1. INTRODUCTION
Among biomaterials, chitosan has emerged as a promising candidate for various biomedical applications, due to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, and bioactivity. The use of chitosan in textiles have been widely investigated by many researches, being antimicrobial, water absorption and tensile properties some of the most important properties to study [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide that is composed of randomly distributed β-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units [
6]. The complexity of chitosan chemistry is influenced by various factors, which comprise the degree of deacetylation, molecular weight, and solution pH. The degree of deacetylation is the proportion of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units that have been transformed into D-glucosamine units. This factor significantly impacts the solubility, reactivity, and charge density of chitosan [
7].One of the most intriguing properties of chitosan is its antibacterial activity. However, there is still a need to enhance its antibacterial properties to further broaden its potential applications, and is a commonly studied topic among researchers [
8,
9,
10,
11].
In the past, have been studied different compounds that can act synergistically with chitosan to create a more potent antibacterial agent, and also offer the potential for a wider spectrum of antibacterial activity against different types of bacteria, such as silver nanoparticles [
10,
12], essential oils [
13,
14], quaternary salts [
15] and plant extracts [
16], ursolic acid [
17] among others. Ursolic acid and chitosan adducts have been relatively less studied, especially chitosan fibres and ursolic acid compounds.
Ursolic acid is a pentacyclic triterpene acid that is commonly found in various traditional medicinal plants, fruits, and ornamental species. It is known to exhibit a broad range of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, hypoglycemic, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties. The compound has been extensively studied for its antibacterial effects, as have other pentacyclic triterpenes and their derivatives.
In addition to its potential therapeutic applications, ursolic acid has also been found to prevent abdominal adiposity and exhibit cytotoxic activities, as well as antiprotozoal effects against Plasmodium falciparum [
18,
19,
20].
The aim of this work was to investigate the effect on the chemical structure and antibacterial activity of chitosan fibres of different immersion times in ursolic acid solution. The ultimate goal was to develop chitosan fibres with enhanced antibacterial properties with potential applications as antibacterial biomaterials.
2. EXPERIMENTAL
In this section is shown the procedure to modify the surface of chitosan fibres with ursolic acid by wet impregnation method.
2.1. Reagents and materials
- -
Deionized water
- -
2-propanol (C3H8O) 99% Pure P.A. commercial product of Eurochem BGD.
- -
Ursolic acid (C30H48O3) ≥ 98% Pure P.A. commercial product of Pol-Aura.
- -
Chitosan fibres, concentration 7%, prepared at the Institute of Materials Science of Textiles and Polymer Composites, Lodz University of Technology from chitosan powder commercial product of Sigma-Aldrich; molecular weight 60 kDa; degree of deacetylation (DDA) 96%.
2.2. Fiber impregnation procedure.
A solution of ursolic was prepared by dissolving ursolic acid in pure 2-propanol at a concentration of 64 μg mL-1. In order to get the chitosan fibres ready for the impregnation process, five separate specimens of chitosan fibres were cut to the same weight of 1.0g each. After that, each specimen was then immersed individually in 100 cm3 of ursolic acid solution at room temperature for varying immersion times of 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours respectively. After each immersion period, the specimens were carefully removed from the ursolic acid solution and rinsed with an aqueous solution of ethanol and distilled water 4:6 (v/v) to remove any excess of ursolic acid solution and then dried at room temperature. This process was repeated for each of the five specimens.
The resulting samples were further characterized and evaluated for their physical, chemical, properties. FTIR and SEM analyses were conducted to investigate the structure and morphology of the chitosan fibres after the wet impregnation. Additionally, an antibacterial activity test was performed to evaluate the effectiveness of the wet impregnation method using ursolic acid as an antibacterial enhancer agent.
3. CHARACTERIZATION OF FIBRES AND RESULTS
3.1. FTIR spectroscopy
The infrared transmission and reflectance spectra were recorded in the range from 4000 to 600 cm-1 with a resolution 4 cm-1 and 32 scans.
