1. Introduction
That research aims to develop an evaluation framework for Distributed Manufacturing (DM) applications that can be used to assess the sustainability and feasibility of a DM supply chain. Authors introduced and discussed the topic in a conference earlier (Radics, Umar, & Duong).
To achieve this goal, the study will seek to answer three key research questions.
Firstly, the study will investigate the critical factors that contribute to the benefits and costs of implementing DM supply chains. This includes identifying the factors that enable DM to provide greater flexibility, responsiveness, and higher supply chain reliability, as well as the factors that may create barriers to its adoption.
Secondly, the study will examine the key trade-offs and constraints involved in implementing DM supply chains. This will involve identifying the trade-offs between cost, time, quality, and sustainability, and assessing the constraints that may limit the ability of firms to implement DM, such as technological maturity and regulatory frameworks.
Finally, the study will explore how to evaluate the feasibility of a DM supply chain. This includes developing a set of evaluation criteria that can be used to assess the suitability of DM for different industries and supply chains.
The research objectives are important because they address the need for a structured evaluation framework for DM applications. By providing a comprehensive understanding of the critical factors, trade-offs, and constraints involved in implementing DM supply chains, the study can help firms to make informed decisions about whether to adopt DM and how to design effective DM strategies. The case studies that will be used to introduce the evaluation framework will provide practical insights into the challenges and opportunities associated with DM, which can be useful for firms looking to implement DM in their operations.
Distributed manufacturing (DM) is a way of manufacturing products close to the end-user, which has gained interest due to enabling technologies such as 3D printing, robots, computerisation, and cloud-based technologies. This method has five essential characteristics: digitalisation, personalisation, new enabling technologies, localisation, and enhanced user and producer participation (Srai et al., 2016). While some industries have previously increased centralisation and specialisation to use the economy of scale, others kept their production close to the end customers due to their perishable products or services (Carlino, 2012). DM offers greater flexibility, responsiveness, and higher supply chain reliability, allowing production anywhere, given the availability of local resources and technologies. This approach is agile, can operate on a small scale, and faces fewer restrictions on location, allowing for small-scale distributed operations in places such as hospitals or disaster areas.
Other industries historically held their production close to their end customers due to perishable products (e.g., bakeries) or services they provide (e.g., catering). Also, there are combined solutions to ensure high productivity by centralising production and finalising the show close to the customer. For instance, large baking companies distribute ready-to-bake dough and pre-baked bread in their network (Matt, Rauch, & Dallasega, 2015).
DM has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to transform traditional manufacturing processes and supply chains (Malik, Haq, Raina, & Gupta, 2022). The World Economic Forum has identified DM as one of the ten most promising emerging technologies, recognizing its potential to drive innovation, economic growth, and sustainability (Meyerson, 2015; Srai et al., 2016). The 2013 McKinsey report on disruptive technologies also highlighted the significant impact that DM could have on various industries (Savastano, Amendola, D′ Ascenzo, & Massaroni, 2016).
The manufacturing sector has been a crucial contributor to New Zealand's economy, but it has been experiencing a decline in recent years (Conway & Meehant, 2013). DM presents an opportunity for the country to rejuvenate its manufacturing industry and create new economic opportunities. By adopting DM practices, businesses can achieve greater flexibility, responsiveness, and supply chain reliability, while also benefiting from lower capital and logistic costs (Purvis, Lahy, Mason, & Wilson, 2021).
Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable and eco-friendly products, and DM presents an opportunity for manufacturers to meet these expectations. By adopting renewable bio-based resources and circular economy principles, manufacturers can reduce their environmental footprint and meet the growing demand for sustainable products (Srai et al., 2016).
The growth of disruptive manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing has also contributed to the significance of DM. 3D printing allows for the rapid and cost-effective production of customized products on-site, reducing the need for spare parts and allowing for personal customization on the spot. This has significant implications for industries such as healthcare, where customized hearing aids and dental implants can be produced quickly and efficiently (Malik et al., 2022).
In summary, the significance of DM lies in its potential to transform traditional manufacturing processes and supply chains, drive innovation and economic growth, and meet the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. With its numerous benefits, DM presents a significant opportunity for businesses, communities, and economies to thrive in the future.
A simple distributed manufacturing supply chain example describes a potential scenario for DM supply chain that utilizes local resources and 3D printing technology to produce a car part.
