1. Introduction
Seafood provides a set of nutrients available, with healthier fats, proteins and vitamin D, among other micronutrients. In coastal regions of developing nations and small island states, 50% of animal protein can come from fishing (FAO 2016). The practice of cultivating penaeid shrimp and their development are of commercial importance and can result in the occurrence of infectious and non-infectious diseases worldwide. Opportunistic microorganisms that are part of the microflora and fauna of the penaeid shrimp cause most of these diseases (Arulmoorthy et al. 2020). Viral pathologies are among the most harmful and lethal diseases described for crustaceans. The knowledge about the genes associated with the viral immune response, as well as the relationship between pathogen and host is still very incomplete. As invertebrates do not have adaptive immunity, they do not have high specificity against invaders. Thus, resistance to disease is based on the innate defense system, which includes a series of coordinated cellular and humoral reactions. Within this set of reactions, Heat Shock Proteins (HSP) is considered the main responses of cell protection against various stressors. There are several studies on the constitutive or inducible responses to thermal shock in HSP70 reported in the literature in the last 20 years.
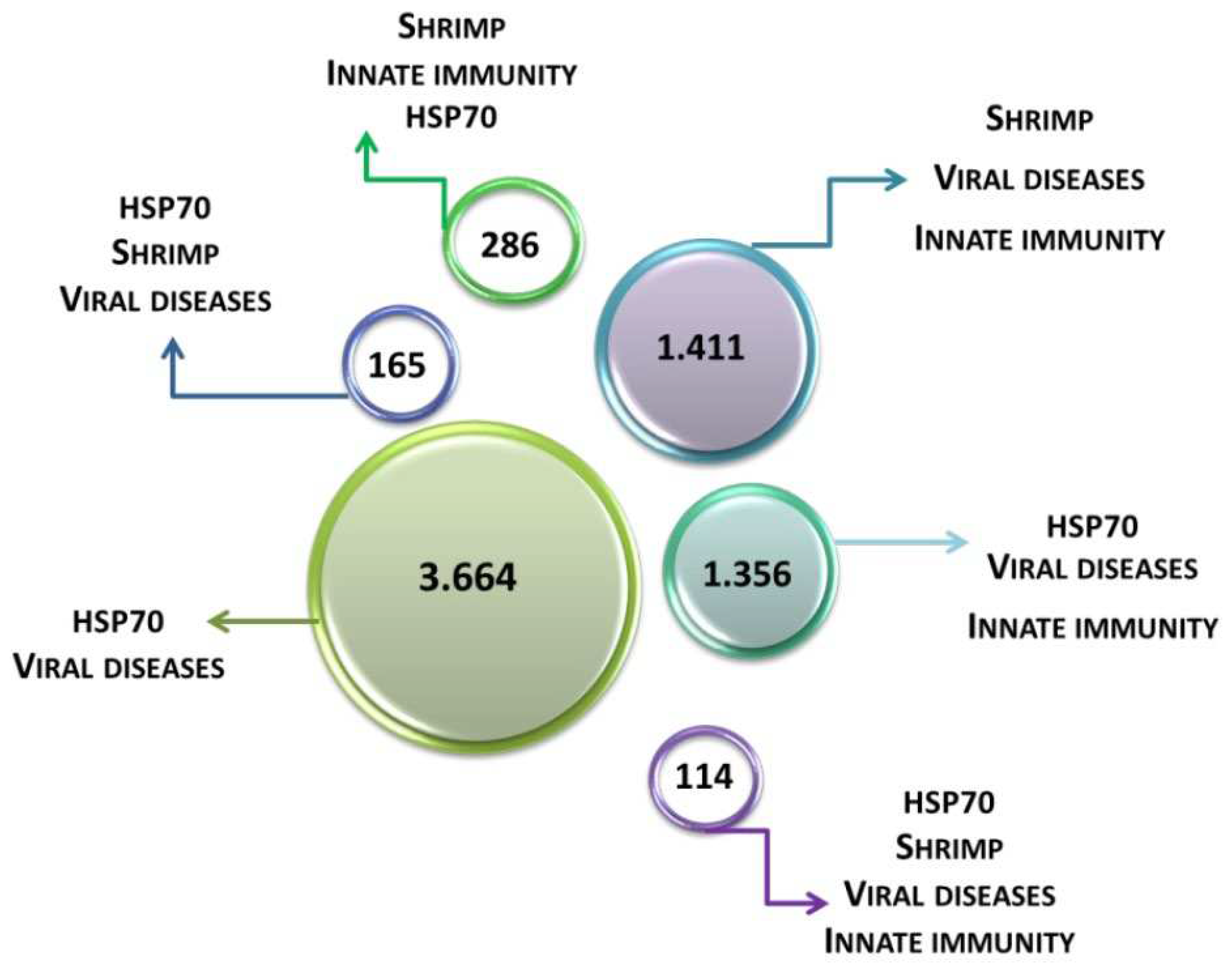
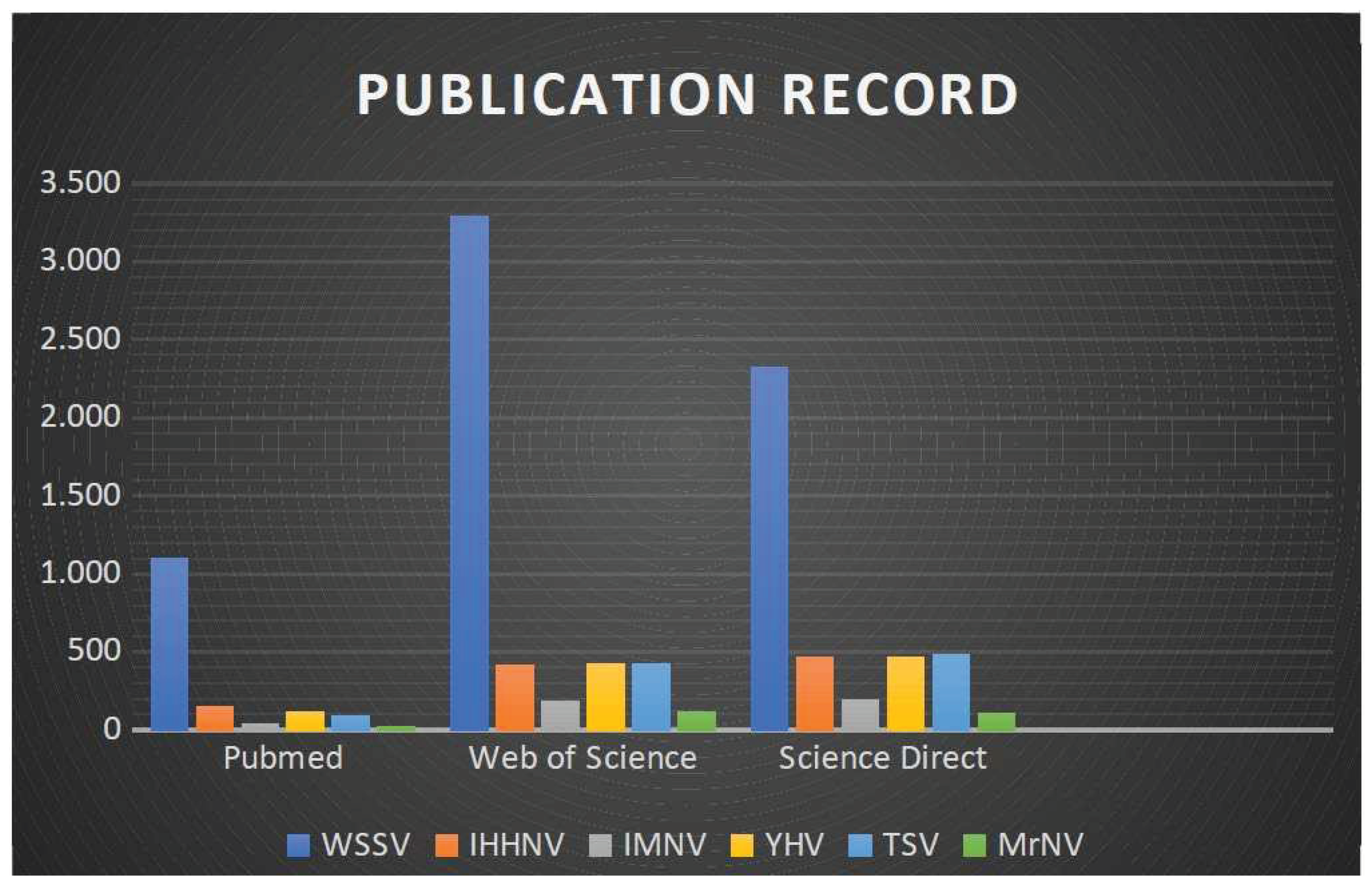
The scientific literature has been revised for publication records touching of studies for the terms HSP70, shrimp, viral diseases, and immunity within the years 2000 and 2020 and therefore the main results were outlined in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. Despite considerable advances in animal virology in recent years and the need for the global aquaculture industry to avoid economic losses, knowledge about aquaculture viruses remains scarce.