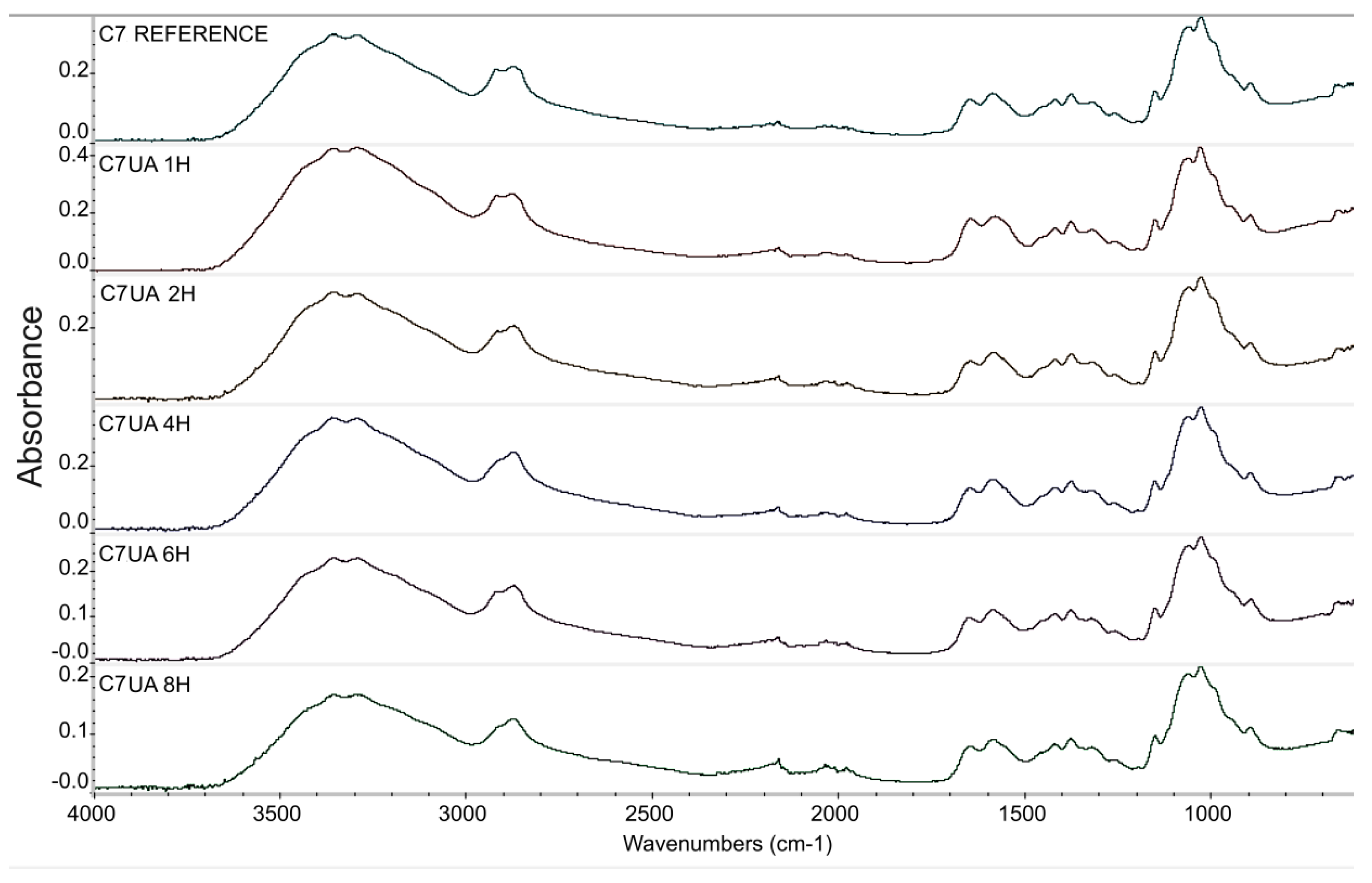
Figure 1.
Infrared spectroscopy spectra graph, fibres samples 7% chitosan reference, 7% chitosan with ursolic acid impregnated 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours.
Figure 1.
Infrared spectroscopy spectra graph, fibres samples 7% chitosan reference, 7% chitosan with ursolic acid impregnated 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours.
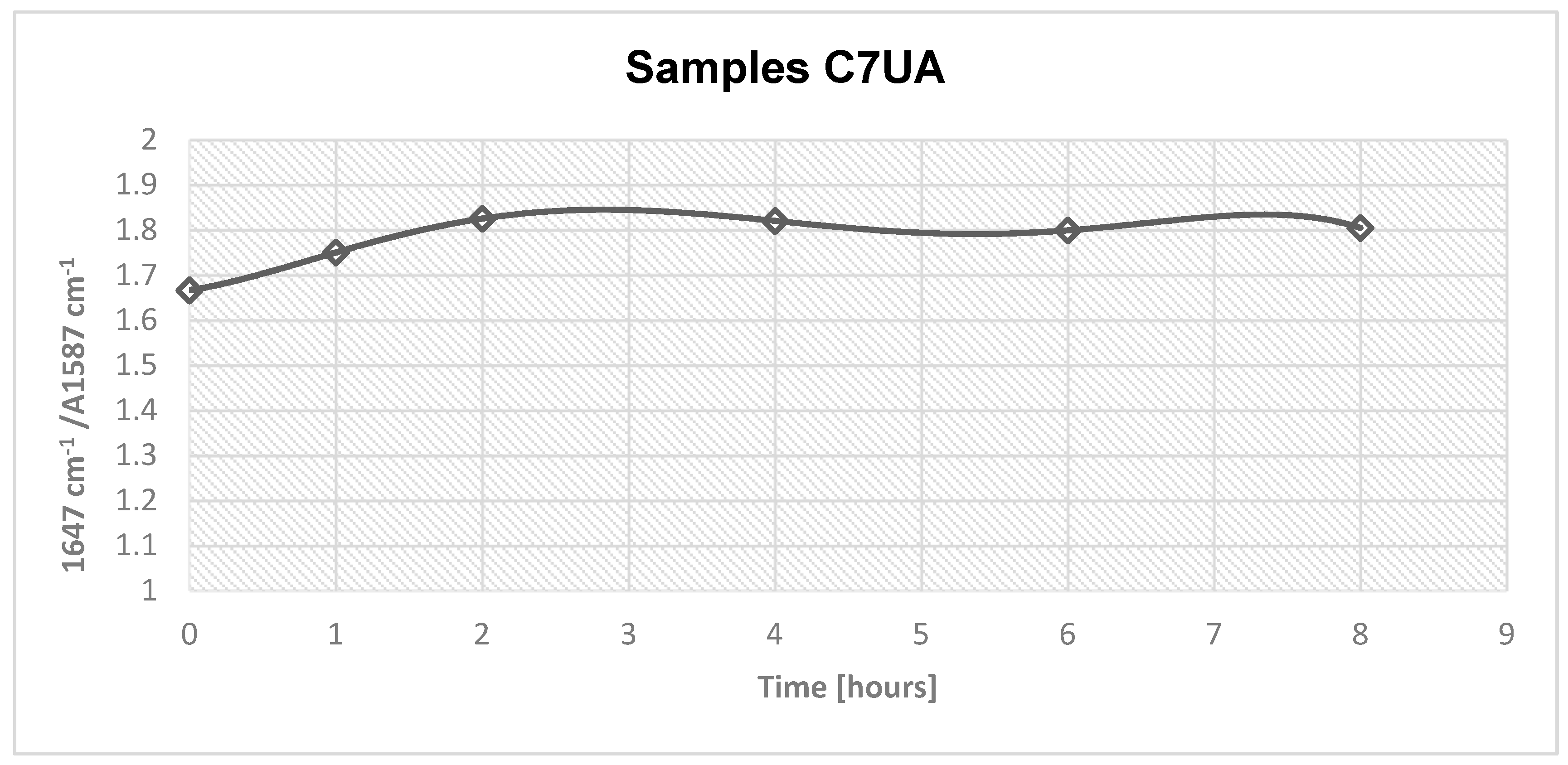
Figure 2.
