Submitted:
17 May 2023
Posted:
18 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
0. Introduction
1. Analysis and Research of Blood Pressure Measurement Methods
1.1. The Arterial Tonometry Method
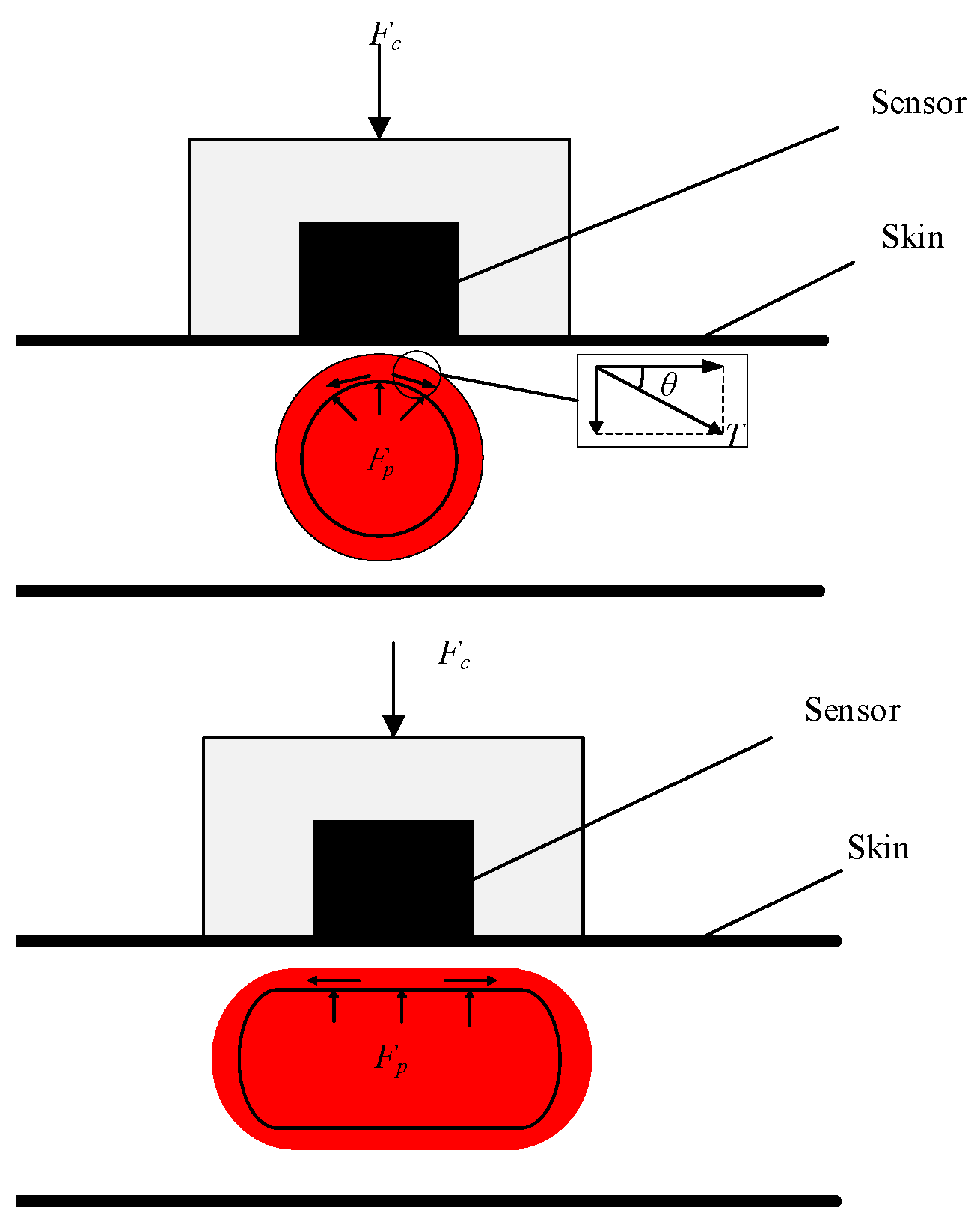
1.2. The Pulse Wave Parameter Method
1.3. A Method Combining Arterial Tonometry and Pulse Wave Parameters Method
2. Flexible Packaging and Testing of Sensors
2.1. MEMS Silicon Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors
2.2. Flexible Packaging Method for Sensors
2.3. Flexible Packaging Process for Sensors
2.4. Performance Testing of Sensors
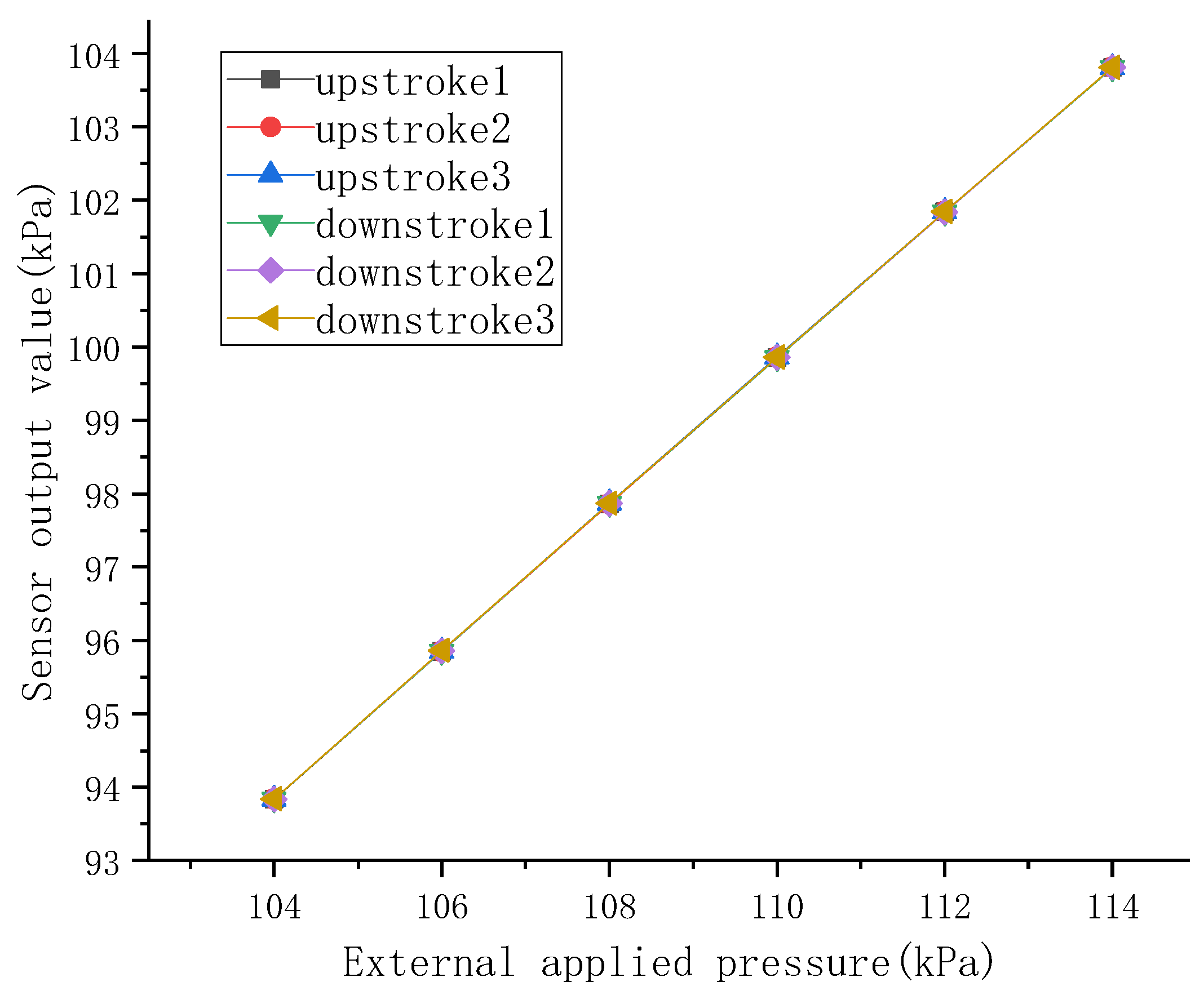
