1. Introduction
Common bean (
Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is a grain legume considered a nutraceutical food worldwide [
1] mainly linked to its high content of protein [
2], anthocyanin, polyphenols and flavonoids [
3]. In addition, the high diversity of common bean varieties allows both low- and high- income regions to produce it, being, for many countries, an important crop for food security and national economics [
4,
5]. And the common bean represents 85% of the world´s production of legumes that benefits in food to about 300 million people related to agriculture [
6].
The necessary production of common bean has an increased risk of loss due to abiotic and biotic variables. One of the most important biotic variables of risk is fungal diseases that infect the crop, such as anthracnose caused by
Colletotrichum lindemuthianum [
7], that´s, once infected, has been reported to yield a loss of 95 to100% [
8]. The fungus overwinters in seed and crop residues and infects all bean plants reaching complete yield losses for susceptible beans [
9]. The most distinctive symptoms of anthracnose are manifested in bean pods as deep and shrunken lesions containing visual flesh-colored spores [
1]. The symptoms appear in developing and full-grown plant tissues frequently forming necrotic areas and finally leading to withering, wilting and death of infected plant tissues [
10].
Currently, the main approach to control fungal diseases in crops is the application of chemical pesticides by their high efficacy and low cost, but there is an increasing negative perception from the population that has associated the excessive use of chemical products in productive systems with severe health and environmental issues [
11,
12]. Researchers have been focusing on the development of new technologies for agriculture application that allows the producers to reduce the use of pesticides in their crops while maintaining (or increasing) the quality and quantity of production [
13,
14].
EASS are saline solutions that, due to an electrolysis activating process, contain oxidant agents and are widely reported as disinfectant and cleaner used in the food industry, highly effective, economical, organic and non-corrosive to the human epithelium as reviewed by [
15]. EASS have shown
in vitro antimicrobial activity for different pathogens even higher than that of commercially available disinfectants [
16,
17]. Furthermore, EASS´s sporicidal strong activity has been reported too [
18]. Additionally, the EASS have shown a priming effect on immune plant mechanisms triggering a stronger activation of defense genes at each application, also a biostimulant effect has been reported which improves growth and production in important crops such as tobacco (
Nicotiana tabacum) and apple (
Malus domestica) has been reported [
19].
The aim of this research was to evaluate the in vitro inhibition effect of EASS to important fungal pathogens of the common bean plant (Phaseolus vulgaris) and the effect of EASS in the symptoms of the infection caused by Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in common bean plants.
To our knowledge, no biological tests have been performed to evaluate the performance of the agricultural application of EASS to ease microbial infection symptoms in plants.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. EASS Production Conditions
EASS was produced from sodium chloride solution with water in an electrochemical cell, its anodes are of titanium recovered with metallic oxides based on ruthenium and iridium, and its cathodes are only of titanium. EASS was produced as described in
Table 1.
The free chlorine concentration (FCC) obtained was 2000 to 4000 ppm, according to electrolysis time. Reported main chlorine species are HClO, ClO-, and Cl- according to pH. Finally, ECAS should be acidified with carbonic acid until the desired pH. Its redox potential (ORP) increased with the solution’s acidity from 0.860 Vat pH = 8.75 to 1.050 V (at pH=7).
2.2. Biological Material
The pathogenic isolates and common bean seeds (Phaseolus vulgaris) variedad “pinto” were kindly provided by the Instituto de Investigaciones Forestales, Agrícolas y Pecuarias (INIFAP) Campo experimental Bajío, Celaya Guanajuato México.
