Submitted:
10 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
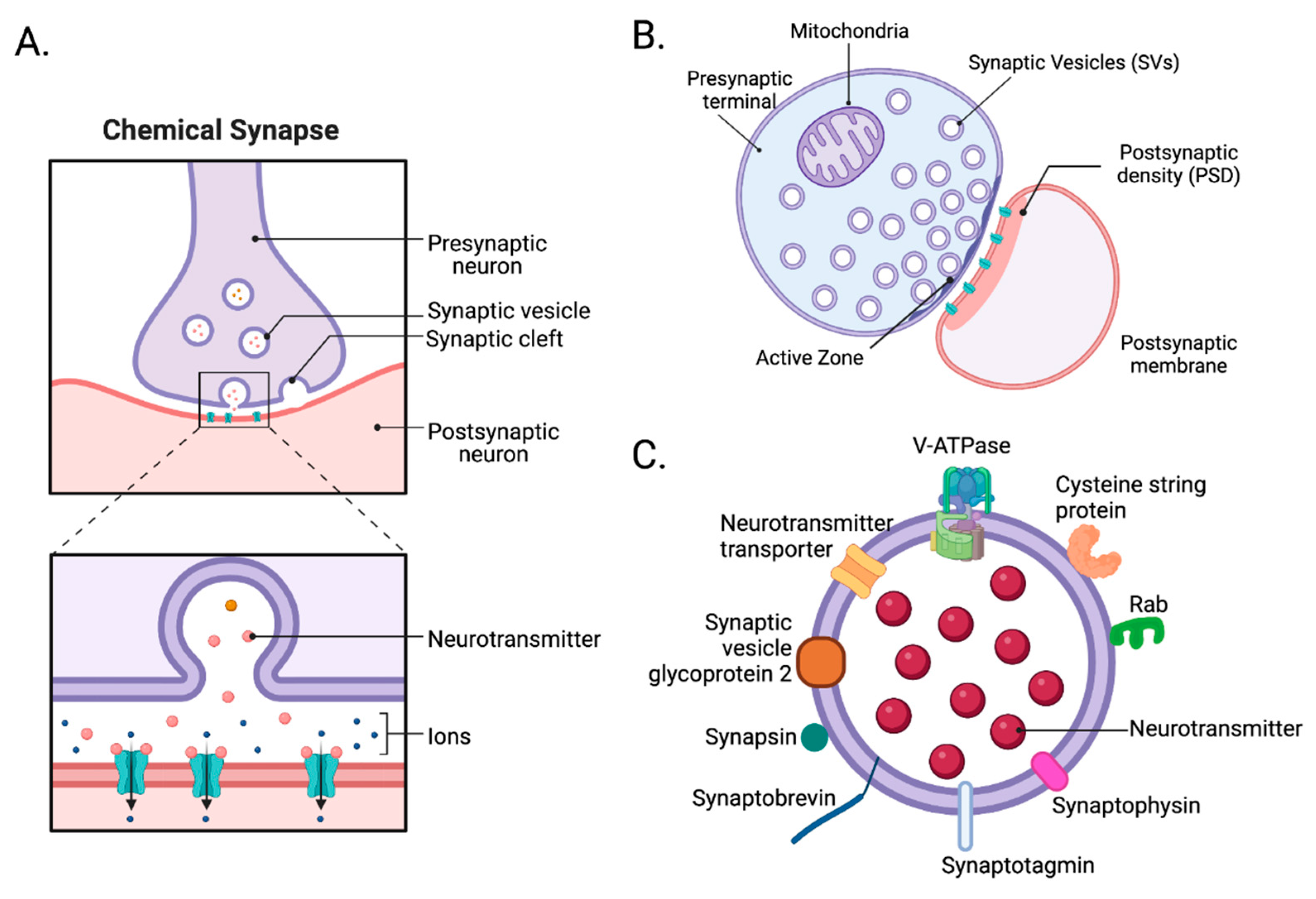
2. Synapse
2.1. Structure of synapses
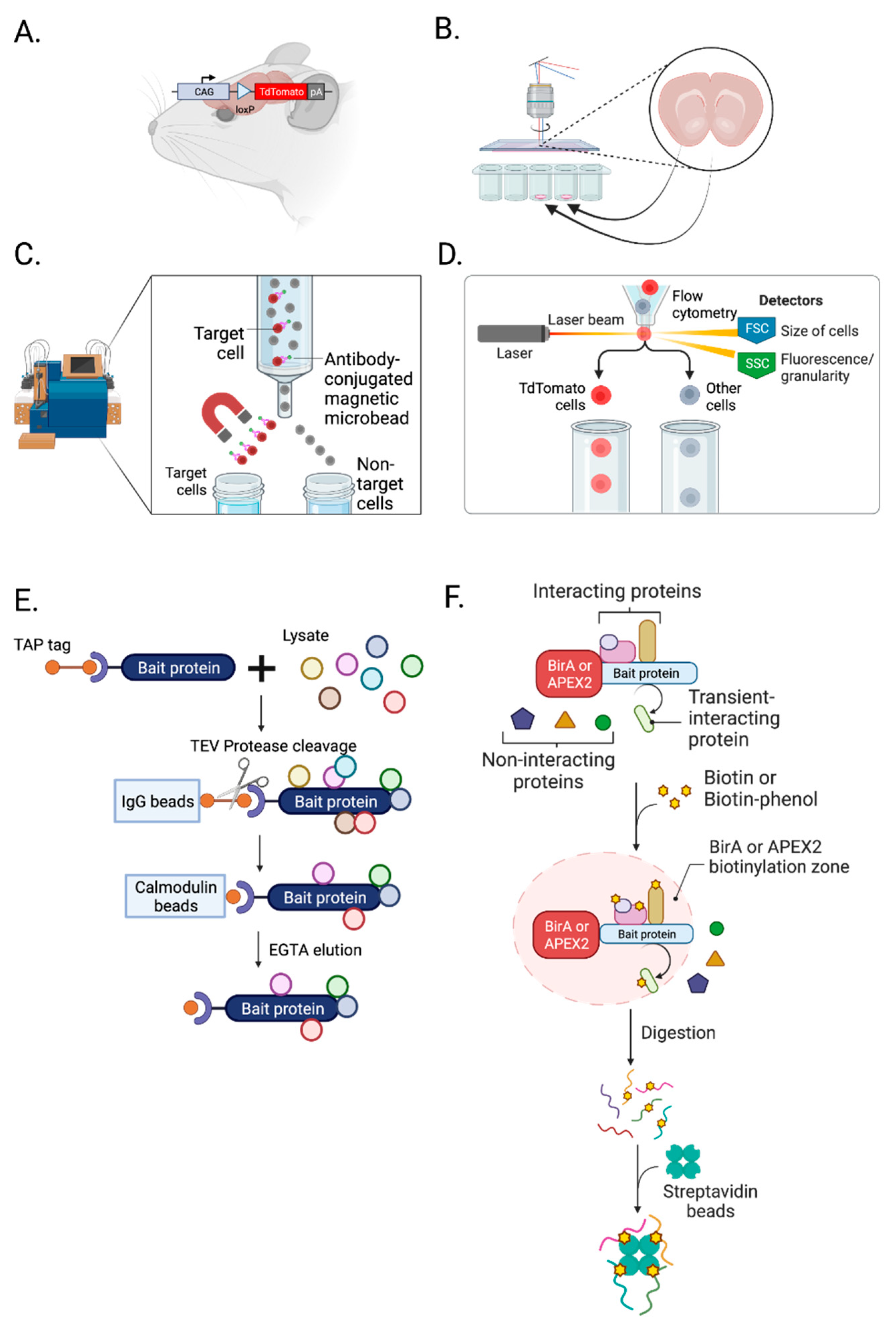
2.2. Isolation of synapses
3. Advancements in neuroproteomics
3.1. Isolation of cell types, subcellular compartments, and cell-type-specific synapses
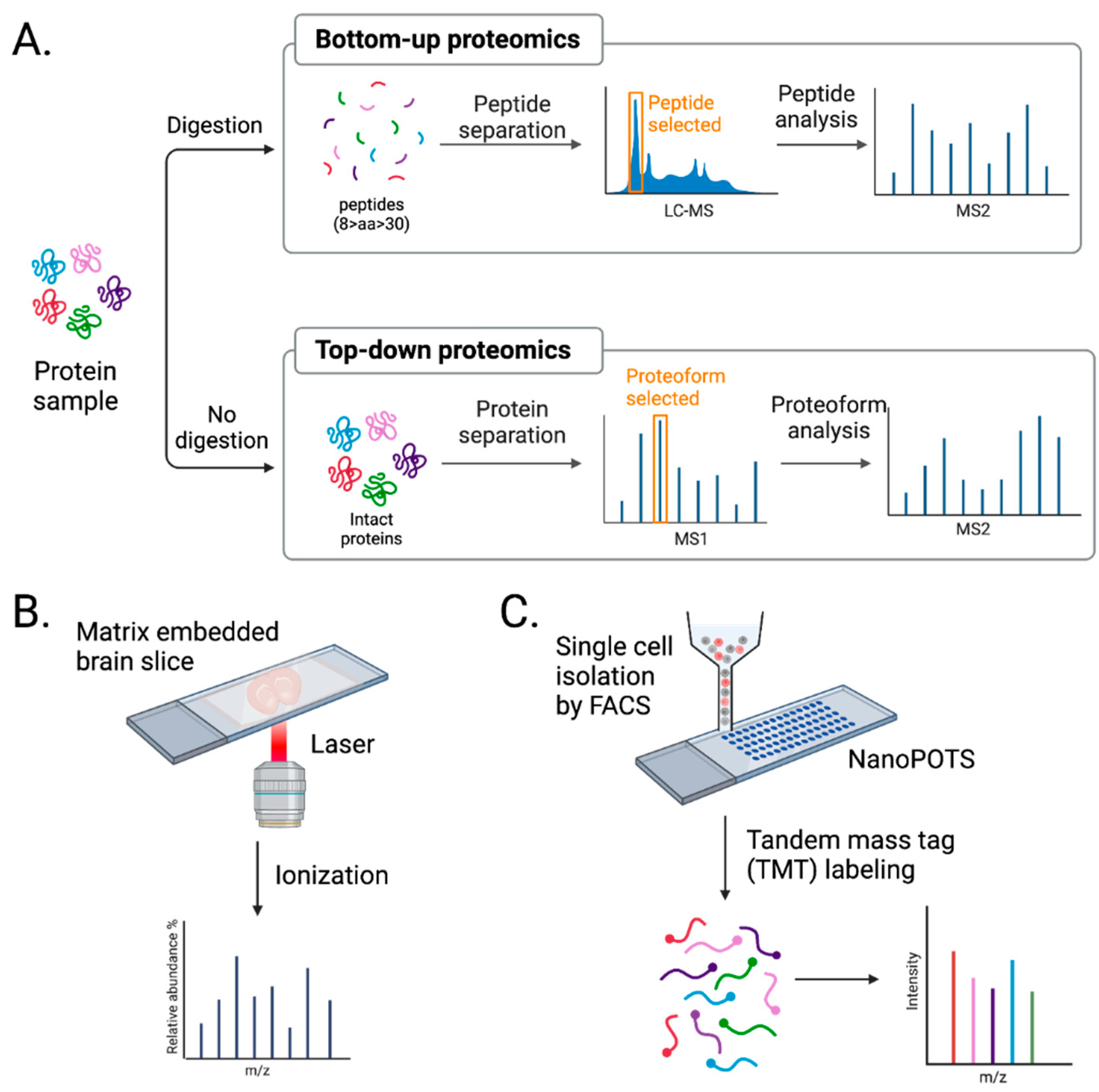
3.2. Advancements in MS approaches
4. Application of neuroproteomic analysis to neuropsychiatric disorders
5. Limitation and future perspectives
Author contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Li, J. Proteomic insights into synaptic signaling in the brain: the past, present and future. Mol Brain 2021, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcassa, G.; Dascenco, D.; de Wit, J. Proteomics-based synapse characterization: From proteins to circuits. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2023, 79, 102690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, J.; Storm, C.S.; Makarious, M.B.; Bandres-Ciga, S. Genetic and Transcriptomic Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Situation and the Road Ahead. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, I.; Ahmad, W.; Ali, A.; Anwar, L.; Nuruddin, S.M.; Ashraf, K.; Kamal, M.A. Functional Neuroproteomics: An Imperative Approach for Unravelling Protein Implicated Complexities of Brain. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2021, 20, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzate, O. Neuroproteomics. In Neuroproteomics; Frontiers in Neuroscience; Alzate, O., Ed.; Boca Raton (FL), 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, F.; Witzmann, F.A. Synaptosome proteomics. Subcell Biochem 2007, 43, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayes, A.; Grant, S.G. Neuroproteomics: understanding the molecular organization and complexity of the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009, 10, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, N.; Uy, J.; Singh, K.K. Emerging proteomic approaches to identify the underlying pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Autism 2020, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzig, J.; Jahn, O.; Tenzer, S.; Wichert, S.P.; de Monasterio-Schrader, P.; Rosfa, S.; Kuharev, J.; Yan, K.; Bormuth, I.; Bremer, J.; et al. Quantitative and integrative proteome analysis of peripheral nerve myelin identifies novel myelin proteins and candidate neuropathy loci. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 16369–16386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, K.; Nishimune, H. Similarity and Diversity of Presynaptic Molecules at Neuromuscular Junctions and Central Synapses. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straka, T.; Schroder, C.; Roos, A.; Kollipara, L.; Sickmann, A.; Williams, M.P.I.; Hafner, M.; Khan, M.M.; Rudolf, R. Regulatory Function of Sympathetic Innervation on the Endo/Lysosomal Trafficking of Acetylcholine Receptor. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 626707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.; Harrison, C.; Eaton, S.L.; Llavero Hurtado, M.; Graham, L.C.; Alkhammash, L.; Oladiran, O.A.; Gale, A.; Lamont, D.J.; Simpson, H.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Anatomy of the Human Neuromuscular Junction. Cell Rep 2017, 21, 2348–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traeger, L.L.; Sabat, G.; Barrett-Wilt, G.A.; Wells, G.B.; Sussman, M.R. A tail of two voltages: Proteomic comparison of the three electric organs of the electric eel. Sci Adv 2017, 3, e1700523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forne, I.; Abian, J.; Cerda, J. Fish proteome analysis: model organisms and non-sequenced species. Proteomics 2010, 10, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caire, M.J.; Reddy, V.; Varacallo, M. Physiology, Synapse. In StatPearls; Treasure Island (FL), 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf, P.; Antileo, E.R.; Schuman, E.M.; Dieterich, D.C. BONCAT: metabolic labeling, click chemistry, and affinity purification of newly synthesized proteomes. Methods Mol Biol 2015, 1266, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, F.; van Nierop, P.; Andres-Alonso, M.; Byrnes, A.; Cijsouw, T.; Coba, M.P.; Cornelisse, L.N.; Farrell, R.J.; Goldschmidt, H.L.; Howrigan, D.P.; et al. SynGO: An Evidence-Based, Expert-Curated Knowledge Base for the Synapse. Neuron 2019, 103, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokina, O.; McLean, C.; Croning, M.D.R.; Heil, K.F.; Wysocka, E.; He, X.; Sterratt, D.; Grant, S.G.N.; Simpson, T.I.; Armstrong, J.D. A unified resource and configurable model of the synapse proteome and its role in disease. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 9967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gelder, C.; Altelaar, M. Neuroproteomics of the Synapse: Subcellular Quantification of Protein Networks and Signaling Dynamics. Mol Cell Proteomics 2021, 20, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natividad, L.A.; Buczynski, M.W.; McClatchy, D.B.; Yates, J.R. , 3rd. From Synapse to Function: A Perspective on the Role of Neuroproteomics in Elucidating Mechanisms of Drug Addiction. Proteomes 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-de-Souza, D. Proteomics, metabolomics, and protein interactomics in the characterization of the molecular features of major depressive disorder. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2014, 16, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abul-Husn, N.S.; Devi, L.A. Neuroproteomics of the synapse and drug addiction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006, 318, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paget-Blanc, V.; Pfeffer, M.E.; Pronot, M.; Lapios, P.; Angelo, M.F.; Walle, R.; Cordelieres, F.P.; Levet, F.; Claverol, S.; Lacomme, S.; et al. A synaptomic analysis reveals dopamine hub synapses in the mouse striatum. