1. Introduction
In the modern world, one of the most pressing issues is the environmental crisis that has arisen as a result of insufficient responsibility towards natural resources in many countries with developed industry. In the absence of a systematic approach to solving environmental problems in some regions of the planet, in others, a complex of negative consequences arises as a result. For example, the population of many countries does not have access to clean drinking water in the presence of water resources in sufficient volume to provide residents. Wastewater from various types of industries is discharged into water bodies either in the absence or in the absence of an insufficient degree of purification. To improve the quality of purified water, as a rule, the technological scheme of treatment facilities includes a filtration stage using various types of natural and synthetic filtration and sorption loads. As such, anthracite is often used, which has a relatively low cost and a wide range of uses [
1,
2,
3,
4]. However, in the global coal mining industry, there has been a trend towards a reduction in the number of mines and, accordingly, in the volume of mined minerals [
5,
6].
The observed trend of environmental degradation and depletion of natural resources has led to the need to develop innovative sorption materials that are most consistent with the principles of the “green” world ecopolitics [
7].
Various types of clays can undoubtedly be attributed to effective sorbents of natural origin. To accomplish the tasks set under certain conditions, the paper [
8] considers various methods for modifying the surface of clay minerals. Surface modification of montmorillonite with cationic surfactants (hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide); method of surface modification of montmorillonite with large-sized inorganic cations Fe, Al, Zr, Ti; The application of zero-valent iron nanopowder to the surface of montmorillonite was used to increase the efficiency of water purification from chromium (VI) and uranium (VI). In [
9], the properties of halloysite were considered based on the results of analyzes and the ability of adequately activated halloysite to effectively remove heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions was confirmed. The adsorption process carried out in the pH range of 6.0–6.5 showed a significant improvement compared to acidic conditions (pH value of 3.0–3.5) and led to a high sorption capacity for lead ions—more than 24.3 mg/g for the sample treated with sulfuric acid. In [
10], cheap natural materials such as zeolites and bentonites were tested as possible sorbents for removing microplastics from wastewater. Wastewater treatment from microplastics has been tested not only on a laboratory scale, but also on a developed semi-functional sorption plant at real wastewater treatment plants throughout the year with an efficiency of more than 90%.
Also, aluminosilicates, which are a cheap and readily available material, have shown their effectiveness in the sorption purification of natural and waste water. In studies [
11], aluminosilicates are used to purify water contaminated with radionuclides. An aqueous solution contaminated with radionuclides in the form of cations of various oxidation states—Cs(I)-137, Co(II)-60 and Am(III)-241, as well as pertechnetate anions—TcO4--99m was treated. proposed hybrid method. In the present work, the influence of important process parameters (i.e., pH, sorbent dosage, temperature and feedstock consumption) on the efficiency of radionuclide removal was studied.
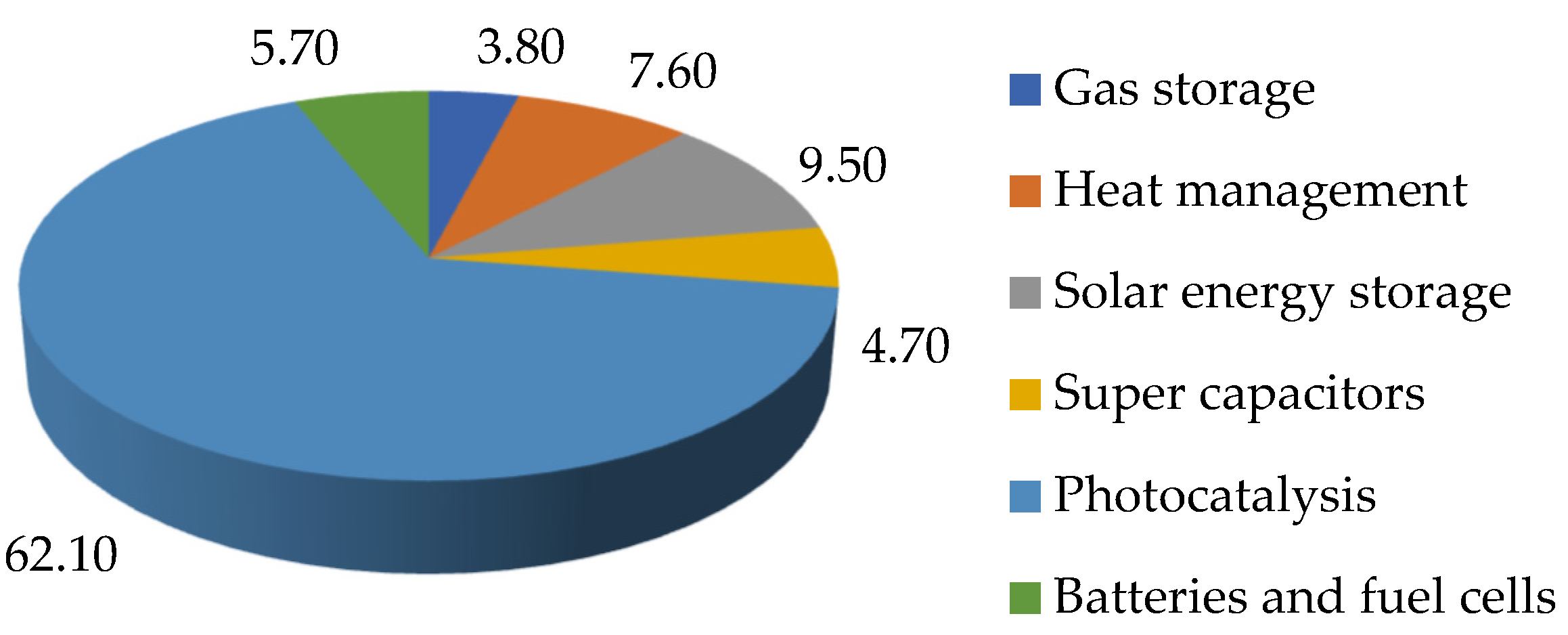
In addition, in recent years, much attention has been paid to nanotechnologies due to the remarkable physicochemical characteristics of nanomaterials. Nanomaterials have a higher surface to volume ratio than their bulkier competitors, resulting in increased reactivity and greater efficiency. Also, compared to traditional methods, nanomaterials have the potential to use unique surface chemistry, which allows them to be synthesized and characterized or introduced into them with functional groups that can target certain molecules of relevant pollutants for effective environmental remediation [
12,
13]. These properties encourage the scientific community to go beyond traditional approaches and reconsider the primary forms of carbon in new “green” technologies for the treatment of natural and waste water.
Figure 1.
Various environmental applications of carbon NMs (search in Scopus) [
14].
Figure 1.
Various environmental applications of carbon NMs (search in Scopus) [
14].
At the same time, in order to intensify the process of sorption of heavy metals by nanosorbents, the authors of [
15] propose their attachment to massive immobile carriers. These studies describe a method for assessing the sorption efficiency of nanosorbents embedded in bulk carriers under nonequilibrium conditions, in particular, the removal of oxyanions from a Zr-organometallic framework (MOR-1) immobilized on cotton fabrics. The results show that the sorption capacity under passive diffusion conditions is approximately 20 mg/g for As(VI) and 36 mg/g Se(IV), which is 10-30 times lower than the capacity determined in periodic sorption studies.
The scientific community also proposes a sorption method for water purification from heavy metals based on waste from the fruit and vegetable industry, including pomace of apples and beets [
16]. Kinetic studies under optimal conditions have shown that the sorption process occurs through complex formation and ion exchange, and the determining stage that limits the sorption rate is the diffusion of lead ions in the sorbent.
Biochar activation methods have attracted much attention due to their great role in improving the sorption properties of carbonaceous materials [
17]. As a result, chemically modified biochars have received the prospect of being used for cleaning soil and water from xenobiotics. The article describes the change in some physical and chemical properties of high-temperature biochar from wheat straw (WS) during its deashing. Dehydration led to an increase in the aromaticity of the sorbent and an increase in the amount of surface hydroxyl groups. Modified biochar can serve as a superabsorbent that immobilizes organic pollutants of various hydrophobicity from water and soil solution.