2.3. In vitro Inhibition Test
A solution of potato dextrose agar was made following the manufacturer instructions and after autoclave-sterilization, EASS were added to final concentrations of 25, 50, 75, 150, 250, 500 and 1000 ppm of FCC respectively for each treatment. Various pathogens such as Stotrichum lindemuthianum, Macrophomina phaseolina, Phytium sp, Sclerotium rolfsii, Rhizoctonia solani, and Fusarium oxysporum were used in the test to assess EASS in Collectrotichum lindemuthiamun. Next, 10 plates per concentration were inoculated with each pathogen by transferring a piece of an earlier established culture and placing it in the center of the sterile plate. Also, a positive control without treatment and several negative control samples, treated with a commercial fungicidal such as (CERCOBIN® 50SC de CERTIS 15g/L) were made. A final number of 540 plates were established and incubated at room temperature for 4 weeks or until the mycelium had covered the plate. Each week the diameter of the colony in each plate was measured with a vernier
2.4. Pathogenicity Test
Colletotrichum lindemuthianum was selected for further in vivo bioassays because of its commercial importance and high rate of EASS-mediated inhibition. Seeds of common bean were germinated and when they showed 2-3 true leaves, plantlets were transplanted into polyethylene bags with commercial substrate (peat moss and tezontle) and grown under greenhouse conditions. One week the plants were inoculated with
Colletotrichum lindemuthianum by foliar spraying a solution with 1.2x10
10 UFC of the pathogen. The EASS treatments (
Table 2) were applied at different concentrations (12.5, 25, 50 and 100 ppm of FCC); additionally, a group of plants were treated only with a commercial pesticide (CERCOBIN® 50SC de CERTIS) as a negative control and another group of plants were inoculated with the pathogen without treatment as a positive control. The six different groups were treated by spraying each solution at all the leaves of the plant until the drop point.
Four blocks of 15 plants settled each treatment. Plants were maintained for 30 days in a greenhouse with controlled humidity and temperature of 40%±10 and 33°C ±10 during the day and 70%±10 and 10°C±10 in the night; it was determined to irrigated with a standard Steiner solution at 30% of concentration.
2.5. Plant Morphological Variables
The plants were monitored and several variables were measured. As morphological variables, plant´s height and the diameter of the stem were measured manually with a vernier and flexometer.
2.6. Plant Severity Level
For evaluate the severity of the infection by
Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in common bean plants, a severity scale was established, and the symptoms of the plants were rated based on a scale adapted according to [
20].
Each plants obtain a severity level from 0 to 5, where 0 are vigorous and healthy plants with no visible symptoms, and 5 are plants with visible black spots of at least half the size of the leaves.
2.7. Plant Enzymatic and Antioxidant Variables
For each sample, 5 random leaves per treatment were collected and stored at -80°C until their analysis. Once in the laboratory, an enzymatic extract was obtained as follows: the vegetal samples were homogenized in a mortar with a pestle and liquid nitrogen, once a fine powder was obtained, 0.3g are measured and mixed with 1mL of extraction buffer (phosphate buffer, 7.8 pH). The mix then was vortexed for during 2 minutes and centrifuged during for 15 minutes at 12000rpm and 4°C in a microcentrifuge. The resulting supernatant is stored at 4°C as the enzymatic extract (EE).
The enzymatic and antioxidant activities of the samples were determined by spectroscopy through specific reactions in a spectrophotometer multiskan SkyHigh from Thermo Scientific. First, the phenylalanine ammonia lyase enzymatic activity (PAL) was measured, as reported by [
21] with modifications by the presence of cinnamic acid in the sample as a result of the L-phenylalaine catalysis by this enzyme. Then, in one well of a 96-well plate, 20µL of EE are mixed with 230µL of reaction buffer (0.1M borate, 10mM L-Phenylalanine, pH 8.8) and incubated at 40°C for during 60minutes. Then 50µL of chlorhydric acid (HCl) was added to stop the reaction and was set 10 minutes at room temperature. The absorbance was read at 290nm.
To determine the catalase activity (CAT) the catalysis of hydrogen peroxide is monitored through time as follows: 200µL of reaction buffer (50mM potassium phosphate, pH 8.0), 20µL of hydrogen peroxide and 10µL of EE were mixed in a well of a 96-well plate and immediately placed to start the absorbance reading at 240nm each minute during 6 minutes. This methodology was based on what was reported by [
22]. The enzymatic activity was calculated with the following formula 1:
Where ∆A is the change of absorbance per minute, Vt is the total volume, Ɛ is the extinction coefficient of hydrogen peroxide and Ve is the added EE.
Later, the enzymatic activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) was measured indirectly by determining the amount of inhibition of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) by the superoxide ion. In a glass assay tube, 1.5mL of reaction buffer (0.05M potassium phosphate, pH 7.8) was mixed with 0.3mL of 0.1mM EDTA-Na, 0.3 mL of 0.13M methionine, 0.3mL of 0.75mM of NBT, 0.3mL of 0.02mM riboflavin, 0.05mL of EE and 0.25mL of distilled water. The tubes were mixed by inversion and let exposed to fluorescent light for 30 minutes. After this, 250µL of each mix are placed in a well of 96-well plates, and the absorbance was read at 560nm as reported by [
23].
