1. Introduction
The first laparoscopy was performed in 1901 on a dog by Georg Kelling during a scientific meeting and he called this intervention „coelioscopy” [
1,
2]. In 1910 a Swedish doctor performed “laparothoracoscopy”, the first endoscopy of the human abdominal cavity and the chest [
3]. The first laparoscopy made in USA was named „organoscopy” and it was performed in 1911 [
4]. The development of laparoscopy required many steps, the greatest progress was made between 1960-1980. A transition of this technique from a diagnostic to a therapeutic purpose was observed. A gynecologist performed the first laparoscopic appendectomy in 1980, in Germany. The rapid development of laparoscopy had an important impact on gynecological surgery [
5]. A reference moment in the development of laparoscopy in the treatment of gynecological diseases was represented by the first bowel resection in the case of a patient with endometriosis in 1988 by Camran Nezahat [
6]. An important progress for gynecological laparoscopy was observed from 1989 to 1992. The laparoscopic hysterectomy technique was developed and improved by Camran Nezhat, Harry Reich, S. Kovac and G. Magi [
7].
Over the years, laparoscopy has been preferred over classical surgical techniques due to the advantages of minimally invasive techniques. It is currently used worldwide in a variety of surgical diseases due to lower operating time, fewer hospitalization days, diminished intraoperative hemorrhage and cosmetic skin incisions [
8,
9]. That is why it is necessary to analyze and standardize the process of learning this type of surgery by evaluating parameters that characterize the surgical act and by using this information to build learning curves [
10]. As a result, young doctors are able to learn the method more efficiently.
Currently, laparoscopy is the gold standard for surgical interventions. The perceptual obstacles, the stressful environment in the operating room as well as the high costs of these types of interventions represented a challenge for the process of learning the basic techniques in laparoscopy. Thus, it was necessary to adopt new educational models. Medical simulation and virtual reality training have been developed with very good results in the learning process [
11].
Each learning process consists of two distinct phases: an initial phase with an increased learning rate, along with a prolonged surgery time and a higher complication rate and a second phase, with reduction of both procedure duration and complication rate [12-14]. Consequently, a graphic representation of learning process has a sinusoidal aspect, being initially ascending and followed by a descending phase after the reach of the plateau level, that marks the end of the learning process. The learning process for less invasive procedures is considered longer and more difficult in comparison to the one for open surgical procedures, but it has been shown that when inexperienced subjects get equal training in these two types of techniques, the overall skill obtained were similar by both methods [
15]. Also, it has been postulated that the rate of complications is decreasing significantly when the volume of surgical workload is getting higher overtime [
16].
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (RCOG) published a guide in which laparoscopic gynecological interventions were divided according to the degree of difficulty into 3 levels. Level 1 included diagnostic laparoscopy, tubal patency tests and sterilization. Level 2 basically included laparoscopic interventions at the level of the adnexals such as cystectomy, adnexectomy, surgical treatment of ectopic pregnancies and subtotal hysterectomy. Difficulty level 3 included myomectomy, total hysterectomy and surgical treatment of endometriosis, urinary incontinence or pelvic floor disorders. It was found that 73% of surgeons perform basic laparoscopic surgeries. Frequent, the explanation is the fact that interventions with a high level of difficulty require a longer operative time and also a long-term learning [
17].
2. Materials and Methods
The aims of this study were to evaluate the learning process of laparoscopic surgery for adnexal benign gynecological pathology and to observe the direction of evolution of this minimally invasive surgery.
This study was performed between November 2019 and June 2020 by retrospectively analyzing clinical data from patients admitted to Bucur Maternity, Bucharest from 4th January 2015 to 19th December 2018. Clinical data were collected anonymously from both observation charts and clinical records of the patients attending the study. Those patients where operated laparoscopic by three gynecologists from Bucur Maternity whose names were concealed due to confidentiality reasons and replaced with the letters A, B and C. Some important observations are that all laparoscopist included in the study were beginners in laparoscopy (with less than 100 operations) and the operation time was noted since the patient entered the operating room until the patients awaked from general anesthesia.
This study included all laparoscopic surgeries that were performed for a benign adnexal pathology. We collected information about patients, diagnosis, surgical technique and complications.
The data collected was analyzed using the SPSS Statistic software, version 23 (Armonk, NY, USA). We used descriptive statistics for mean, standard deviation, median and frequencies. When we wanted to evaluate the relationship between two parameters, we used Independent Sample T Test and One-Way ANOVA. If the p-value was less than 0.05, then the correlation was considered statistically significant. Bar charts and scatter plot were created with data.
