Submitted:
16 May 2023
Posted:
17 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Functional features of IRAG1
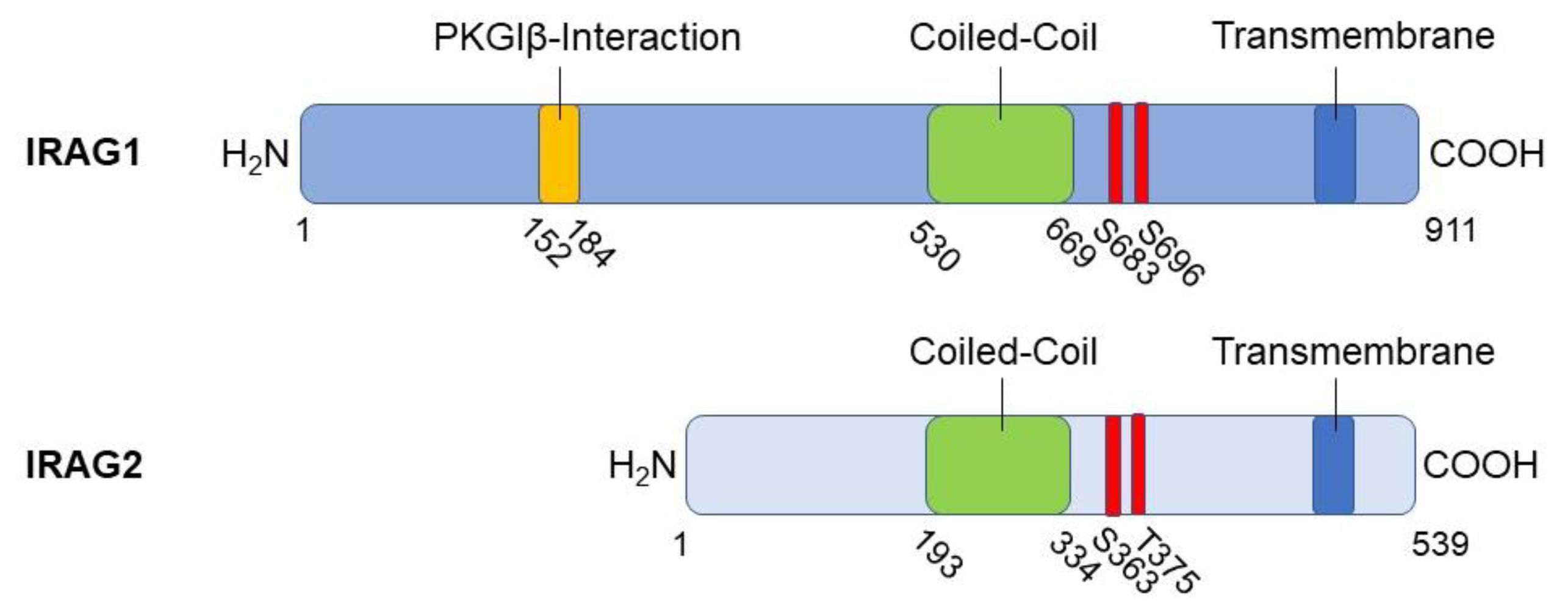
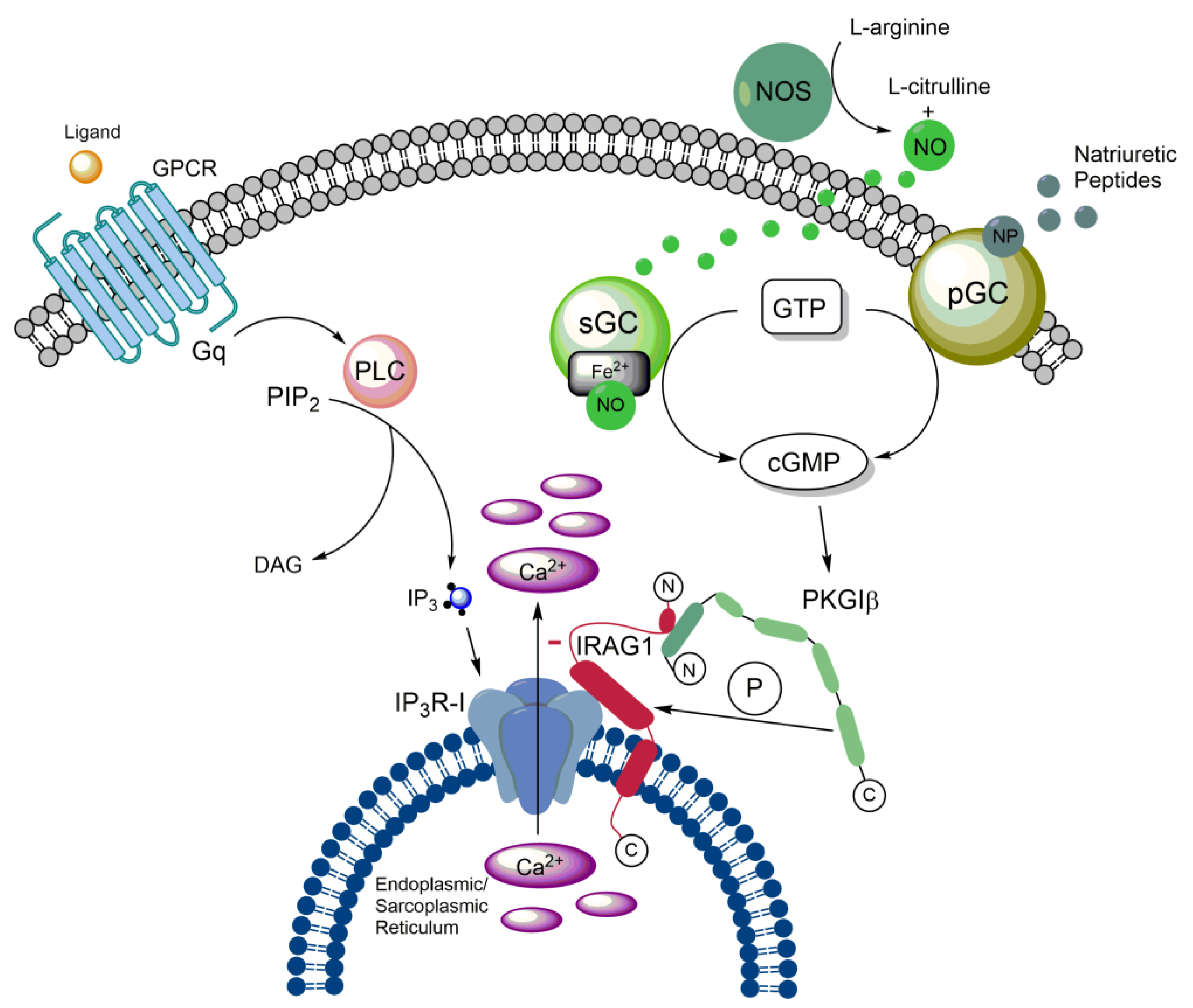
2.1. Structure, interaction partners and cellular functions of IRAG1
2.2. Expression pattern and localization of IRAG1
2.3. Impact of IRAG1 on Ca2+ signaling
2.4. (Patho-)physiological functions of IRAG1
2.4.1. IRAG1 and the gastrointestinal system
2.4.2. IRAG1 and (cardio-)vascular system
2.4.3. IRAG1 and cancer disease
2.4.4. Further (patho-)physiological functions of IRAG1
2.5. Polymorphisms of IRAG1 gene
2.6. Significance of IRAG1 as a diagnostical/prognostic marker
3. Functional features of IRAG2
3.1. Structure of IRAG2
3.2. Expression pattern and localization of IRAG2
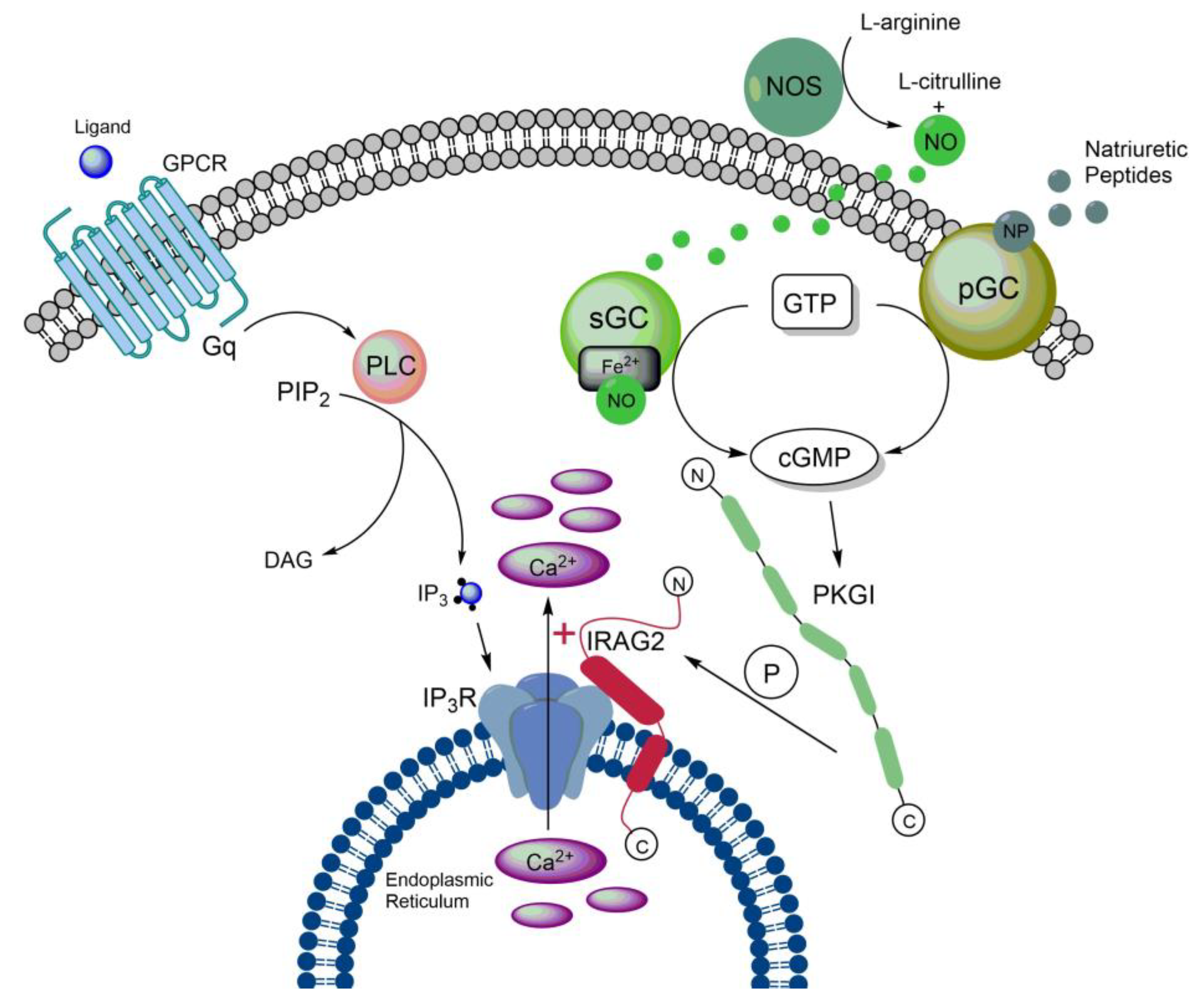
3.3. Cellular functions of IRAG2
3.4. Impact of IRAG2 on Ca2+ signaling
3.5. IRAG2 as a substrate of cGMP-dependent protein kinase I
3.6. (Patho-)physiological functions of IRAG2
3.6.1. Function of IRAG2 in intestinal type 2 immunity
3.6.2. Function of IRAG2 on HCN channels
3.6.3. Potential role of IRAG2 in taste-signal transduction
3.6.4. Function of IRAG2 in exocrine pancreatic acinar cells
3.6.5. Function of IRAG2 in platelets
3.7. Significance of IRAG2 as a prognostic marker of cancer
3.8. Significance of IRAG2 polymorphisms
4. Conclusion and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ammendola, A.; Geiselhöringer, A.; Hofmann, F.; Schlossmann, J. Molecular determinants of the interaction between the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-associated cGMP kinase substrate (IRAG) and cGMP kinase Iβ. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2001, 276, 24153–24159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlossmann, J.; Ammendola, A.; Ashman, K.; Zong, X.; Huber, A.; Neubauer, G.; Wang, G.X.; Allescher, H.D.; Korth, M.; Wilm, M.; et al. Regulation of intracellular calcium by a signalling complex of IRAG, IP3 receptor and cGMP kinase Iβ. Nature 2000, 404, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiselhöringer, A.; Werner, M.; Sigl, K.; Smital, P.; Wörner, R.; Acheo, L.; Stieber, J.; Weinmeister, P.; Feil, R.; Feil, S.; et al. IRAG is essential for relaxation of receptor-triggered smooth muscle contraction by cGMP kinase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4222–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desch, M.; Sigl, K.; Hieke, B.; Salb, K.; Kees, F.; Bernhard, D.; Jochim, A.; Spiessberger, B.; Höcherl, K.; Feil, R.; et al. IRAG determines nitric oxide- and atrial natriuretic peptide-mediated smooth muscle relaxation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 86, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antl, M.; von Brühl, M.-L.; Eiglsperger, C.; Werner, M.; Konrad, I.; Kocher, T.; Wilm, M.; Hofmann, F.; Massberg, S.; Schlossmann, J. IRAG mediates NO/cGMP-dependent inhibition of platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. Blood 2007, 109, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaughnessy, J.D.; Largaespada, D.A.; Tian, E.; Fletcher, C.F.; Cho, B.C.; Vyas, P.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G. Mrvi1, a common MRV integration site in BXH2 myeloid leukemias, encodes a protein with homology to a lymphoid-restricted membrane protein Jaw1. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2069–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T.W.; Jagadeesh, J.; Scherle, P.; Kearns, G.; Yewdell, J.; Staudt, L.M. Jaw1, A lymphoid-restricted membrane protein localized to the endoplasmic reticulum. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md.: 1950) 1994, 153, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, Y.; Kim, M.