Also, the radical scavenging activity (RSA) was determined by the DDPH method developed [
24]. First, 0.5mL of EE and 0.5mL of 0.1mM DPPH were added to a methanol to yield a final volume of 1.5 mL and are vortexed for during 2minutes. Then, the mix was incubated for during 30 minutes at room temperature protected from the light. When the time was up, 250µL of the mix was placed in a well of a 96-well plate and absorbance was read at 525nm. The following formula 2 was used to calculate the percentage of antioxidants or RSA:
Where AC is the absorbance of the control and AT is the absorbance of treatment.
The Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) activity was determined by obtaining a solution of ABTS radical through mixing a 7mM ABTS solution with 2.45nM potassium persulfate and phosphate buffer pH 7.4 until an absorbance of 0.35-0.4 at 734nm. Once obtained the radical, 3mL of it were mixed with 150µL of EE and the absorbance was read at each minute until 6 measurements at 734 nm. This methodology was based on what was reported by [
25].
Finally, the content of proline was measured in leaves similarly to the what was reported by [
26] by mixing 1mL of EE with 1mL of glacial acetic acid and 1mL of 0.5% ninhydrin reagent. After vortexing the mixture was boiled for during 30 minutes and then cooled. The mixture was phase-separated by the addition of 3mL of toluene and 250µL of the upper phase was collected, placed in a well of a 96-well plate and read on a spectrophotometer at 520nm. The amount of proline was calculated by measuring the absorbance of a proline standard curve.
2.8. Statistical Analisys
For each parametric variable a one-way ANOVA was performed to statistically confirm differences between treatments and for severity a Wilcoxon test have been performed. Tukey test (α = 0.05) was used to identify different groups. For statistical analyses the software JMP version 13.2.0 (JMP statistical discovery Cary, NC, USA) was used.
3. Results
3.1. In vitro Inhibition Test
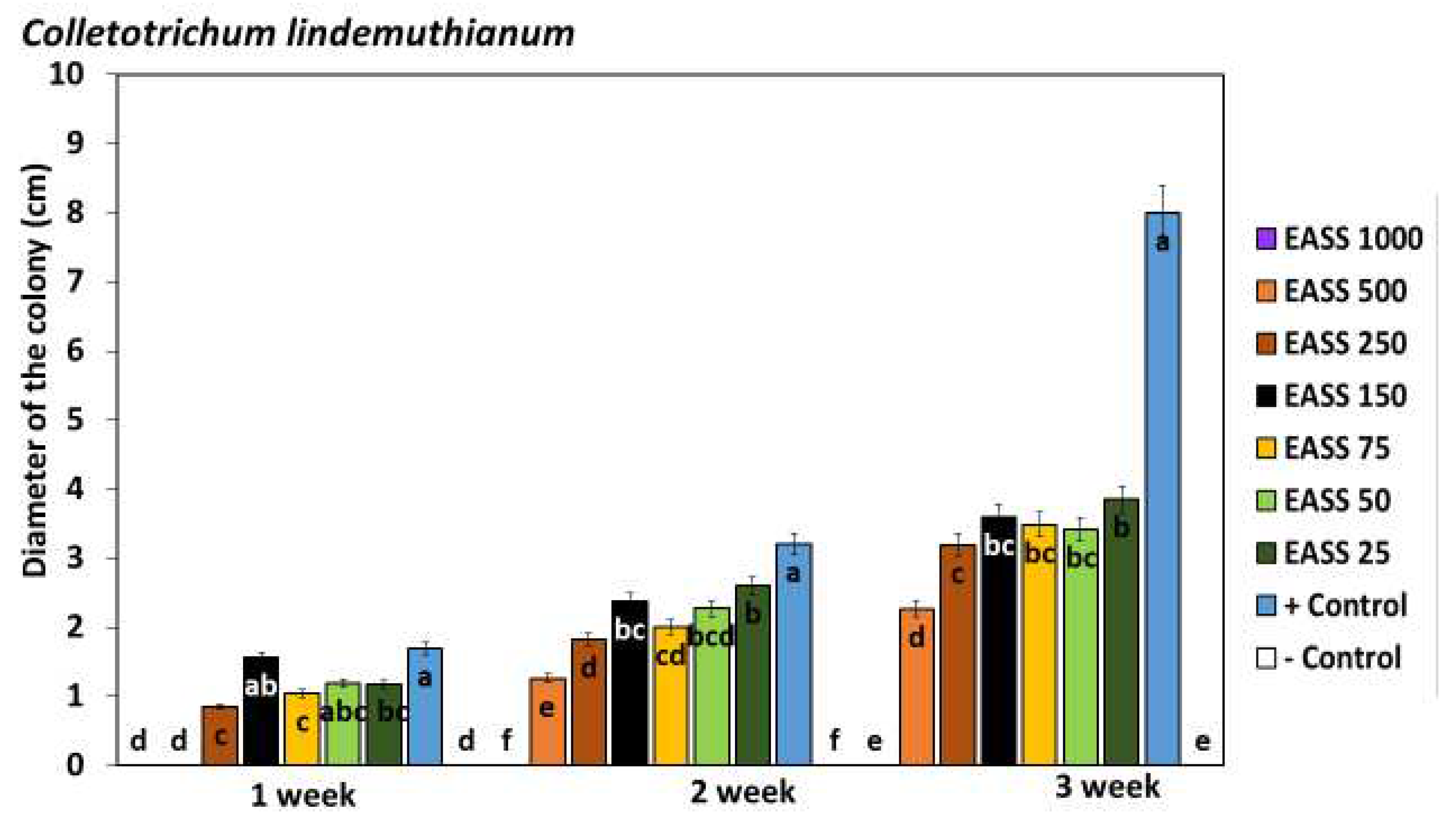
As observed in
Figure 1,
Colletorichum lindemuthianum inhibited development by the presence of EASS at 1000 ppm of FCC equal to the negative control (chemical fungicide) from the first week of incubation until the end of the test. The culture was assessed weekly until the pathogen entirely covered the plates.
Colletotrichum lindemuthianum grew in EASS treatments from 25 to 500 ppm FCC, representing resistance but even in the third week evaluated, none of the treated plaques developed like the untreated control.
