Submitted:
18 May 2023
Posted:
18 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
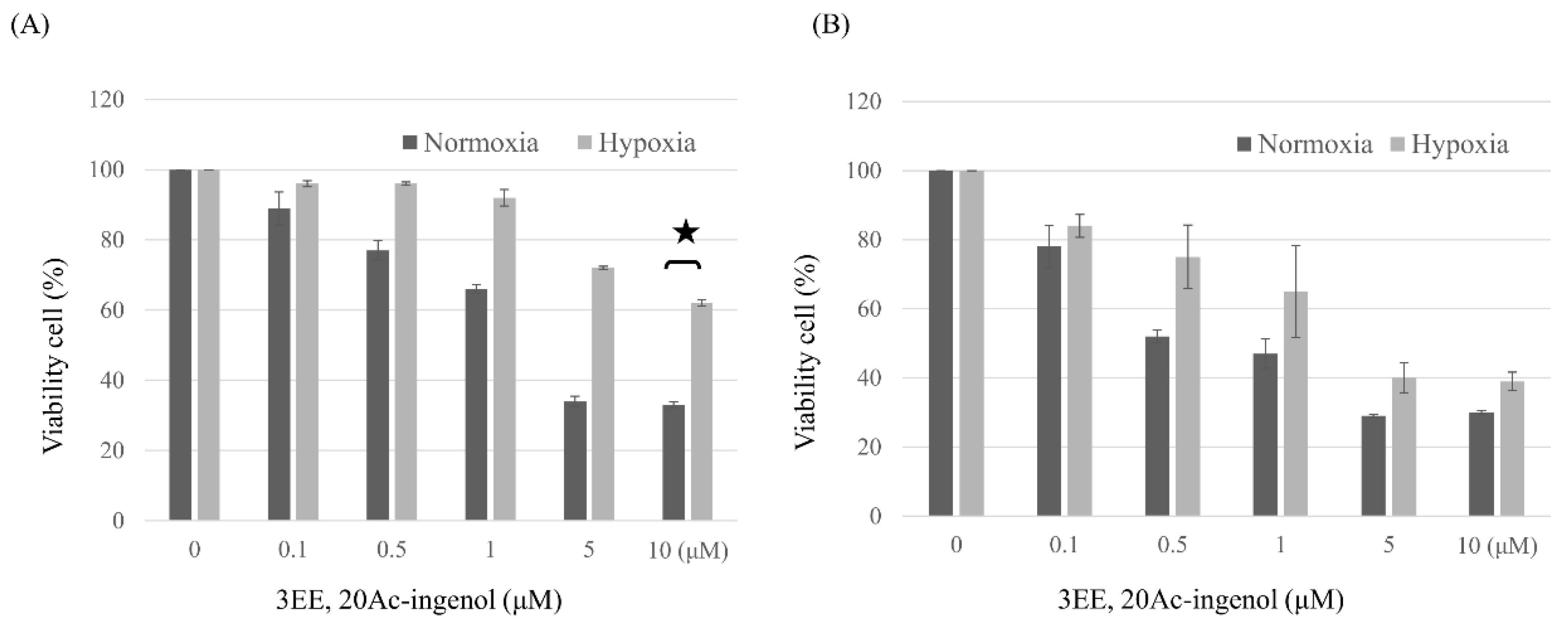
2.1. Effects of 3EE, 20Ac-Ingenol on cell proliferative activity of Jeko-1 and Panc-1 cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions
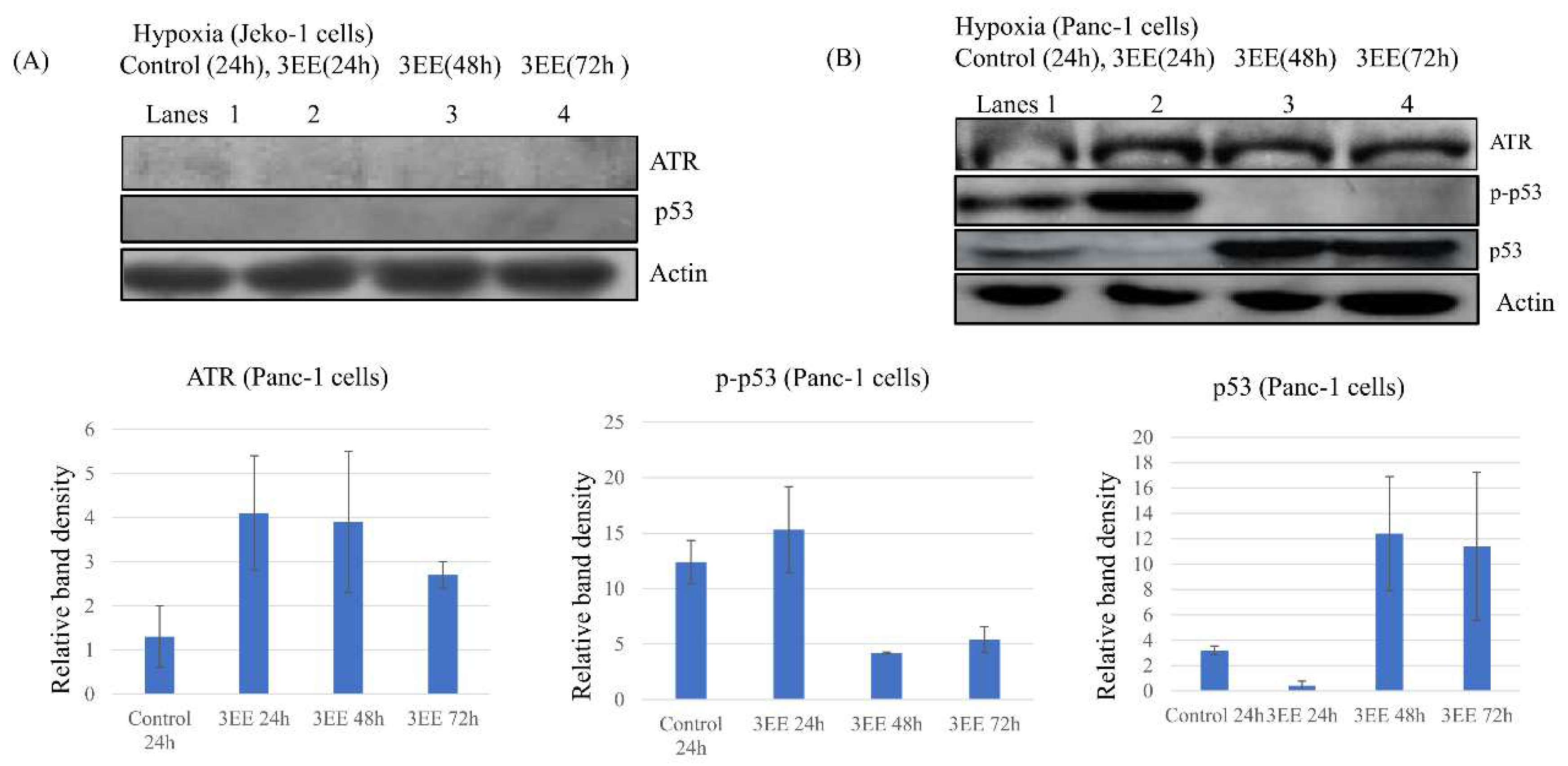
2.2. Effects of 3EE, 20Ac-ingenol on ATR activation and p53 accumulation
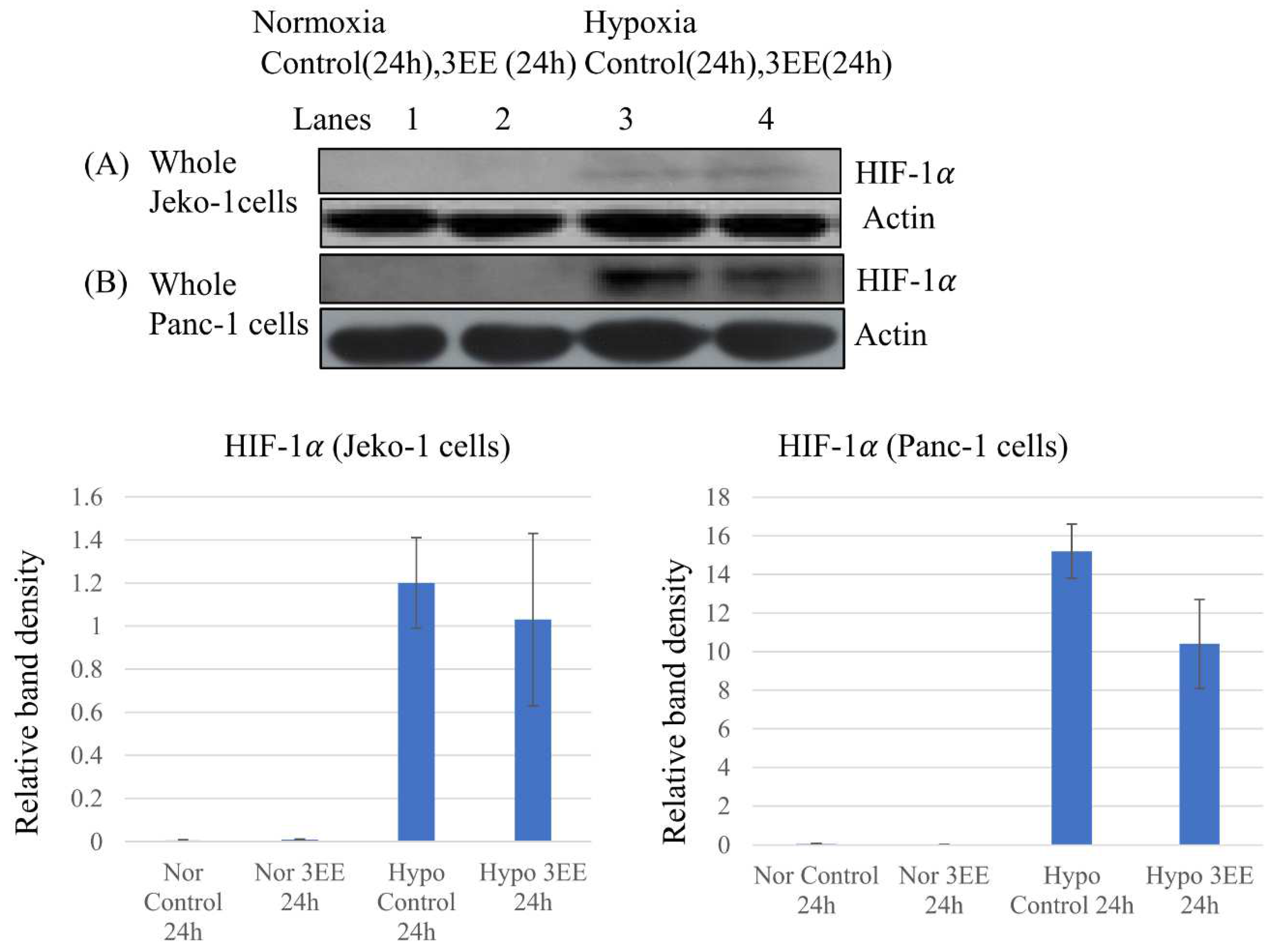
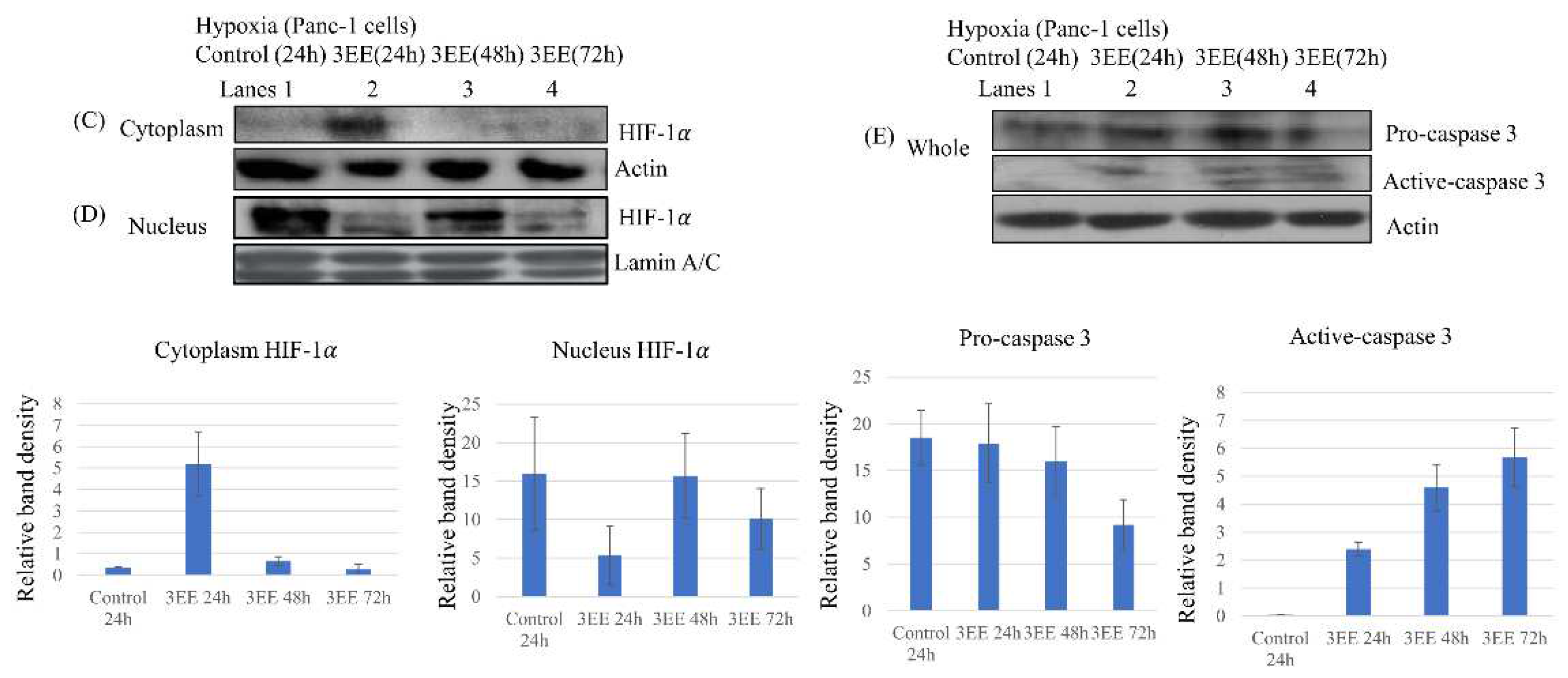
2.3. Effects of 3EE, 20Ac-ingenol treatment on HIF-1𝛼 accumulation and Caspase-3 activation
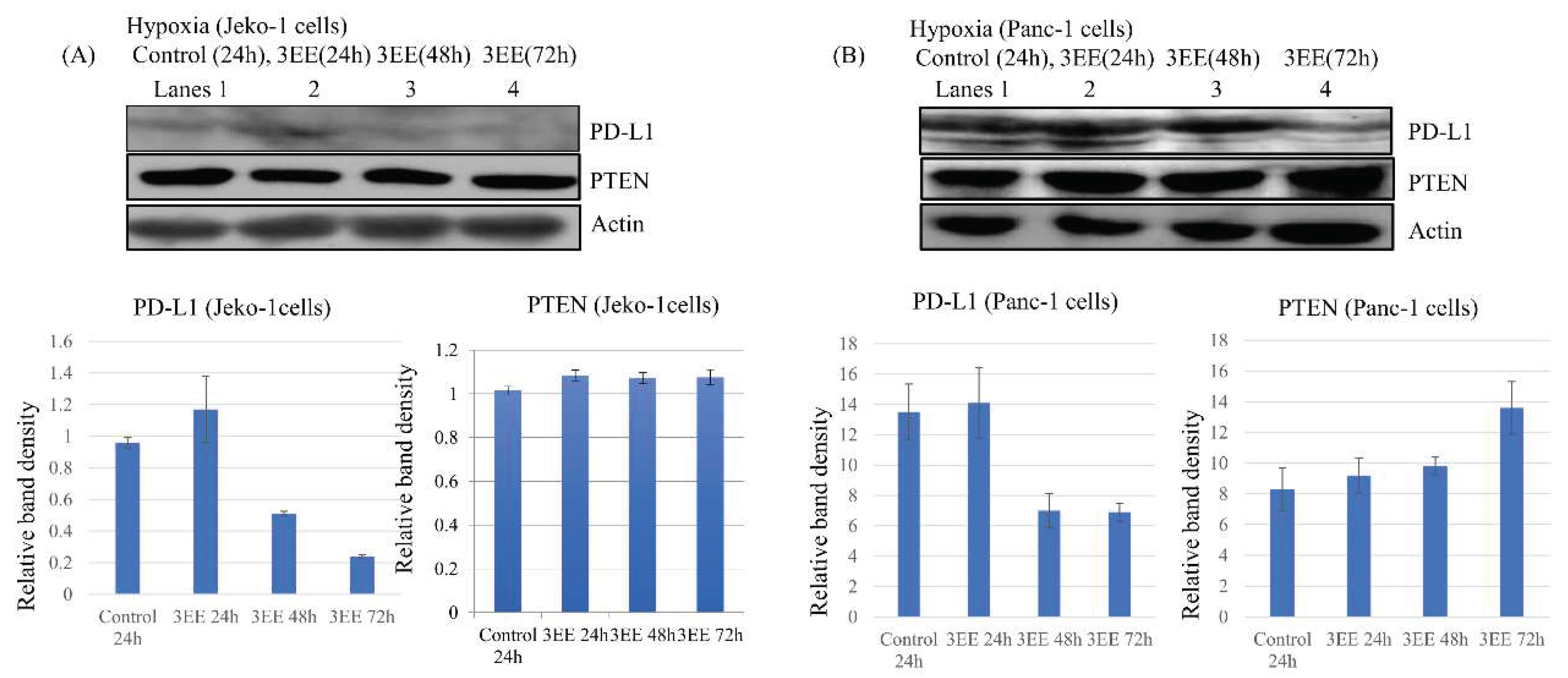
2.4. Effects of 3EE, 20Ac-ingenol treatment on the PD-L1 and PTEN expressions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell lines and cellular proliferation
4.2. Immunoblotting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
Declaration of Competing Interest
References
- Talks, K.L.; Turley, H.; Gatter, K.C.; Maxwell, P.H.; Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Harris, A.L. The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol. 2000, 157, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majmundar, A.J.; Wong, W.J.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell. 2010, 40, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsoum, I.B.; Smallwood, C.A.; Siemens, D.R.; Graham, C.H. A mechanism of hypoxia-mediated escape from adaptive immunity in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 743, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, B.K.; Wheeler, E.; Hornbuckle, K.; Shana'ah, A.Y.; Youssef, Y.; Smith, L.; Hassan, Q., 2nd; Klamer, B.; Zhang, X.; Long, M.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Maddocks, K.; Johnson, A.J.; Byrd, J.C. Modulation of immune checkpoint molecule expression in mantle cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019, 60, 2498–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.Z.; Desantis, G.; Janji, B.; Hasmim, M.; Karray, S.; Dessen, P.; Bronte, V.; Chouaib, S. PD-L1 