Submitted:
21 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Computer Science and Computer Engineering: Professionals with skills in algorithm development, machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision are essential for designing, building, and maintaining AI systems [176].
- Data Science and Analytics: AI systems often rely on large volumes of data. Experts in data science and analytics are needed to preprocess, analyze, and interpret data to generate actionable insights and improve AI models [174].
- Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and Cognitive Science: As AI technologies become more integrated into our daily lives, understanding how humans interact with these systems becomes increasingly important. HCI and cognitive science experts can help design AI systems that are intuitive, user-friendly, and able to adapt to human needs [177].
- Ethics, Philosophy, and Policy: The growing influence of AI technologies raises several ethical and philosophical questions. Experts in these fields are needed to address issues related to fairness, transparency, and accountability, and to develop policies and frameworks that ensure responsible AI development and deployment [171].
- Cybersecurity and Privacy: Protecting sensitive data and maintaining the security of AI systems are critical concerns. Professionals skilled in cryptography, secure multi-party computation, and privacy-preserving machine learning techniques are essential to ensure data privacy and security [178].
- Robotics and Autonomous Systems: As AI-powered robotics and autonomous systems become more prevalent, expertise in areas such as control systems, sensor fusion, and robotics software engineering will be increasingly valuable [179].
3. Results
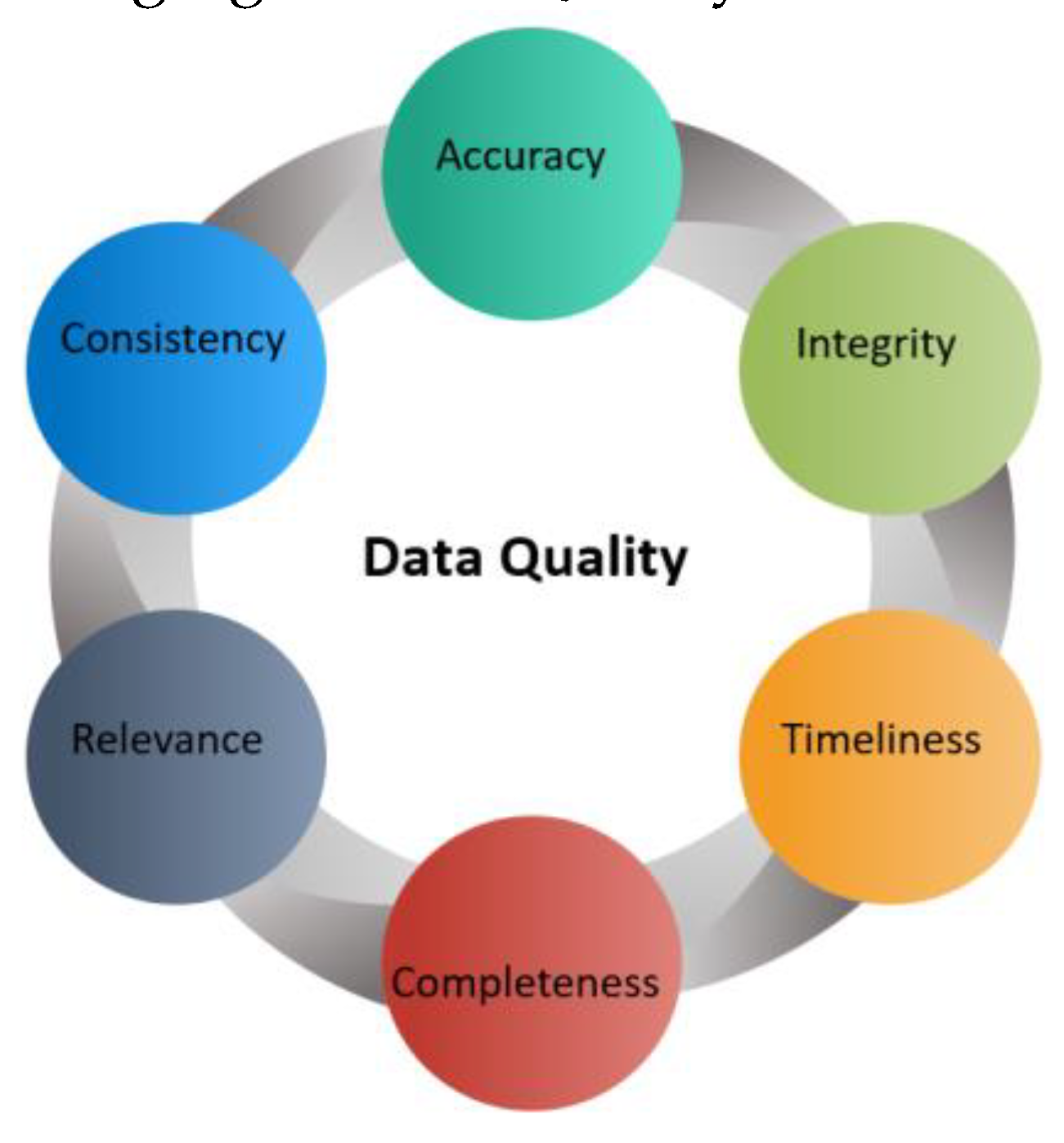
3.1. Dimension of Data Quality and Implication for AI systems
- Accuracy
- Completeness
- Consistency
- Timeliness
- Relevance
- Integrity
3.2. The Role of Data Governance in Ensuring Data Quality
- Quality standards and policies for data must be defined and put into action.