As general results of the experiment of the other pathogens in vitro were obtained; The most vulnerable pathogens were Macrophomina phasedine and Phytium sp., where their mycelium showed the fastest growth, leaving the petri dish covered from the first week of evaluation, being the EASS at 500 and 1000 ppm FCC the ones with the lowest growth, even similar to the negative control.
In Sclerotium rolfsii and Rhizoctonia solani, the positive control covered the petri dish in the second week, and the inhibition was greater in the first week of the assay, decreasing over time, being the concentrations of EASS 1000 ppm of FCC the one that remained inhibitory. together with the negative control. And finally, F. oxysporum, the mycelium covered the cane in the second week; grew in all EASS treatments but showed greater inhibition than the positive control until the second and last week.
3.2. Plant Morphological Variables
As described before, the application of EASS to
in vitro cultures of the phytopathogen fungus
Colletotrichum lindemuthianum was the most effective treatment. The next step was to evaluate the performance of this treatment over an
in vivo assay with common bean plants infected with an isolate of
Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. The EASS were applied in lower concentrations than tested before due to their proven efficiency. Morphological variables were measured to compare the plant growth through the treatments,
Figure 2 represents the statistical results at 30 days of bean culture and infection anthracnose. In these cases, no statistical differences were observed between the positive control (infected), the negative control (infected with a chemical fungicide) and the treatments. Furthermore, if there is a significant difference between treatments.
3.3. Plant Severity Levels
As expected, the symptoms of the plants in the pathogenicity test were the most affected in the positive control (inoculated plants with no treatments) (
Figure 3). Moreover, the lower symptoms were observed in the inoculated plants treated with a chemical fungicide. Regarding the EASS treated groups, at the first time of evaluation, only the higher concentration (100ppm) showed differences with the negative control, meaning that the plants treated with the other concentrations showed the same levels of severity as the infected plants treated with a chemical fungicide. On the other hand, at the second time of evaluation, the first and second higher concentrations showed the same severity levels as the positive control.
