Submitted:
15 May 2023
Posted:
16 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
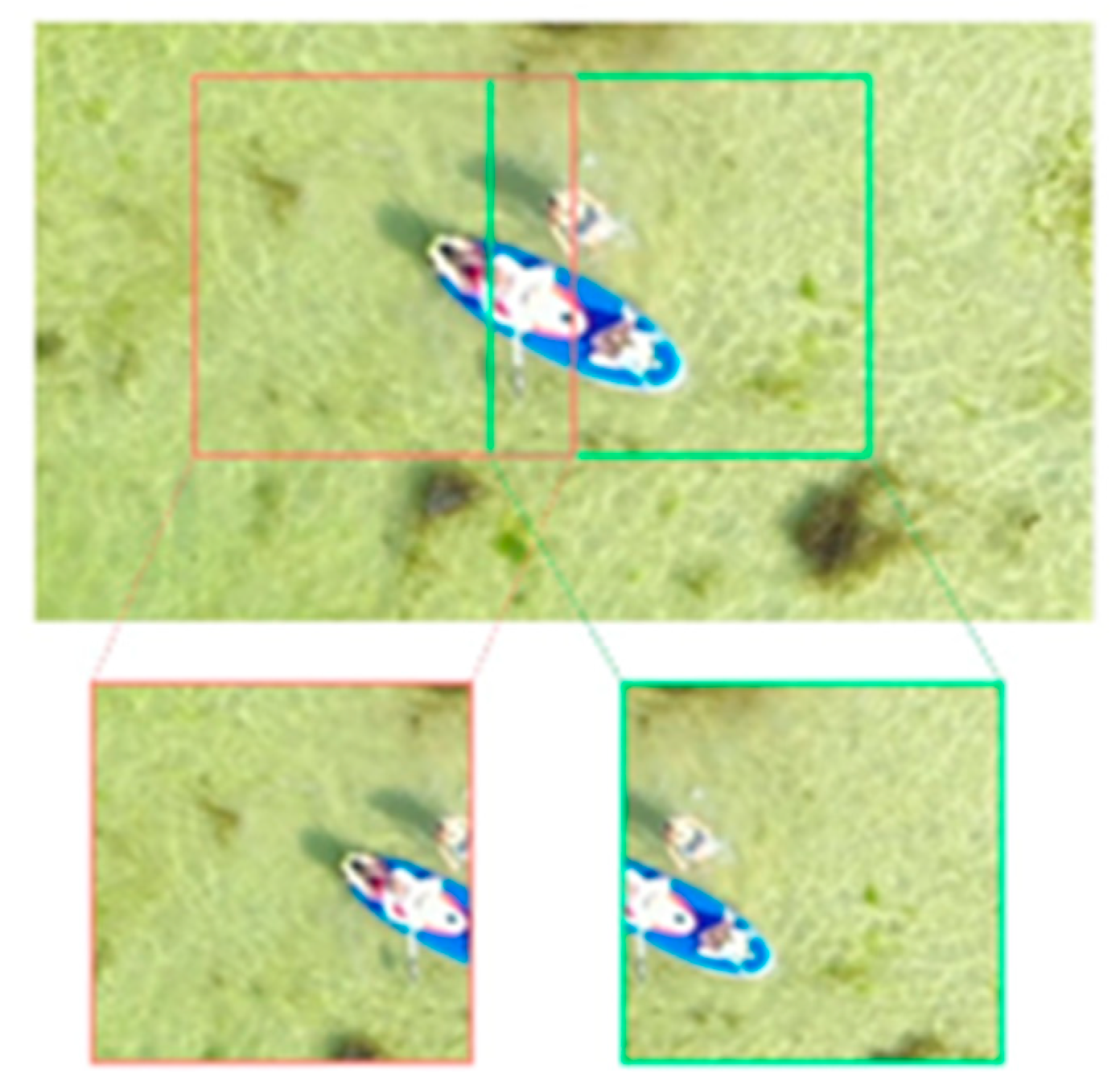
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose a lightweight object detector name SG-Det, which simultaneously meets the requirements of high precision and high-speed detection of UAV images in SAR.
