Submitted:
22 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Lysosomes in cancer
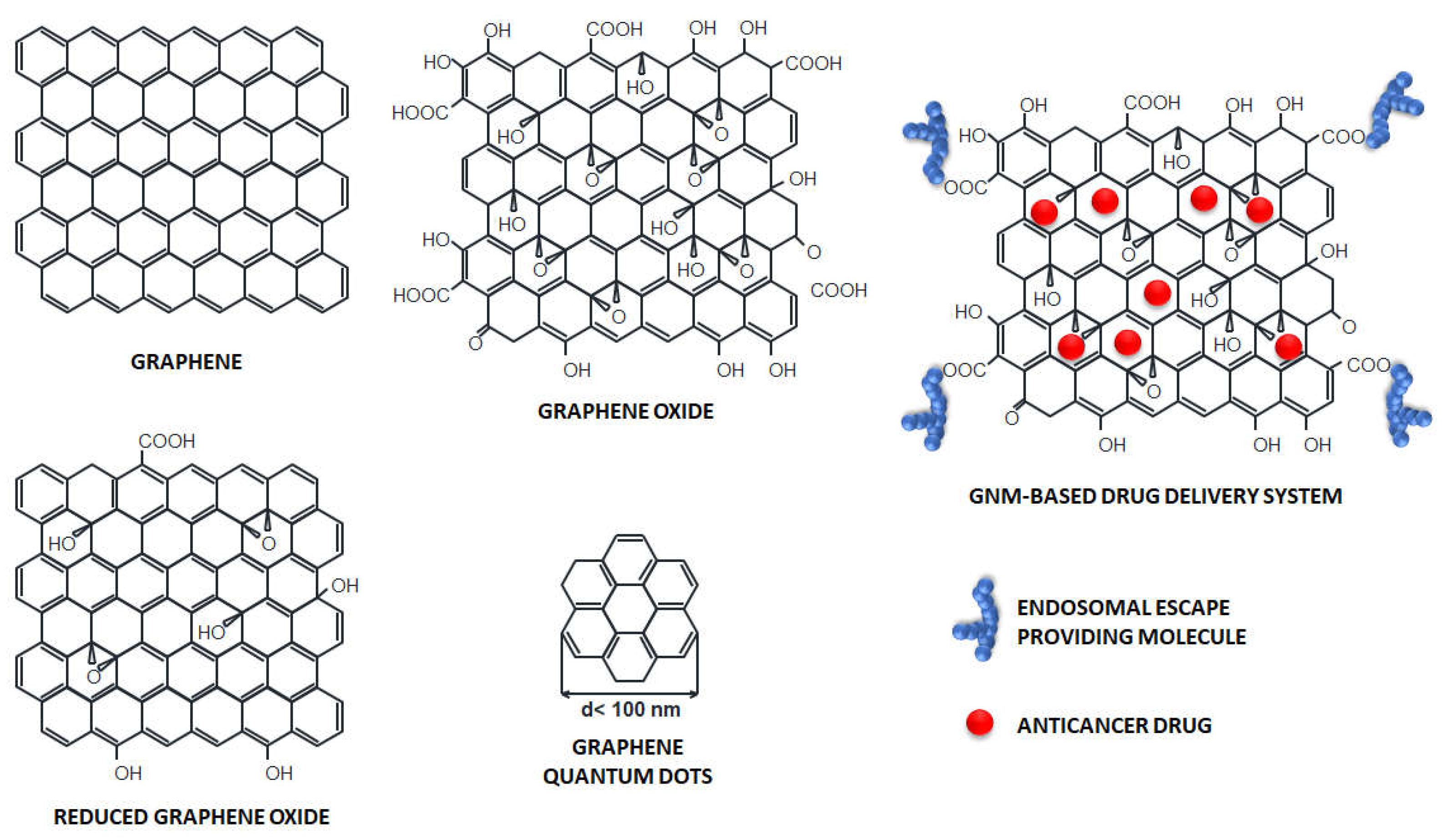
3. Graphene-based nanomaterials in cancer therapy
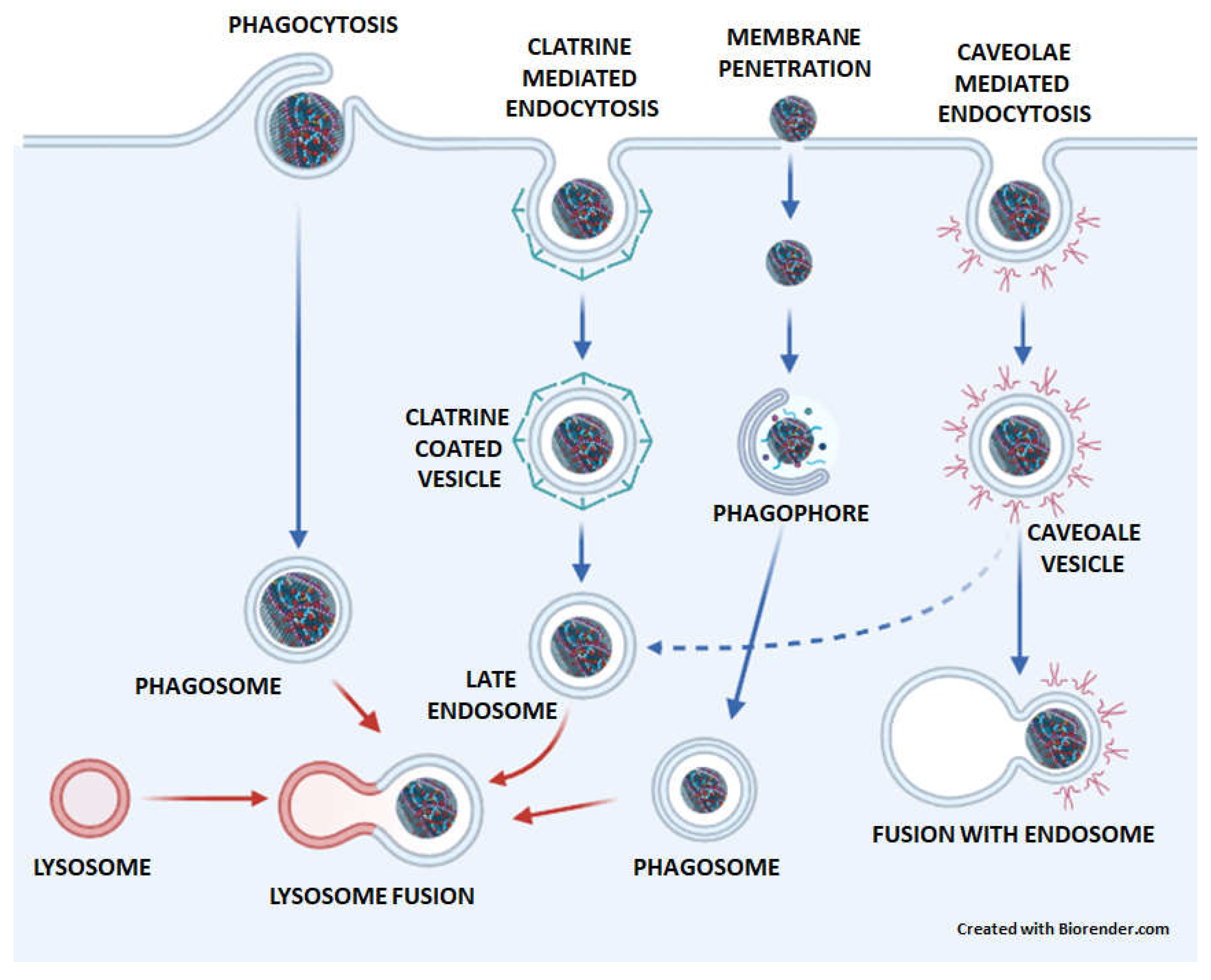
4. The transport of GNMs to lysosomes
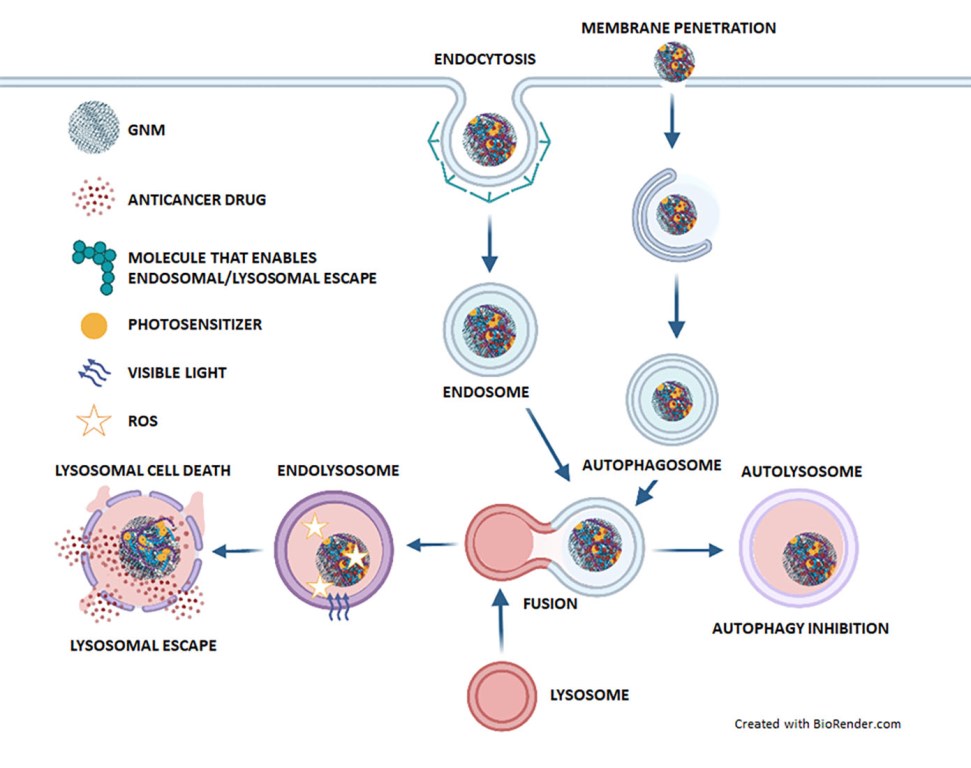
5. The role of lysosomes in GNM-based cancer therapy
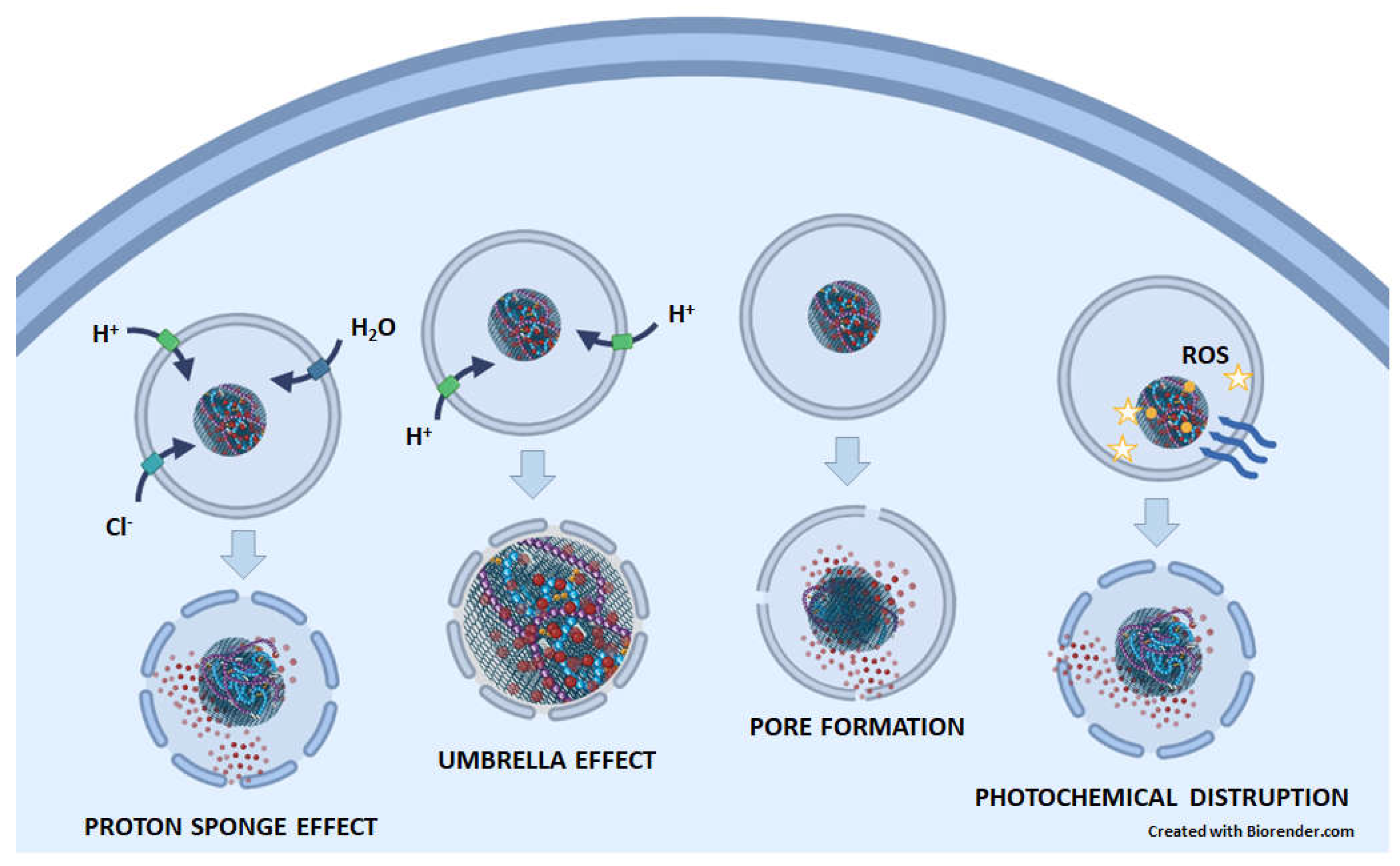
5.1. Lysosomes enable drug release from GNM-containing nanocarriers, whereupon drugs escape from lysosomes
5.2. GNMs induce lysosomal cell death
5.3. GNMs induce tumor cell death by suppressing (auto)lysosomal degradation
5.4. Lysosomes enable detection of cancer cells by the GNMs
6. Conclusions and future perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The global challenge of cancer. Nature cancer 2020, 1, 1–2. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paunovic, V.; Kosic, M.; Misirkic-Marjanovic, M.; Trajkovic, V.; Harhaji-Trajkovic, L. Dual targeting of tumor cell energy metabolism and lysosomes as an anticancer strategy. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular cell research 2021, 1868, 118944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, T. Promising Graphene-Based Nanomaterials and Their Biomedical Applications and Potential Risks: A Comprehensive Review. ACS biomaterials science & engineering 2021, 7, 5363–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampilek, J.; Kralova, K. Advances in Biologically Applicable Graphene-Based 2D Nanomaterials. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linklater, D.P.; Baulin, V.A.; Juodkazis, S.; Ivanova, E.P. Mechano-bactericidal mechanism of graphene nanomaterials. Interface focus 2018, 8, 20170060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M.K.; Thakur, M.; Gurung, R.B.; Srivastava, R. Graphene Quantum Dots for Cell Proliferation, Nucleus Imaging, and Photoluminescent Sensing Applications. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 15858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Tian, S.; Cai, P. Reduced graphene oxide triggered epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 cells. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 15188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoli, F.; Yaqing, Z.; Ruhui, L.; Xuan, L.; Aijie, C.; Yanli, Z.; Chen, H.; Lili, C.; Longquan, S. Graphene oxide disrupted mitochondrial homeostasis through inducing intracellular redox deviation and autophagy-lysosomal network dysfunction in SH-SY5Y cells. Journal of hazardous materials 2021, 416, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Chen, L.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, X.; Shao, L.; Li, Y. Graphene oxide induces p62/SQSTM-dependent apoptosis through the impairment of autophagic flux and lysosomal dysfunction in PC12 cells. Acta biomaterialia 2018, 81, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, X.