Submitted:
18 May 2023
Posted:
19 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The role of GABA and its receptors in pain transduction and modulation
2.1. The role of GABA in pain transduction and regulation
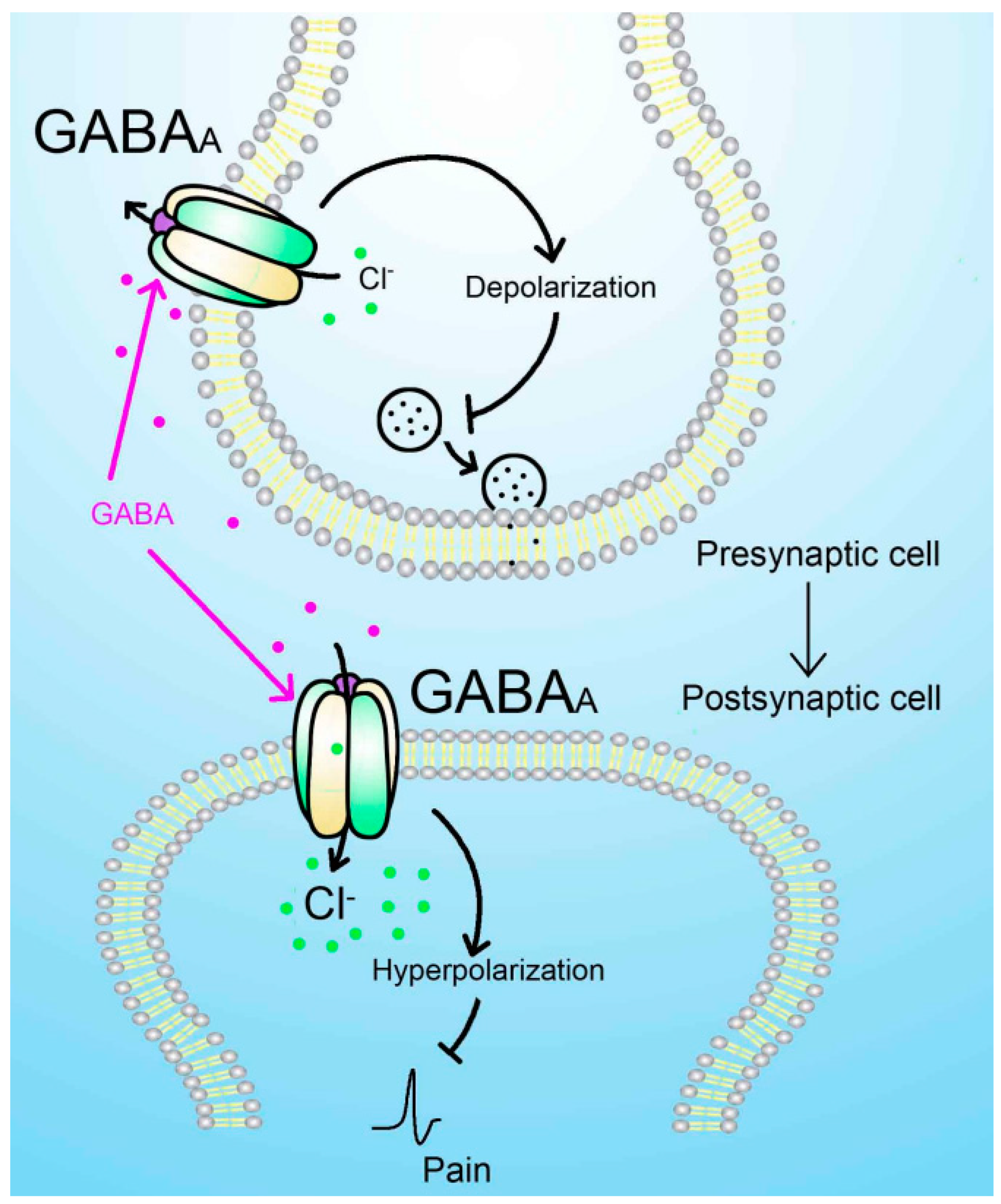
2.2. The role of GABAA receptors in pain transduction and modulation
2.2.1. Mechanism of analgesic action of alpha(α) subtype receptors
| Subunit | Main distribution areas |
|---|---|
| α1 | Hippocampus, cerebral cortex, pericentral canal of spinal cord |
| α2 | Cerebellum, forebrain, superficial dorsal horn of spinal cord |
| α3 | Cortical, dorsal horn of the spinal cord and pericentral canal |
| α4 | Striatum, thalamus |
| α5 | Olfactory bulb, hippocampus |
| α6 | Cochlear nucleus granule cells, Cerebellar granule cells |
2.2.2. Mechanism of analgesic action of delta(δ) subtype receptors
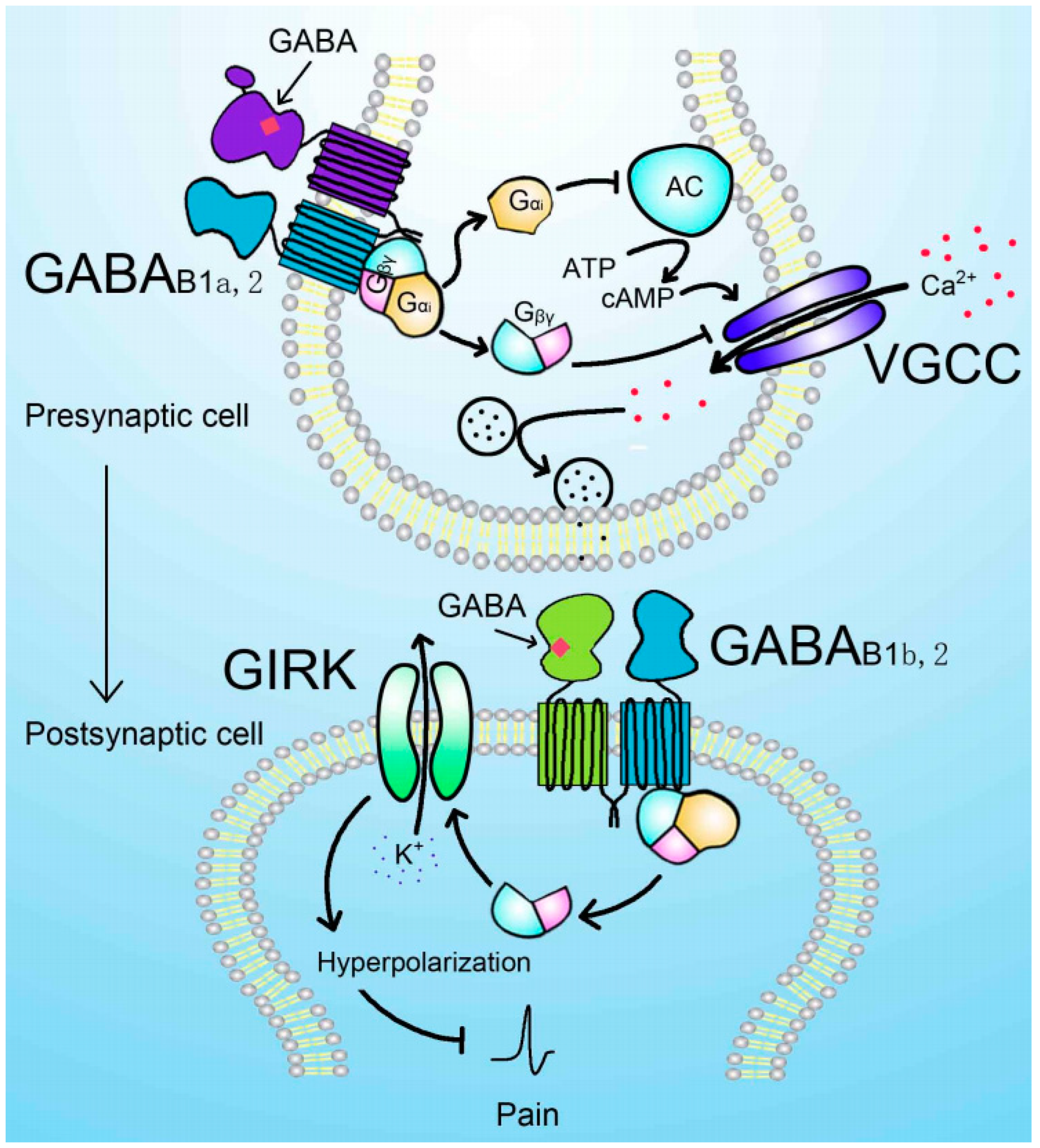
2.3. The role of GABAB receptors in pain transduction and modulation
3. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Institute Of Medicine Us Committee On Advancing Pain Research, C. A. Education. In Relieving pain in america: A blueprint for transforming prevention, care, education, and research; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, T.S.; Baron R; Haanpaa, M. ; Kalso, E.; Loeser, J.D.; Rice, A.; Treede, R.D. A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2011, 152, 2204–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic pain: From mechanisms to treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain. 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; Mcnicol, E.; Baron R; Dworkin, R. H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpaa, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; Kamerman, P.R.; Lund, K.; Moore, A.; Raja, S.N.; Rice, A.S.; Rowbotham, M.; Sena, E.; Siddall, P.; Smith, B.H.; Wallace, M. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalso, E.; Aldington, D.J.; Moore, R.A. Drugs for neuropathic pain. BMJ. 2013, 347, f7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron R; Binder, A. ; Wasner, G. Neuropathic pain: Diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, L.K.; Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S. The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.S.; Hines, R.M. Regulation of GABA(A) receptor subunit expression in substance use disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolund, B.; Ebert, B.; Kristiansen, U.; Liljefors, T.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P. GABA(A) receptor ligands and their therapeutic potentials. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasa, S.B.; Mahendran, R.; Muthusamy, G.; Thankappan, B.; Selta, D.; Angayarkanni, J. A brief review on the non-protein amino acid, gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA): Its production and role in microbes. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enna, S.J.; Mccarson, K.E. The role of GABA in the mediation and perception of pain. Adv Pharmacol. 2006, 54, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cellot, G.; Cherubini, E. GABAergic signaling as therapeutic target for autism spectrum disorders. Front Pediatr. 