The first step in the process involves producing cellulose for bioplastic on a farm. This is an example of using local resources to manufacture raw materials for the bioplastic. By producing the cellulose on the farm, transportation costs and environmental impact associated with shipping the raw materials from a central location are reduced.
The next step involves ordering a car part online. This step requires coordination between the car manufacturer and the local 3D printing centre to ensure that the correct blueprint is provided to the customer. The online ordering process also allows for greater flexibility and customization options for customers (Kang, Önal, Ouyang, Scheffran, & Tursun, 2010).
After the customer has placed their order, they receive the blueprint from the car manufacturer. The blueprint contains the specifications for the car part that needs to be printed. This information is sent to the local 3D printing centre, which is located in a convenient location such as a post office.
Finally, the car part is printed out using locally produced bioplastic. By using locally produced bioplastic, transportation costs and environmental impact associated with shipping the material from a central location are reduced. This also allows for greater sustainability in the manufacturing process, as renewable resources are used to produce the bioplastic.
Overall, this example demonstrates the potential benefits of distributed manufacturing. By utilizing local resources and 3D printing technology, manufacturing processes can be made more efficient, sustainable, and flexible. This approach can also help to revitalize local economies and support small-scale manufacturing businesses (Srai et al., 2016).
DM has many benefits that are often overlooked. While challenges related to DM are mainly focused on its operational aspects, most of the benefits lie in the connected supply chains. One such benefit is the availability of raw materials close to end-users. This can significantly reduce transportation costs and carbon emissions associated with transportation (Purvis et al., 2021).
For example, the production of bioplastic raw materials and biomass production can be done in close proximity to the end-users of DM products. This means that the production of bioplastic raw materials can be decentralized and localized, reducing the need for transportation and lowering associated costs and emissions. Moreover, by utilizing locally available raw materials, manufacturers can create products that are tailored to local needs, thereby increasing the flexibility and responsiveness of the manufacturing process (Weller, Kleer, & Piller, 2015).
In addition, the use of locally available raw materials can help promote sustainable practices. For instance, by using bioplastics made from locally produced biomass, manufacturers can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and promote the use of renewable resources. This can contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and help mitigate the impact of climate change.
Overall, the benefits of DM go beyond operational efficiency and cost savings. By utilizing locally available raw materials and promoting sustainable practices, DM can help create a more resilient and environmentally friendly manufacturing ecosystem.
DM has the potential to alter the way products are manufactured and distributed, but there are several barriers that need to be addressed before it can be widely adopted.
One of the significant barriers to applying DM is the readiness of production and technology. The technology should be mature enough to support DM, and there should be an understanding of material properties and material control. DM also requires a stable consumer base and supplier base to ensure that there is a steady supply and demand for products.
Infrastructure is another critical factor that can affect the adoption of DM. For example, if the infrastructure is not sufficient, the costs of transportation and communication may increase, making it more difficult to implement DM effectively (Jin, 2004).
Additionally, governance and regulatory issues should be addressed to facilitate the acceptance and spread of DM. There may be legal and regulatory barriers to implementing DM, such as intellectual property rights, safety regulations, and environmental regulations. These issues need to be addressed to ensure that DM can be adopted widely and safely (V. Kumar, Sezersan, Garza-Reyes, Gonzalez, & Al-Shboul, 2019).
Distributed manufacturing offers various benefits for SMEs and Maori communities. Firstly, it provides low-cost and highly flexible solutions, which can allow small and middle-sized companies, farmers, and communities to own a more substantial part of the supply chain and produce higher-value products. As a result, they can improve perceived quality and value, which can lead to increased profitability and competitiveness (Srai et al., 2016).
Moreover, distributed manufacturing can lead to regional development opportunities, which can help to strengthen local economies. By enabling local development and higher-value add manufacturing, DM can reduce the competition for land (food versus non-food). For instance, farmers could sell high-value processed products like sawn wood or prefabricated house panels instead of getting the stumpage for their trees. This can increase the value/ha/year by 3 to 10 times, which means they can achieve the same benefit using less land (Smith, 2017).
