1. Introduction
Particles reinforced aluminum matrix composites(PRAMCs) have been widely used in aerospace, and transportation with the characteristics of low density, high specific strength, and low cost [
1,
2]. The PRAMCs consist of the Al matrix phase and the reinforcement phase. The typical reinforcement phases include SiC, ZrB2, and TiB2 particles et al that are widely used as the reinforcement phase of PRAMCs. Among them, TiB2 has been frequently introduced into various aluminum alloys as a reinforcement phase, owing to its wettability, high modulus, and high hardness [
3]. It’s widely accepted that the addition of a reinforcement phase can improve strength of PRAMCs to a great extent, but its toughness was also reduced [
4]. Hence, in order to enhance the mechanical properties of PRAMCs as much as possible, the effect mechanism of reinforcement particles on composite’s mechanical properties needs to be revealed first. And quantifying and analyzing the characteristics of particles is a great way to study this effect mechanism.
Recently, some experimental research showed that the proportion of particles in composites has a significant influence on the load-bearing capacity of the composites [
5,
6]. Lv et al. [
7] fabricated the hybrid aluminum matrix composites reinforced with SiC particles and carbon fibers, and the results showed that the addition of the reinforcement phase improved the composites’ tensile strength and elastic modulus. Yang et al. [
8] fabricated ZrB2/6061Al nanocomposites, and the results showed that the strength of the ZrB2/6061Al was improved by approximately 1.52 times when compared with 6061Al alloy. Moreover, related studies show that the distribution of particles is also a crucial factor for the load-bearing capacity of the composites [
9,
10]. For example, Ma et al. [
11] investigated the mechanical properties of in-situ Al3Ti/A356 composites, and the results showed that the decreased ductility of the composite is due to the clustering of Al3Ti particles. In parallel, the theoretical analytical method is used to predict the mechanical properties of the composite. For instance, Weng [
12] considered the reinforced particles to be ellipsoidal in the model and the interfacial stress and modulus of the composites were obtained. However, this method assumes particles to be simple shapes, and the distribution of particles is taken as uniform, which is not in agreement with the actual microstructure observed. The accuracy of mechanical properties of the composites predicted by the theoretical analytical method needs to be improved.
Aside from the experimental and theoretical analytical methods, the microstructure-based representative volume element (RVE) has also been increasingly adopted to study double phase composites [
13,
14,
15]. Wang et al. [
14] proposed a 2D RVE of SiC/Al by introducing the discrete distribution function of reinforcement and studied the mechanical behavior of SiC/Al. Gad et al. [
16] proposed a 2D FE model to investigate the effects of particle size and volume fraction on the deformation, damage, and failure behaviors of SiC/A356. However, 2D RVE cannot accurately reconstruct the actual microstructure [
17], resulting in inaccurate outcomes. Related works show that 3D microstructure-based modeling has an advantage in studying the complicated and heterogenous microstructure [
18,
19,
20,
21]. Nan et al. [
22] based on the geometric characteristics of TiB2 particles, proposed a computational structural model of TiB2/Cu composites. The accuracy of the model was verified by the agreement of the experimental stress-strain curve, and the mechanical properties of the composite were studied. However, there is still a drawback in his work, the stiffness of a constitutive element is directly removed when it meets the damage criterion without applying the damage evolution law, resulting in the stress-strain curves being underestimated when element removal occurs. To avoid this problem, Ma et al. [
23] proposed a 3D RVE model adopted the linear damage evolution law. A series of computational experiments were carried out to study the influence of clustering degree and volume fraction of particles on the mechanical properties of Al3Ti/A356 composites successfully. But this method is unsuitable for predicting the mechanical properties of composites reinforced with TiB2 particles, due to the difference between the morphology of the Al3Ti particles and the TiB2 particles, which will affect the field of stress on particles. In addition, it can be seen that most of the aforementioned literature focused on aluminum alloys or other alloys, the study on composites of TiB2/6061Al is still lacking now.
To overcome the issues and limitations discussed above, the microscopic geometric characteristics of TiB2/6061Al were extracted from the actual SEM photos in this study. A series of 3D RVEs with different weight fractions and clustering rates were established for TiB2/6061Al composites. The model took into account the ductile damage of the matrix as well as the traction separation behavior of the interface, and a linear damage evolution law was introduced to characterize the stiffness degradation behavior of the element. Furthermore, the mixed boundary conditions were used for RVE tensile experiments. The accuracy of the model was verified by experimental curves. Finally, the effects of particle weight fraction and clustering rate were studied, and the mechanical properties of TiB2/6061Al were predicted and assessed from three aspects: the interface damage, the load-bearing capacity of particles, and the matrix damage.
2. Finite element model
2.1. Material constitutive and fracture behavior
A stable and reliable FE model is helpful in obtaining accurately predicted results, for which it is particularly important to obtain accurate material parameters. Based on previous works, the mechanical properties of TiB2 particles and the 6061Al matrix are presented in
Table 1. The plastic hardening behavior of 6061Al is described by the exponential formula expressed as [
24]:
where
σ is stress,
E is the elastic modulus,
σy and
εp are the yield strength and plastic strain, respectively. The exponent
n is 0.17, which was obtained by fitting a uniaxial tensile stress-strain curve of the 6061Al alloy.
The fracture behavior of TiB2 particles is normally not taken into account in the process of establishing FE models, due to the fact that the fracture of particles is not observed in tensile tests of the composites [
25,
26]. Hence, only the linear elastic behavior of TiB2 particles is considered in this paper. Ductile damage is the main failure behavior of the matrix of Al alloys. Based on the Rice and Tracey criterion [
27], the damage factor
D is used to characterize the degree of ductile damage in the Al matrix:
where
is stress triaxiality,
is the hydrostatic pressure,
is the total stress,
is an equivalent plastic strain (PEEQ), and
is the plastic strain rate tensor.
During the experimental process, with the increase of strain, the damage factor
D in each element will accumulate continuously. When the
D reaches a specified value, the failure of matrix elements will occur. It should be noted that the post failure behavior of the matrix plays a significant role in predicting the stress-strain curves of the failure stage. However, in previous work [
28], the element that still had stiffness was directly deleted when it satisfied the failure criterion during the failure stage of composites. Although this method can simulate the process of crack propagation, the predicted stress-strain curve is underestimated than the experimental result. In this study, a linear damage evolution criterion is used to characterize the post failure behavior of composites [
23]. And the expression of linear damage evolution criterion [
29] is:
where
ε0 is the initial equivalent failure strain,
εeq is the current equivalent stra in, and
kd is a parameter controlling the degradation rate of material’s stiffness. When
d reaches 1, the element’s stiffness becomes 0, and is deleted.
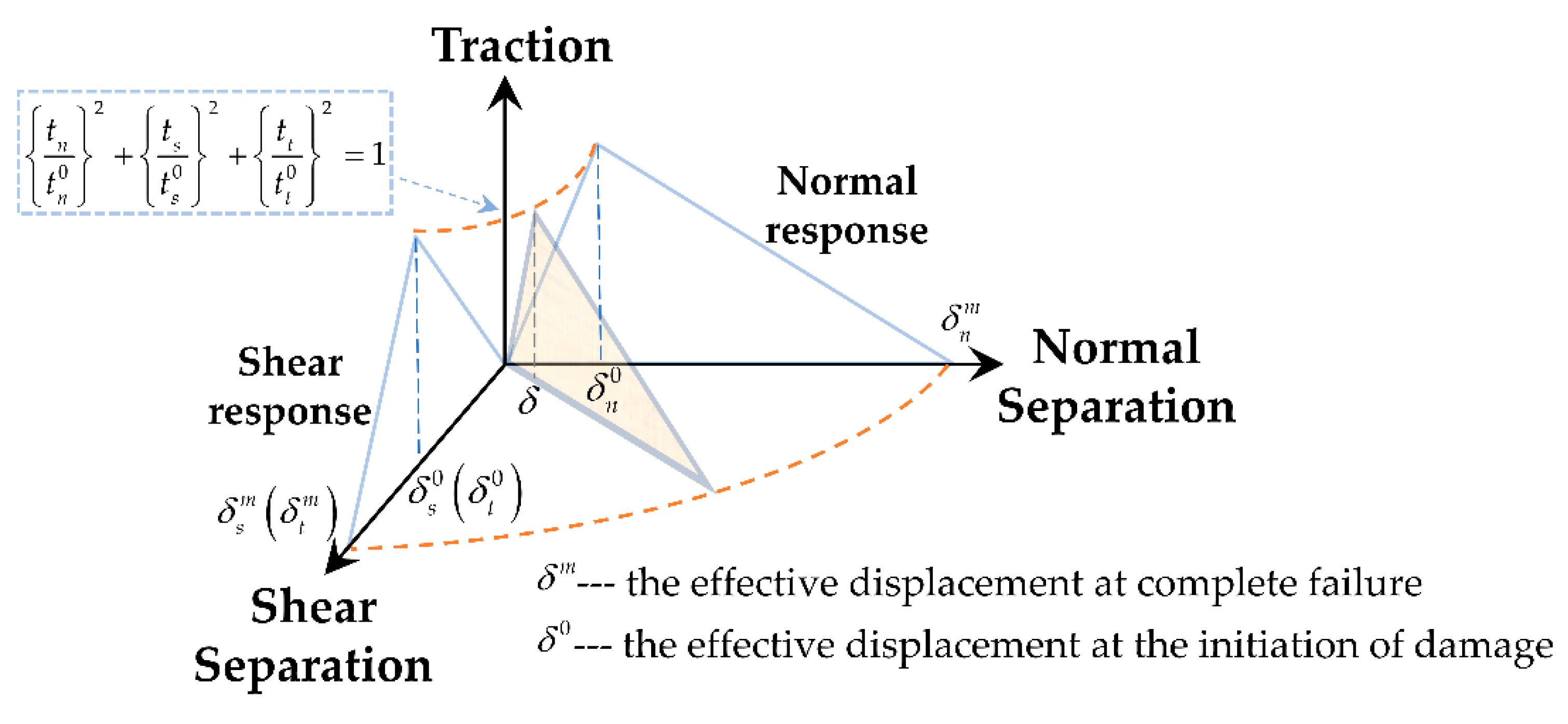
In order to characterize the interfacial failure in the microscale RVE model, a bilinear cohesive model (as shown in
Figure 1) is introduced in the interface between the Al matrix and TiB2 particles to characterize it
s debonding behavior. A cohesive element of 0 thickness is used to discretize the interfacial layer. The linear elastic behavior of the interface layer is defined by the traction separation criterion:
where
t is the nominal stress vector.
tn,
ts, and
tt are the normal and the two shear tractions, respectively, and the corresponding separations are denoted by
,
and
.
K is the stiffness coefficient of the interface, and
is the nominal strain of the interface.
The quads stress criterion is applied to characterize the damage evolution behavior of cohesive element. When the stress on the interface satisfies quads stress criterion, the failure of a cohesive element in interface layer occurs, and this criterion is expressed as:
where
,
,
are maximum tractions in the normal and two shear directions.
However, it is difficult to obtain the material parameters of the cohesive elements of the interface layer by experiment. Generally, the most reasonable parameters of cohesive elements are obtained by comparing the simulation stress-strain curve with the experimental curve [
22,
25,
30]. By comparing with the experimental curve, the parameters of the cohesive element are finally fixed as follows: 700 MPa for the interfacial strength and 0.05 um for the initial separation displacement. As ABAQUS does not provide the required constitutive model, a Vumat subroutine has been developed for the material.
2.2. Quantitative characterization of damage behavior
In the process of failure, the damage behavior of the matrix and interfacial layer are different. In order to quantitatively characterize the damage degree of the interface and matrix, the interface damage ratio
Dinterface and matrix damage ratio
Dmatrix are introduced. The corresponding expressions are as follows:
Where Nd, Nt represent the number of failed elements and the total numbe r of elements, respectively. The Ai and Vi are status values for elements of interface layer and matrix.
