Submitted:
16 May 2023
Posted:
16 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Quality in Manufacturing as Context of Industry 4.0 - Literature Review
2.1. Industry 4.0 and Digital Manufacturing
2.2. Digitization of Organization and Quality
2.3. Quality Management Models and INDUSTRY 4.0
2.4. Quality Engineering Techniques and Industry 4.0
2.5. Quality 4.0 Definitions
2.6. Quality 4.0 in Practice
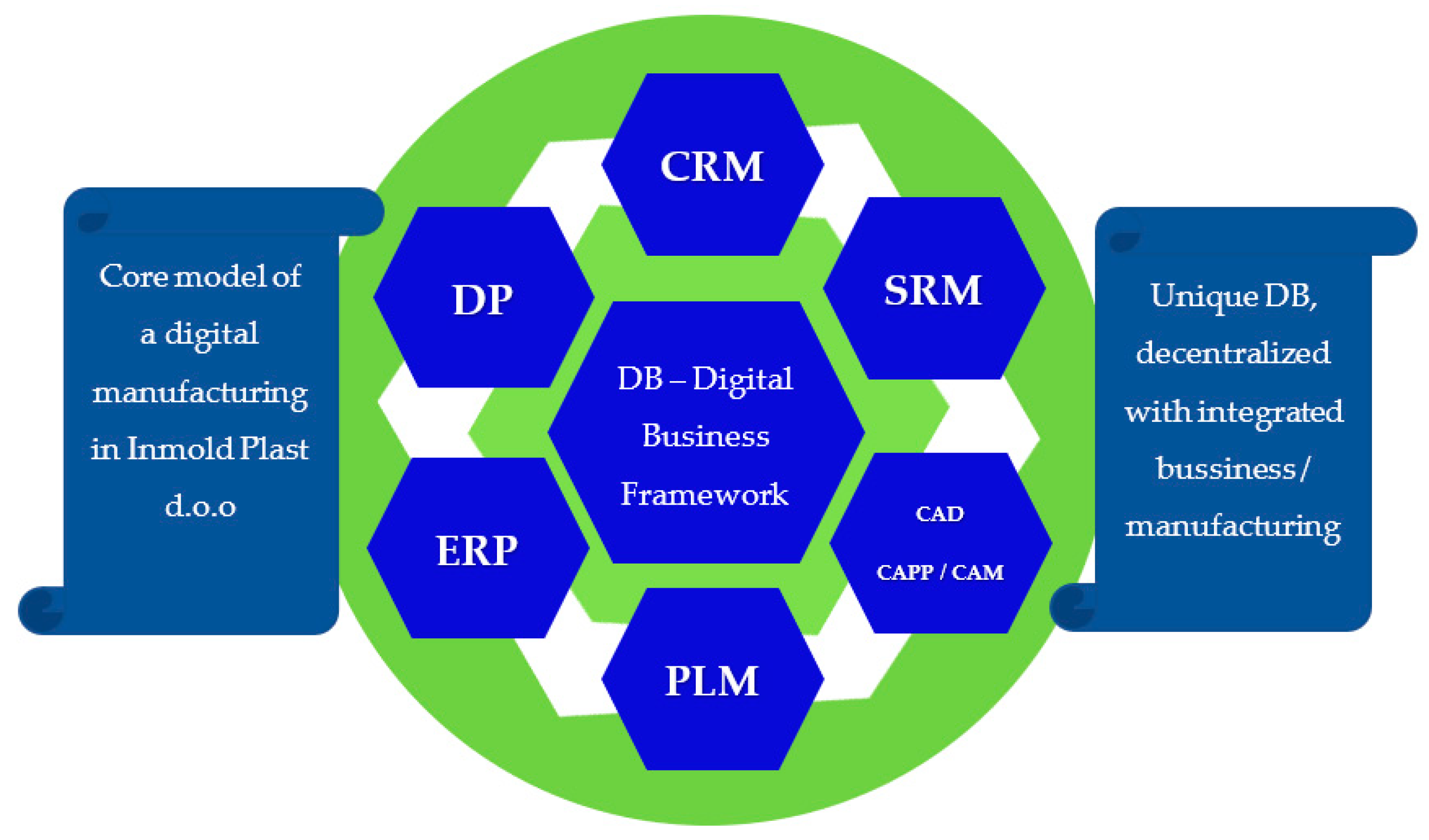
3. Digital Model of Inmold Plast Company
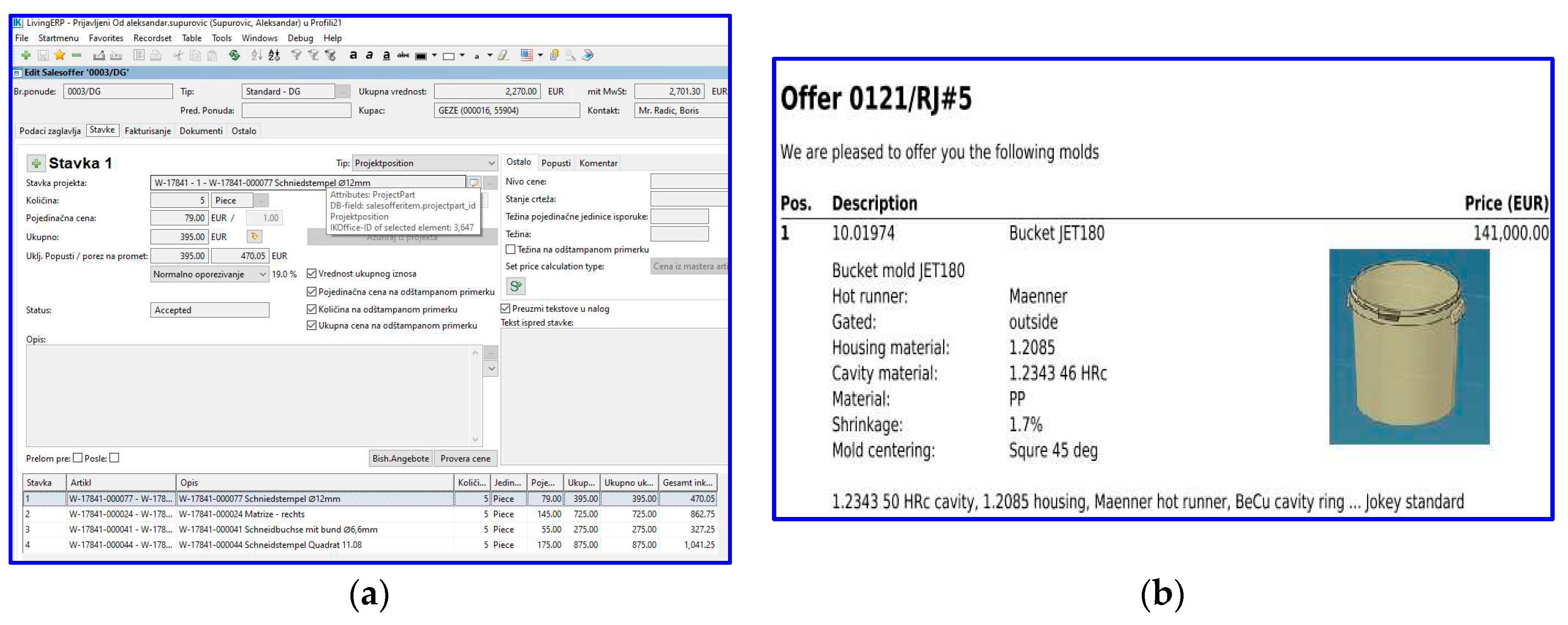
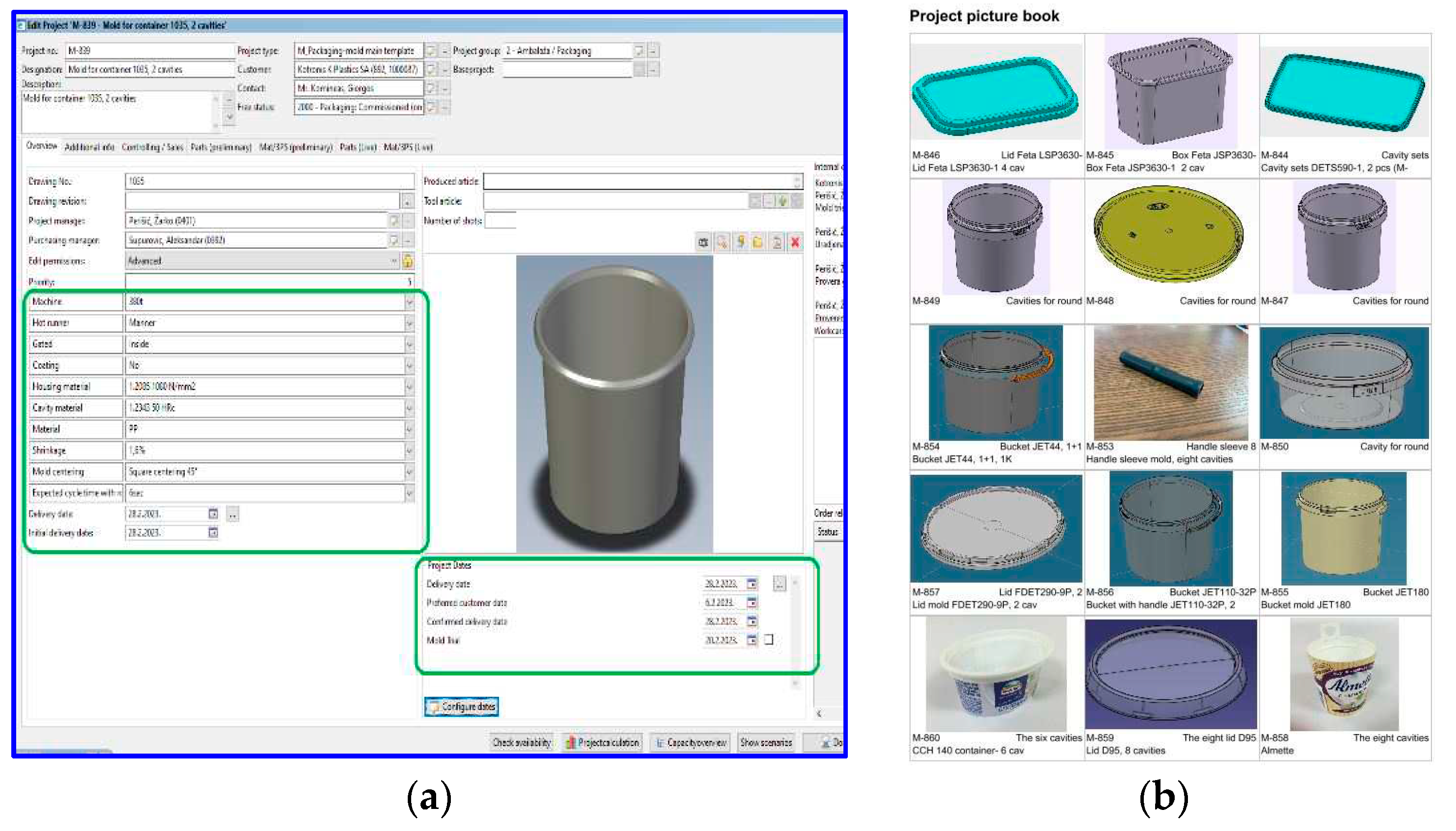
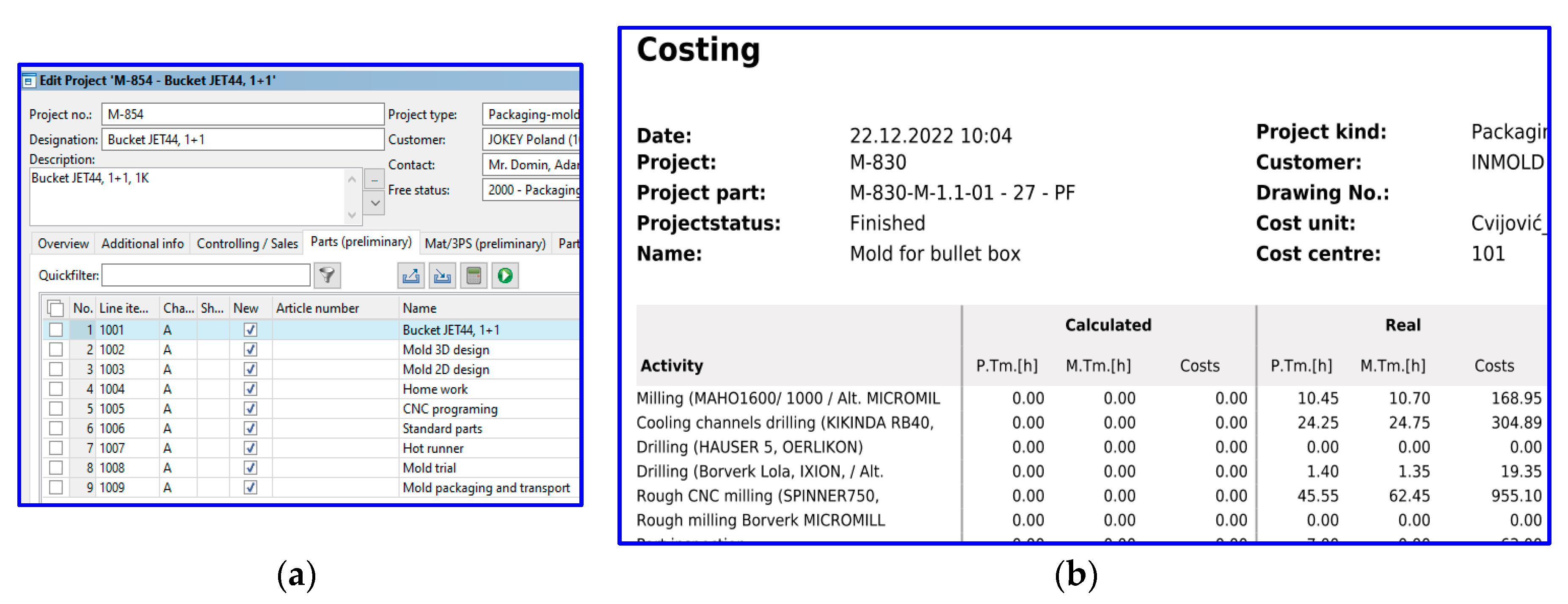
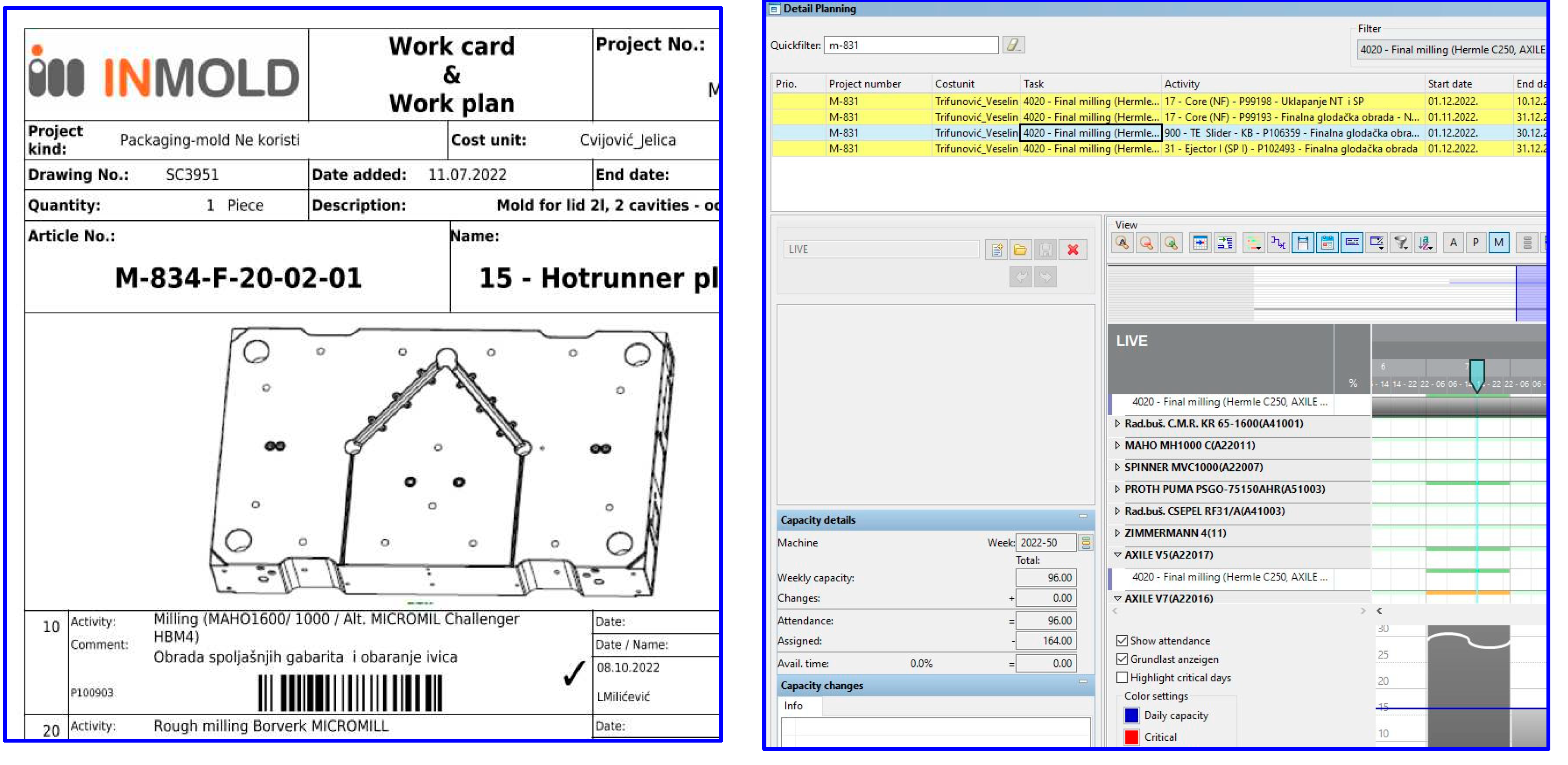
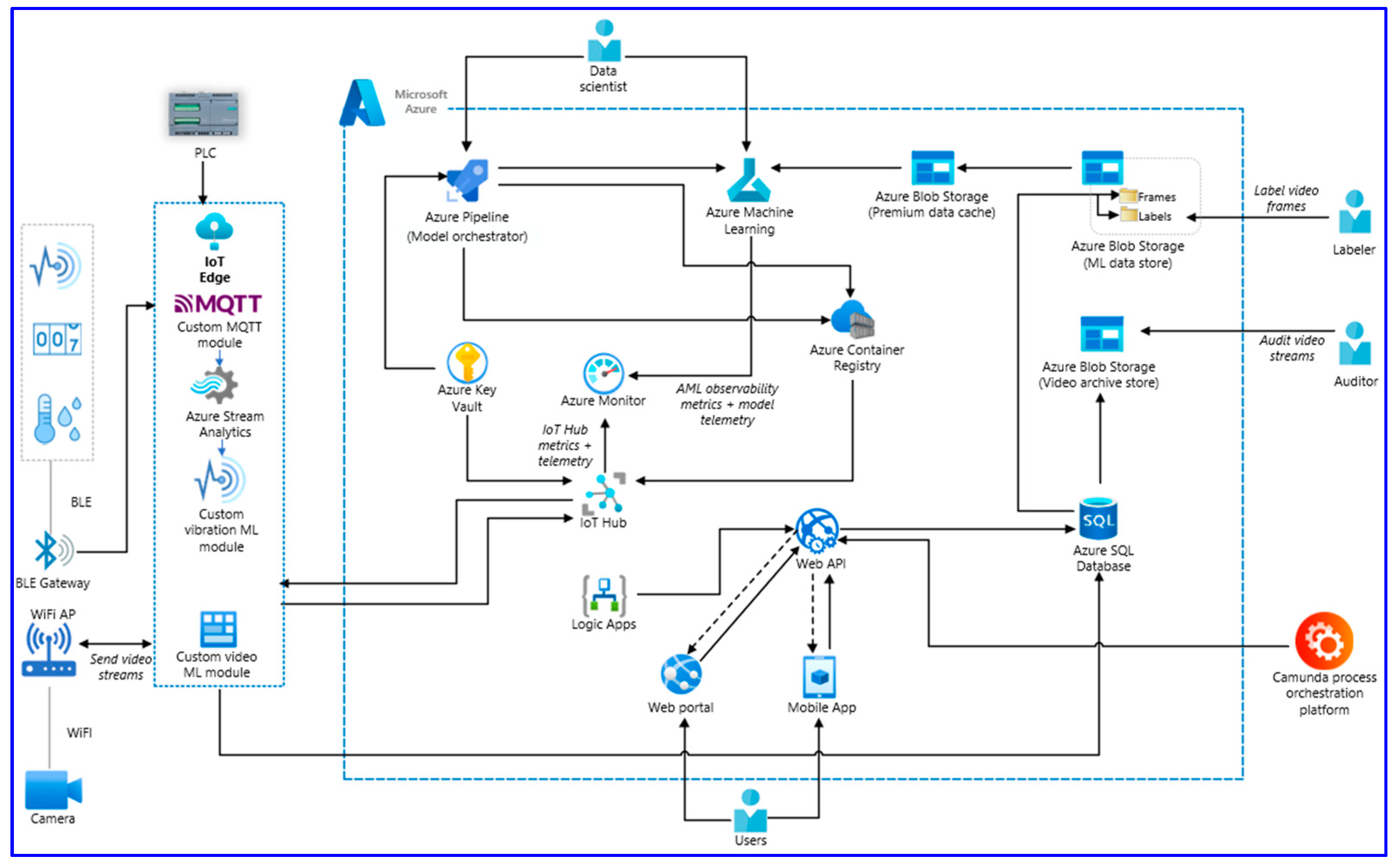
3.1. Functioning of Digital and Q 4.0 Models in Practice - Case Study
3.2. Achieved Results
3.3. What Next
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Javaid, Mohd & Haleem, Abid & Singh, Ravi & Suman, Rajiv. (2021). Significance of Quality 4.0 towards comprehensive enhancement in manufacturing sector. Sensors International. 2. 100109. [CrossRef]
- Broday, EE (2022), “ The evolution of quality: from inspection to quality 4.0 “, International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 3, pp. 368-382. [CrossRef]