| Before Encapsulation | After Encapsulation | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy/mmHg | 0.0017 | 0.1951 | 0.1934 |
| Sensitivity | 0.9996 | 0.9971 | 0.0025 |
2.5. Testing of Pulse Signals
3. Blood Pressure Measurement
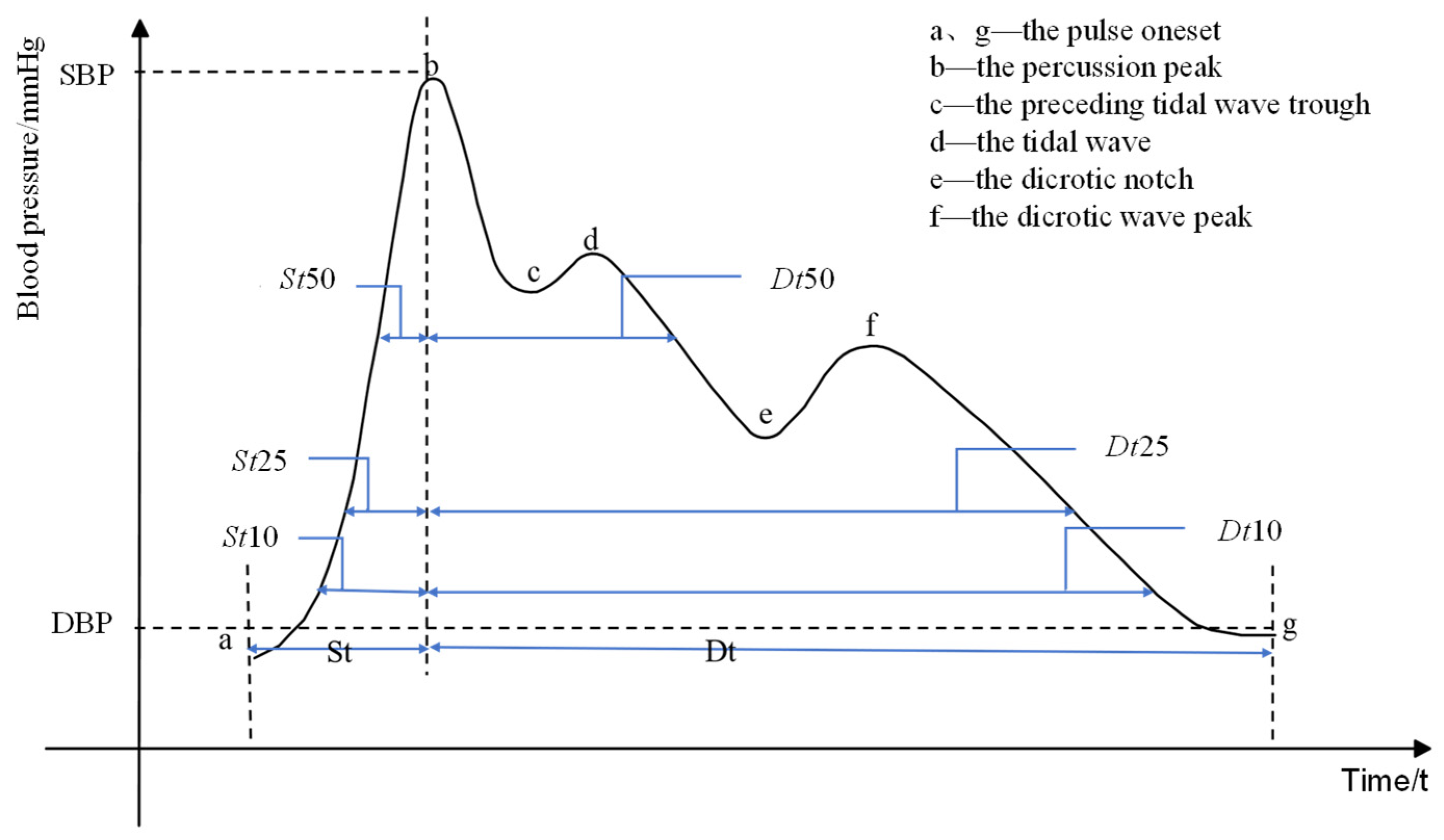
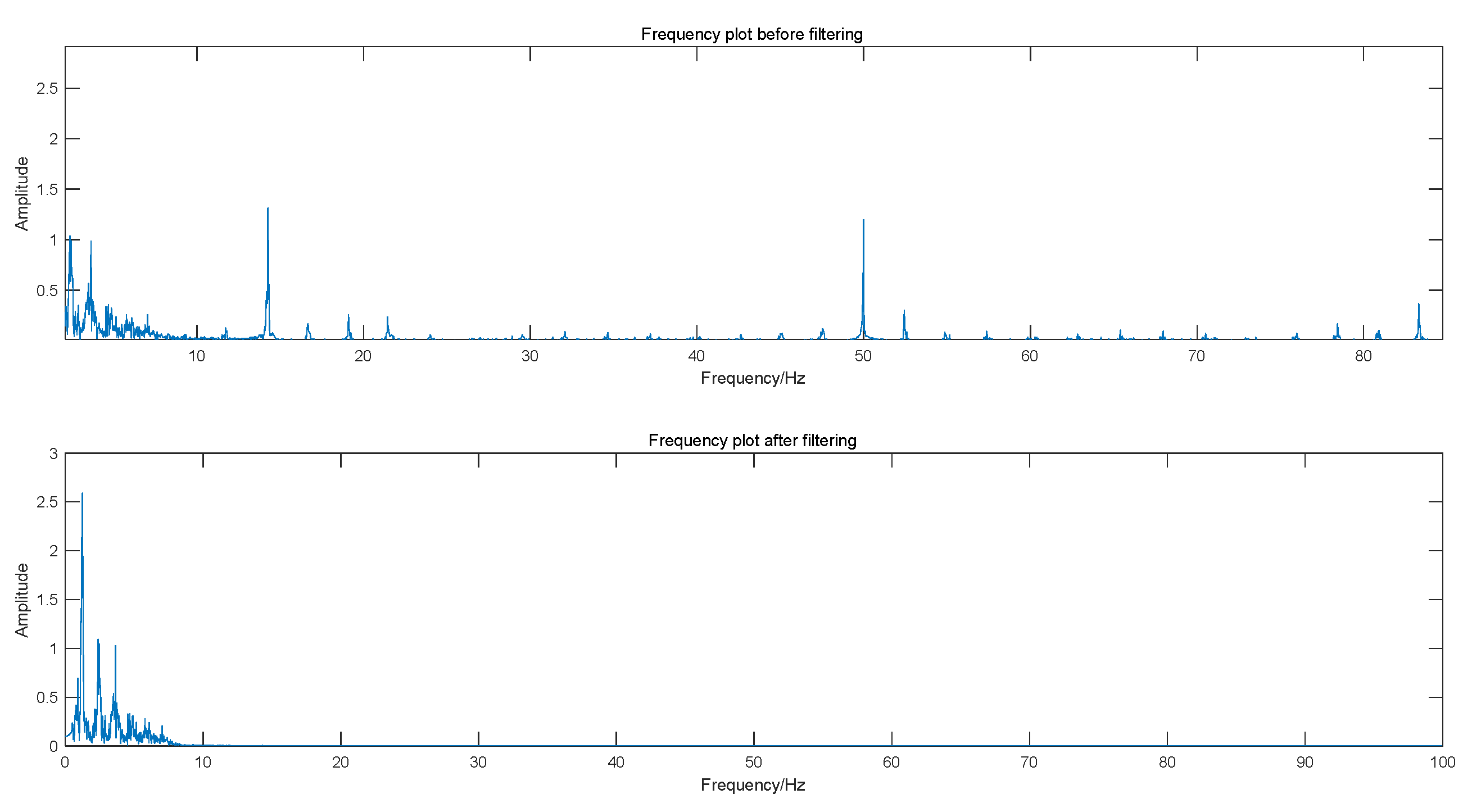
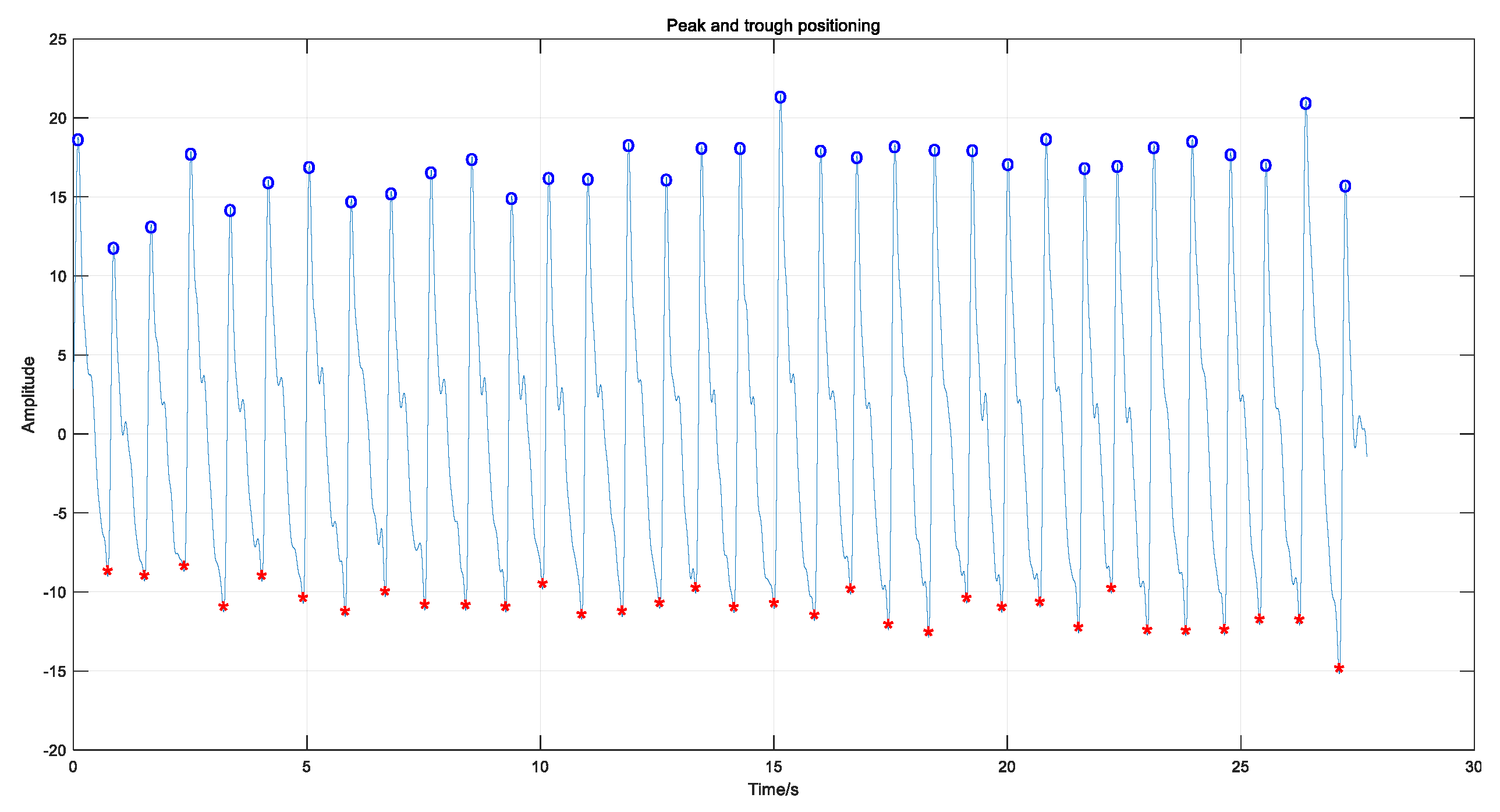
3.1. Pulse Signal Processing and Feature Extraction
3.2. Arterial Tonometry Blood Pressure Calibration
3.3. Bood Pressure Prediction Method Combining Arterial Tonometry and Pulse Wave Parameters
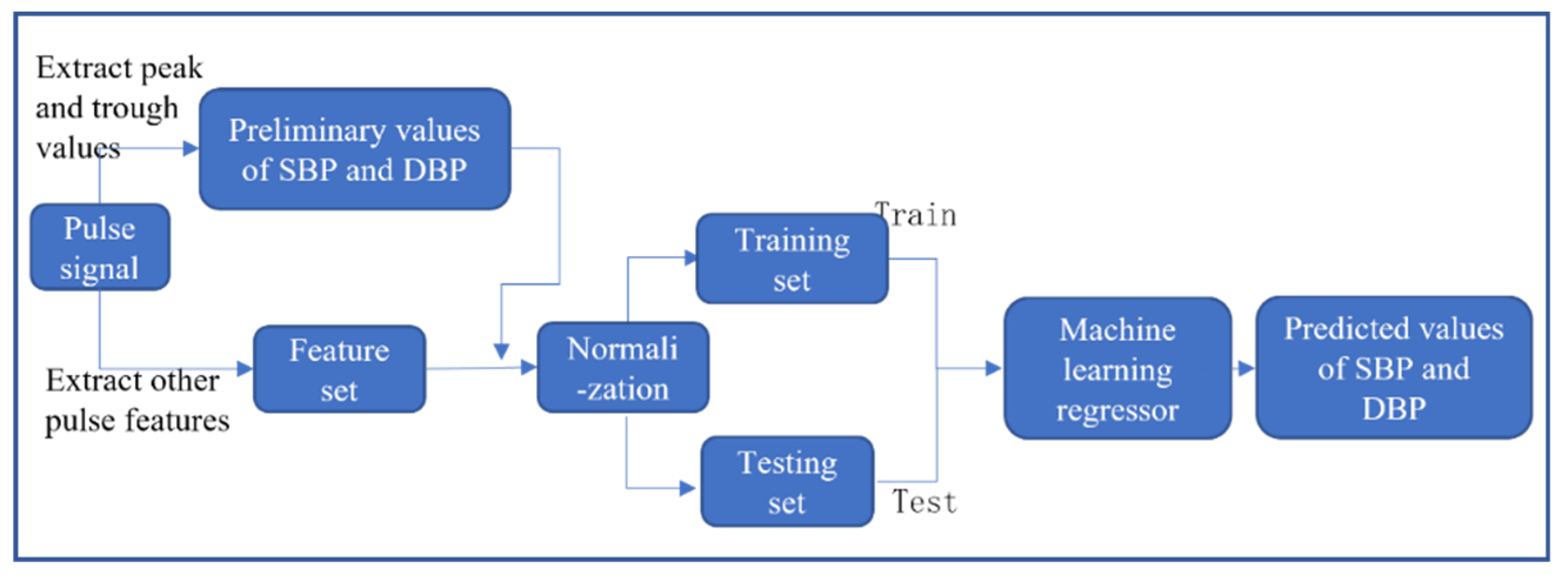
3.3.1. Feature Extraction