In addition, DM can contribute to healthier communities by creating local jobs and manufacturing facilities. This can help to reduce unemployment rates, improve local economies, and promote sustainable development. DM can also improve environmental performance by reducing infrastructure needs, waste, and storage requirements. Moreover, it can promote the development of biobased replacements for petroleum/coal-based manufacturing and society, which can lead to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a more sustainable future.
Furthermore, DM can contribute to low emissions by reducing transport needs on the roads and at sea through close-to-end-use manufacture. This can help to reduce carbon emissions, air pollution, and traffic congestion, which can lead to a cleaner and healthier environment for all. Overall, DM has the potential to provide various benefits for SMEs and Maori communities, including improved profitability, competitiveness, regional development opportunities, and environmental sustainability.
3. Results
The present study engaged in an extensive review of the relevant literature to identify the key indicators that can be employed to evaluate the efficacy of Distributed Manufacturing in the Construction industry (Minhas et al., 2012; Purvis et al., 2021; Rauch, Matt, & Dallasega, 2015; Srai et al., 2016; Turner, Oyekan, & Stergioulas, 2021). Based on the insights gleaned from the literature review, a group of experts convened to deliberate and propose a comprehensive list of indicator structures that can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of Distributed Manufacturing in the Construction domain. The proposed list of indicators has been presented in detail in