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, L. The interrupted effect of autophagic flux and lysosomal function induced by graphene oxide in p62-dependent apoptosis of F98 cells. Journal of nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, T.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; et al. Acid-Triggered Charge-Convertible Graphene-Based All-in-One Nanocomplex for Enhanced Genetic Phototherapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Advanced healthcare materials 2020, 9, e1901187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, F.; Ling, D.; Gao, J. Reactive oxygen species and near-infrared light dual-responsive indocyanine green-loaded nanohybrids for overcoming tumour multidrug resistance. European journal of pharmaceutical sciences: official journal of the European Federation for Pharmaceutical Sciences 2019, 134, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanshahi, M.; Kowsari, E.; Haddadi-Asl, V.; Khoobi, M.; Lee, J.H.; Kadumudi, F.B.; Talebian, S.; Kamaly, N.; Mehrali, M. Sericin grafted multifunctional curcumin loaded fluorinated graphene oxide nanomedicines with charge switching properties for effective cancer cell targeting. International journal of pharmaceutics 2019, 572, 118791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, G.; Han, M.; Ling, D.; Gao, J. A tumor targeted near-infrared light-controlled nanocomposite to combat with multidrug resistance of cancer. Journal of controlled release: official journal of the Controlled Release Society 2018, 288, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Ding, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jia, L.; Yu, J.S.; Ju, H. Folate receptor-targeted and cathepsin B-activatable nanoprobe for in situ therapeutic monitoring of photosensitive cell death. Analytical chemistry 2015, 87, 3841–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, C.P.; Sun, J.H.; Zhang, W.; Ji, L.N.; Mao, Z.W. Graphene Oxide Decorated with Ru(II)-Polyethylene Glycol Complex for Lysosome-Targeted Imaging and Photodynamic/Photothermal Therapy. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2017, 9, 6761–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.L.; Rowson-Hodel, A.; Wheeler, M.R.; Hu, M.; Free, S.R.; Carraway, K.L., III. Engaging the Lysosome and Lysosome-Dependent Cell Death in Cancer. In Breast Cancer, Mayrovitz, H.N., Ed.; Exon Publications Copyright: The Authors.; The authors confirm that the materials included in this chapter do not violate copyright laws. Where relevant, appropriate permissions have been obtained from the original copyright holders, and all original sources have been appropriately acknowledged or referenced.: Brisbane (AU), 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Shi, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, C.Y. Graphene-based nanomaterials for cancer therapy and anti-infections. Bioactive materials 2022, 14, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, T.M.; de Oliveira Vieira, T.; Alencar, L.M.R.; Junior, F.F.M.; Gemini-Piperni, S.; Carneiro, S.V.; Fechine, L.; Freire, R.M.; Golokhvast, K.; Metrangolo, P.; et al. Graphene and its derivatives: understanding the main chemical and medicinal chemistry roles for biomedical applications. Journal of nanostructure in chemistry 2022, 12, 693–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, D.; Tong, X.; Mou, X.; Yang, K. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications: A Recent Study. Frontiers in pharmacology 2018, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheriazam, A.; Abad, G.G.Y.; Hajimazdarany, S.; Imani, M.H.; Ziaolhagh, S.; Zandieh, M.A.; Bayanzadeh, S.D.; Mirzaei, S.; Hamblin, M.R.; Entezari, M.; et al. Graphene oxide nanoarchitectures in cancer biology: Nano-modulators of autophagy and apoptosis. Journal of controlled release: official journal of the Controlled Release Society 2023, 354, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Welsher, K.; Robinson, J.T.; Goodwin, A.; Zaric, S.; Dai, H. Nano-Graphene Oxide for Cellular Imaging and Drug Delivery. Nano research 2008, 1, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellier, N.; Baipaywad, P.; Ryu, N.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H. Recent biomedical advancements in graphene oxide- and reduced graphene oxide-based nanocomposite nanocarriers. Biomaterials research 2022, 26, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, B.S.; Jose, G.; Lu, Y.J.; Chen, J.P. Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Versatile Tool for Cancer Therapy. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari Shareena, T.P.; McShan, D.; Dasmahapatra, A.K.; Tchounwou, P.B. A Review on Graphene-Based Nanomaterials in Biomedical Applications and Risks in Environment and Health. Nano-micro letters 2018, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, W.; Sain, M. Carbonaceous Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications as High-Drug Loading Nanocarriers for Sustained Delivery: A Review. Journal of Composites Science 2022, 6, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajani, C.; Borisa, P.; Karanwad, T.; Borade, Y.; Patel, V.; Rajpoot, K.; Tekade, R.K. 7—Cancer-targeted chemotherapy: Emerging role of the folate anchored dendrimer as drug delivery nanocarrier. In Pharmaceutical Applications of Dendrimers; Chauhan, A., Kulhari, H., Eds.; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 151–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. The Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) Effect: The Significance of the Concept and Methods to Enhance Its Application. Journal of personalized medicine 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhai, S.; Chen, Q.; Xing, D. Dihydroartemisinin and transferrin dual-dressed nano-graphene oxide for a pH-triggered chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2015, 62, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahir, Y. Chapter 7—Graphene and Graphene-Based Nanomaterials Are Suitable Vehicles for Drug Delivery. In Applications of Targeted Nano Drugs and Delivery Systems; Mohapatra, S.S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R.K., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier, 2019; pp. 157–189. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Xing, L.; Guo, H.; Luo, C.; Zhang, X. Dual-targeting SERS-encoded graphene oxide nanocarrier for intracellular co-delivery of doxorubicin and 9-aminoacridine with enhanced combination therapy. The Analyst 2021, 146, 6893–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, S.E.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2008, 105, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Eom, H.J.; Choi, J. A systems toxicology approach to the surface functionality control of graphene-cell interactions. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1109–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle-cell interactions. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, K.; Park, J.; Kim, T.I. Effect of pH-Responsive Charge-Conversional Polymer Coating to Cationic Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanostructures for Tumor Microenvironment-Targeted Drug Delivery Systems. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Li, K.; Shi, X.; Gao, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z. Smart pH-responsive nanocarriers based on nano-graphene oxide for combined chemo- and photothermal therapy overcoming drug resistance. Advanced healthcare materials 2014, 3, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, H.; von dem Bussche, A.; Creighton, M.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B.; Gao, H. Graphene microsheets enter cells through spontaneous membrane penetration at edge asperities and corner sites. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2013, 110, 12295–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaksonen, M.; Roux, A. Mechanisms of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2018, 19, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabi, I.R.; Le, P.U. Caveolae/raft-dependent endocytosis. The Journal of cell biology 2003, 161, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Chen, M.; Sartorius, R.; Zarrabi, A.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Dabbagh Moghaddam, F.; Ma, J.; Mattoli, V.; Tay, F.R. Endocytosis of abiotic nanomaterials and nanobiovectors: Inhibition of membrane trafficking. Nano today 2021, 40, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shi, Y.; Qi, T.; Qiu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Q.; Lin, G. Precise design strategies of nanomedicine for improving cancer therapeutic efficacy using subcellular targeting. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2020, 5, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, S.T.; Adiseshaiah, P.P.; Crist, R.M. Autophagy and lysosomal dysfunction as emerging mechanisms of nanomaterial toxicity. Particle and fibre toxicology 2012, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, E.; Mardente, S.; Morgante, E.; Tafani, M.; Lococo, E.; Fico, F.; Valentini, F.; Zicari, A. Graphene Oxide Nanoribbons Induce