In this paper, it is proposed to use rice straw biochar with metallic silver ions impregnated on its surface by electromagnetic method as a sorption material for post-treatment of wastewater. The use of rice husks in this capacity also has a positive effect on the environment, because. reduces waste from rice production, while at the same time improving the quality of treated wastewater. The proposed method for activating biochar makes it possible to obtain a carbon nanomaterial with attached silver particles with a very short processing time of 2 minutes. The impregnation of silver on the surface of biochar particles significantly expands the scope of this material. First of all, as is known, silver nanoparticles show high efficiency against bacteria, viruses and fungi [
18]. In addition, a popular area of application of silver-containing sorbent is the capture of radioactive forms of iodine from gas flows of industrial enterprises [
19]. As a rule, this kind of sorbent is obtained by impregnating and drying a porous carrier with soluble silver salts. However, this method of impregnating silver is characterized by uneven deposition of silver on the support surface [
20]. A fairly effective method is known for obtaining silver-containing iodine sorbents by applying silver to porous cellular ceramics by chemical reduction from solution and subsequent transfer of silver to an oxidized form, which makes it possible to achieve uniform deposition, but at the same time requiring the use of additional treatment with chemical reagents [
21]. An efficient technique has also been developed for the uniform application of metallic silver to bentonite with a high yield (95%) for its subsequent conversion into compounds suitable for fixing any mobile forms of radioiodine, for example, a soluble anionic form of radioiodine in radioactive waste storages [
22]. There are studies using SBA-15, alumina, cerium, and faujasite Y zeolite as porous supports. These supports impregnated with silver with and without calcination at 500 °C (1 h) were compared for the capture of I2 and CH3 I [
23]. In addition, in order to increase various parameters of sorbents, such as the specific surface area, for example, various methods of impregnating the necessary chemical reagents are used. The results of increasing the adsorption activity for iodine by electromagnetic microwave treatment have been published [
24]. A scientific publication published data on the properties of magnetic porous carbon based on a bimetallic organometallic Zn/Co-MPC framework obtained by introducing cobalt into ZIF-8 (amorphous zeolite imidazolate framework), which has a highly selective focus on the removal of chlorophenols [
25].
In the presented study, metallic silver is impregnated onto the surface of the sorbent by the electromagnetic method in a setting process activation without the use of additional reagents, which greatly simplifies and reduces the cost of manufacturing a silver-containing sorption material.
2. Materials and Methods
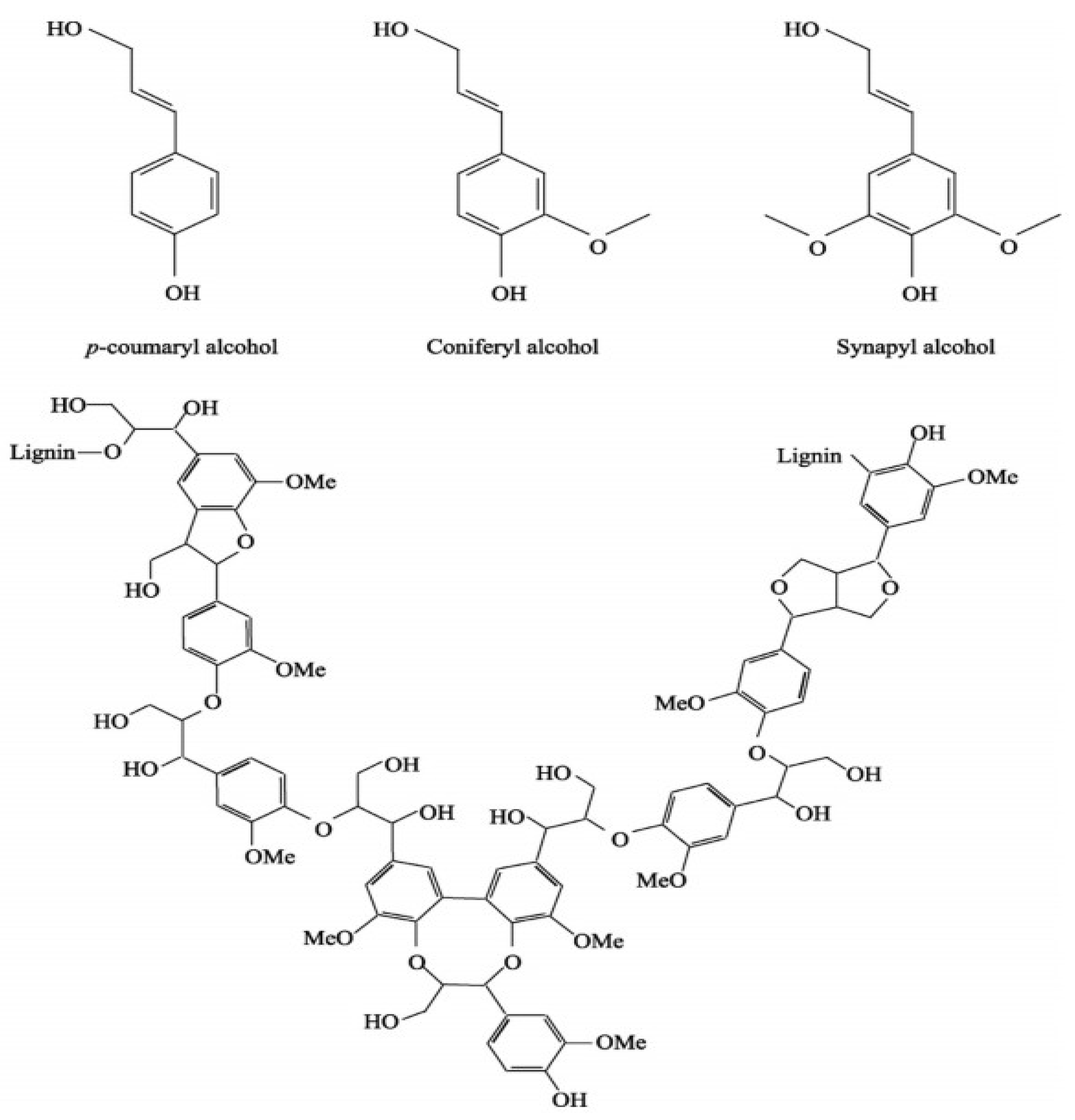
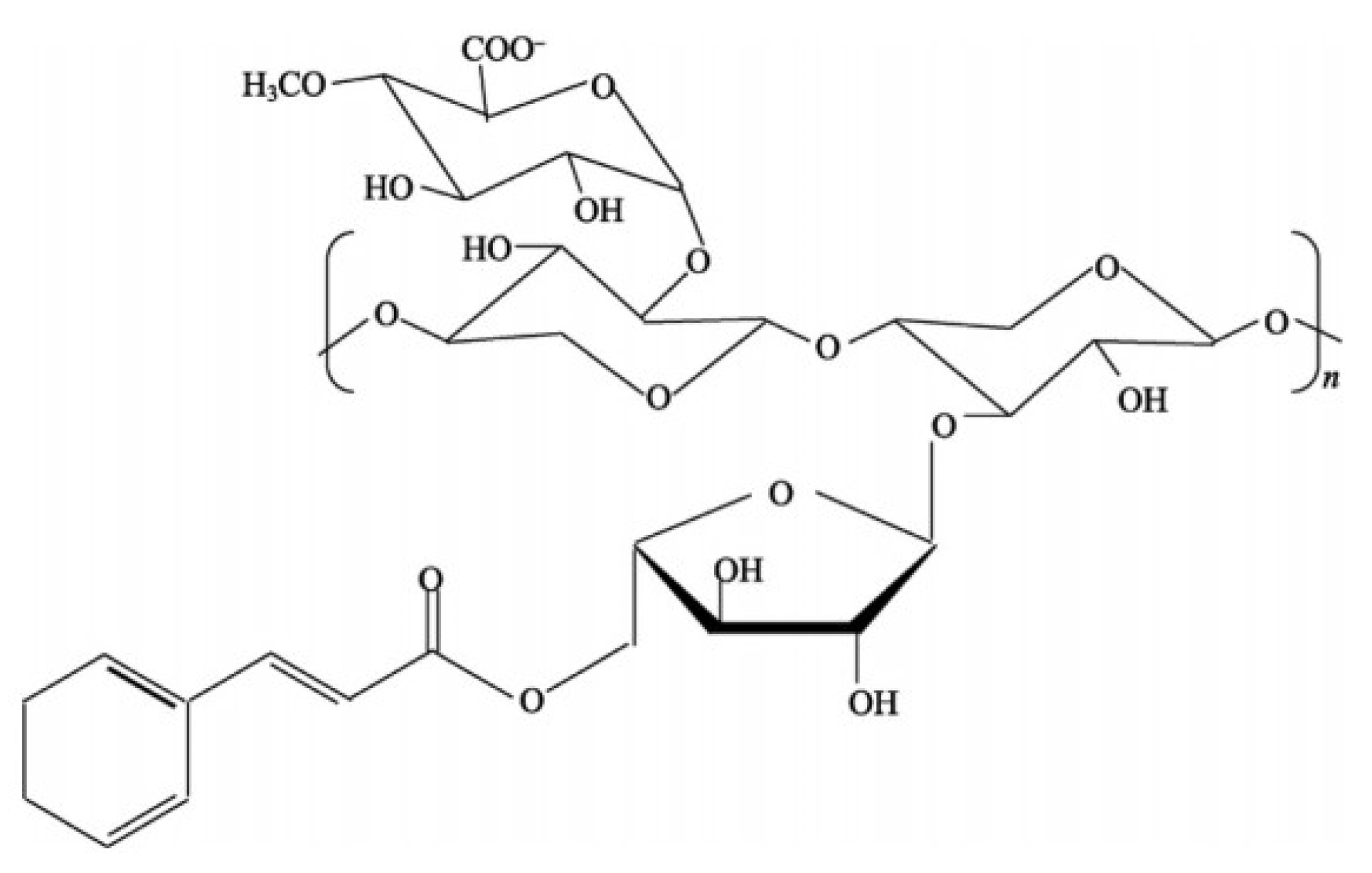
To obtain a silver-containing sorbent from biochar, rice straw was used as a starting material.