HSPs are responses sharply induced by various stressors that denature proteins. In addition to resistance to stress, HSPs are involved in the folding of nascent proteins, in the development of plants and animals, in aging, in adaptation to the environment and in the immune response, demonstrating their fundamental importance for cell survival. HSPs are induced in aquatic organisms by perturbations of environmental parameters, contaminants, handling, hormones and biotic stressors (Sung et al. 2011). Perhaps the lack of data related to HSP responses to viral infections in crustaceans is due to the fact that these molecules have a well-established role in studies with thermal stress. The main factors that disturb the production of shrimp are the fluctuations in the physical and chemical parameters of the water caused by precipitation, temperature, salinity and pH (Nguien et al 2020). These factors have also been identified as risk factors for shrimp disease outbreaks associated to climate change events (Tendencia and Verreth 2011). Some immunological or physiological parameters are modulated in response to stressful conditions that negatively affect aquatic organisms and can act as an important indicator of health status in farm animals such as shrimp, where a rapid and accurate assessment of health conditions is essential to ensure the success of cultivation programs. However, non-lethal heat shock protects aquatic organisms against biotic and abiotic stress, perhaps due in part to the buildup of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) (Sung et al. 2018). Despite the high number of studies involving marine shrimp, most of these studies address species of commercial interest, such as Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and Macrobrachium rosenbergii.. Both are species with zootechnical interest and a well-established production system. Notably, the number of surveys covering responses to HSP70 and viral diseases has been almost restricted to White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV). Among viral pathogens, WSSV remains the most serious for the shrimp industry worldwide. With the intensification of the shrimp farming industry and the international trade in aquatic species, outbreaks of infectious diseases in shrimp-producing regions have become a growing problem (Dorf et al. 2005).
2. Scope of Review
In this review, we describe the main molecules under study, which are related to the immune system discovered by advanced analysis techniques such as genomics and proteomics and the characterization of these immunological molecules that participate in the main defense reactions against pathogenic viruses in crustaceans. We analyzed the history of HSP70 Heat Shock Protein studies that assessed the potential for response to viral diseases in shrimp. We evaluate species, viruses, year of publication, response effectiveness, objectives and efforts, such as optimization and accuracy, and offer recommendations for the development of diagnostic tools for viral diseases in farmed shrimp.
3. Stress physiology and HSP response
Stress may be defined as a physiological disturbance that can be correlated with various abnormalities. The term stress was first used in this context by the physiologist Hans Selye, who found that humans and animals share a specific and consistent pattern of physiological responses to illness or injury (Selye 1936), by which an organism tries to maintain or restore a normal metabolism in face of a physical or chemical force. Living organisms are constantly being subjected to varied situations of stress and the response to these stimuli occurs through changes in cellular metabolism, activating their defense mechanisms. Brett (1958) proposes an additional definition: stress is a change caused by a factor, which exceeds the animal's adaptive responses beyond its normal level, or disrupts normal function in such a way that the chances of survival are reduced. These responses include body attempt to cope with the demands imposed by the disease or lesions.
Marine crustaceans are under the influence of several environmental factors. Among these factors, farmed shrimp are particularly subject to climate change and changes due to agricultural practices that influence the physicochemical water quality. Stress in the aquatic environment as a result of poor environmental quality and intensive agriculture is one of the triggers for the transition from a chronic infectious disease to an acute infection. Stress can modulate the immune capacity of shrimp, as well as causing changes at the biochemical and molecular level. In areas with intensive cultivation system, agricultural effluents are discharged into drainage channels and the chemical and biological contaminants from these effluents recirculate between other rural properties (Kautsky et al. 2000). Abiotic and biotic factors when altered can result in stress for shrimp during the developmental period. Also, these changes in seawater quality can affect animal metabolism, growth, reproduction, immune system and the survival of animals. In fact, shrimps are animals that get stressed easily.
This interpretation of an organism's ability or inability to adjust to a disturbance is consistent with the “General Adaptation Syndrome – GAS” paradigm of Selye (1950), which considers that an organism passes through three stages in response to stress. The first stages are often manifested by measurable physiological changes at different levels of organization, especially at the lowest levels, however the final stage is the maladaptive stage normally related to the development of pathological states, which can alter the body's health condition, eventually resulting in mortality (Barton et al. 2002) in spite of mounting a stress response, also known by “distress” (Selye 1984; Rehman et al. 2017). Organisms and cells can respond to various stress circumstances such as culture system managements, metabolic, or pathophysiological stress by up regulating selectively the expression of a protein group (Bakthisaran et al. 2015). One of the stress responses comprises the action of proteins called HSP, which is one of the primary responses of cell protection (Lindquist and Craig 1988; Sung et al. 2011).
The HSP was first reported by Ritossa (1962), who observed activation of a set of ‘puffs’ in polytene chromosomes in the salivary glands of Drosophila larvae exposed to sudden elevated temperature or to chemical agents that disturbed oxidative phosphorylation. Afterward, Tissiers et al. (1974) observed that exposure of Drosophila to heat shock resulted in the synthesis of a common set of new proteins called “heat shock proteins” or “stress proteins”. The heat shock response has been most extensively studied in Drosophila, but an analogous response has been observed in cells of a broad spectrum of eukaryotes. According to Lindquist and Craig (1988) the heat response is the most highly conserved genetic system known, existing in every organism in which it has been sought, from archaebacteria to eubacteria, from plants to animals.