3.4. Plant Enzymatic and Antioxidant Variables
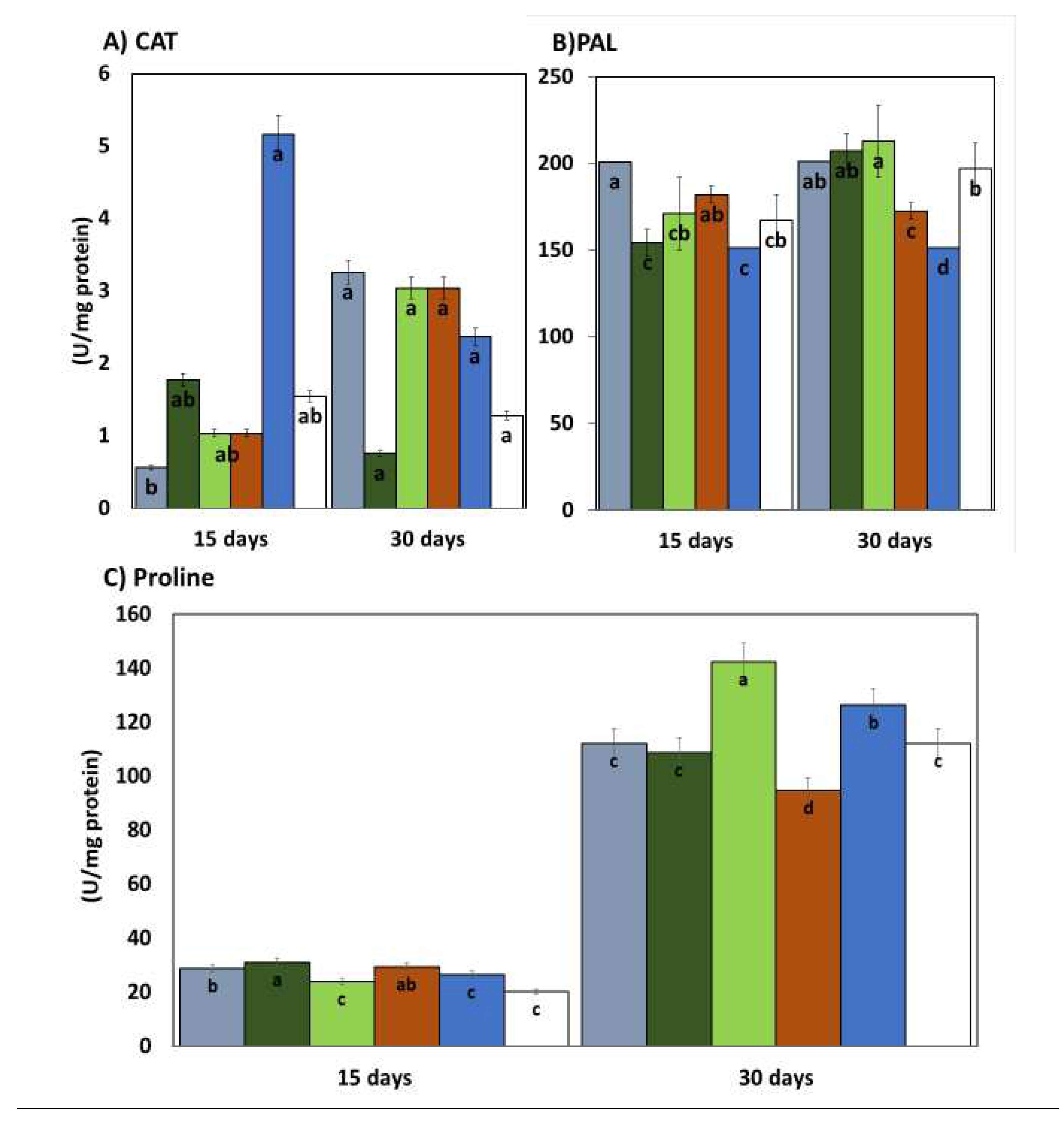
The enzymatic activity of phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) measured 15 days after the application of the treatments was higher in the plants treated with EASS at 12.5 and 100 ppm and inoculated with Colletotrichum lindemuthianum, the following concentration (25ppm) showed the lowest activity in the same statistical group as the plants treated with EASS plants inoculated with the pathogen and without treatment (positive control) (
Figure 4). The other concentrations of EASS treatments, remained between the lower concentration and the positive control as long as the inoculated plants treated with a chemical product (negative control). The results of this enzyme 30 days after EASS treatments show that the highest concentration of PAL was acquired in EASS 12.5, 24 and 50 ppm, PAL lowest activity was obtained in the positive control and the treatments. The response showed an apparent relationship indirectly with the concentration, showing, at a higher concentration, less activity (
Figure 4(B)).
The other measured enzymatic activity was from the enzyme catalase (CAT) which showed differences between the group treated with EASS at 12.5 ppm and without treatment (control positive) at 15 days after the treatments, as shown in
Figure 4 (A), the group treated with EASS at 12.5ppm was the lower CAT activity. At 30 days, no statistical differences were obtained between groups.