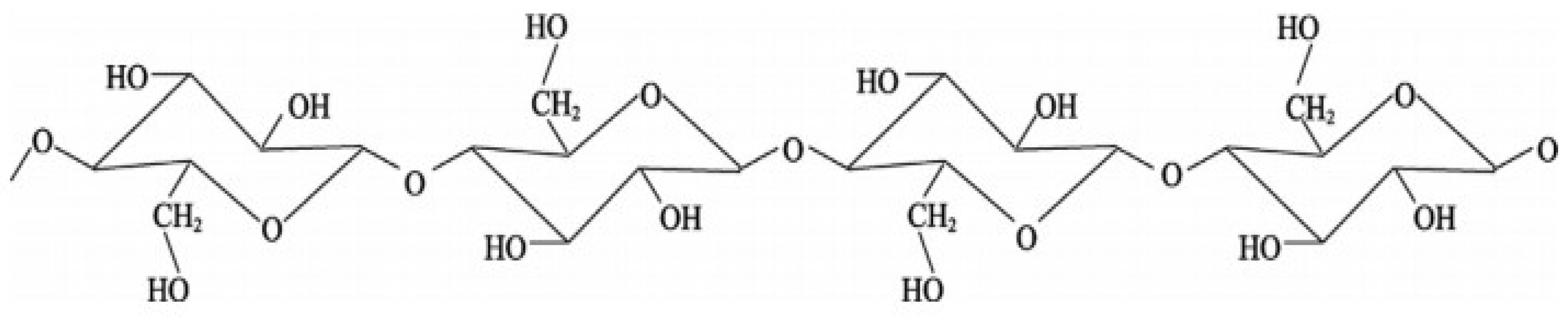
Rice straw and husks contain a combination of cellulose (
Figure 2), hemicelluloses (
Figure 3), and lignin (
Figure 4), along with appreciable amounts of silica and other minor components, as summarized in
Table 1 [
32].
Because of the stability of lignocellulosic materials, separation of the individual cell wall polymers is difficult, although there are various physical, chemical, and/or biological treatments that release the constituent sugars and phenols. Thermal decomposition products, such as chars and ashes, also have useful properties, although these are strongly influenced by the pyrolysis conditions and subsequent additional treatments. However, high value utilization of rice-derived biomass is still poorly developed [
33], and field burning and soil accumulation of rice straw remain common practices, despite their contributions to environmental problems as a result of air pollution or ecosystem deterioration.
Physical activation consists of two stages: carbonization and actual activation.
As a result of mechanical impact on the processed materials. In addition, as a result of the interaction of the field with manifestations of bodies, the mechanical working action of bodies among themselves, with a wall and a number of materials, physicochemical effects, such as magnetostriction, cavitation, ultrasound and electrophysical phenomena, their role, in turn, also have a significant impact on materials. In the working zone, in a unit of its volume, a huge energy is concentrated, which directly affects the substance. In places of collision of ferromagnetic bodies, pressure can rise up to thousands of MPa. Thus, in the vortex layer of ferromagnetic bodies, any processed materials are strongly mixed, subjected to intense deformation, and are activated to a large extent [
31,
35].
The nature of the movement of magnetic particles is determined by many factors—the speed of rotation and the intensity of the applied field, the viscosity of the medium, the size, shape, mass and magnetic properties of the particles, etc. Each particle performs 2 types of motion: translational motion in the direction of rotation of the field at a speed that can reach the speed of its rotation, and rotational motion around its smallest axis at a speed of up to 10 revolutions per second. Finely dispersed particles, being magnetized, are attracted to each other and form chains. Coarse particles, as a rule, move separately from each other. Figure 1.11 shows the trajectory of the center of gravity of one particle in 0.5 s, determined using high-speed filming [67].
Processing (activation) of the source material (rice straw) to obtain its specific sorption properties is possible in various ways. Activation can be carried out by physical or chemical methods. With chemical activation, two stages—carbonization and activation—are carried out simultaneously. The raw material is impregnated with a specific chemical such as phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, potassium (sodium) hydroxide or zinc chloride for several hours [98]. The impregnated product is carbonized at moderate or high temperatures (500–800 °C) in a muffle furnace. To remove the residual activating agent, the impregnated product is washed with distilled water until the pH value of the washed water (pH) becomes equal to the pH value of distilled water. Rice straw biochar obtained as a result of activation with sodium hydroxide at a temperature of 600 °C can be considered as a matrix base for imparting specific properties to it. Thus, biochar was modified by electromagnetic treatment in a process activation apparatus into a silver-containing sorption material, followed by a study of its physicochemical properties, the results of which are presented below.
In the vortex layer of the process activation apparatus, the energy of the rotating electromagnetic field causes an intense mechanical effect of the working bodies (ferromagnetic particles) on the processed materials. In addition, as a result of the interaction of the field with the working bodies, the mechanical action of the working bodies among themselves, with the wall and with the materials, a number of physicochemical effects arise, such as magnetostriction, cavitation, ultrasound and electrophysical phenomena, which, in turn, also have a significant impact for materials. In the working zone, in a unit of its volume, a huge energy is concentrated, which directly affects the substance. In places of collision of ferromagnetic bodies, pressure can rise up to thousands of MPa. Thus, in the vortex layer of ferromagnetic bodies, any processed materials are strongly mixed, subjected to intense deformation, and are largely activated.
A vortex layer of ferromagnetic particles takes place only to a certain degree of filling the working area of the chamber with them, which is characterized by a critical coefficient Kcr (the ratio of the total volume of ferromagnetic bodies to the volume of the working area of the chamber) [
26]. The process of mechanical activation of materials in ABC, as in other mixers, is usually described by several stages [
27,
28]. At the first stage, EMT causes a violation of the crystal lattice of the material, changes in interplanar distances and orientation angles of the structure. In the second stage, the formation of a new surface of the system, the appearance and development of cracks in the material take place. In this case, the increase in the total energy of the system with an increase in the phase interface by 1 cm
2 is determined by the formula:
where σ—the specific surface energy; T—temperature; q—the latent heat of formation of 1 cm
3 of a new surface.