3.3.2. Data Normalization
3.3.3. Regression Prediction Based on Machine Learning Algorithms
3.4. Experimental Method
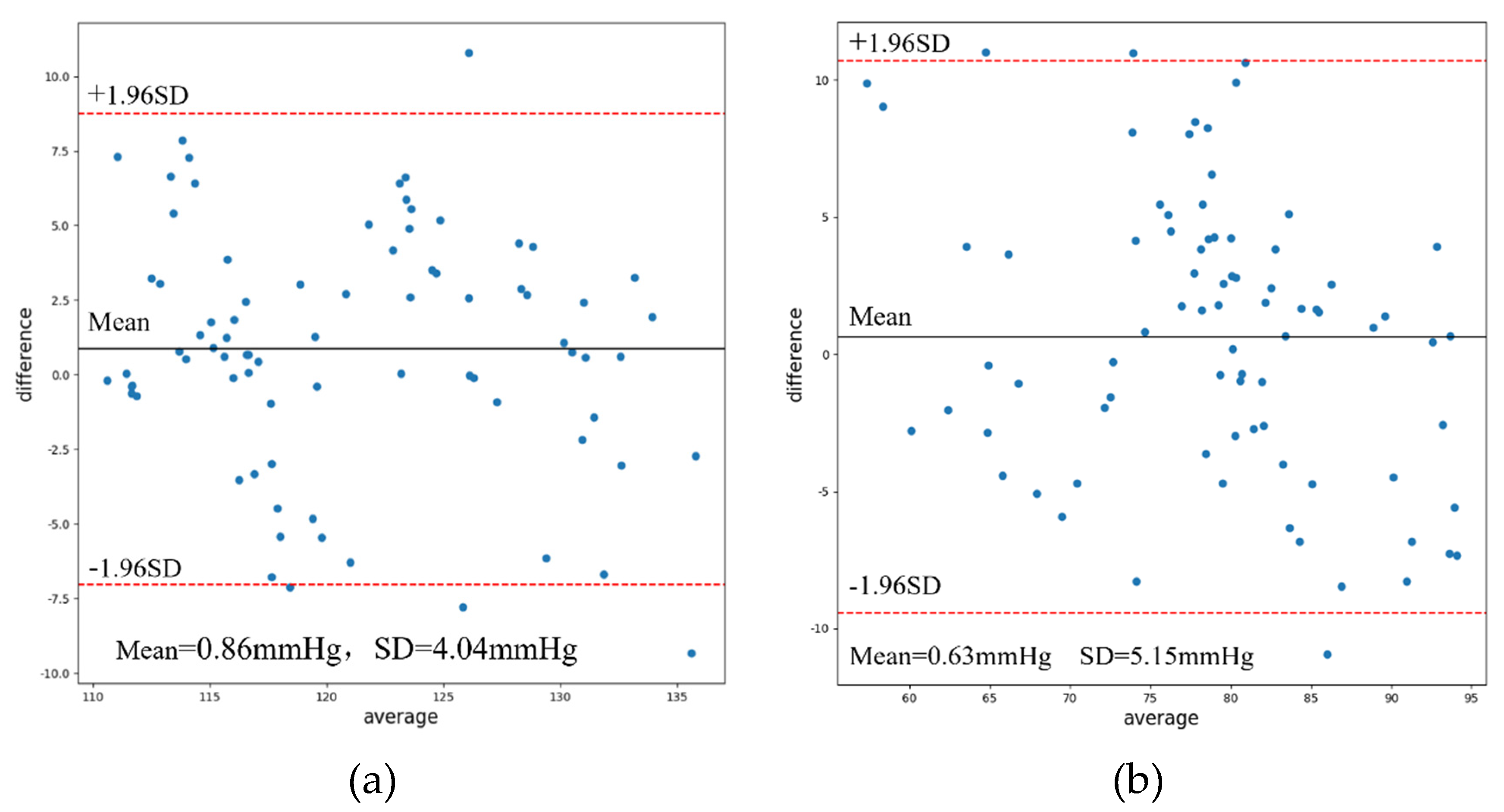
3.5. Result
4. Conclusions
References
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Hao, G.; Zhang, Z.; ... & China Hypertension Survey Investigators*. (2018). Status of hypertension in China: results from the China hypertension survey, 2012–2015. Circulation, 137(22), 2344-2356. [CrossRef]
- Handlogten, K. S.; Wilson, G. A.; Clifford, L.; Nuttall, G. A.; & Kor, D. J. (2014). Brachial artery catheterization: an assessment of use patterns and associated complications. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 118(2), 288-295. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. D.; Liu, J. K.; Wen, B.; He, Q. Y.; Li, Y.; & Miao, F. (2018). Cuffless blood pressure estimation using pressure pulse wave signals. Sensors, 18(12), 4227. [CrossRef]
- Pressman, G. L.; Newgard, P. M. (1963). A transducer for the continuous external measurement of arterial blood pressure. IEEE Transactions on Bio-medical Electronics, 10(2), 73-81. [CrossRef]
- Kachuee, M.; Kiani, M. M.; Mohammadzade, H.; & Shabany, M. (2016). Cuffless blood pressure estimation algorithms for continuous health-care monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 64(4), 859-869. [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Fu, N.; Zhang, Y. T.; Ding, X. R.; Hong, X.; He, Q.; & Li, Y. (2017). A novel continuous blood pressure estimation approach based on data mining techniques. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics, 21(6), 1730-1740. [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, A.; Banerjee, R.; Dutta Choudhury, A.; Sinha, A.; & Kundu, S. (2014, August). Smart phone based blood pressure indicator. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM MobiHoc workshop on pervasive wireless healthcare (pp. 19-24).
