1. Introduction
Atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease of blood vessel [
1,
2], is the major cause of cardiovascular disease, the most common cause of death in Europe [
3]. Hypercholesterolemia is a risk factor for atherosclerosis because elevated plasma cholesterol concentrations, and cholesterol accumulation in different tissues lead to the formation of arterial plaques [
3,
4]. One of the main approaches to decrease the risk of atherosclerosis is to decrease the blood cholesterol levels, either with increased physical activity and dietary changes, such as reducing the intake of saturated fat, or by prescribed drugs [
3]. Scientific interest in new therapeutic strategies, using functional foods to decrease hypercholesterolemia, has recently increased, leading to the search for new bioactive natural products.
Different seaweeds have been characterised by their high hypocholesterolemic potential [
5]. Brown seaweeds are one of the world most consumed seaweeds and one of the furthermost studied seaweeds in this area [
6]. Several studies with different compounds, such as phlorotannins, carotenoids and polysaccharides extracted from brown algae species already reported its hypocholesterolemic effect [
7,
8,
9]. Phlorotannins, a class of bioactive polyphenolic compounds produced by brown algae, have been characterised for their potential to prevent atherosclerosis, with several studies reporting their ability to decrease blood lipid levels and total cholesterol, particularly due to their capacity to reduce cholesterol synthesis and intestinal absorption [
9,
10,
11,
12]. Specifically, an aqueous extract of the brown algae
F. vesiculosus, purified by solid phase extraction (SPE), characterised by Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS/MS) as rich in phlorotannins and peptides, stood out for its
in vitro inhibitory effect on the synthesis and absorption of cholesterol, as well as to its ability to reduce the hepatic expression of NPC1L1, which can result in increased biliary excretion of cholesterol [
10,
11].
It is known that the intestine plays an important role in cholesterol homeostasis in terms of absorption, with cholesterol uptake and secretion by enterocytes [
13]. Therefore, this work aims to study the effect of a purified aqueous extract of
F. vesiculosus, previously characterised as rich in phlorotannins and peptides, on intestinal cells to better understand the mechanism of action of the extract in the different processes that regulate cholesterol homeostasis at the intestinal level. To achieve this objective, the intestinal barrier was simulated
in vitro using a Caco-2 cell line. These cells have been widely used as a model of the intestinal barrier since they can spontaneously differentiate, after approximately 21 days, into a monolayer of polarized cells with morphological and function characteristics of small intestinal enterocytes [
8]. Thus, differentiated Caco-2 cells were exposed to the extract and subsequently analysed by two different omics techniques, namely, gel-based proteomics analysis and untargeted metabolomics analysis. These two techniques are considered promising fields which have led to remarkable results investigating molecular mechanisms associated to different diseases [
14,
15,
16]. Overall, this study contributes to increase the scientific knowledge about the mechanisms of action of the purified aqueous extract of
F. vesiculosus, rich in phlorotannins and peptides, for intestinal cholesterol homeostasis and consequently prevention of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
All chemicals were of analytical grade. Water, methanol (MeOH), formic acid and acetonitrile (LC/MS grade Optima) and chloroform were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Hampton, USA). Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DEMEM), Trypsin, Glutamine, Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS) and Fetal bovine serum (FBS) were obtained from Lonza® (Verviers, Belgium). Ethanol (96%) was purchased from Carlo Erba (Peypin, France). Iodoacetamide and 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Barcelona, Spain). Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and glacial acetic acid were obtained from Merck Milipore® (Massachusetts, EUA). Pierce™ Trypsin Protease MS Grade, Pierce™ DTT (Dithiothreitol), Bolt® MOPS SDS Running Buffer (20X), mini Protein Gel NuPAGE™ 4 to 12% Bis-Tris and 4X Bolt™ LDS Sample Buffer were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, USA). Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 was purchased from BIORAD® (Hercules, USA)., 5× SDS-PAGE Sample Loading Buffer, NZYBlue Protein Marker were purchased from Nzytech® (Lumiar, Portugal).
2.2. Preparation and characterization of algae extract
Dried
F. vesiculosus Linnaeus seaweed harvested in North Atlantic Ocean was bought from Celeiro diet., Lisbon, Portugal (imported by Américo Duarte Paixão Lda, Lot number 03ALG2731901). An aqueous extract from
F. vesiculosus was prepared as described in [
10], briefly, the aqueous extract was prepared as a decoction and purified by Solid Phase Extraction (SPE). The characterization of extract compounds was performed though Liquid Chromatography by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS/MS) using an Elute OLE UHPLC system interfaced with a quadrupole time-of-flight (QqToF) Impact II mass spectrometer equipped with an electrospray source (ESI) (Bruker DaltoniK GmbH, Bremen, German), with the protocol as well as the results presented in [
10].
2.3. Cell culturing and differentiation
Caco-2 cells (ECACC 86010202), a human colorectal adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line, was cultured in DMEM supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine and 20% FBS at 37 °C in an atmosphere with 5% CO2. The culture cells were kept in sub-confluence with trypsinization every 72h. For cells differentiation, Caco-2 cells were seeded at a density of 2 x 104 cells / cm2 with DMEM supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine in a T25 flask. The monolayers were formed after 21 days, presenting a transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) higher than 250 Ω cm2, which was measured using a Millicell ERS-2 V-Ohm Meter from Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany).
2.4. Cytotoxicity studies in Caco-2 cells
The cytotoxicity effect of the purified
F. vesiculosus aqueous extract on Caco-2 cells was study through the MTT viability test as described by [
17].