The limitations of this study were represented by the relatively reduced number of patients included in the study, the small number of surgeons practicing laparoscopy in our hospital and the low frequency of complex ovarian pathologies.
3. Results
Our study included a number of 159 interventions performed by three operators.
The age of the patients varied between 19 and 56 years, with an average of 33.28 ± 7.80 years. Most surgical interventions were performed on patients under 35 years (63.3%). The body mass index had a mean value of 26.12 ± 3.26 kg/m2 with a variation between 19.40 and 37.10 kg/m2.
According to the diagnoses, we found that 64.8% of the cases represented an ovarian pathology while 35.2% had a tubal pathology. The most common diagnoses were functional ovarian cyst (25.8%), ectopic pregnancy (22.0%), endometriotic ovarian cyst (10.7%), adnexal tumour (8.2%), dermoid ovarian cyst (6.9%). Numerous secondary diagnoses were identified. Pelvic adhesion syndrome was present in the case of 39 patients (24.5%), while hemoperitoneum at 23 patients (14.5%). A less common condition like Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome was found in 2 cases (1.2%).
We analysed different technical aspects of the laparoscopic surgery. We found that for pneumoperitoneum the Veress method was the most used laparoscopic approach (59.7%) followed by Hasson method (40.3%). Carbon dioxide pressure varied between 11 and 13 mmHg, in 141 cases a pressure of 12 mmHg was maintained (88.7%). The number of trocars used was between 2 and 5, in 57.9% of cases 3 trocars were used, while 40.3% of cases required the use of 4 trocars.
Ovarian cystectomy was the most common type of surgical intervention performed (49.1%). Other procedures completed were partial salpingectomy (31.9%), unilateral adnexectomy (13.2%), ovariectomy (4.4%) and adhesiolysis (28.9%). Tubal permeability testing with methylene blue was performed in 5.1% of cases.
The duration of the surgical interventions varied between 50 and 180 minutes with an average duration of 113.26 ± 27.28 minutes. The patients were hospitalized for a variable number of days, between 3 and 6 days. Most patients were hospitalized for 4 days (60.4%). Peritoneal drainage was used in 100% of cases and in 1.9% of cases there were use two tubes for peritoneal drainage. The conversion of the laparoscopic intervention into a laparotomy intervention was necessary in 2 cases (1.3%). There were no ureter injury, reinterventions or blood transfusions.
We used the Independent Sample T Test and One-Way ANOVA to analyze the relationship between the duration of the surgery and the pathology, the operator, the type of laparoscopic approach, the number of exchanges used and the days of hospitalization (
Table 1). We identified that the duration of surgery did not have a statistically significant correlation with any of these variables. Despite all this, we noticed that the duration of surgery is significantly correlated with the body mass index of the patients (p < 0.01). The type of procedure performed did not significantly influence the duration of the surgical intervention nor the number of trocars used.
The two surgery conversions into laparotomy interventions were performed by different operators, A and C. Endometriotic ovarian cyst represented the main diagnosis for surgeon A and it was intervention number 27 out of 47 (57.44%). For operator C and the diagnosis was dermoid cyst, representing intervention 43 out of a total of 53 (81.13%).
We choose to evaluate the parameters for two of the most important gynecological surgeries: ovarian cystectomy and unilateral adnexectomy (
Table 2). We found that there was a statistically significant difference between the average time needed to perform the ovarian cystectomy between operation A and C (p < 0.05).