In the third stage, the process of fine grinding takes place, in which the concentration of energy in the surface layer significantly changes the thermodynamic and chemical properties of the substance.
To describe the kinetics of processes occurring in heterogeneous systems, empirical models are used that establish the functional dependence of the degree of conversion (α) on time (t). The Avraami-Erofeev equation, which describes decomposition reactions well, has the form [
29]:
where k—the rate constant; n—the kinetic parameter of the process.
For the case of a topochemical process involving solid phase particles occurring in the kinetic region of reaction, the reaction rate is proportional to the surface of unreacted particles and is described by the equation [
29]:
where n = 1/3, 1/2 and 1 for the cases of three-dimensional, two-dimensional and one-dimensional reacting particles; r
0—the radius of reacting particles. Gray-Weddington’s “shrinking sphere” equation:
also describes well the kinetics of processes occurring in the kinetic region. In practice, to describe the recovery processes occurring in the kinetic regime, the McKevan equation is used [
30]:
where r
i—the average particle size, m; d
0—the oxygen content in the oxide, in fractions of a unit.
Equation (1.7) is an improved equation (1.6), since it takes into account the particle size and the oxygen content in the oxide. The rate constant has the dimension m/s and characterizes the speed of movement of the metal-oxide interface. The advantages of this model include simplicity, ease of use, and good agreement with experimental data on the reduction of powder oxides. If the rate of the process determines the mass transfer, and during the process a gradual growth of the product layer occurs, then the equation describing this process, first obtained by Jander, has the form [
30]:
where D—the diffusion coefficient.
