Submitted:
23 May 2023
Posted:
24 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. District Heating Systems
2.1. History of DH
2.2. DH Sources
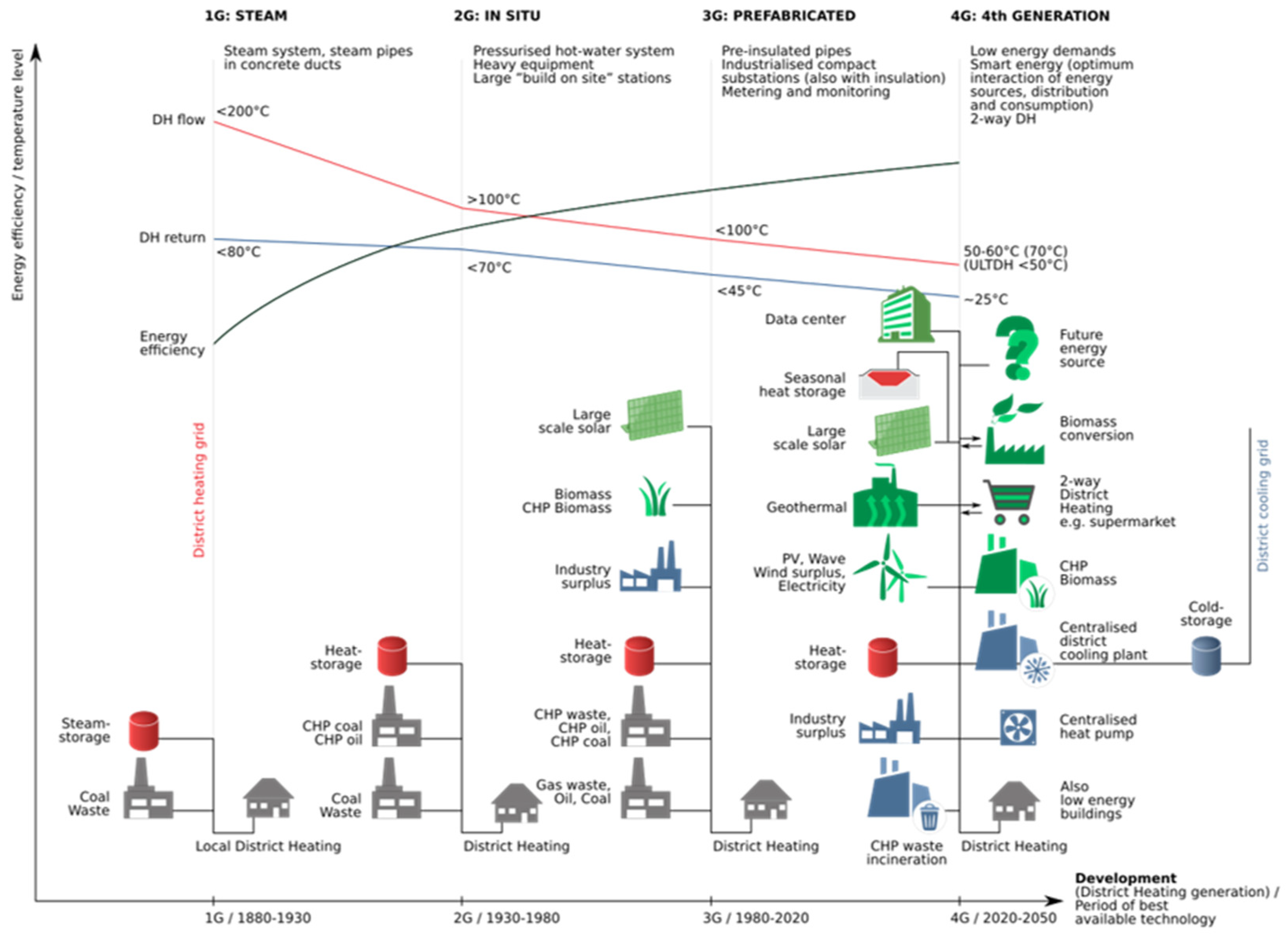
2.3. DH Generations
3. Heating State in Poland
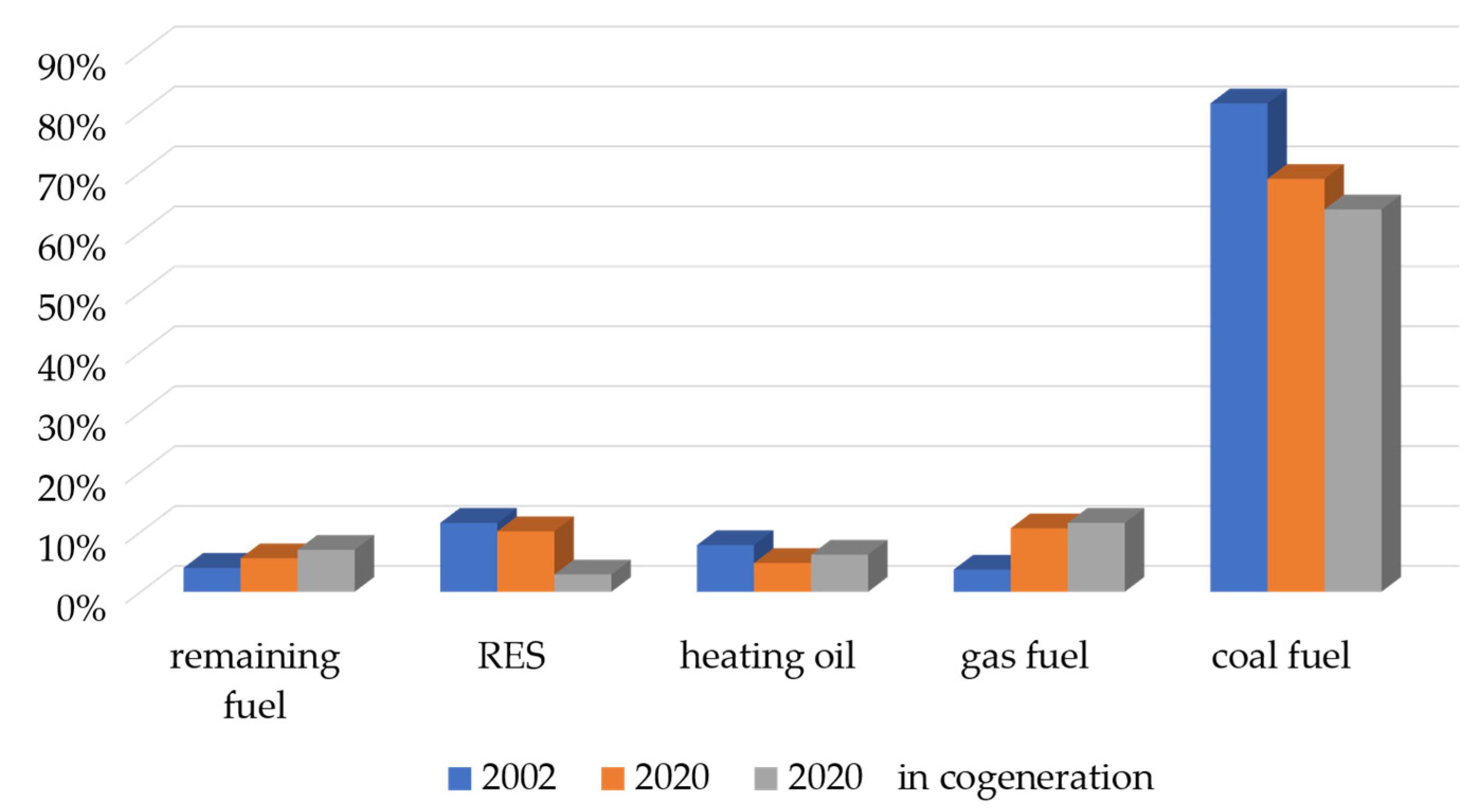
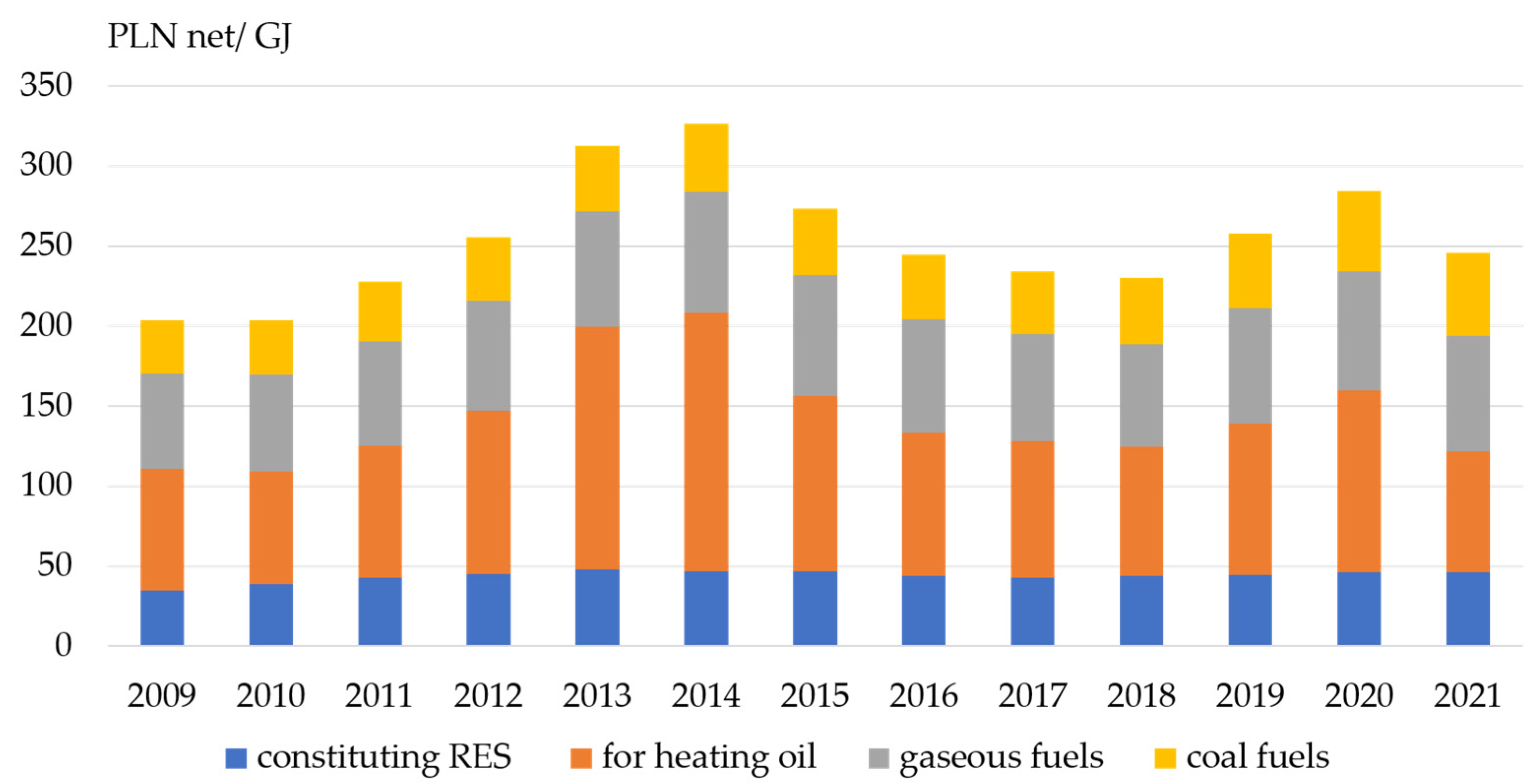
- Coal fuels continue to dominate, the share of which in 2020 accounted for almost 69% fuels used in heat sources (in 2019 it was 71%, in 2018—72.5%, and in 2017—74%);
- Since 2002, the share of coal fuels has decreased by 12.8 pp. At the same time, the share of gaseous fuels is increasing—by 6.9 pp. and renewable energy sources—by 7.2 pp. since 2002;
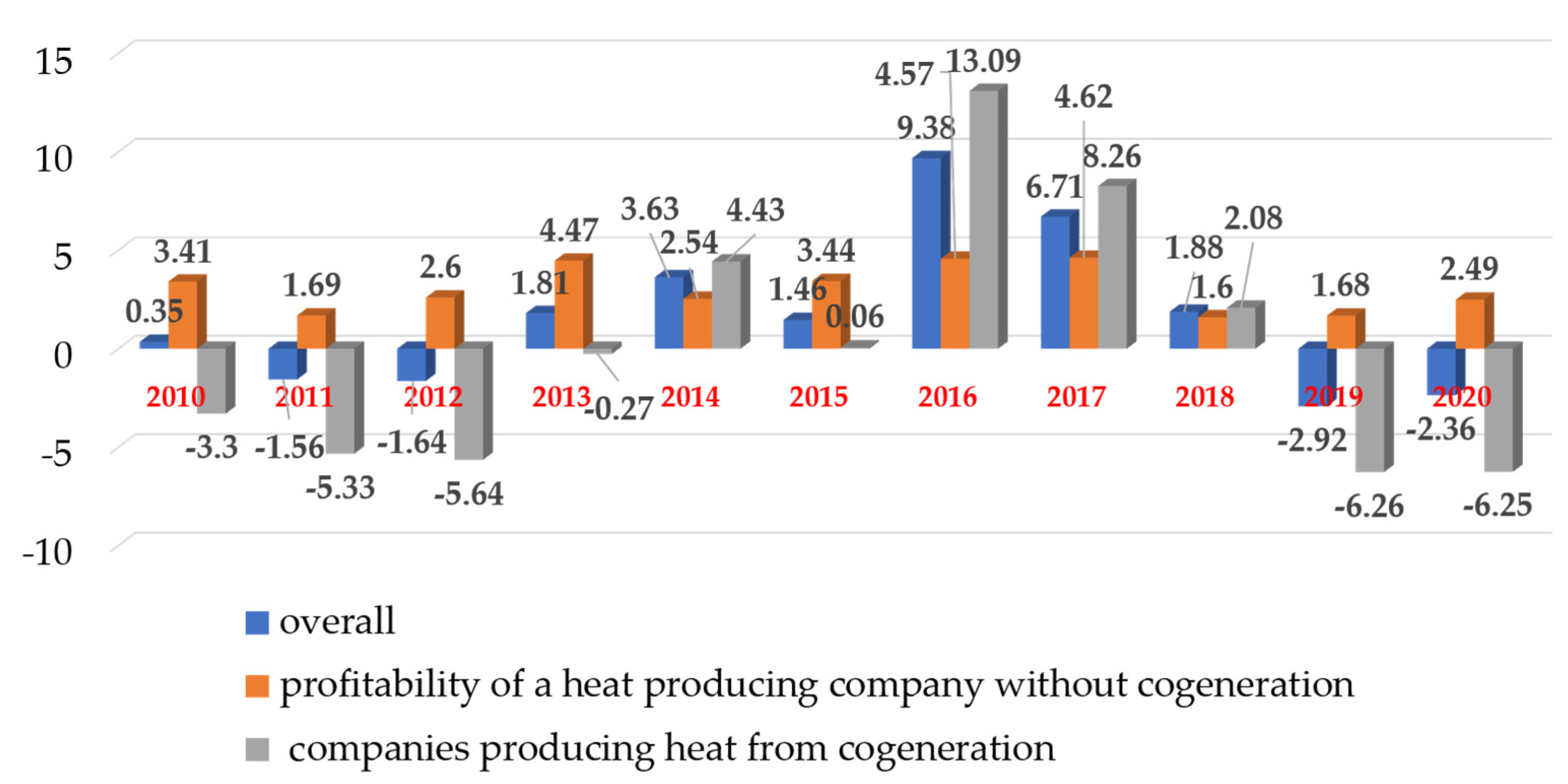
- In 2020, the total debt decreased and the financial liquidity of enterprises in the sector increased;