2014, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.; Carvalho, P.; de Vries, M.G.; Teixeira-Pinto, A.; Wilson, S.P.; Westerink, B.; Tavares, I. GABA acting on GABAB receptors located in a medullary pain facilitatory area enhances nociceptive behaviors evoked by intraplantar formalin injection. Pain. 2015, 156, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braz, J.M.; Wang, X.; Guan, Z.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Basbaum, A.I. Transplant-mediated enhancement of spinal cord GABAergic inhibition reverses paclitaxel-induced mechanical and heat hypersensitivity. Pain. 2015, 156, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braz, J.M.; Sharif-Naeini, R.; Vogt, D.; Kriegstein, A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Basbaum, A.I. Forebrain GABAergic neuron precursors integrate into adult spinal cord and reduce injury-induced neuropathic pain. Neuron. 2012, 74, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiger, J.L.; Russek, S.J. GABAA receptors: Building the bridge between subunit mRNAs, their promoters, and cognate transcription factors. Pharmacol Ther. 2004, 101, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieghart, W.; Fuchs, K.; Tretter, V.; Ebert, V.; Jechlinger, M.; Hoger, H.; Adamiker, D. Structure and subunit composition of GABA(A) receptors. Neurochem. Int. 1999, 34, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backus, K.H.; Arigoni, M.; Drescher, U.; Scheurer, L.; Malherbe, P.; Mohler, H.; Benson, J.A. Stoichiometry of a recombinant GABAA receptor deduced from mutation-induced rectification. Neuroreport. 1993, 5, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Kusay, A.S.; Jiang, T.; Chebib, M.; Balle, T. Delta-containing GABA(A) receptors in pain management: Promising targets for novel analgesics. Neuropharmacology. 2021, 195, 108675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.J.; Cervero, F.; de Koninck, Y. Role of cation-chloride-cotransporters (CCC) in pain and hyperalgesia. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, K.T.; Staley, K.J.; Nahed, B.V.; Gamba, G.; Hebert, S.C.; Lifton, R.P.; Mount, D.B. Roles of the cation-chloride cotransporters in neurological disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2008, 4, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, W.D. John Eccles' studies of spinal cord presynaptic inhibition. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 78, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Nicas, E.; Laird, J.M.; Cervero, F. GABAA-Receptor blockade reverses the injury-induced sensitization of nociceptor-specific (NS) neurons in the spinal dorsal horn of the rat. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirker, S.; Schwarzer, C.; Wieselthaler, A.; Sieghart, W.; Sperk, G. GABA(A) receptors: Immunocytochemical distribution of 13 subunits in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience. 2000, 101, 815–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortnagl, H.; Tasan, R.O.; Wieselthaler, A.; Kirchmair, E.; Sieghart, W.; Sperk, G. Patterns of mRNA and protein expression for 12 GABAA receptor subunits in the mouse brain. Neuroscience. 