Autophagic Vacuoles in Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. International journal of molecular sciences 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Miao, H.; Luo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, F.; You, C.; Peng, S.; Tang, G.; Yang, C.; et al. FePt/GO Nanosheets Suppress Proliferation, Enhance Radiosensitization and Induce Autophagy of Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. International journal of biological sciences 2019, 15, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girish, C.M.; Sasidharan, A.; Gowd, G.S.; Nair, S.; Koyakutty, M. Confocal Raman imaging study showing macrophage mediated biodegradation of graphene in vivo. Advanced healthcare materials 2013, 2, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurapati, R.; Mukherjee, S.P.; Martín, C.; Bepete, G.; Vázquez, E.; Pénicaud, A.; Fadeel, B.; Bianco, A. Degradation of Single-Layer and Few-Layer Graphene by Neutrophil Myeloperoxidase. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2018, 57, 11722–11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurapati, R.; Martìn, C.; Palermo, V.; Nishina, Y.; Bianco, A. Biodegradation of graphene materials catalyzed by human eosinophil peroxidase. Faraday discussions 2021, 227, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoli, F.; Yaqing, Z.; Ruhui, L.; Xuan, L.; Aijie, C.; Yanli, Z.; Chen, H.; Lili, C.; Longquan, S. Graphene oxide disrupted mitochondrial homeostasis through inducing intracellular redox deviation and autophagy-lysosomal network dysfunction in SH-SY5Y cells. Journal of hazardous materials 2021, 416, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, A.; Hindré, F.; Vignes-Colombeix, C.; Benoit, J.P.; Garcion, E. The importance of endo-lysosomal escape with lipid nanocapsules for drug subcellular bioavailability. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7542–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, J.M.; Haque, S. Strategies in the design of endosomolytic agents for facilitating endosomal escape in nanoparticles. Biochimie 2019, 160, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.G.; Han, Y.H.; Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.B.; Chen, A.Z. Subcellular Performance of Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy. International journal of nanomedicine 2020, 15, 675–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanares, D.; Ceña, V. Endocytosis: The Nanoparticle and Submicron Nanocompounds Gateway into the Cell. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseenkov, S.; Kuznetsov, V.; Kolesov, B.; Zavorin, A.; Serkova, A.; Zolotarev, N. Design of effective surface contacts on polymer composites modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Express Polymer Letters 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zong, C.; Shen, H.