Absorbance area, amide/amine ratio for samples C7UA 0, 1, 2, 4, 6 and 8 hours.
Figure 2.
Absorbance area, amide/amine ratio for samples C7UA 0, 1, 2, 4, 6 and 8 hours.
The FTIR results of the samples C7UA immersed in ursolic acid for different time set points (0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours) showed an increasing absorbance ratio from 1.66 to 1.82 over the course of 2 hours. This suggests that there was an ongoing chemical reaction between chitosan and ursolic acid during this time, resulting in changes to the chemical structure of the sample. However, after 2 hours, the absorbance ratio remained relatively constant, suggesting that the reaction had reached completion and that the chemical structure of the sample remained stable. The peaks observed at 1647 cm-1 and 1587 cm-1 are attributed to the amide and amine groups in chitosan, respectively. The appearance of these peaks in the FTIR spectra indicates that the chitosan fibres-ursolic acid adduct was formed through the interaction of the amine groups in chitosan with the carboxylic acid groups in ursolic acid. Following their surface morphology was analyzed.
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscope images
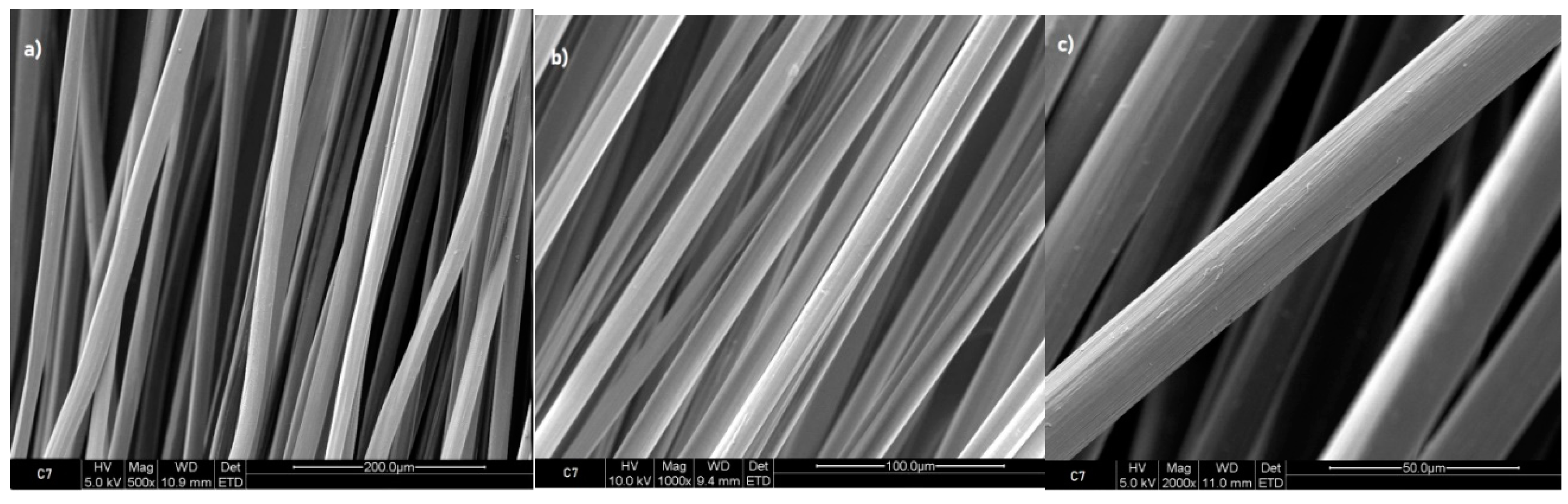
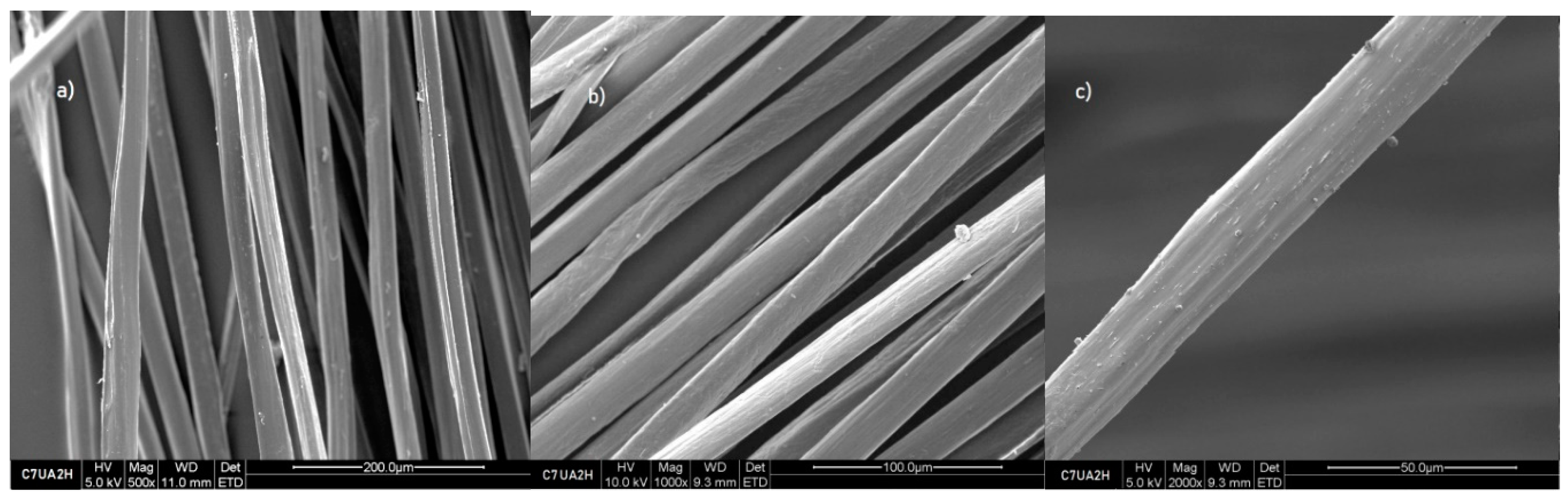