- Throughout the lifecycle of data, it is important to keep a close eye on its quality and maintain control.
- Quality data and holding ourselves accountable should be a culture we strive to create.
- Sharing, integration, and management of data can be enhanced through various means. Optimization of data management techniques should be prioritized. Improved sharing of data is crucial for seamless exchange among different systems. Integration of various data types can be achieved using appropriate methods.
- Regulations and laws must be followed carefully to remain compliant.
3.3. Best Practices to ensure Data Quality for AI:
4. Discussion
4.1. Broader Implications
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Future Research Directions
- Investigate the role of organizational culture, leadership, and technical infrastructure in ensuring data quality for AI systems.
- Conduct empirical research to assess the effectiveness of different data governance practices and data quality management strategies in real-world AI applications.
- Examine the relationship between specific dimensions of data quality and AI performance across different industries and use cases.
- Develop novel AI and machine learning techniques to automatically detect, diagnose, and resolve data quality issues.
- Explore the ethical and legal implications of data quality challenges in AI, particularly in relation to privacy, transparency, and fairness.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russell, S. J. , & Norvig, P. (2016). Artificial intelligence: a modern approach. Pearson Education Limited.
- Lavanya Sharma; Pradeep Kumar Garg, Artificial Intelligence: Technologies, Applications, and Challenges by Publisher: Taylor & Francis, 2021.
- Aguiar-Pérez, Javier M., et al. "Understanding Machine Learning Concepts." Encyclopedia of Data Science and Machine Learning. IGI Global, 2023. 1007-1022.
- Devlin, J. , Chang, M. W., Lee, K., & Toutanova,, K. (2019). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT), 1(1), 4171-4186. [Google Scholar]
- Gumbs, Andrew A., et al. "The advances in computer vision that are enabling more autonomous actions in surgery: a systematic review of the literature." Sensors 22.13 (2022): 4918.
- Enholm, Ida Merete, et al. "Artificial intelligence and business value: A literature review" Information Systems Frontiers 24.5 (2022): 1709-1734.
- Wang, Zeyu, et al. "Business Innovation based on artificial intelligence and Blockchain technology." Information Processing & Management 59.1 (2022): 102759.
- Dahiya, Neelam, Sheifali Gupta, and Sartajvir Singh. "A Review Paper on Machine Learning Applications, Advantages, and Techniques." ECS Transactions 107.1 (2022): 6137.
- Marr, B. (2018). Artificial Intelligence in Practice: How 50 Successful Companies Used AI and Machine Learning to Solve Problems. John Wiley & Sons.
- Géron, A. (2019). Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems. O'Reilly Media, Inc.
- Liu, Xiaofeng, et al. "Deep unsupervised domain adaptation: A review of recent advances and perspectives." APSIPA Transactions on Signal and Information Processing 11.1 (2022).
- Li, Yuxi. "Deep reinforcement learning: An overview arXiv preprint. arXiv:1701.07274 (2017).
- Zhuang, Fuzhen, et al. "A comprehensive survey on transfer learning." Proceedings of the IEEE 109.1 (2020): 43-76.
- Pouyanfar, Samira, et al. "A survey on deep learning: Algorithms, techniques, and applications." ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 51.5 (2018): 1-36.
- Sun, X. , Liu, Y., & Liu, J. (2018). Ensemble learning for multi-source remote sensing data classification based on different feature extraction methods. IEEE Access, 6, 50861-50869.