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Z. Tracking the intracellular drug release from graphene oxide using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10591–10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Fu, D.; Liu, Y.; Rui, D.; Yu, D.; Guo, Z.; Cui, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Mao, C. Cancer cell targeting, controlled drug release and intracellular fate of biomimetic membrane-encapsulated drug-loaded nano-graphene oxide nanohybrids. Journal of materials chemistry. B 2018, 6, 5080–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, A.; Mallick, A.; More, P.; Sengupta, P.; Ballav, N.; Basu, S. Cisplatin-induced self-assembly of graphene oxide sheets into spherical nanoparticles for damaging sub-cellular DNA. Chemical communications (Cambridge, England) 2017, 53, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Guan, X.; Tian, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, Y. Single wavelength light-mediated, synergistic bimodal cancer photoablation and amplified photothermal performance by graphene/gold nanostar/photosensitizer theranostics. Acta biomaterialia 2017, 53, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Feng, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Peng, R. Functionalization of graphene oxide generates a unique interface for selective serum protein interactions. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2013, 5, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNay, G.; Eustace, D.; Smith, W.E.; Faulds, K.; Graham, D. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering (SERRS): a review of applications. Applied spectroscopy 2011, 65, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Omar, H.; Tang, N.; Zhang, J.; Nie, Z.; Khashab, N.M. “Two-Step” Raman Imaging Technique To Guide Chemo-Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 2015, 21, 17274–17281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Tian, Y.; Guan, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. “Triple-Punch” Anticancer Strategy Mediated by Near-Infrared Photosensitizer/CpG Oligonucleotides Dual-Dressed and Mitochondria-Targeted Nanographene. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2018, 10, 6942–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nature materials 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, W. Graphene nanosheets damage the lysosomal and mitochondrial membranes and induce the apoptosis of RBL-2H3 cells. The Science of the total environment 2020, 734, 139229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Puebla, A.; Boya, P. Lysosomal membrane permeabilization as a cell death mechanism in cancer cells. Biochemical Society transactions 2018, 46, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, I.; Amano, A.; Mizushima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kamimoto, T.; Nara, A.; Funao, J.; Nakata, M.; Tsuda, K.; et al. Autophagy defends cells against invading group A Streptococcus. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2004, 306, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, T.O.; Fengsrud, M.; Strømhaug, P.E.; Berg, T.; Seglen, P.O. Isolation and characterization of rat liver amphisomes. Evidence for fusion of autophagosomes with both early and late endosomes. The Journal of biological chemistry 1998, 273, 21883–21892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wan, B.; Yang, Y.; Cui, X.; Xin, Y.; Guo, L.H. Cytotoxicity and autophagy induction by graphene quantum dots with different functional groups. Journal of environmental sciences (China) 2019, 77, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y.; Meng, C.L.; Lin, K.C.; Tuan, H.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Chen, C.L.; Li, K.C.; Chiang, C.S.; Hu, Y.C. Graphene oxide as a chemosensitizer: diverted autophagic flux, enhanced nuclear import, elevated necrosis and improved antitumor effects. Biomaterials 2015, 40, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, Z.M.; Ristic, B.Z.; Arsikin, K.M.; Klisic, D.G.; Harhaji-Trajkovic, L.M.; Todorovic-Markovic, B.M.; Kepic, D.P.; Kravic-Stevovic, T.K.; Jovanovic, S.P.; Milenkovic, M.M.; et al. Graphene quantum dots as autophagy-inducing photodynamic agents. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7084–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krunić, M.; Ristić, B.; Bošnjak, M.; Paunović, V.; Tovilović-Kovačević, G.; Zogović, N.; Mirčić, A.; Marković, Z.; Todorović-Marković, B.; Jovanović, S.; et al. Graphene quantum dot antioxidant and proautophagic actions protect SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells from oxidative stress-mediated apoptotic death. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2021, 177, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, B.D.; Mittal, S.; Joshi, P.; Pandey, A.K.; Ramirez-Vick, J.E.; Singh, S.P. Graphene oxide-chloroquine nanoconjugate induce necroptotic death in A549 cancer cells through autophagy modulation. Nanomedicine (London, England) 2018, 13, 2261–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.C.; Lin, M.W.; Hsu, M.N.; Yu-Chen, G.; Chao, Y.C.; Tuan, H.Y.; Chiang, C.S.; Hu, Y.C. Graphene oxide sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapeutics by inducing early autophagy events, promoting nuclear trafficking and necrosis. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.; Harhaji-Trajkovic, L.; Bosnjak, M.; Dakic, I.; Mijatovic, S.; Trajkovic, V. Modulation of Cancer Cell Autophagic Responses by Graphene-Based Nanomaterials: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhong, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, L.W. From the Cover: Potentiation of Drug-Induced Phospholipidosis In Vitro through PEGlyated Graphene Oxide as the Nanocarrier. Toxicological Sciences 2016, 156, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonoyama, T.; Fukuda, R. Drug-induced Phospholipidosis -Pathological Aspects and Its Prediction. Journal of Toxicologic Pathology 2008, 21, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaiab, T.; In, I.; Park, S.Y. Temperature and pH-tunable fluorescence nanoplatform with graphene oxide and BODIPY-conjugated polymer for cell