2.3. Establish the RVE model
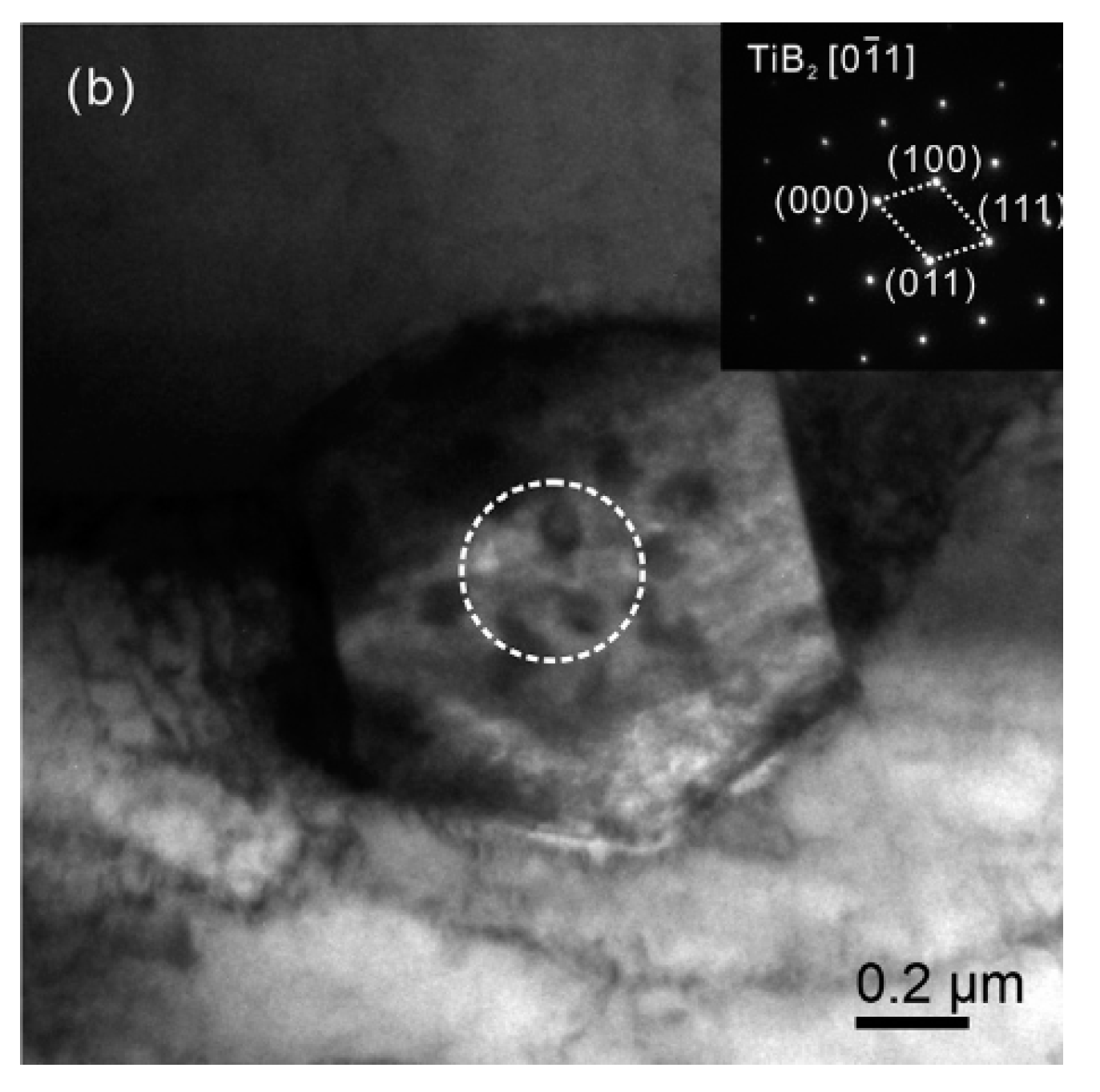
Figure 2 is the bright-field TEM image of TiB2, as the picture shows that TiB2 is obtained as a hexagonal prism particle [
5]. So, in this paper, the TiB2 particle is treated as a hexagonal particle, and the 6061Al matrix as a continuous homogeneous material.
Based on the random adsorption algorithm (RSA) [
31], a three-dimensional RVE model for TiB2/6061Al composites is established. The location of each micro particle to be adsorbed into the RVE is required to meet two conditions: (1) No overlapping between two particles. (2) The distances between particles, as well as the distances from particles to the RVE faces, should exceed a certain threshold to ensure the quality of the finite elements during meshing.
The control equations of RSA can be written as follows:
where
x,
r, and
L represent the coordinate vector of the particle center, the particle radius, and the side length of the RVE, respectively.
d1 and
d2 are user-selected distances.
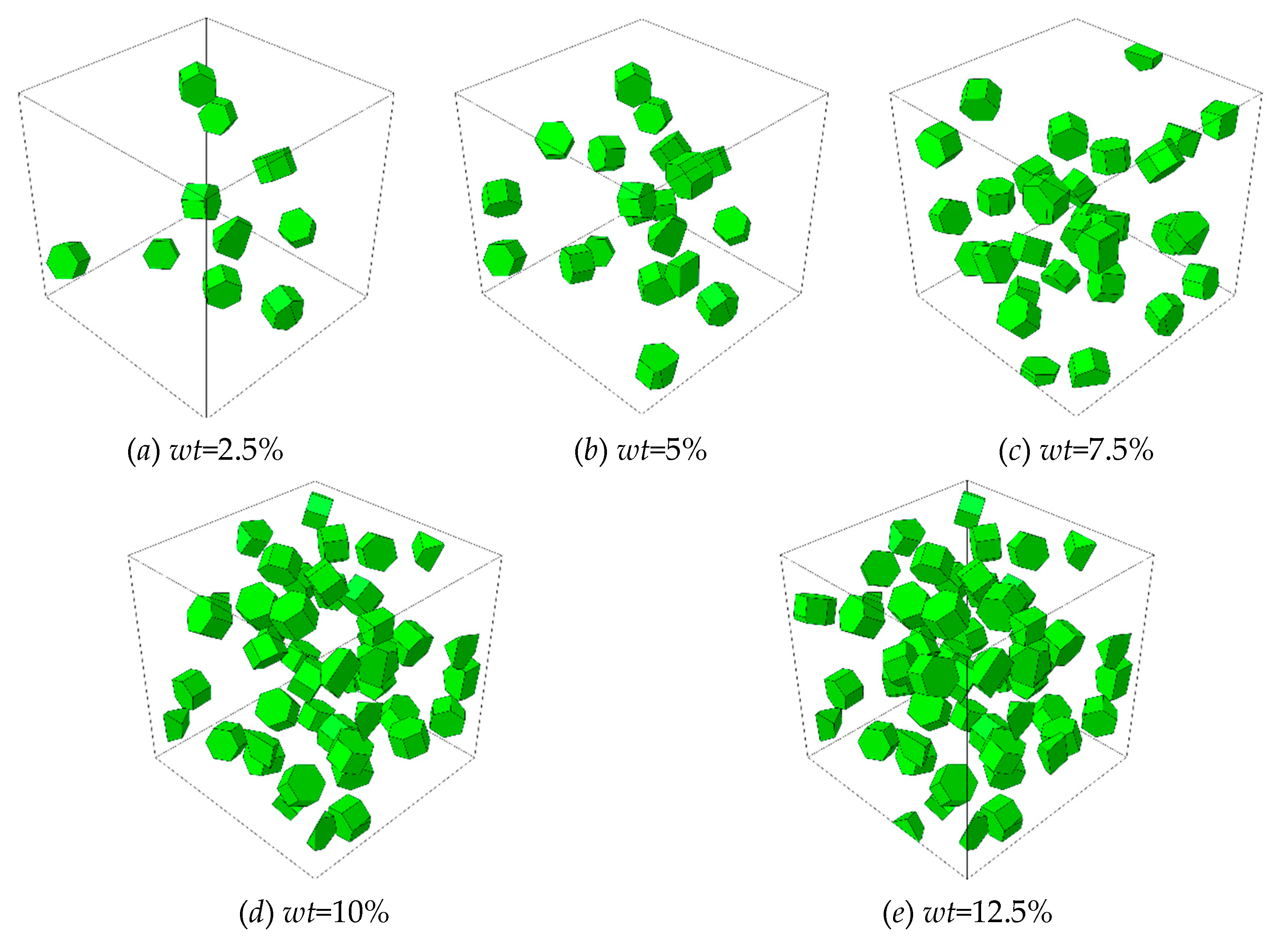
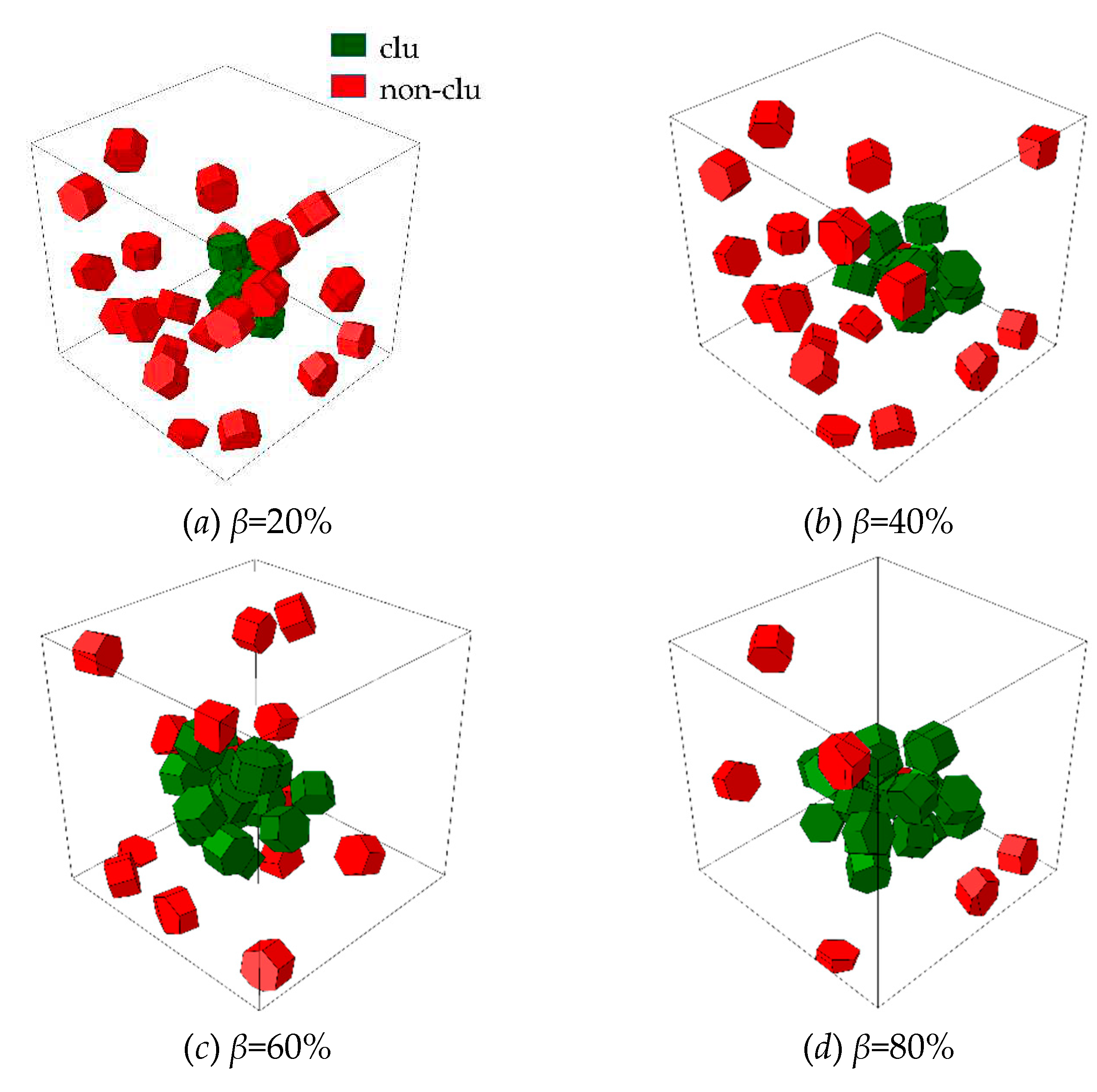
To analyze the influence of microstructural parameters on the mechanical properties of composites, the RVE models with different particle weight fractions (
wt) of range from 5% to 12.5%, and different clustering rates (
β) of range from 20% to 80% are established as shown in
Figure 3 and Figure 4 (The dark green part represents clustered particles, and the dark red part represents non-clustered particles.). In order to quantitatively characterize the degree of particle clustering, based on the reconstructing algorithm, several box-like subdomains are randomly generated in the cubic RVE, a parameter
β is introduced [
32], and its expression is as follows:
Where
and
are the volume of clustered particles and total particles respectively.