The surface structure of the obtained fibres was analyzed using microscopy obtained by means Scanning electron microscope Nova Nanosem 230.
When compared to the surface of the reference sample of 7% chitosan (
Figure 3), which did not undergo any treatment with ursolic acid, the images on
Figure 4 demonstrate that the surface of sample of 7% chitosan with ursolic acid impregnated 2 hours is slightly rougher. This indicates that the impregnation process have successfully modified the surface of the fibres. The photos that were obtained from the samples that were taken after 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours of immersion exhibited a similarity to the images from the sample that was immersed for only 2 hours.
3.3. UV-Vis spectroscopy
The UV-Vis spectra were obtained by means of UV-Vis from Jasco Company, model V-670, the scan range used was from 190 to 400 nm. Resolution 1 nm. Standard stock solutions containing ursolic acid were prepared in methanol at final concentration of 2.7mg/10mL. After that, serial standard dilutions at three concentrations were analyzed by means UV-Vis, and linearity was verified by regression analysis. Calibration results are presented in
Figure 5, and
Table 1.
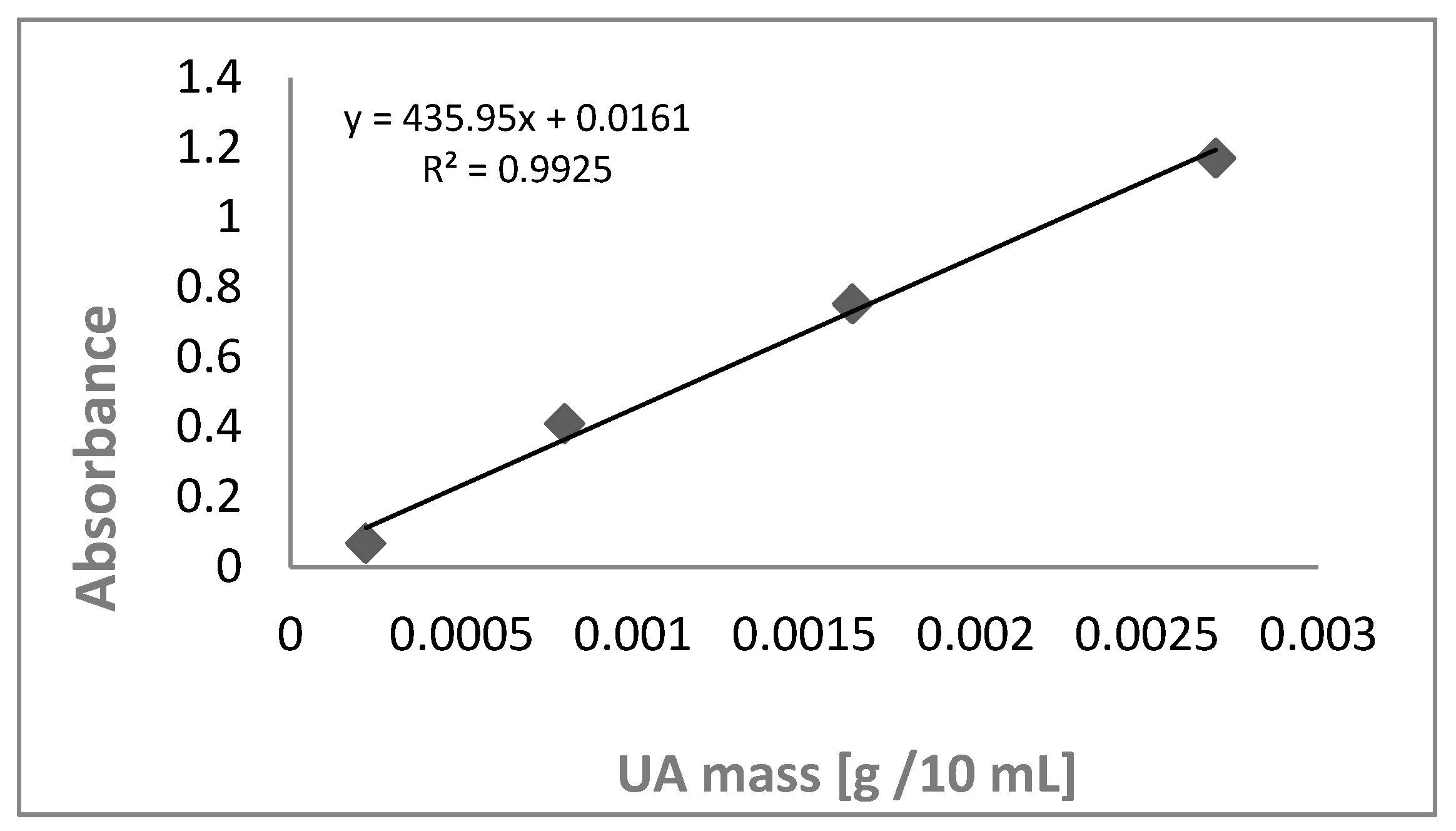
Figure 5.