2.5. Metabolomic analysis through liquid chromatography combined with high resolution tandem mass spectrometry (LC/HRMS)
The differentiated Caco-2 cells were exposed, during 24h, to purified aqueous extract of
F. vesiculosus at 0.25 mg/mL dissolved in culture medium without FBS (cells exposed to extract), and to culture medium without FBS (control). After the incubation time the cells were collected water–methanol–chloroform (10:27:3) and analysed using liquid chromatography combined with high resolution tandem mass spectrometry LC/HRMS/MS with an Elute OLE UHPLC system interfaced with a quadrupole time-of-flight Impact II mass spectrometer equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, German) as described in [
11]. Statistical analysis of the results of the untargeted metabolomic analysis as well as the identification of metabolites were also performed using MetaboScape 4.0 software (Bruker Daltonics) as described in [
11].
2.6. Membrane protein extract and one-dimension polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
The differentiated Caco-2 cells were under contact, during 24h, with 0.25 mg/mL of purified aqueous extract of F. vesiculosus dissolved in culture medium without FBS (cells exposed to extract), and to culture medium without FBS (control). Cell harvesting and extraction of the membrane protein fraction with Mem-PER Plus Membrane Protein Extraction Kit (Thermo Scientific™) was performed following the manufacturer’s indications. The different samples of both protein fractions were separated under reducing conditions in NuPAGE 4 to 12% gradient gels (Invitrogen™, Carlsbad, USA) using a Mini Gel Tank (Invitrogen™, Carlsbad, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The gels were stained with 40% of Coomassie R-250 blue, 50% of methanol and 10% of glacial acetic acid during 1h and distaining with a solution of 7.5 % glacial acetic acid, 10 % ethanol and 82.5 % distilled water overnight. Gels were photographed using ImageQuant LAS 50 (GE Healthcare Life Sciences®, Illinois, USA) and the images were analysed using ImageJ software.
2.7. In-gel protein digestion, Nano-LC−ESI−MS/MS and DataAnalysis
For protein identification, firstly was performed the in-gel protein digestion as described in [
18] and then the resulting peptides were analysed by nLC-MS/MS analysis as described in [
19], using an Ultimate 3000 nLC apparatus coupled to a UHR-QqTOF IMPACT HD apparatus (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, German) with a CaptiveSpray ion source (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, German). The LC−MS/MS data were processed in MaxQuant (V.1.6.10.43) for automated protein identification. MS raw files were analyzed by MaxQuant software, version 1.6.10.43 [
20], and peptide lists were searched against the human Uniprot FASTA database. A contaminant database generated by the Andromeda search engine [
21] was configured with cysteine carbamidomethylation as a fixed modification and N-terminal acetylation and methionine oxidation as variable modifications. We set the false discovery rate (FDR) to 0.01 for protein and peptide levels with a minimum length of seven amino acids for peptides, and the FDR was determined by searching a reverse database. Enzyme specificity was set as C terminal to arginine and lysine as expected using trypsin. A maximum of two missed cleavages were allowed. Data processing was performed using Perseus (version 1.6.2.3) with default settings [
22].
All proteins and peptides matching the reversed database were filtered out. Subcellular localization and gene ontology analysis were performed using STRING online resources at
https://string-db.org/, and ClueGo plug-in in Cytoscape (V3.9.0), respectively [
23].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of the purified F. vesiculosus aqueous extract in enterocyte-like Caco-2 cells
Before the metabolomic and proteomic studies, Caco-2 cells differentiated into enterocyte-like cells were exposed 24h to 0.25 mg/mL of F. vesiculosus aqueous extract, the cytotoxic effect of the extract on the cells in study was evaluated. F. vesiculosus extract showed no cytotoxicity effect on differentiated Caco-2 cells. When the cells were exposed to different extract concentrations (0.2 – 0.8 mg/mL), cell viability was always approximately 100%.
3.1.1. Metabolomic analysis
To study the effect of purified
F. vesiculosus aqueous extract on the metabolites of Caco-2 cells differentiated into enterocyte-like cells an untargeted metabolomic analysis through LC-HRMS/MS was performed. The results from metabolomic analysis were interpreted using unsupervised principal component analysis (PCA) and t-test. Also, it was identified the metabolites with positive fold change,
p-value below 0.05 and that presented MS/MS spectra to be compared with MS/MS from database (
Table 1).
The difference in metabolite expression could be quantified by the fold change (FC), which is the ratio between the signal intensity of metabolites of the differentiated cells exposed to the extract and the signal intensity of metabolites of control differentiated cells. A positive FC means that the metabolites are up-regulated in control cells while a negative FC means that the metabolites are up-regulated in cells exposed to the extract.