On the basis of the Yander model, the Ginstling-Brownstein, Carter, anti-Yander models (counter-diffusion is taken into account), etc. were developed. Thus, one of the prerequisites for effective grinding in liquid and mixed media is the appearance of acoustic phenomena. The frequency range of sound waves is from tens of Hz to tens of MHz. In the liquid and mixed phases, acoustic waves are the source of cavitation. Studies [
31] show that the share of acoustic oscillations is no more than 2% of the total energy, but the resulting cavitation phenomena have a significant impact on the course of many physicochemical processes. In addition, the influence of an alternating magnetic field in the working area of the apparatus on ferromagnetic needles leads to the appearance of induction currents. The liquid component of processed raw materials is often water with dissolved salts, so electrolysis processes occur in such systems.
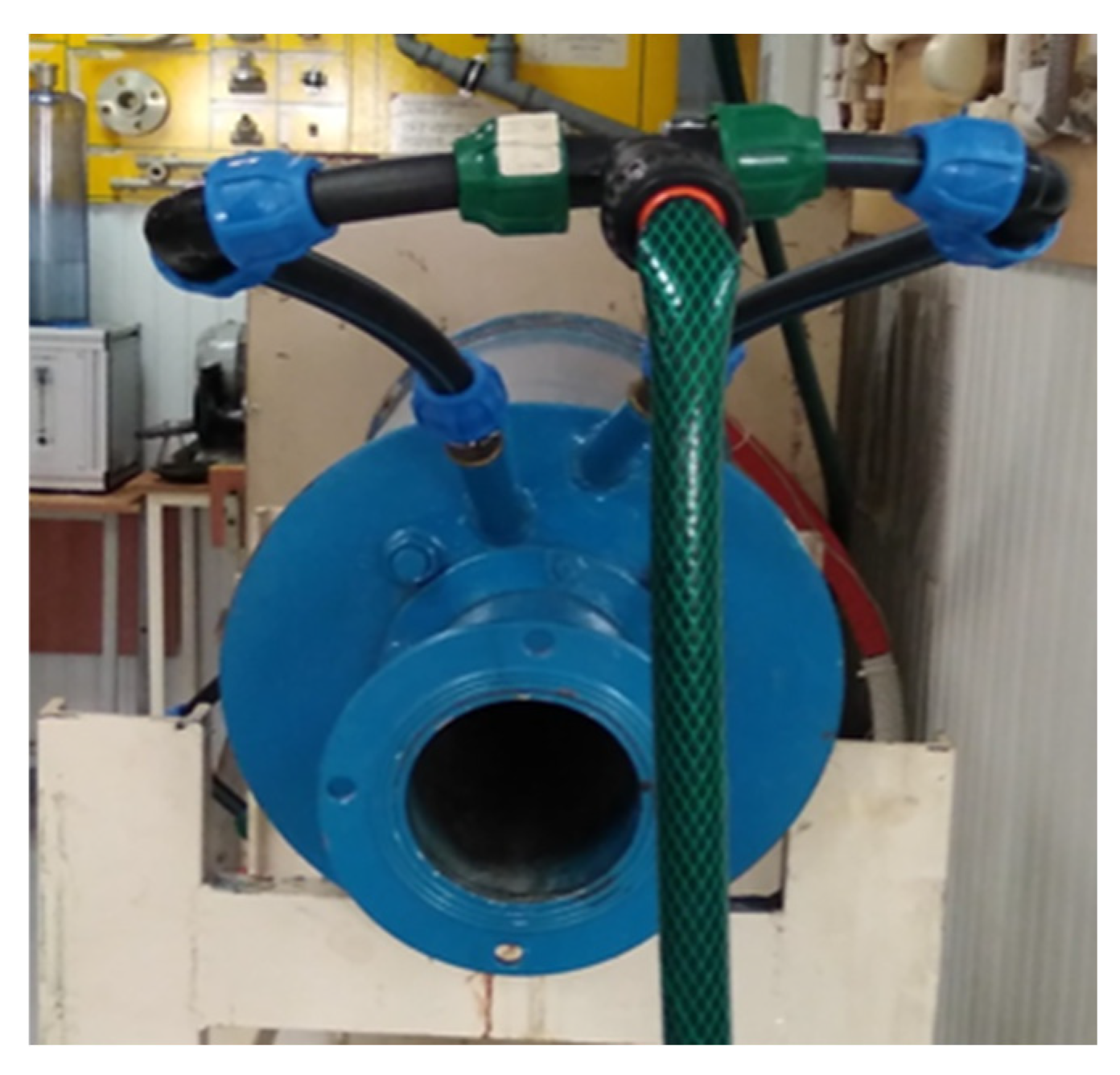
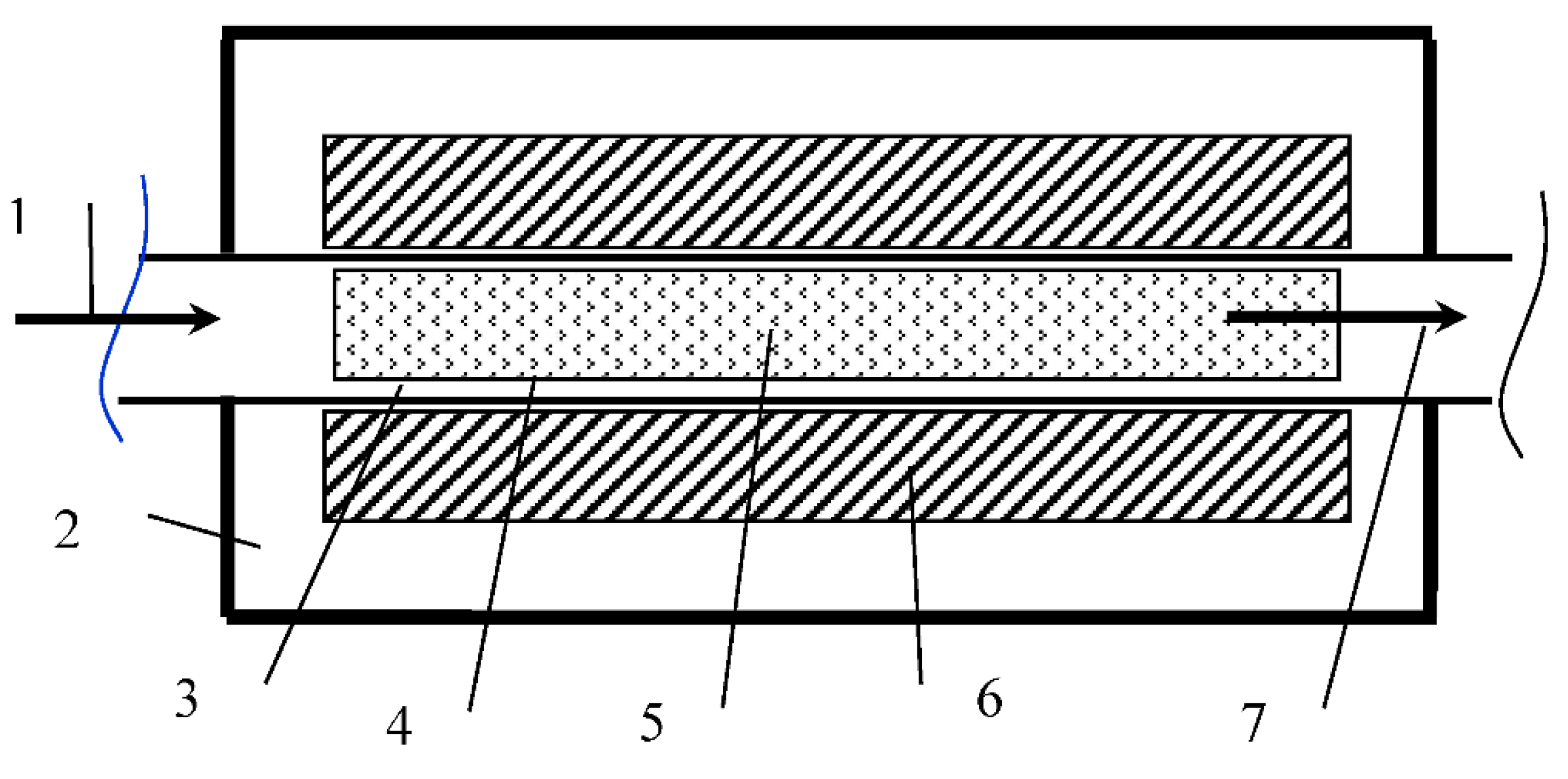
The process activation plant (PAP) allows changing the structure and properties of processed materials with small equipment sizes and low specific energy costs (
Figure 5).
Figure 5.
PAP scheme. 1—Incoming fluid flow for processing; 2—Cooling jacket housing; 3—Working area; 4—Replaceable insert; 5—Working bodies—ferromagnets (needles); 6—Induction coils; 7—Processed stream.
Figure 5.
PAP scheme. 1—Incoming fluid flow for processing; 2—Cooling jacket housing; 3—Working area; 4—Replaceable insert; 5—Working bodies—ferromagnets (needles); 6—Induction coils; 7—Processed stream.
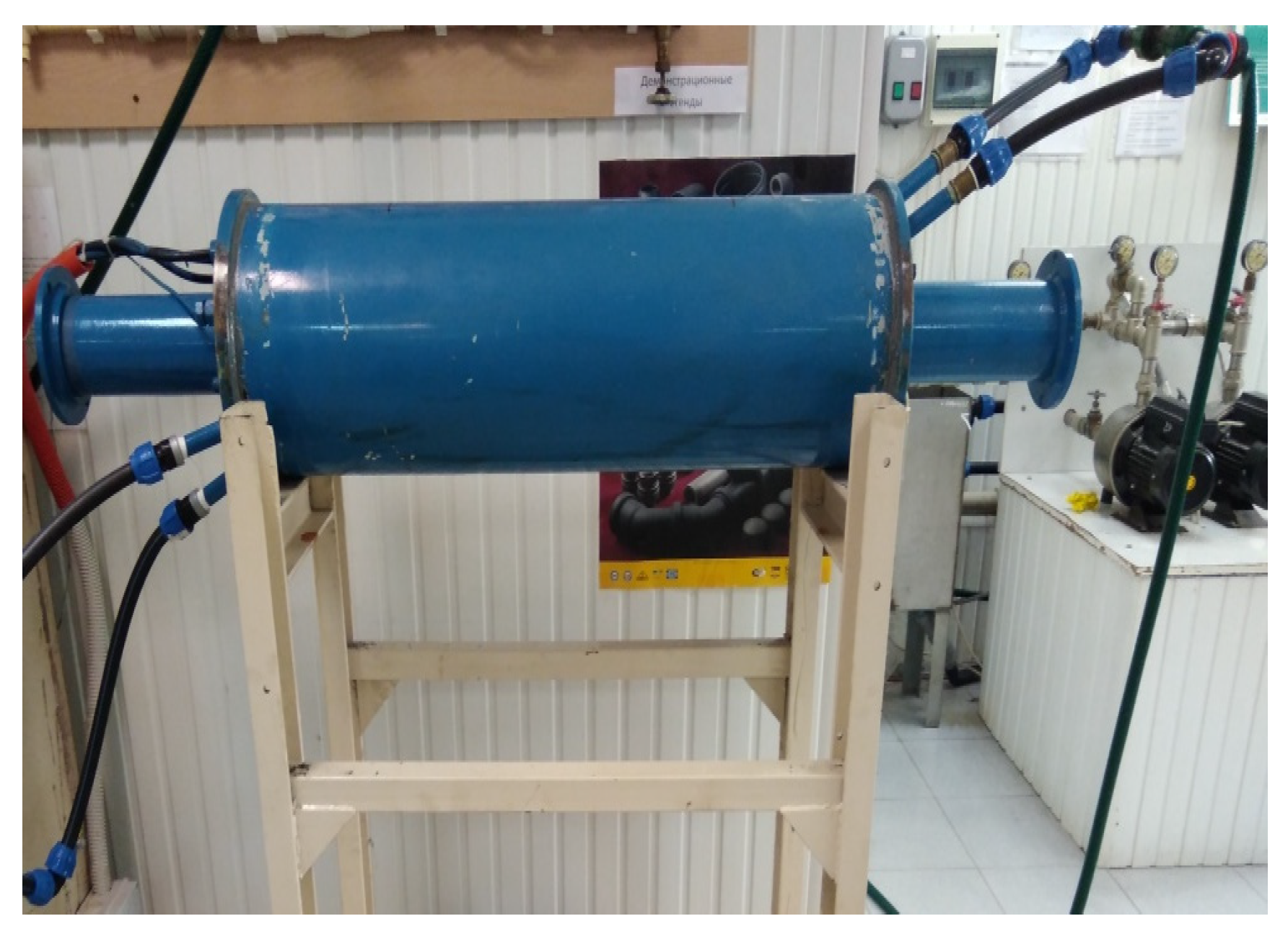
Figure 6.
PAP working building.
Figure 6.
PAP working building.
Figure 7.
Side view of the working body of the PAP.
Figure 7.
Side view of the working body of the PAP.
The principle of operation of the PAP was described by the author in the article when studying the properties of concrete with biochar from rice straw [
36].