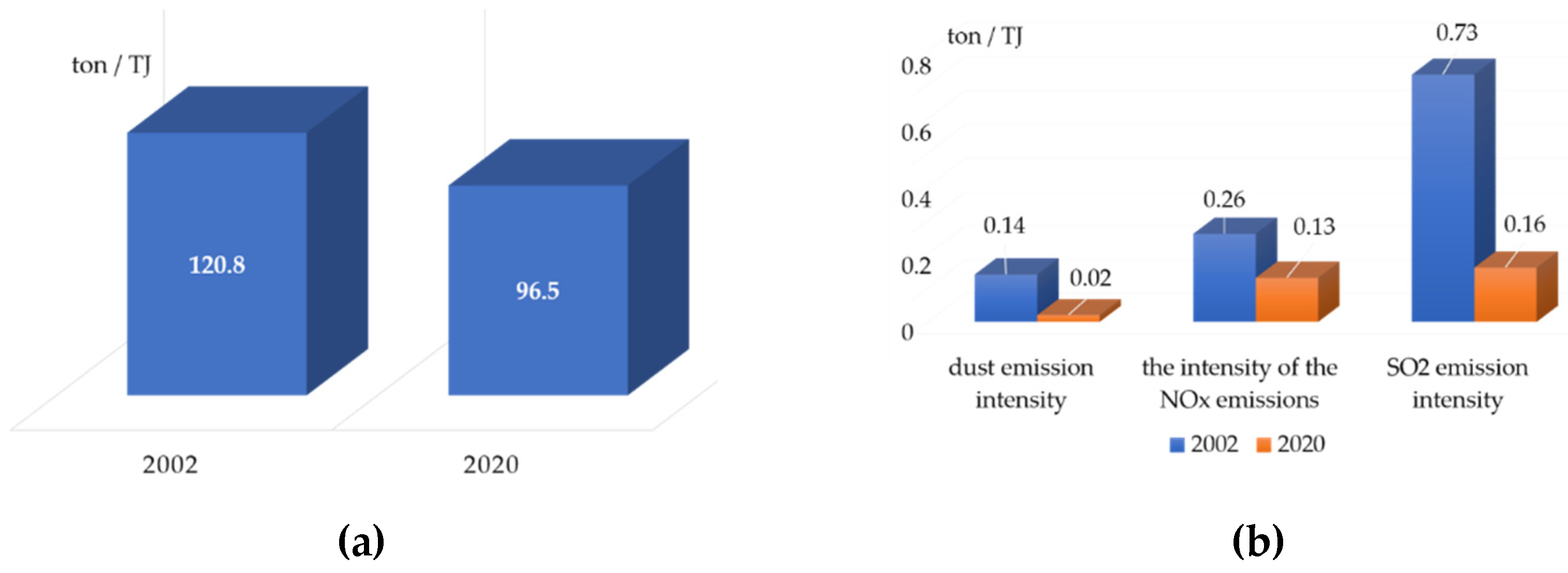
- In the years 2002–2020, a significant increase in the replacement rate of fixed assets was recorded. This value increased by 37.5%, which indicates a high degree of investment, exceeding the level of depreciation of fixed assets;
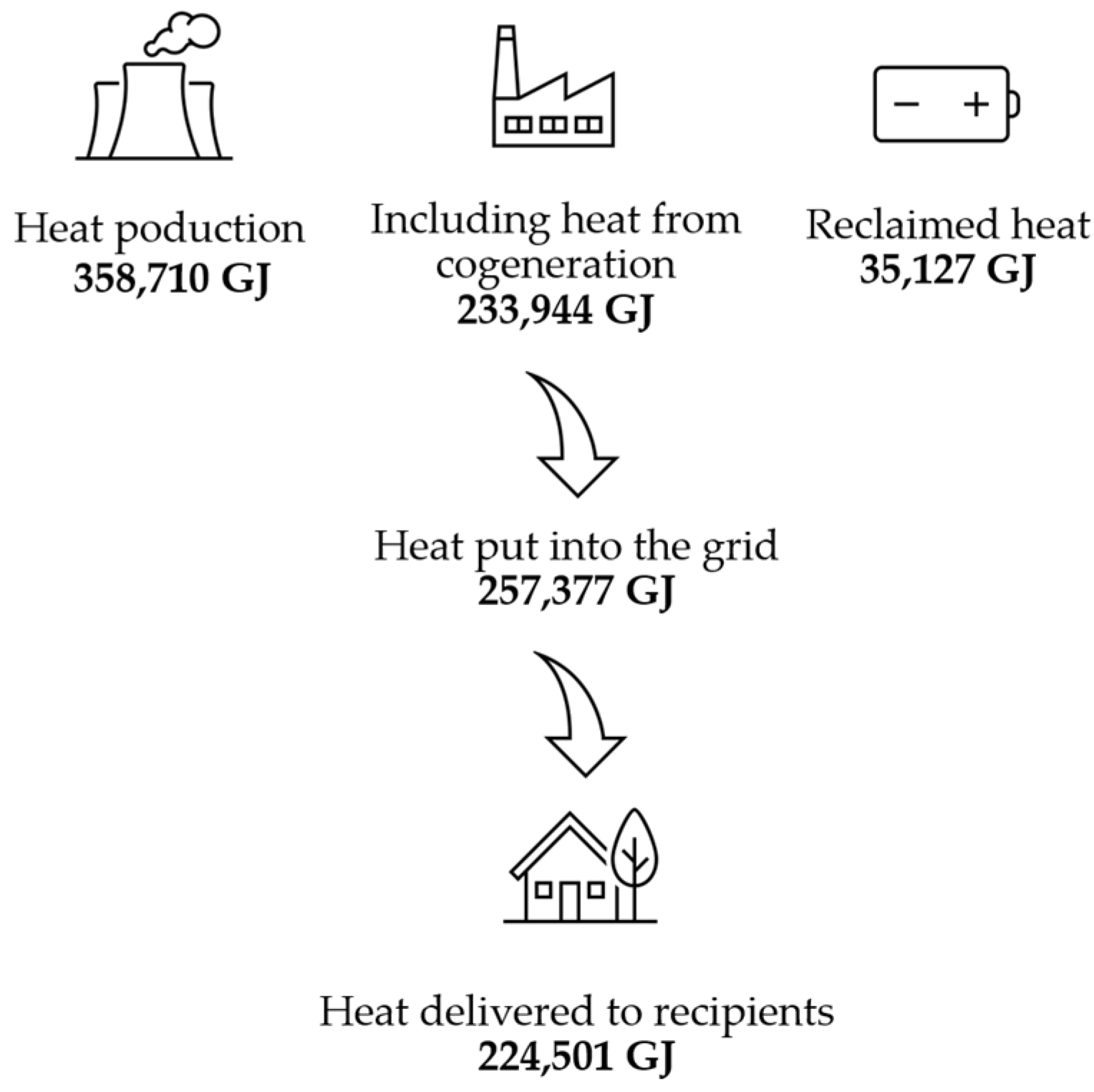
- In 2020, more than 90 % of all surveyed heating companies dealt with the production of heat. They generated, including heat recovered in technological processes, almost 394,000 TJ of heat, which means a decrease in production by 1.6% compared to the previous year;
- In 2020, the share of heat from cogeneration was 65.2% of total heat production;
- 370 companies producing heat participated in the study, 128 of them also generate heat in cogeneration (i.e. 34.6%);