- (2)
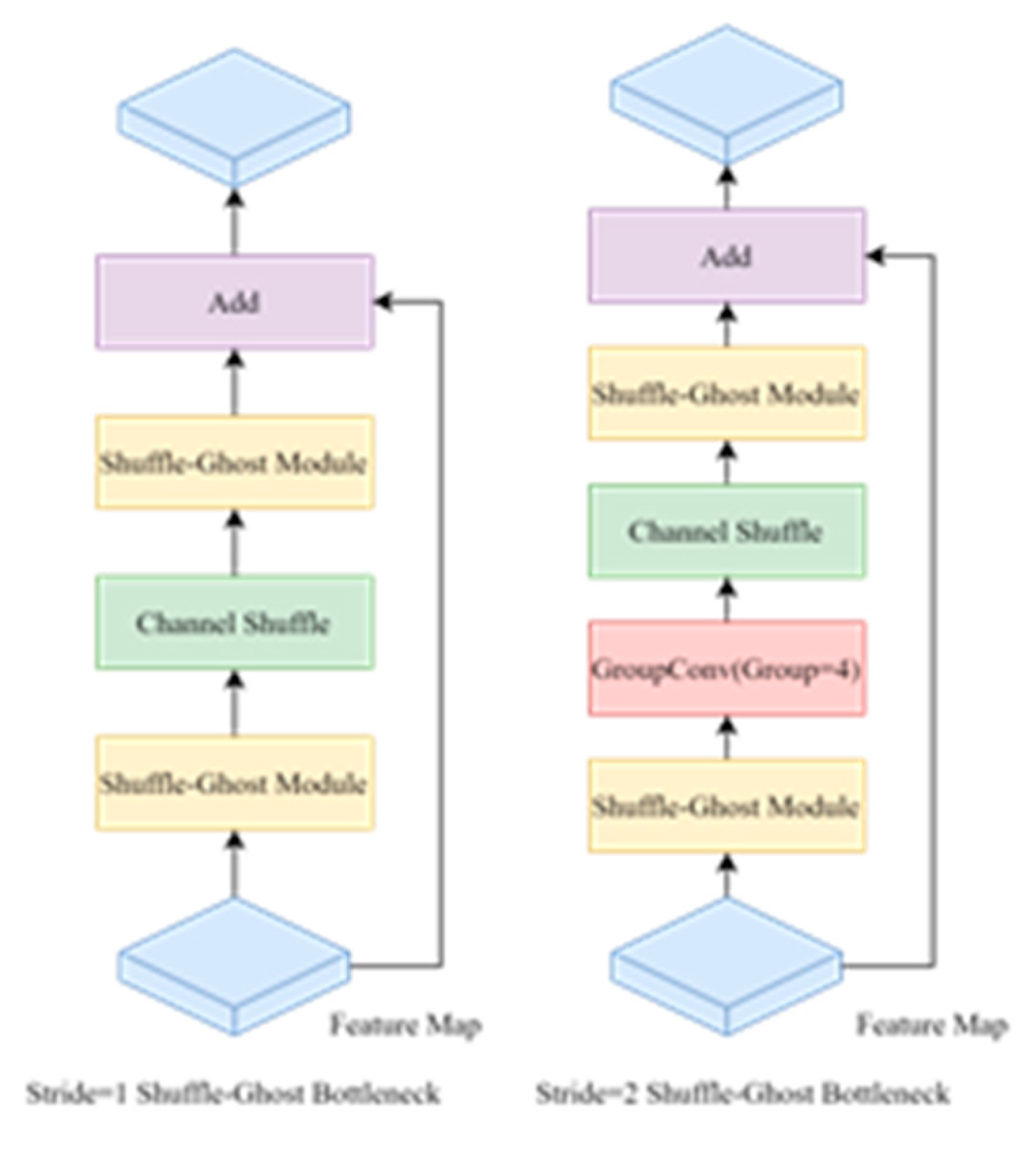
- We design a lightweight classification network name Shuffle-GhostNet, refactor the original GhostNet, and introduce the channel shuffle operation to enhance the flow between information groups and the robustness of the network model.