- Ram, M. R.; Madhav, K. V.; Krishna, E. H.; Komalla, N. R.; & Reddy, K. A. (2011). A novel approach for motion artifact reduction in PPG signals based on AS-LMS adaptive filter. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 61(5), 1445-1457. [CrossRef]
- Kollias, A.; Ntineri, A.; Kyriakoulis, K. G.; Stambolliu, E.; Lagou, S.; Boubouchairopoulou, N.; & Stergiou, G. S. (2018). Validation of the professional device for blood pressure measurement Microlife WatchBP Office in adults and children according to the American National Standards Institute/Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation/International Organization for Standardization standard. Blood Pressure Monitoring, 23(2), 112-114. [CrossRef]
- Anwar, Y. A.; Tendler, B. E.; McCabe, E. J.; Mansoor, G. A.; & White, W. B. (1997). Evaluation of the Datascope Accutorr Plus according to the recommendations of the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation. Blood pressure monitoring, 2(2), 105-110.
- Sorvoja, H.; & Myllyla, R. (2006). Noninvasive blood pressure measurement methods. Molecular and quantum acoustics, 27, 239-264.
- Lin, W. Q.; Wu, H. H.; Su, C. S.; Yang, J. T.; Xiao, J. R.; Cai, Y. P.; ... & Chen, G. Z. (2017). Comparison of continuous noninvasive blood pressure monitoring by TL-300 with standard invasive blood pressure measurement in patients undergoing elective neurosurgery. Journal of neurosurgical anesthesiology, 29(1), 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Steiner, L. A.; Johnston, A. J.; Salvador, R.; Czosnyka, M.; & Menon, D. K. (2003). Validation of a tonometric noninvasive arterial blood pressure monitor in the intensive care setting. Anaesthesia, 58(5), 448-454. [CrossRef]