ξ and
ζ are the particle volume fraction in the subdomains and the nominal particle volume fraction in the whole RVE.
is the volume of each subdomain.
V is the total volume of RVE.
The boundary conditions of RVE are mainly divided into two types: the periodic boundary conditions (PBC) and the mixed boundary conditions. Although some previous works [
33] adopted periodic boundary conditions and obtained relatively accurate results, study [
17] shows that PBC is only applicable to statics and implicit numerical simulation. When they are used in explicit dynamic simulations, not only the calculation cost is high, but also the high frequency oscillations of the model will occur, affecting the accuracy of the numerical solution. Considering the above disadvantages of PBC, the mixed boundary conditions are adopted in this work. As shown in
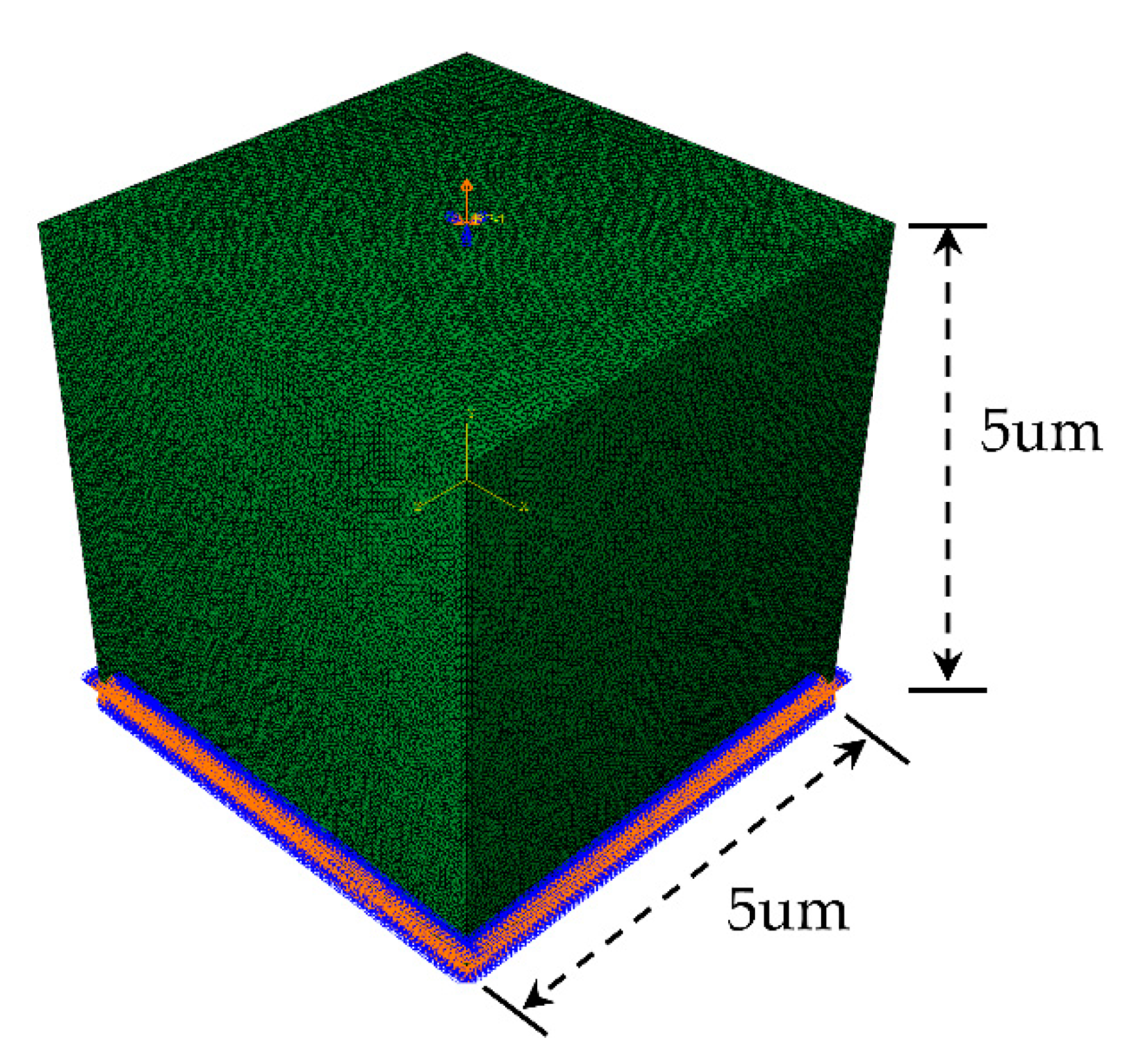
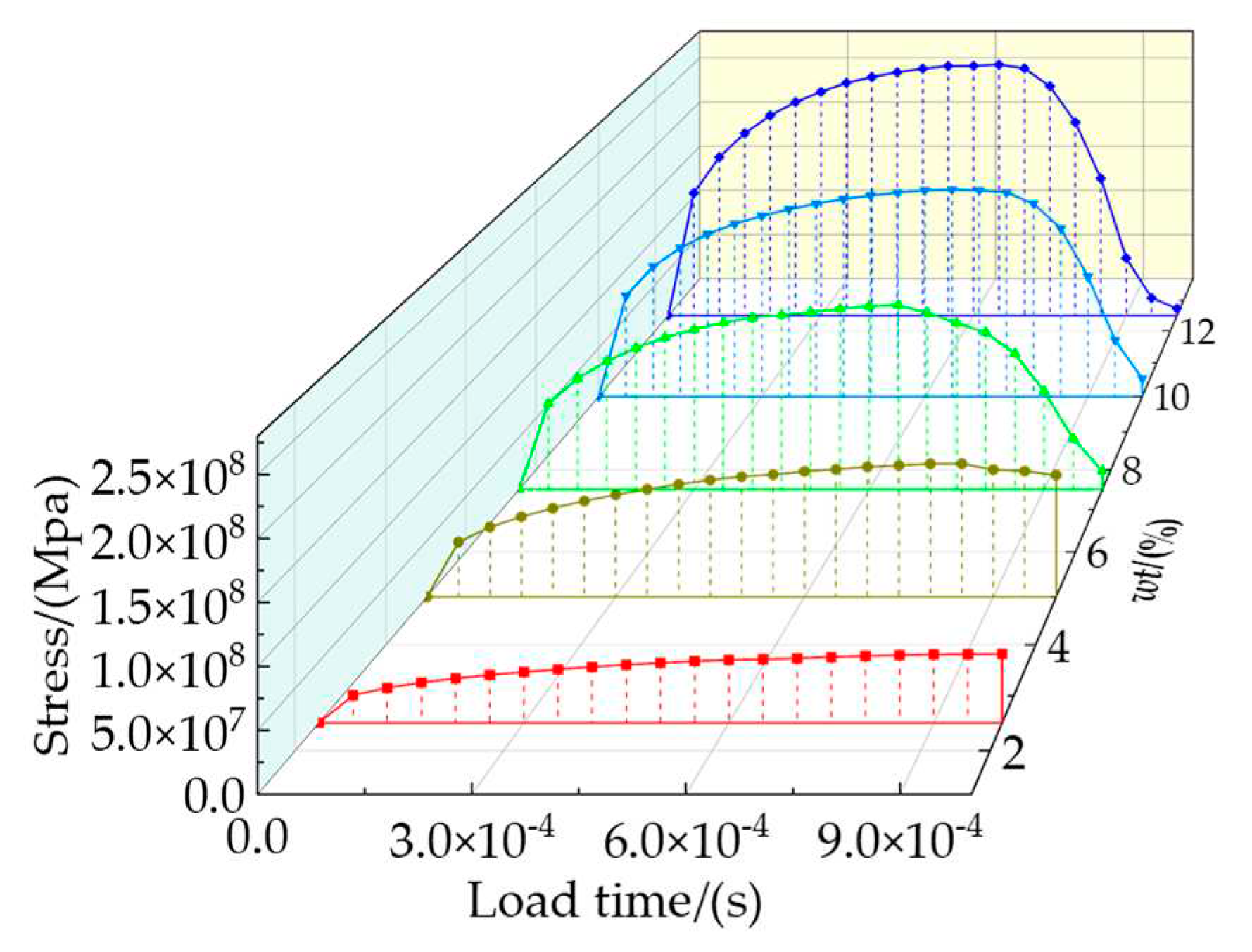
Figure 5, all degrees of freedom on the bottom surface of RVE are constrained, and the coupling command is used to couple all degrees of freedom on the top surface to the reference point. The linear displacement load is applied to the reference point, the load amplitude curve is defined by Tabular command, and the total time of the analysis step is set as 0.01s.
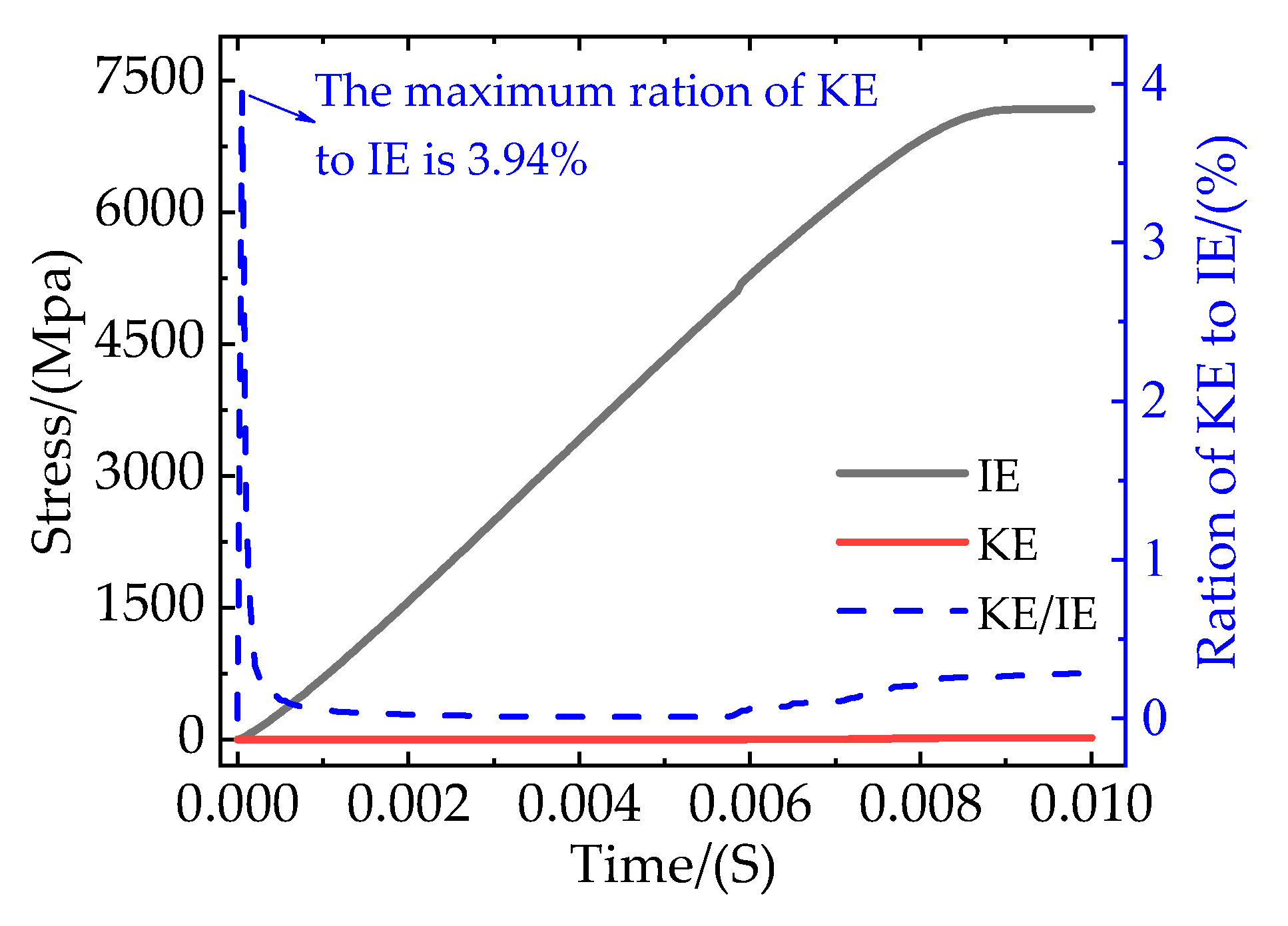
In this paper, the ABAQUS/Explicit dynamic method is used to investigate the quasi-static tensile process of composites. During the process of simulation, the stability of the model is an important factor affecting the accuracy of the calculation results, and the above settings can ensure that the kinetic energy(KE) to the internal energy(IE) ratio of the model is less than 5% and it has good stability, as shown in
Figure 6.