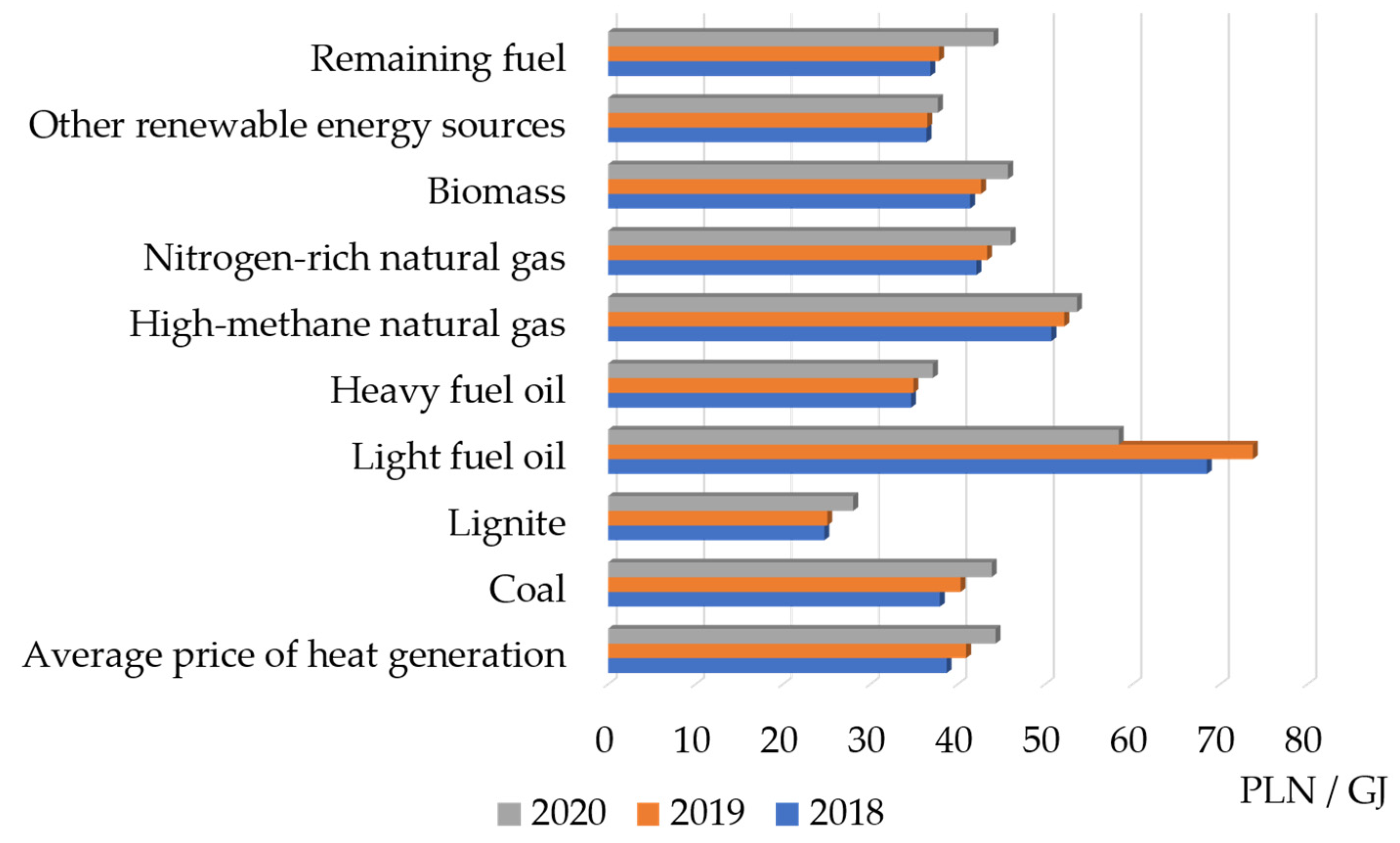
- The average single-component price of heat in 2020 amounted to PLN 55.95 / GJ and was higher by 7.7 % than the 2019 price (PLN 51.93 / GJ), and by 13.1% (PLN 49.46 / GJ) comparing to the 2018 price;
- In 2020, the total volume of heat sales by licensed heating companies (including resale to other enterprises) amounted to approx. 344,000 TJ and was 0.3% lower than in 2019;
- In 2020, the average price of heat sold from all licensed heat generating sources amounted to PLN 44.33 / GJ, thus showing an increase by 8.2%. compared to 2019 (PLN 40.97 / GJ), with the average price of heat sold from licensed heat-generating sources without cogeneration being PLN 51.87 / GJ, and the average price of heat sold from licensed heat-generating sources in cogeneration was 41.32 PLN / GJ.