- Souza, FFd, Corsi, A., Pagani, RN, Balbinotti, G. and Kovaleski, JL (2022), “ Total quality management 4.0: adapting quality management to Industry 4.0 “, The TQM Journal, Vol. 34 No. 4, pp. 749-769. [CrossRef]
- Rauch, Erwin. (2020). Industry 4.0+: The Next Level of Intelligent and Self-optimizing Factories. [CrossRef]
- Butt, J. A Strategic Roadmap for the Manufacturing Industry to Implement Industry 4.0 . Designs 2020 , 4 , 11. [CrossRef]
- Majstorovic VD, Mitrovic R. (2019) Industry 4.0 Programs Worldwide. In: Monostori L., Majstorovic V., Hu S., Djurdjanovic D. (eds) Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on the Industry 4.0 Model for Advanced Manufacturing. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Cham. ( pp. 78-99). [CrossRef]
- Zulqarnain, A.; Wasif, M.; Iqbal, SA Developing a Quality 4.0 Implementation Framework and Evaluating the Maturity Levels of Industries in Developing Countries . Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 11298. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shahzadi, A.; Khan, YD Unfolding the Impact of Quality 4.0 Practices on Industry 4.0 and Circular Economy Practices: A Hybrid SEM-ANN Approach . Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 15495. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Frank & Li, Zhaoyan & Arokiam, Alan & Gorman, Terry. (2016 ). Closed Loop PMI Driven Dimensional Quality Lifecycle Management Approach for Smart Manufacturing System. Proceeding CIRP. 56. 614-619. [CrossRef]
- Vidosav, Majstorovic & Jankovic, Goran & Zivkov, Srdjan & Stojadinovic, Slavenko. (2021). Digital Manufacturing in SMEs based on the context of the Industry 4.0 framework—one approach. Procedia Manufacturing. 54. 52-57. [CrossRef]
- Filz, Marc-André & Gellrich, Sebastian & Lang, Felix & Zietsch, Jakob & Abraham, Tim & Herrmann, Christoph. (2021). Data-driven Analysis of Product Property Propagation to Support Process-integrated Quality Management in Manufacturing Systems. Proceeding CIRP. 104 (2021) 900-905. [CrossRef]
- Ranjith Kumar, R. , Ganesh, LS and Rajendran, C. (2022), “ Quality 4.0—a review of and framework for quality management in the digital era “, International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, Vol. 39 No. 6, pp. 1385-1411. [CrossRef]
- Maganga, DP and Taifa, IWR (2023), “ Quality 4.0 conceptualisation: an emerging quality management concept for manufacturing industries “, The TQM Journal, Vol. 35 No. 2, pp. 389-413. [CrossRef]
- Jason Martin, Quoc Hung Dang & Ida Gremyr (2023) The influence of digitalisation on the role of quality professionals and their practices , Cogent Business & Management, 10:1, 2164162. [CrossRef]
- Daniel Küpper , Claudio Knizek , Dave Ryeson , Jan Noecker . Quality 4.0 takes more than technology . Available online: https://web-assets.bcg.com/img-src/BCG-Quality-4.0-Takes-More-Than-Technology-Aug-2019_tcm9-224161.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Sony, M. , Antony, J. and Douglas, JA (2020), “ Essential ingredients for the implementation of Quality 4.0: A narrative review of literature and future directions for research “, The TQM Journal, Vol. 32 No. 4, pp. 779-793. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, AMD, Sampaio, P., Rebentisch, E., & Oehmen, J. (2020 ). Technology and quality management: A review of concepts and opportunities in the digital transformation. International Conference on Quality Engineering and Management, 698-714. Minho, Portugal, 21.09.2020.
- Villegas Forero, Daniel & Sisodia, Raoul. (2020 ). Quality 4.0 - How to Handle Quality in the Industry 4.0 Revolution. Master’s thesis in Quality and Operations Management, Department of technology management and economics, Chalmers University of technology, Gothenburg, Sweden 2020.