2.4. Model verification
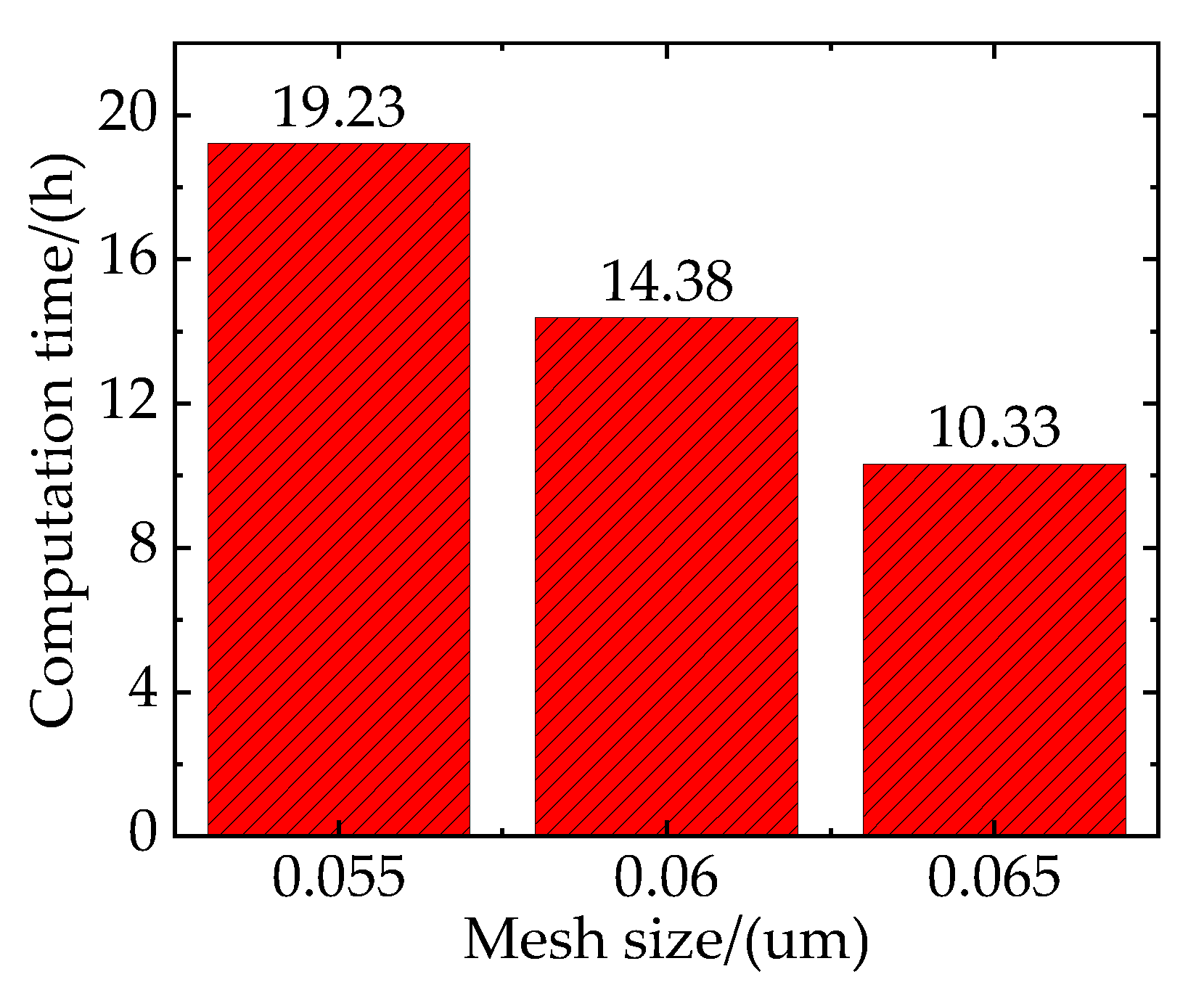
To ensure the computational accuracy and efficiency of the RVE model, the effect of mesh size should be excluded before the simulation begins. However, as the mesh size decreases and the number of elements increases, the scale of calculation also increases. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the balance of computing accuracy and time cost for choosing the mesh size. As shown in the
Figure 7, the simulation time corresponding to the mesh sizes of 0.55 m, 0.6 m, and 0.65 m is 19.23 h, 14.38 h, and 10.33 h, respectively.
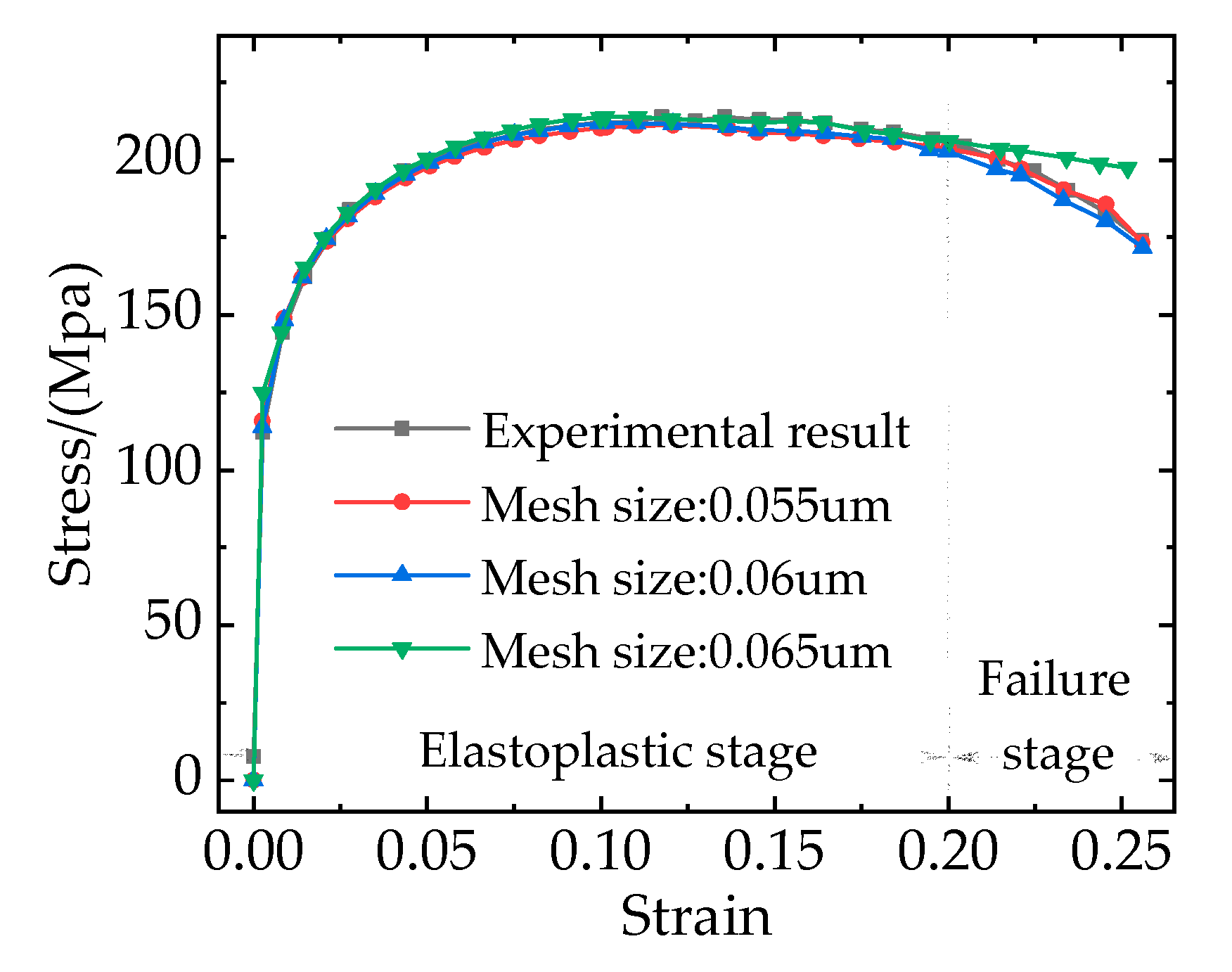
The stress-strain curves of the RVE model at different mesh sizes are shown in
Figure 8. It can be seen that when the composite is in the elastoplastic stage, the effect of different mesh sizes on the stress-strain curves isn’t obvious. When the composite enters the failure stage, there are still no obvious differences between the stress-strain curves with the mesh size of 0.055 um and 0.06 um and the FE results agree well with the experimental results [
3], but the stress-strain curve with the mesh size of 0.065 um shows a large error. Hence, on the balance of computing accuracy and time cost, the mesh size of 0.06 um is chosen for the subsequent simulation analysis.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Effects of different particle weight fractions on TiB2/6061Al composites
For PRAMCs, the fraction of reinforcement particles in composites is considered as a crucial factor that affects the mechanical properties of composites. Therefore, in this paper, the particle weight fraction is treated as a variable to investigate its effect on mechanical properties.
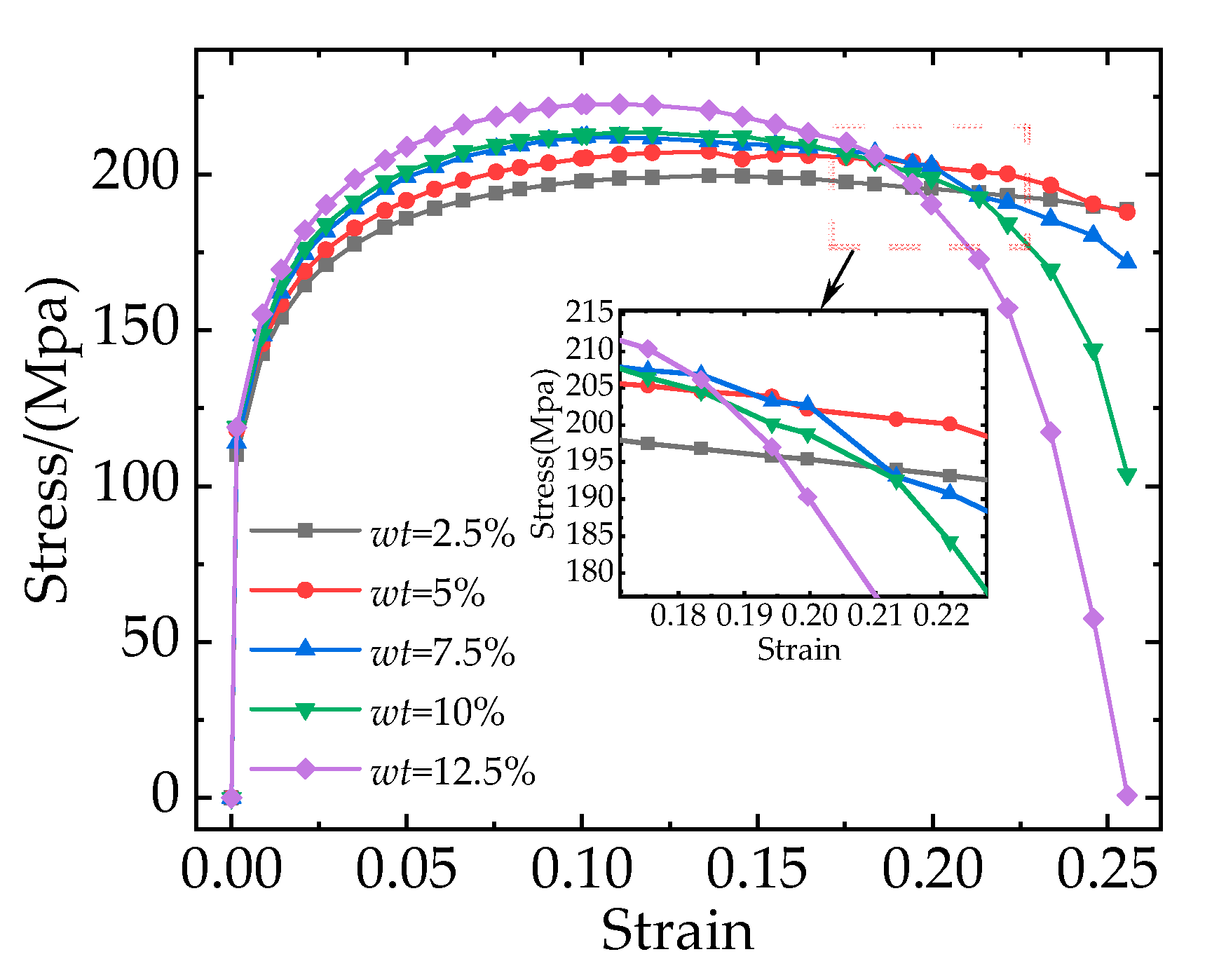
Figure 9 shows the stress-strain curves of composites with different particle weight fractions. It is obvious that with the increase of strain, although all the stress-strain curves initially increase and then decrease, the stress values of curves with different particle weight fractions differ greatly. The composite with a higher particle weight fraction enters the failure stage earlier and the damage occurs earlier. And with the increase of particle weight fraction from 2.5% to 12.5%, the elastic modulus, yield strength, and tensile strength of the composites increase from 73.33 GPa to 79.19 GPa, 164 MPa to 181 MPa, and 199 MPa to 222 MPa, respectively, but the elongation decreases from 25% to 15%. The numerical experimental result shows that the increase in particle weight fraction has a beneficial effect on improving the load-bearing capacity of the composites.