3.1. The Structure of Heating Companies in Poland
3.2. Fuel Consumption for Heat Production.
2.3. Sale and Sale Prices for Heat.
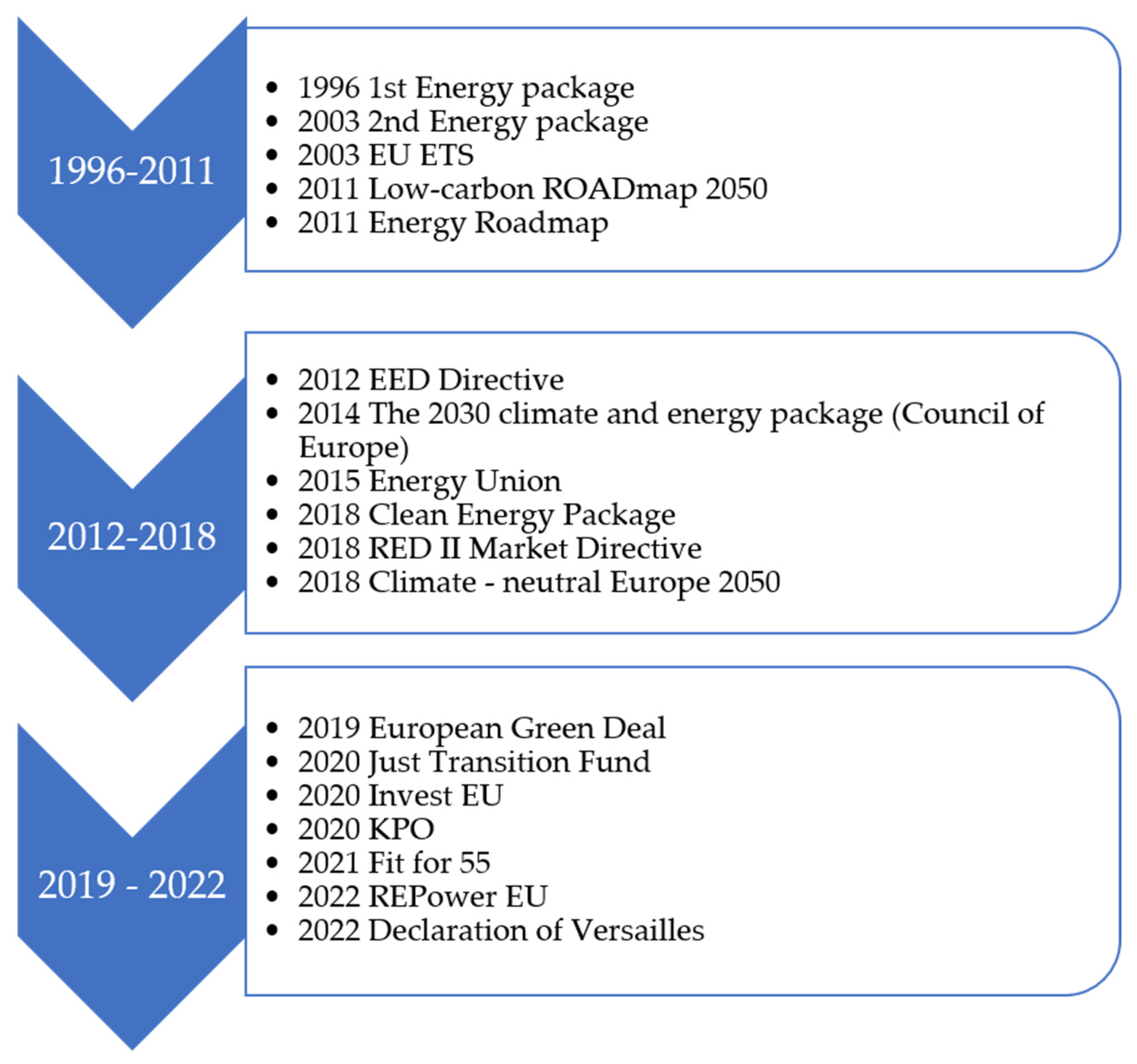
4. Development goals
4.1. Goals of the European Union and Poland
- at least 50% of energy from renewable sources or
- at least 50% of waste heat, or
- at least 75% of heat from cogeneration, or
- at least 50% combination of such energy and heat.
- By 2040, the thermal needs of all households are to be covered by system heat and by zero-emission or low-emission individual sources;
- There should be a significant increase in the installed capacity of photovoltaics, approx. 5–7 GW in 2030 and approx. 10–16 GW in 2040, which will enable low-cost use of electricity used to drive heat pumps and switch to heat generation from electricity auto producers and prosumers;
- It is expected that natural gas will be a bridge fuel in the energy transformation, and in 2030 the capacity to transport a mixture containing about 10% of decarbonized gases via gas networks will be achieved, which will enable low-emission heat generation in cogeneration, both in economic activity and in own needs. The possibility of using decarbonized fuel will facilitate the transformation of energy companies towards effective heating systems (an appropriate share of heat from cogeneration, heat from RES or waste heat in the system;
- The low-emission direction of transformation of individual sources should be implemented through the use of heat pumps, solar collectors and electric heating, which will facilitate the achievement of the goal of abandoning coal combustion in households in cities by 2030, and in rural areas by 2040;
-
The most anticipated innovations for heating may be:
- heat storage technologies that will allow for the optimization and effective operation of sources generating heat and electricity in cogeneration, regardless of the passing peaks of the demand for these products, which will increase the operational safety of the entire power system;
- electricity storage facilities, which will allow for further dynamic development of sources based on solar and wind energy, as they will eliminate their most serious disadvantage, instability and dependence on natural conditions;
- hydrogen technologies, especially technologies enabling the production of "green hydrogen", which will allow the development of local hydrogen clusters based on local production of hydrogen associated with decentralized production of renewable energy (including "green heat") and local demand, and the dedicated hydrogen infrastructure can use hydrogen for the production and supply of heat to residential and commercial buildings.
- The need to cover heat needs on an individual basis by using sources with the lowest possible emission (heat pumps, electric heating, natural gas—preferably with decarbonized gas) and the coal phase-out—in cities by 2030, and in rural areas by 2040;
- The assumption that approx. 1.5 million new households will be connected to the heating network by 2030;
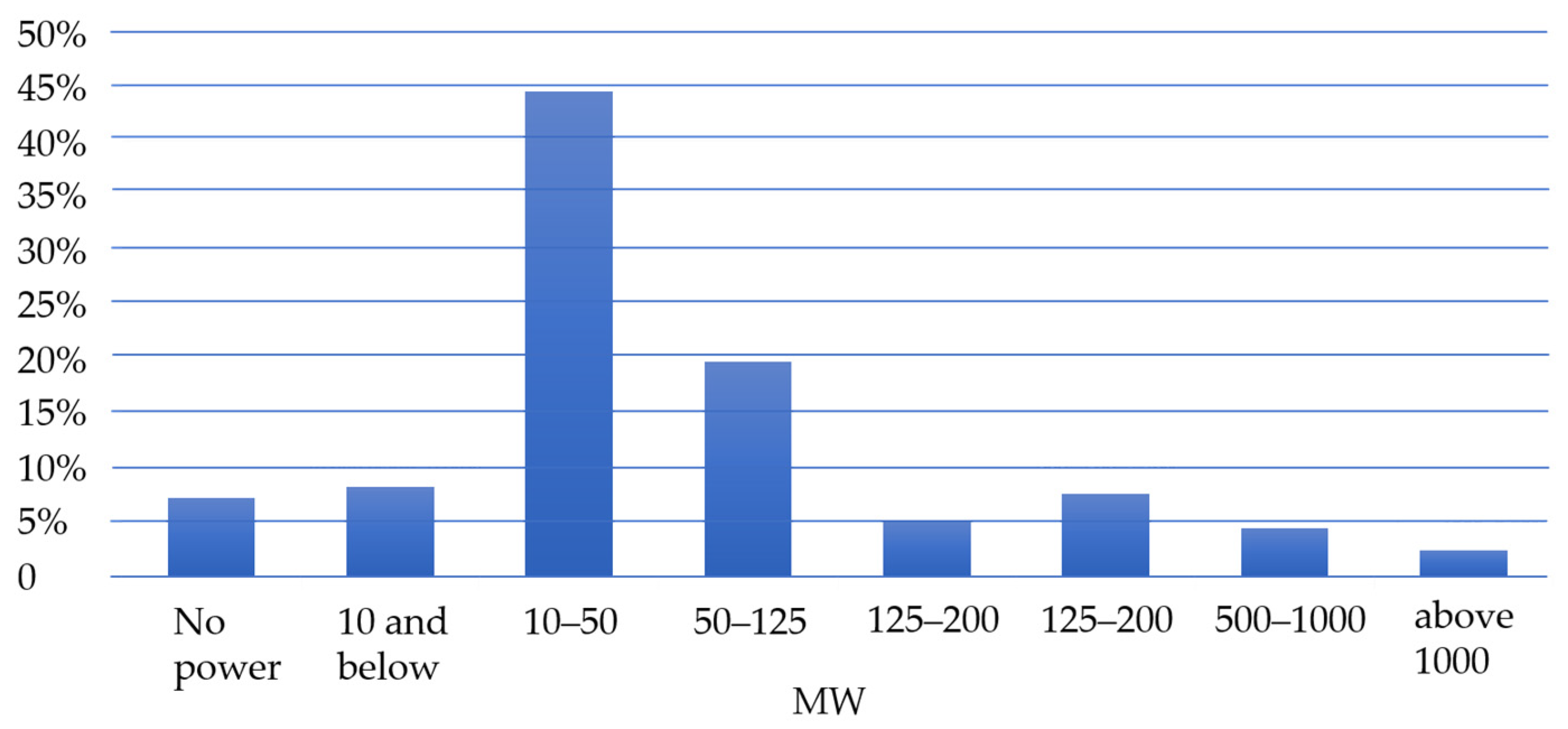
- Heating or cooling systems, in which the ordered capacity exceeds 5 MW, at least 85% in 2030 will meet the criteria of an energy-efficient heating system (currently it is approx. 10%);
- Assumption that in the next decade there will be an increase in heat generation from RES by at least 1.1 pp. every year, which, according to the (KPEiK), gives the expected 28.4% share of renewable sources in the entire heating sector in 2030.
- there is a new criterion to introduce a limit for direct CO2 emissions (for units using fossil fuels) of less than 270 g CO2 per kWh of combined heat and power (combined heat, electricity and mechanical energy). The direct emissions limit will apply from the entry into force of the recast directive, while its role will be particularly important from 1 January 2026, when the criteria in the definition of an efficient heating and cooling system will refer directly to high-efficiency cogeneration;
- prevent coal-fired cogeneration from maintaining its high-efficiency status and, at the same time, introduce an emission limit for gas-fired units. The entry of the new criterion will mean that coal-fired cogeneration units, which will not be modernized by the end of 2025, will lose the status of high-efficiency cogeneration, which in the vast majority of systems will also translate into the loss of the status of an effective heating and cooling system. The draft EED directive does not explicitly define the methodology for calculating the new emission criterion. This is important in the context of the operating conditions of cogeneration units, including the seasonal change in the heat curve and system services provided for the power system—factors affecting the level of direct CO2 emissions.
- by 31 December 2025, a system using at least 50% renewable energy, 50% waste heat, 75% cogeneration heat or 50% a combination of such energy and heat (existing definition);
- from 1 January 2026, a system using at least 50% of energy from renewable sources, 50% of waste heat, 80% of heat from high-efficiency cogeneration or at least a combination of such heat supplied to a network with a renewable energy share of at least 5%, and the total share of renewable energy, waste heat or heat from high-efficiency cogeneration is at least 50%;
- •from 1 January 2035, a system using at least 50% of energy from renewable sources and waste heat with a share of energy from renewable sources of at least 20%;
- from 1 January 2045, a system using at least 75% of energy from renewable sources and waste heat, with a share of energy from renewable sources of at least 40%;
- •from 1 January 2050, a system using only renewable energy and waste heat with a share of energy from renewable sources of at least 60%.