- Zha, Daochen, et al. "Data-centric Artificial Intelligence: A Survey arXiv preprint. arXiv:2303.10158 (2023).
- Ntoutsi, Eirini, et al. "Bias in data-driven artificial intelligence systems—An introductory survey." Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 10.3 (2020): e1356.
- Jarrahi, Mohammad Hossein, Ali Memariani, and Shion Guha. "The Principles of Data-Centric AI (DCAI) arXiv preprint. arXiv:2211.14611 (2022).
- Zha, Daochen, et al. "Data-centric AI: Perspectives and Challenges arXiv preprint. arXiv:2301.04819 (2023).
- Mazumder, Mark, et al. "Dataperf: Benchmarks for data-centric ai development arXiv preprint. arXiv:2207.10062 (2022).
- Miranda, Lester James. "Towards data-centric machine learning: a short review." ljvmiranda921. github. io (2021).
- Alvarez-Coello, Daniel, et al. "Towards a data-centric architecture in the automotive industry." Procedia Computer Science 181 (2021): 658-663.
- Uddin, Muhammad Fahim, and Navarun Gupta. "Seven V's of Big Data understanding Big Data to extract value." Proceedings of the 2014 zone 1 conference of the American Society for Engineering Education. IEEE, 2014.
- O'Leary, Daniel E. "Artificial intelligence and big data." IEEE intelligent systems 28.2 (2013): 96-99.
- Broo, Didem Gürdür, and Jennifer Schooling. "Towards data-centric decision making for smart infrastructure: Data and its challenges." IFAC-PapersOnLine 53.3 (2020): 90-94.
- Jakubik, Johannes, et al. "Data-centric Artificial Intelligence arXiv preprint. arXiv:2212.11854 (2022).
- Li, Xiao-Hui, et al. "A survey of data-driven and knowledge-aware explainable ai." IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 34.1 (2020): 29-49.
- Ntoutsi, Eirini, et al. "Bias in data-driven artificial intelligence systems—An introductory survey." Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 10.3 (2020): e1356.
- Kanter, James Max, Benjamin Schreck, and Kalyan Veeramachaneni. "Machine Learning 2.0: Engineering Data Driven AI Products arXiv preprint. arXiv:1807.00401 (2018).
- Xu, Ke, et al. "Advanced data collection and analysis in data-driven manufacturing process." Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering 33.1 (2020): 1-21.
- Maranghi, Marianna, et al. "AI-based Data Preparation and Data Analytics in Healthcare: The Case of Diabetes arXiv preprint. arXiv:2206.06182 (2022).
- Bergen, Karianne J., et al. "Machine learning for data-driven discovery in solid Earth geoscience." Science 363.6433 (2019): eaau0323.
- Jöckel, Lisa, and Michael Kläs. "Increasing Trust in Data-Driven Model Validation: A Framework for Probabilistic Augmentation of Images and Meta-data Generation Using Application Scope Characteristics." Computer Safety, Reliability, and Security: 38th International Conference, SAFECOMP 2019, Turku, Finland, September 11–13, 2019, Proceedings 38. Springer International Publishing, 2019.
- Burr, Christopher, and David Leslie. "Ethical assurance: a practical approach to the responsible design, development, and deployment of data-driven technologies." AI and Ethics (2022): 1-26.
- Lomas, James, Nirmal Patel, and Jodi Forlizzi. "Continuous improvement: How systems design can benefit the data-driven design community." (2018).
- Yablonsky, S. "Multidimensional data-driven artificial intelligence innovation." Technology innovation management review 9.12 (2019): 16-28.
- Batista, G. E. , & Monard, M. C. (2018). Data quality in machine learning: A study in the context of imbalanced data. Neurocomputing, 275, 1665-1679.
- Pipino, L. L. , Lee, Y. W., & Wang, R. Y. (2018). Data quality assessment. In Data and Information Quality (pp. 219-253). Springer, Cham.
- Halevy, A. , Korn, F., Noy, N., Olston, C., Polyzotis, N., Roy, S., & Whang, S. (2020). Goods: Organizing Google's datasets. Communications of the ACM, 63(11), 50-57.
- Redman, T. C. (1996). Data quality for the information age. Artech House, Inc.
- Juran, J. M. , & Godfrey, A. B. (2018). Juran's Quality Handbook: The Complete Guide to Performance Excellence. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Yang, Y. , Zheng, L., Zhang, J., Cui, Q., Li, Z., & Yu, P. S. (2018). TI-CNN: Convolutional neural networks for fake news detection arXiv preprint. arXiv:1806.00749.