is a novel direct target of HIF-1α, and its blockade under hypoxia enhanced MDSC-mediated T cell activation. J Exp Med. 2014, 211, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.Y.; Liu, X.W.; Zhu, H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Lou, J.S.; He, Q.J.; Yang, B. Tirapazamine sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to topoisomerase I inhibitors via cooperative modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, K.; Fidler, I.J. Hypoxia increases resistance of human pancreatic cancer cells to apoptosis induced by gemcitabine. Clin Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Mayer, F.; Honecker, F.; Schittenhelm, M.; Bokemeyer, C. Efficacy of cytotoxicagents used in the treatment of testicular germ cell tumours under normoxic and hypoxic conditions in vitro. Br J Cancer. 2003, 89, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, E.M.; Denko, N.C; Dorie, M.J.; Abraham, R.T.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxia links ATR and p53 through replication arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 1834–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallone, F.; Britton, S.; Nieto, L.; Salles, B.; Muller, C. ATR controls cellular adaptation to hypoxia through positive regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) expression. Oncogene. 2013, 32, 4387–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Dor, Y.; Herbert, J.M.; Fukumura, D.; Brusselmans, K.; Dewerchin, M.; Neeman, M.; Bono, F.; Abramovitch, R.; Maxwell, P.; Koch, C.J.; Ratcliffe, P.; Moons, L.; Jain, R.K.; Collen, D.; Keshert, E. Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature. 1998, 394, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.G.; Kanekal, M.; Simon, M.C.; Maltepe, E.; Blagosklonny, M.V.; Neckers, L.M. Stabilization of wild-type p53 by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Nature. 