Table 1, which represents an exhaustive and systematic classification of the various parameters that can be used to evaluate the performance of Distributed Manufacturing in Construction. In addition to identifying the key indicators, the proposed framework also provides detailed guidance on the weightage assigned to each parameter, as well as the sub-categories that can be used to further delineate and assess each indicator.
During the evaluation process, the panel of experts carefully assessed each individual indicator included in the proposed evaluation framework for Distributed Manufacturing in Construction. In doing so, they utilized a scale consisting of three possible outcomes: 1) unfavorable, 2) neutral, or 3) favorable. The experts engaged in a comprehensive and rigorous discussion surrounding each indicator to arrive at a consensus regarding its appropriate value on the aforementioned scale. The discussion entailed comparisons between current and future scenarios, as well as assumptions that could impact the final evaluation of each indicator. Furthermore, the panel of experts carefully considered the limitations of the evaluation process to ensure that the indicators were evaluated as accurately and comprehensively as possible.
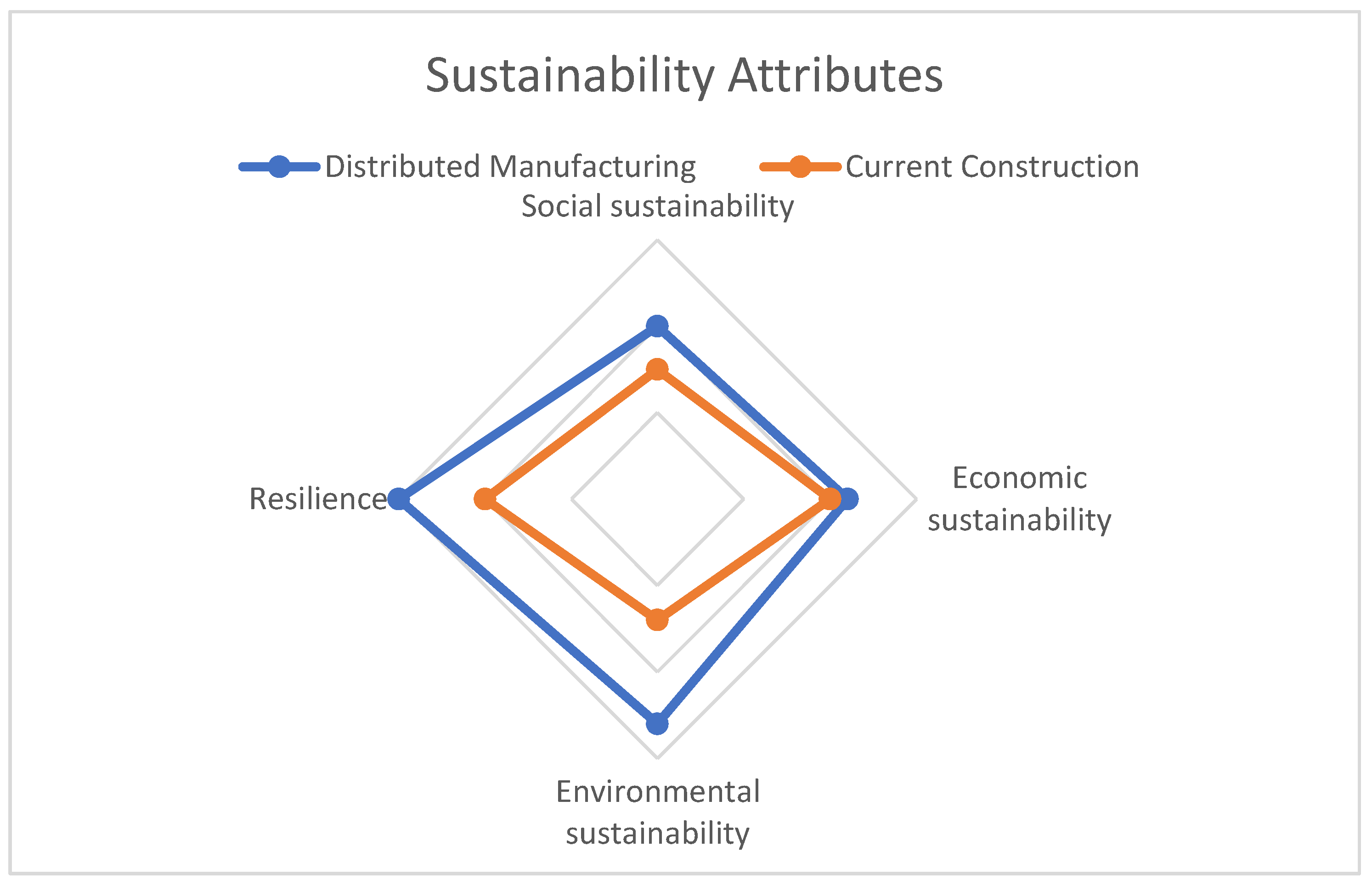
In order to assess and compare the sustainability of DM in construction with traditional building methods in New Zealand, all indicators identified by the expert panel were plotted on spider web diagrams. The resulting figure,