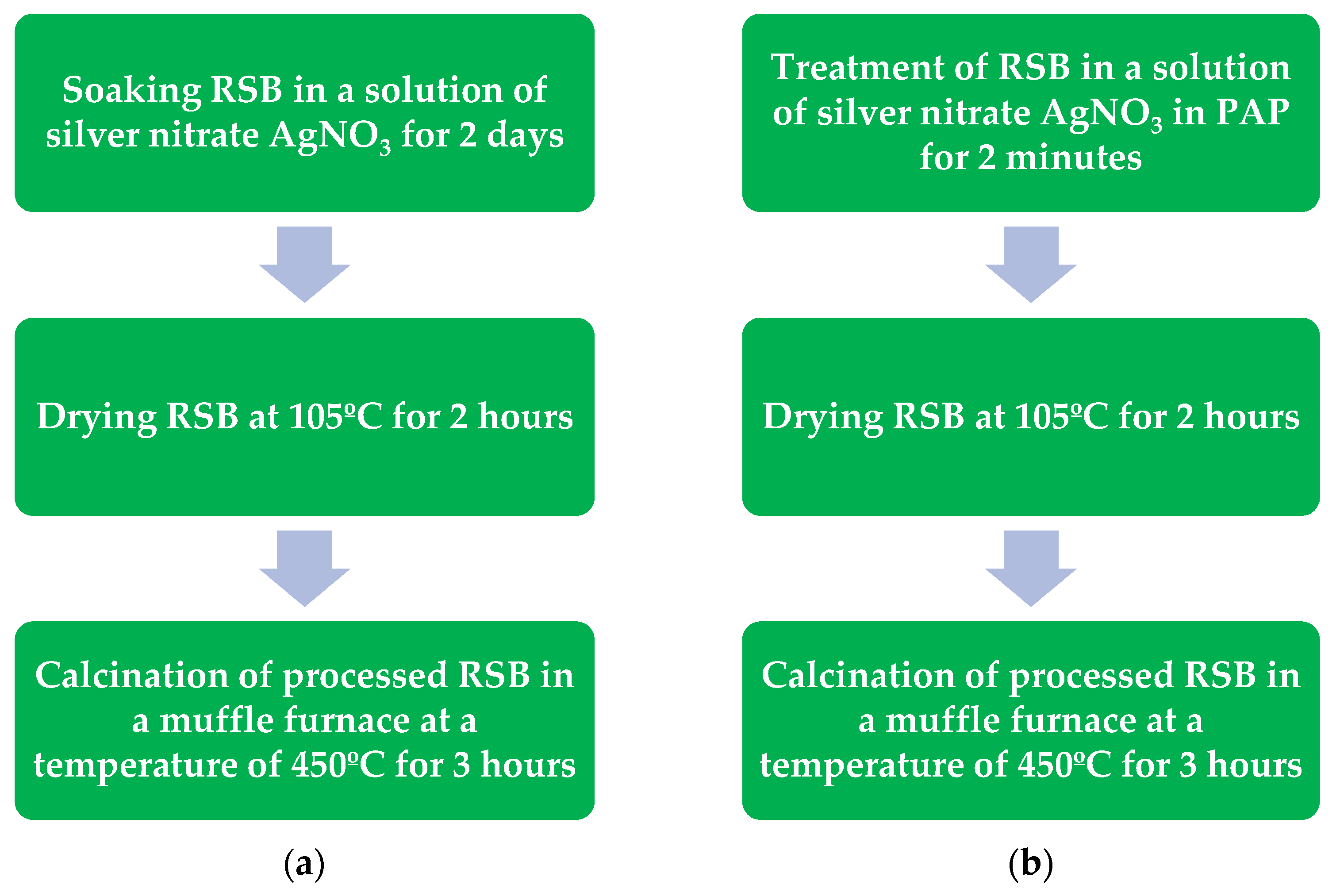
A sample of RSB weighing 35 g was stirred in a volume of 150 ml of distilled water with silver nitrate AgNO
3 weighing 10 g, after which it was placed in the PAP in a replaceable insert 4 (
Figure 8a) with ferromagnetic particles m = 200 g, which have a magnetostrictive effect under the influence of an electromagnetic field, then contact of biochar impregnated with a solution of silver nitrate and ferromagnetic particles was carried out for 2 minutes under electromagnetic influence, after which the treated sample was dried in an oven for 4 hours at t = 105 °C, followed by calcination in a muffle furnace at 450 °C for 3 hours.
3. Results and Discussion
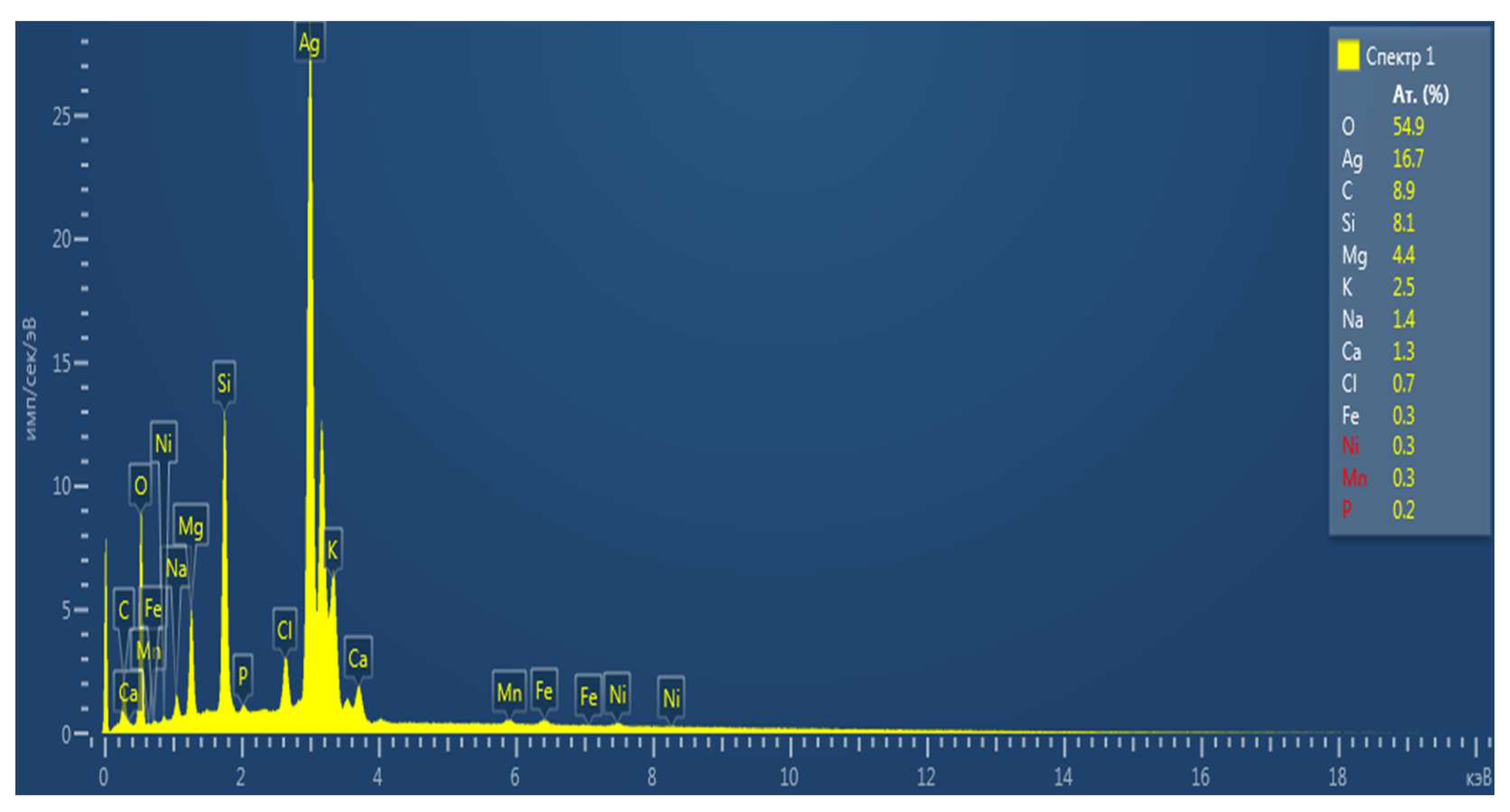
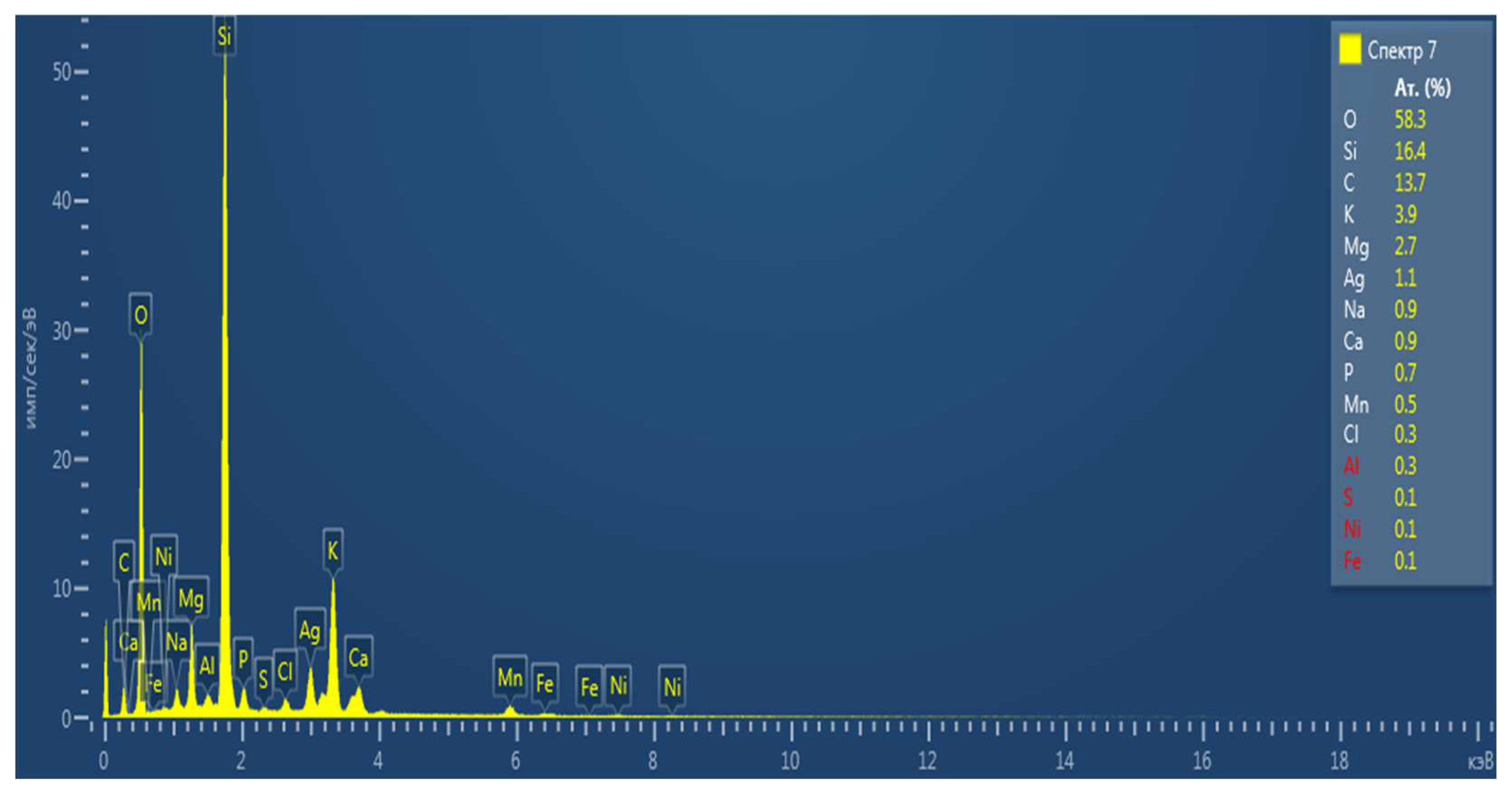
Table 2.
Chemical composition of rice straw biochar samples with treatment.
Table 2.
Chemical composition of rice straw biochar samples with treatment.
| № |
Chemical element, % |
EP |
S |
| 1 |
C |
8,9 |
13,7 |
| 2 |
O |
54,9 |
58,3 |
| 3 |
Si |
8,1 |
16,4 |
| 4 |
Ag |
16,7 |
1,1 |
| 5 |
K |
2,5 |
3,9 |
| 6 |
Ca |
1,3 |
0,9 |
| 7 |
Mg |
4,4 |
2,7 |
| 8 |
Na |
1,4 |
0,9 |
| 9 |
Cl |
0,7 |
0,3 |
| 10 |
Fe |
0,3 |
0,1 |
| 11 |
Ni |
0,3 |
0,1 |
| 12 |
Mn |
0,3 |
0,5 |
| 13 |
P |
0,2 |
0,7 |
| 14 |
Al |
- |
0,3 |
| 15 |
S |
- |
0,1 |
Table 3.
Physico-chemical characteristics of treated rice straw biochar samples.
Table 3.
Physico-chemical characteristics of treated rice straw biochar samples.
| № |
Characteristic |
EP |
S |
| 1 |
Ash content |