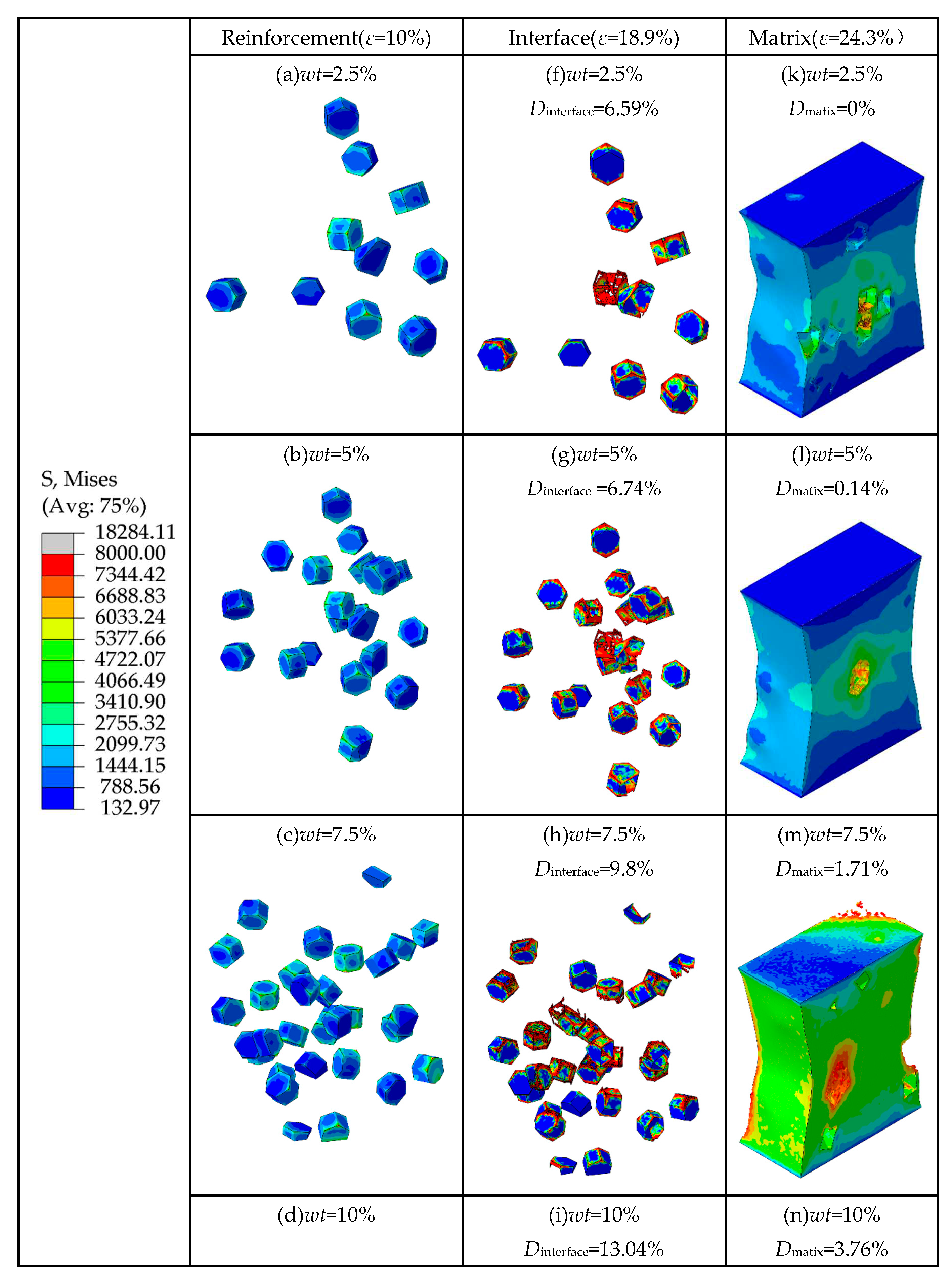
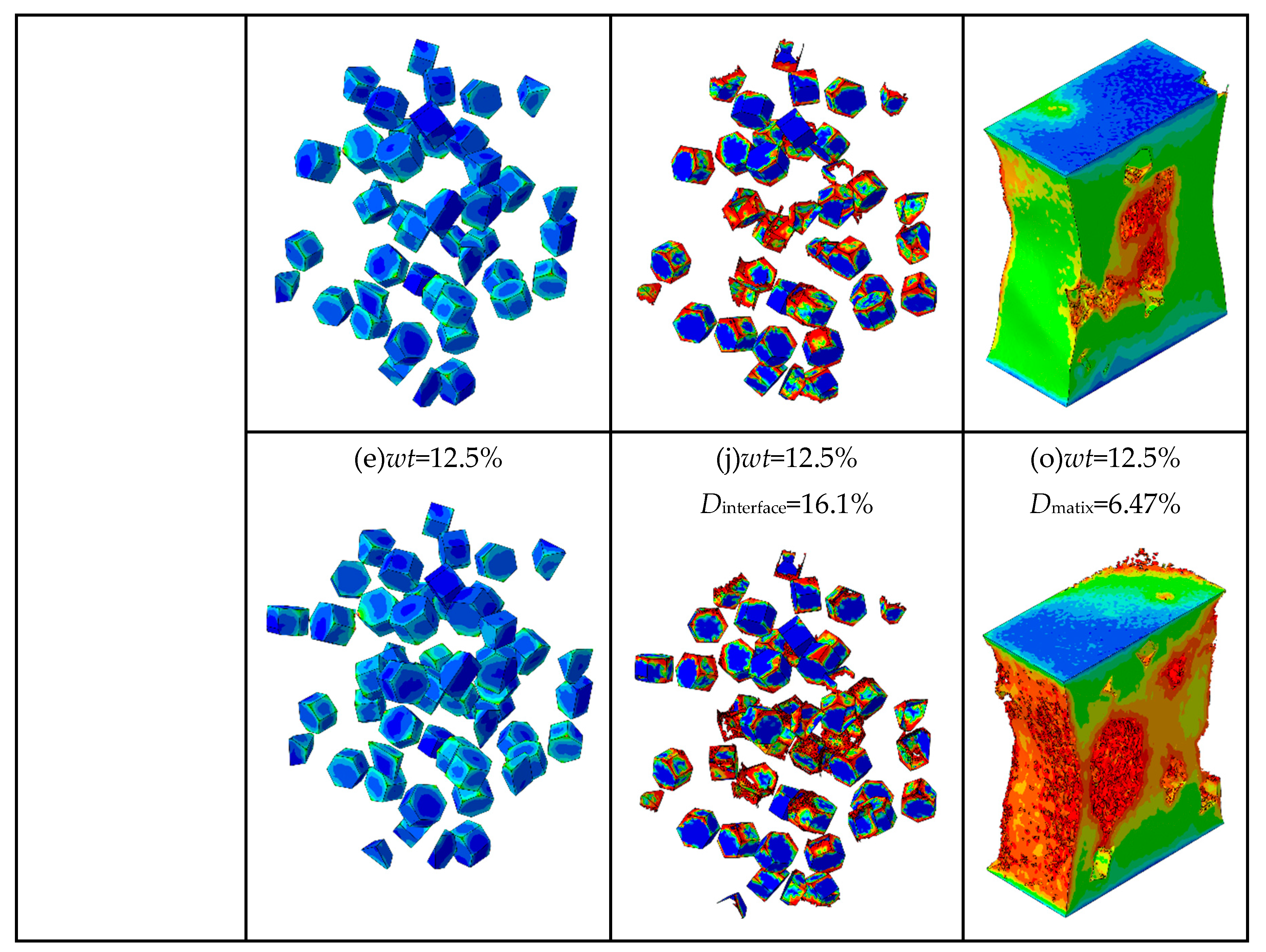
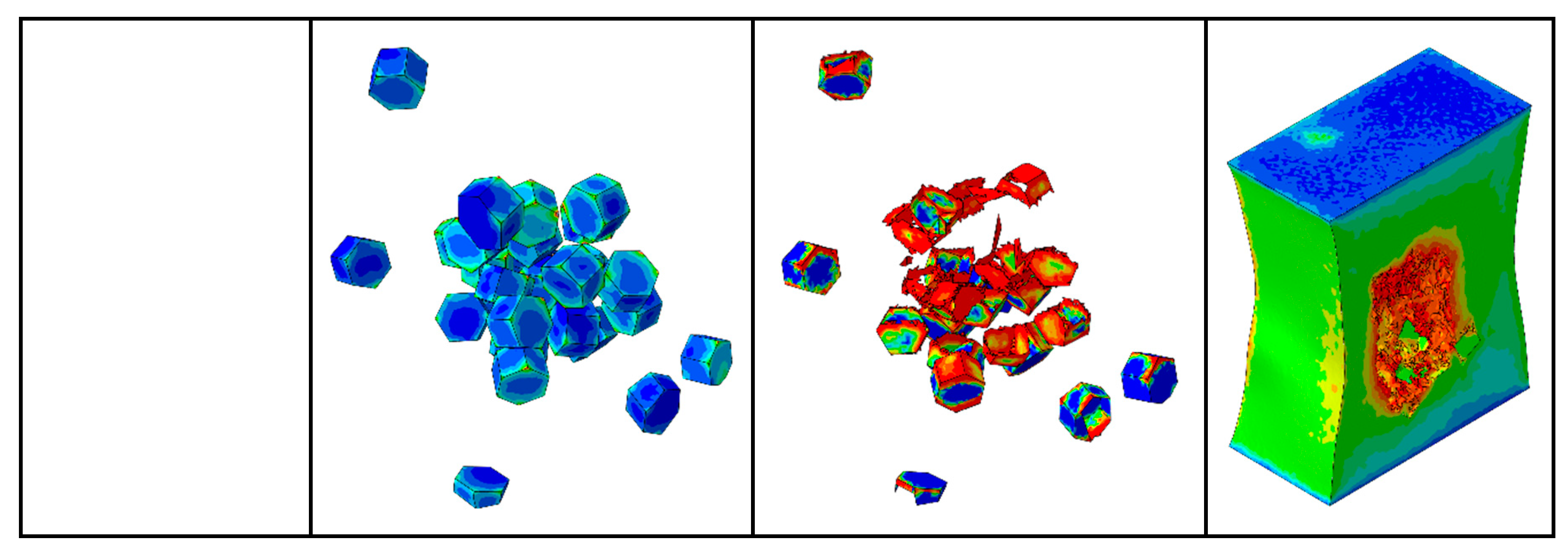
The total stresses on the particles at different weight fractions are shown in Figure 10. The von Mises stress of the TiB2 particles, the SDEG of the damage of the interfacial layer, and the equivalent plastic strain (PEEQ) of the matrix phase are shown in Figure 11.