In this work the non-enzymatic antioxidant activity was also measured by determining ABTS and DDPH presence, both have the same comportment (
Figure 4 (D-E)). For these variables we found similar results on EASS at 25 ppm with the higher activity at 15 days and being of group the with the higher activity at 30 days. The groups with the lower concentrations of EASS, presented the higher antioxidant activity of ABTS and DPPH percentage, even higher than both of controls for the two measured times
Finally, the presence of proline in the leaves was determined, showing an increased concentration along the measured days.
The proline concentration at 30 days ranged from 94.5 to 142.5 ug/mg protein; at 15 days, the range of concentrations was 23.9 to 31 ug/mg protein. At 15 days the treatments with EASS showed more proline than the two controls. Contrastingly, at 30 days after treatments the EASS treated plants showed the lower proline content than positive control and lower or the same than negative control. For this determination, the group treated with EASS at 100 ppm behaved differently showing the highest proline content at 15 days but the lowest proline content at 30 days (
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
Currently, the search for safer alternatives to promote agricultural yield has been increasing. The common bean is a highly diverse crop that adapts to very different weathers resulting in multiple available varieties. This diversity suggests also high diversity in the defense mechanisms of each variety, available to activation with the correct elicitation design.
In this paper, we propose using EASS as plants elicitors by the activation of multiple biosynthetic pathways resulting in defenses and secondary metabolites activation, both highly desired in the agricultural production. Furthermore, this alternative is not toxic for the field workers, environment, or the final consumer. Here we evaluated the in vitro effect of the EASS directly applied to several phytopathogenic microbes and Colletotrichum was selected for further in vivo evaluations of EASS elicited plants-pathogen interaction being this work a step further into the application of EASS as an agricultural treatment in primary production systems.
As expected, the best EASS concentration for microbe inhibition were 500 and 1000 ppm but all the concentrations showed some inhibition. The behavior of inhibition depended on the evaluated microorganism, but the stronger inhibition resulted generally resulted at the beginning of the test. This could be influenced by a lower persistence of the EASS in the environment which turn to be an advantage to become a safer agricultural product but it suggests the need to apply more than once in the crop cycle.
The morphological effect in plants was evaluated with no differences reported. This was not expected as the activation of biological pathways requires energy investment, commonly this energy is taken from biological events such as plant growth and development. With this result we suggest that EASS elicitation mechanism allows the plants to efficiently distribute the energy in order to continue its normal growth and development and at the same time activate defense signaling cascades. This should not lower the yield of EASS treated bean crops.
Interestingly, the infection with Colletotrichum showed higher severity in plants treated with the most concentrated EASS; this suggests important levels of distress in plants due to the EASS treatment in additional to the pathogenic infection. Also, the lower concentrations of EASS (12.5, 25 and 50 ppm) showed statistically identical results in the severity of plants. These results provide information related to the hormetic behavior of the elicitation effect of EASS in common bean plants, at the same, time allows the researchers to design controlled elicitation plans in future agricultural treatments.
The phenylpropanoid pathway (ppp) and antioxidant activity are highly desired variables for both crop producers and final consumers, especially in common bean where important levels have been reported. Researchers have successfully elicitated these two biological systems in common bean by ultrasound [
27], thermal variations [
28] and NaCl and Glutaminc acid application [
29]. Now, the present work allowed us to confirm an elicitation of ppp and antioxidant activity by EASS foliar treatment which remain active even 30 days before the application of the treatment.
The results showed statistically higher antioxidant activity for ABTS and DPPH but not for CAT, this may suggest that EASS elicitate the activation of a non-enzymatic antioxidant system that remained significant until 30 days after the application of the treatment. Therefore, the activation of synthetic pathways such a ppp where PAL is one of the earliest involved enzymes that raises the concentration of non-enzymatic antioxidants may be the main defense mechanism activated by the application of EASS in common bean [
30]. Supporting this possibility, we can also observe accumulation of proline in some EASS treatments, the proline is an aminoacid with several important roles in plants metabolism, one of them as antioxidative defense molecule [
31].
By the results, we can propose that the main reason of a difference in the severity of the infection is the elicitation of the plants and activates defenses rather than the antimicrobial activity that EASS have. However, as the elicitation of plants may affect a specific kind of pathogens it would be interesting to test different pathogenic microorganisms to validate the EASS efficiency as a treatment for pest management.