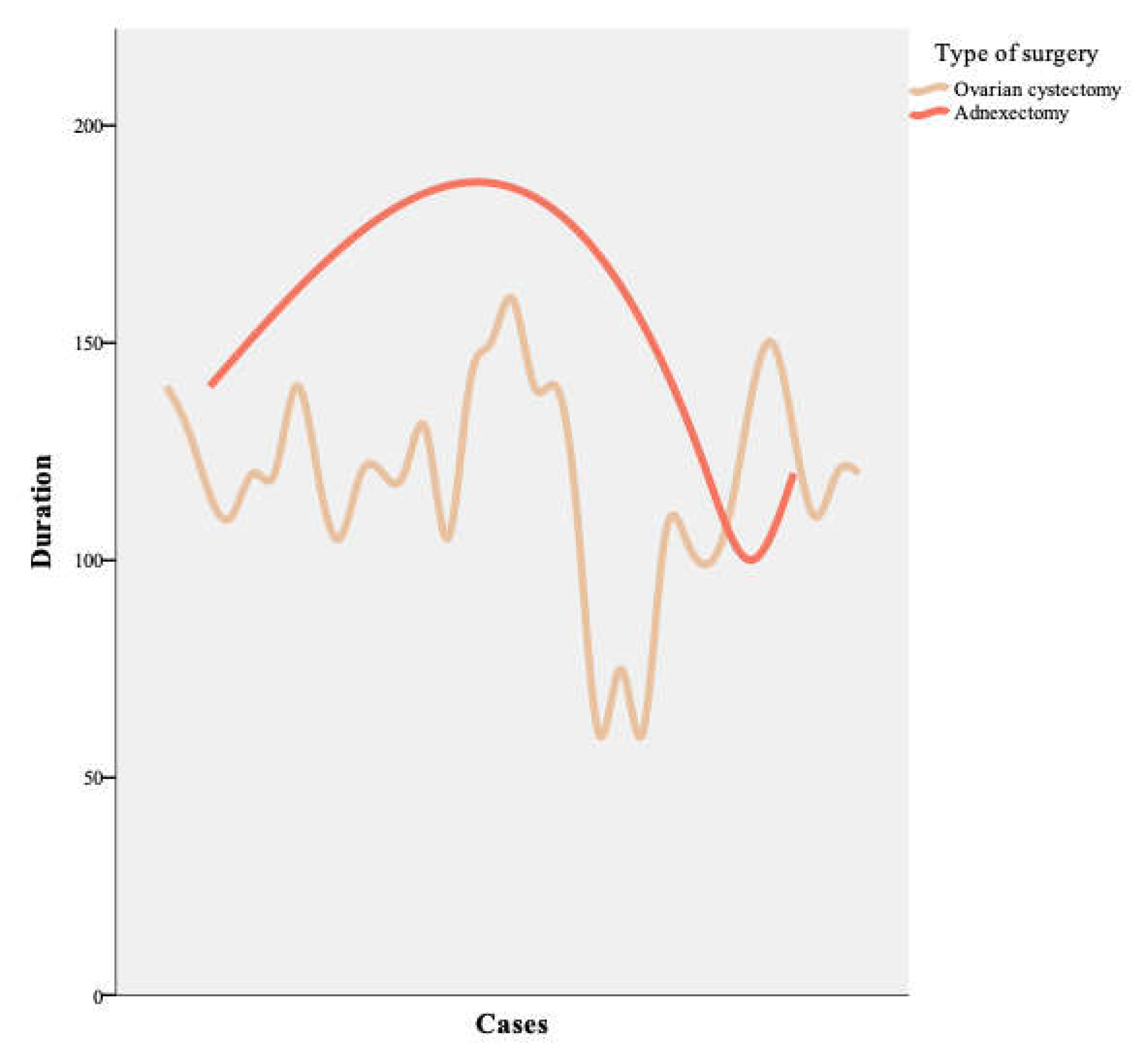
The evolution over time of the duration of surgeries was analyzed. We noticed that for gynecologic surgeon A there is an improvement in the operating time for the adnexectomy (
Figure 1).
We divided the total number of surgeries for each gynecologist into two phases. In this division, the type of surgery performed was not considered and it was established that each case brought improvements in the technique and surgical skills of the operator.
Thus, the first phase was represented by the first 20 laparoscopic surgeries, the second phase was represented by the rest of the surgeries for each operator.
We compared the duration of ovarian cystectomy and total or partial salpingectomy in the two phases using Independent Samples T Test. We observed that there was a statistically significant improvement in terms of operating time for ovarian cystectomy for surgeons A and B (
Table 3). Operator C had a significant improvement for performing salpingectomy (
Table 4).
