, 29, 528-534. [CrossRef]
- Holmseth, S.; Dehnes, Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Follin-Arbelet, V.V.; Grutle, N.J.; Mylonakou, M.N.; Plachez, C.; Zhou, Y.; Furness, D.N.; Bergles, D.E.; et al. The density of EAAC1 (EAAT3) glutamate transporters expressed by neurons in the mammalian CNS. J Neurosci 2012, 32, 6000-6013. [CrossRef]
- Furness, D.N.; Dehnes, Y.; Akhtar, A.Q.; Rossi, D.J.; Hamann, M.; Grutle, N.J.; Gundersen, V.; Holmseth, S.; Lehre, K.P.; Ullensvang, K.; et al. A quantitative assessment of glutamate uptake into hippocampal synaptic terminals and astrocytes: new insights into a neuronal role for excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2). Neuroscience 2008, 157, 80-94. [CrossRef]
- Danbolt, N.C.; Furness, D.N.; Zhou, Y. Neuronal vs glial glutamate uptake: Resolving the conundrum. Neurochemistry international 2016. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Watase, K.; Manabe, T.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, K.; Iwama, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Ichihara, N.; Kikuchi, T.; et al. Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 1997, 276, 1699-1702.
- Gegelashvili, G.; Danbolt, N.C.; Schousboe, A. Neuronal soluble factors differentially regulate the expression of the GLT1 and GLAST glutamate transporters in cultured astroglia. Journal of neurochemistry 1997, 69, 2612-2615. [CrossRef]
- Gegelashvili, G.; Dehnes, Y.; Danbolt, N.C.; Schousboe, A. The high-affinity glutamate transporters GLT1, GLAST, and EAAT4 are regulated via different signalling mechanisms. Neurochemistry international 2000, 37, 163-170. [CrossRef]
- Plachez, C.; Danbolt, N.C.; Récasens, M. Transient expression of the glial glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT in hippocampal neurons in primary culture. Journal of neuroscience research 2000, 59, 587-593. [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lozada, Z.; Guillem, A.M.; Robinson, M.B. Transcriptional Regulation of Glutamate Transporters: From Extracellular Signals to Transcription Factors. Advances in pharmacology (San Diego, Calif.) 2016, 76, 103-145. [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.C.; Cui, H.; Tymianski, M. The use of propidium iodide to assess excitotoxic neuronal death in primary mixed cortical cultures. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.) 2007, 399, 15-29. [CrossRef]
- Semkova, I.; Krieglstein, J. Neuroprotection mediated via neurotrophic factors and induction of neurotrophic factors. Brain research. Brain research reviews 1999, 30, 176-188. [CrossRef]
- Bullock, R.; Zauner, A.; Woodward, J.J.; Myseros, J.; Choi, S.C.; Ward, J.D.; Marmarou, A.; Young, H.F. Factors affecting excitatory amino acid release following severe human head injury. J Neurosurg 1998, 89, 507-518. [CrossRef]
- O'Byrne, M.; Tipton, K.; McBean, G.; Kollegger, H. Assessment of neurotoxicity and "neuroprotection". J Neural Transm Suppl 1997, 50, 153-164. [CrossRef]
- Bauersachs, H.G.; Bengtson, C.P.; Weiss, U.; Hellwig, A.; García-Vilela, C.; Zaremba, B.; Kaessmann, H.; Pruunsild, P.; Bading, H. N-methyl-d-aspartate Receptor-mediated Preconditioning Mitigates Excitotoxicity in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Brain Organoids. Neuroscience 2022, 484, 83-97. [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Takahashi, K.; Shigemoto-Mogami, Y.; Chujo, K.; Sekino, Y. Glypican 6 Enhances N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Function in Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons. Front Cell Neurosci 2016, 10, 259. [CrossRef]
- Wilton, D.K.; Stevens, B. The contribution of glial cells to Huntington's disease pathogenesis. Neurobiology of disease 2020, 143, 104963. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, V.J.; Rushton, D.J.; Tom, C.M.; Allen, N.D.; Kemp, P.J.; Svendsen, C.N.; Mattis, V.B. Huntington's Disease Patient-Derived Astrocytes Display Electrophysiological Impairments and Reduced Neuronal Support. Frontiers in neuroscience 2019, 13, 669. [CrossRef]
- Tyzack, G.; Lakatos, A.; Patani, R. Human Stem Cell-Derived Astrocytes: Specification and Relevance for Neurological Disorders. Current stem cell reports 2016, 2, 236-247. [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Van Kammen, M.; Levey, A.I.; Martin, L.J.; Kuncl, R.W. Selective loss of glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Annals of neurology 1995, 38, 73-84. [CrossRef]
- Fontana, I.C.; Souza, D.G.; Souza, D.O.; Gee, A.; Zimmer, E.R.; Bongarzone, S. A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective on Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 2 Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2023, 66, 2330-2346. [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.R.; Willnow, T.E. Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters in Physiology and Disorders of the Central Nervous System. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20. [CrossRef]
- Heider, J.; Vogel, S.; Volkmer, H.; Breitmeyer, R. Human iPSC-Derived Glia as a Tool for Neuropsychiatric Research and Drug Development. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Takaki, J.; Fujimori, K.; Miura, M.; Suzuki, T.; Sekino, Y.; Sato, K. L-glutamate released from activated microglia downregulates astrocytic L-glutamate transporter expression in neuroinflammation: the 'collusion' hypothesis for increased extracellular L-glutamate concentration in neuroinflammation. Journal of neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 275. [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Pascente, R.; Triolo, D.; Bassani, C.; De Angelis, A.; Ruffini, F.; Ottoboni, L.; Comi, G.; Martino, G.; Farina, C. Laquinimod Modulates Human Astrocyte Function and Dampens Astrocyte-Induced Neurotoxicity during Inflammation. Molecules 2020, 25. [CrossRef]
- Cudkowicz, M.E.; Titus, S.; Kearney, M.; Yu, H.; Sherman, A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Hayden, D.; Shui, A.; Brooks, B.; Conwit, R.; et al. Safety and efficacy of ceftriaxone for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a multi-stage, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet. Neurology 2014, 13, 1083-1091. [CrossRef]
- Hama, H.; Hioki, H.; Namiki, K.; Hoshida, T.; Kurokawa, H.; Ishidate, F.; Kaneko, T.; Akagi, T.; Saito, T.; Saido, T.; et al. ScaleS: an optical clearing palette for biological imaging. Nat Neurosci 2015, 18, 1518-1529. [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, N.; Odawara, A.; Katoh, H.; Okuyama, N.; Yokoi, R.; Suzuki, I. Detection of synchronized burst firing in cultured human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons using a 4-step method. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2018, 497, 612-618. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