- Vial, Gregory. (2019). Understanding digital transformation: A review and a research agenda . The Journal of Strategic Information Systems. 28. [CrossRef]
- Singh, Jagmeet & Ahuja, IPS & Singh, Harwinder & Singh, Amandeep. (2022). Development and Implementation of Autonomous Quality Management System (AQMS) in an Automotive Manufacturing using Quality 4.0—A Case Study . Computers & Industrial Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, Adriana & Enrique, Daisy & Chouchene, Amal & Charrua Santos, Fernando. (2021). Quality 4.0: An Overview . Procedia Computer Science. 181. 341-346. [CrossRef]
- Ammar, Mohd & Haleem, Abid & Javaid, Mohd & Walia, Rinku & Bahl, Shashi. (2021). Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies in self-healing materials and digitally managing the quality of manufacturing. Materials Today: Proceedings. 52 (2022) 2285–2294. [CrossRef]
- Silva, CS, Borges, AF and Magano, J. (2022), “ Quality Control 4.0: a way to improve the quality performance and engage shop floor operators “, International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, Vol. 39 No. 6, pp. 1471-1487. [CrossRef]
- Prashar, A. (2023), “ Quality management in industry 4.0 environment: a morphological analysis and research agenda “, International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, Vol. 40 No. 3, pp. 863-885. [CrossRef]
- Chiarini, A. (2020), “ Industry 4.0, quality management and TQM world. A systematic literature review and a proposed agenda for further research “, The TQM Journal, Vol. 32 No. 4, pp. 603-616. [CrossRef]
- Sung Hyun Park, Wan Seon Shin, Young Hyun Park & Youngjo Lee (2017) Building a new culture for quality management in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution , Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 28:9-10, 934- 945. [CrossRef]
- Tim Komkowski, Jiju Antony, Jose Arturo Garza-Reyes, Guilherme Luz Tortorella & Tanawadee Pongboonchai-Empl (2023) A systematic review of the integration of Industry 4.0 with quality-related operational excellence methodologies , Quality Management Journal, 30:1, 3-15. [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, Angappa & Subramanian, Nachiappan & Ngai, Eric. (2018). Quality Management in the 21st Century Enterprises: Research pathway towards Industry 4.0. International Journal of Production Economics. 207. [CrossRef]
- Asif, Muhammad. (2020). Are QM models aligned with Industry 4.0? A perspective on current practices . Journal of Cleaner Production. [CrossRef]
- Neal, Aaron & Sharpe, Richard & van Lopik, Katherine & Tribe, James & Goodall, Paul & Lugo, Heinz & Segura Velandia, Diana & Conway, Paul & Jackson, Lisa & Jackson, Thomas & West, Andrew. (2021). The potential of industry 4.0 Cyber Physical System to improve quality assurance: An automotive case study for wash monitoring of returnable transit items . CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology. 32. 461-475. [CrossRef]
- Daryl Powella, Ragnhild Eleftheriadisa, Odd Myklebusta, Digitally Enhanced Quality Management for Zero Defect Manufacturing , Procedia CIRP 104 (2021) 1351–1354. [CrossRef]
- Escobar, Carlos & Macias, Daniela & McGovern, Megan & Hernández de Menéndez, Marcela & Morales-Menéndez, Ruben. (2022). Quality 4.0—an evolution of Six Sigma DMAIC . International Journal of Lean Six Sigma. 13. [CrossRef]
- Sureshchandar, GS (2022), “ Quality 4.0—understanding the criticality of the dimensions using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) technique “, International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, Vol. 39 No. 6, pp. 1336-1367. [CrossRef]
- Avigdor Zonnenshain & Ron S. Kennett (2020): Quality 4.0—the challenging future of quality engineering , Quality Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Dounia Skalli, Abdelkabir Charkaoui, Anass Cherrafi, Jose Arturo Garza-Reyes, Jiju Antony & Alireza Shokri (2023) Industry 4.0 and Lean Six Sigma integration in manufacturing: A literature review, an integrated framework and proposed research perspectives, Quality Management Journal, 30:1, 16-40. 1. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Antonino, Pablo & Capilla, Rafael & Pelliccione, Patrizio & Schnicke, Frank & Espen, Daniel & Kuhn, Thomas & Schmid, Klaus. (2022). A Quality 4.0 Model for architecting industry 4.0 systems. Advanced Engineering Informatics. 54. [CrossRef]
- Andrea Chiarini & Maneesh Kumar (2021): What is Quality 4.0? An exploratory sequential mixed methods study of Italian manufacturing companies, International Journal of Production Research. [CrossRef]
- Antony, Jiju, McDermott, Olivia, & Sony, Michael. (2021). Quality 4.0 conceptualisation and theoretical understanding: a global exploratory qualitative study . The TQM Journal. [CrossRef]
- Sami Sader, Istvan Husti & Miklos Daroczi (2021): A review of quality 4.0: definitions, features, technologies, applications, and challenges, Total Quality Management & Business Excellence. [CrossRef]
- Goecks, Lucas & Santos, Alex & Korzenowski, André. (2020). Decision-making trends in quality management: a literature review about Industry 4.0. Production. 30. e20190086. [CrossRef]
- Ioannis T. Christou, Nikos Kefalakis, John K. Soldatos, Angela-Maria Despotopoulou, End-to-end industrial IoT platform for Quality 4.0 applications , Computers in Industry, Volume 137, 2022, 103591. [CrossRef]
- Panagiotis Stavropoulos, Alexios Papacharalampoulos, Kyriakos Sabatakakis, Dimitris Mourtzis , Quality Monitoring of Manufacturing Processes based on Full Data Utilization, Procedia CIRP 104 (2021) 1656–1661. [CrossRef]
- Escobar, Carlos & Macias , Daniela & Morales- Menendez , Ruben . (2021). Process monitoring for quality - A multiple classifier system for highly unbalanced data . Heliyon. 7. [CrossRef]
- 4Brandenburger, Jens & Schirm, Christoph & Melcher, Josef & Hancke, Edgar & Vannucci, Marco & Colla, Valentina & Cateni, Sivia & Sellami, Rami & Dupont, Sébastien & Majchrowski, Annick & Arteaga, Asier. (2020). Quality4.0 - Transparent product quality supervision in the age of Industry 4.0. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.06502. (accessed on April 2, 2023).
- Carvalho, AV; Lima, TM Quality 4.0 and Cognitive Engineering Applied to Quality Management Systems: A Framework. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022, 5, 115. [CrossRef]
- Alexandros Bousdekis, Katerina Lepenioti, Dimitris Apostolou & Gregoris Mentzas (2022): Data analytics in quality 4.0: literature review and future research directions, International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing. [CrossRef]
- Nenadál, J.; Vykydal, D.; Halfarová, P.; Tyleˇcková, E. Quality 4.0 Maturity Assessment in Light of the Current Situation in the Czech Republic . Sustainability 2022, 14, 7519. [CrossRef]
- Barsalou, Matthew. (2023). Root Cause Analysis in Quality 4.0: A Scoping Review of Current State and Perspectives. TEM Journal. 12. 73-79. [CrossRef]
- Armani, Camila & Oliveira, Karina & Munhoz, Igor & Akkari, Alessandra. (2021). Proposal and application of a framework to measure the degree of maturity in Quality 4.0: A multiple case study. In book: Advances in Mathematics for Industry 4.0, Editor: Mangey Ram. (pp.131-163). [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, J.; Jassbi, J. Quality 4.0 in Action: Smart Hybrid Fault Diagnosis System in Plaster Production. Processes 2020, 8, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, M. , Antony, J. and Douglas, JA (2020), “ Essential ingredients for the implementation of Quality 4.0: A narrative review of literature and future directions for research “, The TQM Journal, Vol. 32 No. 4, pp. 779-793. [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, Jacqueline & Bönig, Jochen & Borggräfe, Thorbjörn & Beitinger, Gunter & Deuse, Jochen. (2020). Predictive model-based quality inspection using Machine Learning and Edge Cloud Computing . Advanced Engineering Informatics. 45. [CrossRef]
- Song, Zhiting & Sun, Yanming & Wan, Jiafu & Liang, Peipei. (2016). Data quality management for service-oriented manufacturing cyber-physical systems. Computers & Electrical Engineering. 64. [CrossRef]
- Sader, Sami & Husti, István & Daróczi, Miklós. (2019). Quality Management Practices in the Era of Industry 4.0. Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Częstochowskiej Zarządzanie. 35. [CrossRef]
- Krco, S., et al., IoT Project in Metalac Comapny , In progress, 2023, Gornji Milanovac.