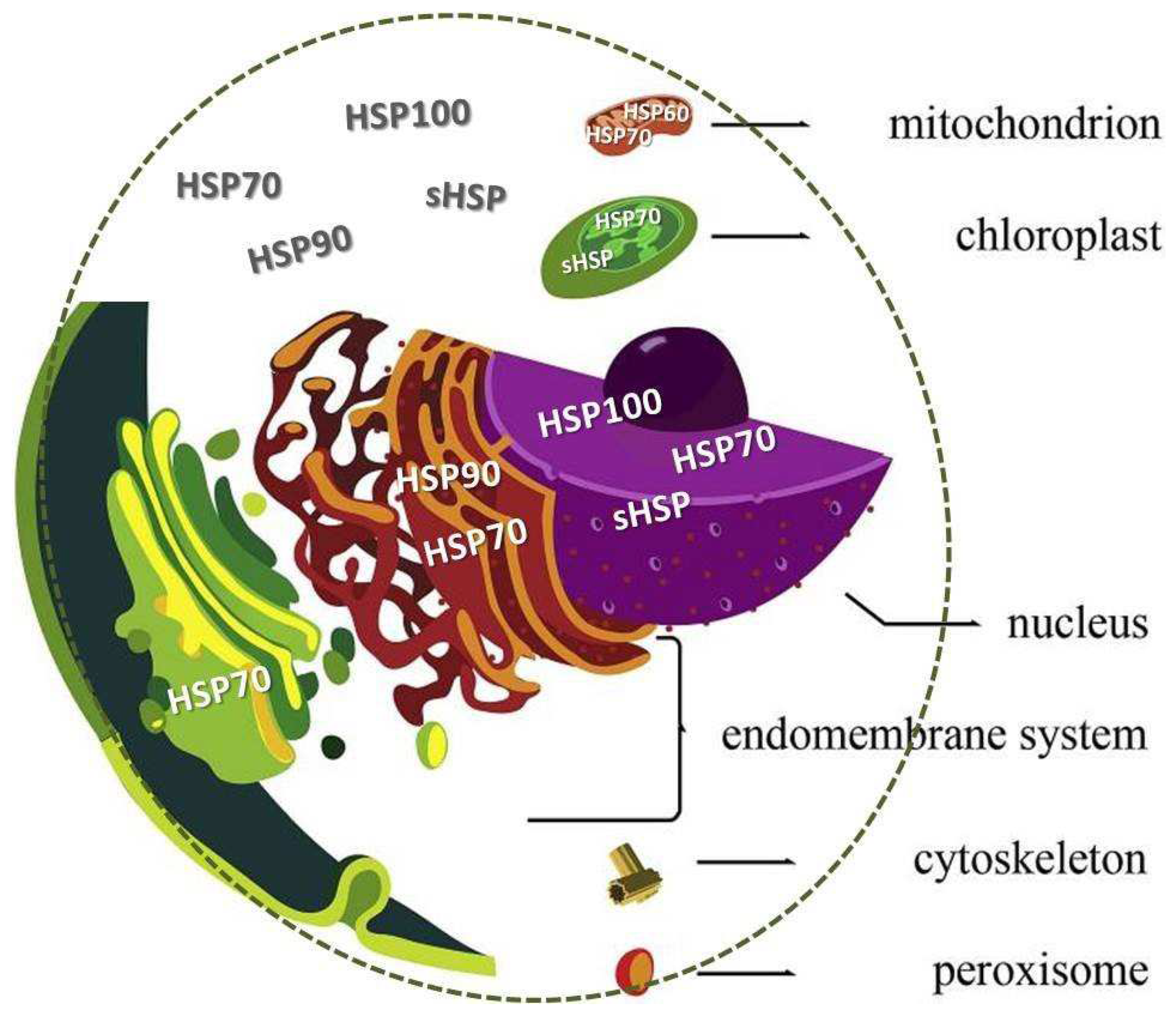
The HSPs comprises a family of proteins with a high degree of homology. Different HSPs classes are found in various cellular compartments, semiautonomous organelles, mitochondria, and chloroplasts and normally represent 5-10% of the total protein in most cells. Subcellular compartmentalization is a fingerprint of eukaryotic cells (Gabaldón and Pittis 2015).
Figure 3 illustrates a schematic representation of a generalized eukaryotic cell showing the main compartments and some HSP location. The size of HSP range from 15 to 110 kDa and they are classified based on the size, site of synthesis, and function. Six structurally conserved distinct classes are: HSP40, HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, HSP100, approximately 17–30 kDa molecular weights referred to as small HSPs (sHSPs). They are expressed both constitutively (cognate proteins) and under stressful conditions (inducible forms) (Danwattananusorn et al. 2011). In addition, HSPs can perform a multitude of housekeeping functions that are essential for cell stability (Srivastava 2002). Under normal conditions, may participate in cellular processes such as protein folding and transport, cell cycle regulation and apoptosis (Mallouk et al. 1999; Johnston et al. 2018), as well as in physiological processes such as embryonic development, gonadal development and spermatogenesis (Binder 2014; Chan et al. 2014). They act as molecular chaperones, maintaining homeostasis and acting against the proteotoxic effects (Huang et al. 2011; de la Vega et al. 2006). Small heat shock proteins (sHSPs) are conserved across species and are key actors in stress tolerance. Several sHSPs exhibit chaperone-like activity to avoid aggregation of target proteins, keeping them in a folding–competent state and refolding them by themselves or with other ATP-dependent chaperones (Bakthisaran et al. 2015).
vacuoles, vesicles, and endosomes. Figure modified from Gabaldón & Pittis (2015).
Mainly, the HSP70 family includes the constitutive cytosolic Hsc70 (or HSP73), the stress-induced cytosolic HSP70 (or HSP72), the endoplasmic reticulum Bip (or Grp78), and the mitochondrial mt-HSP70. The HSP70 is composed of two major functional domains according to Lindquist and Craig (1988). The NH2-terminal, very conserved ATPase domain binds ADP and ATP tightly and hydrolyzes ATP, while the COOH-terminal domain is essential for polypeptide binding (Lindquist and Craig 1988; Hartl and Hayer-Hartl 2002). Thus, HSP70 is an important molecule that acts in the immune defense in response to viral infections in shrimp (Janewanthanakul et al. 2020). On the other hand, a survey in the existing literature shows that little importance has been given to these molecules regarding defense against viruses.
4. Immune response in viral infections
A wide range of pathogens and parasites can host in decapod crustaceans. However, viral pathogens appear to exercise the most significant restrictions on the growth and survival of these farmer animals. Approximately 60% of the current losses associated with the disease in shrimp aquaculture may be due to viral pathogens, with more than 20% due to bacterial pathogens, while the losses associated with fungal and parasitic agents are lower (Flegel 2006, 2012). Viral infections have been found in wild and cultured crustaceans, since its initial discovery in the 1960s (Vago 1966), more than 50 viruses have been described from several groups of crustaceans. Due to their larger size and pathological characteristics, DNA viruses were mostly described in groups of hosts studied with any level of detail (Takahashi et al. 1994; Stentiford 2008; Behringer et al. 2011). Viruses with RNA genomes, some of which have devastating consequences for cultivated animals, are also being increasingly described, particularly in penaeid shrimp in intensive farming systems (Hasson et al. 1995; Poulos et al. 2006; Lightner 2011).
In general terms, since the beginning of the industry, shrimp farming has been hampered by pathogens that continue to appear despite efforts to create specific pathogen-free (SPF) stocks and specific pathogen resistant (SPR) shrimp. According with Moss et al. (2012) although SPF shrimp are, by definition, free of specifically listed pathogens, SPF shrimp may not be disease free. Also, those authors highlight that SPF shrimp have no innate resistance to any particular pathogen, nor are they innately susceptible. Resistance or susceptibility to disease can be maintained in a shrimp strain through selective breeding, but these characteristics do not influence the status of the SPF.
Shrimps that have compromised immunity As a result of abiotic stress shrimps may be more susceptible to disease and infection, which can lead to mass mortality. To protect against pathogens the defense mechanisms of crustaceans depend completely on the innate immune system (Barracco et al. 2014).. Crustaceans do not have an adaptive immune system, as present in vertebrates, thus, there is no participation of antibodies and memory cells as protection highly specific and long-term (Barracco et al. 2014). The carapace or exoskeleton is the first line of defense. In addition, part of the gastrointestinal is coated with chitin and consists of an acidic environment and full of digestive enzymes and antimicrobial effectors (Soonthornchai et al. 2010). In general, The best known immune defenses in crustaceans are those linked to haemolymph, fluid tissue responsible for transporting nutrients, excreta, hormones, oxygen, and immune system components. The comprehension of innate immune response in shrimps against invading pathogens provides important information for establishing effective methods to control these and, potentially, those of related emerging infectious diseases (Tassanakajon et al. 2013).