Figure 1, provides a visual summary of the evaluation's sustainability attributes. The spider web diagrams represent the various indicators as lines radiating out from a central point. The closer the line is to the outer edge of the diagram, the more favorable the outcome is for that particular indicator. Conversely, the closer the line is to the center of the diagram, the less favorable the outcome is.
Upon analyzing the spider web diagrams, the expert panel found that DM construction showed a more favorable sustainability outcome than traditional building methods in New Zealand. The evaluation indicated that DM offered the greatest advantages in terms of environmental and sustainability indicators, followed by social indicators, and finally economic indicators. These findings suggest that DM in construction has the potential to offer a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly approach to building, which can have significant long-term benefits for both the construction industry and the wider community.
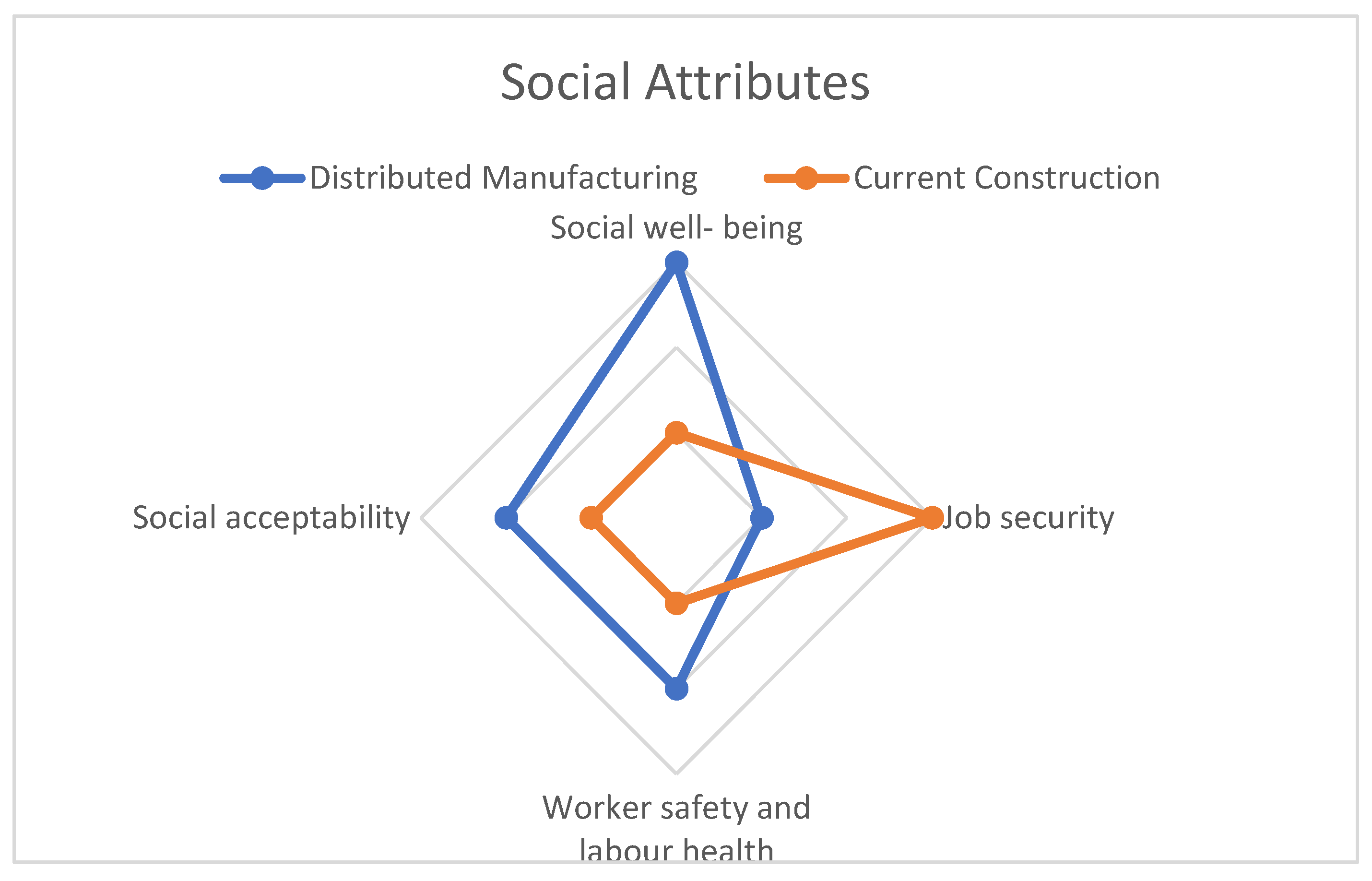
The social attributes included in the evaluation were social well-being, cultural identity, job security, and labour relations. The spider web diagram in
Figure 2 summarises the evaluation of these attributes. The closer the edges of the spider web, the more favourable the outcome, and the closer to the centre, the less favourable the result. The results showed that DM construction was advantageous in most social attributes, with social well-being being the most favourable.