- (3)
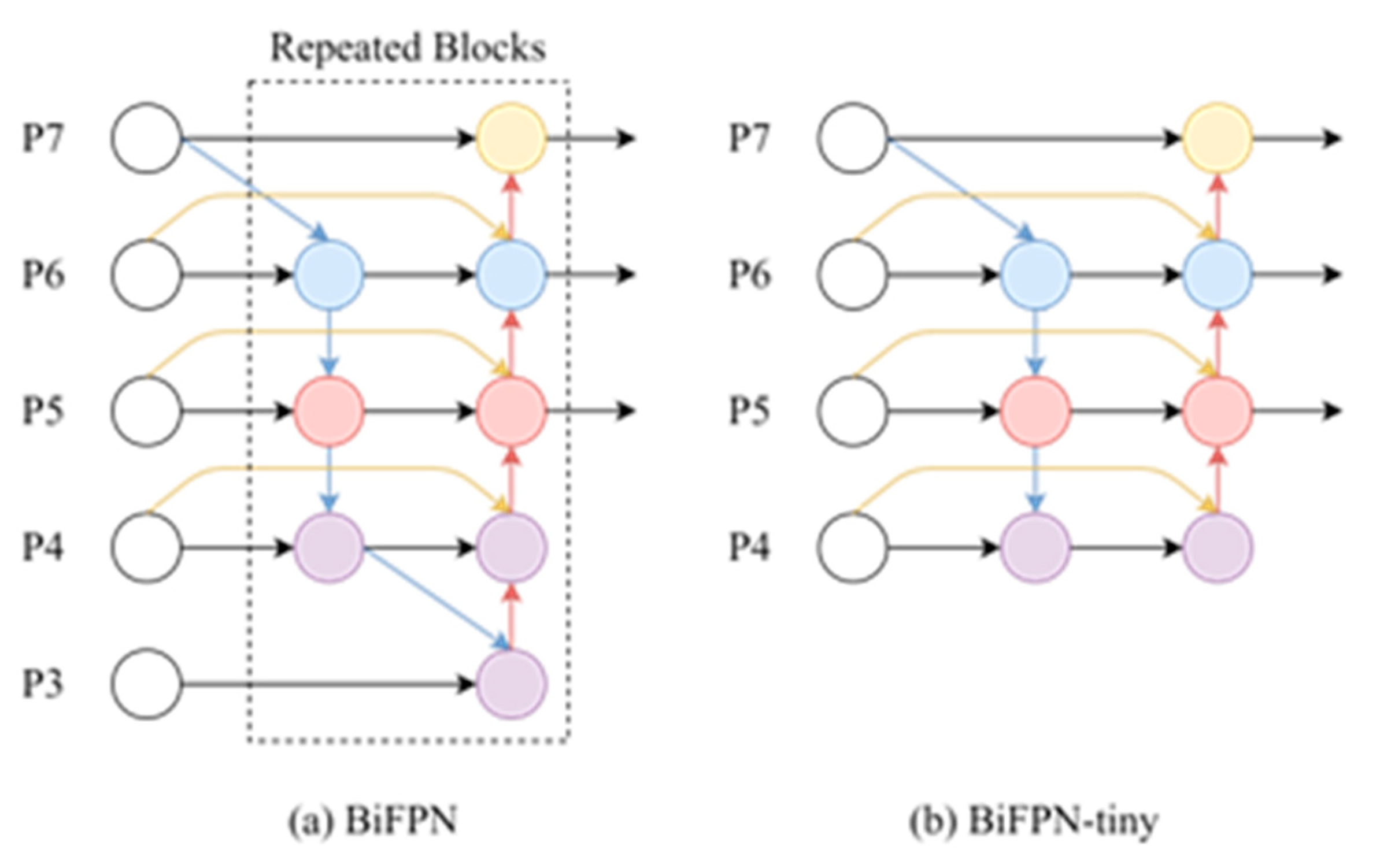
- We design a lightweight feature fusion architecture named BiFPN-tiny, which enhances the corresponding features to capture the characteristics of dense small objects in UAV images.
- (4)
- We validate the effectiveness of the proposed network on the aerial-drone floating objects (AFO) dataset, demonstrating its ability to achieve real time detection with high accuracy.