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapkota, D.; Kater, M.S.J.; Sakers, K.; Nygaard, K.R.; Liu, Y.; Koester, S.K.; Fass, S.B.; Lake, A.M.; Khazanchi, R.; Khankan, R.R.; et al. Activity-dependent translation dynamically alters the proteome of the perisynaptic astrocyte process. Cell Rep 2022, 41, 111474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradberry, M.M.; Mishra, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; McKetney, J.M.; Vestling, M.M.; Coon, J.J.; Chapman, E.R. Rapid and Gentle Immunopurification of Brain Synaptic Vesicles. J Neurosci 2022, 42, 3512–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Schmitt, S.; Bergner, C.G.; Tyanova, S.; Kannaiyan, N.; Manrique-Hoyos, N.; Kongi, K.; Cantuti, L.; Hanisch, U.K.; Philips, M.A.; et al. Cell type- and brain region-resolved mouse brain proteome. Nat Neurosci 2015, 18, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, M.D.; Li, H.; Siemsen, B.M.; Healey, K.L.; Tran, P.K.; Woronoff, N.; Boger, H.A.; Kalivas, P.W.; Reissner, K.J. Cocaine Self-Administration and Extinction Leads to Reduced Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Expression and Morphometric Features of Astrocytes in the Nucleus Accumbens Core. Biol Psychiatry 2016, 80, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, S.; Gundelfinger, E.D. Molecular organization of the presynaptic active zone. Cell Tissue Res 2006, 326, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhof, T.C. The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu Rev Neurosci 2004, 27, 509–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.G.; Bellen, H.J. Hauling t-SNAREs on the microtubule highway. Nat Cell Biol 2004, 6, 918–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.P.; Sudhof, T.C. Cell biology of Ca2+-triggered exocytosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2010, 22, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzberger, A.J.B.; Kiessling, V.; Stroupe, C.; Liang, B.; Preobraschenski, J.; Ganzella, M.; Kreutzberger, M.A.B.; Nakamoto, R.; Jahn, R.; Castle, J.D.; et al. In vitro fusion of single synaptic and dense core vesicles reproduces key physiological properties. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birinci, Y.; Preobraschenski, J.; Ganzella, M.; Jahn, R.; Park, Y. Isolation of large dense-core vesicles from bovine adrenal medulla for functional studies. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhof, T.C.; Malenka, R.C. Understanding synapses: past, present, and future. Neuron 2008, 60, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Kim, K.T. Short-term plasticity of small synaptic vesicle (SSV) and large dense-core vesicle (LDCV) exocytosis. Cell Signal 2009, 21, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresbach, T.; Qualmann, B.; Kessels, M.M.; Garner, C.C.; Gundelfinger, E.D. The presynaptic cytomatrix of brain synapses. Cell Mol Life Sci 2001, 58, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhof, T.C. Neurotransmitter release: the last millisecond in the life of a synaptic vesicle. Neuron 2013, 80, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.A.; Nuwer, J.L.; Jacob, T.C. The Yin and Yang of GABAergic and Glutamatergic Synaptic Plasticity: Opposites in Balance by Crosstalking Mechanisms. Front Synaptic Neurosci 2022, 14, 911020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhof, T.C. Towards an Understanding of Synapse Formation. Neuron 2018, 100, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, G.; Navarrete, M.; Araque, A. Tripartite synapses: astrocytes process and control synaptic information. Trends Neurosci 2009, 32, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhy-Tselnicker, I.; Allen, N.J. Astrocytes, neurons, synapses: a tripartite view on cortical circuit development. Neural Dev 2018, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelini, G.; Pantazopoulos, H.; Durning, P.; Berretta, S. The tetrapartite synapse: a key concept in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Eur Psychiatry 2018, 50, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruyer, A.; Chioma, V.C.; Kalivas, P.W. The Opioid-Addicted Tetrapartite Synapse. Biol Psychiatry 2020, 87, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves Filho, A.J.M.; Mottin, M.; Los, D.B.; Andrade, C.H.; Macedo, D.S. The tetrapartite synapse in neuropsychiatric disorders: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) as promising targets for treatment and rational drug design. Biochimie 2022, 201, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, V.N.; De Camilli, P. Cell biology of the presynaptic terminal. Annu Rev Neurosci 2003, 26, 701–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, Y.Y.; Zurawski, Z.; Hamm, H. GPCR regulation of secretion. Pharmacol Ther 2018, 192, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeta, K.; Lourenco, M.V.; Schweitzer, B.C.; Martino Adami, P.V.; Banerjee, P.; Catuara-Solarz, S.; de La Fuente Revenga, M.; Guillem, A.M.; Haidar, M.; Ijomone, O.M.; et al. Synaptopathies: synaptic dysfunction in neurological disorders - A review from students to students. J Neurochem 2016, 138, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Kim, E. The postsynaptic organization of synapses. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.H.; Stawski, P.S.; Draycott, A.S.; Udeshi, N.D.; Lehrman, E.K.; Wilton, D.K.; Svinkina, T.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Stevens, B.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Unbounded Cellular Compartments: Synaptic Clefts. Cell 2016, 166, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederer, T.; Kaeser, P.S.; Blanpied, T.A. Transcellular Nanoalignment of Synaptic Function. Neuron 2017, 96, 680–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Ichtchenko, K.; Sudhof, T.C.; Brose, N. Neuroligin 1 is a postsynaptic cell-adhesion molecule of excitatory synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999, 96, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhoff, M.W.; Lauren, J.; Cassidy, R.M.; Dobie, F.A.; Takahashi, H.; Nygaard, H.B.; Airaksinen, M.S.; Strittmatter, S.M.; Craig, A.M. An unbiased expression screen for synaptogenic proteins identifies the LRRTM protein family as synaptic organizers. Neuron 2009, 61, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chih, B.; Gollan, L.; Scheiffele, P. Alternative Splicing Controls Selective Trans-Synaptic Interactions of the Neuroligin-Neurexin Complex. Neuron 2006, 51, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Katayama, K.