-R.; Miura, H.; Yuuki, T.; Kanda, T.; Hino, A.; Kusakabe, Y. Lrmp/Jaw1 is expressed in sweet, bitter, and umami receptor-expressing cells. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüschenk, S.; Majer, M.; Schreiber, R.; Schlossmann, J. IRAG2 Interacts with IP3-Receptor Types 1, 2, and 3 and Regulates Intracellular Ca2+ in Murine Pancreatic Acinar Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedoldi, S.; Paterson, J.C.; Cordell, J.; Tan, S.-Y.; Jones, M.; Manek, S.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Roberton, H.; Masir, N.; Natkunam, Y.; et al. Jaw1/LRMP, a germinal centre-associated marker for the immunohistological study of B-cell lymphomas. The Journal of pathology 2006, 209, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, N.; Lundholm, M.; Holmberg, D. The Idd6.2 diabetes susceptibility region controls defective expression of the Lrmp gene in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, C.H.; Rogner, U.C.; Avner, P. Lrmp and Bcat1 are candidates for the type I diabetes susceptibility locus Idd6. Autoimmunity 2003, 36, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Werder, A.; Mayr, M.; Schneider, G.; Oesterle, D.; Fritsch, R.M.; Seidler, B.; Schlossmann, J.; Hofmann, F.; Schemann, M.; Allescher, H.D.; et al. Truncated IRAG variants modulate cGMP-mediated inhibition of human colonic smooth muscle cell contraction. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C1445–C1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casteel, D.E.; Boss, G.R.; Pilz, R.B. Identification of the interface between cGMP-dependent protein kinase Iβ and its interaction partners TFII-I and IRAG reveals a common interaction motif. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2005, 280, 38211–38218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteel, D.E.; Zhang, T.; Zhuang, S.; Pilz, R.B. cGMP-dependent protein kinase anchoring by IRAG regulates its nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, M.; Prueschenk, S.; Schlossmann, J. Loss of PKGIβ/IRAG1 Signaling Causes Anemia-Associated Splenomegaly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Kojonazarov, B.; Hadzic, S.; Majer, M.; Bajraktari, G.; Novoyatleva, T.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Grimminger, F.; Seeger, W.; Weissmann, N.; et al. IRAG1 Deficient Mice Develop PKG1β Dependent Pulmonary Hypertension. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.H.; Myers, M.E.; Juchno, J.; Haimbaugh, C.; Bichraoui, H.; Du, Y.; Bankston, J.R.; Walker, L.A.; Proenza, C. Isoform-specific regulation of HCN4 channels by a family of endoplasmic reticulum proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2020, 117, 18079–18090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiselhöringer, A.; Gaisa, M.; Hofmann, F.; Schlossmann, J. Distribution of IRAG and cGKI-isoforms in murine tissues. FEBS Lett. 2004, 575, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Solano, A.S.; Gonzales, A.L.; Thakore, P.; Krishnan, V.; Yamasaki, E.; Earley, S. Nitric Oxide Signals Through IRAG to Inhibit TRPM4 Channels and Dilate Cerebral Arteries. Function (Oxf) 2021, 2, zqab051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, R.M.; Saur, D.; Kurjak, M.; Oesterle, D.; Schlossmann, J.; Geiselhöringer, A.; Hofmann, F.; Allescher, H.-D. InsP3R-associated cGMP kinase substrate (IRAG) is essential for nitric oxide-induced inhibition of calcium signaling in human colonic smooth muscle. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2004, 279, 12551–12559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, W.; Betzenhauser, M.J.; Yule, D.I. InsP3R-associated cGMP kinase substrate determines inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor susceptibility to phosphoregulation by cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 37927–37938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, A.; Klatt, P.; Massberg, S.; Ny, L.; Sausbier, M.; Hirneiss, C.; Wang, G.X.; Korth, M.; Aszódi, A.; Andersson, K.E.; et al. Defective smooth muscle regulation in cGMP kinase I-deficient mice. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3045–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, E.; Huster, M.; Smital, P.; Schlossmann, J.; Hofmann, F.; Wegener, J.W. Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent inhibition of contraction by cGMP/cGKI in intestinal smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G834–G839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, K.; Hmida, D.; Schlossmann, J.; Landgraf, D.; Reisch, N.; Schuelke, M.; Huebner, A. Homozygous mutation in murine retrovirus integration site 1 gene associated with a non-syndromic form of isolated familial achalasia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, O.; Mazza, T.; Bassotti, G.; Merla, A.; Tolone, S.; Biagini, T.; Cuttitta, A.; Bossa, F.; Martino, G.; Latiano, T.; et al. microRNA-mRNA network model in patients with achalasia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angermeier, E.; Domes, K.; Lukowski, R.; Schlossmann, J.; Rathkolb, B.; Angelis, M.H.; Hofmann, F. Iron deficiency anemia in cyclic GMP kinase knockout mice. Haematologica 2016, 101, e48–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Föller, M.; Feil, S.; Ghoreschi, K.; Koka, S.; Gerling, A.; Thunemann, M.; Hofmann, F.; Schuler, B.; Vogel, J.; Pichler, B.; et al. Anemia and splenomegaly in cGKI-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 6771–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Spiessberger, B.; Zheng, W.; Xiao, F.; Lukowski, R.; Wegener, J.W.; Weinmeister, P.; Saur, D.; Klein, S.; Schemann, M.; et al. Neuronal cGMP kinase I is essential for stimulation of duodenal bicarbonate secretion by luminal acid. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2012, 26, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, M.; Schinner, E.; Kees, F.; Hofmann, F.; Seifert, R.; Schlossmann, J. Cyclic cytidine 3',5'-monophosphate (cCMP) signals via cGMP kinase I. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3979–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, C.; Giugliano, T.; Kraemer, M.; Torella, A.; Schwitalla, J.C.; Cirillo, M.; Melis, D.; Berlit, P.; Nigro, V.; Perrotta, S.; et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies MRVI1 as a susceptibility gene for moyamoya syndrome in neurofibromatosis type 1. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0200446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Qin, F.; Li, X.; Du, X.; Li, T. Identification of novel proteins for lacunar stroke by integrating genome-wide association data and human brain proteomes. BMC medicine 2022, 20, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.J.; Cummins, C.; Radhakrishnan, R.S. Sildenafil Recovers Burn-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, C.H.; Singh, R.K.; Bankston, J.R.; Proenza, C. Regulation of HCN Channels by Protein Interactions. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 928507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massberg, S.; Sausbier, M.; Klatt, P.; Bauer, M.; Pfeifer, A.; Siess, W.; Fässler, R.; Ruth, P.; Krombach, F.; Hofmann, F. Increased adhesion and aggregation of platelets lacking cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate kinase I. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinner, E.; Salb, K.; Schlossmann, J. Signaling via IRAG is essential for NO/cGMP-dependent inhibition of platelet activation. Platelets 2011, 22, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, J.D.; Chami, N.; Kacprowski, T.; Nomura, A.; Chen, M.-H.; Yanek, L.R.; Tajuddin, S.M.; Schick, U.M.; Slater, A.J.; Pankratz, N.; et al. Platelet-Related Variants Identified by Exomechip Meta-analysis in 157,293 Individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, J.D.; Xue, L.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Beswick, A.D.; Johnson, A.D. Replication and hematological characterization of human platelet reactivity genetic associations in men from the Caerphilly Prospective Study (CaPS). J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 41, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.D.; Yanek, L.R.; Chen, M.-H.; Faraday, N.; Larson, M.G.; Tofler, G.; Lin, S.J.; Kraja, A.T.; Province, M.A.; Yang, Q.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analyses identifies seven loci associated with platelet aggregation in response to agonists. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Gillis, L.C.; Jarvis, J.D.; Yang, S.; Huang, K.; Der, S.; Barber, D.L. Tyrosine kinase chromosomal translocations mediate distinct and overlapping gene regulation events. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Li, F.; Si, T.; Renzhi, P.; Yu, M.; Chen, D.; Ye, P.; Lu, Y. High Expression of CD300A Predicts Poor Survival in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Acta Haematol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Hwan, J.D.; Bae, S.; Bae, D.-H.; Shick, W.A. Identification of differentially expressed genes using an annealing control primer system in stage III serous ovarian carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, Y.-P.; Wang, L.-J.; Kong, Y. miR-940 potentially promotes proliferation and metastasis of endometrial carcinoma through regulation of MRVI1. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Li, K.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.-A.; Zhu, X. MRVI1 and NTRK3 Are Potential Tumor Suppressor Genes Commonly Inactivated by DNA Methylation in Cervical Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 802068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumawidjaja, G.; Kayed, H.; Giese, N.; Bauer, A.; Erkan, M.; Giese, T.; Hoheise, J.D.; Friess, H.; Kleeff, J. Basic transcription factor 3 (BTF3) regulates transcription of tumor-associated genes in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Sun, Z.-Q.; Zhou, G.-L.; Li, G.-J.; Deng, S.-F. The Higher Expression of CDCA2 Associated with Poor Prognosis in Glioma. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 2184867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-E.; Oum, B.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, S.U.; Lee, J.S. Evaluation of differentially expressed genes identified in keratoconus. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 2480–2487. [Google Scholar]
- Yaroslavskiy, B.B.; Turkova, I.; Wang, Y.; Robinson, L.J.; Blair, H.C. Functional osteoclast attachment requires inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-associated cGMP-dependent kinase substrate. Lab. Invest. 2010, 90, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, Y.; Kong, C.; Ren, Y.; Lu, H. Label-free proteomic analysis and functional analysis in patients with intrauterine adhesion. J. Proteomics 2023, 277, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Oberwinkler, H.; Werner, F.; Gaßner, B.; Nakagawa, H.; Feil, R.; Hofmann, F.; Schlossmann, J.; Dietrich, A.; Gudermann, T.; et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide-mediated inhibition of microcirculatory endothelial Ca2+ and permeability response to histamine involves cGMP-dependent protein kinase I and TRPC6 channels. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K.; Ramírez, J.; Warren, H.R.; Aung, N.; Lee, A.M.; Tzanis, E.; Petersen, S.E.; Munroe, P.B. Genome-wide association study identifies loci for arterial stiffness index in 127,121 UK Biobank participants. Scientific reports 2019, 9, 9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gormley, P.; Anttila, V.; Winsvold, B.S.; Palta, P.; Esko, T.; Pers, T.H.; Farh, K.-H.; Cuenca-Leon, E.; Muona, M.; Furlotte, N.A.; et al. Meta-analysis of 375,000 individuals identifies 38 susceptibility loci for migraine. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghals, I.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Danning, R.; Gormley, P.; Malik, R.; Amouyel, P.; Metso, T.; Pezzini, A.; Kurth, T.; Debette, S.; et al. Migraine, Stroke, and Cervical Arterial Dissection: Shared Genetics for a Triad of Brain Disorders With Vascular Involvement. Neurol. Genet. 2022, 8, e653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudzik, R.; Dziedziejko, V.; Rać, M.E.; Sawczuk, M.; Maciejewska-Skrendo, A.; Safranow, K.; Pawlik, A. Polymorphisms in GP6, PEAR1A, MRVI1, PIK3CG, JMJD1C, and SHH Genes in Patients with Unstable Angina. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.A.R.; Mathur, R.; Vonk, J.M.; Szwajda, A.; Brumpton, B.; Granell, R.; Brew, B.K.; Ullemar, V.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Genetic Architectures of Childhood- and Adult-Onset Asthma Are Partly Distinct. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 665–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xia, X.; Han, R.; Fei, G.; Zeng, D.; Wang, R. Identification of three hub genes related to the prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis using bioinformatics analysis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Fan, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W. A prognostic model based on clusters of molecules related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Frontiers in genetics 2022, 13, 1109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T.W.; Kearns, G.M.; Rivard, J.J.; Bernstein, H.D.; Yewdell, J.W.; Staudt, L.M. Carboxyl-terminal targeting and novel post-translational processing of JAW1, a lymphoid protein of the endoplasmic reticulum. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1996, 271, 23528–23534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozono, T.; Tadahira, K.; Okumura, W.; Itai, N.; Tamura-Nakano, M.; Dohi, T.; Tonozuka, T.; Nishikawa, A. Jaw1/LRMP has a role in maintaining nuclear shape via interaction with SUN proteins. J. Biochem. 2018, 164, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, H.F.; Kim, D.; Wright, G.D.; Wong, E.S.M.; Stewart, C.L.; Burke, B.; Roux, K.J. A mammalian KASH domain protein coupling meiotic chromosomes to the cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozono, T.; Jogano, C.; Okumura, W.; Sato, H.; Matsui, H.; Takagi, T.; Okumura, N.; Takao, T.; Tonozuka, T.; Nishikawa, A. Cleavage of the Jaw1 C-terminal region enhances its augmentative effect on the Ca2+ release via IP3 receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2023, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Yue, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, F.; Inclan-Rico, J.M.; Ponessa, J.J.; et al. Tumor suppressor p53 regulates intestinal type 2 immunity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prüschenk, S.; Schlossmann, J. Function of IRAG2 Is Modulated by NO/cGMP in Murine Platelets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, D.A. A nuclear-envelope bridge positions nuclei and moves chromosomes. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.; Ke, H.; Gao, F.; Ren, J.; Wang, M.; Huo, L.; Gong, W.; Feng, W. Coiled-Coil Domains of SUN Proteins as Intrinsic Dynamic Regulators. Structure 2016, 24, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa, B.A.; Rothballer, A.; Kutay, U.; Schwartz, T.U. LINC complexes form by binding of three KASH peptides to domain interfaces of trimeric SUN proteins. Cell 2012, 149, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Z.; Jiao, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Greene, M.I.; Zhou, Z. Structural insights into SUN-KASH complexes across the nuclear envelope. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, M.; Liu, Q.; Roux, K.; Rattner, J.B.; Shanahan, C.; Burke, B.; Stahl, P.D.; Hodzic, D. Coupling of the nucleus and cytoplasm: role of the LINC complex. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozono, T.; Sato, H.; Okumura, W.; Jogano, C.; Tamura-Nakano, M.; Kawamura, Y.I.; Rohrer, J.; Tonozuka, T.; Nishikawa, A. The N-terminal region of Jaw1 has a role to inhibit the formation of organized smooth endoplasmic reticulum as an intrinsically disordered region. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapp, E.L.; Hegde, R.S.; Francolini, M.; Lombardo, F.; Colombo, S.; Pedrazzini, E.; Borgese, N.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Formation of stacked ER cisternae by low affinity protein interactions. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, M.L.; Sengstag, C.; Rine, J.D.; Wright, R.L. Identification of the sequences in HMG-CoA reductase required for karmellae assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 1995, 6, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasana, E.; Fossati, M.; Ruggiano, A.; Brambillasca, S.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; Navone, F.; Francolini, M.; Borgese, N. A VAPB mutant linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis generates a novel form of organized smooth endoplasmic reticulum. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, A.H.; Crick, S.L.; Vitalis, A.; Chicoine, C.L.; Pappu, R.V. Net charge per residue modulates conformational ensembles of intrinsically disordered proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 8183–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, M.M.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Pappu, R.V. Structural biology. Versatility from protein disorder. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2012, 337, 1460–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, O.; Bigman, L.; Friedler, A. A role of disordered domains in regulating protein oligomerization and stability. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2014, 50, 10797–10800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hieda, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Isobe, M.; Kurono, S.; Yuka, K.; Kametaka, S.; Wang, J.-Y.; Chi, Y.-H.; Kameda, K.; Kimura, H.; et al. The SUN2-nesprin-2 LINC complex and KIF20A function in the Golgi dispersal. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimpel, P.; Lee, Y.L.; Sobota, R.M.; Calvi, A.; Koullourou, V.; Patel, R.; Mamchaoui, K.; Nédélec, F.; Shackleton, S.; Schmoranzer, J.; et al. Nesprin-1α-Dependent Microtubule Nucleation from the Nuclear Envelope via Akap450 Is Necessary for Nuclear Positioning in Muscle Cells. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2999–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, K.J.; Crisp, M.L.; Liu, Q.; Kim, D.; Kozlov, S.; Stewart, C.L.; Burke, B. Nesprin 4 is an outer nuclear membrane protein that can induce kinesin-mediated cell polarization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, W.; Tadahira, K.; Kozono, T.; Tamura-Nakano, M.; Sato, H.; Matsui, H.; Dohi, T.; Rohrer, J.; Tonozuka, T.; Nishikawa, A. Jaw1/LRMP is associated with the maintenance of Golgi ribbon structure. J Biochem 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 1993, 361, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, W.; Kozono, T.; Sato, H.; Matsui, H.; Takagi, T.; Tonozuka, T.; Nishikawa, A. Jaw1/LRMP increases Ca2+ influx upon GPCR stimulation with heterogeneous effect on the activity of each ITPR subtype. Scientific reports 2022, 12, 9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhoul, S.; Walter, E.; Pagel, O.; Walter, U.; Sickmann, A.; Gambaryan, S.; Smolenski, A.; Zahedi, R.P.; Jurk, K. Effects of the NO/soluble guanylate cyclase/cGMP system on the functions of human platelets. Nitric Oxide 2018, 76, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, E.; Nolte, C.; Schulz, S.; Beltman, J.; Beavo, J.A.; Jastorff, B.; Walter, U. Analysis of the functional role of cGMP-dependent protein kinase in intact human platelets using a specific activator 8-para-chlorophenylthio-cGMP. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 43, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.-C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Xue, J.-B.; Zhao, D.-X.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, S.-M.; Du, Y.-W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; et al. Infection by the parasitic helminth Trichinella spiralis activates a Tas2r-mediated signaling pathway in intestinal tuft cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2019, 116, 5564–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiFrancesco, D.; Tortora, P. Direct activation of cardiac pacemaker channels by intracellular cyclic AMP. Nature 1991, 351, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainger, B.J.; DeGennaro, M.; Santoro, B.; Siegelbaum, S.A.; Tibbs, G.R. Molecular mechanism of cAMP modulation of HCN pacemaker channels. Nature 2001, 411, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicks, N.L.; Wong, T.; Sun, J.; Madden, Z.; Young, E.C. Cytoplasmic cAMP-sensing domain of hyperpolarization-activated cation (HCN) channels uses two structurally distinct mechanisms to regulate voltage gating. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011, 108, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisatsune, C.; Yasumatsu, K.; Takahashi-Iwanaga, H.; Ogawa, N.; Kuroda, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Ninomiya, Y.; Mikoshiba, K. Abnormal taste perception in mice lacking the type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2007, 282, 37225–37231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hoon, M.A.; Chandrashekar, J.; Mueller, K.L.; Cook, B.; Wu, D.; Zuker, C.S.; Ryba, N.J.P. Coding of sweet, bitter, and umami tastes: different receptor cells sharing similar signaling pathways. Cell 2003, 112, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, E.K.; Petersen, O.H.; Williams, J.A. Pancreatic acinar cells: acetylcholine-induced membrane depolarization, calcium efflux and amylase release. J. Physiol. 1973, 234, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, O.H. Ca2+ signaling in pancreatic acinar cells: physiology and pathophysiology. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2009, 42, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, Y. Gaisano, Subhankar Dolai, and Toshimasa Takahashi. Physiologic Exocytosis in Pancreatic Acinar Cells and Pathologic Fusion Underlying Pancreatitis, 2020.