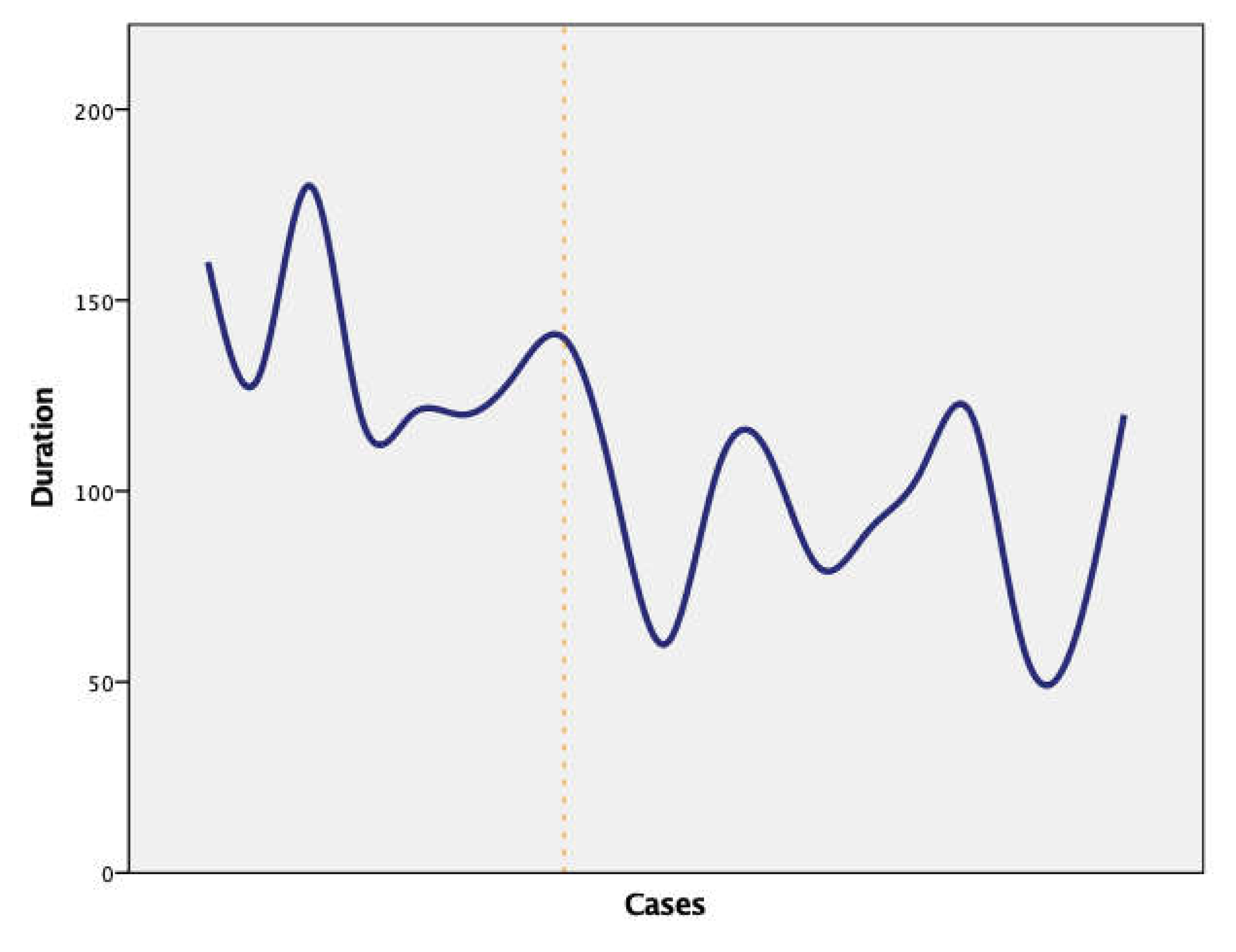
The evolution of performing salpingectomy by gynecologist C was represented in
Figure 2 where the two learning phases were separated by a vertical line.
4. Discussion
Laparoscopic surgery, in contrast to laparotomy, had demonstrated numerous advantages during the past 30 years, as it is a less invasive procedure and presents faster recovery time, shorter hospitalization, fewer infections and less pain [
8,
9]. Our data showed that the mean duration of laparoscopic procedures was about 113 minutes and most patients required four days of hospitalization after surgery. A decrease in perioperative complications and in mean operating time has been used often to evaluate the learning process [18-21].
In our study, the most common gynecological pathology was represented by the ovarian cyst. A study conducted in a hospital from Poland analyzed 326 fertile women who needed a surgery on the ovarian tumor and concluded that unilateral benign cysts were the most frequent pathology. Furthermore, few patients had a malignant tumor, but it was usually in an early stage of the disease [
22]. It was also observed in a prospective study that laparoscopy was safe and feasible for patients with large benign ovarian cysts [
23].
The rate of intraoperative and postoperative complications was reduced, which can be explained through the young patients, the normal or slightly raised BMI, the professionalism of the operating team. Leon Morgenstern highlighted in his publication the risks of the learning curve, the morbidity or even the mortality rate caused by this learning process, and he considered the possibility of complications of not being enough reported [
24]. Hopkins reported in his publication an increased risk for ureteral injury and vesical-vaginal fistula in the early stages of learning laparoscopy in gynecologic procedures [
25].