imaging and therapy. Macromolecular rapid communications 2013, 34, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Salvati, A.; Boya, P. Lysosome-dependent cell death and deregulated autophagy induced by amine-modified polystyrene nanoparticles. Open biology 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagala, A.; Fidyt, K.; Bobrowicz, M.; Stachura, J.; Szczygiel, K.; Firczuk, M. Typical and Atypical Inducers of Lysosomal Cell Death: A Promising Anticancer Strategy. International journal of molecular sciences 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Li, P.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, M.; Kuang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D. Optical Visualization of Red-GQDs’ Organelles Distribution and Localization in Living Cells. Frontiers in pharmacology 2022, 13, 932807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Graphene-based DDSs | Cells | Drug detachment mechanism | Escape mechanism | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPCP/miR-21i/ICG | MDA-MB-231 | low pH → charge conversion of PLL-Cit from positive to negative → conformational changes of PAMAM → cleavage ICG/graphene interaction | proton sponge effect | [12] |
| ICG/GPP | MCF-7 | ROS → cleavage of diselenide bond between GO and PAMAM-Poloxamer 188 → ICG release | proton sponge effect | [13] |
| GO/AuNS-PEG/Ce6 | EMT6 | ? | heat and ROS disrupted lysosomal membrane | [58] |
| FPS-Cur | HeLa | hydrolysis of amide links + charge reversion to positive FPS → electrostatic repulsion → structure opening | ? | [14] |
| ICG/DOX/GO-PPF68 | MCF-7/ADR | NIR → ICG → ROS → cleavage of diselenide bond | proton sponge effect | [15] |
| DOX@-GO@AuNR | HeLa | low pH → DOX release | ? | [61] |
| Ag-GO/DOX | Ca Ski | low pH → breakdown of π-π DOX/GO interaction | ? | [55] |
| NGO/DOX@SPC-FA | HeLa | low pH → protonation effect → DOX release | ? | [56] |
| NGO-PEG-DA/DOX | MCF-7 | low pH → DOX protonation → ↑ DOX hydrophilicity/solubility+ electrostatic repulsion with charge reversion to positive NGO-PEG-DA | ? | [37] |
| PK5E7(PEI-rGO) | HeLaA549 | low pH → DOX protonation → electrostatic repulsion with charge reversion to positive PEI-rGO | ? | [36] |
| GPC-NP and GDC-NP | HeLa | low pH → DOX and proflavine release + cleavage of carboxylate bonds and cisplatin release → GO converts from 3D into 2D | ? | [57] |
| GT/IR820/DP-CpG | EMT6 | ? | Destabilization of lysosomal membrane | [62] |
| GNMs/graphene-based DDSs | Cell type | Mechanism of LMP induction | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| GNSs | RBL2H3 | sharp edges and rough surface of GNSs + ↓ mitochondrial electron transport chain → ROS | [12] |
| DSPE-PEG2000-FA + Ce6-Pep + GO | HeLa | light → Ce6 → 1O2 → cathepsin B release | [16] |
| rGO-Ru-PEG | A549 | light → Ru → ROS → cathepsin B release | [17] |
| DHA-GO-Tf | EMT6 | low pH → release of Fe+3 from the Tf → Fe+3 reduced to Fe+2 → Fe+2 + DHA → ROS → lysosomal damage | [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