- Barocas, S., Hardt, M., & Narayanan, A. (2021). Fairness and machine learning. Limitations and Opportunities, 1(1), 1-269.
- Little, R. J. , & Rubin, D. B. (2019). Statistical analysis with missing data. John Wiley & Sons.
- Hassan, N. U., Asghar, M. Z., Ahmed, S., & Zafar, H. (2021). A survey on data quality issues in big data. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 54(1), 1-37.
- Chen, H. , Chiang, R. H., & Storey, V. C. (2012). Business intelligence and analytics: From big data to big impact. MIS Quarterly, 36(4), 1165-1188.
- Gandomi, A. , & Haider, M. (2015). Beyond the hype: Big data concepts, methods, and analytics. International Journal of Information Management, 35(2), 137-144.
- Karkouch, A. , Mousannif, H., Al Moatassime, H., & Noel, T. (2018). Data quality in the Internet of Things: A state-of-the-art survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 124, 289-310.
- Mnih, V. , Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Rusu, A. A., Veness, J., Bellemare, M. G.,... & Petersen, S. (2015). Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 518(7540), 529-533.
- Daries, J. P. , Reich, J., Waldo, J., Young, E. M., Whittinghill, J., Ho, A. D.,... & Chuang, I. (2014). Privacy, anonymity, and big data in the social sciences. Communications of the ACM, 57(9), 56-63.
- García, S. , Luengo, J., & Herrera, F. (2016). Data preprocessing in data mining. Springer.
- Kelleher, J. D. , Mac Namee, B., & D'Arcy, A. (2018). Fundamentals of Machine Learning for Predictive Data Analytics: Algorithms, Worked Examples, and Case Studies. MIT Press.
- Guyon, I., Gunn, S., & Ben-Hur, A. (2004). Result analysis of the NIPS 2003 feature selection challenge. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 17, 545-552.
- Khatri, V., & Brown, C. V. (2010). Designing data governance. Communications of the ACM, 53(1), 148-152.
- Otto, B. (2011). Organizing data quality management in enterprises. Proceedings of the 17th Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS), 1-9.
- Weill, P. , & Ross, J. W. (2004). IT governance: How top performers manage IT decision rights for superior results. Harvard Business Press.
- Tallon, P. P. (2013). Corporate governance of big data: Perspectives on value, risk, and cost. IEEE Computer, 46(6), 32-38.
- Panian, Z. (2010). Some practical experiences in data governance. World Academy of Science, Engineering, and Technology, 66, 1248-1253.
- Laney, D. (2012). Infonomics: The economics of managing, measuring, and monetizing information. Gartner Research.
- Thomas, G. , & Griffin, R. (2015). Data governance: A taxonomy of data quality interventions. International Journal of Information Quality, 4(1), 4-17.
- Begg, C. , & Caira, T. (2013). Data governance: More than just keeping data clean. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 26(6), 595-610.
- Rubin, D. B. (2004). Multiple imputation for nonresponse in surveys. John Wiley & Sons.
- Candès, E. J., & Recht, B. (2009). Exact matrix completion via convex optimization. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 9(6), 717-772.
- Chandrashekar, G. , & Sahin, F. (2018). A survey on feature selection methods. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 66, 31-47.
- Hastie, T. , Tibshirani, R., & Wainwright, M. (2019). Statistical learning with sparsity: the Lasso and generalizations. Chapman and Hall/CRC.
- Wong, S. C. , Gatt, A., Stamatescu, V., & McDonnell, M. D. (2018). Understanding data augmentation for classification: when to warp? In 2018 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
- Cubuk, E. D. , Zoph, B., Mane, D., Vasudevan, V., & Le, Q. V. (2018). Autoaugment: Learning augmentation policies from data arXiv preprint. arXiv:1805.09501.
- Yang, Y., Loog, M., & Hospedales, T. M. (2018). Active Learning by Querying Informative and Representative Examples. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 40(10), 2436- 2450. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. , & Guo, Y. (2019). Adaptive Active Learning for Image Classification. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2019), pp. 7663-7671. [CrossRef]
- Siddiquie, B., & Gupta, A. (2019). Human Effort Estimation for Visual Tasks. International Journal of Computer Vision, 127(8), 1161-1179. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. , Chen, T., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Challenges and countermeasures of big data in artificial intelligence. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1237(3), 032023.