Despite the multiple defense mechanisms against viruses, viral diseases continue to be frequent in aquatic environment and shrimp frmas. They represent one of the most significant infectious diseases and can be destroyed by the innate immune response (Machado et al. 2004). A wide range of life stages of shrimp may be susceptible to certain viral infections causing mortality, slow growth, and deformations (Rahman et al. 2007). Shrimp production by aquaculture has been seriously impacted by diseases during the last decades. Among the several viral problems that affect shrimp, there are seven main ones: White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV), Infectious Hypodermal and Haematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV), Infectious Myonecrosis Virus (IMNV), Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodavirus (MrNV), Taura Syndrome Virus (TSV) and Yellow Head Virus (YHV) (Seibert and Pinto 2012), actually part of the OIE listed viral diseases of shrimp (Marques et al. 2006; OIE 2016). Together, the top five viral pathogens (WSSV, IHHNV, IMNV, TSV and YHV) can represent additional annual losses of around $ 500 million, causing a total annual loss of $ 1.5 billion (or 15% of production). If we consider the rates of loss of production by WSSV (10% of the total) and the five main viral diseases (15% of the total), it is equivalent to the total that is imported into the United States and the European Union combined (Stentiford et al. 2012 ).
White spot syndrome virus (WSSV): is classified in the Nimaviridae family as the only known member of the Whispovirus genus, comprise a large, circular, double-stranded DNA genome with ̴ 300,000 nucleotides (van Hulten et al. 2001). In 1992 WSSV appeared in shrimp farms in northern Taiwan causing massive mortality. A rapidly replicating and extremely virulent pathogen, is the most serious disease-causing agent in shrimp aquaculture worldwide (OIE 2016). The WSSV is spreading across the world causing production breaks and economic losses. One of the last records was in the mud shrimp Austinogebia edulis in Taiwan (Zhu et al. 2019).
Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV): the first widespread epizooty that seriously affected the commercial penaeid shrimp industry and was first reported in Hawaii on blue shrimp Penaeus stylirostris in 1980 (Lightner et al. 1983; Lightner 2011). IHHNV possesses a single-stranded linear DNA genome comprising 4,100 nucleotides and is classified as a member of the Parvoviridae family that is not formally classified but likely to be a member to the genus Brevidensovirus (Shike et al. 2000). In addition, recent studies suggest that IHHNV may act as an immunostimulant that triggers the shrimp's immune response against viral infection (Jariyapong et al. 2019a).
Infectious myonecrosis virus (IMNV): is likely to be a member to Totiviridae family, and the first member of this family to infect a host other than fungus or protozoan (Nibert 2007; Poulos et al. 2006). Is a non-enveloped virion with 40 nm in diameter whose icosahedral capsid has fibrous protrusions (Nibert 2007; Takahashi et al. 2000). The long non-segmented double-stranded RNA genome (dsRNA) contains 7,560 nucleotids. Is the most recently emergent virus that infects Pacific white shrimps Litopenaeus vannamei. Epizootic events due to IMNV infection were initially reported in 2002 in Northeastern Brazil (Lightner et al. 2006). IMNV is an emerging virus from Penaeid shrimp. It is endemic to Brazil and Indonesia, with a potential chance of spreading across borders. The OIE lists it as one of the main viral pathogens for crustaceans and has initiated active surveillance (Prasad et al. 2017).
Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodavirus (MrNV): the virus belongs to the family of Nodaviridae (Hameed et al. 2004), which is a small icosahedral, non-enveloped virus of 27 to 30 nm in diameter, causes white tail disease (WTD) in Giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Citarasu et al. 2019). The viral genome contains two segments of positive-sense, single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) with 1146 nucleotides. The first report was in the Guadeloupe Island in the French West Indies in 1997 (Arcier et al. 1999). The latest studies show that white tail disease infection caused by MrNV, occurs only in nauplii, and not in adults. The functions related to the immune system derived from hematopoietic tissue and haemocyte homeostasis in adult shrimp are believed to play roles in resistance to viral infection. (Jariyapong et al. 2019b).
Taura syndrome virus (TSV): a member of the Dicistroviridae family, comprising of a small, non-enveloped, icosahedral virion with 31-32 nm in diameter. Its genome comprises 10,250 nucleotides in a single-stranded linear RNA of positive polarity (Mari et al. 2002). One of the most important pathogens affecting farm-reared shrimp was first reported in 1992 in Litopenaeus vannamei collected from shrimp farms in Taura River, Ecuador (Lightner et al. 1995; Lightner 2011). The mechanisms of TSV transmission occur by cannibalism of infected moribund or dead shrimp by healthy shrimp in a pond or in an experimental tank. The current TSV control methods emphasize biosecurity at the farm level and the utilization of SPF, TSV-resistant shrimp for stocking (Dhar and Allnut 2008).
Yellow head virus (YHV): is classified in the Roniviridae family, genus Okavirus, within the Nidovirales order (Wongteerasupaya et al. 1995). YHV genome is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA of approximately 26,662 nucleotides (Sittidilokratna et al. 2008) and is one of six known genotypes in the yellow head complex of viruses, was the cause of the second most serious viral epizootic of penaeid shrimp that occurred in Thailand in 1990 in cultured Penaeus monodon (OIE 2016). Moreover, Gill-associated virus (GAV) was assigned as the type species of Okavirus genus in Roniviridae based on the evolutionary divergence of GAV and YHV from other nidoviruses (Gorbalenya 2008; Gorbalenya et al. 2006). Interestingly, their rod-shaped enveloped virions being distinct from the spherical enveloped virions formed by viruses in either the Coronaviridae or the Arteriviridae families of the Nidovirales known to exist at that time. Suppositions about vertical transmission come by analogy with GAV and can be very accurate. However, the prevalence of YHV in healthy shrimp appears to be far lower than for GAV and other genotypes, and it is unclear how it maintains a cycle of natural infection (Walker and Sittidilokratna 2008).
Shrimp haemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV): one of the last viral diseases discovered and still little studied, according to a review by Arulmoorphy et al. (2020), was first identified and described by Qiu et al. (2017). A large icosahedral virus classified in the family Iridoviridae with diameters in the range of 120 to 300 nm, reaching up to 350 nm, this new iridescent virus does not belong to the five known genera of this family (Iridovirus, Chloriridovirus, Ranavirus, Lymphocystivirus, and Magalocytivirus). The SHIV virion core comprises a single linear double stranded DNA (dsDNA) molecule of 140–303 kbp. This family of viruses has a wide range of hosts, including from invertebrates (such as insects) to pecilothermic vertebrates, such as fish, amphibians and reptiles (Jancovich et al. 2012).
Several molecules concerning immunology in penaeid shrimp have been discovered, and can assist the animal defense against viral pathologies, most through the analysis of expressed sequence libraries, microarray studies, biochemical, genomic and proteomic approaches (e.g., Aoki et al. 2011; Hirono et al. 2011; Robalino et al. 2009; Somboonwiwat et al. 2010; Liu et al. 2011; Valentim-Neto et al. 2014; Valentim-Neto et al. 2015; Chen et al. 2016; Ren et al. 2019). Rowley and Pope (2012) mention that the immune system of invertebrates is composed of a cellular and a humoral part that are closely related. The main effector cells of this immune system in crustaceans are haemolymph cells or haemocytes, while the hepatopancreas is responsible for the biosynthesis of some humoral factors. These factors may be naturally occurring and/or formed after antigenic stimulation (Ratcliffe et al. 1985). In shrimp, as in other crustaceans, there appear to be three main types of haemocytes (blood cells), hyaline cells, semi-granular cells and granular cells (called granulocytes by some authors). Immune molecules include antimicrobial peptides, serine proteinases and inhibitors, phenoloxidases (PO), oxidative enzymes, coagulable proteins, pattern recognition proteins (PRP), lectins, Toll receptors, HSPs and other humoral factors that can participate in the shrimp's innate immune system (Tassanakajon et al. 2013; Janewanthanakul et al. 2020).
The modulation of some immunological or physiological parameters, as a response to a viral infection stress, may function as an important indicator of health status in farmed animals such as shrimps, where a rapid and precise assessment of health conditions is crucial to ensure the success of farm programs.