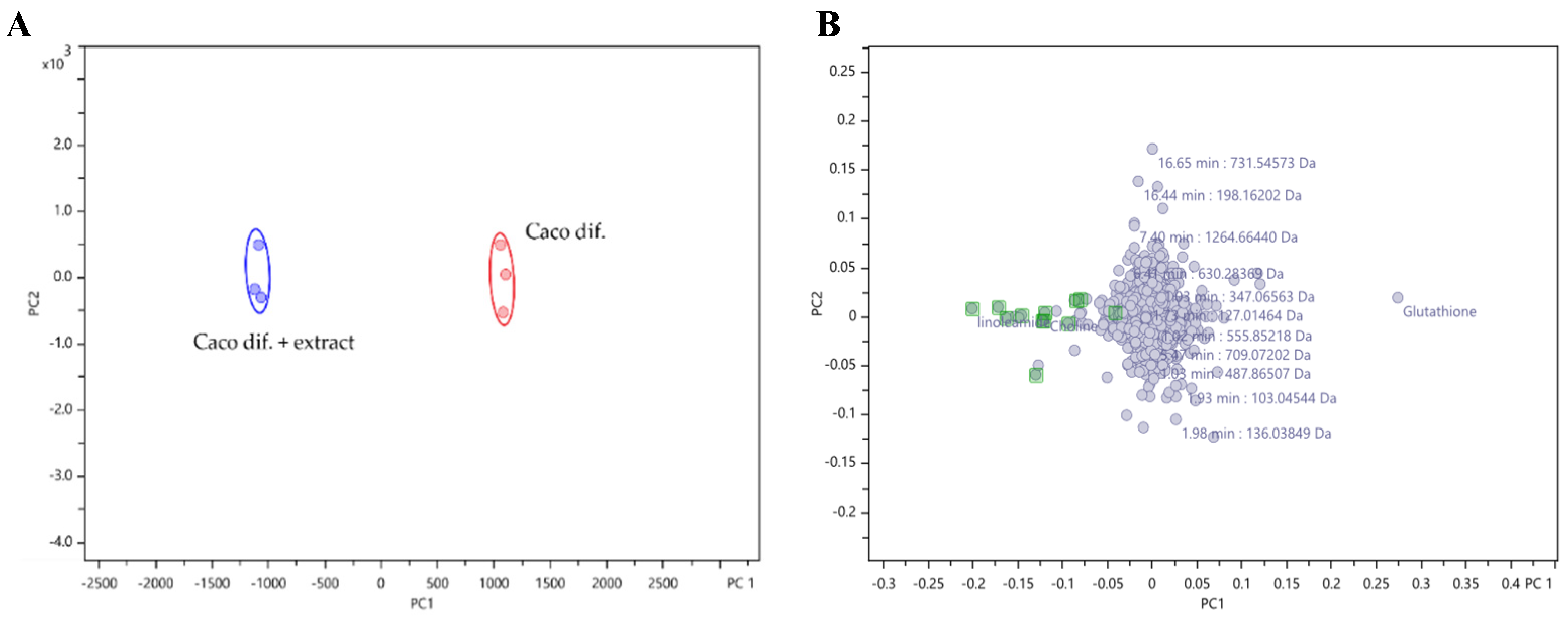
The PCA plot represented in
Figure 2, demonstrated a good separation between the control cells and the cells exposed to the extract at a confidence level of 98 %.
The
Figure 2B demonstrates the overlap of most metabolites, meaning that there are no differences between the intensities of these metabolites. However, it is possible to observe the existence of some metabolites with negative PC1 (
Figure 2C), which means that their intensities were higher in the cells exposed to the extract compared to control cells.
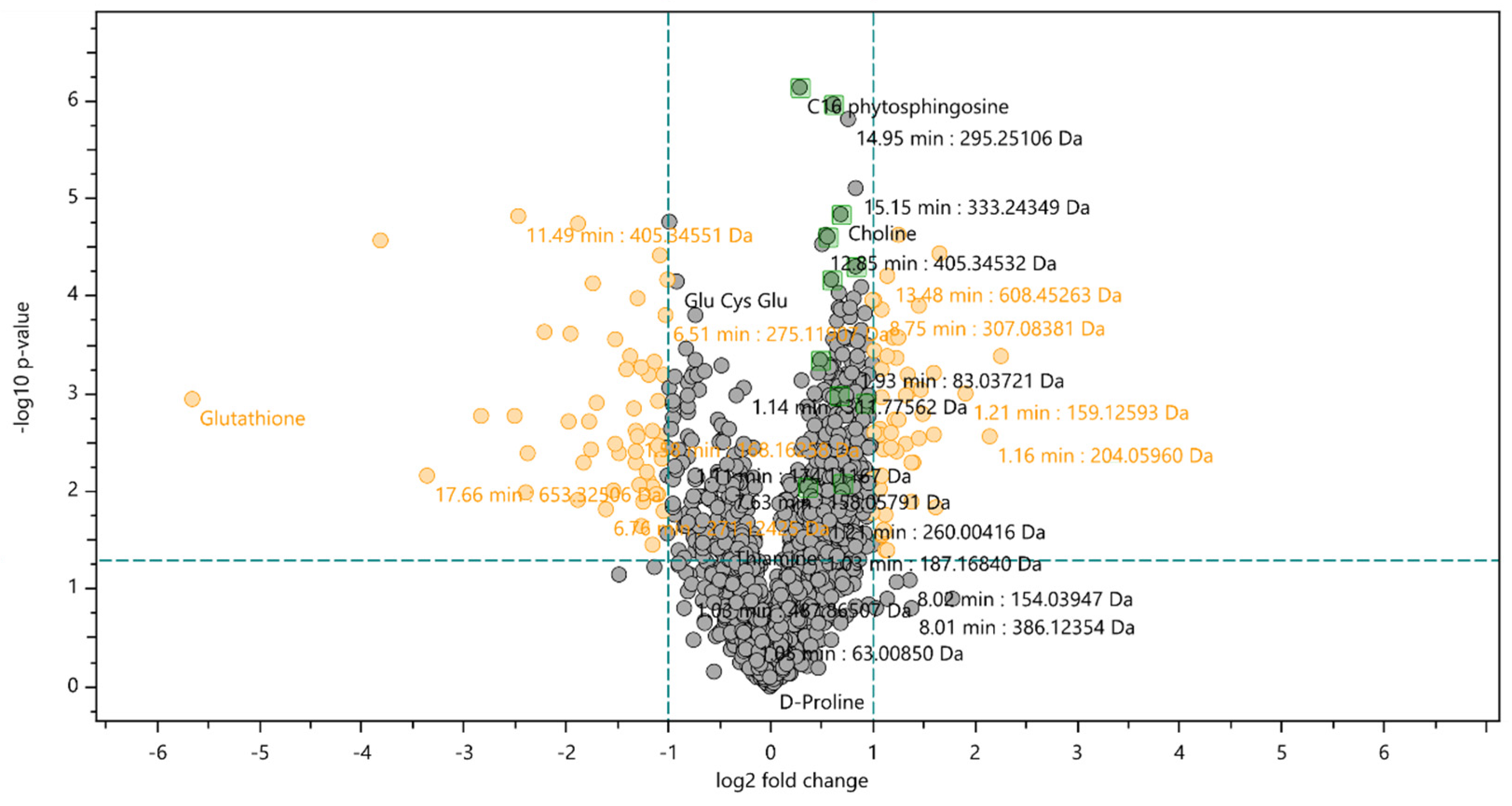
Based on identification criteria (fold change value,
p-value below 0.05 and correspondent MS/MS spectra on database) 11 compounds were identified (
Table 1). However, when the results were analysed with a t-test with a confidence level of 98 %, the changes in these compounds intensity were not considered significant. Therefore, this group of compounds is found in the volcano plot's black zone (
Figure 3).