- a national building renovation plan to replace long-term renovation strategies. One of the elements of the plan is to identify policies and measures to decarbonize the heating and cooling sector through district heating and cooling, and phase out fossil fuels in these sectors with a view to their complete phase-out by 2040 at the latest;
- complete gas elimination by 2040—target inconsistent with overall policy objectives;
- inability to connect new buildings after 2030 to efficient heating systems that are not completely decarbonized.
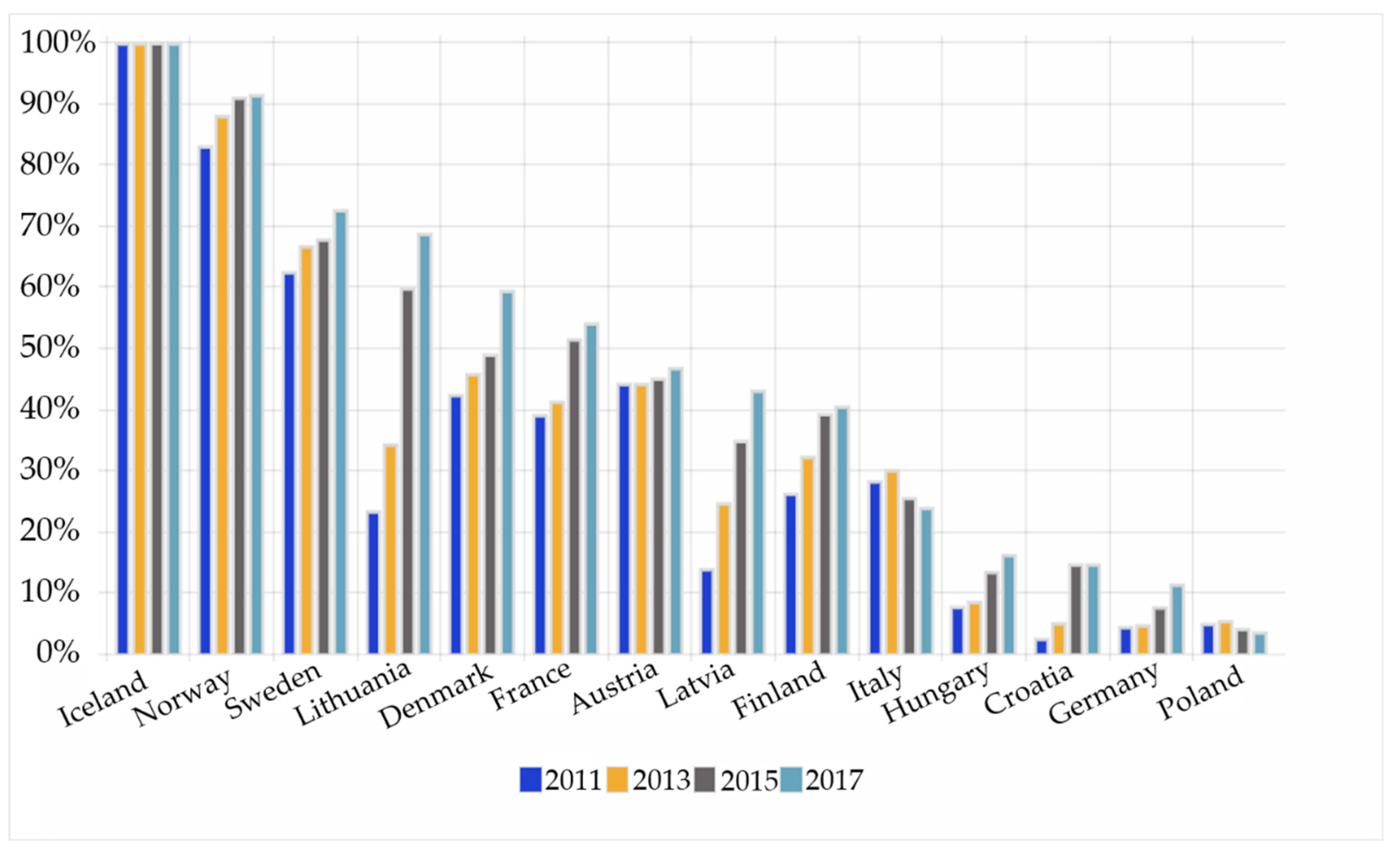
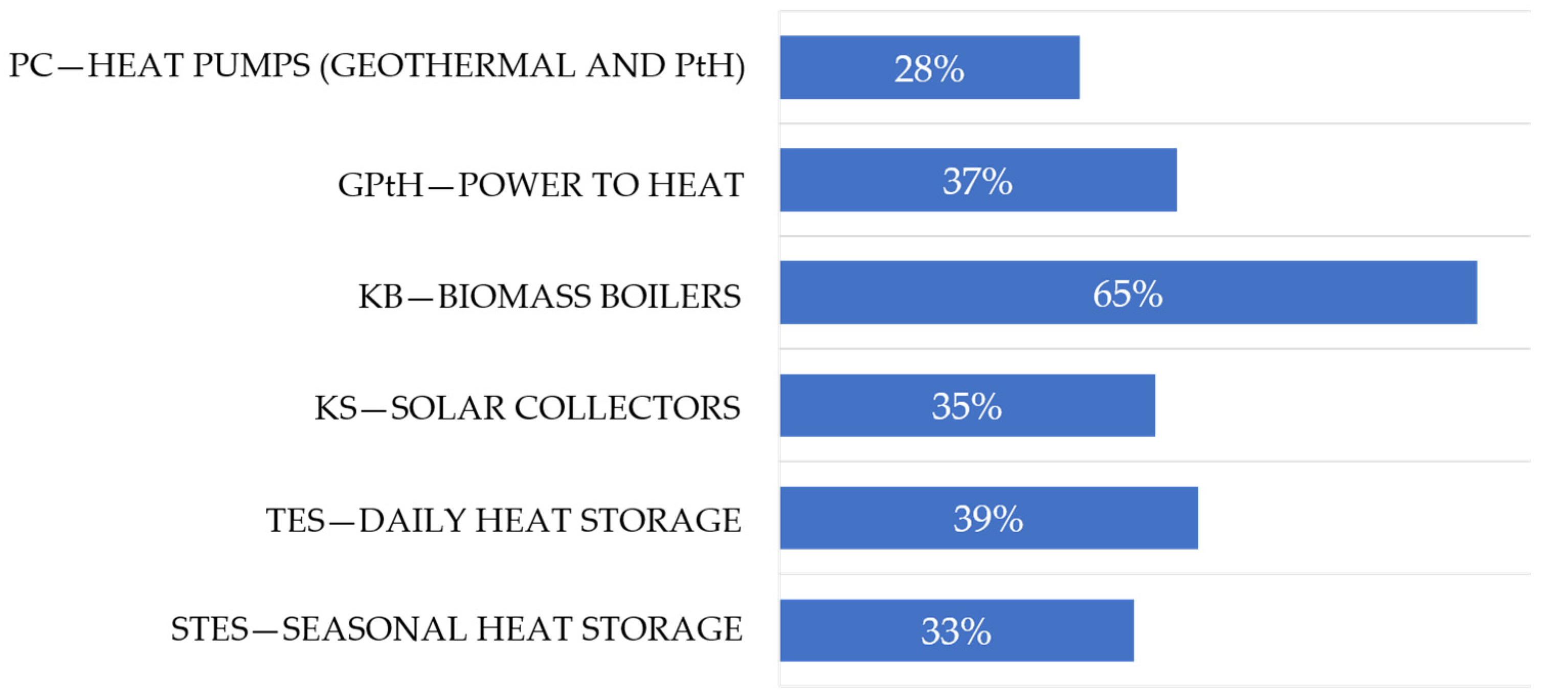
4.2. The Involvement of Renewable Energy Sources in Heat Engineering and Potential Directions of Development
- Generation of energy from emission-free sources;
- Energy storage;
- Development of decentralized production of energy from renewable sources;
- Electrification of the heating sector;
- Promoting more sustainable and efficient technologies and solutions;
- Closer integration of the electricity and heating sectors;
- Use of waste for energy production;
- Development of modern, low-temperature heating systems;
- Improving the energy infrastructure and making it resistant to climate change;
- Adapt infrastructure with intelligent and cybersecurity digital solutions.
- 1440 TJ from solar thermal energy (solar collectors, efficiency 40%);
- 360 TJ from solar photovoltaic energy (efficiency 10%);
- up to 150 TJ from wind energy (with a high density of windmills of 20 MW / km2);
- up to 15 TJ from biomass (with the most efficient energy crops).
4.3. New Technologies for Construction
- Alkaline (AFC—Alkaline Fuel Cell);
- With molten carbonate (MCFC—Molted Carbonate Fuel Cell);
- With phosphoric acid (PAFC—Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell);
- With a proton exchange membrane (PEMFC—Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell);
- Oxide (SOFC—Solid Oxide Fuel Cell).
- Implement hydrogen technology in the energy sector along with the definition of the legal framework;
- Launch a P2G class 1 MW installation—support for stabilizing the operation of distribution networks; such installation will produce 3150 MWh of hydrogen / year;
- Implement the possibility of co-firing hydrogen in gas turbines (depending on the technical capabilities of the turbine);
- Start up cogeneration and polygeneration installations, e.g., medium-sized combined heat and power plants (50 MWt), where the main fuel will be hydrogen (demand around 580 GWh per year);
- Start using hydrogen as an energy store;
- Installation of polygeneration berths for apartment blocks, small housing estates and public utility buildings from 10 kW to 250 kW with the use of fuel cells.