In our study there was no case which required reintervention. Wattiez et al. conducted a study on 1647 cases to evaluate the possibility of introducing the laparoscopic technique in the treatment of the benign uterine pathology and the results revealed a reduced necessity of reintervention in the second phase of the study. Moreover, conversion to laparotomy was needed more frequently in the first phase of the study because of ureteral lesions and diminished in the second phase, where it was needed only in complicated cases [
26]. The conversion to laparotomy was needed in less than 1.3% of interventions, especially in older patients, with a higher BMI or with conditions such as extrauterine pregnancy and pelvic adhesions. The rate for conversion to laparotomy varied in the literature from 0.03% to 6.6% [
9,
27,
28]. The conversion of the procedure generally occurs in the early learning phase, but sometimes there are situations which require changing a laparoscopy into a laparotomy, even for surgeons who completed the learning curve. Garett et al. mentioned in their study the necessity for conversion in six of eight patients due to broad adhesions and advanced diseases [
29].
The results of this study showed no ureteral lesions but there are other studies that reported such injuries. Wattiez et al. mentioned an incidence of 0.6% for ureteral injuries during the early process of learning for hysterectomy and a lower incidence (0.2%) during the second period of learning (managed intraoperatively, without the need for conversion). They noted as risk factors for ureteral injuries the excessive bleeding, very large uterus and endometriosis [
13]. Another retrospective analysis performed on 1706 patients after a laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy described a total of five intraoperative cases (0.3%) complicated with bladder injury, ureter injury or severe bleeding [
28]. No patient registered in our study received blood transfusions, although they may be necessary in some circumstances. It is well known in literature that bleeding is one of the most major complications and it’s a main reason for conversion to laparotomy [
26].
In the learning process for laparoscopic hysterectomy (LH), Twijnstra et al. concluded that 22-25 LHs should be performed for reaching the plateau [
30]. Similar to them, Garry et al. suggested that after 25 cases the learning curve is completed [
31]. There has also been a study published in 2016 by Terzi H et al. that analyzed the surgical learning process in benign pathology which detected a significant reduction in operating time between cases 50-100, without an additional decrease after this group. They also concluded that the plateau occurred during cases 71-80 [
32]. A similar tendency was observed in another study, that evaluated the learning curve of laparoscopic hysterectomy associated with removal of pelvic and paraaortic lymph nodes in patients with cervix cancer [
33]. A study that included 576 laparoscopic hysterectomies concluded that the learning process of this type of surgery was safe for the patient and an improvement in operative time was observed after 100 interventions but without reaching a plateau [
34]. The most challenging moment in laparoscopic hysterectomy is when the uterus is excised, the incision is made at the level of the vagina and then the vaginal cuff is sutured. This step requires a long period of training to prevent complications [
35].
Regarding the surgical treatment of pelvic organ prolapse, it was observed that in the case of laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy, the operating time decreased after 30 interventions, and an adequate operative performance appears after 60 performed procedures. It was found that in the case of laparoscopic pectopexy, the operating time stabilized after 28 interventions. The CUSUM analysis showed that 38-40 interventions of this type are necessary to master the surgical technique [
36].
Laparoscopy is a safe and feasible technique also in the case of malignant gynecological pathologies. The increase in the experience of the surgeon was accompanied by a decrease in the amount of blood lost intraoperatively, but it was found that it did not influence the number of excised lymph nodes or the number of days of postoperative hospitalization [
37].
We found that after a number of 20 laparoscopic interventions, all three operators included in the study presented a significant decrease in operating time for different types of surgical interventions. Two out of three operators showed an improvement in the operative time for performing the ovarian cystectomy, and the third operator showed a decrease in the time for performing interventions on the fallopian tubes. This threshold of 20 laparoscopic interventions may mark an improvement in the skills for this type of surgery. After learning the laparoscopic techniques and decreasing the operating time, an increase in the difficulty of the cases selected for laparoscopic intervention can be noted.
A major problem regarding the training of residents was represented by the lack of established learning protocols. Many times, the gynecologists who practice in university hospitals were still dealing with their learning curve and thus there was a reduced opportunity for the residents to practice in the operating room. Other negative factors were represented by the reduced number of resident working hours or the small number of major laparoscopic interventions [
17].
Acquiring skills in laparoscopic surgery such as manipulating the camera and instruments, hands-eyes coordination and depth perception is difficult and requires a long learning process. A possibility to practice repeatedly without endangering the safety of the patient is represented by medical simulators. Halstead's classic surgical teaching principle "see one, do one, teach one" has lost value in front of new medical simulation techniques that can improve laparoscopic skills but without risk for patients [
38]. Medical simulation is an effective way of learning laparoscopy. However, its implementation is difficult due to considerations related to money and time [
39].