Calibration graph, relationship absorbance/UA concentration 0.0220 mg mL-1, 0.080 mg mL-1, 0.164 mg mL-1 and 0.270 mg mL-1 .
Figure 5.
Calibration graph, relationship absorbance/UA concentration 0.0220 mg mL-1, 0.080 mg mL-1, 0.164 mg mL-1 and 0.270 mg mL-1 .
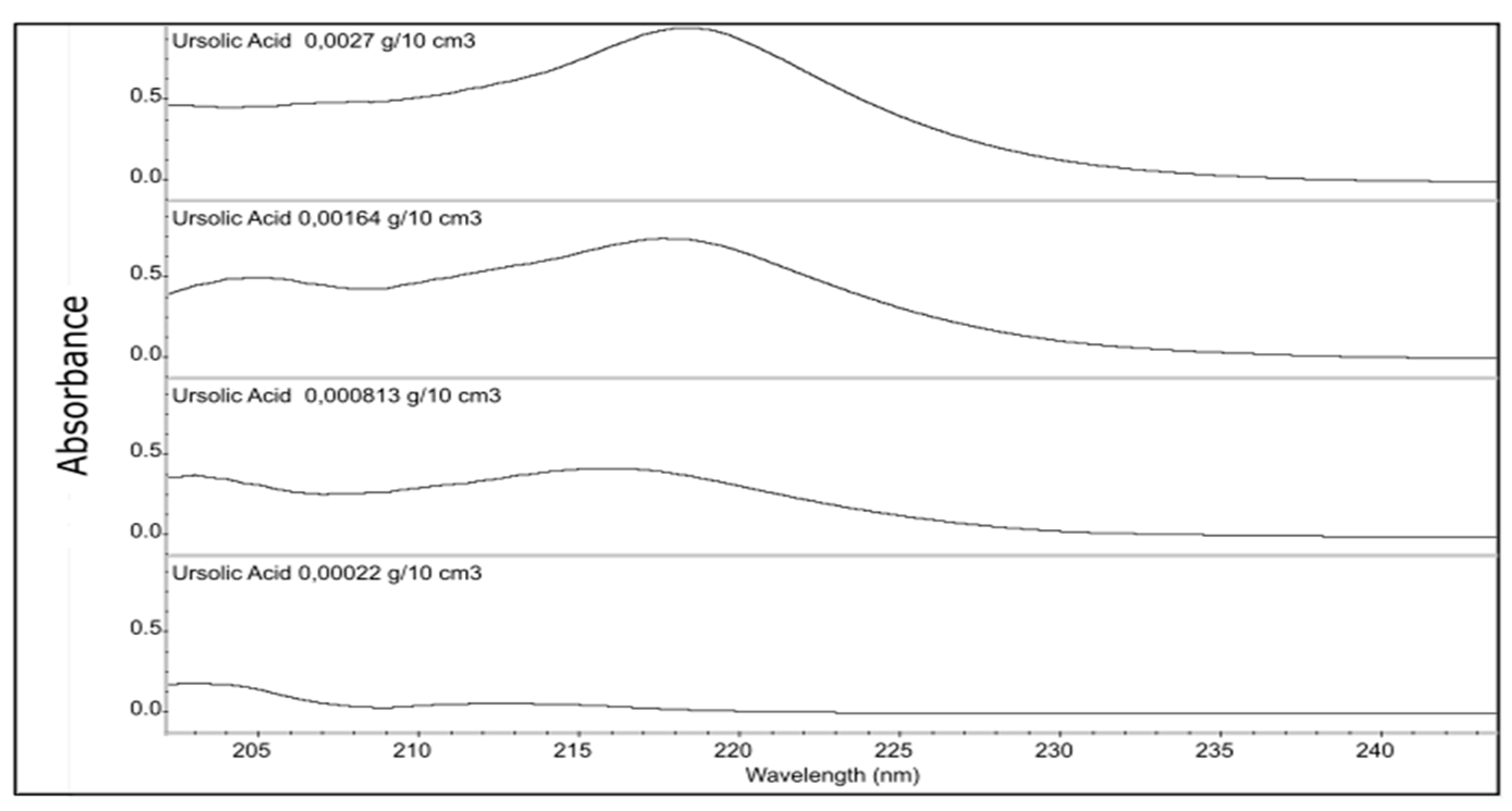
Figure 6.