1998, 392, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, T.; Zhou, J.; Köhl, R.; Brüne, B. p300 relieves p53-evoked transcriptional repression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Biochem J. 2004, 380(Pt 1), 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y.; Jin, H.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, D. ERK/MAPK activation involves hypoxia-induced MGr1-Ag/37LRP expression and contributes to apoptosis resistance in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010, 127, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.H.; Jiang, G.; Zheng, J.Z.; Lu, Z.; Hunter, T.; Vogt, P.K. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling controls levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell Growth Differ. 2001 l, 12, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Argyriou, P.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Panteleon. V.; Psyrri, A.; Bakou, V.; Pappa, V.; Spathis, A.; Economopoulou, P.; Papageorgiou, E.; Economopoulos, T.; Rontogianni, D. Hypoxia-inducible factors in mantle cell lymphoma: implication for an activated mTORC1→HIF-1α pathway. Ann Hematol. 2011, 90, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokas, E.; Prevo, R.; Hammond, E.M.; Brunner, T.B.; McKenna, W.G.; Muschel, RJ. Targeting ATR in DNA damage response and cancer therapeutics. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014, 40, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, L.I.; Murga, M.; Zur, R.; Soria, R.; Rodriguez, A.; Martinez, S.; Oyarzabal, J.; Pastor, J.; Bischoff, J.R; Fernandez-Capetillo, O. A cell-based screen identifies ATR inhibitors with synthetic lethal properties for cancer-associated mutations. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011, 18, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Pommier, Y. Targeting Topoisomerase I in the Era of Precision Medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6581–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, U.; Senatorov, I.S.; Zimmermann, A.; Saha, L.K.; Murai, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Elloumi, F.; Takahashi, N.; Schultz, C.W.; Thomas, A.; Zenke, F.T.; Pommier, Y. Novel and Highly Potent ATR Inhibitor M4344 Kills Cancer Cells With Replication Stress, and Enhances the Chemotherapeutic Activity of Widely Used DNA Damaging Agents. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, J.; Bonetti, A. FOLFIRINOX is a cost-effective combination chemotherapy in first-line for advanced pancreatic Cancer. Pancreatology. 2019, 19, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Mohanty, A.; Sandoval, N.; Tran, T.; Bedell, V.; Wu, J.; Scuto, A.; Murata-Collins, J.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Ngo, V.N. Cyclin D1 depletion induces DNA damage in mantle cell lymphoma lines. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017, 58, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, S.; Wang, L.Y.; Kitanaka, S. 3EZ, 20Ac-ingenol induces cell-specific apoptosis in cyclin D1 over-expression through the activation of ATR and downregulation of p-Akt. Leuk Res. 2018, 64, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S.; Nakamura, T.; Kitanaka, S. 3EZ, 20Ac-ingenol-induced Apoptosis in Chemoresistant Cancers With Cyclin D1 Accumulation. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 6237–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Wu, X.W.; Agama, K.; Pommier, Y.; Du, J.; Li, D.; Gu, L.Q.; Huang, Z.S.; An, L.K. A novel DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor with different mechanism from camptothecin induces G2/M phase cell cycle arrest to K562 cells. Biochemistry. 