- Ruggeri, Z.M. Platelets in atherothrombosis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwald, A.; Wright, G.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; Campo, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Smeland, E.B.; Giltnane, J.M.; et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossos, I.S.; Czerwinski, D.K.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Wechser, M.A.; Tibshirani, R.; Botstein, D.; Levy, R. Prediction of survival in diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma based on the expression of six genes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, H.L.; Bacík, I.; Bennink, J.R.; Kearns, G.; Behrens, T.W.; Bächi, T.; Orlowski, M.; Yewdell, J.W. Two novel routes of transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP)-independent major histocompatibility complex class I antigen processing. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.P.; Lippman, S.M.; Spier, C.M.; Slymen, D.J.; Grogan, T.M. HLA-DR (Ia) immune phenotype predicts outcome for patients with diffuse large cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Invest. 1988, 82, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimsza, L.M.; Roberts, R.A.; Miller, T.P.; Unger, J.M.; LeBlanc, M.; Braziel, R.M.; Weisenberger, D.D.; Chan, W.C.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Loss of MHC class II gene and protein expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is related to decreased tumor immunosurveillance and poor patient survival regardless of other prognostic factors: a follow-up study from the Leukemia and Lymphoma Molecular Profiling Project. Blood 2004, 103, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, P.; Antonov, A.; Anemona, L.; Vangapandou, C.; Montanaro, M.; Botticelli, A.; Mauriello, A.; Melino, G.; Catani, M.V. New immunological potential markers for triple negative breast cancer: IL18R1, CD53, TRIM, Jaw1, LTB, PTPRCAP. Discov. Oncol. 2021, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, N.; Ni, H.; Zu, L.; He, J.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; et al. LRMP Associates With Immune Infiltrates and Acts as a Prognostic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 711928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Itoh, T.; Imamichi, S.; Kikuhara, S.; Fujimori, H.; Hirai, T.; Saito, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Proteomic analysis of cellular response induced by boron neutron capture reaction in human squamous cell carcinoma SAS cells. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2015, 106, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariboldi, M.; Manenti, G.; Canzian, F.; Falvella, F.S.; Radice, M.T.; Pierotti, M.A.; Della Porta, G.; Binelli, G.; Dragani, T.A. A major susceptibility locus to murine lung carcinogenesis maps on chromosome 6. Nat. Genet. 1993, 3, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manenti, G.; Dragani, T.A. Pas1 haplotype-dependent genetic predisposition to lung tumorigenesis in rodents: a meta-analysis. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, G.; Galbiati, F.; Giannì-Barrera, R.; Pettinicchio, A.; Acevedo, A.; Dragani, T.A. Haplotype sharing suggests that a genomic segment containing six genes accounts for the pulmonary adenoma susceptibility 1 (Pas1) locus activity in mice. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4495–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, G.; Galbiati, F.; Pettinicchio, A.; Spinola, M.; Piconese, S.; Leoni, V.P.; Conti, B.; Ravagnani, F.; Incarbone, M.; Pastorino, U.; et al. A V141L polymorphism of the human LRMP gene is associated with survival of lung cancer patients. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, D.A.; Manenti, G.; Galbiati, F.; Ribeiro, O.G.; Cabrera, W.H.K.; Barrera, R.G.; Pettinicchio, A.; de Franco, M.; Starobinas, N.; Siqueira, M.; et al. Pulmonary adenoma susceptibility 1 (Pas1) locus affects inflammatory response. Oncogene 2003, 22, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