- Seyedin, S.; Zhang, P.; Naebe, M.; Qin, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; & Razal, J. M. (2019). Textile strain sensors: a review of the fabrication technologies, performance evaluation and applications. Materials Horizons, 6(2), 219-249. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Gan, C.; & Zhu, C. (2021). Hydrophobic and stable MXene/reduced graphene oxide/polymer hybrid materials pressure sensors with an ultrahigh sensitive and rapid response speed pressure sensor for health monitoring. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 271, 124729. [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Sun, Z.; Hang, T.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Duan, G.; ... & Chen, Y. (2022). Flexible piezoresistive pressure sensors based on nanocellulose aerogels for human motion monitoring: A review. Composites Communications, 101351. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. (2021). Flexible and wearable capacitive pressure sensor for blood pressure monitoring. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research, 33, 100434. [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Xiao, X.; Wei, W.; Chen, G.; Nashalian, A.; Shen, S.; ... & Chen, J. (2022). Wearable pressure sensors for pulse wave monitoring. Advanced Materials, 34(21), 2109357. [CrossRef]
- Choong, C. L.; Shim, M. B.; Lee, B. S.; Jeon, S.; Ko, D. S.; Kang, T. H.; ... & Chung, U. I. (2014). Highly stretchable resistive pressure sensors using a conductive elastomeric composite on a micropyramid array. Advanced materials, 26(21), 3451-3458. [CrossRef]
- Teng, X. F.; & Zhang, Y. T. (2003, September). Continuous and noninvasive estimation of arterial blood pressure using a photoplethysmographic approach. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37439) (Vol. 4, pp. 3153-3156). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Matthys, K.; & Verdonck, P. (2002). Development and modelling of arterial applanation tonometry: a review. Technology and Health Care, 10(1), 65-76. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Cho, J. H.; & Yoon, G. (2009). Non-constrained blood pressure monitoring using ECG and PPG for personal healthcare. Journal of medical systems, 33, 261-266. [CrossRef]