The limitation of the time given to teaching laparoscopy determined the need to develop some didactic methods for learning laparoscopy outside the operating room. Thus, several methods of practicing laparoscopic techniques appeared. They have been developed from simple training boxes to simulators that use virtual reality. A controversial practice is preparation on cadavers [
40].
Traditionally, surgical techniques were acquired in the operating room and were dependent on a mentor. The effectiveness of this method was variable. Thus, the need to develop some modern training models of surgical procedures appeared. A study that analyzed 58 trails about training models in laparoscopy, concluded that both virtual reality training and video training had the same results in the learning process. The two techniques represented valid learning methods, and their combination was recommended. The results are superior to those obtained by learning surgical techniques in the operating room. The results were contradictory in the case of practicing robotic technologies [
41]. It was observed that the use of virtual reality training determined the reduction of operative time by 17-50% depending on the principles used for the exercise and the type of simulator. The implementation of training models in laparoscopy resulted in shortening the learning curve. Thus, it was concluded that the skills acquired through virtual reality training can be transferred to the operating room [
11].
Another method of acquiring surgical skills is training at home. In this situation, each surgeon can adapt his practice style according to his needs. This method has become a feasible one for learning laparoscopy and the self-evaluation process is important [
42].
The difference between the use of 2D versus 3D laparoscopy was also analyzed. In the case of using a box trainer, the number of errors was significantly higher among those who used the 2D technique compared to those who used the 3D technique. The time required to perform a laparoscopic hysterectomy was not significantly different between the two groups. It was concluded that 3D laparoscopy is useful for beginning surgeons and facilitates the learning process [
43]. A study by Degirmenci et al. showed that in the case of 3D laparoscopy performed for complex urogynecological pathologies, a shorter operating time and a smaller amount of blood loss were found than in the case of 2D laparoscopy [
44].
Single-site laparoendoscopic surgery (LESS) was developed and the surgical intervention is performed by using a single transumbilical multiport. In several studies the feasibility and safety of this surgical technique in the treatment of benign gynecological diseases was confirmed. This presents a series of advantages compared to conventional laparoscopic surgery, such as a lower rate of postoperative complications, a faster recovery and a lower need for post-interventional analgesia. This technique requires advanced laparoscopy skills, which makes it difficult to be accepted on a large scale. There are studies that have shown that between 30 and 55 interventions of this type are necessary for benign gynecological pathologies to master the technique [
45].
Robotic surgery developed from the desire to perfect laparoscopic instruments and to obtain an image of increased quality. This seems to be developing as a separate field. The use of minimally invasive surgical techniques in the treatment of gynecological diseases is encouraged [
46]. A meta-analysis concluded that mortality is similar between the laparoscopic and the robotic approach [
47].
5. Conclusions
The process of learning laparoscopy is laborious and difficult compared to learning classical surgery techniques. We identified a significant decrease in operating time after a number of twenty laparoscopy interventions. After learning the laparoscopic techniques, there may be an increase in operative time by dealing with complicated surgical cases.
It is important to develop and improve new models of laparoscopy learning, from practicing at home and using box trainers to virtual reality training or video training.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: title; Table S1: title; Video S1: title.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.-M.S., A.C., B.H.H.; methodology, L.P., M.A., F.B.; software, M.-T.G., G.-P.G.; validation, L.P., B.H.H.; formal analysis, A.C., M.-T.G.; investigation, G.P.G, A.C.; resources, R.-M.S., A.C.; data curation, F.B., M.A.; writing - original draft preparation, R.-M.S., A.C.; writing - review and editing, L.P., F.B.; visualization, M.-T.G., M.A.; supervision, B.H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of “Sf. Ioan” Emergency Hospital, Bucharest, Romania (protocol code 27248 and date 16.12.2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are available from the corresponding author and the authors can share the information if they are reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Publication of this paper was supported by the University of Medicine Pharmacy Carol Davila, through the institutional program Publish not Perish.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schollmeyer T, Soyinka AS, Schollmeyer M, Meinhold-Heerlein I. Georg Kelling (1866-1945): the root of modern day minimal invasive surgery. A forgotten legend? Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2007 Nov; 276(5): p. 505-9.
- Hatzinger M, Badawi JK, Häcker A, Langbein S, Honeck P, Alken P. Georg Kelling (1866-1945): the man who introduced modern laparoscopy into medicine. Urologe A. 2006 Jul; 45(7): p. 868-71.
- Hatzinger M, Häcker A, Langbein S, Kwon S, Hoang-Böhm J, Alken P. Hans-Christian Jacobaeus (1879-1937): The inventor of human laparoscopy and thoracoscopy. Urologe A. 2006 Sep; 45(9): p. 1184-6.