2010, 49, 10131–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, Y.; Kanbe,M. ; Watanabe, M.; Dan, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kitanaka, S.; Miyata S. 3EZ,20Ac-ingenol, a catalytic inhibitor of topoisomerases, downregulates p-Akt and induces DSBs and apoptosis of DT40 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 2013, 36, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimprich, K.A.; Cortez, D. ATR: an essential regulator of genome integrity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Niimi, A.; Yasuhara, T.; Permata, T.B.M.; Hagiwara, Y.; Isono, M.; Nuryadi, E.; Sekine, R.; Oike, T.; Kakoti, S.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Held, K.D.; Suzuki, Y.; Kono, K.; Miyagawa, K.; Nakano, T.; Shibata, A. DNA double-strand break repair pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. Nat Commun. 2017, 8, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, D.W.; Anderson, C.W. Posttranslational modification of p53: cooperative integrators of function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009, 1, a000950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, W.; Meier, F.; Stroka, D.M.; Giuliani, M.; Kugelmeier, P.; Nett, P.C.; Lehmann, R.; Candinas, D.; Gassmann, M.; Weber, M. Apoptosis in hypoxic human pancreatic islets correlates with HIF-1alpha expression. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.; Kasperczyk, H.; Fulda, S.; Debatin, K.M. Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha in modulation of apoptosis resistance. Oncogene. 2007, 26, 2027–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cha, G.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.; Xu, D.; Ge, M. HIF1α/PD-L1 axis mediates hypoxia-induced cell apoptosis and tumor progression in follicular thyroid carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 6461–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, A.T.; Waldron, J.S.; Panner, A.; Crane, C.A.; Parney, I.F.; Barry. J.J.; Cachola, K.E.; Murray, J.C.; Tihan, T.; Jensen, M.C.; Mischel, P.S.; Stokoe, D.; Pieper, R.O. Loss of tumor suppressor PTEN function increases B7-H1 expression and immunoresistance in glioma. Nat Med. 2007, 13, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Singh, A.R.; Durden, D.L. MDM2 regulates hypoxic hypoxia-inducible factor 1α stability in an E3 ligase, proteasome, and PTEN-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 2014, 289, 22785–22797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, E.M.; Dorie, M.J.; Giaccia, A.J. ATR/ATM targets are phosphorylated by ATR in response to hypoxia and ATM in response to reoxygenation. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278, 12207–12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, B.J.; Dreher, M.R.; Rabbani, Z.N.; Schroeder, T.; Cao, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Dewhirst, M.W. Pleiotropic effects of HIF-1 blockade on tumor radiosensitivity. Cancer Cell. 2005, 8, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Strome, S.E.; Salomao, D.R.; Tamura, H.; Hirano, F.; Flies, D.B.; Roche, P.C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; Lennon, V.A.; Celis, E.; Chen, L. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 2002, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, M.; Barsoum, I.B.; Truesdell, P.; Cotechini, T.; Macdonald-Goodfellow, S.K.; Petroff, M.; Siemens, D.R.; Koti, M.; Craig, A.W.; Graham, C.H. Activation of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint confers tumor cell chemoresistance associated with increased metastasis. Oncotarget. 2016, 7, 10557–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.A.; Gupta, H.B.; Sareddy, G.; Pandeswara, S.; Lao, S.; Yuan, B.; Drerup, J.M.; Padron, A.; Conejo-Garcia, J.; Murthy, K.; Liu, Y.; Turk, M.J.; Thedieck, K.; Hurez, V.; Li, R.; Vadlamudi, R.; Curiel, T.J. Tumor-Intrinsic PD-L1 Signals Regulate Cell Growth, Pathogenesis, and Autophagy in Ovarian Cancer and Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6964–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Yao, S.; Zhu, G.; Flies, A.S.; Flies, S.J.; Chen, L. B7-H1 is a ubiquitous antiapoptotic receptor on cancer cells. Blood. 