5. HSP70 and cell death
For successful viral replication within an individual cell, a remarkable cascade of interactions between the virus and the host is required, beginning at the first involvement of the cell receptor until the final release of progeny virions. Verbruggen et al. (2016) have list a variety of molecular mechanisms to response and even prevent virus infectivity responses in host. These mechanisms involve some of genes related to heat shock responses. Shrimp showed high induced genes like Caspase, Ubiquitin and HSP in severity viral load, shown a role play of responsive proteins in pathological processes. Further HSPs also play a role in apoptosis mechanism.
Apoptosis, a programmed cell death, is considered an important mechanism in the development, homeostasis and cell defense that inhibits viral multiplication and eliminates infected cells in multicellular organisms (Tschopp et al. 1998; Everett and McFadden 1999; Koyama et al. 2000). The apoptosis mechanism of infected cells is triggered by cytolytic cells activated during the antiviral immune response or may be a direct result of viral infection, if apoptosis occurs at the early stage of viral infection, i.e., before complete viral replication, the production of progeny virions will be severely hampered, limiting virus spread in the host. Consequently, many viruses have developed various strategies that inhibit apoptosis during virus infection, thereby prolonging cell viability until sufficient progeny viruses have been produced (Tschopp et al. 1998; Hay and Kannourakis 2002). However, the viruses could intentionally induce apoptosis at the late stage of viral infection in order to facilitate the assembly or release of progeny virus, or to promote the spread of progeny virus within a host without triggering inflammatory responses (Best and Bloom 2004; Best 2008). Some proteins that were predominantly anti-apoptotic were HSP27, HSP70, and HSP90, whereas HSP60 is pro-apoptotic (Murthy and Ravishankar 2016). HSP90 and HSP70 are critical to the folding and assembly of other cellular proteins and are also involved in regulation of kinetic partitioning between folding, translocation, and aggregation within the cell (Roberts et al. 2010).
HSP70 genes in aquatic invertebrates have also been experimentally shown to decrease the mortality rate of certain organisms (Ferreira et al. 2017; Yan et al. 2010). In L. vannamei, several HSP (HSP10, HSP27, HSP30, HSP60, HSP70 and HSP90) were consistently or specifically expressed in response to bacterial or viral infection (Chaurasia et al. 2016; Junprung et al. 2017; Yuan et al. 2017), and was demonstrate that HSC70 reduced protein aggregation and mortality after viral infection (Yuan et al. 2017). In the same way HSP70 was predominantly induced in hepatopancreas and gills of Fenneropenaeus chinensis when the shrimp were exposed to heat shock and Vibrio anguillavium-challenged stresses (Zhenyu et al. 2004). Under WSSV treated condition, three HSP (HSP21, HSP70 and HSP90) genes were commonly expressed in all examined tissue suggesting that all three forms of HSP gene products were required to maintain cellular homeostasis (Venkatesan and Hammed 2014).
The expression of HSP70 was increased as a part of an immune response against Vibrio harvey in P. monodon (Rungrassamee et al. 2010). According to Valentim-Neto et al. (2014) was observed that the shrimp positive to IHHNV or WSSV infection with changes in HSP70 fold had a higher rate of survival during the period of cultivation in comparison with others. Also, an association between resistance to TSV and HSP70 gene polymorphisms among Asian commercial L. vannamei populations has been reported by Zeng et al. (2008). In addition to that, induction of HSP70 gene transcription caused by increasing the water temperature to 32°C, during WSSV infection, suggests a connection between this gene and WSSV resistance in shrimp (Lin et al. 2011).
Xu et al. (2009) propose HSP70 is one of the binding partners of VP28 through virus infection and its expression was enhanced by WSSV infection at the early stage of the process. Like other animal viruses, WSSV infection induces apoptosis. Leu et al. (2013) propose a model for apoptotic interaction between white spot syndrome virus and shrimp. The basic sequence of events is as follows: first, when a WSSV infection occurs, cellular sensors detect the invading virus, and activate signaling pathways that lead to (1) the expression of pro-apoptosis proteins, like Caspase modulators, and (2) mitochondrial changes, including the induction of mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and increased oxidative stress.
Caspases are central effectors in apoptosis cascade. In marine shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus was found to be significantly upregulated in survivors of WSSV-challenged shrimp, suggesting that it might be involved in shrimp antiviral immunity (Wang et al. 2008). Likewise, Ubiquitin protein has been associated with several processes, including cellular progression, organelles biogenesis, transcriptional regulation, antigen processing, and apoptosis according with Chen et al. (2008) and Shen et al. (2009). Induction of this gene has been expressed in studies with WSSV- infected shrimp (Wang et al. 2006; He et al. 2005) shown to play an important role in viral latency regulation.
WSSV infection can induce characteristic signs of apoptosis (nuclear fragmentation, chromosomal DNA fragmentation and increased activity of caspases) in different tissues. Apoptosis is also known as a defense mechanism against the TSV and YHV viruses. The occurrence of a rapid and progressive spread of apoptosis in infected P. monodon with YHV is the main cause of dysfunction and death of the host (Flegel and Sritunyalucksana 2011). Given this, the induction of apoptosis only becomes effective as an antiviral response if it is triggered in an early stage of infection, which may limit the production of particles and reduce or eliminate the spread of the viral progeny to other tissues (Xu et al. 2014).
Janewanthanakul et al. (2020), report that HSP70 enhanced the expression of the key gene in the prophenoloxidase (proPO) activating system but reduced the expression of caspase2 and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAP) in WSSV-infected L. vannamei. These results suggested that the HSP70 is an important molecule involved in antiviral defense in shrimp presumably via modulating the proPO system and apoptosis.
The health of aquatic species is dependent on interactions between the environment, pathogens, and the host itself. Different aspects related to each one of them can contribute to impact the interaction among pathogen and host (Moser 2005). Farmed animals can coexist with potential pathogens with little or no impact on production (Bachère 2003), while some pathogens dramatically impact production, like the WSSV. Hyperthermal, hypoxic or hyposmotic conditions, for example, have been recognized as triggers for the transition from chronic to acute viral infections in shrimp populations (de la Vega et al. 2007; de la Vega et al. 2006; Liu et al. 2006). This transition appears to be the result of a reduction in the immunity and defense capacity of shrimp (Hall and van Ham 1998; Le Moullac and Haffner 2000).
6. Concluding remarks
Current progress in aquaculture is a reality and biosafety practices to prevent outbreaks of shrimp disease are a necessity. Stress in aquatic animals can occur due to several factors, including opportunistic diseases, climate changes and increased stocking density, which leads to the appearance of physiological disorders. Marine crustaceans, such as shrimp, are under the influence of these factors, which can cause pathologies, including some viral diseases. Within this framework, several techniques are being developed to minimize the impacts, among them the study of HSP70. Several authors have disclosed in important research that this protein can help to fight infections and the animal immune defense. However, we are still at the beginning of this process and other studies and measures are extremely important to improve understanding these animals health status, use of certified broodstock, regular monitoring of aquaculture ponds, developing good management practices and the safe maintenance of aquaculture crops, avoiding economic losses.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank everyone involved in the execution of this work and the background information accumulated over the years in the laboratory, which helped the manuscript a lot. This work was carried out together with professionals from the Laboratory of Biomarkers of Aquatic Contamination and Immunochemistry (LABCAI), Department of Biochemistry, and Laboratory of Molecular Biology (BIOMOL), Agrarian Science Center, Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC), Florianópolis, SC, Brazil.