5. Future of DH—Selected Case Studies
5.1. Berlin, Germany
5.2. Albertslund, Denmark
5.3. Malmö, Sweden
5.4. Ostrów Wielkopolski, Poland
5.5. Wałcz, Poland
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASHP | air source heat pump |
| ATES | Aquifer thermal energy storage |
| BTES | Borehole thermal energy storage |
| CCHP | combined heating, cooling and power |
| CHP | Combined heating and power |
| ECO | Opolszczyzna District Heating |
| EED | Energy Efficiency Directive |
| EfW | Energy from waste |
| EPDB | Energy Performance of Buildings Directive |
| GPtH | green power to heat |
| GSHP | ground source heat pump |
| IED | Industrial Emissions Directive |
| IEO | Institute of Renewable Energy |
| LPEC | Lublin Heat Energy Company |
| MC | Municipal Heating Company |
| MPEC | Municipal Heat Energy Company |
| KB | biomass boilers |
| KPEiK | National Energy and Climate Plan |
| KS | solar collectors |
| PC | heat pumps |
| PEP2040 | Polish Energy Policy up to 2040 |
| PRL | Polish People's Republic |
| PSE | Polish Power Grids |
| PTES | Pit thermal energy storage |
| PV | photovoltaics |
| RED III | Renewable Energy Directive |
| RES | renewable energy sources |
| SEC | Szczecin District Heating |
| STES | seasonal heat storage |
| TES | Thermal energy storage |
| TTES | Tank thermal energy storage |
| URE | Energy Regulatory Office |
| WTG | wind turbine generator |
| WPEC | Voivodship Heat Energy Company |
| ZEC | Heat Energy Plant in Wałcz |
| ZSC | Łódź District Heating Plant |
References
- United Nations. Day of eight billlion. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/events/day-eight-billionUnited Nations (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Report: Pathways to a Clean Energy System; Energy Technology Perspectives, I.E. Agency, 2012.
- Mertens, R.; Manual for Statistics on Energy Consumptionin Households. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, 2013. Available on: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/3859598/5935825/KS-GQ-13-003-EN.PDF/baa96509-3f4b-4c7a-94dd-feb1a31c7291 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Mirzaei, P.A. Recent challenges in modeling of urban heat island. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 19, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, P.A.; Olsthoorn, D.; Torja, M.; Haghighat, F. Urban neighborhood characteristics influence on a building indoor environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 19, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report: Energy transition outlook 2022. A global and regional forecast to 2050. DNV Group, 2022.
- Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council Amending Directive 2003/87/EC Establishing a System for Greenhouse Gas Emission Allowance Trading within the Union, Decision (EU) 2015/1814 Concerning the Establishment and Operation of a Market Stability Reserve for the Union Greenhouse Gas Emission Trading Scheme and Regulation (EU) 2015/757. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/default/files/revision-eu-ets_with-annex_en_0.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- RePowerEU: A Plan to Rapidly Reduce Dependence on Russian Fossil Fuels and Fast Forward the Green Transition. 2022. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52022DC0230&from=EN (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Polityka Energetyczna Polski do 2040 r./Poland’s Energy Policy until 2040 (PEP2040). Ministry of Climate and Environment: Warsaw, Poland. 2021. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WMP20210000264 (accessed on 11 August 2022). (In Polish).
- Krajowy Plan na Rzecz Energii i Klimatu na Lata 2021–2030 (KPEiK)/The National Energy and Climate Plan for the Years 2021–2030. 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/aktywa-panstwowe/krajowy-plan-na-rzecz-energii-i-klimatu-na-lata-2021-2030-przekazany-do-ke (accessed on 18 August 2022). (In Polish).
- Reda, F.; Ruggiero,S.; Auvinen, K.; Temmes, A. Towards low-carbon district heating: Investigating the socio-technical challenges of the urban energy transition. Smart Energy 2021, 4, 100054. [CrossRef]
- Werner, S. International review of district heating and cooling. Energy 2017, 137, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, A.R.; Liu, S.; Shukla, A. A state of art review on the district heating systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2018, 96, 420–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, B.; Mirzaei, P.A.; Bastani, A.; Haghighat, F. A Review of District Heating Systems: Modeling and Optimization. Front. Built Environ. 2016, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, S.; Fouladfar, M.H.; Franchini, G.; Lozano Gabarre, I.; Andrés Chicote, M. Advanced Control and Fault Detection Strategies for District Heating and Cooling Systems—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, A.; Rezaie, B.; Beyerlein, S. Review of district heating and cooling systems for a sustainable future. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2017, 67, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, C.A; Li, H.; Li, P.; Yan, J. Improve the flexibility provided by combined heat and power plants (CHPs)–a review of potential technologies. Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2021, 1, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Rindt, C.; Smeulders, D.M.J. Optimal Planning of Future District Heating Systems—A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinelski, G.; Stęchły, J.; Sienicki, A.; Czornik, K.; Borkowski, P. Application of Smart Technologies in Metropolis GZM to Reduce Harmful Emissions in District Heating Systems. Energies 2021, 14, 7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegórska, A.; Rybarczyk, P.; Lukoševičius, V.; Sobczak, J.; Rogala, A. Smart Asset Management for District Heating Systems in the Baltic Sea Region. Energies 2021, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.; Sdringola, P.; Tamburrino, S.; Puglisi, G.; Donato, E.D.; Ancona, M.A.; Melino, F. Efficient District Heating in a Decarbonisation Perspective: A Case Study in Italy. Energies 2022, 15, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, M.; Duckheim, M.; Franken, M.; Heger, H.J.; Huber, M.; Knittel, M.; Kolster, T.; Kueppers, M.; Meier, C.; Most, D.; Paulus, S.; Wyrwoll, L.; Moser, A.; Niessen, S. Pathways toward a Decarbonized Future—Impact on Security of Supply and System Stability in a Sustainable German Energy System. Energies 2021, 14, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, M.-A.; Burnside, N.M.; Yu, Z. District Heating Challenges for the UK. Energies 2019, 12, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neirotti, F.; Noussan, M.; Riverso, S.; Manganini, G. Analysis of Different Strategies for Lowering the Operation Temperature in Existing District Heating Networks. Energies 2019, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Bianchini, A. The Innovative Concept of Cold District Heating Networks: A Literature Review. Energies 2018, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjorgievski, V.Z.; Markovska, N.; Abazi, A.; Neven Duić, N. The potential of power-to-heat demand response to improve the flexibility of the energy system: An empirical review. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, A; Poier, H. ; Holter, C. BIG Solar Graz: Solar district heating in Graz – 500,000 m² for 20% solar fraction. Energy Procedia 2016, 91, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, A.; Mathiesen, B.V.; Averfalk, H.; Werner, S.; Lund, H. Heat Roadmap Europe: Large-Scale Electric Heat Pumps in District Heating Systems. Energies 2017, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teräsvirta, A.; Syri, S.; Hiltunen, P. Small Nuclear Reactor—Nordic District Heating Case Study. Energies 2020, 13, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez Blázquez, C.; Farfán Martín, A.; Nieto, I.M.; González-Aguilera, D. Economic and Environmental Analysis of Different District Heating Systems Aided by Geothermal Energy. Energies 2018, 11, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, D.; Leiss, B. Geothermal energy at different depths for district heating and cooling of existing and future building stock. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2022, 167, 112727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djørup, S.; Sperling, K.; Nielsen, S.; Østergaard, P.A.; Zinck Thellufsen, J.; Sorknæs, P.; Lund, H.; Drysdale, D. District Heating Tariffs, Economic Optimisation and Local Strategies during Radical Technological Change. Energies 2020, 13, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltshire, R. Wiltshire, R. Advanced district heating and cooling (DHC) systems. Woodhead Publishing Ltd: Cambridge, 2015.
- Sayegh, M.A.; Danielewicz, J.; Nannou, T.; Miniewicz, M.; Jadwiszczak, P.; Piekarska, K.; Jouhara, H. Trends of European research and development in district heating technologies. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2017, 68, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J. The history of district heating. Dist Heat 1959, 44, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson, G.; Gunnlaugsson, E.; Jónasson, T.; Ólafsson, M. Low-temperature geothermal utilization in Iceland – Decades of experience. Geothermics 2010, 39, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Major issues and solutions in the management system of space heating system in North China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2015, 49, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E. Öffentliche Heizkraftwerke und Elekrizitätswirtschaft in Städten. Springer Verlag: Berlin, 1933. (In German).
- Margolis, A. Experiences with district heating in Europe and USA and its further development. J Inst Heat Vent Eng 1935, 3, 361–413. [Google Scholar]
- Margolis, A. Area Heating. Nature 1944, 153, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, A. Continental practise. Bull Natl Dist Heat Assoc 1947, 33, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, A. District heating in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland. Bull Natl Dist Heat Assoc 1948, 34, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Frederiksen, S.; Werner, S. District Heating and Cooling. Studentlitteratur: Lund, 2013.
- Sto lat, sto lat już grzeje, grzeje nam…Magazyn Ciepła Systemowego 2018, 3(40), 20–22. Available online: https://magazyncieplasystemowego.pl/cieplownictwo/sto-lat-sto-lat-juz-grzeje-grzeje-nam/ (accessed on 5 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Wojdyga, K. Polish District Heating Systems—Developmen Perspectives. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 10, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veolia Energia Warszawa S.A., Available online: https://energiadlawarszawy.pl/# (accessed on 18 February 2023). (In Polish).
- MPEC S.A. Kraków, Available online: https://www.mpec.krakow.pl/ (accessed on 18 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Veolia Energia Łódź S.A., Available online: https://energiadlalodzi.pl/ (accessed on 18 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Veolia Energia Poznań S.A., Available online: https://energiadlapoznania.pl/ (accessed on 15 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Lubelskie Przedsiębiorstwo Energetyki Cieplnej S.A., Available online: https://lpec.pl/ (accessed on 15 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Zespół Elektrociepłowni Wrocławskich Kogeneracja S.A. Available online: https://www.kogeneracja.com.pl/en/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Szczecińska Energetyka Cieplna Sp. z o.o., Available online: https://sec.com.pl/en/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Energetyka Cieplna Opolszczyzny S.A., Avaliable online: https://www.ecosa.pl/ (accessed on 15 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Wei, B.; Wang, S-L.; Li, L. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of district heating systems. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 5947–5955.