2. Related Work
2.1. Lightweight Neural Network
2.2. Feature Pyramid Network
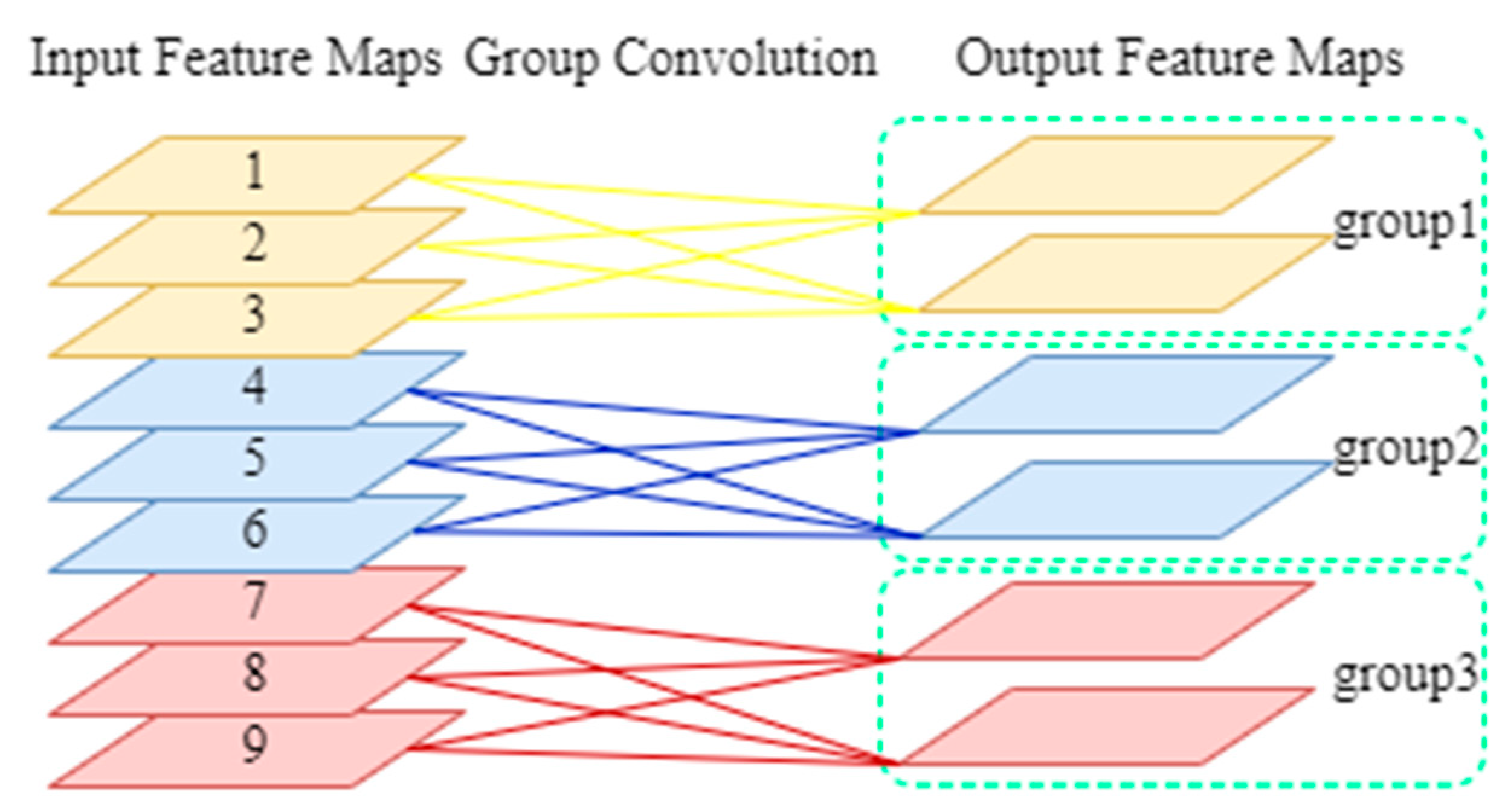