In this work, the effect of EASS on in phytopathogen survival and infection severity was evaluated. The results suggests that the EASS applied at low concentrations, are viable, functional, and organic treatments that help to manage fungal pests in crops.
5. Conclusions
In this work we were able to detect the activation of multiple defense plant mechanisms such as the activity of the enzyme phenylalanine ammonia lyase, the antioxidant system and the production of proline.
Our data suggest the activated defenses were strong enough to successfully decrease the severity of the disease from the lower concentrations of the treatment.
Applying EASS in common bean crops could be an effective treatment for Colletotrichum infection management. However, treatment doses should be carefully selected and supplied to avoid distress in the plants.
Author Contributions
Yunny Meas-Vong was the coordinator of EAAS synthesis and the coordinator of general project management of CIDETEQ; Irineo Torres-Pacheco was the coordinator and supervisor of all laboratory and field production experimental actions and the collaboration between CIDETEQ, UAQ, and INIFAP; Adrian E. Ortega-Torres collaborated on supervising experiments in the laboratory and field, analyzing and interpreting the data information, and writing manuscript; María G. Marquez-Blanco collaborated on the manual establishment of all experiments, conditions setting, measurements, sample collection, and the analyses and interpretation of the data information; Samantha de J. Rivero-Cornejo and Brenda Z. Guerrero-Aguilar were in charge of laboratory analyses, data curation and biological resources availability; Ramón G. Guevara-González and Mario M. González-Chavira were collaborating in the supervision general of experimental actions and manuscript writing; Luis M. Contreras-Medina was involved revision of the manuscript and the analyses of the results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support received from CONACYT- PRONACES 2021 “Desarrollo de Innovaciones tecnológicas para una agricultura mexicana libre de insumos tóxicos” within the project no. 315956. “Manejo de la sanidad del maíz y frijol mediante unas soluciones activadas electroquímicamente no tóxicas al ser humano ni al ambiente”.
Acknowledgments
Thank the UAQ for allowing us to be part of this research and being assigned for the link, CECYTEQ for developing and validating the EASS, and INIFAP for supporting the biological material to carry out the research. I would also like to thank everyone who made this research possible, especially CONACyT, for their support and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Padder, B.A.; Sharma, P.N.; Awale, H.E.; Kelly, J.D. COLLETOTRICHUM LINDEMUTHIANUM, THE CAUSAL AGENT OF BEAN ANTHRACNOSE. J. plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 317–330. [Google Scholar]
- Luna-vital, D.A.; Mojica, L.; Gonz, E. Biological potential of protein hydrolysates and peptides from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): A review. FRIN 2014.26, 39-50. [CrossRef]
- Aquino-Bolaños, E.N.; García-Díaz, Y.D.; Chavez-Servia, J.L.; Carrillo-Rodríguez, J.C.; Vera-Guzmán, A.M.; Heredia-García, E. Anthocyanin, polyphenol, and flavonoid contents and antioxidant activity in Mexican common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces. Emirates J. Food Agric 2016, 28, 581–588. [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Fitsum, S.; Selvaraj, T.; Mulugeta, N. Field Management of Anthracnose (Colletotrichum lindemuthianum) in Common Bean through Fungicides and Bioagents. Adv Crop Sci Tech 2014, 2, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanzadeh, A.; Khahani, B.; Taghavi, S.M.; Khojasteh, M.; Osdaghi, E. Genome - wide meta - QTL analyses provide novel insight into disease resistance repertoires in common bean. BMC Genomics 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, S.; Shaheen, H.; Murtaza, G.; Tinghong, T.; Arfan, M.; Idrees, M. Socioeconomic Evaluation of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Cultivation in Providing Sustainable Livelihood to the Mountain Populations of Kashmir Himalayas. Plants 2023, 12, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillard, C. L.; Ranatunga, N. K.; Conner, R. L. The control of dry bean anthracnose through seed treatment and the correct application timing of foliar fungicides. Crop Protection 2012, 37, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrekiristos, E.; Wondimu, M. Emerging and Remerging Diseases of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Major Production Areas: In the Case of Ethiopia. Journal of Agricultural Science 2022, 14(4): 19-34. [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Corrales, M.A.; Tu, J.C. Anthracnose, in: Bean Production Problems in the Tropics.2. ed. In: Schwartz, H.F.; Pastor-Corrales, M.A. (eds.). 1989,77–104.