2008, 111, 3635–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Diehl, J.A. Nuclear cyclin D1: an oncogenic driver in human cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2009, 220, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.H.; Hansen, L.K. Cyclin D1 promotes mitogen-independent cell cycle progression in hepatocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1999, 10, 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Stambolic, V.; MacPherson, D.; Sas, D.; Lin, Y.; Snow, B.; Jang, Y.; Benchimol, S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of PTEN transcription by p53. Mol Cell. 2001, 8, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stambolic, V.; Suzuki, A.; de la Pompa, J.L.; Brothers, G.M.; Mirtsos, C.; Sasaki, T.; Ruland, J.; Penninger, J.M.; Siderovski, D.P.; Mak, T.W. Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell. 1998, 95, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Tamura, M.; Yamada, K.M. Tumor suppressor PTEN inhibits integrin- and growth factor-mediated mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling pathways. J Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hamrouni, A.; Wolowiec, D.; Coiteux, V.; Kuliczkowski, K.; Hetuin, D.; Saudemont, A.; Quesnel, B. Plasma cells from multiple myeloma patients express B7-H1 (PD-L1) and increase expression after stimulation with IFN-{gamma} and TLR ligands via a MyD88-, TRAF6-, and MEK-dependent pathway. Blood. 2007, 110, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, C.A.; Panner, A.; Murray, J.C.; Wilson, S.P.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Simko, J.P.; Waldman, F.M.; Pieper, R.O.; Parsa, A.T. PI(3) kinase is associated with a mechanism of immunoresistance in breast and prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2009, 28, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, J.