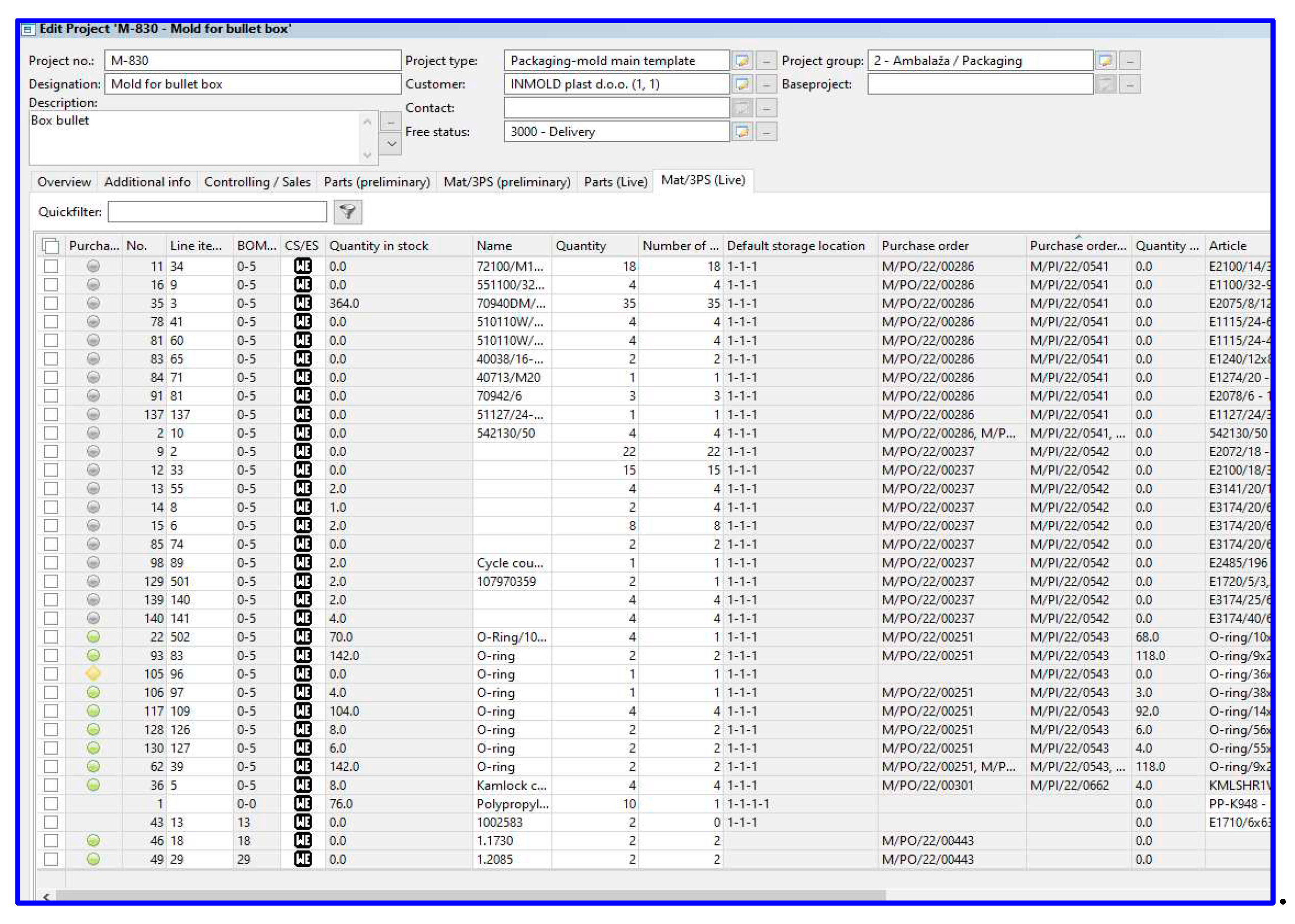
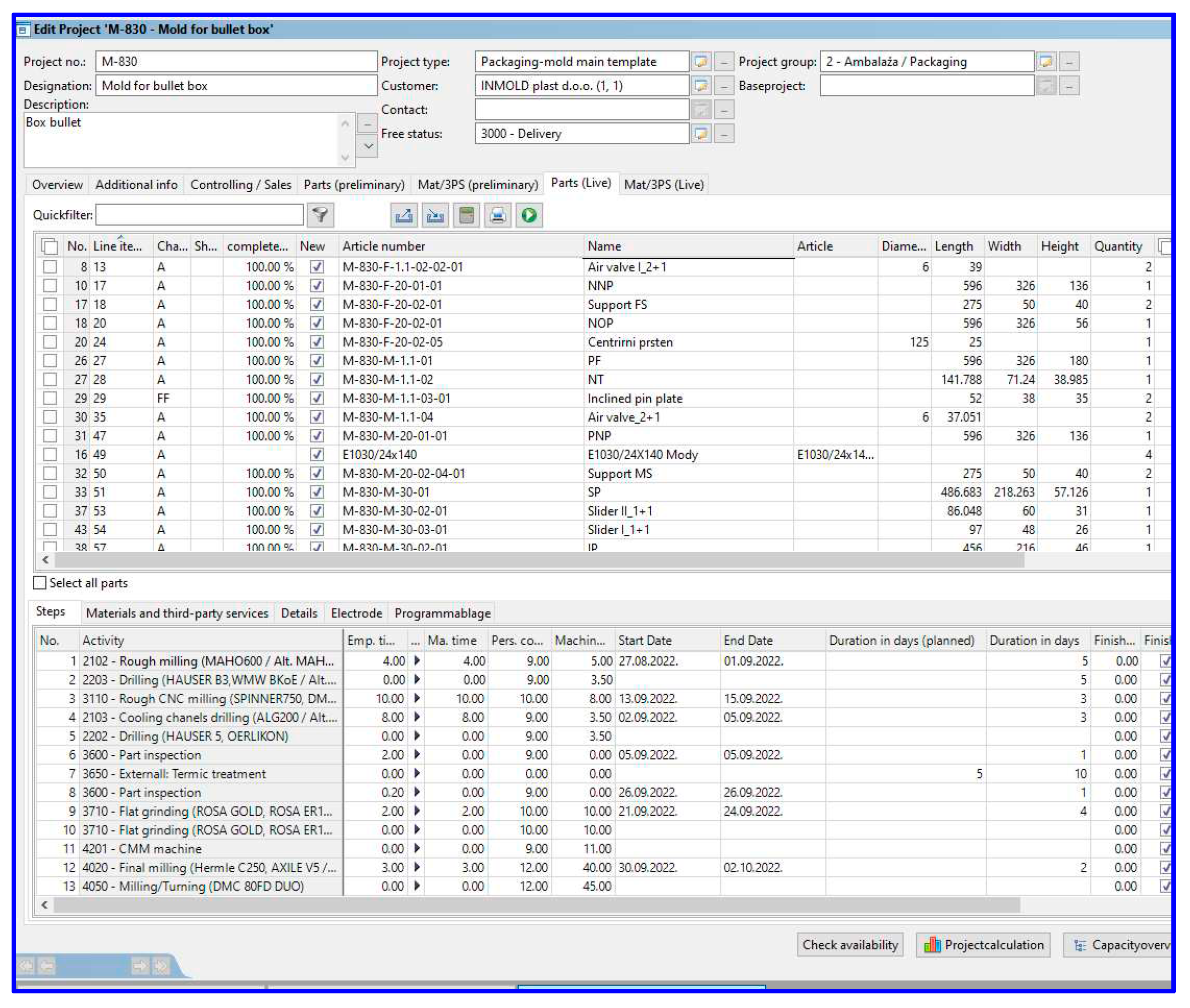
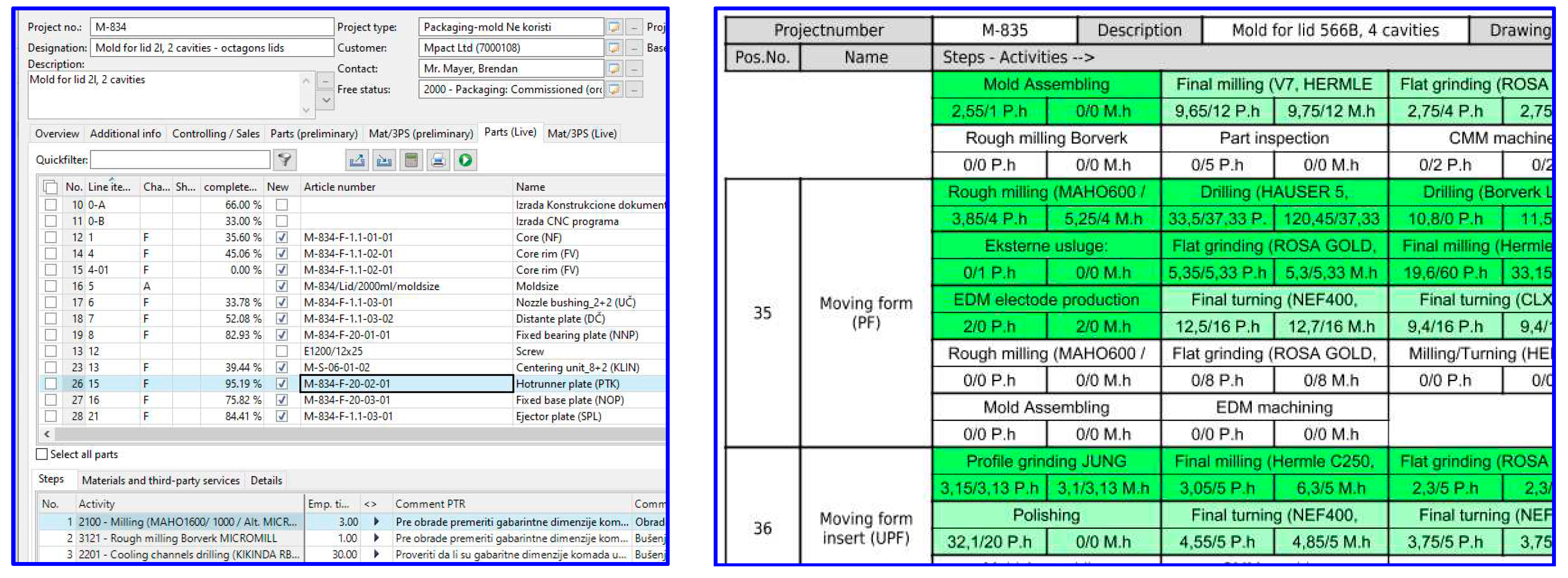
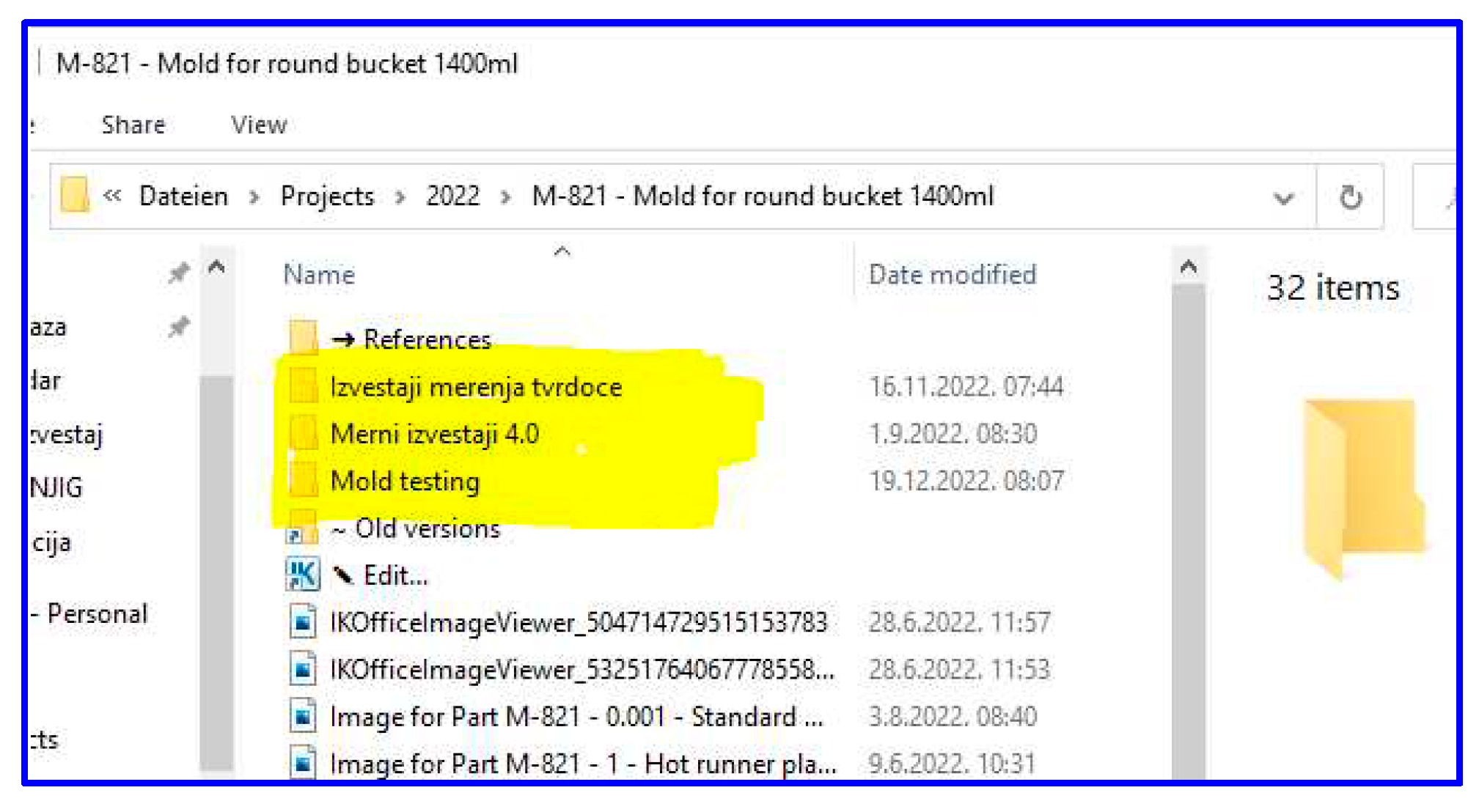

| Main issue | Source | Main messages |
| Strategies and roadmaps for the development of the national Indsutry 4.0 Project | [5,6] | Digital manufacturing is a key element for the application of the Industry 4.0 model |
| A model for evaluating QM with eleven dimensions in an organization. | [7] | The digital manufacturing model and Q4.0 are being integrated |
| AI/ML in support of Q 4.0 for SMEs | [8] | Application of one element of Industry 4.0 in the digital manufacturing model for Q 4.0. |
| Industry 4.0 and Q 4.0 as technologically driven innovations in application. | [4] | The next level of these models in application will be data - driven innovation (BDA, AI / ML - Intelligent and Self-Opimizing Factory ). |
| PMI (Product and Manufacturing Information). Driven Dimensional Quality Lifecycle Management. | [9] | Digital Q 4.0 as a subsystem of PMI. |
| Main issue | Source | Main messages |
| Digitization and QM at manufacturing level. | [11] | Driven analysis of product property propagation based on AI/ML models for product inspection. |
| And 4.0 as a disruptive technology. | [12] | Q 4.0 as a technological dimension of quality (MES). |
| Digitization of the TQM model, with the support of top management. | [13] | Q 4.0: BDA and MES. |
| Professional competencies of employees for promotions and teamwork. | [14] | New models of education for Q 4.0. |
| Q 4.0 as an integration of strategic, cultural and technological issues. | [15] | Q 4.0 as a model for working in real time. |
| The elements of I 4.0 essential for the development of the Q 4.0 model are: BDA, AI/ML horizontal and vertical automation. | [16] | Quality elements for Q 4.0 are: strategy, leadership, training and organizational culture. |
| Integrated model Q 4.0 of digital product development and their digital manufacturing. | [17] | Digital product model. |
| TQM as infrastructure Q 4.0. | [18] | Digitization of quality as TQM 4.0. |
| Digital transformation is the basic framework for building I 4.0, as well as Q 4.0. | [19] | Digital transformation is an innovative process. |
| Main issue | Source | Main messages |
| Q 4.0 as a QMS model. | [20] | Sigma manufacturing level increased from 1.5 to 5.5. |
| Q 4.0 as a QMS model with seven elements (ISO 9001:2015). | [21] | Increased sigma level. |
| SOP model of material quality management. | [22] | Q 4.0 based on IioT, SPC and BDA. |
| Factors for applying the PDCA model in the I 4.0 organization. | [23] | The PDCA 4.0 model for the automotive industry. |