UV Absorption spectra of methanolic solutions of ursolic acid analyzed at different concentrations.
Figure 6.
UV Absorption spectra of methanolic solutions of ursolic acid analyzed at different concentrations.
The resulting spectra were analyzed at specific wavelengths to detect the distinctive peaks associated with ursolic acid. Previous research studies have reported the UV spectra of ursolic acid, which display absorbance peaks between 210 nm and 220 nm [
21,
22]. The resulting absorbance values were obtained in ascending order and corresponded to increasing concentrations, with values of 214 nm, 216 nm, 217 nm, and 218 nm. After conducting the linear analysis, a stock fiber suspension was prepared with methanol at a concentration of 2.3 mg/10mL from the sample of fibres that was impregnated with ursolic acid for 2 hours. By adding the fibres into methanol, it was possible to dissolve the ursolic acid deposited on the surface of the fibres in order to perform the UV-Vis test. This sample was chosen based on the FTIR test results indicating completion of the reaction at that time set point. UV spectra were performed and the absorbance peak height was appointed at 213 nm and absorbance was 0,056 and based on the linear model, the mass of ursolic acid deposited on the fibres per gram was calculated as follows.
Where,
mUAf =Mass of ursolic acid on the surface of the fibres
y= absorbance at UV spectrum
x= concentration [mg/ml]