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Wargo, J.; Hodi, F.S. The activation of MAPK in melanoma cells resistant to BRAF inhibition promotes PD-L1 expression that is reversible by MEK and PI3K inhibition. Clin Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, N.; Gao, S.; Yin, H.; Li, J.A.; Wu, W.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, L; Rong, Y. ; Xu, X; Wang, D.; Kuang, T.; Jin, D,; Yu, J.; Lou, W. Cell-intrinsic PD-1 promotes proliferation in pancreatic cancer by targeting CYR61/CTGF via the hippo pathway. Cancer Lett. 2019, 460, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurin, M.R.; Umansky, V. Cross-talk between HIF and PD-1/PD-L1 pathways in carcinogenesis and therapy. J Clin Invest. 2022, 132, e159473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Yao, W.; Tang, Y.; Ding, A. An Ingenol Derived from Euphorbia kansui Induces Hepatocyte Cytotoxicity by Triggering G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Regulating the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway in Vitro. Molecules. 2016, 21, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Li, Z.; Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ding, A. Bio-guided isolation of the cytotoxic terpenoids from the roots of Euphorbia kansui against human normal cell lines L-O2 and GES-1. Int J Mol Sci. 2012, 13, 11247–11259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, S.; Fukuda, Y.; Tojima, H.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kitanaka, S.; Sawada, H. Mechanism of the inhibition of leukemia cell growth and induction of apoptosis through the activation of ATR and PTEN by the topoisomerase inhibitor 3EZ, 20Ac-ingenol. Leuk Res. 2015, 39, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.Y.; Wang, N.L.; Yao, X.S.; Miyata, S.; Kitanaka, S. Diterpenes from the roots of kansui and their in vitro effects on the cell division of Xenopus. J Nat Prod. 2002, 65, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