As shown in Figure 11 (a-e), when the strain is 10%, the number of particles loaded with high stress (more than 5377 MPa) increases. It indicates that the particles with higher weight fraction can better bear the stress from the matrix. When the plastic deformation of composites occurs, a geometric mismatch is caused by the varying degrees of strain on different parts of the composites occurs, which causes the particles to move in different directions. It changes the original particle spacing, resulting in higher stresses on neighboring particles that are close to each other and lower stresses on neighboring particles that are farther apart. It means that the particle spacing is an important factor affecting the stress distribution. Meanwhile, due to the geometric discontinuity, most of the stress concentrates on the edges and corners of the hexagonal prism particles. Also combined with
Figure 10, it can be seen that with the increase of the particles weight fraction, the total stresses borne by the particle phase increases, which means that the higher particle weight fraction is beneficial for transferring stresses from the matrix to the particle. Therefore, the composites with higher particle weight fractions can bear higher loads.
As shown in Figure 11 (f-j), when the strain is 18.9%, as the particle weight fraction increases from 2.5% to 12.5%, the interfacial damage ratios of TiB2/6061 Al composites are 6.59%, 6.74%, 9.8%, 13.04%, and 16.1%, respectively. This indicates that the higher particle weight fraction leads to more severe interfacial damage. It is because most of the stress concentrates on the edges and corners of the particles, the interfacial layers in these areas are prone to damage. Hence, it can be concluded that excessive stress is an important factor for causing interfacial failures.
As shown in
Figure 11 (k-o), when the strain is 24.3%, and the particle weight fraction increases from 2.5% to 12.5%, the damage ratios of the matrix are 0%, 0.14%, 1.71%, 3.76%, and 6.47%, respectively. Due to the increase in the number of particles, the continuity of the particles also increases and the particle spacing inside the matrix starts to decrease, which leads to a further increase in the stress on the particles [
27] and the region between neighboring particles. This causes the composite with a higher particle weight fraction to damage earlier and more severely. Combined with
Figure 11 (a-e), it can be seen that the largest stress is concentrated on the particles’ edges and corners, which eventually leads to the occurrence of matrix damage.
It is necessary to study the mechanism of crack generation and propagation, because the elongation of composites is mainly affected by it.
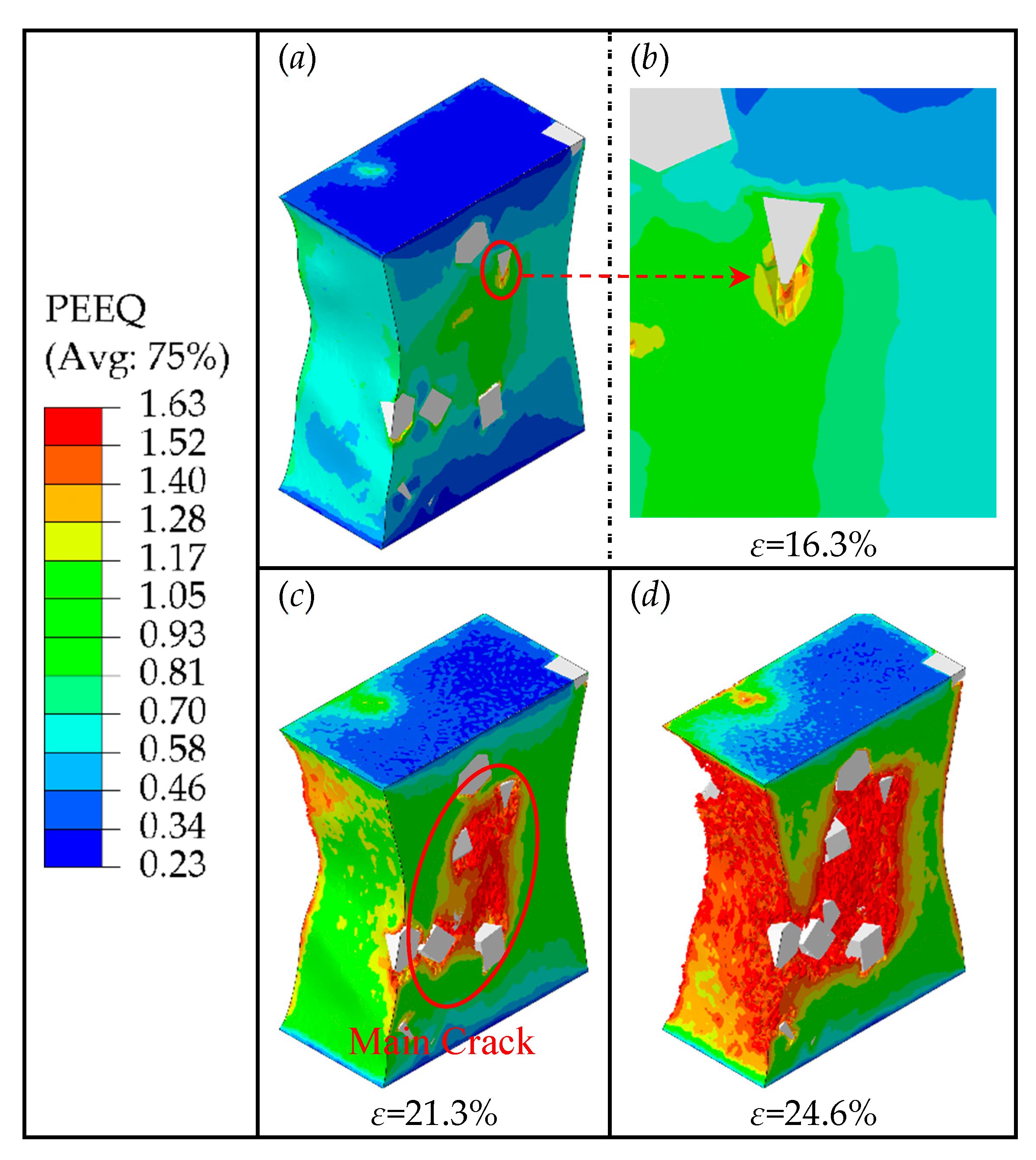
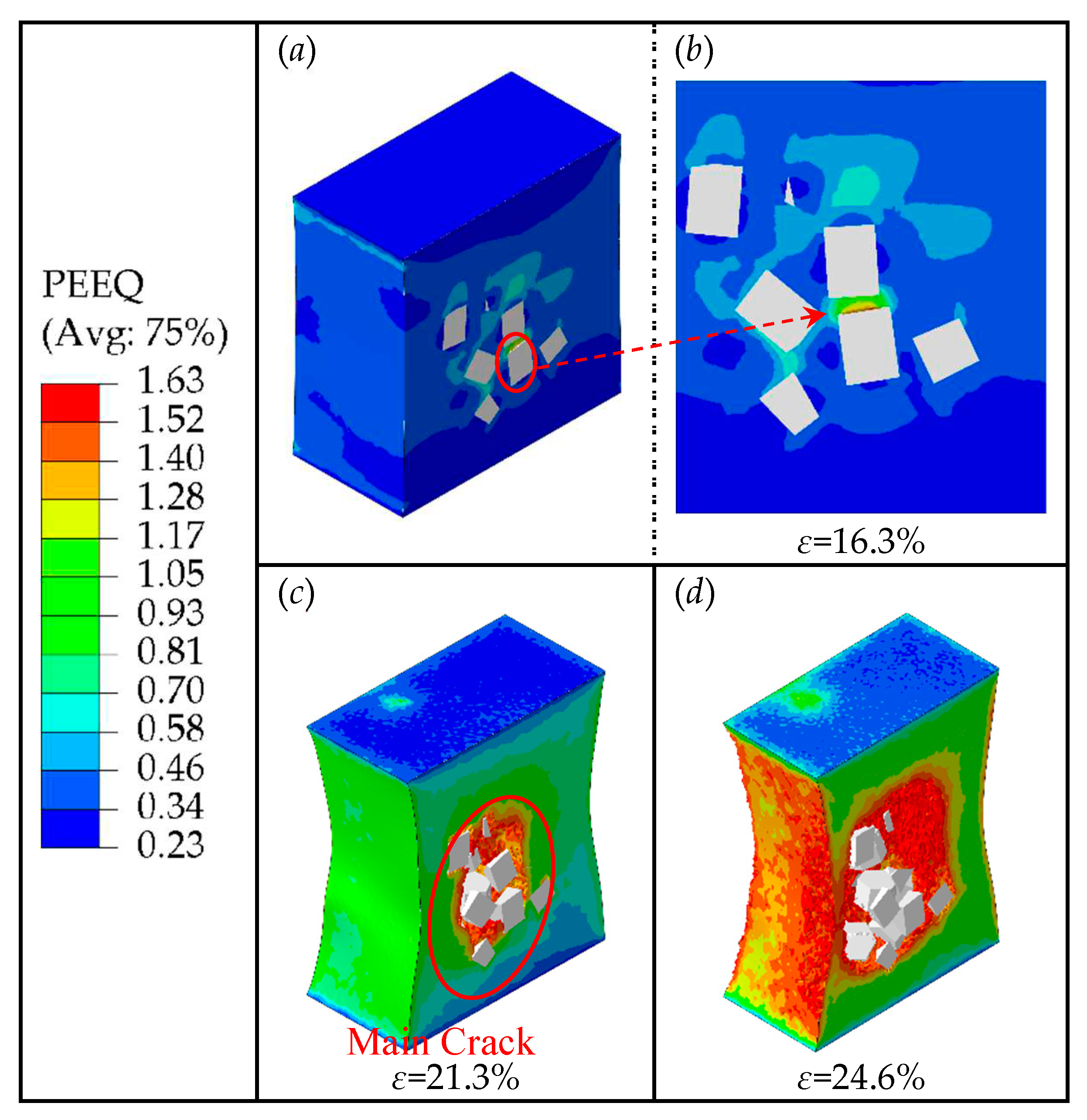
Figure 12 shows the PEEQ distribution contour of the composite matrix with particle weight fractions of 7.5% at strains of 16.3%, 21.3%, and 24.6%, respectively. When the strain is lower than 16.3%, no cracks are generated. However, when the strain reaches 16.3%, excessive stress concentrates on the areas of particles' edges and corners, creating high strain in these areas. This can lead to the interfacial debonding and matrix damage in the high strain area, which can further evolve into fine cracks inside the matrix. At the same time, it can also be seen that there is severe stress concentration at the crack tip, which causes crack propagation during the loading process. And with the increase of strain, the fine crack shown in
Figure 12 (a) and (b) propagate further along the edges of particles, as the strain reaches 21.3%, the fine crack continues to propagate along the high strain area and merges with other fine cracks caused by the other particles, forming a main crack (as shown in
Figure 12 (c)). Further, as the strain continues to increase, when the strain reaches 24.6%, the main crack continues to propagate and merges with the fine cracks around the other particles, forming a larger crack damage area (as shown in
Figure 12 (d)), which eventually leads to the macro-level weakening of the composite's load-bearing capacity.
3.2. Effect of different clustering rates on TiB2/6061Al composites
According to previous works [
23,
34,
35], the damage of composites is related to not only the particle weight fraction but also the degree of the particle clustering. As is shown in the
Figure 9, the RVE with particle weight fraction of 7.5% owns the most balanced mechanical property. So, this section takes composites with a weight fraction of 7.5% as an example to investigate the effect of particle clustering rates on mechanical properties.