- Zhu, Y. , & Lapata, M. (2020). Learning to attend, copy, and generate for session-based query suggestion. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). [Google Scholar]
- Halevy, A., Norvig, P., & Pereira, F. (2020). The unreasonable effectiveness of data. In IEEE Intelligent Systems, 24(2), 8-12.
- X., Li, Q., Dong, S., & Ye, S. (2021). Storage challenges and solutions in the AI era. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 22(6), 743-767.
- Li, T. , Sahu, A. K., Talwalkar, A., & Smith, V. (2020). Federated learning: Challenges, methods, and future directions. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 37(3), 50-60.
- Wu, Y., Liu, J., He, H., Chen, H., & Chen, J. (2021). Data storage technology in artificial intelligence. IEEE Access, 9, 37864-37881.
- Hutter, F. , Kotthoff, L., & Vanschoren, J. (Eds.). (2019). Automated machine learning: Methods, systems, challenges. Springer Nature.
- Sharma, H. , Park, J. , Mahajan, D., Amaro, E., Kaeli, D., & Kim, Y. (2020). From high-level deep neural models to FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. , Wang, T., Yang, Y., & Zhang, B. (2020). Deep model compression: Distilling knowledge from noisy teachers arXiv preprint. arXiv:1610.09650.
- Ratner, A. , Bach, S., Ehrenberg, H., Fries, J., Wu, S., & Ré, C. (2019). Snorkel: Rapid training data creation with weak supervision. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 11(3), 269-282.
- Zhang, H. , Wu, J., Zhang, Z., & Yang, Q. (2021). Collaborative learning for data privacy and data utility. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering.
- Yang, Q. , Liu, Y., Chen, T., & Tong, Y. (2019). Federated machine learning: Concept and applications. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 10(2), 1-19.
- Kairouz, P. , McMahan, H. B., Avent, B., Bellet, A., Bennis, M., Bhagoji, A. N.,... & Zhang, Y. (2021). Advances and open problems in federated learning. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 14(1-2), 1-210.
- Shi, W. , Cao, J., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., & Xu, L. (2020). Edge computing: Vision and challenges. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 3(5), 637-646.
- Baltrušaitis, T. , Ahuja, C., & Morency, L. P. (2018). Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 41(2), 423-443.
- McMahan, H. B. , Moore, E. , Ramage, D., Hampson, S., & y Arcas, B. A. (2017). Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS). [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, F. , Wiedemann, S., Müller, K. R., & Samek, W. (2019). Robust and communication-efficient federated learning from non-IID data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 31(9), 3400-3413.
- Bagdasaryan, E. , Veit, A. , Hua, Y., Estrin, D., & Shmatikov, V. (2020). How to backdoor federated learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). [Google Scholar]
- Yurochkin, M. , Agarwal, N. , Ghosh, S., Greenewald, K., Hoang, L., & Khazaeni, Y. (2019). Bayesian nonparametric federated learning of neural networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). K. [Google Scholar]
- onečný, J. , McMahan, H. B., Ramage, D., & Richtárik, P. (2016). Federated optimization: Distributed machine learning for on-device intelligence arXiv preprint. arXiv:1610.02527.
- Truex, S. , Baracaldo, N. , Anwar, A., Steinke, T., & Ludwig, H. (2020). A hybrid approach to privacy-preserving federated learning. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security (AISec). [Google Scholar]
- Roman, R. , Lopez, J., & Mambo, M. (2018). Mobile edge computing, Fog et al.: A survey and analysis of security threats and challenges. Future Generation Computer Systems, 78, 680-698.
- Wang, S. , Tuor, T. , Salonidis, T., Leung, K. K., Makaya, C., He, T., & Chan, K. (2019). Adaptive deep learning model selection on embedded systems. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing (SEC). [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A. , Goyal, S., Varma, M., & Jain, P. (2021). Resource-constrained distributed machine learning: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 54(5), 1-34.
- Zhang, Z. , Mao, Y., & Letaief, K. B. (2019). Energy-efficient user association and resource allocation in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 37(5), 1107-1121.
- Zhang, H. , Wu, J., Zhang, Z., & Yang, Q. (2021). Collaborative learning for data privacy and data utility. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering.
- Liang, X., Zhao, J., Shetty, S., Liu, J., & Li, D. (2020). Integrating blockchain for data sharing and collaboration in mobile healthcare applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC).