References
- Aoki, T.; Wang, H.-C.; Unajak, S.; Santos, M.D.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I. Microarray Analyses of Shrimp Immune Responses. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 13, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcier, J.; Herman, F.; Lightner, D.; Redman, R.; Mari, J.; Bonami, J. A viral disease associated with mortalities in hatchery-reared postlarvae of the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 38, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmoorthy, M.P.; Anandajothi, E.; Vasudevan, S.; Suresh, E. Major viral diseases in culturable penaeid shrimps: a review. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 1939–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachère, E. Anti-infectious immune effectors in marine invertebrates: potential tools for disease control in larvicultura. Aquaculture 2003, 227, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakthisaran, R.; Tangirala, R.; Rao, C.M. Small heat shock proteins: Role in cellular functions and pathology. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Proteins Proteom. 2015, 1854, 291–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barracco, M.A.; Perazzolo, L.M.; Rosa, R.D. Avances en la Inmunología del Camarón. In Guía Técnica - Patología e inmunnología de camarones penaeidos, 2. ed.; Morales, V.Q.Y., Cuéliar-Angel., J., Eds.; [s.n.]: Panamá, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, B.A.; Morgan, J.D.; Vijayan, M.M. Physiological and condition-related indicators of environmental stress in fish. In Biological Indicators of Aquatic Ecosystem Stress; Adams, S.M., Ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, 2002; pp. 111–148. [Google Scholar]
- Behringer, D.; Mj, I.B.; Shields, J.; Moss, J. Review of Panulirus argus virus 1—a decade after its discovery. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 94, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, S.M.; Bloom, M.E. Caspase activation during virus infection: more than just the kiss of death? Virology 2004, 320, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, S.M. Viral Subversion of Apoptotic Enzymes: Escape from Death Row. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, R.J. Functions of Heat Shock Proteins in Pathways of the Innate and Adaptive Immune System. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5765–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, V.; Narwade, S.; Paingankar, M.; Deobagkar, D. White Spot Syndrome Virus infection in Penaeus monodon is facilitated by housekeeping molecules. J. Biosci. 2013, 38, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonrawd, S.; Supungul, P.; Tassanakajon, A.; Rimphanitchayakit, V. Antimicrobial activity of a serine proteinase inhibitor SPIPm5 from the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 77, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, J.R. Implications and assessments of environmental stress. In The Investigation of Fish-Power Problems; Larkin, P.A., Ed.; H. R. MacMillan Lectures in Fisheries. University British Columbia: Vancouver, Canada, 1958; pp. 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.F.; He, J.-G.; Chu, K.H.; Sun, C.B. The Shrimp Heat Shock Cognate 70 Functions as a Negative Regulator in Vitellogenin Gene Expression1. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, M.K.; Nizam, F.; Ravichandran, G.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arshad, A.; Elumalai, P.; Arockiaraj, J. Molecular importance of prawn large heat shock proteins 60, 70 and 90. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 48, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-H.; Lin, S.-W.; Liu, K.-F.; Chang, C.-I.; Hseu, J.-R.; Tsai, J.-M. Comparative proteomic analysis of Litopenaeus vannamei gills after vaccination with two WSSV structural proteins. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 49, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.T.; Lin, C.H.; Ji, W.T.; Li, S.K.; Liu, H.J. Proteasome inhibition reduces avian reovirus replication and apoptosis induction in cultured cells. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 151, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citarasu, T.; Lelin, C.; Thirumalaikumar, E.; Babu, M.M.; Vakharia, V.N. Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV)-CP-RNA-2 DNA vaccine confers protective immunity in giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii against MrNV infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 86, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danwattananusorn, T.; Fagutao, F.F.; Shitara, A.; Kondo, H.; Aoki, T.; Nozaki, R.; Hirono, I. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of heat shock proteins 40, 70 and 90 from kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus. Fish. Sci. 2011, 77, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Allnutt, F.C.T. Taura Syndrome Virus: in Encyclopedia of Virology, 3rd ed.; Academis Press, 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- de la Vega, E.; Degnan, B.M.; Hall, M.R.; Wilson, K.J. Differential expression of immune-related genes and transposable elements in black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) exposed to a range of environmental stressors. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2007, 23, 1072–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Vega, E.; Hall, M.R.; Degnan, B.M.; Wilson, K.J. Short-term hyperthermic treatment of Penaeus monodon increases expression of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and reduces replication of gill associated virus (GAV). Aquaculture 2006, 253, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorf, B.A.; Hons, C.; Varner, P. A Three-Year Survey of Penaeid Shrimp and Callinectid Crabs from Texas Coastal Waters for Signs of Disease Caused by White Spot Syndrome Virus or Taura Syndrome Virus. J. Aquat. Anim. Heal. 2005, 17, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, H.; McFadden, G. Apoptosis: an innate immune response to virus infection. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture: contributing to food security and nutrition for all; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, FAO, 2016; 204p. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.L., Jr.; Maggioni, R.; Conceição, D.; Perazzolo, L.M.; Petersen, R.L. Hsp70 gene polymorphisms in farmed marine shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei populations exposed to white spot disease and infectious myonecrosis. Genetics and Molecular Research 2017, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegel, T.W. Disease testing and treatment. In Operating Procedures for Shrimp Farming, Global Shrimp OP Survey Results and Recommendations; Boyd, C.E., Jory, D., Chamberlain, G.W., Eds.; Global Aquaculture Alliance: St. Louis, 2006; pp. 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Flegel, T.W. Historic emergence, impact and current status of shrimp pathogens in Asia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K. Shrimp Molecular Responses to Viral Pathogens. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 13, 587–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabaldón, T.; Pittis, A.A. Origin and evolution of metabolic sub-cellular compartmentalization in eukaryotes. Biochimie 2015, 119, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Enjuanes, L.; Ziebuhr, J.; Snijder, E.J. Nidovirales: Evolving the largest RNA virus genome. Virus Res. 2006, 117, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbalenya, A.E. Genomics and evolution of the Nidovirales. In Nidoviruses; Perlman, S., Gallagher, T., Snijder, E.J., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, 2008; pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, P.; Bartlett, T.; Browdy, C.; Chapman, R.; Warr, G. Immune gene discovery by expressed sequence tag analysis of hemocytes and hepatopancreas in the Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, and the Atlantic White Shrimp, L. setiferus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.R.; van Ham, E.H. The Effects of Different Types of Stress on Blood Glucose in the Giant Tiger Prawn Penaeus monodon. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1998, 29, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.S.S.; Yoganandhan, K.; Widada, J.S.; Bonami, J.R. Experimental transmission and tissue tropism of Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and extra small virus like-particles in Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 62, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, F.U.; Hayer-Hartl, M. Molecular Chaperones in the Cytosol: from Nascent Chain to Folded Protein. Science 2002, 295, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, K.; Lightner, D.; Poulos, B.; Redman, R.; White, B.; Brock, J.; Bonami, J. Taura syndrome in Penaeus vannamei:demonstration of a viral etiology. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 23, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, S.; Kannourakis, G. A time to kill: viral manipulation of the cell death program. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1547–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.; Qin, Q.; Xu, X. Differential profile of genes expressed in hemocytes of White Spot Syndrome Virus-resistant shrimp (Penaeus japonicus) by combining suppression subtractive hybridization and differential hybridization. Antivir. Res. 2005, 66, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirono, I.; Fagutao, F.F.; Kondo, H.; Aoki, T. Uncovering the Mechanisms of Shrimp Innate Immune Response by RNA Interference. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 13, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B. Priming the immune system of Litopenaeus vannamei with bacterial heat shock protein 70 homologue DnaK against Vibrio campbellii and white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection. PhD Thesis, Gent University, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.-J.; Leu, J.-H.; Tsau, M.-T.; Chen, J.-C.; Chen, L.-L. Differential expression of LvHSP60 in shrimp in response to environmental stress. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2011, 30, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janewanthanakul, S.; Supungulb, P.; Tangb, S.; Tassanakajon, A. Heat shock protein 70 from Litopenaeus vannamei (LvHSP70) is involved in the innate immune response against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection. Dev Comp Immunol 2020, 102, 103476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jancovich, J.K.; Chingar, V.; Hyatt, A.D.; Miyazaki, T.; Williams, T.; Zhang, Q.Y. Family Iridoviridae. In Virus Taxonomy: Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses. Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Elsevier/Academic Press: Amsterdam, 2012; pp. 193–210. [Google Scholar]