- Zvingilaite, E.; Balyk, O. Heat savings in buildings in a 100% renewable heat and power system in Denmark with different shares of district heating. Energy Build 2014, 82, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Werner, S; Wiltshire, R.; Svendsen, S.; Thorsen, J.E.; Hvelplund F.; et al. 4th Generation District Heating (4GDH). Integrating smart thermal grids into future sustainable energy systems. Energy 2014, 68, 1–11.
- Persson, U.; Werner, S. District heating in sequential energy supply. Appl. Energy 2012, 95, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Xia, J.; Jiang, Y. Key issues and solutions in a district heating system using low-grade industrial waste heat. Energy 2015, 86, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhang, S. Experimental and theoretical investigation of a novel full-open absorption heat pump applied to district heating by recovering waste heat of flue gas. Energy Build. 2018, 173, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, O.; Finnveden, G.; Ekvall, T.; Bjorklund, A. Life cycle assessment of fuels for district heating: a comparison of waste incineration, biomass- and natural gascombustion. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 1346–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, U.; Münster, M. Current and future prospects for heat recovery from waste in European district heating systems: A literature and data review. Energy 2016, 110, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsri, S.; Bales, C.; Martin, A.R.; Martin, V. Decentralised cooling in district heating network: monitoring results and calibration of simulation model. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 3311–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric Ilic, D.; Dotzauer, E.; Trygg, L.; Broman, G. Introduction of large-scale biofuel production in a district heating system —an opportunity for reduction of global greenhouse gas emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 64, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric Ilic, D.; Dotzauer, E.; Trygg, L.; Broman, G. Integration of biofuel production into district heating—part II: An evaluation of the district heating production costs using Stockholm as a case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 69, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karschin, I.; Geldermann, J. Efficient cogeneration and district heating systems in bioenergy villages: an optimization approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 104, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.G.; Dosoky, N.S.; Zoromba, M.S.; Shafik, H.M. Algal Biofuels: Current Status and Key Challenges. Energies 2019, 12, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpaneto E, Lazzeroni P, Repetto M. Optimal integration of solar energy in a district heating network. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 714–721. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenberger, D.; Bruckner, T.; Groscurth, H.M.; Kümmel, R. Optimization of solar district heating systems: seasonal storage, heat pumps, and cogeneration. Energy 2000, 25, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.; Bauer, D.; Drueck, H. Energy efficient integration of heat pumps into solar district heating systems with seasonal thermal energy storage. Energy Procedia 2014, 57, 2706–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rahim, N.A. Global advancement of solar thermal energy technologies for industrial process heat and its future prospects: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 885–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamankaradeniz, N. Thermodynamic performance assessments of a district heating system with geothermal by using advanced exergy analysis. Renew Energy 2016, 85, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekret, R.; Nitkiewicz, A. Exergy analysis of the performance of low-temperature district heating system with geothermal heat pump. Arch Thermodyn 2014, 35, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, D.; Leiss, B. Geothermal energy at different depths for district heating and cooling of existing and future building stock. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez Blázquez, C.; Farfán Martín, A.; Nieto, I.M.; González-Aguilera, D. Economic and Environmental Analysis of Different District Heating Systems Aided by Geothermal Energy. Energies 2018, 11, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calise, F.; Cappiello, F,L. ; Cimmino, L.; d'Accadia, M.D.; Vicidomini, M. Optimal design of a 5th generation district heating and cooling network based on seawater heat pumps. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 267, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, P.A.; Andersen, A.N. Economic feasibility of booster heat pumps in heat pump-based district heating systems. Energy 2018, 155, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; You, S.; Ye, T. Heat transfer performance of a seawater-source heat pump with radiant floor heating system in cold areas of China. Sci Technol Built Environ 2017, 23, 469–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, A.; Merzkirch, A.; Roesler, J. Leyer, S.; Scholzen, F.; Maas, S. Experimental and analytical evaluation of exhaust air heat pumps in ventilation-based heating systems. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102638. [CrossRef]
- Carroll, P.; Chesser, M.; Lyons, P. Air Source Heat Pumps field studies: A systematic literature review. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kensby, J.; Trüschel, A.; Dalenbäck, J.O. Heat source shifting in buildings supplied by district heating and exhaust air heat pump. Energy Procedia 2017, 116, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarragona, J.; Pisello, A.L.; Fernández, C.; de Gracia, A.; Cabeza, L.F. Systematic review on model predictive control strategies applied to active thermal energy storage systems. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2021, 149, 111385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahash, A.; Ochs, F.; Bianchi Janetti, M.; Streicher, W. Advances in seasonal thermal energy storage for solar district heating applications: A critical review on large-scale hot-water tank and pit thermal energy storage systems. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 296–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuytten, T.; Claessens, B.; Paredis, .; Van Bael, J.; Six, D. Flexibility of a combined heat and power system with thermal energy storage for district heating. Appl Energy 2013, 104, 583–591. [CrossRef]
- EuroHeat and Power. Guidelines for district heating substations & countrywise survey. Brussels, 2008.
- Sørensen, P.A., Schmidt, T. Design and Construction of Large Scale Heat Storages for District Heating in Denmark, In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Energy Storage, Adana, Turkey, 25–28 April 2018.
- Task 45 Large Systems. Seasonal thermal energy storage. Report: on state of the art and necessary further R+D; SHC, IEA Germany: Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. Available online: http://task45.iea-shc.org/data/sites/1/publications/IEA_SHC_Task45_B_ Report.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Wiltshire, R. Advanced district heating and cooling (DHC) systems, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, Great Britain; 2015. Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge.
- Lund, H.; Werner, S.; Wiltshire, R.; Svendsen, S.; Thorsen, J.E.; Hvelplund, F, et al. Generation District Heating (4GDH): Integrating smart thermal grids into future sustainable energy systems. Energy 2014, 68, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Skagestad, B.; Mildenstein, P. District heating and cooling connection handbook. NOVEM: Netherlands Agency for Energy and the Environment, 2002.
- Wikimedia Commons. Available online: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/83/Generations_of_ district_heating_systems_EN.svg (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Tomaszewski, R. Research: Ciepło do zmiany. Jak zmodernizować sektor ciepłownictwa systemowego w Polsce. Polityka INSIGHT, 2020. (In Polish).
- Energy Regulatory Office (URE). https://www.ure.gov.pl/en (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Raport: Dekarbonizacja ciepłownictwa systemowego w Polsce w świetle pakietu „Fit for 55”/ Report: Decarbonisation of system heating in Poland in the light of the "Fit for 55" package; Polskie Towarzystwo Elektrowni Zawodowych, Kraków, Poland, 2022. (In Polish).
- Raport: Energetyka Cieplna w Liczbach—2020/Report: Thermal Energy in Numbers—2020. URE: Warsaw, Poland. 2022. Available online: https://www.ure.gov.pl/pl/cieplo/energetyka-cieplna-w-l/10096,2020.html (accessed on 18 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Statystyka Ciepłownictwa Polskiego 2020/Statistics of Polish Heating 2020, Yearbook ARE: Warsaw, Poland. 2021. Available online: https://www.are.waw.pl/badania-statystyczne/wynikowe-informacje-statystyczne/publikacje-roczne (accessed on 20 February 2022). (In Polish). 2021.
- Forum Energii, Available online: https://forum-energii.eu/pl/dane-o-energetyce (accessed on 18 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Raport: Energetyka Cieplna w Liczbach—2021/Report: Thermal Energy in Numbers—2021. URE: Warsaw, Poland. 2022. Available online: https://www.ure.gov.pl/pl/cieplo/energetyka-cieplna-w-l/10763,2021.html (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Dane Systemowe/System Data, Polish Energy Networks PSE. Available online: https://www.pse.pl/dane-systemowe/funkcjonowanie-rb/raporty-dobowe-z-funkcjonowania-rb/podstawowe-wskazniki-cenowe-i-kosztowe/rozliczeniowa-cena-uprawnien-do-emisji-co2-rcco2 (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- Urząd Regulacji Energetyki/Energy Regulatory Office. Available online: https://www.ure.gov.pl/en (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Energy Efficiency Directive 2012/27/EU. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1399375464230&uri=CELEX:32012L0027 (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Renewable Energy Directive 2018/2001/EU. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2018.328.01.0082.01.ENG&toc=OJ:L:2018:328:TOC (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Energy Performance of Buildings Directive 2010/31/EU. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/;ELX_SESSIONID=FZMjThLLzfxmmMCQGp2Y1s2d3TjwtD8QS3pqdkhXZbwqGwlgY9KN!2064651424?uri=CELEX:32010L0031 (accessed on 18 May 2023).00.
- Hoicka, C.E.; Lowitzsch, J.; Brisbois, M.C.; Kumar, A.; Camargo, L.R. Implementing a just renewable energy transition: Policy advice for transposing the new European rules for renewable energy communities. Energy Policy 2021, 156, 112435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instytut Energetyki Odnawialnej (IEO)/Institute of Renewable Energy. Available online: https://ieo.pl/en/ (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Analiza: Dekarbonizacja ciepłownictwa systemowego w Polsce w świetle pakietu „Fit for 55”—2022/ Analysis: Decarbonisation of district heating in Poland in the light of the "Fit for 55" package. Polskie Towarzystwo Elektrociepłowni Zawodowych 2022. Available online: http://ptez.pl/files/news_attachment/364/dekarbonizacja_cieplownictwa_systemowego_w_polsce_w_swietle_pakietu_fit_for_55.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Raport w zakresie kierunków transformacji sektora ciepłownictwa systemowego—2021/Report on the directions for transformation of the district heating sector—2021. Izba Gospodarcza Ciepłownictwo Polskie 2021. (In Polish).
- Ekspertyza: Założenia do ustanowienia przez Narodowy Fundusz Ochrony Środowiska i Gospodarki Wodnej programu wsparcia dla ciepłownictwa w zakresie budowy, modernizacji i rozwoju systemów ciepłowniczych współpracujących z OZE i magazynami ciepła—2018/Expert opinion: Assumptions for establishing a support programme for the heating sector by the National Fund for Environmental Protection and Water Management with regard to the construction, modernisation and development of district heating systems cooperating with RES and heat storage facilities. Instytut Energetyki Odnawialnej: Warsaw, Poland. 2018. (In Polish). W: Odnawialnej.