However, job security was evaluated better in the case of traditional construction. This suggests that while DM can provide significant benefits in terms of social well-being and cultural identity, there may be some challenges in terms of job security for workers in the construction industry. It is important to note that the evaluation framework used in this study can help stakeholders identify these challenges and work towards addressing them to ensure the long-term sustainability of DM in construction.
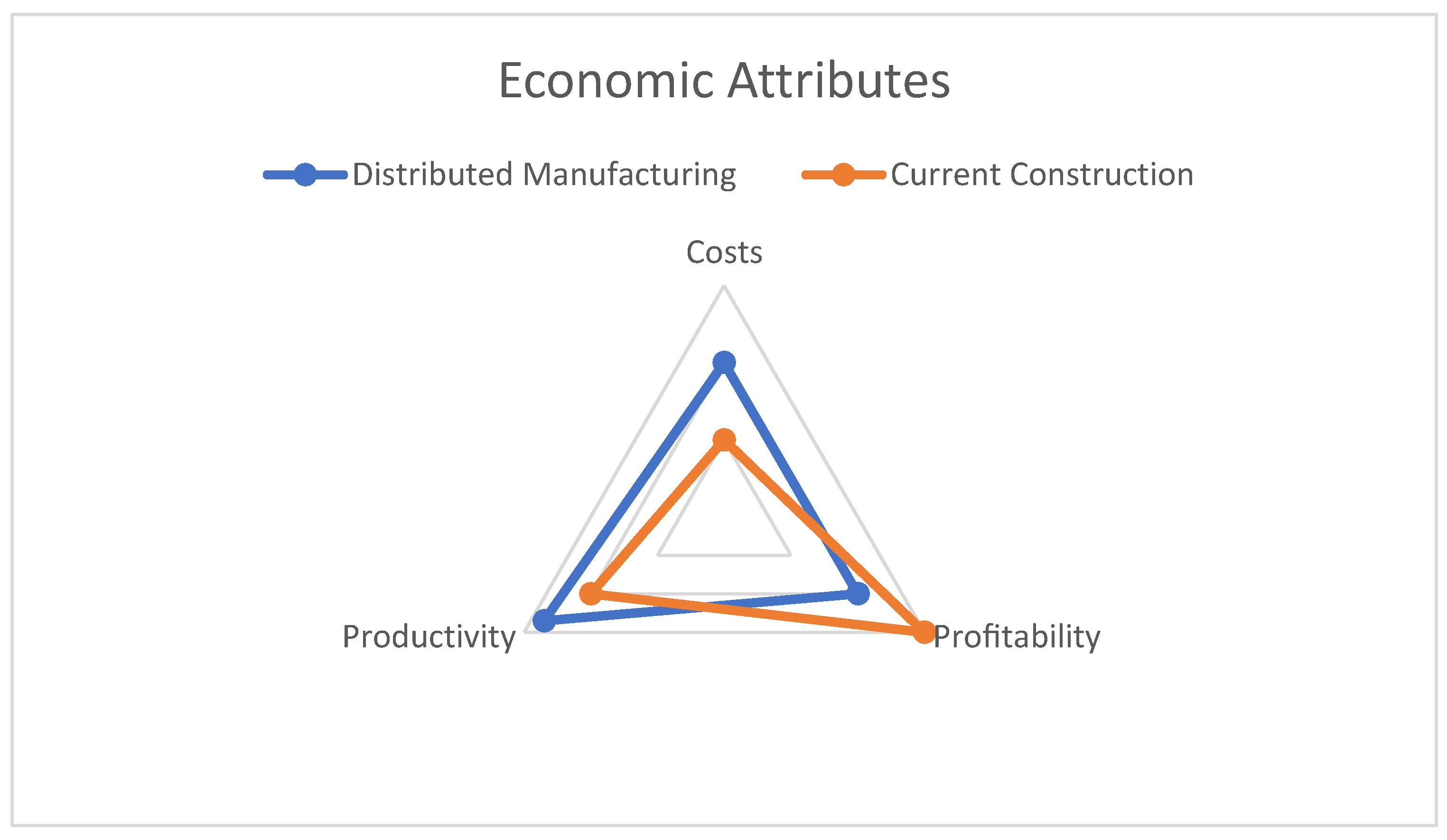
The economic attributes evaluation is presented in
Figure 3, which displays the comparison between Distributed Manufacturing (DM) and traditional construction from different economic perspectives (Rauch, Dallasega, & Matt, 2017). The analysis shows that DM performs slightly better than traditional construction in terms of costs and productivity, indicating that DM can achieve cost savings and improve production efficiency. However, DM was found to be slightly poorer than traditional construction in terms of profitability, suggesting that the initial investment in DM technology and infrastructure may affect profitability in the short term. These findings align with previous research that highlighted the potential of DM to reduce production costs and increase production efficiency in various sectors. However, it is important to note that economic performance is context-specific and depends on various factors such as market conditions, available resources, and technology maturity. Therefore, a careful evaluation of the economic feasibility of DM in each specific case is necessary before making any decisions.