- Jariyapong, P.; Chotwiwatthanakun, C.; Pooljun, C.; Weerachatyanukul, W. Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus-like particles encapsulating VP28 double-stranded RNA protect shrimp from white spot syndrome virus. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariyapong, P.; Pudgerd, A.; Cheloh, N.; Hirono, I.; Kondo, H.; Vanichviriyakit, R.; Weerachatyanukul, W.; Chotwiwatthanakun, C. Hematopoietic tissue of Macrobrachium rosenbergii plays dual roles as a source of hemocyte hematopoiesis and as a defensive mechanism against Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 86, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.L.; Marzano, N.R.; van Oijen, A.M.; Ecroyd, H. Using Single-Molecule Approaches to Understand the Molecular Mechanisms of Heat-Shock Protein Chaperone Function. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 4525–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junprung, W.; Supungul, P.; Tassanakajon, A. HSP70 and HSP90 are involved in shrimp Penaeus vannamei tolerance to AHPND-causing strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus after non-lethal heat shock. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 60, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautsky, N.; Rönnbäck, P.; Tedengren, M.; Troell, M. Ecosystem perspectives on management of disease in shrimp pond farming. Aquaculture 2000, 191, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, A.; Fukumori, T.; Fujita, M.; Irie, H.; Adachi, A. Physiological significance of apoptosis in animal virus infection. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moullac, G.; Haffner, P. Environmental factors affecting immune responses in Crustacea. Aquaculture 2000, 191, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, J.-H.; Lin, S.-J.; Huang, J.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; Lo, C.-F. A model for apoptotic interaction between white spot syndrome virus and shrimp. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 34, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V.; Poulos, B.T.; Tang-Nelson, K.F.J.; Pantoja, C.R.; Nunan, L.M.; A Navarro, S.; Redman, R.M.; Mohney, L.L. Application of molecular diagnostic methods to penaeid shrimp diseases: advances of the past 10 years for control of viral diseases in farmed shrimp. Dev Biol (Brasel) 2006, 126, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Bell, T.A. Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis, a newly recognized virus disease of penaeid shrimp. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1983, 42, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Hasson, K.W.; Pantoja, C.R. Taura syndrome in Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Decapoda): gross signs, histopathologyand ultrastructure. Dis Aquat Org 1995, 21, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D. Virus diseases of farmed shrimp in the Western Hemisphere (the Americas): A review. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 106, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-R.; Hung, H.-C.; Leu, J.-H.; Wang, H.-C.; Kou, G.-H.; Lo, C.-F. The Role of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase and Hsp70 in Suppression of White Spot Syndrome Virus Replication at High Temperature. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; hen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Cheng, W.; Hsu, C.; Tsui, W. Characterization of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei integrin β and its role in immunomodulation by dsRNA-mediated gene silencing. Developmental & Comparative Immunology 2013, 40, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist, S.; Craig, N.E. The heat shock protein. Annual Review of Genetics 1988, 22, 631–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yu, Z.; Song, X.; Guan, Y.; Jian, X.; He, J. The effect of acute salinity change on white spot syndrome (WSS) outbreaks in Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Aquaculture 2006, 253, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qian, D.; Yan, X. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in hemolymph of Scylla serrata response to white spot syndrome virus infection. Aquaculture 2011, 314, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, J. Cloning and expression of glucose regulated protein 78 (GRP78) in Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2007, 36, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, P.R.L.; Araújo, M.I.A.S.; Carvalho, L.; Carvalho, E.M. Immune response mechanisms to infections. An Bras Dermatol 2004, 79, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallouk, Y.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonventre, J.V.; Polla, B.S. Heat shock protein 70 and ATP as partners in cell homeostasis (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 1999, 4, 463–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, J.; Poulos, B.T.; Lightner, D.V.; Bonami, J.R. Shrimp Taura syndrome virus, genomic characterization and similarity with member of the genus Cricket paralysis-like viruses. J Gen Virol 2002, 83, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.R.F.; Moser, J.R.; Muller, I.C. Crustacean virology and molecular diagnostic methods. In Health of aquatic organisms in Brazil; Silva-Souza, A.T. (Org.); ABRAPOA: Maringa, 2006; pp. 159–185. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, J.R. Biomarcadores moleculares no camarão branco, Litopenaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Decapoda), submetido a estresse ambiental e infectado pelo vírus da síndrome da mancha branca (White Spot Syndrome Virus, WSSV). PhD Thesis, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, S.M.; Moss, D.R.; Arce, S.M.; Lightner, D.V.; Lotz, J.M. The role of selective breeding and biosecurity in the prevention of disease in penaeid shrimp aquaculture. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.S.; Ravishankar, K.V. Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Shock Proteins and Thermotolerance in Plants; Abiotic Stress Physiology of Horticultural Crops:, 2016; pp. 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Nibert, M.L. ‘2A-like’ and ‘shifty heptamer’ motifs in penaeid shrimp infectious myonecrosis virus, a monosegmented double-stranded RNA virus. J Gen Virol 2007, 88, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.A.T.; Nguyen, T.A.T.; Jolly, C.; Nguelifack, B.M. Economic Efficiency of Extensive and Intensive Shrimp Production under Conditions of Disease and Natural Disaster Risks in Khánh Hòa and Trà Vinh Provinces, Vietnam. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIE (World Organisation for Animal Health). Manual of diagnostic tests for aquatic animals, 6th ed.; Office International des Epizooties: Paris, France, 2016; 589p. [Google Scholar]
- Poulos, B.T.; Tang, K.F.J.; Pantoja, C.R.; Bonami, J.R.; Lightner, D.V. Purification and characterization of infectious myonecrosis virus of penaeid shrimp. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prapavorarat, A.; Pongsomboon, S.; Tassanakajon, A. Identification of genes expressed in response to yellow head virus infection in the black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon, by suppression subtractive hybridization. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.P.; Shyam, K.; Banu, H.; Jeena, K.; Krishnan, R. Infectious Myonecrosis Virus (IMNV) – An alarming viral pathogen to Penaeid shrimps. Aquaculture 2017, 477, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Chen, M.-M.; Wan, X.-Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Wang, R.-Y.; Cheng, D.-Y.; Dong, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.-H.; et al. Characterization of a new member of Iridoviridae, Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV), found in white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Corteel, M.; Wille, M.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Pensaert, M.; Sorgeloos, P.; Nauwynck, H. The effect of raising water temperature to 33 °C in Penaeus vannamei juveniles at different stages of infection with white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). Aquaculture 2007, 272, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Bhassu, S.; Bing, R.Z.Y.; Alinejad, T.; Hassan, S.S.; Wang, J. A transcriptome study on Macrobrachium rosenbergii hepatopancreas experimentally challenged with white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 136, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratcliffe, N.A.; Rowley, A.F.; Fitzgerald, S.W. Invertebrate immunity—basic concepts and recent advances. International Review of Cytology 1985, 97, 183–350. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, S.; Gora, A.H.; Ahmad, I.; Rasool, S.I. Stress in Aquaculture Hatcheries: Source, Impact and Mitigation. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences 2017, 6, 3030–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, J. Comparative proteomic investigation of Marsupenaeus japonicus hepatopancreas challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus and white spot syndrome virus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 93, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritossa, F. A new puffing pattern induced by heat shock and DNP in Drosophila. Experientia 1962, 18, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robalino, J.; Carnegie, R.B.; O, N.; Ouvry-Patat, S.A.; de la Vega, E.; Prior, S.; Gross, P.S.; Browdy, C.L.; Chapman, R.W.; Schey, K.L. Contributions of functional genomics and proteomics to the study of immune responses in the Pacific white leg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 2009, 128, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.J.; Agius, C.; Saliba, C.; Bossier, P.; Sung, Y.Y. Heat shock proteins (chaperones) in fish and shellfish and their potential role in relation to fish health: a review. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, A.F.; Pope, E.C. Vaccines and crustacean aquaculture—A mechanistic exploration. Aquaculture 2012, 334-337, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Leelatanawit, R.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Klinbunga, S.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Expression and distribution of three heat shock protein genes under heat shock stress and under exposure to Vibrio harveyi in Penaeus monodon. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, C.H.; Pinto, A.R. Challenges in shrimp aquaculture due to viral diseases: distribution and biology of the five major penaeid viruses and interventions to avoid viral incidence and dispersion. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selye, H. A Syndrome produced by Diverse Nocuous Agents. Nature 1936, 138, 32–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selye, H. Stress and the General Adaptation Syndrome. Br. Med. J. 1950, 1, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selye, H. The stress of life. McGraw Hill Publisher: New York, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Lin, P.; Wang, S.; Zou, Z. Differential expression of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2r in the developing ovary and testis of penaeid shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2008, 36, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shike, H.; Dhar, A.K.; Burns, J.C.; Shimizu, C.; Jousset, F.X.; Klimpel, K.R.; Bergoin, M. Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus of Shrimp Is Related to Mosquito Brevidensoviruses. Virology 2000, 277, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittidilokratna, N.; Dangtip, S.; Cowley, J.A.; Walker, P.J. RNA transcription analysis and completion of the genome sequence of yellow head nidovirus. Virus Res. 2008, 136, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboonwiwat, K.; Chaikeeratisak, V.; Wang, H.; Lo, C.F.; Tassanakajon, A. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in Penaeus monodon hemocytes after Vibrio harvey infection. Proteome Science 2010, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soonthornchai, W.; Rungrassamee, W.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Jarayabhand, P.; Klinbunga, S.; Söderhäll, K.; Jiravanichpaisal, P. Expression of immune-related genes in the digestive organ of shrimp, Penaeus monodon, after an oral infection by Vibrio harveyi. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P. Roles of heat-shock proteins in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stentiford, G.D. Diseases of the European edible crab (Cancer pagurus): a review. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1578–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.; Neil, D.; Peeler, E.; Shields, J.; Small, H.; Flegel, T.; Vlak, J.; Jones, B.; Morado, F.; Moss, S.; et al. Disease will limit future food supply from the global crustacean fishery and aquaculture sectors. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Rahman, N.A.; Shazili, N.A.M.; Chen, S.; Lv, A.; Sun, J.; Shi, H.; MacRae, T.H. Non-lethal heat shock induces Hsp70 synthesis and promotes tolerance against heat, ammonia and metals in post-larvae of the white leg shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Aquaculture 2018, 483, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.Y.; MacRae, T.H.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Stress response for disease control in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2011, 3, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Kondo, M.; Itami, T.; Honda, T.; Inagawa, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Soma, G.I.; Yokomizo, Y. Enhancement of disease resistance against penaeid acute viraemia and induction of virus inactivating activity in haemolymph of kuruma shrimp, Penaeus japonicus, by oral administration of Pantoea agglomerans lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2000, 10, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Itami, T.; Kondom, M.; Maeda, M.; Fuji, R.; Tomonaga, S.; Supamattaya, K.; Boonyaratpalin, S. Electron microscopic evidence of baciliform virus infection in Kuruma shrimp (Penaeus japonicus). Fish Pathol. 1994, 29, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassanakajon, A.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Supungul, P.; Tang, S. Discovery of immune molecules and their crucial functions in shrimp immunity. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 34, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendencia, E.A.; Verreth, J.A.J. Temperature fluctuation, low salinity, water microflora: risk factors for WSSV outbreaks in Penaeus monodon. Israeli Journal of Aquaculture Bamidgeh 2011, 63, 63–548. [Google Scholar]
- Tissiéres, A.; Mitchell, H.K.; Tracy, U.M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: Relation to chromosome puffs. J. Mol. Biol. 1974, 84, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschopp, J.; Thome, M.; Hofmann, K.; Meinl, E. The fight of viruses against apoptosis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vago, C. A virus disease in Crustacea. Nature (London) 1966, 209, 1290. [Google Scholar]
- Valentim-Neto, P.A.; Fraga, A.P.M.; Marques, M.R.F. Differential expression of proteins in the gills of Litopenaeus vannamei infected with white spot syndrome virus. Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 1605–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentim-Neto, P.A.; Fraga, A.P.M.; Müller, G.A.S.; Marques, M.R.F. Protein expression profiling in the gill of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) naturally infected with white spot syndrome virus. Crustaceana 2015, 88, 747–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentim-Neto, P.A.; Moser, J.R.; Fraga, A.P.M.; Marques, M.R.F. Hsp70 expression in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in response to IHHNV and WSSV infection. VirusDisease 2014, 25, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hulten, M.C.; Witteveldt, J.; Peters, S.; Kloosterboer, N.; Tarchini, R.; Fiers, M.; Sandbrink, H.; Lankhorst, R.K.; Vlak, J.M. The white spot syndrome virus DNA genome sequence. Virology 2001, 286, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, C.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. Analysis of Immune Genes and Heat Shock Protein Genes under Exposure to White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) and Herbal Immune Stimulant in Litopenaeus vannamei. J Bacteriol Parasitol 2014, 5, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Verbruggen, B.; Bickley, L.K.; Van Aerle, R.; Bateman, K.S.; Stentiford, G.D.; Santos, E.M.; Tyler, C.R. Molecular Mechanisms of White Spot Syndrome Virus Infection and Perspectives on Treatments. Viruses 2016, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Girão, P.R.N.; Rocha. R.C.B.; Costa, F.H.F.; Rádis-Baptista, G. Differential induction of HSP-70 expression in response to IHHNV in white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei naturally co-infected with IHHNV and IMNV. Int. Aquat. Res. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Sittidilokratna, N. Yellow Head Virus: in Encyclopedia of Virology, 3rd ed.; Academis Press, 2008; pp. 476–483. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, F.; Dong, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, J. Discovery of the Genes in Response to White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) Infection in Fenneropenaeus chinensis Through cDNA Microarray. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhi, B.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X. Requirement for shrimp caspase in apoptosis against virus infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongteerasupaya, C.; Vickers, J.; Sriurairatana, S.; Nash, G.; Akarajamorn, A.; Boonsaeng, V.; Panyim, S.; Tassanakajon, A.; Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Flegel, T. A non-occluded, systemic baculovirus that occurs in cells of ectodermal and mesodermal origin and causes high mortality in the black tiger prawn Penaeus monodon. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 21, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liu, W.; Alvarez, A.; Huang, T. Cellular immune responses against viral pathogens in shrimp. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 47, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yan, F.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Zou, T.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, Y. The interaction of white spot syndrome virus envelope protein VP28 with shrimp Hsc70 is specific and ATP-dependent. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2009, 26, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Xia, D.; Hu, J.; Yuan, H.; Zou, T.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, L.; Qi, Y.; Xu, H. Heat shock cognate protein 70 gene is required for prevention of apoptosis induced by WSSV infection. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Yuan, F.-H.; He, H.-H.; Bi, H.-T.; Weng, S.-P.; He, J.-G.; Chen, Y.-H. Heat shock 70 kDa protein cognate 5 involved in WSSV toleration of Litopenaeus vannamei. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 72, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Peng, M.; Li, Y.; Ma, N.; Jiang, W.; Yang, C. Analysis of Hsp70 in Litopenaeus vannamei and Detection of SNPs. J. Crustac. Biol. 2008, 28, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenyu, G.; Chuanzhen, J.; Jianhai, X. Heat-shock protein 70 expression in shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis during thermal and immune-challenged stress. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2004, 22, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Twan, W.-H.; Tseng, L.-C.; Peng, S.-H.; Hwang, J.-S. First detection of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in the mud shrimp Austinogebia edulis in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).