- Morgenstern, L. The First Laparoscopist in the United States: Bertram M. Bernheim, MD. Surg. Innov. 2007, 14, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkatout, I.; Mechler, U.; Mettler, L.; Pape, J.; Maass, N.; Biebl, M.; Gitas, G.; Laganà, A.S.; Freytag, D. The Development of Laparoscopy—A Historical Overview. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 799442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezhat, C.; Hajhosseini, B.; King, L.P. Laparoscopic Management of Bowel Endometriosis: Predictors of Severe Disease and Recurrence. JSLS : J. Soc. Laparosc. Robot. Surg. 2011, 15, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley WEJ. The evolution of laparoscopy and the revolution in surgery in the decade of the 1990s. JSLS. 2008 Oct-Dec; 12(4): p. 351-7.
- Kim, S.M.; Park, E.K.; Jeung, I.C.; Kim, C.J.; Lee, Y.S. Abdominal, multi-port and single-port total laparoscopic hysterectomy: eleven-year trends comparison of surgical outcomes complications of 936 cases. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014, 291, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnez, O.; Jadoul, P.; Squifflet, J.; Donnez, J. A series of 3190 laparoscopic hysterectomies for benign disease from 1990 to 2006: evaluation of complications compared with vaginal and abdominal procedures. BJOG: Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 116, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, E.M.; Grantcharov, T.P.; Husslein, H.; Shirreff, L.; Dedy, N.J.; McDermott, C.D.; Lefebvre, G.G. Validating a standardized laparoscopy curriculum for gynecology residents: a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 204–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.R.; Oestergaard, J.; Ottesen, B.S.; Soerensen, J.L. The efficacy of virtual reality simulation training in laparoscopy: a systematic review of randomized trials. Acta Obstet. et Gynecol. Scand. 2012, 91, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardon, S.F.; van Gastel, L.A.; Horeman, T.; Daams, F. Assessment of technical skills based on learning curve analyses in laparoscopic surgery training. Surgery 2021, 170, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardon, S.F.; Horeman, T.; Bonjer, H.J.; Meijerink, W.J.H.J. Force-based learning curve tracking in fundamental laparoscopic skills training. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 3609–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnadara, R.R.; Mui, C.; McQueen, S.; Mironova, P.; Nousiainen, M.; Safir, O.; Kraemer, W.; Ferguson, P.; Alman, B.; Reznick, R. Reflections on Competency-Based Education and Training for Surgical Residents. J. Surg. Educ. 2014, 71, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Gu, J. Open surgery in the era of minimally invasive surgery. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 34, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudelist G, Korell M, Burkhardt M,. etal. Rates of severe complications in patients undergoing colorectal surgery for deep endometriosis-a retrospective multicenter observational study. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica. 2022 Oct; 101(10): p. 1057-1064.
- Jansen, F.W.; Kolkman, W. Implementation difficulties of advanced techniques in gynecological laparoscopy. Gynecol. Surg. 2008, 5, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, R.L. The Danger of Time-Consuming Operative Laparoscopies: Avoiding Severe Complications. Geburtshilfe Und Frauenheilkd. 2012, 72, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paek, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, M.; Yim, G.-W.; Nam, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-T. Learning Curve and Surgical Outcome for Single-Port Access Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy in 100 Consecutive Cases. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2011, 72, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krentel, H.; De Wilde, R.L. Factors for a Successful Laparoscopic Hysterectomy in Very Large Uteri. Case Rep. Med. 2017, 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, R.; Wattiez, A.; Tanos, V.; Sardo, A.D.S.; Grimbizis, G.; Wallwiener, D.; Brucker, S.; Puga, M.; Molinas, R.; O’donovan, P.; et al. Gynaecological endoscopic surgical education and assessment. A diploma programme in gynaecological endoscopic surgery. Gynecol. Surg. 2016, 13, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltabbakh, G.H.; Charboneau, A.M.; Eltabbakh, N.G. Laparoscopic surgery for large benign ovarian cysts. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 108, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottomley, C.; Bourne, T. Diagnosis and management of ovarian cyst accidents. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 23, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, L. Warning! Dangerous curve ahead: the learning curve. Surg Innov. 2005 Mar; 12(1): p. 101-3.
- Hopkins, MP. The myths of laparoscopic surgery. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Jul; 183(1): p. 1-5.