From the 11 compounds identified with increased expression on cells exposed to the extract, 7 were identified as fatty acid amides (2-ketoctadec-9-enamide, Heptadec-2-enamide, Linoleic acid hydroxamate, Palmitoleoyl ethanolamide, Myristamide, Linoleamide and Dodecanamide), and the remaining four were identified as choline, 3-ketosphingosine, C
16 phytosphingosine and Glutathione oxidized (
Table 1). In a previous untargeted metabolomic study with HepG2 cells, it was seen that this extract lead to an significant increase in the expression of different fatty acid amides, which are known to have the ability to inhibit the enzyme responsible for cholesterol esterification, the ACAT, which consequently can lead to inhibition of intestinal cholesterol absorption [
11]. It is possible that the changes in the expression of these lipid compounds in Caco-2 cells were smaller than the effect reported in HepG2 cells, since Caco-2 cells are more resistant compared to HepG2 cells [
11]. Previous results demonstrated that for differentiated Caco-2 cells in the presence of 0.4 mg/mL of extract were observed, approximately, 100 % of cells viability, while in HepG2 cells under the same conditions, only 60 % of cells viability was observed [
11], which demonstrates that Caco-2 cells are more resistant to the effects of extract compounds than HepG2 cells.
Analysing the PCA plot and the volcano plot, it is possible to observe a decrease in glutathione expression when cells were exposed to the extract.
Although in a previous
in vitro study, using the DPPH method, this
F. vesiculosus extract showed approximately 76 % of antioxidant activity at 100 µg/ml [