| Dimensions of Q 4.0 for organization. | [24] | The consistency matrix for the organization. |
| TQM in model I 4.0. | [25] | TQM 4.0 through four dimensions. |
| The QM model as a quality loop. | [26] | The quality loop as a framework for Q 4.0. |
| The elements of the model are: TQM, Lean Six Sigma and Business Process Management. | [27] | BE as a basis for the development of BE 4.0. |
| Building the organization’s business model from the point of view of quality. | [28] | Q 4.0 is a framework for quality costing, monitoring and decision-making, and manufacturing technology (CPS). |
| T(QM) models as static structures. | [29] | Q 4.0 as dynamic, networked structures for real-time operation. |
| Characteristics of Q 4.0 | From (T)QM today | To Q 4.0 tomorrow (as a part of I 4.0) |
| (T)QM models | 1. By automation 2. Used of standardized routines 3. Compliance with requirements and procedures |
1. Cognitive engagement 2. Mindful task execution 3. The direction of attention towards one ‘s ongoing experience 4. Evaluating and questioning the value of a routine |
| Intellectual capital management (HR) |
1. Managing employees (experience, training) 2. Managing human resources (education) |
1. Managing human, social, and intellectual capitals |
| Making quality predictions from big data (BDA and AI/ML) |
1. Anticipating customer requirements and addressing them | 1. Making accurate predictions using big data. 2. Using big data to determine changing customer preferences, enable agility, flexibility, and responsiveness, to create delightful customer experiences. |
| Lean structures (organization and/or processes) (ERP and MES) | 1. Developing formal systems through manuals, procedures, work instructions, and records (documented information) 2. Establishing documented evidence for quality processes |
1. Coexistence of technology and human-based simplicity 2. Alignment of human-side with new lean structures |
| Managing networked firms in business ecosystems (products or suppliers)—I 4.0 |
1. Define boundaries and scope of operations 2. Management of a relatively stable set of partners and suppliers 3. Supplier management |
1. Management of networked firms operating in business ecosystems 2. Managing collective value creation 3. Going beyond supplier management to integration with other firms for strategic advantage. |
| Main issue | Source | Main messages |
| CPS with RFID and IoT in the automotive industry. | [30] | Traceability and high KPI values - Q 4.0. |
| ZDM is the ideal framework for Q 4.0. | [31] | Bring people to the six sigma level. |
| Big data and decision making. | [32] | The IADLPR 2 model as an intelligent decision support. |
| AHP technique for ranking 12 quality parameters. | [33] | The three most important parameters in Q 4.0 are: analytic thinking, competence and customer centricity. |