35,8 |
35,5 |
| 2 |
Moisture contents, % |
- |
- |
| 3 |
Specific surface, m2/g |
7,45 |
7,37 |
| 4 |
Relative pore volume diameter up to 900 Å, cm3/g |
0,034 |
0,036 |
| 5 |
Average mesopore diameter by desorption, Å |
196 |
238 |
| 6 |
Micropore volume, cm3/g |
0,0026 |
0,0019 |
| 7 |
Average micropore diameter, Å |
4,08 |
3,68 |
Thermal analysis of rice straw biochar samples impregnated with silver nitrate by the electromagnetic method and by the soaking method during their heating was carried out by the method of synchronous thermal analysis on an STA 449 F1 Jupiter device (Germany). Thermal analysis was carried out in air. Temperature program: heating at a rate of 5 °C/min up to 950 °C.
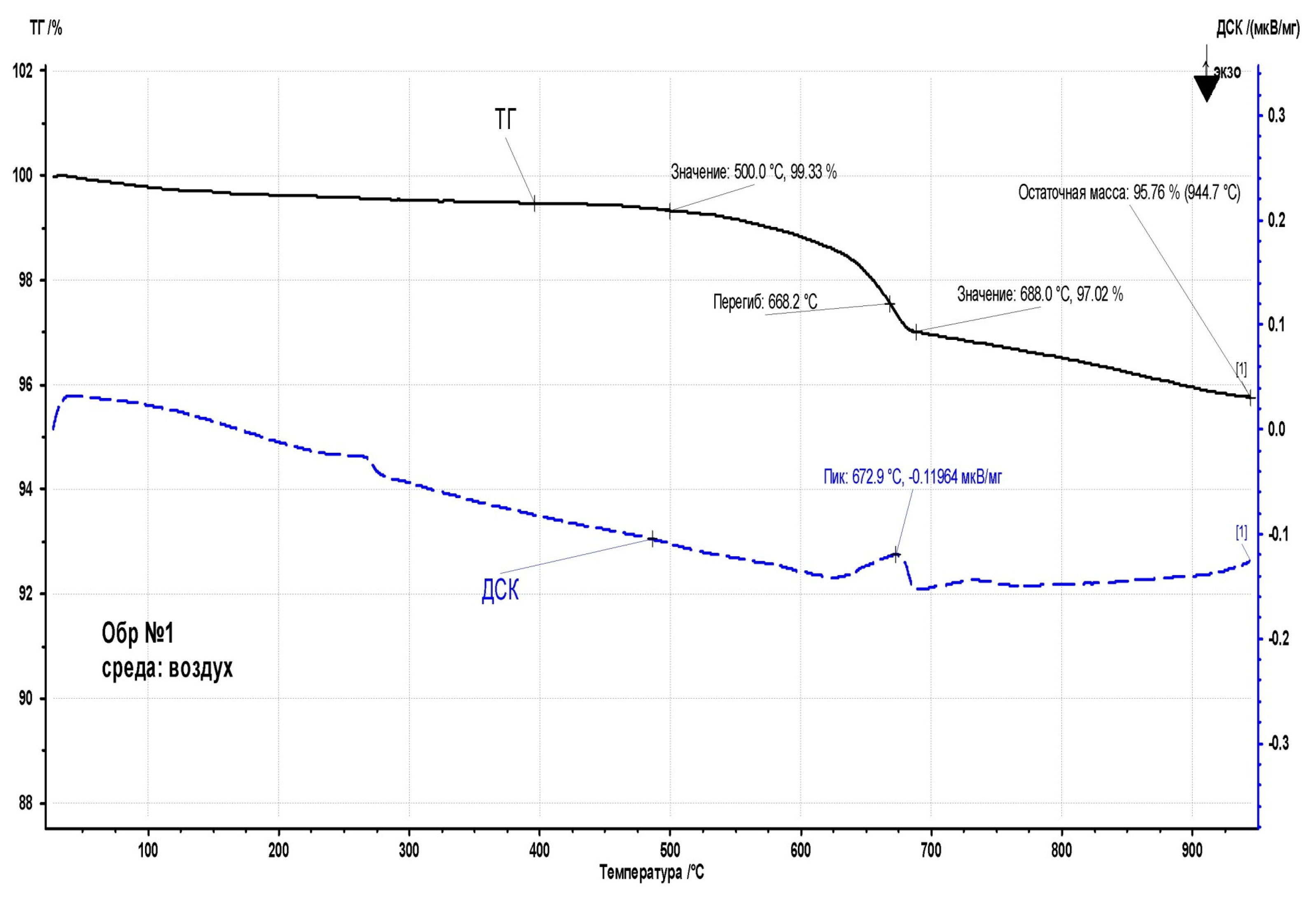
When heated to 500 °C, the calcined sample (
Figure 15)practically does not lose weight. The loss of 0.7% by the time of heating to 500 °C may indicate a small amount of moisture gained during the preparation of the sample for analysis. Since a very small amount of sample (less than 20 mg) is needed for thermal analysis, even a small amount of moisture from the air during sample preparation can have some effect on the result. In the range of 500-688 °C, the sample loses about 3.3% of the mass, which is accompanied by a signal of the endothermic effect on the DSC curve. Probably, the nature of the process is similar to the transformations occurring at 620-685 °C with sample No. 5: the release of chemically bound moisture, as well as a certain amount of organic volatile substances.