-i.; Sohya, K.; Miyamoto, H.; Prasad, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ota, M.; Yasuda, H.; Tsumoto, T.; Aruga, J.; et al. Selective control of inhibitory synapse development by Slitrk3-PTPδ trans-synaptic interaction. Nature Neuroscience 2012, 15, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varoqueaux, F.; Jamain, S.; Brose, N. Neuroligin 2 is exclusively localized to inhibitory synapses. European Journal of Cell Biology 2004, 83, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkley, P.R.; Robinson, P.J. Synaptosome Preparations: Which Procedure Should I Use? In Synaptosomes; Neuromethods; 2018; pp. 27–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, E.G.; Whittaker, V.P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat 1962, 96, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, P.R.; Hardy, J.A.; Oakley, A.E.; Edwardson, J.A.; Perry, E.K.; Delaunoy, J.P. A rapid method for preparing synaptosomes: comparison, with alternative procedures. Brain Res 1981, 226, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotman, C.W.; Matthews, D.A. Synaptic plasma membranes from rat brain synaptosomes: isolation and partial characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta 1971, 249, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, R.F.; Clark, J.B. A rapid method for the preparation of relatively pure metabolically competent synaptosomes from rat brain. Biochem J 1978, 176, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkley, P.R.; Jarvie, P.E.; Robinson, P.J. A rapid Percoll gradient procedure for preparation of synaptosomes. Nat Protoc 2008, 3, 1718–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, B.G.; Mandad, S.; Truckenbrodt, S.; Krohnert, K.; Schafer, C.; Rammner, B.; Koo, S.J.; Classen, G.A.; Krauss, M.; Haucke, V.; et al. Composition of isolated synaptic boutons reveals the amounts of vesicle trafficking proteins. Science 2014, 344, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burre, J.; Volknandt, W. The synaptic vesicle proteome. J Neurochem 2007, 101, 1448–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Holt, M.; Riedel, D.; Jahn, R. Small-scale isolation of synaptic vesicles from mammalian brain. Nat Protoc 2013, 8, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, J.W.; Maycox, P.R.; Stadler, H.; Jahn, R. Uptake of GABA by rat brain synaptic vesicles isolated by a new procedure. EMBO J 1988, 7, 3023–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantranupong, L.; Saulnier, J.L.; Wang, W.; Jones, D.R.; Pacold, M.E.; Sabatini, B.L. Rapid purification and metabolomic profiling of synaptic vesicles from mammalian brain. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzumdar, M.D.; Tasic, B.; Miyamichi, K.; Li, L.; Luo, L. A global double-fluorescent Cre reporter mouse. genesis 2007, 45, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gasperi, R.; Rocher, A.B.; Sosa, M.A.G.; Wearne, S.L.; Perez, G.M.; Friedrich Jr, V.L.; Hof, P.R.; Elder, G.A. The IRG mouse: A two-color fluorescent reporter for assessing Cre-mediated recombination and imaging complex cellular relationships in situ. genesis 2008, 46, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, H.; Koizumi, K.; Kaneko, R.; Ikeda, K.; Egawa, R.; Yanagawa, Y.; Muramatsu, S.-i.; Onimaru, H.; Ishizuka, T.; Yawo, H. A Novel Reporter Rat Strain That Conditionally Expresses the Bright Red Fluorescent Protein tdTomato. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0155687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yu, L.; Pan, S.; Gao, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Dong, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, R.; Huang, L.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeting of the Rosa26 locus produces Cre reporter rat strains for monitoring Cre–loxP-mediated lineage tracing. The FEBS Journal 2017, 284, 3262–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryda, E.C.; Men, H.; Davis, D.J.; Bock, A.S.; Shaw, M.L.; Chesney, K.L.; Hankins, M.A. A novel conditional ZsGreen-expressing transgenic reporter rat strain for validating Cre recombinase expression. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 13330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Endo, H.; Ajiki, T.; Hakamata, Y.; Okada, T.; Murakami, T.; Kobayashi, E. Establishment of Cre/LoxP recombination system in transgenic rats. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2004, 319, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Im, S.-K.; Fang, S. Mouse Cre-LoxP system: general principles to determine tissue-specific roles of target genes. lar 2018, 34, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A.; Hirokawa, K.E.; Sorensen, S.A.; Gu, H.; Mills, M.; Ng, L.L.; Bohn, P.; Mortrud, M.; Ouellette, B.; Kidney, J.; et al. Anatomical characterization of Cre driver mice for neural circuit mapping and manipulation. Frontiers in Neural Circuits 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcholok, T.; Eftekharpour, E. Cre-recombinase systems for induction of neuron-specific knockout models: a guide for biomedical researchers. Neural Regen Res 2023, 18, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, Q.; Chen-Tsai, R.Y. Establishment of a Cre-rat resource for creating conditional and physiological relevant models of human diseases. Transgenic Research 2021, 30, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witten, Ilana B. ; Steinberg, Elizabeth E.; Lee, Soo Y.; Davidson, Thomas J.; Zalocusky, Kelly A.; Brodsky, M.; Yizhar, O.; Cho, Saemi L.; Gong, S.; Ramakrishnan, C.; et al. Recombinase-Driver Rat Lines: Tools, Techniques, and Optogenetic Application to Dopamine-Mediated Reinforcement. Neuron 2011, 72, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Brown, A.; Fisher, D.; Wu, Y.; Warren, J.; Cui, X. Tissue Specific Expression of Cre in Rat Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Dopamine Active Transporter-Positive Neurons. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0149379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espina, V.; Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Calvert, V.S.; VanMeter, A.; Zhou, W.; Coukos, G.; Geho, D.H.; Petricoin, E.F.; Liotta, L.A. Laser-capture microdissection. Nature Protocols 2006, 1, 586–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Piehowski, P.D.; Zhao, R.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.; Moore, R.J.; Shukla, A.K.; Petyuk, V.A.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Mathews, C.E.; et al. Nanodroplet processing platform for deep and quantitative proteome profiling of 10–100 mammalian cells. Nature Communications 2018, 9, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum, S.; Steinbach, S.; Attems, J.; Keers, S.; Riederer, P.; Gerlach, M.; May, C.; Marcus, K. Proteomic characterization of neuromelanin granules isolated from human substantia nigra by laser-microdissection. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 37139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, E.; Wisniewski, T. The use of localized proteomics to identify the drivers of Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Neural Regeneration Research 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijholt, D.A.T.; Stingl, C.; Luider, T.M. Laser Capture Microdissection of Fluorescently Labeled Amyloid Plaques from Alzheimer’s Disease Brain Tissue for Mass Spectrometric Analysis. In Clinical Proteomics: Methods and Protocols, Vlahou, A., Makridakis, M., Eds.; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2015; pp. 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Berrocoso, T.; Llombart, V.; Colas-Campas, L.; Hainard, A.; Licker, V.; Penalba, A.; Ramiro, L.; Simats, A.; Bustamante, A.; Martinez-Saez, E.; et al. Single Cell Immuno-Laser Microdissection Coupled to Label-Free Proteomics to Reveal the Proteotypes of Human Brain Cells After Ischemia. Mol Cell Proteomics 2018, 17, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Bogdanovic, N.; Nakagawa, H.; Volkmann, I.; Aoki, M.; Winblad, B.; Sakai, J.; Tjernberg, L.O. Analysis of microdissected neurons by 18O mass spectrometry reveals altered protein expression in Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 2012, 16, 1686–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.L.; Favo, D.; Garver, M.; Sun, Z.; Arion, D.; Ding, Y.; Yates, N.; Sweet, R.A.; Lewis, D.A. Laser capture microdissection–targeted mass spectrometry: a method for multiplexed protein quantification within individual layers of the cerebral cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesser, E.; Wyatt, H.; Ten Have, S.; Stierstorfer, B.; Lenter, M.; Lamond, A.I. Quantitative Profiling of the Human Substantia Nigra Proteome from Laser-capture Microdissected FFPE Tissue*. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2020, 19, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Canto, A.M.; Vieira, A.S.; A, H.B.M.; Carvalho, B.S.; Henning, B.; Norwood, B.A.; Bauer, S.; Rosenow, F.; Gilioli, R.; Cendes, F.; et al. Laser microdissection-based microproteomics of the hippocampus of a rat epilepsy model reveals regional differences in protein abundances. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensaddek, D.; Narayan, V.; Nicolas, A.; Brenes Murillo, A.; Gartner, A.; Kenyon, C.J.; Lamond, A.I. Micro-proteomics with iterative data analysis: Proteome analysis in C. elegans at the single worm level. PROTEOMICS 2016, 16, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.P.; Ludhiadch, A.; Munshi, A. Chapter 9 - Single-Cell Genomics: Technology and Applications. In Single-Cell Omics; Barh, D., Azevedo, V., Eds.; Academic Press, 2019; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, L.M.; Olsen, M.L. Novel Applications of Magnetic Cell Sorting to Analyze Cell-Type Specific Gene and Protein Expression in the Central Nervous System. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0150290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayaprolu, S.; Gao, T.; Xiao, H.; Ramesha, S.; Weinstock, L.D.; Shah, J.; Duong, D.M.; Dammer, E.B.; Webster, J.A., Jr.; Lah, J.J.; et al. Flow-cytometric microglial sorting coupled with quantitative proteomics identifies moesin as a highly-abundant microglial protein with relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener 2020, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungblut, M.; Tiveron, M.C.; Barral, S.; Abrahamsen, B.; Knöbel, S.; Pennartz, S.; Schmitz, J.; Perraut, M.; Pfrieger, F.W.; Stoffel, W.; et al. Isolation and characterization of living primary astroglial cells using the new GLAST-specific monoclonal antibody ACSA-1. Glia 2012, 60, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokum, J.A.; Shim, B.; Huang, W.; Kane, M.; Smith, J.A.; Gerzanich, V.; Simard, J.M. A large portion of the astrocyte proteome is dedicated to perivascular endfeet, including critical components of the electron transport chain. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 2021, 41, 2546–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaraju, S.; Dammer, E.B.; Raza, S.A.; Gao, T.; Xiao, H.; Betarbet, R.; Duong, D.M.; Webster, J.A.; Hales, C.M.; Lah, J.J.; et al. Quantitative proteomics of acutely-isolated mouse microglia identifies novel immune Alzheimer’s disease-related proteins. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2018, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, E.; Cools, N.; Willems, H.; Baggerman, G. FACS-Based Proteomics Enables Profiling of Proteins in Rare Cell Populations. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.; Schoendube, J.; Zimmermann, S.; Steeb, M.; Zengerle, R.; Koltay, P. Technologies for Single-Cell Isolation. Int J Mol Sci 2015, 16, 16897–16919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postupna, N.O.; Latimer, C.S.; Keene, C.D.; Montine, K.S.; Montine, T.J.; Darvas, M. Flow cytometric evaluation of crude synaptosome preparation as a way to study synaptic alteration in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuromethods 2018, 141, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesemann, C.; Gronborg, M.; Luquet, E.; Wichert, S.P.; Bernard, V.; Bungers, S.R.; Cooper, B.; Varoqueaux, F.; Li, L.; Byrne, J.A.; et al. Proteomic screening of glutamatergic mouse brain synaptosomes isolated by fluorescence activated sorting. EMBO J 2014, 33, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husi, H.; Ward, M.A.; Choudhary, J.S.; Blackstock, W.P.; Grant, S.G.N. Proteomic analysis of NMDA receptor–adhesion protein signaling complexes. Nature Neuroscience 2000, 3, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosemeci, A.; Makusky, A.J.; Jankowska-Stephens, E.; Yang, X.; Slotta, D.J.; Markey, S.P. Composition of the synaptic PSD-95 complex. Mol Cell Proteomics 2007, 6, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemmer, P.; Smit, A.B.; Li, K.W. Proteomics analysis of immuno-precipitated synaptic protein complexes. Journal of Proteomics 2009, 72, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, J.A.; Brucker, W.J.; Hawrot, E. Proteomic Analysis of an α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Interactome. Journal of Proteome Research 2009, 8, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, C.D.; Gafken, P.R.; Norbeck, A.D.; Doneanu, C.E.; Stapels, M.D.; Barofsky, D.F.; Minami, M.; Saugstad, J.A. Proteomic analysis of native metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 protein complexes reveals novel molecular constituents. Journal of Neurochemistry 2004, 91, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.O.; Husi, H.; Yu, L.; Brandon, J.M.; Anderson, C.N.G.; Blackstock, W.P.; Choudhary, J.S.; Grant, S.G.N. Molecular characterization and comparison of the components and multiprotein complexes in the postsynaptic proteome. Journal of Neurochemistry 2006, 97, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaut, G.; Shevchenko, A.; Rutz, B.; Wilm, M.; Mann, M.; Séraphin, B. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. Nature Biotechnology 1999, 17, 1030–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. The tandem affinity purification technology: an overview. Biotechnol Lett 2011, 33, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; Collins, M.O.; Uren, R.T.; Kopanitsa, M.V.; Komiyama, N.H.; Croning, M.D.; Zografos, L.; Armstrong, J.D.; Choudhary, J.S.; Grant, S.G. Targeted tandem affinity purification of PSD-95 recovers core postsynaptic complexes and schizophrenia susceptibility proteins. Mol Syst Biol 2009, 5, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Collins, M.O.; Harmse, J.; Choudhary, J.S.; Grant, S.G.N.; Komiyama, N.H. Cell-type-specific visualisation and biochemical isolation of endogenous synaptic proteins in mice. Eur J Neurosci 2020, 51, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.E.; Glenn, W.S.; Hamblin, G.D.; Tirrell, D.A. Cell-selective proteomics for biological discovery. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2017, 36, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingleton, E.; Li, Y.; Roche, K.W. Advances in Proteomics Allow Insights Into Neuronal Proteomes. Front Mol Neurosci 2021, 14, 647451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Castelao, B.; Schanzenbacher, C.T.; Hanus, C.; Glock, C.; Tom Dieck, S.; Dorrbaum, A.R.; Bartnik, I.; Nassim-Assir, B.; Ciirdaeva, E.; Mueller, A.; et al. Cell-type-specific metabolic labeling of nascent proteomes in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 2017, 35, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Castelao, B.; Schanzenbacher, C.T.; Langer, J.D.; Schuman, E.M. Cell-type-specific metabolic labeling, detection and identification of nascent proteomes in vivo. Nat Protoc 2019, 14, 556–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Bathla, S.; Williams, K.R.; Nairn, A.C. Deciphering Spatial Protein-Protein Interactions in Brain Using Proximity Labeling. Mol Cell Proteomics 2022, 21, 100422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Jensen, S.C.; Noble, K.A.; Kc, B.; Roux, K.H.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Roux, K.J. An improved smaller biotin ligase for BioID proximity labeling. Molecular Biology of the Cell 2016, 27, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branon, T.C.; Bosch, J.A.; Sanchez, A.D.; Udeshi, N.D.; Svinkina, T.; Carr, S.A.; Feldman, J.L.; Perrimon, N.; Ting, A.Y. Efficient proximity labeling in living cells and organisms with TurboID. Nature Biotechnology 2018, 36, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.S.; Martell, J.D.; Kamer, K.J.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Mootha, V.K.; Ting, A.Y. Directed evolution of APEX2 for electron microscopy and proximity labeling. Nature Methods 2015, 12, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cijsouw, T.; Ramsey, A.M.; Lam, T.T.; Carbone, B.E.; Blanpied, T.A.; Biederer, T. Mapping the Proteome of the Synaptic Cleft through Proximity Labeling Reveals New Cleft Proteins. Proteomes 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuster, S.A.; Li, J.; Chon, U.; Sinantha-Hu, M.C.; Luginbuhl, D.J.; Udeshi, N.D.; Carey, D.K.; Takeo, Y.H.; Xie, Q.; Xu, C.; et al. In situ cell-type-specific cell-surface proteomic profiling in mice. Neuron 2022, 110, 3882–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumrongprechachan, V.; Salisbury, R.B.; Soto, G.; Kumar, M.; MacDonald, M.L.; Kozorovitskiy, Y. Cell-type and subcellular compartment-specific APEX2 proximity labeling reveals activity-dependent nuclear proteome dynamics in the striatum. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, K.D.; Shi, S.M.; Wyss-Coray, T. Unraveling protein dynamics to understand the brain - the next molecular frontier. Mol Neurodegener 2022, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uezu, A.; Kanak, D.J.; Bradshaw, T.W.A.; Soderblom, E.J.; Catavero, C.M.; Burette, A.C.; Weinberg, R.J.; Soderling, S.H. Identification of an elaborate complex mediating postsynaptic inhibition. Science 2016, 353, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, E.F.; Dube, S.; Uezu, A.; Locke, M.; Soderblom, E.J.; Soderling, S.H. In vivo proximity proteomics of nascent synapses reveals a novel regulator of cytoskeleton-mediated synaptic maturation. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayaprolu, S.; Bitarafan, S.; Santiago, J.V.; Betarbet, R.; Sunna, S.; Cheng, L.; Xiao, H.; Nelson, R.S.; Kumar, P.; Bagchi, P.; et al. Cell type-specific biotin labeling in vivo resolves regional neuronal and astrocyte proteomic differences in mouse brain. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Wallace, J.T.; Baldwin, K.T.; Purkey, A.M.; Uezu, A.; Courtland, J.L.; Soderblom, E.J.; Shimogori, T.; Maness, P.F.; Eroglu, C.; et al. Chemico-genetic discovery of astrocytic control of inhibition in vivo. Nature 2020, 588, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, B.D.; Choi, S.J.; Mosharov, E.V.; Soni, R.K.; Sulzer, D.; Sims, P.A. Subcellular proteomics of dopamine neurons in the mouse brain. Elife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.M.T.; Kim, J.; Doan, T.T.; Lee, M.-W.; Lee, M. APEX Proximity Labeling as a Versatile Tool for Biological Research. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupree, E.J.; Jayathirtha, M.; Yorkey, H.; Mihasan, M.; Petre, B.A.; Darie, C.C. A Critical Review of Bottom-Up Proteomics: The Good, the Bad, and the Future of this Field. Proteomes 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fonslow, B.R.; Shan, B.; Baek, M.C.; Yates, J.R. , 3rd. Protein analysis by shotgun/bottom-up proteomics. Chem Rev 2013, 113, 2343–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Linial, M.; Goodlett, D.; Langridge-Smith, P.; Ah Goo, Y.; Safford, G.; Bonilla*, L.; Kruppa, G.; Zubarev, R.; et al. Proteoform: a single term describing protein complexity. Nature Methods 2013, 10, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherman, A.D.; Skinner, O.S.; Kelleher, N.L. Top Down proteomics: facts and perspectives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014, 445, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melby, J.A.; Roberts, D.S.; Larson, E.J.; Brown, K.A.; Bayne, E.F.; Jin, S.; Ge, Y. Novel Strategies to Address the Challenges in Top-Down Proteomics. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 2021, 32, 1278–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.S.; Nairn, A.C. Cell-Type-Specific Proteomics: A Neuroscience Perspective. Proteomes 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, C.; Wang, H.A.O.; Schapiro, D.; Zivanovic, N.; Jacobs, A.; Hattendorf, B.; Schüffler, P.J.; Grolimund, D.; Buhmann, J.M.; Brandt, S.; et al. Highly multiplexed imaging of tumor tissues with subcellular resolution by mass cytometry. Nature Methods 2014, 11, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, L.V.D.; Sarah, M.G.; Corey, M.W.; Austin, B.K.; Kristen, I.F.; Irene, C.; Christopher, D.D.; Eli, R.Z. A developmental atlas of the mouse brain by single-cell mass cytometry. bioRxiv 2022, 2022.2007.2027.501794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gaiteri, C.; Bodea, L.G.; Wang, Z.; McElwee, J.; Podtelezhnikov, A.A.; Zhang, C.; Xie, T.; Tran, L.; Dobrin, R.; et al. Integrated systems approach identifies genetic nodes and networks in late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Cell 2013, 153, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nature Reviews Genetics 2012, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa Abreu, R.; Penalva, L.O.; Marcotte, E.M.; Vogel, C. Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression levels. Molecular BioSystems 2009, 5, 1512–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuri, M.S.; Williams, K.; Nairn, A.C. Uncovering biology by single-cell proteomics. Commun Biol 2023, 6, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budnik, B.; Levy, E.; Harmange, G.; Slavov, N. SCoPE-MS: mass spectrometry of single mammalian cells quantifies proteome heterogeneity during cell differentiation. Genome Biol 2018, 19, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.F.; Zhao, R.; Williams, S.M.; Moore, R.J.; Schultz, K.; Chrisler, W.B.; Pasa-Tolic, L.; Rodland, K.D.; Smith, R.D.; Shi, T.; et al. An Improved Boosting to Amplify Signal with Isobaric Labeling (iBASIL) Strategy for Precise Quantitative Single-cell Proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 2020, 19, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto-Silva, L.; Junqueira, M. Single-cell proteomics: A treasure trove in neurobiology. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 2021, 1869, 140658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Song, F.; Lei, H. Genomics in neurological disorders. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2014, 12, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reim, D.; Distler, U.; Halbedl, S.; Verpelli, C.; Sala, C.; Bockmann, J.; Tenzer, S.; Boeckers, T.M.; Schmeisser, M.J. Proteomic Analysis of Post-synaptic Density Fractions from Shank3 Mutant Mice Reveals Brain Region Specific Changes Relevant to Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front Mol Neurosci 2017, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shweiki, M.R.; Oeckl, P.; Steinacker, P.; Barschke, P.; Dorner-Ciossek, C.; Hengerer, B.; Schonfeldt-Lecuona, C.; Otto, M. Proteomic analysis reveals a biosignature of decreased synaptic protein in cerebrospinal fluid of major depressive disorder. Transl Psychiatry 2020, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, K.; Beasley, C.L.; Dicker, P.; Fagan, A.; English, J.; Pariante, C.M.; Wait, R.; Dunn, M.J.; Cotter, D.R. Prominent synaptic and metabolic abnormalities revealed by proteomic analysis of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2008, 13, 1102–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullin, A.P.; Gokhale, A.; Moreno-De-Luca, A.; Sanyal, S.; Waddington, J.L.; Faundez, V. Neurodevelopmental disorders: mechanisms and boundary definitions from genomes, interactomes and proteomes. Transl Psychiatry 2013, 3, e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.; Elsabbagh, M.; Baird, G.; Veenstra-Vanderweele, J. Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet 2018, 392, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wang, T.; Wan, H.; Han, L.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Berton, F.; Francesconi, W.; et al. Fmr1 deficiency promotes age-dependent alterations in the cortical synaptic proteome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, E4697–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.J.; Paranjape, S.R.; Walker, M.P.; Choudhury, R.; Wolter, J.M.; Fragola, G.; Emanuele, M.J.; Major, M.B.; Zylka, M.J. The autism-linked UBE3A T485A mutant E3 ubiquitin ligase activates the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by inhibiting the proteasome. J Biol Chem 2017, 292, 12503–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matic, K.; Eninger, T.; Bardoni, B.; Davidovic, L.; Macek, B. Quantitative phosphoproteomics of murine Fmr1-KO cell lines provides new insights into FMRP-dependent signal transduction mechanisms. J Proteome Res 2014, 13, 4388–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.O.; Yu, L.; Coba, M.P.; Husi, H.; Campuzano, I.; Blackstock, W.P.; Choudhary, J.S.; Grant, S.G. Proteomic analysis of in vivo phosphorylated synaptic proteins. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 5972–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wilkinson, B.; Clementel, V.A.; Hou, J.; O'Dell, T.J.; Coba, M.P. Long-term potentiation modulates synaptic phosphorylation networks and reshapes the structure of the postsynaptic interactome. Sci Signal 2016, 9, rs8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amal, H.; Barak, B.; Bhat, V.; Gong, G.; Joughin, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wishnok, J.S.; Feng, G.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Shank3 mutation in a mouse model of autism leads to changes in the S-nitroso-proteome and affects key proteins involved in vesicle release and synaptic function. Mol Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, N.; Cheng, A.A.; Brown, C.O.; Meka, D.P.; Hong, S.; Uy, J.A.; El-Hajjar, J.; Pipko, N.; Unda, B.K.; Schwanke, B.; et al. Neuron-specific protein network mapping of autism risk genes identifies shared biological mechanisms and disease-relevant pathologies. Cell Rep 2022, 41, 111678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilot, A.K.; Bebek, G.; Niazi, F.; Altemus, J.B.; Romigh, T.; Frazier, T.W.; Eng, C. Neural transcriptome of constitutional Pten dysfunction in mice and its relevance to human idiopathic autism spectrum disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2016, 21, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xu, H. Proteolytic processing of Alzheimer's beta-amyloid precursor protein. J Neurochem 2012, 120 Suppl 1, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, S.; Won, H.H.; Yu, T.Y.; Lee, E.M.; Kang, J.M.; Lewis, M.