| Framework for Q 4.0 with nine elements. | [34] | Q 4.0 as contex I 4.0. |
| Integration of I 4.0 and LSS. | [35] | Q 4.0 as a basis for LSS 4.0. |
| Main issue | Source | Main messages |
| Q 4.0 model for software structure I 4.0. | [36] | ISO / IEC 25010:2011 is the framework for this model. |
| Digital quality chain in the product life cycle. | [1] | Q 4.0 with support for: BDA IoT, AI/ML and VR/AR. |
| Building Q 4.0 models using digital tools. | [2] | Translation of the QM model (QMS, TQM, BE) into the Q 4.0 model. |
| Q 4.0 can be defined as the integration of I 4.0 technologies, quality and people. | [3] | From QC, through TQM to TQM 4.0. |
| Q 4.0 model for manufacturing organizations from the automotive industry. | [37] | Robust Q 4.0 model with eleven elements. |
| Q 4.0 is based on strategic, cultural and technological entities. | [38] | Quality experts with soft and hard skills are needed. |
| Integration of traditional QC models with I 4.0 technologies. | [39] | Q 4.0—improvement of quality performance. |
| Making decisions. | [40] | Q 4.0 - outsourcing management, forecasting, customer expectations, as well as employee involvement. |
| Main issue | Source | Main messages |
| IoT platform. | [41] | Predictive maintenance and ZDM. |
| SBD model for welding quality management - BDA. | [42] | 7V and ANN for BDA. |
| BDA analyzes are hyperdimensional spaces of quality characteristics. | [43] | MCS model for BDA analyses. |
| Horizontal exchange of quality information in the supply chain. | [44] | FADI Platform. |
| Product development on platform I 4.0. | [45] | Q 4.0 as an integrated model of CE and QMS. |
| Q 4.0 in production quality control. | [46] | BDA model: multiple given sources, integrate data and knowledge, data - driven, predictive and prescriptive analytics algorithms. |
| Q 4.0 Maturity Assessment Model. | [47] | Seven levels of maturity. |
| Quality engineering techniques as the basis of Q 4.0. | [48] | BDA model for QA, cause-effect analysis and prediction of quality characteristics. |
| Measuring the maturity of the Q 4.0 model. | [49] | Eleven organizational dimensions and five maturity levels. |
| Q 4.0 in plaster manufacturing. | [50] | ANN and ES for quality management using SPC. |
| The most important factors for implementing Q 4.0 in practice. | [51] | Three technical and three organizational factors. |
| Q 4.0 model for PCB manufacturing. | [52] | ML and edge cloud computing model framework. |
| Service-oriented manufacturing (SOM) and Q 4.0. | [53] | Formal semantic network and process-oriented ontology. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