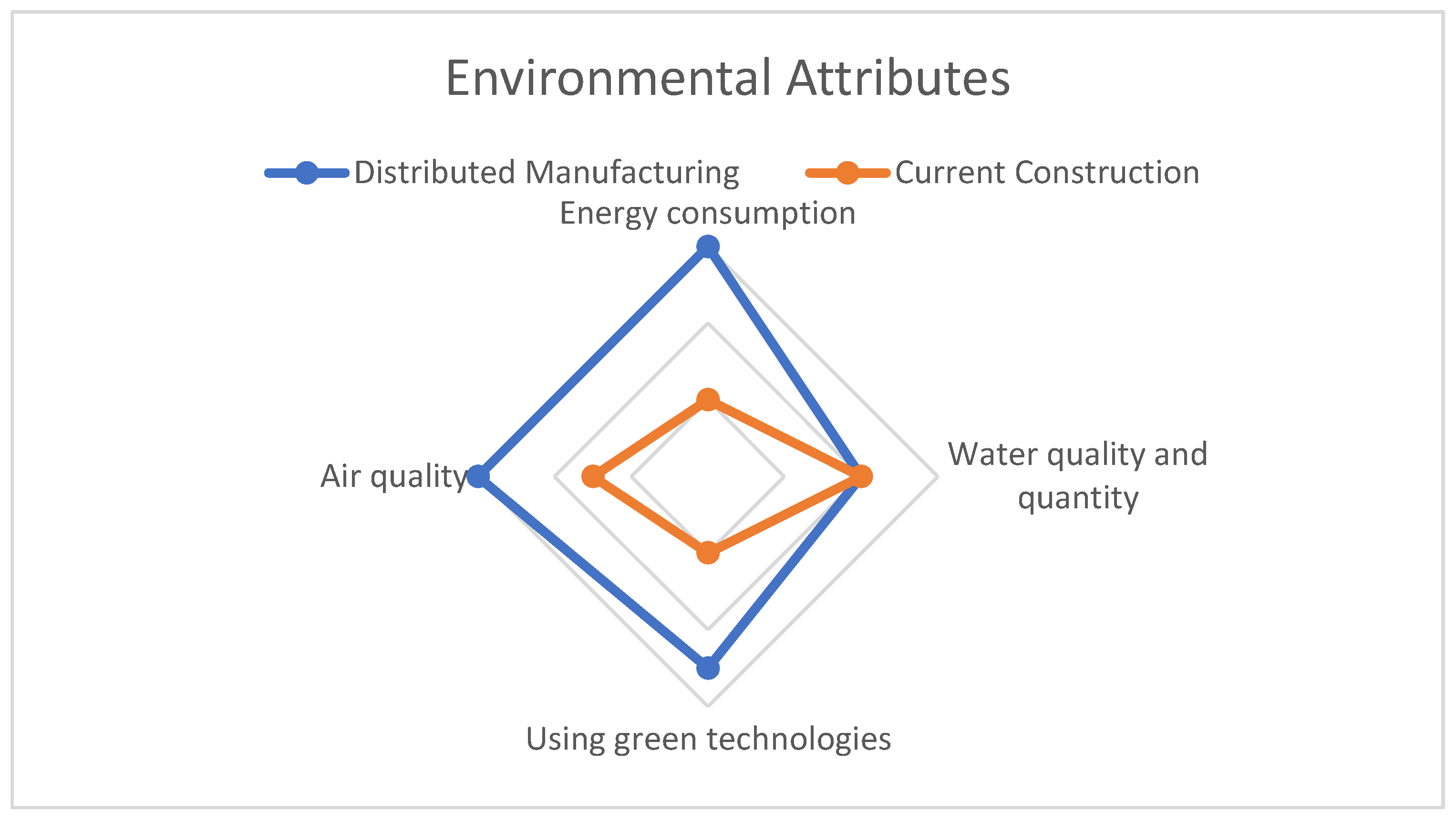
The environmental attributes of DM construction were evaluated and presented in
Figure 4. The results indicate that DM construction largely overperformed traditional construction from an ecological perspective, with DM construction having a more favorable impact on the environment in most of the evaluated categories (M. Kumar, Tsolakis, Agarwal, & Srai, 2020).
DM construction showed significant advantages in categories such as Energy Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions, where it had a substantially lower environmental impact compared to traditional construction. It also performed better in the categories of Air Quality and Waste Reduction.
However, the evaluation did not show any significant difference between DM and traditional construction in terms of Water Quality. Further research could be done to explore this aspect and potentially identify areas where DM construction could be improved to have a more positive impact on water quality. Overall, the evaluation demonstrated that DM construction has the potential to be a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to construction.