Upon further heating to 950 °C, the sample continues to lose mass at a lower rate. The residual mass at 950 °C is 95.76%. In this case, the TG signal also does not reach a stationary level, which indicates the further course of the sample decomposition process.
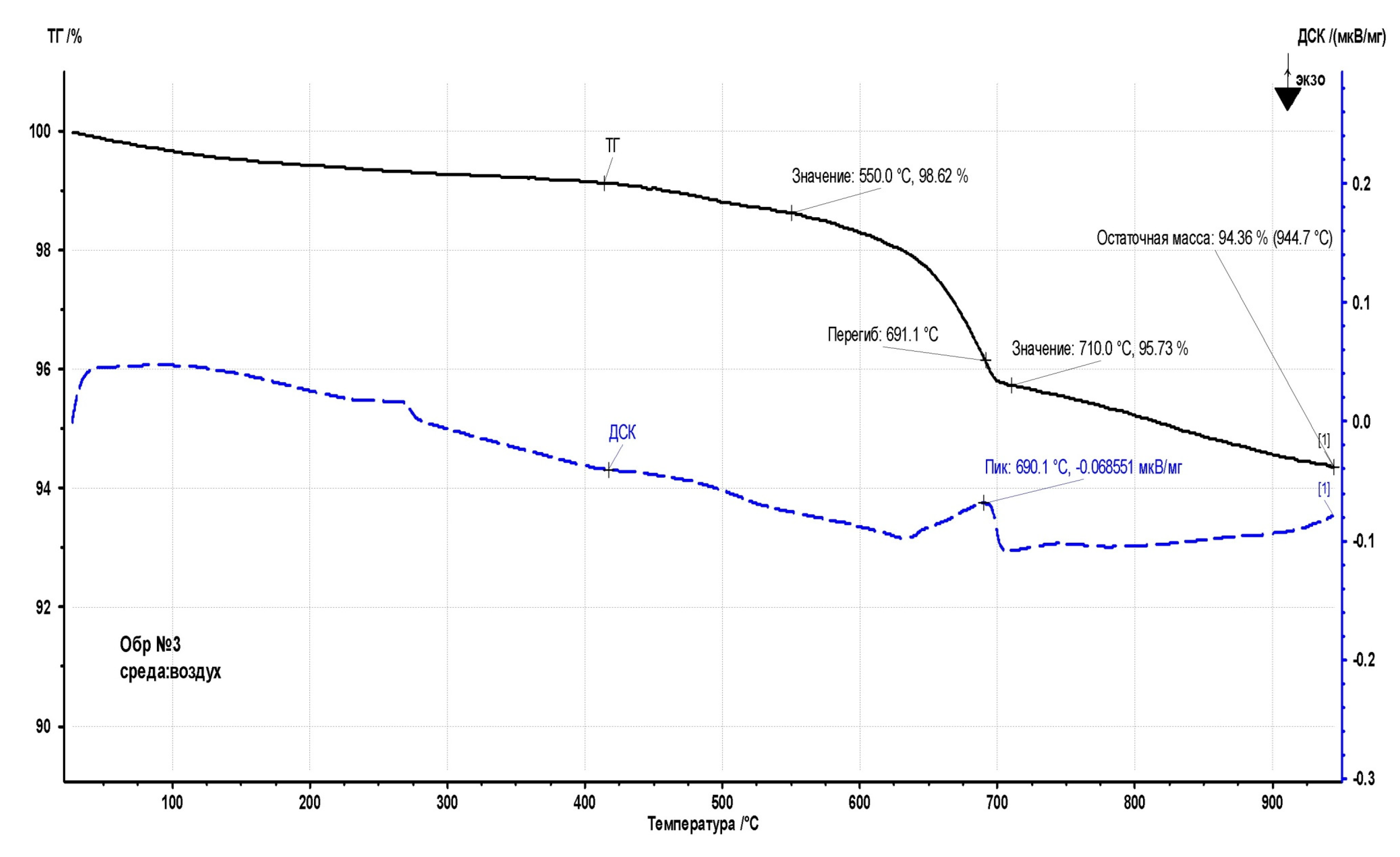
When heated to 450 °C, the calcined sample of Biochar from Rice Straw impregnated with silver nitrate by soaking (S) (
Figure 16) practically does not lose weight: a loss of 1% may indicate a small amount of moisture gained during sample preparation for analysis. Since a very small amount of sample (less than 20 mg) is needed for thermal analysis, even a small amount of moisture from the air during sample preparation can have some effect on the result. In the range of 450-710 °C, the sample loses about 4.3% of the mass, which is accompanied by a signal of the endothermic effect on the DSC curve. Probably, the nature of the process is similar to the transformations occurring at 620-685 °C with sample No. 5: the release of chemically bound moisture, as well as a certain amount of organic volatile substances.
Upon further heating to 950 °C, the sample continues to lose mass at a lower rate. The residual mass at 950 °C is 94.36%. In this case, the TG signal also does not reach a stationary level, which indicates the further course of the sample decomposition process.
The resulting silver-containing nanosorbent from rice straw biochar with electromagnetic treatment (
Figure 17) was tested on natural water in order to confirm its disinfecting properties: total microbial count (TMK), common coliform bacteria (CCB), thermotolerant coliform bacteria (TCB). Microbiological analysis of well water was carried out by the Non-Governmental Institution “Testing Laboratory “NIKA and K” (NU “IL “NIKA and K”) (Accreditation No. RA.RU.21AB55 dated May 13, 2015).
Under laboratory conditions, well water was subjected to sorption treatment with silver-containing rice straw biochar. The treatment was carried out in the carbonation mode on a flocculator for 2 minutes at a speed of 45 rpm, then 30 minutes at a speed of 20 rpm. After carbonization, the treated water was coagulated with SKIF at a dose of 1.0 mg/l in the mixing mode for 5 minutes at a speed of 10 rpm and settled for 40 minutes (
Figure 18).
According to the results of microbiological analysis of the studied samples, it was found that the treatment of rice straw with silver-containing biochar showed high efficiency—according to TMC—90.5%, according to OKB—100%, which meets the requirements for drinking water (
Table 4).