- Chen, X. , Zhang, W., Wang, X., & Li, T. (2021). Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning for IoT Applications: A Review. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(8), 6078-6093. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. , & Fan, L. (2021). A secure data sharing scheme for cross-border cooperation in the artificial intelligence era. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Carlini, N. , Liu, C., Erlingsson, U., Kos, J., Song, D., & Wicker, M. (2019). The Secret Sharer: Evaluating and Testing Unintended Memorization in Neural Networks. Proceedings of the 28th USENIX Security Symposium, 267-284. Retrieved from https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec19-carlini.pdf.
- Jayaraman, B. , & Evans, D. (2020). Evaluating Membership Inference Attacks in Machine Learning: An Information Theoretic Framework. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 15, 1875-1890. [CrossRef]
- Dwork, C. , Roth, A., & Naor, M. (2018). Differential Privacy: A Survey of Results. In Theory and Applications of Models of Computation (pp. 1-19). Springer. [CrossRef]
- Truex, S., Xu, C., Calandrino, J., & Boneh, D. (2019). The Limitations of Differential Privacy in Practice. Proceedings of the 28th USENIX Security Symposium, 1045-1062.
- Goodfellow, I., Shlens, J., & Szegedy, C. (2022). Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples. Communications of the ACM, 65(1), 56-65. [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N. , & Mian, A. (2018). Threat of Adversarial Attacks on Deep Learning in Computer Vision: A Survey. IEEE Access, 6, 14410-14430. [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, J. , Koh, P. W., & Liang, P. (2018). Certified Defenses Against Adversarial Examples. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations.
- Zhu, M., Yin, H., & Yang, X. (2021). A Comprehensive Survey of Poisoning Attacks in Federated Learning. IEEE Access, 9, 57427-57447. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Zhang, T., Wang, J., & Wang, X. (2020). A Survey of Deep Neural Network Backdoor Attacks and Defenses. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 31(10), 4150-4169. [CrossRef]
- Gu, T. , Dolan-Gavitt, B., & Garg, S. (2019). BadNets: Identifying Vulnerabilities in the Machine Learning Model Supply Chain. Proceedings of the 28th USENIX Security Symposium, 1965-1980.
- Liu, Y., Ma, X., Ateniese, G., & Hsu, W. L. (2018). Trojaning Attack on Neural Networks. Proceedings of the 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 27-41. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y. , Sun, X., Zhang, Y., & Liu, J. (2021). Trojan Attacks on Federated Learning Systems: An Overview. IEEE Network, 35(2), 144-150. [CrossRef]
- Tramèr, F. , et al. (2016). Stealing Machine Learning Models via Prediction APIs. Proceedings of the 25th USENIX Security Symposium, 601-618. Retrieved from https://www.usenix.org/system/files/conference/usenixsecurity16/sec16_paper_tramer.pdf.
- Jagielski, M. , et al. (2020). Model Theft and Out-of-Distribution Detection in Machine Learning. Proceedings of the 2020 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 212-226. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. , Chen, J., Liu, T., & Yang, Y. (2020). Trojan Detection via Fine-Pruning. Proceedings of the 2020 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 1151-1168. [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M. , et al. ( 2016). Deep Learning with Differential Privacy. Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 308–318. [CrossRef]
- Xu, W. , et al. ( 2021). Bridging the Gap Between Input Validation and Trustworthy AI. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, 1395–1412. [CrossRef]
- Bonawitz, K., et al. (2019). Towards Federated Learning at Scale: System Design. Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Systems for ML at Scale, 1-6.
- Rai, S. , et al. (2021). A Survey of Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning Techniques. ACM Computing Surveys, 54(2), 1-42. [CrossRef]
- Madry, A. , et al. ( 2018). Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, 297–306.
- Yuan, X. , et al. (2019). Adversarial Examples: Attacks and Defenses for Deep Learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 30(9), 2805-2824.
- Paudice, A. , et al. (2018). MAMADroid: Detecting Android Malware by Building Markov Chains of Behavioral Models. Proceedings of the 27th USENIX Security Symposium, 1355-1372.
- Chen, Y. , et al. (2020). Data Poisoning Attacks on Machine Learning: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 32(4), 685-706. [CrossRef]
- Polonetsky, J. , & Tene, O. (2018). GDPR and AI: Friends or Foes? IEEE Security & Privacy, 16(3), 26-33. [CrossRef]
- Barocas, S. , Hardt, M., & Narayanan, A. (2019). Fairness and machine learning. FairMLBook.org.