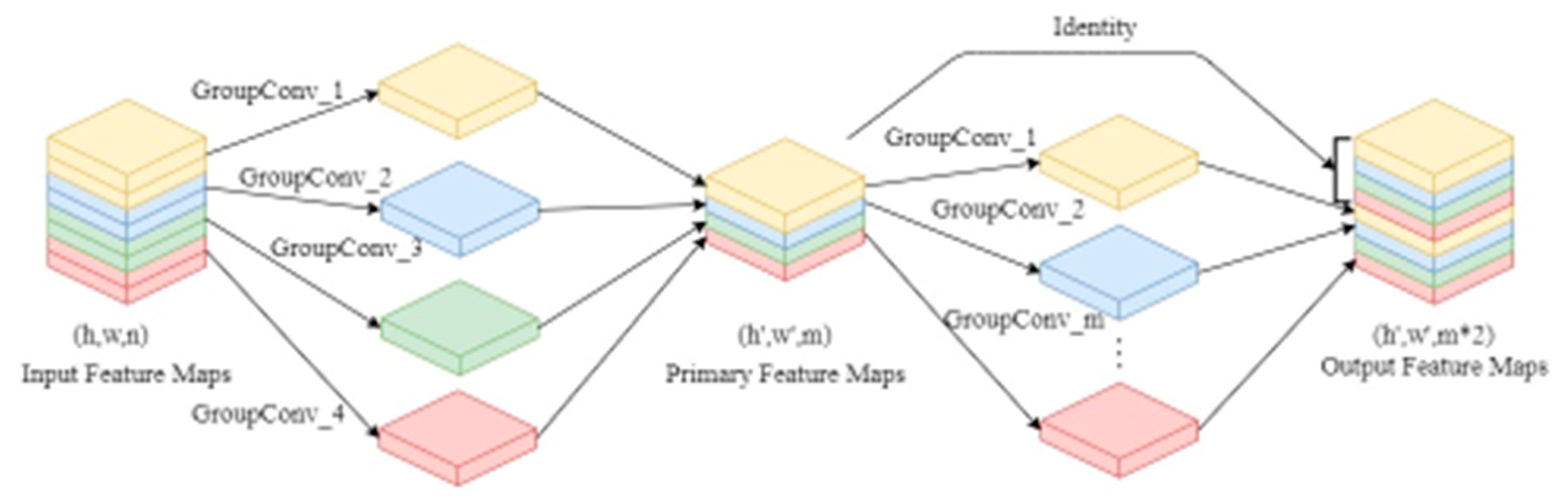
2.3. Group Convolution
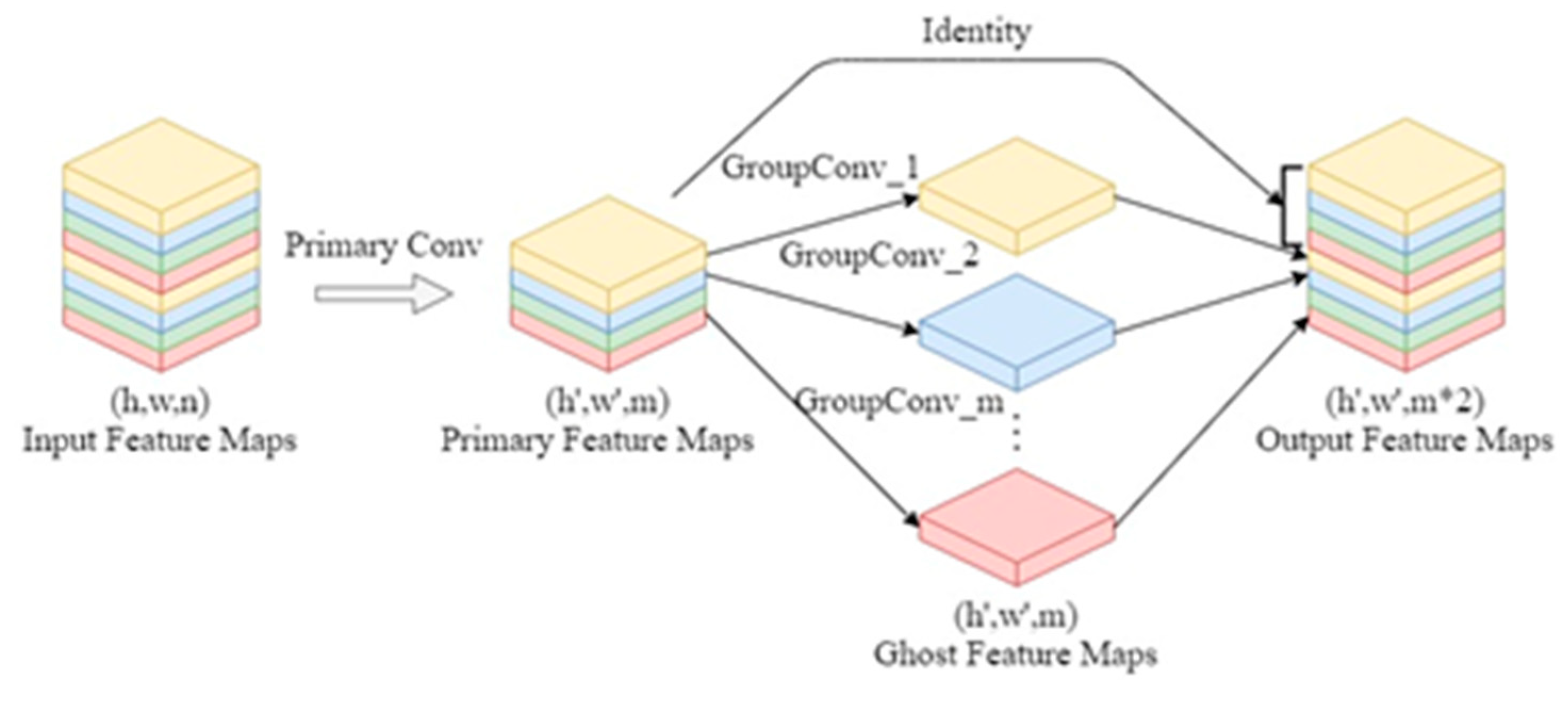