2013, 236, 345–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusi-Oukari, M.; Korpi, E.R. Regulation of GABA(A) receptor subunit expression by pharmacological agents. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 97–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Ning, G.; Guo, Y.; Ali, R.; Macdonald, R.L.; De Blas, A.L.; Luscher, B.; Chen, G. Gamma-Aminobutyric acid type a (GABAA) receptor alpha subunits play a direct role in synaptic versus extrasynaptic targeting. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 27417–27430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckernan, R.M.; Rosahl, T.W.; Reynolds, D.S.; Sur, C.; Wafford, K.A.; Atack, J.R.; Farrar, S.; Myers, J.; Cook, G.; Ferris, P.; Garrett, L.; Bristow, L.; Marshall, G.; Macaulay, A.; Brown, N.; Howell, O.; Moore, K.W.; Carling, R.W.; Street, L.J.; Castro, J.L.; Ragan, C.I.; Dawson, G.R.; Whiting, P.J. Sedative but not anxiolytic properties of benzodiazepines are mediated by the GABA(A) receptor alpha1 subtype. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crestani, F.; Low, K.; Keist, R.; Mandelli, M.; Mohler, H.; Rudolph, U. Molecular targets for the myorelaxant action of diazepam. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, G.; Ahring, P.K.; Mirza, N.R. Developing analgesics by enhancing spinal inhibition after injury: GABAA receptor subtypes as novel targets. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knabl, J.; Witschi, R.; Hosl, K.; Reinold, H.; Zeilhofer, U.B.; Ahmadi, S.; Brockhaus, J.; Sergejeva, M.; Hess, A.; Brune, K.; Fritschy, J.M.; Rudolph, U.; Mohler, H.; Zeilhofer, H.U. Reversal of pathological pain through specific spinal GABAA receptor subtypes. Nature. 2008, 451, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, N.R.; Larsen, J.S.; Mathiasen, C.; Jacobsen, T.A.; Munro, G.; Erichsen, H.K.; Nielsen, A.N.; Troelsen, K.B.; Nielsen, E.O.; Ahring, P.K. NS11394 [3'- [5-(1-hydroxy-1-methyl-ethyl)-benzoimidazol-1-yl]-biphenyl-2-carbonitrile], a unique subtype-selective GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator: In vitro actions, pharmacokinetic properties and in vivo anxiolytic efficacy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 954–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, G.; Lopez-Garcia, J.A.; Rivera-Arconada, I.; Erichsen, H.K.; Nielsen, E.O.; Larsen, J.S.; Ahring, P.K.; Mirza, N.R. Comparison of the novel subtype-selective GABAA receptor-positive allosteric modulator NS11394 [3'- [5-(1-hydroxy-1-methyl-ethyl)-benzoimidazol-1-yl]-biphenyl-2-carbonitrile] with diazepam, zolpidem, bretazenil, and gaboxadol in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scott-Stevens, P.; Atack, J.R.; Sohal, B.; Worboys, P. Rodent pharmacokinetics and receptor occupancy of the GABAA receptor subtype selective benzodiazepine site ligand L-838417. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2005, 26, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atack, J.R.; Wafford, K.A.; Tye, S.J.; Cook, S.M.; Sohal, B.; Pike, A.; Sur, C.; Melillo, D.; Bristow, L.; Bromidge, F.; Ragan, I.; Kerby, J.; Street, L.; Carling, R.; Castro, J.L.; Whiting, P.; Dawson, G.R.; Mckernan, R.M. TPA023 [7-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-(2-ethyl-2H-1,2,4-triazol-3-ylmethoxy)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazolo [4,3-b]pyridazine], an agonist selective for alpha2- and alpha3-containing GABAA receptors, is a nonsedating anxiolytic in rodents and primates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickolls, S.; Mace, H.; Fish, R.; Edye, M.; Gurrell, R.; Ivarsson, M.; Pitcher, T.; Tanimoto-Mori, S.; Richardson, D.; Sweatman, C.; Nicholson, J.; Ward, C.; Jinks, J.; Bell, C.; Young, K.; Rees, H.; Moss, A.; Kinloch, R.; Mcmurray, G. A comparison of the alpha2/3/5 selective positive allosteric modulators l-838,417 and TPA023 in preclinical models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011, 2011, 608912. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lio, A.; Benke, D.; Besson, M.; Desmeules, J.; Daali, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Edwankar, R.; Cook, J.M.; Zeilhofer, H.U. HZ166, a novel GABAA receptor subtype-selective benzodiazepine site ligand, is antihyperalgesic in mouse models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology. 2011, 60, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralvenius, W.T.; Benke, D.; Acuna, M.A.; Rudolph, U.; Zeilhofer, H.U. Analgesia and unwanted benzodiazepine effects in point-mutated mice expressing only one benzodiazepine-sensitive GABAA receptor subtype. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrant, M.; Nusser, Z. Variations on an inhibitory theme: Phasic and tonic activation of GABA(A) receptors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Chen, G.D.; Lee, S.D.; Lai, C.Y.; Chiu, C.H.; Cheng, C.L.; Chang, Y.S.; Hsieh, M.C.; Tung, K.C.; Lin, T.B. Neuroactive steroids inhibit spinal reflex potentiation by selectively enhancing specific spinal GABA(A) receptor subtypes. Pain. 2009, 143, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iura, A.; Takahashi, A.; Hakata, S.; Mashimo, T.; Fujino, Y. Reductions in tonic GABAergic current in substantia gelatinosa neurons and GABA(A) receptor delta subunit expression after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in mice. Eur. J. Pain. 2016, 20, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataka, T.; Gu, J.G. Relationship between tonic inhibitory currents and phasic inhibitory activity in the spinal cord lamina II region of adult mice. Mol. Pain. 2006, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.; Kerby, J.; Bonnert, T.P.; Whiting, P.J.; Wafford, K.A. Pharmacological characterization of a novel cell line expressing human alpha(4)beta(3)delta GABA(A) receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonin, R.P.; Labrakakis, C.; Eng, D.G.; Whissell, P.D.; De Koninck, Y.; Orser, B.A. Pharmacological enhancement of delta-subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors that generate a tonic inhibitory conductance in spinal neurons attenuates acute nociception in mice. Pain. 2011, 152, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szelenyi, I. Flupirtine, a re-discovered drug, revisited. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S.; Wiltfang, J.; Maler, M.; Parsons, C.G. Flupirtine shows functional NMDA receptor antagonism by enhancing Mg2+ block via activation of voltage independent potassium channels. Rapid communication. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 1999, 106, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinger, F.; Bajric, M.; Salzer, I.; Dorostkar, M.M.; Khan, D.; Pollak, D.D.; Kubista, H.; Boehm, S.; Koenig, X. Delta Subunit-containing GABAA receptors are preferred targets for the centrally acting analgesic flupirtine. Br J Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4946–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, D. GABA(B) receptors and pain. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022, 52, 213–239. [Google Scholar]
- Terunuma, M. Diversity of structure and function of GABA(B) receptors: A complexity of GABA(B)-mediated signaling. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2018, 94, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcangio, M. GABA(B) receptors and pain. Neuropharmacology. 2018, 136, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, S.R.; Durham, P.L. Grape seed extract suppresses calcitonin gene-related peptide secretion and upregulates expression of GAD 65/67 and GABAB receptor in primary trigeminal ganglion cultures. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022, 13, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, S.P.; Liu, D.Q.; Manyande, A.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.B.; Xiong, B.R.; Fu, Q.C.; Song, Z.P.; Rittner, H.; Ye, D.W.; Tian, Y.K. The role of spinal GABAB receptors in Cancer-Induced bone pain in rats. J. Pain. 2017, 18, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.P.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.M.; Guo, W.Y.; Guo, Y.X.; Wang, X.L. Activation of spinal GABAB receptors normalizes N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in diabetic neuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 341, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcangio, M.; Ghelardini, C.; Giotti, A.; Malmberg-Aiello, P.; Bartolini, A. CGP 35348, a new GABAB antagonist, prevents antinociception and muscle-relaxant effect induced by baclofen. Br J Pharmacol. 1991, 103, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, V.; Luscher, C.; Blanchet, C.; Klix, N.; Sansig, G.; Klebs, K.; Schmutz, M.; Heid, J.; Gentry, C.; Urban, L.; Fox, A.; Spooren, W.; Jaton, A.L.; Vigouret, J.; Pozza, M.; Kelly, P.H.; Mosbacher, J.; Froestl, W.; Kaslin, E.; Korn, R.; Bischoff, S.; Kaupmann, K.; van der Putten, H.; Bettler, B. Epilepsy, hyperalgesia, impaired memory, and loss of pre- and postsynaptic GABA(B) responses in mice lacking GABA(B(1)). Neuron. 2001, 31, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, M.; Shaban, H.; Vigot, R.; Sansig, G.; Haller, C.; Barbieri, S.; Humeau, Y.; Schuler, V.; Muller, M.; Kinzel, B.; Klebs, K.; Schmutz, M.; Froestl, W.; Heid, J.; Kelly, P.H.; Gentry, C.; Jaton, A.L.; Van der Putten, H.; Mombereau, C.; Lecourtier, L.; Mosbacher, J.; Cryan, J.F.; Fritschy, J.M.; Luthi, A.; Kaupmann, K.; Bettler, B. Redistribution of GABAB(1) protein and atypical GABAB responses in GABAB(2)-deficient mice. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6086–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