- Dastin, J. (2018). Amazon scraps secret AI recruiting tool that showed bias against women. Reuters.
- Simonite, T. (2018). When it comes to gorillas, Google Photos remains blind. Wired.
- Vincent, J. (2016). Twitter taught Microsoft's AI chatbot to be a racist in less than a day. The Verge.
- Harding, S. (2019). Apple's credit card gender bias draws regulatory scrutiny. Forbes.
- Angwin, J. , Larson, J., Mattu, S., & Kirchner, L. (2016). Machine bias: There's software used across the country to predict future criminals. And it's biased against blacks. ProPublica.
- Olteanu, A. , Castillo, C., Diaz, F., & Kıcıman, E. (2019). Social data: Biases, methodological pitfalls, and ethical boundaries. Frontiers in Big Data Science, 2, 13.
- Sun, T. , Gaut, A., Tang, S., Huang, Y., ElSherief, M., Zhao, J.,... & Wang, W. Y. (2019). Mitigating gender bias in natural language processing: Literature review. Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 1630-1640.
- Torralba, A. , & Efros, A. A. ( 2011). Unbiased look at dataset bias. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1521–1528.
- Zhao, Z. , Wallace, B. C., Jang, E., Choi, Y., & Lease, M. (2021). Combating human trafficking: A survey of AI techniques and opportunities for technology-enabled counter-trafficking. ACM Computing Surveys, 54(1), 1-35.
- Nickerson, R. S. (1998). Confirmation bias: A ubiquitous phenomenon in many guises. Review of General Psychology, 2(2), 175-220.
- Krueger, J. I. , & Funder, D. C. (2004). Towards a balanced social psychology: Causes, consequences, and cures for the problem-seeking approach to social behavior and cognition. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 27(3), 313-327.
- Gupta, P. , & Raghavan, H. (2021). Temporal bias in machine learning arXiv preprint. arXiv:2104.12843.
- Gutierrez, M. , & Serrano-Guerrero, J. (2020). Bias-aware feature selection in machine learning arXiv preprint. arXiv:2007.07956.
- Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, fast and slow. Farrar, Straus, and Giroux.
- Lee, J. D. , & See, K. A. (2004). Trust in automation: Designing for appropriate reliance. Human Factors, 46(1), 50-80.
- Buolamwini, J. , & Gebru, T. (2018). Gender shades: Intersectional accuracy disparities in commercial gender classification. Conference on fairness, accountability and transparency, 77-91.
- Crawford, K. (2021). Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial Intelligence. Yale University Press.
- Wachter, S. , Mittelstadt, B., & Russell, C. (2018). Counterfactual explanations without opening the black box: Automated decisions and the GDPR. Harvard Journal of Law & Technology, 31(2), 841-887.
- Pleiss, G., Raghavan, M., Wu, F., Kleinberg, J., & Weinberger, K. Q. (2020). On fairness and calibration. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33.
- Zhao, J. , Wang, T., Yatskar, M., Ordonez, V., & Chang, K. W. (2019). Gender bias in contextualized word embeddings. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 1, 629-634.
- Bellamy, R. K. E. , Dey, K., Hind, M., Hoffman, S. C., Houde, S., Kannan, K.,... & Nagar, S. (2018). AI Fairness 360: An extensible toolkit for detecting, understanding, and mitigating unwanted algorithmic bias. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 63(4/5), 4-1.
- Verma, S. , & Rubin, J. ( 2018). Fairness definitions explained. Proceedings of the International Workshop on Software Fairness, 1–7.
- Dwork, C., Hardt, M., Pitassi, T., Reingold, O., & Zemel, R. (2012). Fairness through awareness. Proceedings of the 3rd Innovations in Theoretical Computer Science Conference, 214-226.
- Arrieta, A. B., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot, A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., ... & Herrera, F. (2020). Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Information Fusion, 58, 82-115.
- Hao, K. (2020). This is how AI bias really happens—and why it’s so hard to fix. MIT Technology Review.
- Arrieta, A. B. , Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot, A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A.,... & Herrera, F. (2020). Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Information Fusion, 58, 82-115.
- Goodfellow, I. , Bengio, Y., & Courville, A. (2016). Deep learning. MIT press.
- Adadi, A. , & Berrada, M. (2018). Peeking inside the black-box: A survey on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access, 6, 52138-52160.