- Wiśniewski G.: Zmiana paradygmatu w energetyce—rolnik podmiotem i producentem energii/ A paradigm shift in energy—farmer as subject and energy producer. Energetyka-Społeczeństwo-Polityka 2016, 1(3), 61–81. Available online: http://energetyka-collegium.pl/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Grzegorz-Wisniewski_OK_n.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2023) (In Polish).
- National Fund for Environmental Protection and Water Management. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/nfosigw-en (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- National Center for Research and Development. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/ncbr-en (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Koponen. K.; Le Net, E. Towards robust renewable energy investment decisions at the territorial level. Appl. Energy 2021, 287, 116552. [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, G.; Więcka, A.; Kowalak, T.; Tokarczyk, P.; Gręda, D. OZE i magazyny ciepła w miejskich systemach ciepłowniczych. Analiza kosztów i możliwości przeciwdziałania wzrostom cen ciepła/ RES and heat storage in district heating systems. Analysis of costs and options for counteracting heat price increases. Energetyka Cieplna i Zawodowa 2019, 5, 102–110. (In Polish).
- Leśniak , A. Światowy rynek ogniw paliwowych/ The global fuel cell market. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 2020, 96(4), 197-202. [CrossRef]
- Żyjewska, U. Rodzaje ogniw paliwowych i ich potencjalne kierunki wykorzystania/ Types of fuel cells and their potential fields of application. Nafta–Gaz 2020, 5, 332–339. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskowska-Wasiak, J. Doświadczenia i perspektywy procesu Power to Gas/ Experiences and perspectives of the Power to Gas process. Nafta–Gaz 2017, 8, 332–339. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; William Miller, W.; Sheaffer, P.; Tutterow, V.; Rapp, V. Opportunities for installed combined heat and power (CHP) to increase grid. Energy Policy 2021, 157, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belik, B.; Dreissigacker, V.; Zunft, S. Power-to-heat integration in regenerator storage: Enhancing thermal storage capacity and performance. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polska Strategia Wodorowa do Roku 2030 z Perspektywą do Roku 2040/Polish Hydrogen Strategy until 2030 with a Perspective until 2040. Ministry of Climate and Environment: Warsaw, Poland. 2021. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WMP20210001138/O/M20211138.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2023). (In Polish).
- Case studies: Steps to achieving 100% renewable energy use: Malmö, Sweden. International Renewable Energy Agency IRENA 2018. Available online: https://www.irena.org//media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2018/Dec/IRENA_Cities_2018e_ Malm.pdf?la=en&hash=15AAEB18677CA4C7575A1D86F75E9BA6C941661A (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Talarek, K.; Knitter-Piątkowska, A.; Garbowski, T. Wind Parks in Poland—New Challenges and Perspectives. Energies 2022, 15, 7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- alarek, K.; Garbowski, T. OZE przyszłością ciepłownictwa systemowego/ RES as the future of district heating. Przegląd Budowlany 2023, 3-4, 66-75 (In Polish). -4.
- Ustawa z Dnia 9 marca 2023 r. o zmianie ustawy o inwestycjach w zakresie elektrowni wiatrowych oraz niektórych innych ustaw/Act of 9 March 2023 on on amending the Act on investments in wind power plants and certain other acts. 2023. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20230000553 (accessed on 18 May 2023). (In Polish).

| Type | Reservoir | Reservoir in a soil excavation |
Ground battery | Battery in an aquifer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English name and abbreviation used |
Tank thermal energy storage (TTES) | Pit thermal energy storage (PTES) | Borehole thermal energy storage (BTES) | Aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES) |
| Storage potential kWh/m3 | 60–80 | 30–80 | 15–30 | 30–40 |
| Characteristics | Ground or semi-underground water reservoir | A water reservoir formed in a pit dug in the ground filled with water or water and gravel | Storage of heat in the ground by supplying and receiving heat through boreholes | Heat storage in aquifers, access via two wells |
| Tasks | 2002 | 2019 | 2020 | Dynamics 2020/02 (%) | Dynamics 2020/19 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of licensed heating companies |
894 | 396 | 387 | 43.29 | 97.73 |
| Number of enterprises participating in the survey |
849 | 404 | 399 | 47 | 98.76 |
| Installed capacity (MW) | 70,953.80 | 53,560.80 | 53,271.10 | 75.08 | 99.46 |
| Power ordered (MW) | 38,937.00 | 34,408.00 | 34,665.54 | 89.03 | 100.75 |
| Network length (km) 1 | 17,312.50 | 21,701.20 | 22,123.11 | 127.79 | 101.94 |
| Employment in full-time jobs | 60,239.00 | 29037 | 28737 | 47.70 | 98.97 |
| Total heat sales (TJ) | 469,355.50 | 344,712.64 | 343,690.65 | 73.23 | 99.70 |
| Heat transferred to the grid (TJ) | 336,043.00 | 258,909.40 | 257,377.29 | 76.59 | 99.41 |
| Share (%) | Local government units (%) | Joint-stock companies (%) |
Limited liability companies (%) | Housing companies (%) |
State-owned enterprises (%) |
Other companies (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 9 | 26.1 | 54.4 | 2.7 | 3.4 | 4.4 |
| 2020 | 0.8 | 18 | 77.4 | 77.4 | 0 | 2.8 |
| Energy carrier | Commercial Power Industry (%) |
Production and distribution companies (%) |
Other heat producing companies (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 2019 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2020 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Energetic hard coal | 2019 | 51.1 | 73.09 | 4.68 |
| 2020 | 49.15 | 71.2 | 4.33 | |
| Coking coal | 2019 | - | - | 11.55 |
| 2020 | - | - | 10.38 | |
| Hard coal briquettes | 2019 | - | - | - |
| 2020 | - | - | - | |
| Lignite | 2019 | 33.6 | 0.08 | 0.03 |
| 2020 | 33.39 | 0.07 | 0.02 | |
| Lignite briquette | 2019 | - | - | - |
| 2020 | - | - | - | |
| Coke and semi-coke | 2019 | - | 0.01 | 0.29 |
| 2020 | - | 0.01 | 0.32 | |
| Firewood | 2019 | 2 | 4.23 | 0.75 |
| 2020 | 2.26 | 4.71 | 0.82 | |
| Petroleum and gasoline |
2019 | - | - | 40.45 |
| 2020 | - | - | 39.07 | |
| Light fuel oil | 2019 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| 2020 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.16 | |
| Light fuel oil | 2019 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.96 |
| 2020 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 1 | |
| Diesel and (ON I) | 2019 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 1.18 |
| 2020 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 1.06 | |
| Other diesel oils | 2019 | - | - | 0.01 |
| 2020 | - | - | 0.12 | |
| Petrol engine fuels (excl. aviation) | 2019 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.3 |
| 2020 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.2 | |
| Aviation fuels | 2019 | - | - | - |
| 2020 | - | - | - | |
| Jet fuel | 2019 | - | - | - |
| 2020 | - | - | - | |
| Liquefied gas | 2019 | - | - | 0.19 |
| 2020 | - | - | 0.2 | |
| High-methane natural gas |
2019 | 2.03 | 4.43 | 10.57 |
| 2020 | 3.23 | 5.13 | 11.05 | |
| Nitrogen-rich natural gas |
2019 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 2.21 |
| 2020 | 1.48 | 0.31 | 2.21 | |
| Gas from minemethane drainage | 2019 | 0.24 | 0.93 | 0.08 |
| 2020 | 0.28 | 0.76 | 0.1 | |
| Dry post-refinery gas | 2019 | - | - | 1.96 |
| 2020 | - | - | 1.88 | |
| Coke gas | 2019 | 0.71 | 0.95 | 1.68 |
| 2020 | 0.5 | 0.94 | 1.55 | |
| Blast furnace gas | 2019 | 1.18 | 0.01 | - |
| 2020 | 1.04 | 0.02 | - | |
| Heat in steam and hot water | 2019 | 1.27 | 10.42 | 8.88 |
| 2020 | 1.34 | 10.5 | 8.96 | |
| Electricity | 2019 | 4.44 | 3.14 | 5.82 |
| 2020 | 4.85 | 3.08 | 5.72 | |
| Waste fuel | 2019 | 0.1 | 0.36 | 2.04 |
| 2020 | 0.11 | 0.45 | 4.03 | |
| Biogas | 2019 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.18 |
| 2020 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0.18 | |
| Semi-processed crude oil | 2019 | - | - | 0.97 |
| 2020 | - | - | 1.26 | |
| Other products | 2019 | 1.15 | 1.6 | 5.06 |
| 2020 | 1.55 | 2.36 | 5.31 |
| Fuel | Total (GJ) |
Fuel consumption in cogeneration (GJ) |
Heat (%) |
Heat in cogeneration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 285,345,066.45 | 201,428,781.97 | 67.72 | 62.42 |
| Lignite | 4,916,154.41 | 4,347,275.31 | 1.17 | 1.35 |
| Light fuel oil | 1,226,226.07 | 1,070,092.40 | 0.29 | 0.33 |
| Heavy fuel oil | 18,996,757.45 | 18,978,012.08 | 4.51 | 5.88 |
| High-methane natural gas |
36,257,839.32 | 29,113,523.84 | 8.60 | 9.02 |
| Nitrogen-rich natural gas |
8,425,678.24 | 8,048,812.44 | 2.00 | 2.49 |
| Biomass | 41,548,379.86 | 36,921,746.47 | 9.86 | 11.44 |
| Biogas | 175,368.53 | 175,368.53 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Other renewable energy sources | 721,500.30 | 0.0 | 0.17 | 0.0 |
| Solid municipal waste | 7,762,979.37 | 7,761,746.17 | 1.84 | 2.41 |
| Non-renewable industrial waste | 1,207,719.95 | 1,207,719.95 | 0.29 | 0.37 |
| Other fuels | 14,794,759.45 | 13,653,837.21 | 3.51 | 4.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