10], the present results demonstrate that when differentiated Caco-2 cells were exposed to extract at 0.25 mg/mL oxidative stress occurs and consequent glutathione depletion. At first sight this may be a negative effect of the extract since it is known that oxidative stress contributes to the development of differences diseases, including atherosclerosis [
24]. On the other hand, studies have been carried out in search of therapeutic agents that cause glutathione depletion to be used in the treatment of cancer [
25,
26]. These studies were developed since GSH depletion proved to improve the therapeutic efficacy of ROS-based therapy ferroptosis and chemotherapy as cancer cells became more susceptible to chemotherapeutic agent [
25].
3.1.2. Proteomic analysis
The effect of the purified
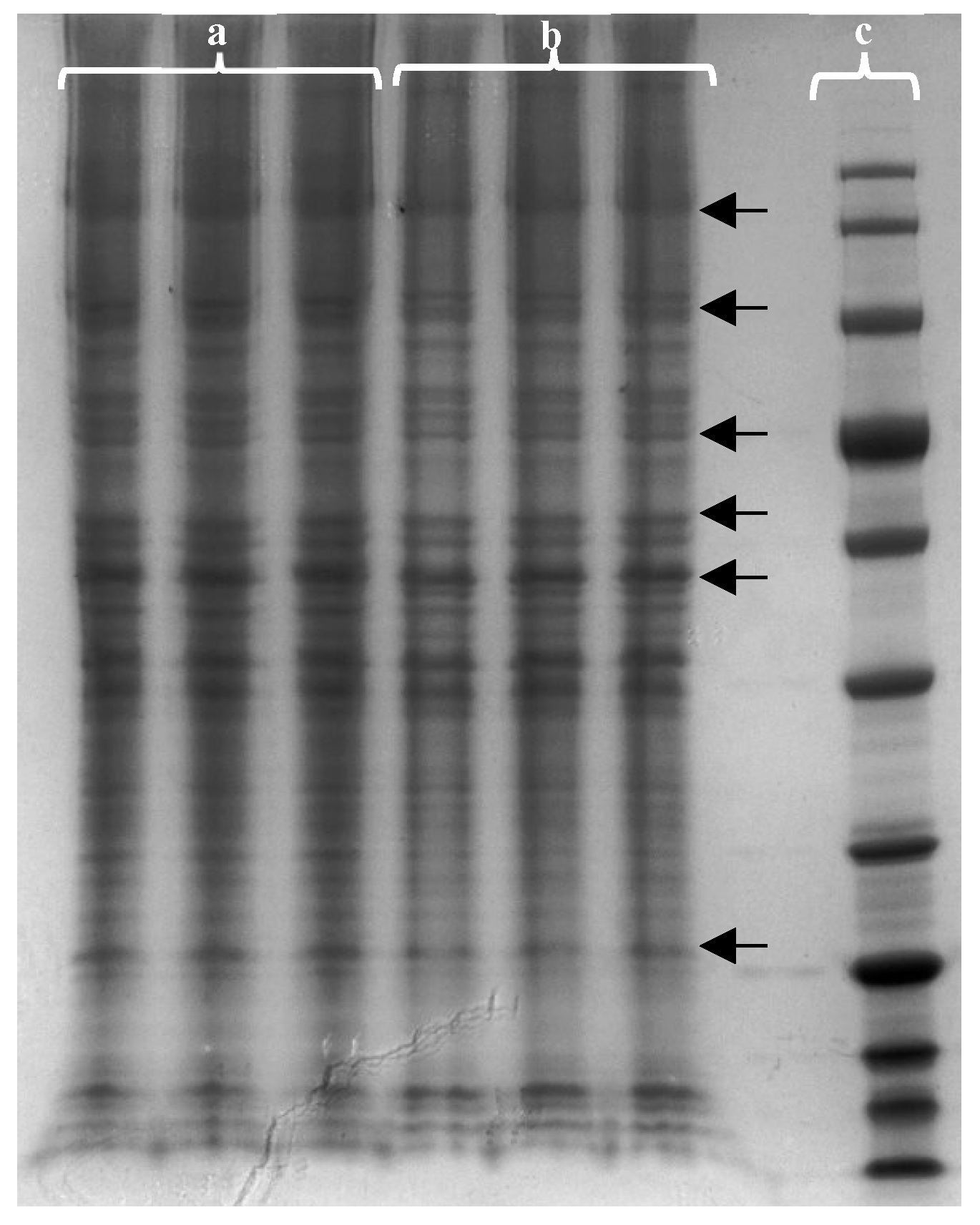
F. vesiculosus aqueous extract on proteins from differentiated Caco-2 cells was studied by gel-based proteomic analysis. Firstly, the effect of the extract on the membrane proteins of differentiated cells was evaluated by one-dimension polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) to separate and visualise proteins before identification.
Figure 4 shows the changes caused by the extract in the intensity of the different proteins. It is possible to highlight six different gel zones (indicated by an ARROW in
Figure 4) where there were significant changes in protein intensities when the cells were exposed to the extract.