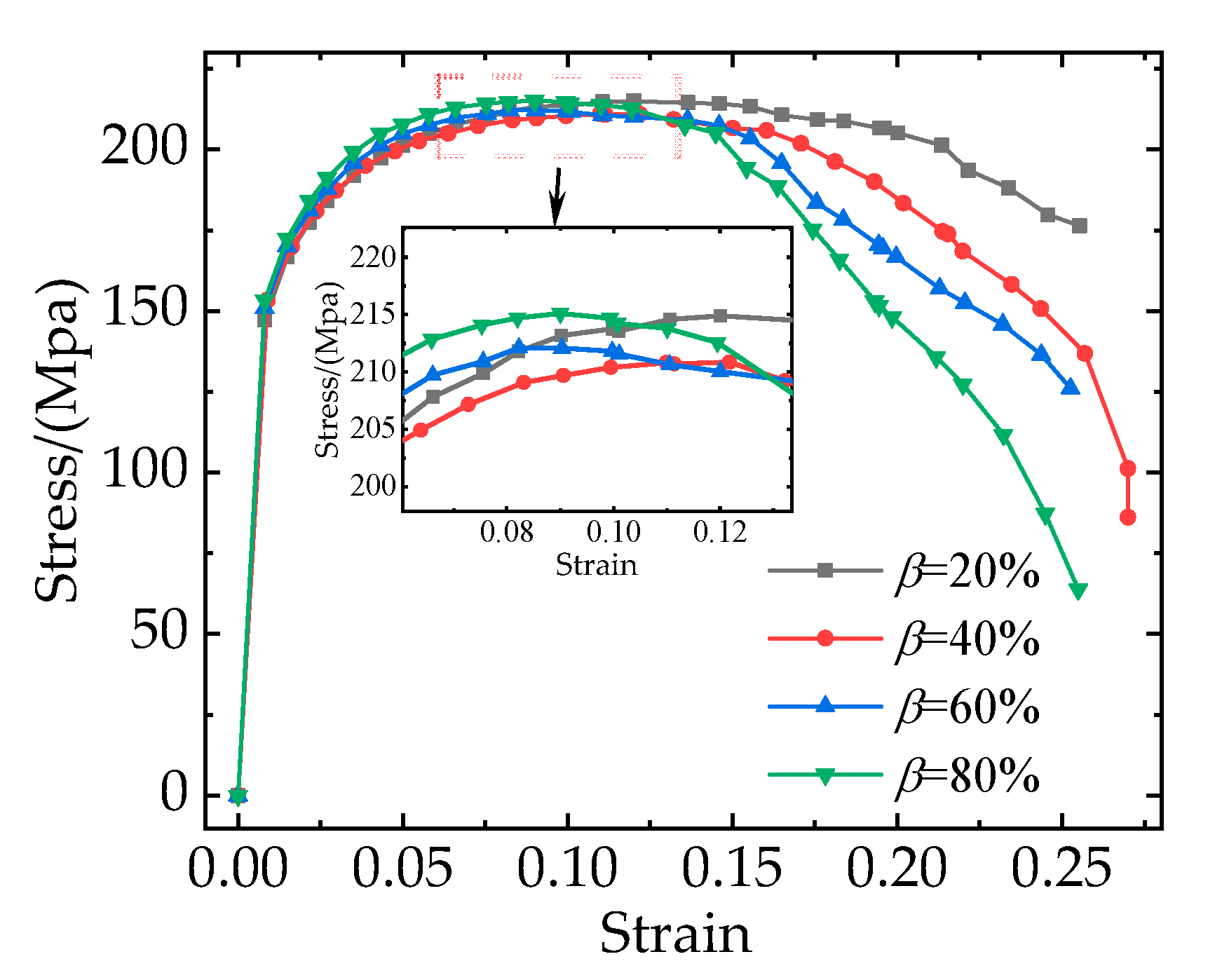
Figure 13 shows the stress-strain curves corresponding to different particle clustering rates. It is obvious that as the particle clustering rates increase, the damage occurs earlier and the stress on the composites decreases more rapidly in the failure stage. With the increase in particle clustering rates, the elastic modulus, yield strength, and tensile strength of the composites don’t show an obvious difference. However, the elongation of the composites decreases from 22% to 14%.
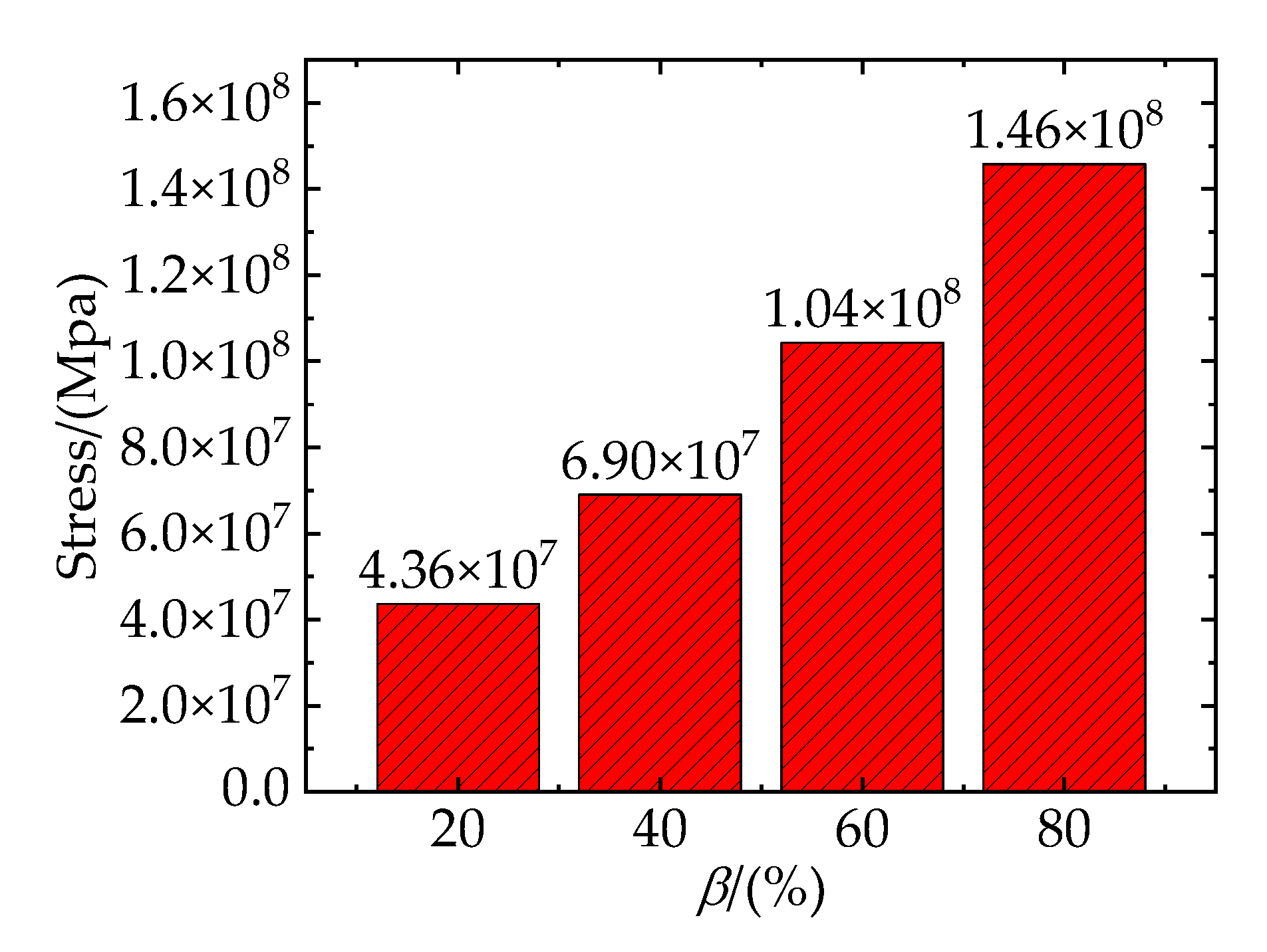
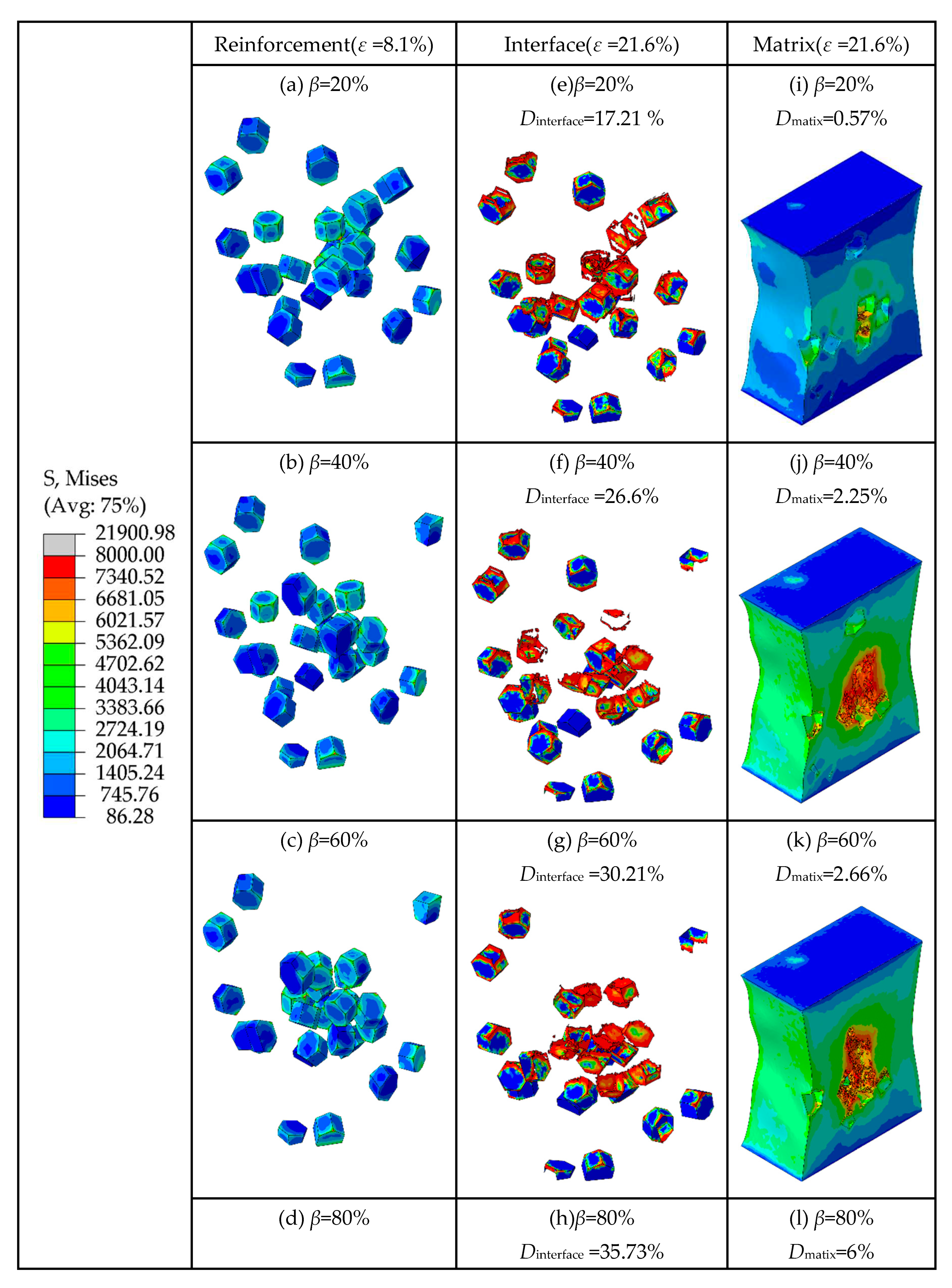
Figure 14 shows the total stresses on the clustered particles with different clustering rates at the strain of 8.1%. It shows an approximately linear increase of stress in terms of . Figure 15 shows the von Mises stress of TiB2 particles at the strain of 8.1%, the SDEG of the interfacial layer damage at the strain of 21.6%, and the PEEQ of the matrix phase at the strain of 21.6%, respectively.
As shown in Figure 15 (a-d), with the increase of particle clustering rate, the number of clustered particles increases. Most of the stress on the particles within the clustered particles area is between 3383 MPa to 5362 MPa, while the most of stress on the particles within the non-clustered particles area is below 3383 MPa, which indicates that the clustered particles are borne a higher stress than the non-clustered particles. It can also be seen that due to the geometric discontinuity, most of the stress concentrates on the edges and corners of the TiB2 particles. Combined with
Figure 14, it can be observed that as the clustering rate increases, the stress borne by clustered particles also increases. This implies that a higher clustering rate of particles will result in a higher stress borne by clustered particles.