- Gilpin, L. H. , Bau, D., Yuan, B. Z., Bajwa, A., Specter, M., & Kagal, L. (2018). Explaining explanations: An overview of interpretability of machine learning. In 2018 IEEE 5th International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA) (pp. 80-89). IEEE.
- Bhatt, U., Xiang, A., Sharma, S., Weller, A., Taly, A., Jia, Y., ... & Eckersley, P. (2020). Explainable machine learning in deployment. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (pp. 648-657).
- Wachter, S. , Mittelstadt, B., & Russell, C. (2017). Counterfactual explanations without opening the black box: Automated decisions and the GDPR. Harvard Journal of Law & Technology, 31(2), 841-887.
- Jobin, A., Ienca, M., & Vayena, E. (2019). The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nature Machine Intelligence, 1(9), 389-399.
- Guidotti, R., Monreale, A., Ruggieri, S., Turini, F., Giannotti, F., & Pedreschi, D. (2018). A survey of methods for explaining black box models. ACM computing surveys (CSUR), 51(5), 1-42.
- Rudin, C. (2019). Stop explaining black-box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead. Nature Machine Intelligence, 1(5), 206-215.
- Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., & Guestrin, C. (2016). "Why should I trust you?": Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 1135-1144).
- Lundberg, S. M., & Lee, S. I. (2017). A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 4765-4774).
- Maaten, L. V. D. , & Hinton, G. (2008). Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of machine learning research, 9(11).
- Carter, S. , Armstrong, Z., Schönberger, L., & Olah, C. (2019). Activation atlases: Unsupervised exploration of high-dimensional model internals. Distill, 4(6), e00020.
- Doshi-Velez, F. , & Kim, B. (2017). Towards a rigorous science of interpretable machine learning arXiv preprint . arXiv:1702.08608.
- Holzinger, A. , Langs, G., Denk, H., Zatloukal, K., & Müller, H. (2019). Causability and explainability of artificial intelligence in medicine. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 9(4), e1312.
- Mittelstadt, B., Russell, C., & Wachter, S. (2019). Explaining explanations in AI. In Proceedings of the conference on fairness, accountability, and transparency (pp. 279-288).
- Vinuesa, R., Azizpour, H., Leite, I., Balaam, M., Dignum, V., Domisch, S., ... & Langhans, S. D. (2020). The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nature Communications, 11(1), 233.
- Brown, T. B. , Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P.,... & Agarwal, S. (2020). Language models are few-shot learners arXiv preprint . arXiv:2005.14165.
- Knight, W. (2021). The future of AI depends on a huge workforce of human teachers. Wired.
- Kaplan, A. , & Haenlein, M. (2019). Siri, Siri, in my hand: Who’s the fairest in the land? On the interpretations, illustrations, and implications of artificial intelligence. Business Horizons, 62(1), 15-25.
- Wang, S., Fisch, A., Oh, J., & Liang, P. (2020). Data Programming for Learning with Noisy Labels. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33, 14883-14894.
- Crawford, K., & Calo, R. (2021). There is a blind spot in AI research. Nature, 538(7625), 311-313.
- Mittelstadt, B. , Russell, C., & Wachter, S. (2021). Explaining explanations in AI. Proceedings of the Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency - FAT* '19, 279-288.
- Whittlestone, J. , Nyrup, R., Alexandrova, A., Dihal, K., & Cave, S. (2019). Ethical and societal implications of algorithms, data, and artificial intelligence: a roadmap for research. Nuffield Foundation.
- Bughin, J. , Hazan, E., Ramaswamy, S., Chui, M., Allas, T., Dahlström, P.,... & Trench, M. (2018). Skill shift: Automation and the future of the workforce. McKinsey Global Institute.
- World Economic Forum. (2021). Jobs of Tomorrow:Mapping Opportunity in the New Economy. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Jobs_of_Tomorrow_2020.pdf.
- Bessen, J. E. , Impink, S. M., Reichensperger, L., & Seamans, R. (2019). The Business of AI Startups. NBER Working Paper No. 24255.
- Miller, T. (2019). Explanation in artificial intelligence: Insights from the social sciences. Artificial Intelligence, 267, 1-38.
- Xu, H. , Gu, L., Choi, E., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Secure and privacy-preserving machine learning: A survey. Frontiers of Computer Science, 15(2), 1-38.
- Yang, G. Z., Bellingham, J., Dupont, P. E., Fischer, P., Floridi, L., Full, R., ... & Wood, R. (2020). The grand challenges of Science Robotics. Science Robotics, 3(14), eaar7650.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