The bands from these six zones from control cells and cells exposed to the extract were cut and subjected to in-gel trypsin digestion. The peptides that resulted from gel digestion were analysed in duplicate by nLC-ESI-MS/MS followed by Andromeda® database search. In the analysis of the results, the proteins identified in the two technical replicates were selected and the protein identification was performed with at least two peptides and a protein FDR < 1%. With data analysis was possible to identify 119 proteins detected only in cells exposed to extract, 84 proteins detected only in control cells and a total of 507 proteins present in both groups of cells.
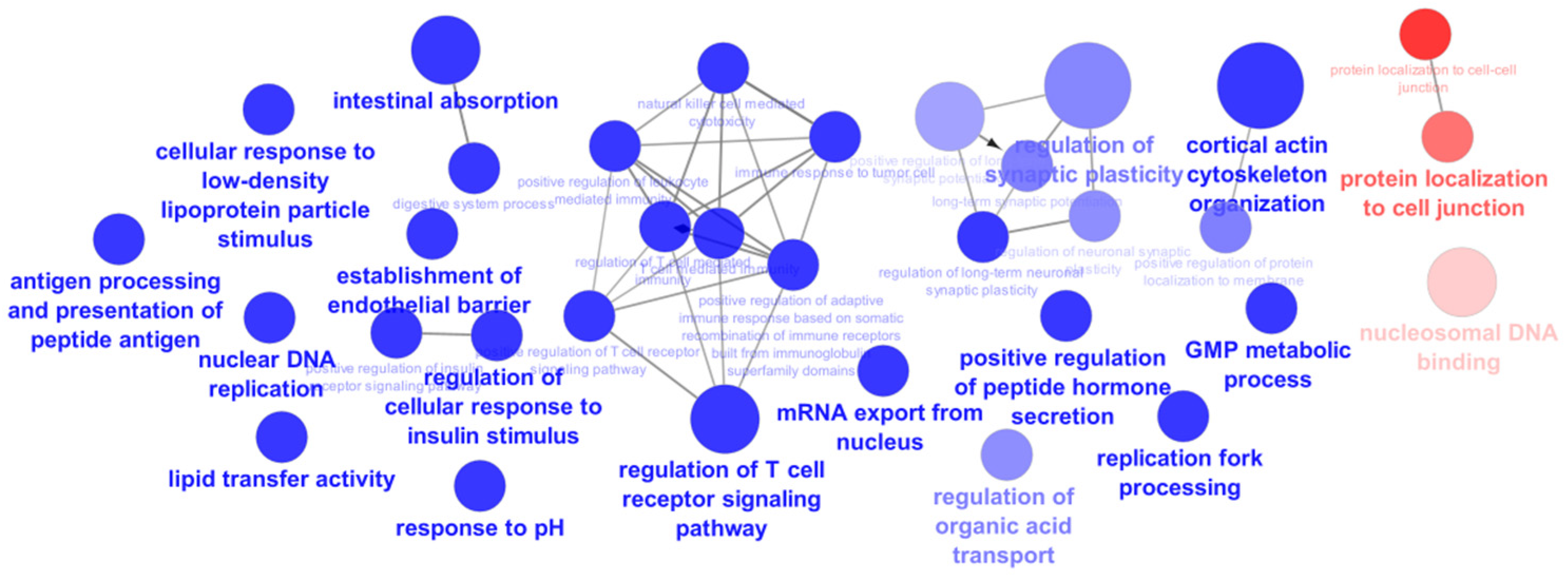
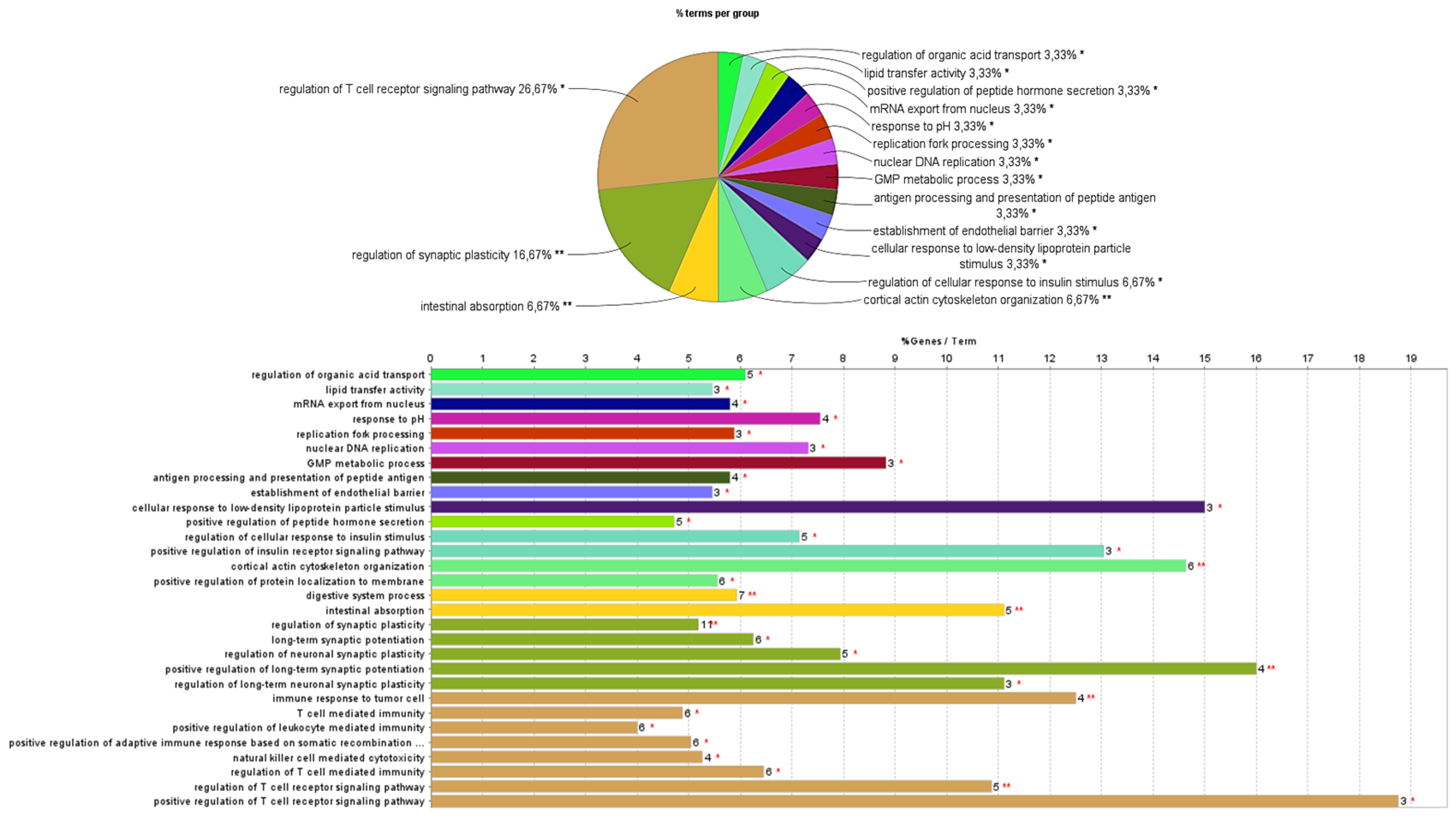
The proteins detected only in the cells exposed to the extract and those detected only in the control cells were submitted to analysis using ClueGo Cytoscape for the GO terms biological process (BO) and molecular function (MP). The network from ClueGo enrichment, represented in
Figure 5, demonstrates that the proteins present only in the cells exposed to the extract have 16 statistically significant (
p-value < 0.05) enrichment terms.
In this study, it is intended to highlight the proteins from the enrichment terms intestinal absorption and digestive system process (
Figure 6) due to the already reported inhibitory effect of the
F. vesiculosus extract under study on the synthesis and intestinal absorption of cholesterol [
10], and also due to the already reported high hipocholesterolemic potential of different brown algae [
5]. However, a large percentage of the enrichment terms of the proteins from cells exposed to the extract participate in the regulation of the T cell receptor signaling pathway (26.67%) (
Figure 6), which could be correlated with the already described antitumor activity of phlorotannins derived from
F. vesiculosus [
27], but further studies are needed.