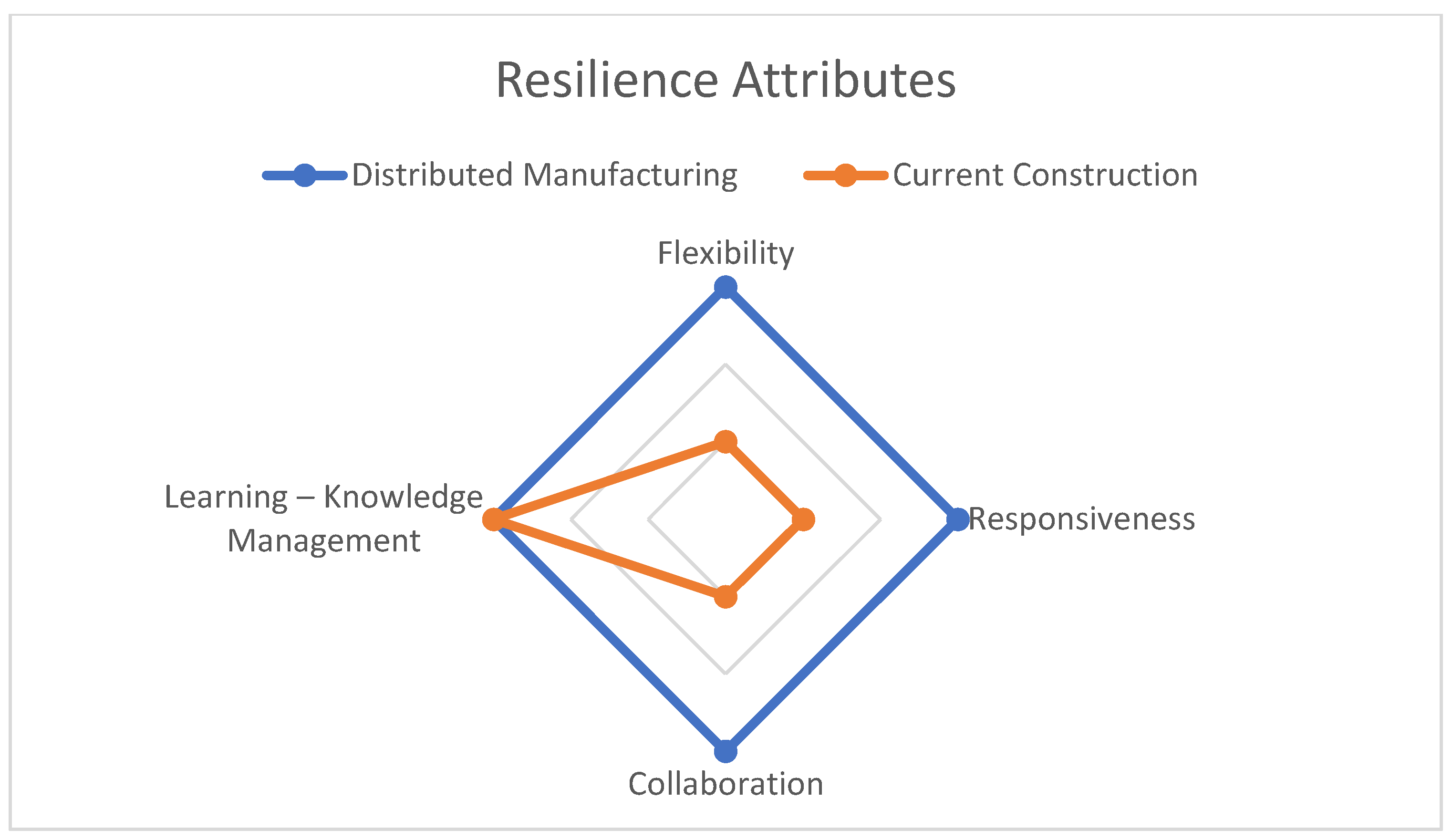
The evaluation of the resilience attributes of Distributed Manufacturing (DM) and traditional construction is presented in
Figure 5. The experts evaluated each resilience attribute, and the results indicate that DM performs better than traditional construction in all categories except knowledge management.
The experts agreed that DM enhances the diversity of available knowledge, leading to increased resilience. DM allows for decentralization of knowledge sources, which enhances the availability and diversity of information, enabling more informed decision-making in the face of disruptions. However, traditional construction's well-organized, centralized training methods provide advantages over DM, leading to better knowledge management, as acknowledged by the expert panel.
Overall, DM provides better resilience performance than traditional construction, as it enables decentralization, adaptability, and flexibility, which are essential for increasing resilience. The results indicate that DM can lead to more robust and adaptable construction supply chains, contributing to increased resilience in the construction industry.