This process was repeated for all samples 7% chitosan with ursolic acid that were wet impregnated for 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours. Subsequently, the mass calculation of ursolic acid per gram of chitosan fibres was performed based on the knowledge that 0.091 mg of ursolic acid are present in 2.3 mg of fibres.
Table 2.
Mass per gram of ursolic acid in chitosan fibres.
Table 2.
Mass per gram of ursolic acid in chitosan fibres.
| C7UA |
Mass of UA/g in chitosan fibres |
| 2 hours |
0.039 |
| 4 hours |
0.038 |
| 6 hours |
0.040 |
| 8 hours |
0.038 |
3.4. Antibacterial activity test
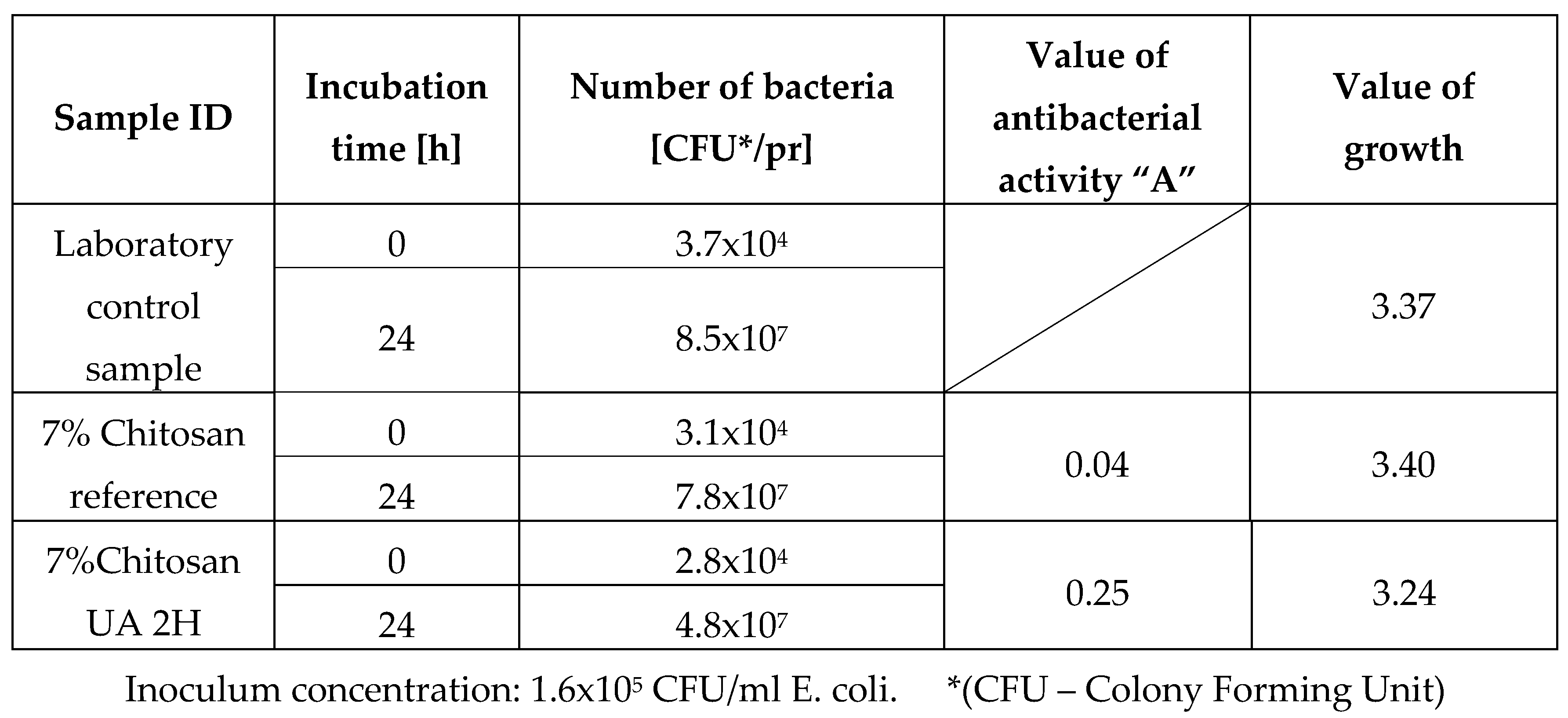
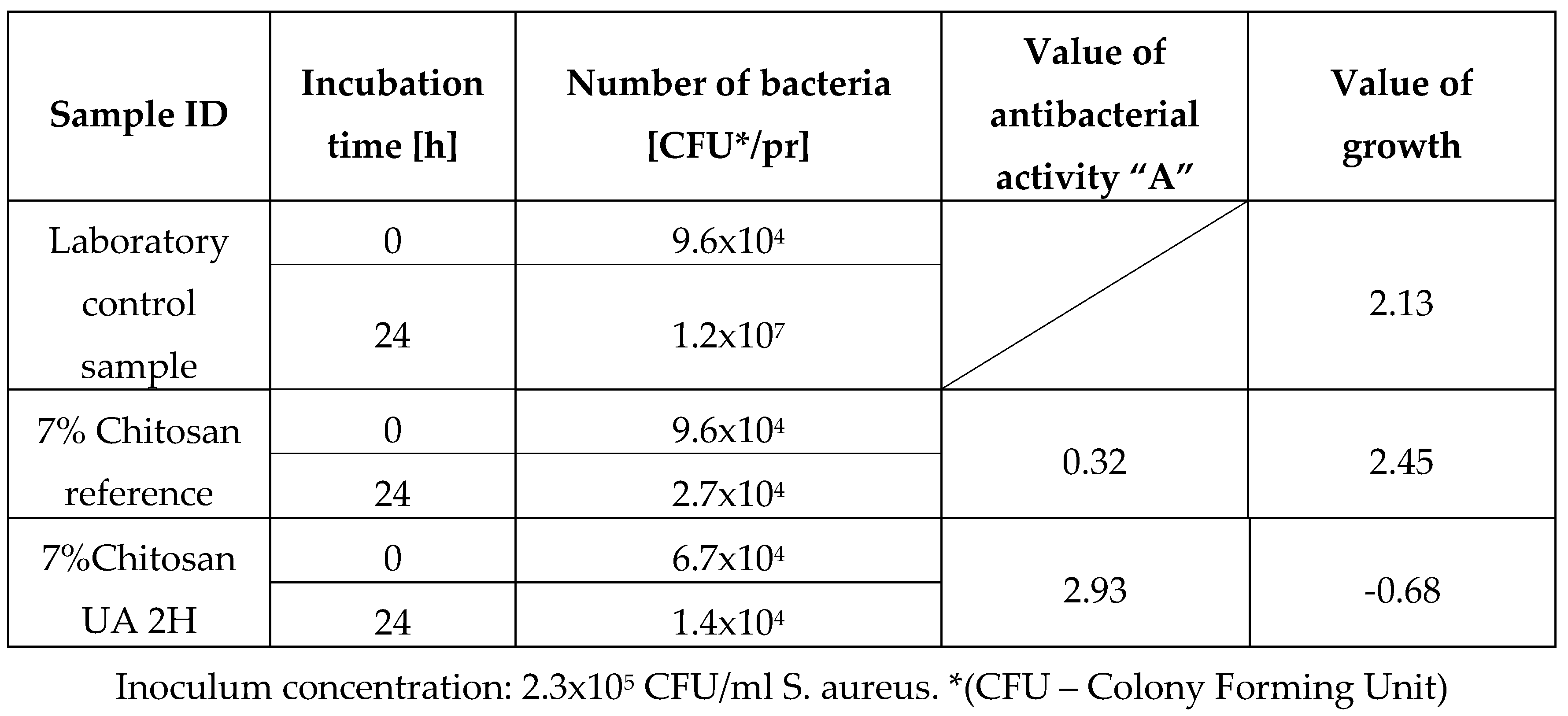
This test was performed by the Laboratory of Biodegradation and Microbiological Research of the Lodz institute of Technology in accordance to the standard PN-EN ISO 20743:2021 2021 – Determination of antibacterial activity of textiles – count plate method.
The antibacterial activity of the samples 7% chitosan reference and 7% chitosan with ursolic acid impregnated 2 hours was tested and the results were later compared.
Table 3.
Antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli ATCC 11 229.
Table 3.
Antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli ATCC 11 229.
Table 4.
Antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538.
Table 4.
Antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538.
Table 5.
Criteria for assessing antibacterial activity.
Table 5.
Criteria for assessing antibacterial activity.
| Efficacy of antibacterial properties |
Value of antibacterial activity |
| low |
A < 2 |
| significant |
2 ≤ A < 3 |
| strong |
A ≥ 3 |
Table 6.
Comparison of antibacterial activity.
Table 6.