- Chakraborty, N.; Mukherjee, K.; Sarkar, A.; Acharya, K. Interaction between bean and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides: Understanding through a biochemical approach. Plants 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, M.R.; Alavanja, M.C.R. Pesticides, human health, and food security. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolopoulou-stamati, P. Chemical Pesticides and Human Health : The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture. Front. Public Healt, Sec Environmental health and Exposome 18 July, 2016, 4, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- García-Mier, L.; Guevara-González, R.G.; Mondragón-Olguín, V.M.; Verduzco-Cuellar, B. del R.; Torres-Pacheco, I. Agriculture and bioactives: Achieving both crop yield and phytochemicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 4203–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, F.; Hélène, M.; Julia, J.; Edith, J.; Cadre, L.; Litrico, I.; Malausa, T.; Reboud, X.; Huyghe, C. Pesticide - free agriculture as a new paradigm for research. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebezov, M.; Saeed, K.; Khaliq, A.; Junaid, S.; Rahman, U.; Sameed, N.; Semenova, A.; Khayrullin, M.; Dydykin, A.; Abramov, Y.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Bangar, S.P. Lorenzo, J.M. Application of Electrolyzed Water in the Food Industry: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6639. [CrossRef]
- Helme, A.J.; Ismail, M.N.; Scarano, F.J.; Yang, C.-L. Bactericidal efficacy of electrochemically activated solutions and of commercially available hypochlorite. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 67, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, R.M.S.; Lee, S.W.H.; Robinson, G.M.; Greenman, J.; Reynolds, D.M. Electrochemically activated solutions: Evidence for antimicrobial efficacy and applications in healthcare environments. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol Infect. Dis 2011, 5, 641–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.M.; Lee, S.W.; Greenman, J.; Salisbury, V.C.; Reynolds, D.M. Evaluation of the efficacy of electrochemically activated solutions against nosocomial pathogens and bacterial endospores. Letters in Applied Microbiology 2010, 3, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarattini, M.; Bastiani, M. De; Bernacchia, G.; Ferro, S.; Battisti, A. De The use of ECAS in plant protection: a green and efficient antimicrobial approach that primes selected defense genes. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1996–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Teniente, L.; Dúran-Flores, B.A.; Torres-Pacheco, I.; González-Chavira, M. M.; Rivera-Bustamante, R. J.; Feregrino-Perez, A. A.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.; Rocha-Gúzman, N. E.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Guevara-González, R. G. Hydrogen peroxide portects pepper ( Capsicum annuum L.)against pepper Golden mosaic geminivirus (PepGMV) infections. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 2019, 106,23-29. [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, D. P.; Pascholati, S. F.; Hagerman, A. E.; Butler, L. G.; Nicholson, R. L. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and hydroxycinnamate: CoA ligase in maize mesocotyls inoculated with Helminthosporium maydis or Helminthosporium carbonum. Physiological Plant Pathology 1984, 2, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods in enzymology, Elsevier 1984, 105 121–126. [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C. , and Fridovich, I. 1971. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 44, 276–287.
- Blois, M. S. Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 1958, 181, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, R.; Haenen, G. R. M. M.; van den Berg, H.; Bast, A. Applicability of an improved Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assay for evaluation of antioxidant capacity measurements of mixtures. Food Chem 1999, 66,4:511-517. [CrossRef]
- Bates, L. S.; Waldren, R. P.; & Teare, I. D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant and Soil 1973, 1, 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ampofo, J.; Ngadi, M.; Ramaswamy, H. S. Elicitation kinetics of phenolics in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) sprouts by thermal treatments. Legume Science 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampofo, J. O.; Ngadi, M. Ultrasonic assisted phenolic elicitation and antioxidant potential of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) sprouts. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry 2020, 64, 104974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampofo, J. O.; Ngadi, M. Stimulation of the phenylpropanoid pathway and antioxidant capacities by biotic and abiotic elicitation strategies in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) sprouts. Process Biochemistry 2021, 100, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Riaz, M.; Arif, M. S.; Rasheed, R.; Iqbal, M.; Hussain, I.; Mubarik, M., S. The role of non-enzymatic antioxidants in improving abiotic stress tolerance in plants. In Plant tolerance to environmental stress, First edition 2019, 1-16.
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M. N.; Wani, A. S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of proline under changing environments: A review. Plant Signaling and Behavior 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).