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Associations between vascular risk factors and subsequent Alzheimer's disease in older adults. Alzheimers Res Ther 2020, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgilio, E.; De Marchi, F.; Contaldi, E.; Dianzani, U.; Cantello, R.; Mazzini, L.; Comi, C. The Role of Tau beyond Alzheimer's Disease: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, N.N.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Sharma, M.; Luo, W. The complexity of tau in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 2019, 705, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chetelat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, G.M.; Li, S.; Mehta, T.H.; Garcia-Munoz, A.; Shepardson, N.E.; Smith, I.; Brett, F.M.; Farrell, M.A.; Rowan, M.J.; Lemere, C.A.; et al. Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer's brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med 2008, 14, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejanovic, B.; Huntley, M.A.; De Maziere, A.; Meilandt, W.J.; Wu, T.; Srinivasan, K.; Jiang, Z.; Gandham, V.; Friedman, B.A.; Ngu, H.; et al. Changes in the Synaptic Proteome in Tauopathy and Rescue of Tau-Induced Synapse Loss by C1q Antibodies. Neuron 2018, 100, 1322–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, M.; Clayton, E.; Kaminski Schierle, G.S. Synaptic tau: A pathological or physiological phenomenon? Acta Neuropathol Commun 2021, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzioras, M.; McGeachan, R.I.; Durrant, C.S.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 2023, 19, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.Y.; Nouwens, A.S.; Dodd, P.R.; Etheridge, N. The synaptic proteome in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 2013, 9, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesse, R.; Hurtado, M.L.; Jackson, R.J.; Eaton, S.L.; Herrmann, A.G.; Colom-Cadena, M.; Tzioras, M.; King, D.; Rose, J.; Tulloch, J.; et al. Comparative profiling of the synaptic proteome from Alzheimer's disease patients with focus on the APOE genotype. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2019, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoyama, K.; Matsuura, K.; Takano, M.; Otani, M.; Tomiyama, T.; Mori, H.; Matsuyama, S. Proteomic analysis involved with synaptic plasticity improvement by GABA(A) receptor blockade in hippocampus of a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Res 2021, 165, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Cherian, J.; Gohil, K.; Atkinson, D. Schizophrenia: overview and treatment options. P T 2014, 39, 638–645. [Google Scholar]
- Luvsannyam, E.; Jain, M.S.; Pormento, M.K.L.; Siddiqui, H.; Balagtas, A.R.A.; Emuze, B.O.; Poprawski, T. Neurobiology of Schizophrenia: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e23959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, M.J.; Sawa, A.; Mortensen, P.B. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2016, 388, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisch, R.; Saniotis, A.; Wolf, R.; Bielau, H.; Bernstein, H.G.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B.; Braun, K.; Jankowski, Z.; Kumaratilake, J.; et al. The role of dopamine in schizophrenia from a neurobiological and evolutionary perspective: old fashioned, but still in vogue. Front Psychiatry 2014, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.J.; Weinberger, D.R. Schizophrenia genes, gene expression, and neuropathology: on the matter of their convergence. Mol Psychiatry 2005, 10, 40–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimo, E.F.; Beck, K.; Reis Marques, T.; Howes, O.D. Synaptic loss in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis and systematic review of synaptic protein and mRNA measures. Mol Psychiatry 2019, 24, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, R.; Weinberger, D.R. Genetic insights into the neurodevelopmental origins of schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 2017, 18, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, M.; Stringer, S.; Gebuis, T.; Paliukhovich, I.; Li, K.W.; Posthuma, D.; Sullivan, P.F.; Smit, A.B.; van Kesteren, R.E. Combined cellomics and proteomics analysis reveals shared neuronal morphology and molecular pathway phenotypes for multiple schizophrenia risk genes. Mol Psychiatry 2021, 26, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focking, M.; Lopez, L.M.; English, J.A.; Dicker, P.; Wolff, A.; Brindley, E.; Wynne, K.; Cagney, G.; Cotter, D.R. Proteomic and genomic evidence implicates the postsynaptic density in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2015, 20, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; Howrigan, D.P.; Wilkinson, B.; Souaiaia, T.; Evgrafov, O.V.; Genovese, G.; Clementel, V.A.; Tudor, J.C.; et al. Spatiotemporal profile of postsynaptic interactomes integrates components of complex brain disorders. Nat Neurosci 2017, 20, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Administration., S.A.a.M.H.S. Administration., S.A.a.M.H.S. Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56). 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Martins-de-Souza, D. Comprehending depression through proteomics. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2012, 15, 1373–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, C.L.; Pennington, K.; Behan, A.; Wait, R.; Dunn, M.J.; Cotter, D. Proteomic analysis of the anterior cingulate cortex in the major psychiatric disorders: Evidence for disease-associated changes. Proteomics 2006, 6, 3414–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston-Wilson, N.L.; Sims, C.D.; Hofmann, J.P.; Anderson, L.; Shore, A.D.; Torrey, E.F.; Yolken, R.H. Disease-specific alterations in frontal cortex brain proteins in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. The Stanley Neuropathology Consortium. Mol Psychiatry 2000, 5, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-de-Souza, D.; Guest, P.C.; Harris, L.W.; Vanattou-Saifoudine, N.; Webster, M.J.; Rahmoune, H.; Bahn, S. Identification of proteomic signatures associated with depression and psychotic depression in post-mortem brains from major depression patients. Transl Psychiatry 2012, 2, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-de-Souza, D.; Guest, P.C.; Vanattou-Saifoudine, N.; Rahmoune, H.; Bahn, S. Phosphoproteomic differences in major depressive disorder postmortem brains indicate effects on synaptic function. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2012, 262, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditzen, C.; Tang, N.; Jastorff, A.M.; Teplytska, L.; Yassouridis, A.; Maccarrone, G.; Uhr, M.; Bronisch, T.; Miller, C.A.; Holsboer, F.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for major depression confirm relevance of associated pathophysiology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B.; Zhang, R.F.; Luo, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L.; Li, W.J.; Mu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of plasma from major depressive patients: identification of proteins associated with lipid metabolism and immunoregulation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2012, 15, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, R.E. Neural substrates of conditioned-cued relapse to drug-seeking behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2002, 71, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.J.; Wolf, M.E. Psychomotor stimulant addiction: a neural systems perspective. J Neurosci 2002, 22, 3312–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasinska, A.J.; Chen, B.T.; Bonci, A.; Stein, E.A. Dorsal medial prefrontal cortex (MPFC) circuitry in rodent models of cocaine use: implications for drug addiction therapies. Addict Biol 2015, 20, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Oever, M.C.; Spijker, S.; Smit, A.B.; De Vries, T.J. Prefrontal cortex plasticity mechanisms in drug seeking and relapse. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2010, 35, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, P.J.; Peng, L.; Kivell, B.M. Proteomics Analysis of Dorsal Striatum Reveals Changes in Synaptosomal Proteins following Methamphetamine Self-Administration in Rats. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0139829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lull, M.E.; Erwin, M.S.; Morgan, D.; Roberts, D.C.; Vrana, K.E.; Freeman, W.M. Persistent proteomic alterations in the medial prefrontal cortex with abstinence from cocaine self-administration. Proteomics Clin Appl 2009, 3, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, S.; Xue, X.; Salisbury, R.; Shelton, M.A.; Kim, S.M.; Hildebrand, M.A.; Glausier, J.R.; Freyberg, Z.; Tseng, G.C.; Yocum, A.K.; et al. Uncovering circadian rhythm disruptions of synaptic proteome signaling in prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens associated with opioid use disorder. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, M.D.; Heinsbroek, J.A.; Gipson, C.D.; Kupchik, Y.M.; Spencer, S.; Smith, A.C.; Roberts-Wolfe, D.; Kalivas, P.W. The Nucleus Accumbens: Mechanisms of Addiction across Drug Classes Reflect the Importance of Glutamate Homeostasis. Pharmacol Rev 2016, 68, 816–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.G.; Hendrickson, C.L. High-resolution mass spectrometers. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif) 2008, 1, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chu, S.; Tan, S.; Yin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Dai, X.; Gong, X.; Fang, X.; Tian, D. Towards Higher Sensitivity of Mass Spectrometry: A Perspective From the Mass Analyzers. Front Chem 2021, 9, 813359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, J.N.; Baker, E.S. Ion Mobility Spectrometry: Fundamental Concepts, Instrumentation, Applications, and the Road Ahead. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 2019, 30, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, A.D.; Thielert, M.; Vasilopoulou, C.; Ammar, C.; Coscia, F.; Mund, A.; Hoerning, O.B.; Bache, N.; Apalategui, A.; Lubeck, M.; et al. Ultra-high sensitivity mass spectrometry quantifies single-cell proteome changes upon perturbation. Mol Syst Biol 2022, 18, e10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, M.K.; Covington, H.E., 3rd; Chaudhury, D.; Friedman, A.K.; Sun, H.; Damez-Werno, D.; Dietz, D.M.; Zaman, S.; Koo, J.W.; Kennedy, P.J.; et al. Cell type-specific loss of BDNF signaling mimics optogenetic control of cocaine reward. Science 2010, 330, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, A.V.; Tye, L.D.; Kreitzer, A.C. Distinct roles for direct and indirect pathway striatal neurons in reinforcement. Nat Neurosci 2012, 15, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calipari, E.S.; Bagot, R.C.; Purushothaman, I.; Davidson, T.J.; Yorgason, J.T.; Pena, C.J.; Walker, D.M.; Pirpinias, S.T.; Guise, K.G.; Ramakrishnan, C.; et al. In vivo imaging identifies temporal signature of D1 and D2 medium spiny neurons in cocaine reward. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, 2726–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, P.E.; Kieffer, B.L. The multiple facets of opioid receptor function: implications for addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2013, 23, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.D.; Kashima, D.T.; Manz, K.M.; Grueter, C.A.; Grueter, B.A. Synaptic Plasticity in the Nucleus Accumbens: Lessons Learned from Experience. ACS Chem Neurosci 2018, 9, 2114–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartoff, E.H.; Connery, H.S. It's MORe exciting than mu: crosstalk between mu opioid receptors and glutamatergic transmission in the mesolimbic dopamine system. Front Pharmacol 2014, 5, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Cizeron, M.; Qiu, Z.; Benavides-Piccione, R.; Kopanitsa, M.V.; Skene, N.G.; Koniaris, B.; DeFelipe, J.; Fransen, E.; Komiyama, N.H.; et al. Architecture of the Mouse Brain Synaptome. Neuron 2018, 99, 781–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, O.E.; Qiu, Z.; Smith, C.; Grant, S.G.N. A single-synapse resolution survey of PSD95-positive synapses in twenty human brain regions. Eur J Neurosci 2021, 54, 6864–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cizeron, M.; Qiu, Z.; Koniaris, B.; Gokhale, R.; Komiyama, N.H.; Fransen, E.; Grant, S.G.N. A brainwide atlas of synapses across the mouse life span. Science 2020, 369, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minehart, J.A.; Speer, C.M. A Picture Worth a Thousand Molecules-Integrative Technologies for Mapping Subcellular Molecular Organization and Plasticity in Developing Circuits. Front Synaptic Neurosci 2020, 12, 615059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