As shown in Figure 15 (e-h), when the strain is 21.6%, the interfacial damage ratios of the composites are 17.21%, 26.6%, 30.21%, and 35.73%, respectively, and the clustering rate is 20%, 40%, 60%, and 80%. With the increase of particle clustering rates, the interfacial damage ratios increase, which indicates that the high particle clustering rates lead to severe interfacial damage. For the interface layer, as similar as the conclusion in Section 3.1, the damage of the edges and corners is more severe than other parts. As discussed above, the clustered particles are borne higher stress than the non-clustered particles. So, the damage degree of the interface layer in the clustered particle area is higher than that in the non-clustered particle area. By comparing the damaged area of the interface layer with the stress distribution area of the particle in Figure 15 (a-d), it can be seen that the damaged area of the interfacial layer is basically consistent with the area of high stress on the clustered particle, which indicates that the clustered particles are more prone to bear the high stress that exceeds the strength limit of the interfacial layer under the influence of the clustering effect, eventually leading to the failure of the interfacial layer elements occur.
As shown in
Figure 15 (i-l), the matrix damage ratios gradually increase as the particle clustering rates increase, which indicates that the increasement of particle clustering rates can increase the damage ratios of the matrix. Considering that the RVE model is stretched in the vertical direction, when the matrix is loaded, inward contraction strain in the horizontal direction is simultaneously generated. So, this contraction strain causes the particle spacing in the clustered particle area to decrease, and the stress on the particles to further increase due to the clustering effect. This causes the stress on the edges and corners of the particles in the clustered area as well as the region between the neighboring particles to exceed the strength limit of the matrix, which eventually leads to the occurrence of matrix damage.
The
Figure 16 shows that the PEEQ distribution contour of the matrix of composites. When the strain is lower than 16.3%, no cracks are generated. However, when the strain reaches 16.3%, the excessive local stress in the clustered particles area causes matrix damage to occur. As discussed above, due to the clustered particles being borne by the large stress, the region between neighboring particles turns into a high strain region. It results in an initial fine crack in the matrix generated (as shown in
Figure 16(a) and (b)). As the strain increases continually, when it reaches 21.3%, the crack propagates further along the high strain area and merges with other particle-induced fine cracks, eventually forming the main crack (as shown in
Figure 16 (c)). Furthermore, when the strain reaches 24.6%, the main crack continues to propagate rapidly in the high strain area and merges with the fine cracks around the other particles outside the high strain area, forming a larger crack damage area (as shown in
Figure 16 (d)), which leads to the macro-level weakening of the composite's bearing capacity. It concludes that the high strain area between clustered particles provides a fast expansion path for crack propagation.
4. Conclusions
For TiB2/6061Al composites, a 3D RVE based on the actual microstructure acquired by SEM is developed. The mechanical behavior is predicted, and the process of fracture is simulated. By comparing with the experimental results in previous work, the accuracy of the RVE is verified. The effect of microstructural parameters of composites on the mechanical properties of PRAMC is discussed. Some conclusions are summarized below:
(1). The RVE model comprehensively considers the ductile fracture of the matrix and the traction separation behavior of the interface. It also introduces the linear damage evolution law to characterize the stiffness degradation behavior of the element. It was successfully applied to predict the mechanical properties of composites.
(2). For TiB2/6061Al composites, increasing the particle weight fraction is beneficial for strength improvement but harmful for toughness. With the weight fraction of TiB2 increasing from 2.5% to 12.5%, the elastic modulus, yield strength, and tensile strength increased by 8%, 10.37%, and 11.55% respectively, but the elongation decreased by 10%.
(3). Clustered particles have an important effect on the internal stress field of composites. The results show that the clustering rate of particles has a great effect on the toughness. When the clustering rate increases from 20% to 80%, the elongation of composites decreases by 8%. However, it has little effect on yield strength, tensile strength, and elastic modulus.
(4). The mechanism of the crack generation and propagation is also studied. A fine crack is generated around the particles first. Then, this fine crack merges with other fine cracks nearby, forming a main crack, and leading to the fracture of the composites eventually.
(5). The high strain region in the matrix provides a fast expansion path for crack propagation, and the reduction of particle spacing will causes the stresses on the particles to increase.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.F. and J.M.; methodology, J.M.; software, J.M.; validation, B.W., W.F. and J.M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M.; writing—review and editing, J.M. and W.F.; supervision, W.F., J.M., Z.L., Y.F., B.W., and H.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Civil Aviation Education and Talent Project of China, grant number MHJY2023012.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The simulation results in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bi, S.; Xiao, B.L.; Ji, Z.H.; Liu, B.S.; Liu, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.Y. Dispersion and Damage of Carbon Nanotubes in Carbon Nanotube/7055Al Composites During High-Energy Ball Milling Process. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2021, 34, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, W.; Chen, H. Synthesis of Nano- to Micrometer-Sized B4C Particle-Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites via Powder Metallurgy and Subsequent Heat Treatment. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Que, B.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, C. Effects of TiB2 Particle and Local Aspect Ratio on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of an I-Shaped TiB2/6061Al Composite Profile. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2022, 846, 143284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Nie, J.; Hu, K.; Ma, X.; Liu, X. Improvement of High-Temperature Strength of 6061 Al Matrix Composite Reinforced by Dual-Phased Nano-AlN and Submicron-Al2O3 Particles. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China 2022, 32, 3197–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, W.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, F.; Dong, G.; Xiao, P. Microstructures and Properties of Hybrid Copper Matrix Composites Reinforced by TiB Whiskers and TiB2 Particles. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2019, 797, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, K.; Xie, H.; Dai, L.; Zhao, G. Precipitation of Ceramic Particles in Fe-TiB2 and Fe-Ni-TiB2 Cast Steels during the Sub-Rapid Solidification Process. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2023, 943, 169148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Sha, J.; Lin, G.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Dong, S. Mechanical and Thermal Expansion Behavior of Hybrid Aluminum Matrix Composites Reinforced with SiC Particles and Short Carbon Fibers. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2023, 947, 169550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, M.; Jiao, L.; Chen, L. Microstructure-Property Analysis of ZrB 2 /6061Al Hierarchical Nanocomposites Fabricated by Direct Melt Reaction. Materials Characterization 2016, 112, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J. Investigation on Peripheral Coarse Grains and Precipitation Behavior of In-Situ TiB2/Al–Cu–Mg Composites with Various Mg Contents. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2021, 826, 142000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.J.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Pan, F.; Geng, L.; Peng, H.X. Tailoring a Novel Network Reinforcement Architecture Exploiting Superior Tensile Properties of in Situ TiBw/Ti Composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2012, 545, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, X. Mechanical Properties and Fracture of In-Situ Al3Ti Particulate Reinforced A356 Composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2019, 754, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, G.J. SOME ELASTIC PROPERTIES OF REINFORCED SOLIDS, WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ISOTROPIC ONES CONTAINING SPHERICAL INCLUSIONS.
- Farkash, A.; Mittelman, B.; Hayun, S.; Priel, E. Aluminum Matrix Composites with Weak Particle Matrix Interfaces: Effective Elastic Properties Investigated Using Micromechanical Modeling. Materials 2021, 14, 6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; He, X.; Lan, X.; Sha, A.; Hao, W. Effects of Strength and Distribution of SiC on the Mechanical Properties of SiCp/Al Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, B.; Yin, W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, R.; He, X. A New Algorithm to Generate Non-Uniformly Dispersed Representative Volume Elements of Composite Materials with High Volume Fractions. Materials & Design 2022, 219, 110750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, S.I.; Attia, M.A.; Hassan, M.A.; El-Shafei, A.G. Predictive Computational Model for Damage Behavior of Metal-Matrix Composites Emphasizing the Effect of Particle Size and Volume Fraction. Materials 2021, 14, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Asqardoust, S.; Sarmah, A.; Jain, M.K. Elastoplastic Analysis of AA7075-O Aluminum Sheet by Hybrid Micro-Scale Representative Volume Element Modeling with Really-Distributed Particles and in-Situ SEM Experimental Testing. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2022, 123, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, G.; Tang, H.; Chen, Z.; Fenner, J.; Meng, Z.; Jain, M.; Su, X. A Combined Experimental and Computational Analysis of Failure Mechanisms in Open-Hole Cross-Ply Laminates under Flexural Loading. Composites Part B: Engineering 2021, 215, 108803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, G.; Meng, Z.; Jain, M.; Su, X. An Integrated Computational Materials Engineering Framework to Analyze the Failure Behaviors of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites for Lightweight Vehicle Applications. Composites Science and Technology 2021, 202, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, G.; Guo, H.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Kang, H.; Su, X. Failure Mechanisms of Cross-Ply Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Laminates under Longitudinal Compression with Experimental and Computational Analyses. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 167, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, G.; Meng, Z.; Guo, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Kang, H.; Keten, S.; Su, X. Failure Criteria of Unidirectional Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites Informed by a Computational Micromechanics Model. Composites Science and Technology 2019, 172, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Qian, L.; Yihui, J.; Yishi, S.; Wenting, T.; Shuhua, L. Composite Structural Modeling and Mechanical Behavior of Whisker Reinforced Cu Matrix Composites. Computational Materials Science 2021, 195, 110492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, X. 3D Micromechanical Simulation of the Mechanical Behavior of an In-Situ Al3Ti/A356 Composite. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 176, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.; Chollacoop, N.; Van Vliet, K.J.; Venkatesh, T.A.; Suresh, S. Computational Modeling of the Forward and Reverse Problems in Instrumented Sharp Indentation. Acta Materialia 2001, 49, 3899–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cao, F.; Feng, P.; Zuo, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, W.; Liang, S. Experimental Verification and Numerical Analysis on Plastic Deformation and Mechanical Properties of the In-Situ TiB2 Homogeneous Composites and TiB2/Cu Network Composites Prepared by Powder Metallurgy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2022, 920, 165897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Xi, Z.; Qiangqiang, Z.; Yihui, J.; Yishi, S.; Qian, L.; Pengfa, F.; Wenting, T.; Shuhua, L. Numerical Evaluation and Experimental Verification of Mechanical Properties and Fracture Behavior for TiB2/Cu Composites Prepared by in-Situ Mixing Casting. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2022, 895, 162475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.R.; Tracey, D.M. On the Ductile Enlargement of Voids in Triaxial Stress Fields∗. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 1969, 17, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursun, G.; Weber, U.; Soppa, E.; Schmauder, S. The Influence of Transition Phases on the Damage Behaviour of an Al/10vol.%SiC Composite. Computational Materials Science 2006, 37, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, H. Automatic Generation of 2D Micromechanical Finite Element Model of Silicon–Carbide/Aluminum Metal Matrix Composites: Effects of the Boundary Conditions. Materials & Design 2013, 44, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ouyang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Fan, G.; Su, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lavernia, E.J.; Schoenung, J.M.; Zhang, D. 3D Microstructure-Based Finite Element Modeling of Deformation and Fracture of SiCp/Al Composites. Composites Science and Technology 2016, 123, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintoul, M.D.; Torquato, S. Reconstruction of the Structure of Dispersions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 1997, 186, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhu, P.; Ma, Y. Effects of Particle Clustering on the Tensile Properties and Failure Mechanisms of Hollow Spheres Filled Syntactic Foams: A Numerical Investigation by Microstructure Based Modeling. Materials & Design 2013, 47, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Rama Sreekanth, P.S. Multiscale RVE Modeling for Assessing Effective Elastic Modulus of HDPE Based Polymer Matrix Nanocomposite Reinforced with Nanodiamond. Int J Interact Des Manuf 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.J.; Flom, Z.; Amell, A.A.; Chawla, N.; Xiao, X.; De Carlo, F. Damage Evolution in SiC Particle Reinforced Al Alloy Matrix Composites by X-Ray Synchrotron Tomography. Acta Materialia 2010, 58, 6194–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyar, A.; Crawford, G.A.; Williams, J.J.; Chawla, N. Numerical Simulation of the Effect of Particle Spatial Distribution and Strength on Tensile Behavior of Particle Reinforced Composites. Computational Materials Science 2008, 44, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).