- Wattiez, A.; Soriano, D.; Cohen, S.; Nervo, P.; Canis, M.; Botchorishvili, R.; Mage, G.; Poul, J.; Mille, P.; Bruhat, M. The Learning Curve of Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Comparative Analysis of 1647 Cases. J. Am. Assoc. Gynecol. Laparoscopists 2002, 9, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkman, W.; Engels, L.E.; Smeets, M.J.; Jansen, F.W. Teach the Teachers: An Observational Study on Mentor Traineeship in Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2006, 64, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojahr, B.; Raatz, D.; Schonleber, G.; Abri, C.; Ohlinger, R. Perioperative complication rate in 1706 patients after a standardized laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy technique. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2006, 13, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, A.J.; Nascimento, M.C.; Nicklin, J.L.; Perrin, L.C.; Obermair, A. Total laparoscopic hysterectomy: The Brisbane learning curve. Aust. New Zealand J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2007, 47, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twijnstra, A.; Blikkendaal; Kolkman, W. ; Smeets, M.; Rhemrev, J.; Jansen, F. Implementation of Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Maintenance of Skills after a Mentorship Program. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2010, 70, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garry, R.; Fountain, J.; Mason, S.; Hawe, J.; Napp, V.; Abbott, J.; Clayton, R.; Phillips, G.; Whittaker, M.; Lilford, R.; et al. The eVALuate study: two parallel randomised trials, one comparing laparoscopic with abdominal hysterectomy, the other comparing laparoscopic with vaginal hysterectomy. BMJ 2004, 328, 129–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzi, H.; Biler, A.; Demirtas, O.; Guler, O.T.; Peker, N.; Kale, A. Total laparoscopic hysterectomy: Analysis of the surgical learning curve in benign conditions. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 35, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasbi Rad M, Wallwiener M, Rom J, Sohn C, Eichbaum M. Learning curve for laparoscopic staging of early and locally advanced cervical and endometrial cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2013 Sep; 288(3): p. 635-42.
- Schützendübel, M.; Boosz, A.; Baev, E.; Häberle, L.; Müller, A. Learning laparoscopic hysterectomy: analysis of different surgeons’ individual learning curves. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2022, 307, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakay, K. Introduction of a Novel Modification in Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: The Bakay Technique. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2018, 25, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, P.; Grzybowska, M.E.; Sawicki, S.; Wydra, D.G. Laparoscopic Pectopexy—CUSUM Learning Curve and Perioperative Complications Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togami, S.; Kawamura, T.; Fukuda, M.; Yanazume, S.; Kamio, M.; Kobayashi, H. Learning curve and surgical outcomes for laparoscopic surgery, including pelvic lymphadenectomy, for early stage endometrial cancer. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 49, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charokar, K.; Modi, J.N. Simulation-based structured training for developing laparoscopy skills in general surgery and obstetrics & gynecology postgraduates. 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Appleton S, Huguelet P. Laparoscopy Skills Simulation for the Obstetrics and Gynecology Resident. MedEdPORTAL. 2016 Sep; 12(10460).
- Elessawy, M.; Mabrouk, M.; Heilmann, T.; Weigel, M.; Zidan, M.; Abu-Sheasha, G.; Farrokh, A.; Bauerschlag, D.; Maass, N.; Ibrahim, M.; et al. Evaluation of Laparoscopy Virtual Reality Training on the Improvement of Trainees’ Surgical Skills. Medicina 2021, 57, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willaert, W.; Van De Putte, D.; Van Renterghem, K.; Van Nieuwenhove, Y.; Ceelen, W.; Pattyn, P. Training Models in Laparoscopy: a Systematic Review Comparing their Effectiveness in Learning Surgical Skills. Acta Chir. Belg. 2013, 113, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thinggaard, E. Take-Home Training in Laparoscopy. . 2017, 64. [Google Scholar]
- vision versus two-dimensional vision on laparoscopic performance of trainee surgeons: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Updates Surg. 2023 Apr; 75(3): p. 455-470.
- Degirmenci, Y.; Schepers, M.; Steetskamp, J.; Hasenburg, A.; Skala, C. Three-dimensional vs two-dimensional endoscopic approach in urogynecology: A retrospective cohort study of laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2022, 49, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Cheng, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. The Learning Curve of Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery in Benign Gynecological Diseases. J. Investig. Surg. 2021, 35, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas-López, R.; Sandoval-García-Travesí, F.A. Robotic surgery in gynecology: A review of literature. 2023, 88. [CrossRef]
- Behbehani, S.; Suarez-Salvador, E.; Buras, M.; Magtibay, P.; Magrina, J. Mortality Rates in Benign Laparoscopic and Robotic Gynecologic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2019, 27, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).