The proteins involved in intestinal absorption as well in the digestive system process that were identified only in cells exposed to the extract were: Ezrin (EZR), Fatty acid-binding protein, liver (FAB1), Niemann-Pick C1 protein (NPC1), Plastin-1 (PLS1) and Solute carrier family 26 member 6 (SLC26A6). Also, only on cells exposed to the extract were identified the proteins Filamin-B (FLNB) and Mucin-13 (MUC13) that participate in the digestive system process. From this group of proteins, only proteins NPC1 and FABP1 are related to cholesterol transport and homeostasis. However, FABP1 protein is only involved in lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol uptake in hepatocytes, in intestine this protein participates in the different processes in which nutrients are removed from there [
28]. Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) protein is considered a key protein in the cellular cholesterol trafficking [
29], being responsible for the transport of free cholesterol from the late endosome/lysosome to the plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum [
30]. This protein has been linked to the prevention of atherosclerosis. Although the link between NPC1-Atherosclerosis is still an area that needs further studies, it is known that the expression of this protein promotes the upregulation of the ABCA1 protein as it leads to transport of cholesterol from late endosome/ lysosome to plasm membrane [
29,
30]. In turn, the ABCA1 protein is responsible for transporting cellular cholesterol to apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) to form high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) particles, and HDL levels are known to be inversely related to the risks of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [
30,
31]. NPC1 protein is also associated with atherosclerosis since in the presence of advanced atherosclerotic lesions macrophages accumulate large amounts of unesterified cholesterol, and NPC1 protein promote the transport the cholesterol from the late endosome/ lysosome to the endoplasmic reticulum which, consequently, leads to stimulation of macrophage apoptosis and to plaque rupture [
30].
As the
F. vesiculosus extract under study is rich in phlorotannins and peptides [
10] and as the NPC1 protein was only identified in cells exposed to the extract, we can propose that the compounds in the extract induce the expression of this protein. This effect is in line with different studies with
F. vesiculosus algae and with extracts from other different seaweeds rich in phlorotannins that describe the hypocholesterolemic effect of these compounds and their potential in the prevention of atherosclerosis [
9,
12,
32,
33].
4. Conclusions
The effect of F. vesiculosus aqueous extract, purified by SPE, on differentiated Caco-2 cells was also characterized for the first time by untargeted metabolomics and proteomics analyses. Considering the statistically significant differences, the metabolomic analysis highlights the effect of the extract in reducing glutathione, which can be a beneficial effect in the treatment of cancer, while the proteomic analysis highlights the increase in the expression of the NPC1 protein, one of the main proteins involved in the transport of cholesterol, being directly related to the prevention of atherosclerosis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A. and R.P.; methodology, M.L.S and H.M.S.; formal analysis, R.A.; investigation, R.A.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A.; writing—review and editing, R.P., M.L.S and H.M.S.; supervision, R.P., M.L.S and H.M.S; project administration, M.L.S.; funding acquisition, M.L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financed by UIDB/04046/2020 and UIDP/04046/2020 Centre grants from FCT, Portugal (to BioISI); research project PTDC/BIA-BQM/28355/2017. Centro de Química Estrutural is a Research Unit (RU) funded by FCT, projects UIDB/00100/2020 and UIDP/00100/2020. Institute of Molecular Sciences is an Associate Laboratory funded by FCT, project LA/P/0056/2020. R.A. is the recipient of a fellowship from BioSys PhD programme PD65-2012 (PD/BD/142861/2018) from FCT (Portugal). PROTEOMASS Scientific Society is acknowledged by the funding provided to the Laboratory for Biological Mass Spectrometry Isabel Moura (#PM001/2019 and #PM003/2016). H.M.S acknowledges the Associate Laboratory for Green Chemistry-LAQV (LA/P/0008/2020) funded by FCT/MCTES (Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia and Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior) for his research contract, and the funding provided to the Associate Laboratory for Green Chemistry LAQV, which is financed by national funds from FCT/MCTES through the projects UIDB/50006/2020 and UIDP/50006/2020. Supported also by Bioisi MassSpec Facility.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hansson GK, Hermansson A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol 2011;12:204–12. [CrossRef]
- Townsend N, Kazakiewicz D, Lucy Wright F, Timmis A, Huculeci R, Torbica A, et al. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in Europe. Nat Rev Cardiol 2022;19:133–43. [CrossRef]
- Wilkins E, Wilson L, Wickramasinghe K, Bhatnagar P. European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017. Eur Hear Netw 2017:94–100.
- Carson JAS, Lichtenstein AH, Anderson CAM, Appel LJ, Kris-Etherton PM, Meyer KA, et al. Dietary Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Risk: A Science Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020;141:e39–53. [CrossRef]
- André R, Pacheco R, Bourbon M, Serralheiro ML. Brown Algae Potential as a Functional Food against Hypercholesterolemia: Review. Foods 2021;10. [CrossRef]
- Aniket K, Roshan D. Algae products Market - Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2022-2031. 2022.