- Chou, N.; Yoo, S.; & Kim, S. (2012). A largely deformable surface type neural electrode array based on PDMS. IEEE Transactions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineering, 21(4), 544-553. [CrossRef]
- Kim, B. J.; & Meng, E. (2016). Micromachining of Parylene C for bioMEMS. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 27(5), 564-576. [CrossRef]
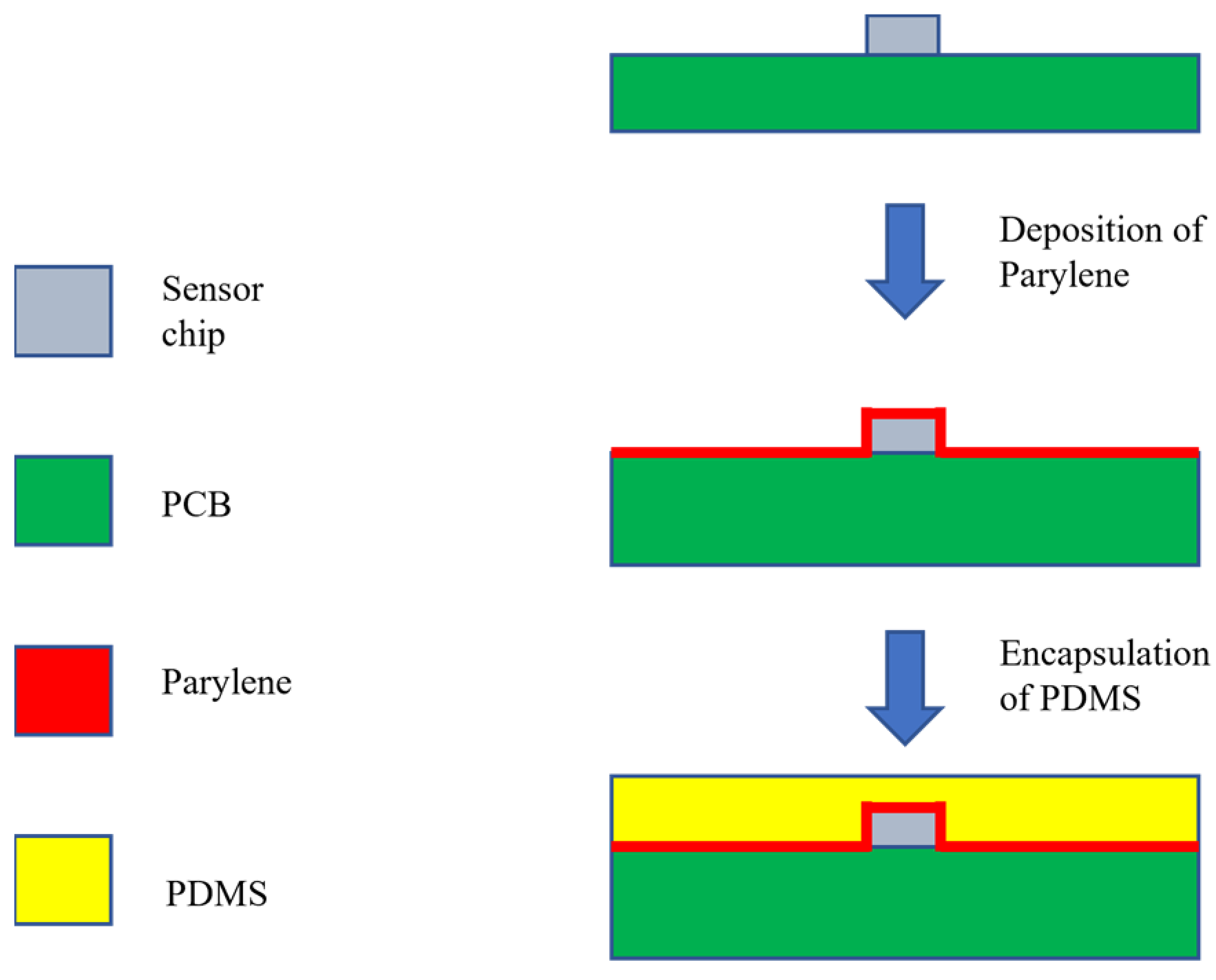
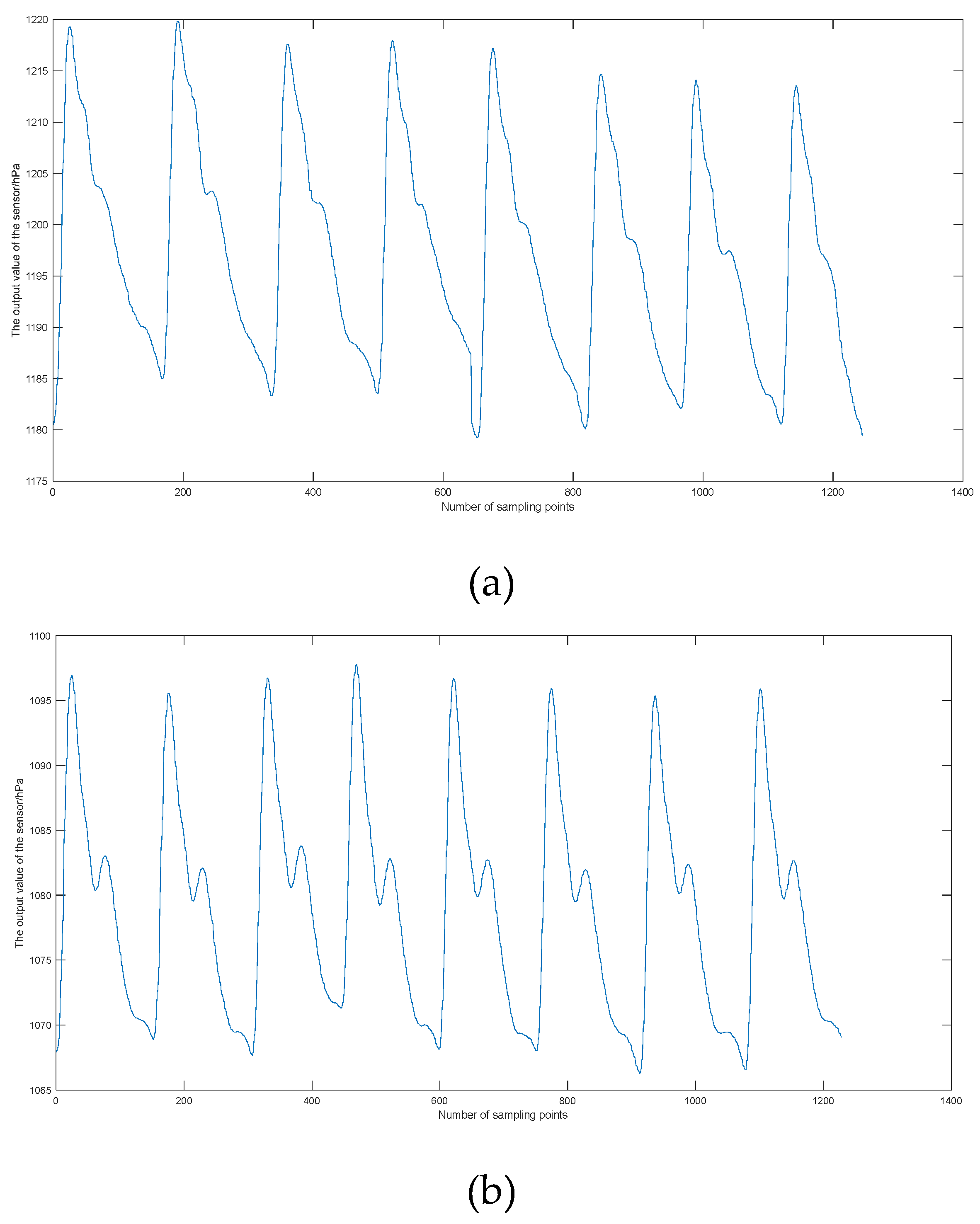
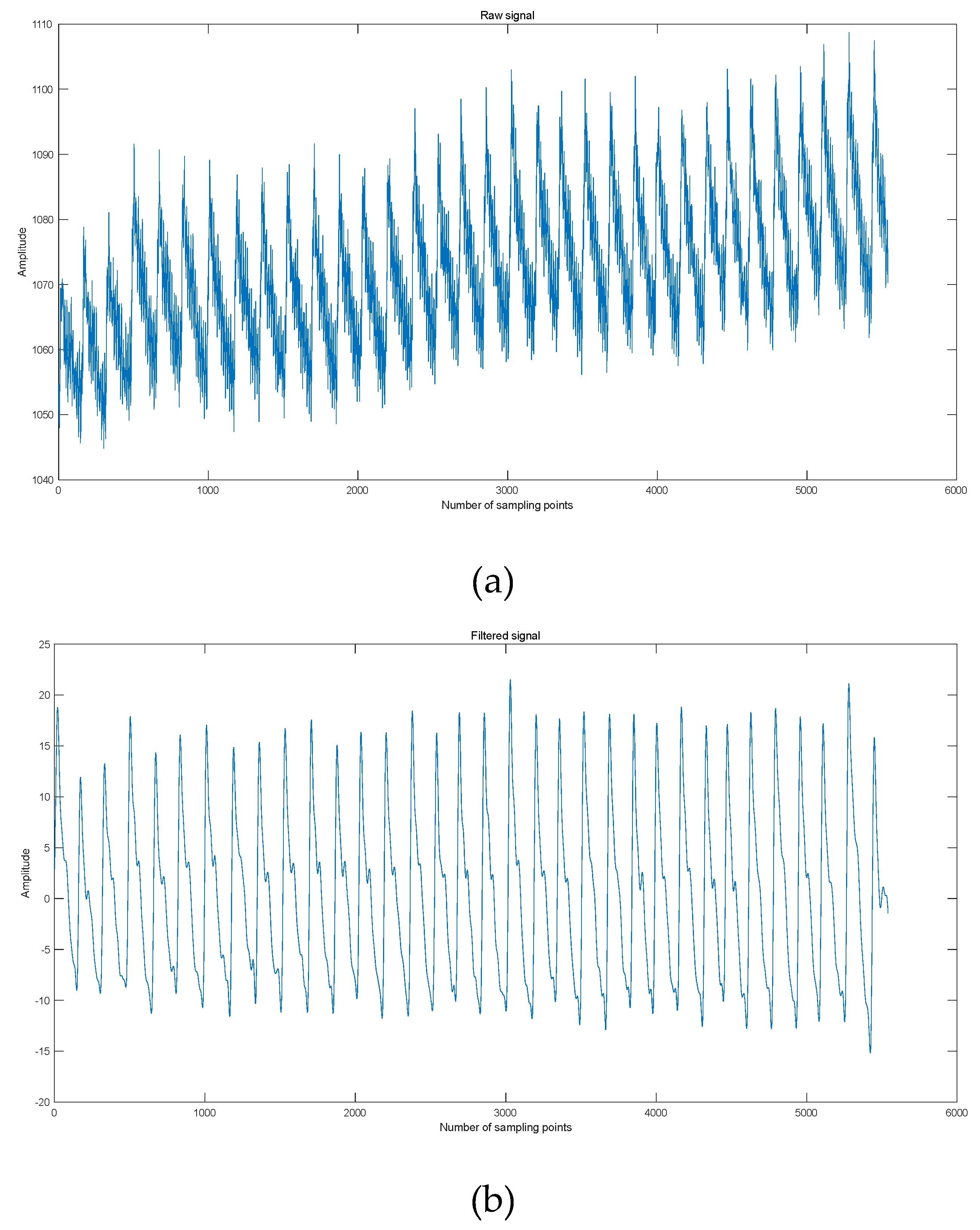
| Feature parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| St | Systolic time |
| Dt | Diastolic time |
| HR | Heart rate |
| S-PTT | transit time between two peaks |
| St10+Dt10 | Addition of Systolic time and diastolic time @ 10% of the pulse amplitude |
| St10/Dt10 | Division of Diastolic time and systolic time @ 10% of the pulse amplitude |
| St25+Dt25 | Addition of Systolic time and diastolic time @ 25% of the pulse amplitude |
| St25/Dt25 | Division of Diastolic time and systolic time @ 25% of the pulse amplitude |
| St50+Dt50 | Addition of Systolic time and diastolic time @ 50% of the pulse amplitude |
| St50/Dt50 | Division of Diastolic time and systolic time @ 50% of the pulse amplitude |
| Pre-sbp | SBP obtained by arterial tonometry method |
| Pre-sdp | DBP obtained by arterial tonometry method |
| Method | SBP | DBP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | SD | MAE | SD | |
| AT | 4.72 | 4.77 | 5.38 | 5.66 |
| Method | Machine Learning Algorithms | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | Ridge Regression | Support Vector Regression | XGBoost | Random Forest Regression | |||||||
| MAE | SD | MAE | SD | MAE | SD | MAE | SD | MAE | SD | ||
| SBP | PWP | 6.95 | 8.26 | 6.25 | 7.66 | 6.03 | 7.44 | 7.05 | 8.58 | 6.58 | 7.89 |
| AT-PWP | 3.64 | 4.75 | 3.96 | 4.92 | 3.29 | 4.22 | 3.24 | 4.26 | 3.24 | 4.04 | |
| DBP | PWP | 7.87 | 9.94 | 7.51 | 9.64 | 7.73 | 9.78 | 8.55 | 10.98 | 7.57 | 9.88 |
| AT-PWP | 4.38 | 5.28 | 5.11 | 6.46 | 4.96 | 6.35 | 4.33 | 5.38 | 4.25 | 5.15 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