Comparison of antibacterial activity.
| Sample ID |
Value of antibacterial activity “A” |
| E. coli |
S. Aureus |
| 7% Chitosan reference |
0.32 |
0.04 |
| Non antibacterial |
Non antibacterial |
| 7%Chitosan UA 2H |
0.25 |
2.93 |
| Non antibacterial |
Significant |
After the antibacterial activity test it was observed that sample 7% chitosan reference, did not exhibit any noteworthy antibacterial activity against either of the two bacterial strains. The obtained value was below the efficacy threshold of A < 2. In contrast, the sample treated two hours with ursolic acid showed a significant and almost strong antibacterial activity with a value of 2.93, indicating that adding ursolic acid improved the antibacterial properties of the fibres. It is important to note that this significant antibacterial activity was only observed against the Gram-positive strain, S. aureus. The fact that the antibacterial activity of the fibres from the sample 7% Chitosan UA 2H was only displaying antibacterial activity against S. aureus and not E. coli is likely due to the difference in bacterial cell wall structure between the two organisms. Gram-positive bacteria, such as S. aureus, have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall that is more susceptible to damage from antibacterial agents, while Gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli, have a thinner peptidoglycan layer and an additional outer membrane that provides extra protection against external agents. Therefore, it is possible that the antibacterial activity of the fibres treated with ursolic acid were not strong enough to overcome the protective mechanisms of E. coli, while it is effective against S. aureus.
4. CONCLUSIONS
Surface modification of chitosan fibres is possible by wet impregnation method with ursolic acid solution. Incorporating ursolic acid on the surface of the fibres can significantly enhance their antibacterial properties, particularly against gram-positive strains, specifically Staphylococcus aureus. The fibres showed good potential for their application in wound dressings or scaffolds with enhanced antibacterial.
References
- Albanna, M. Z.; Bou-Akl, T. H.; Blowytsky, O.; Walters, H. L.; Matthew, H. W. T. Chitosan Fibers with Improved Biological and Mechanical Properties for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 20, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antaby, E.; Klinkhammer, K.; Sabantina, L. Electrospinning of Chitosan for Antibacterial Applications—Current Trends. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(24), 11937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Hu, Q. Super Absorption Behavior of Chitosan by Freeze-Blasting in Different Alkaline Solvents. J. Renew. Mater. 1970, 6(5), 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Lin, Y.; Chen, S.; Shi, S.; Cai, Y.; Li, L.; Peng, X. Superior Strength and Toughness of Graphene/Chitosan Fibers Reinforced by Interfacial Complexation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 194, 108174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, D.; Bauer, M.; Frączyk, J.; Draczyński, Z. Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Modified Chitosan Nonwovens. Polymers 2022, 14(9), 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan: Properties and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31(7), 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M. R. Various Methods for Determination of the Degree of N-Acetylation of Chitin and Chitosan: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57(5), 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabesh, E.; Salimijazi, H.; Kharaziha, M.; Hejazi, M. Antibacterial Chitosan-Copper Nanocomposite Coatings for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5(7, Part 3), 15806–15812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, S. Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan and Its Derivatives and Their Interaction Mechanism with Bacteria: Current State and Perspectives. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 138, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawro, D. Włodzimierz Stęplewski, Marzena Dymel, Serafina Sobczak, *Ewa Skrzetuska, *Michał Puchalski, *Izabella Krucińska. 2012, 20 (6).
- Factors Influencing the Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan and Chitosan Modified by Functionalization - PMC. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8303267/ (accessed 2023-05-12).
- Gadkari, R. R.; Ali, S. W.; Joshi, M.; Rajendran, S.; Das, A.; Alagirusamy, R. Leveraging Antibacterial Efficacy of Silver Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles on Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembled Coated Cotton Fabric. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, F.; Oliva, A.; Sabatino, M.; Imbriano, A.; Hanieh, P. N.; Garzoli, S.; Mastroianni, C. M.; De Angelis, M.; Miele, M. C.; Arnaut, M.; Di Timoteo, F.; Marianecci, C.; Ragno, R.; Carafa, M. Antimicrobial Essential Oil Formulation: Chitosan Coated Nanoemulsions for Nose to Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12(7), 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Lv, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, X. Combined Effect of Cinnamon Essential Oil and Pomegranate Peel Extract on Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Physical Properties of Chitosan Films. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2016, 22(2), 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; shen, D.; Xu, W. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities of Quaternary Ammonium Salt of Chitosan. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 333(1), 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, H.; Jahanshahi, M.; Peyravi, M.; Darzi, G. N. A New Antibacterial Insight of Herbal Chitosan-Based Membranes Using Thyme and Garlic Medicinal Plant Extracts. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GHASEMZADEH, F.; NAJAFPOUR, G. D.; MOHAMMADI, M. Antiinfective Properties of Ursolic Acid-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles against Staphylococcus Aureus. Turk. J. Chem. 2021, 45(5), 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska, K. I.; Grudniak, A. M.; Fiecek, B.; Kraczkiewicz-Dowjat, A.; Kurek, A. Antibacterial Activity of Oleanolic and Ursolic Acids and Their Derivatives. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2010, 5(5), 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, P.; Lemos, T.; Bizerra, A.; Arriaga, Â.; Ferreira, D.; Santiago, G.; Braz-Filho, R.; Costa, J. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Ursolic Acid and Derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19(1), 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, W. R.; de Matos, G. X.; Souza, M. G. M.; Tozatti, M. G.; Andrade e Silva, M. L.; Martins, C. H. G.; da Silva, R.; Da Silva Filho, A. A. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of the Methylene Chloride Extract of Miconia Ligustroides, Isolated Triterpene Acids, and Ursolic Acid Derivatives. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48(2), 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewska, M. Optimization and Validation of an HPLC-UV Method for Analysis of Corosolic, Oleanolic, and Ursolic Acids in Plant Material: Application to Prunus Serotina Ehrh. Acta Chromatogr. 2008, 20(4), 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.-C.; Yang, Y.-C. Extraction Characteristics and Kinetic Studies of Oleanolic and Ursolic Acids from Hedyotis Diffusa under Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).