- Ferruzza S, Rossi C, Scarino ML, Sambuy Y. A protocol for differentiation of human intestinal Caco-2 cells in asymmetric serum-containing medium. Toxicol In Vitro 2012;26:1252–5. [CrossRef]
- Lea T. Caco-2 Cell Line BT - The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: in vitro and ex vivo models. In: Verhoeckx K, Cotter P, López-Expósito I, Kleiveland C, Lea T, Mackie A, et al., editors., Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2015, p. 103–11. [CrossRef]
- Tung Y-T, Wu C-H, Chen W-C, Pan C-H, Chen Y-W, Tsao S-P, et al. Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus Extracts Improved Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation in High-Energy Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia Rats. Nutrients 2022;14. [CrossRef]
- André R, Guedes L, Melo R, Ascensão L, Pacheco R, Vaz PD, et al. Effect of food preparations on in vitro bioactivities and chemical components of fucus vesiculosus. Foods 2020;9:1–20. [CrossRef]
- André R, Guedes R, López J, Serralheiro ML. Untargeted metabolomic study of HepG2 cells under the effect of Fucus vesiculosus aqueous extract. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2021;35:1–8. [CrossRef]
- Yoon NY, Kim HR, Chung HY, Choi JS. Anti-hyperlipidemic effect of an edible brown algae, Ecklonia stolonifera, and its constituents on poloxamer 407-induced hyperlipidemic and cholesterol-fed rats. Arch Pharm Res 2008;31:1564–71. [CrossRef]
- van der Wulp MYM, Verkade HJ, Groen AK. Regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2013;368:1–16. [CrossRef]
- Schumacher-Schuh A, Bieger A, Borelli W V, Portley MK, Awad PS, Bandres-Ciga S. Advances in Proteomic and Metabolomic Profiling of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Neurol 2021;12:792227. [CrossRef]
- Chen Z-Z, Gerszten RE. Metabolomics and Proteomics in Type 2 Diabetes. Circ Res 2020;126:1613–27. [CrossRef]
- Panner Selvam MK, Finelli R, Agarwal A, Henkel R. Proteomics and metabolomics — Current and future perspectives in clinical andrology. Andrologia 2021;53:e13711. [CrossRef]
- Falé P, Amaral F, Amorim Madeira PJ, Sousa Silva M, Florêncio MH, Frazão FN, et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition, antioxidant activity and toxicity of Peumus boldus water extracts on HeLa and Caco-2 cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol 2012;50:2656–62. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira E, Araújo JE, Gómez-Meire S, Lodeiro C, Perez-Melon C, Iglesias-Lamas E, et al. Proteomics analysis of the peritoneal dialysate effluent reveals the presence of calcium-regulation proteins and acute inflammatory response. Clin Proteomics 2014;11:17. [CrossRef]
- Jorge S, Capelo JL, LaFramboise W, Dhir R, Lodeiro C, Santos HM. Development of a Robust Ultrasonic-Based Sample Treatment To Unravel the Proteome of OCT-Embedded Solid Tumor Biopsies. J Proteome Res 2019;18:2979–86. [CrossRef]
- Cox J, Mann M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 2008;26:1367–72. [CrossRef]
- Cox J, Neuhauser N, Michalski A, Scheltema RA, Olsen J V, Mann M. Andromeda: A Peptide Search Engine Integrated into the MaxQuant Environment. J Proteome Res 2011;10:1794–805. [CrossRef]
- Tyanova S, Cox J. Perseus: A Bioinformatics Platform for Integrative Analysis of Proteomics Data in Cancer Research. In: von Stechow L, editor. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, New York, NY: Springer New York; 2018, p. 133–48. [CrossRef]
- Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, et al. ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009;25:1091–3. [CrossRef]
- Duarte MMMF, Moresco RN, Duarte T, Santi A, Bagatini MD, Da Cruz IBM, et al. Oxidative stress in hypercholesterolemia and its association with Ala16Val superoxide dismutase gene polymorphism. Clin Biochem 2010;43:1118–23. [CrossRef]
- Niu B, Liao K, Zhou Y, Wen T, Quan G, Pan X, et al. Application of glutathione depletion in cancer therapy: Enhanced ROS-based therapy, ferroptosis, and chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2021;277:121110. [CrossRef]
- Yoo D, Jung E, Noh J, Hyun H, Seon S, Hong S, et al. Glutathione-Depleting Pro-Oxidant as a Selective Anticancer Therapeutic Agent. ACS Omega 2019;4:10070–7. [CrossRef]
- Catarino MD, Fernandes I, Oliveira H, Carrascal M, Ferreira R, Silva AMS, et al. Antitumor Activity of Fucus vesiculosus-Derived Phlorotannins through Activation of Apoptotic Signals in Gastric and Colorectal Tumor Cell Lines. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22. [CrossRef]
- FABP1 - Fatty acid-binding protein, liver - Function n.d. https://www.nextprot.org/entry/NX_P07148/ (accessed May 4, 2023).
- Zhang JR, Coleman T, Langmade SJ, Scherrer DE, Lane L, Lanier MH, et al. Niemann-Pick C1 protects against atherosclerosis in mice via regulation of macrophage intracellular cholesterol trafficking. J Clin Invest 2008;118:2281–90. [CrossRef]
- Yu XH, Jiang N, Yao PB, Zheng XL, Cayabyab FS, Tang CK. NPC1, intracellular cholesterol trafficking and atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta 2014;429:69–75. [CrossRef]
- Marques LR, Diniz TA, Antunes BM, Rossi FE, Caperuto EC, Lira FS, et al. Reverse cholesterol transport: Molecular mechanisms and the non-medical approach to enhance HDL cholesterol. Front Physiol 2018;9:526. [CrossRef]
- Shin H-C, Kim SH, Park Y, Lee BH, Hwang HJ. Effects of 12-week oral supplementation of Ecklonia cava polyphenols on anthropometric and blood lipid parameters in overweight Korean individuals: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Phytother Res 2012;26:363–8. [CrossRef]
- Yeo A-R, Lee J, Tae IH, Park S-R, Cho YH, Lee BH, et al. Anti-hyperlipidemic Effect of Polyphenol Extract (Seapolynol(TM)) and Dieckol Isolated from Ecklonia cava in in vivo and in vitro Models. Prev Nutr Food Sci 2012;17:1–7. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).