2.4. Ghost Convolution
3. Methods
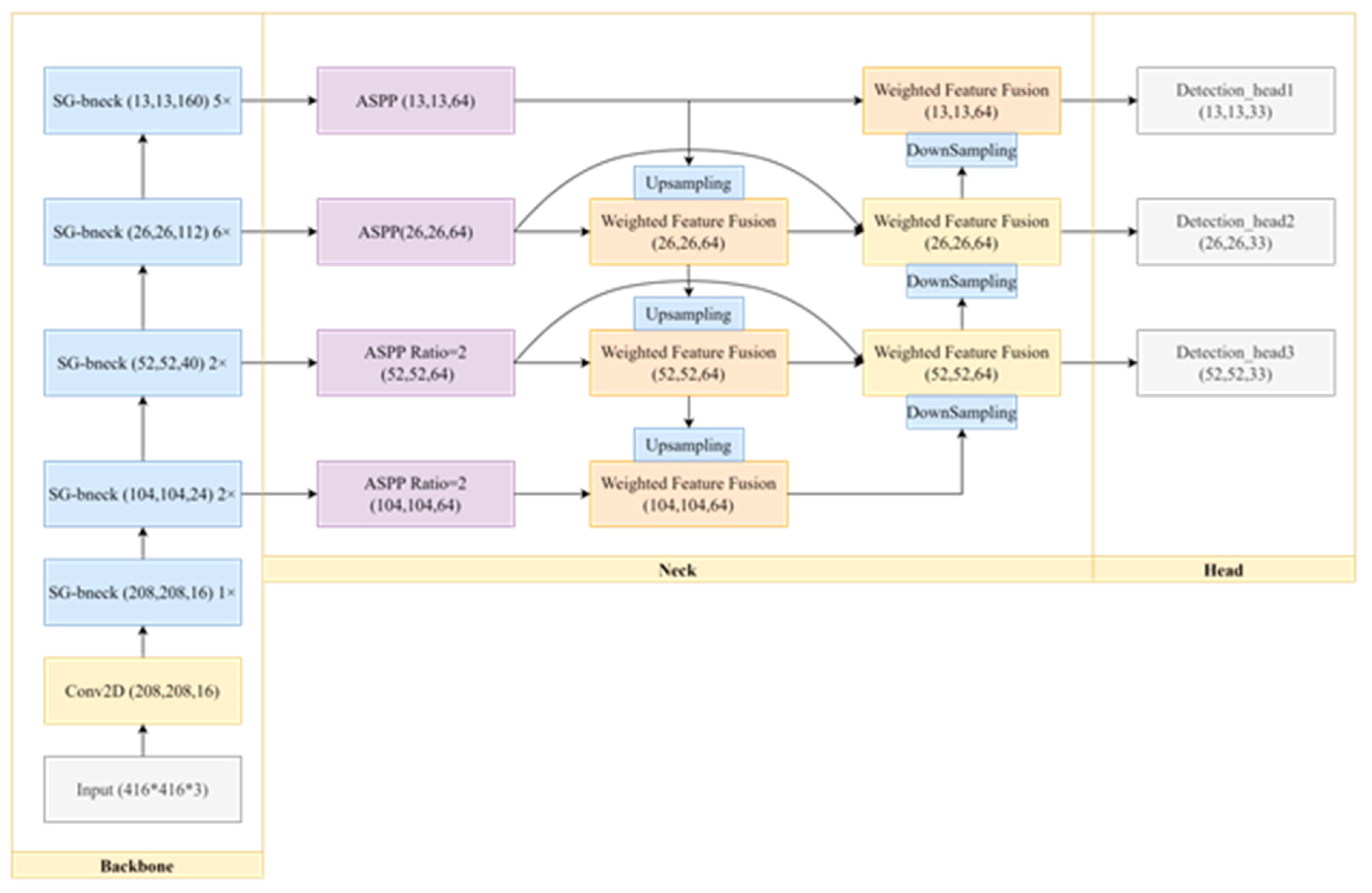
3.1. Overall Framework
3.1. Backbone
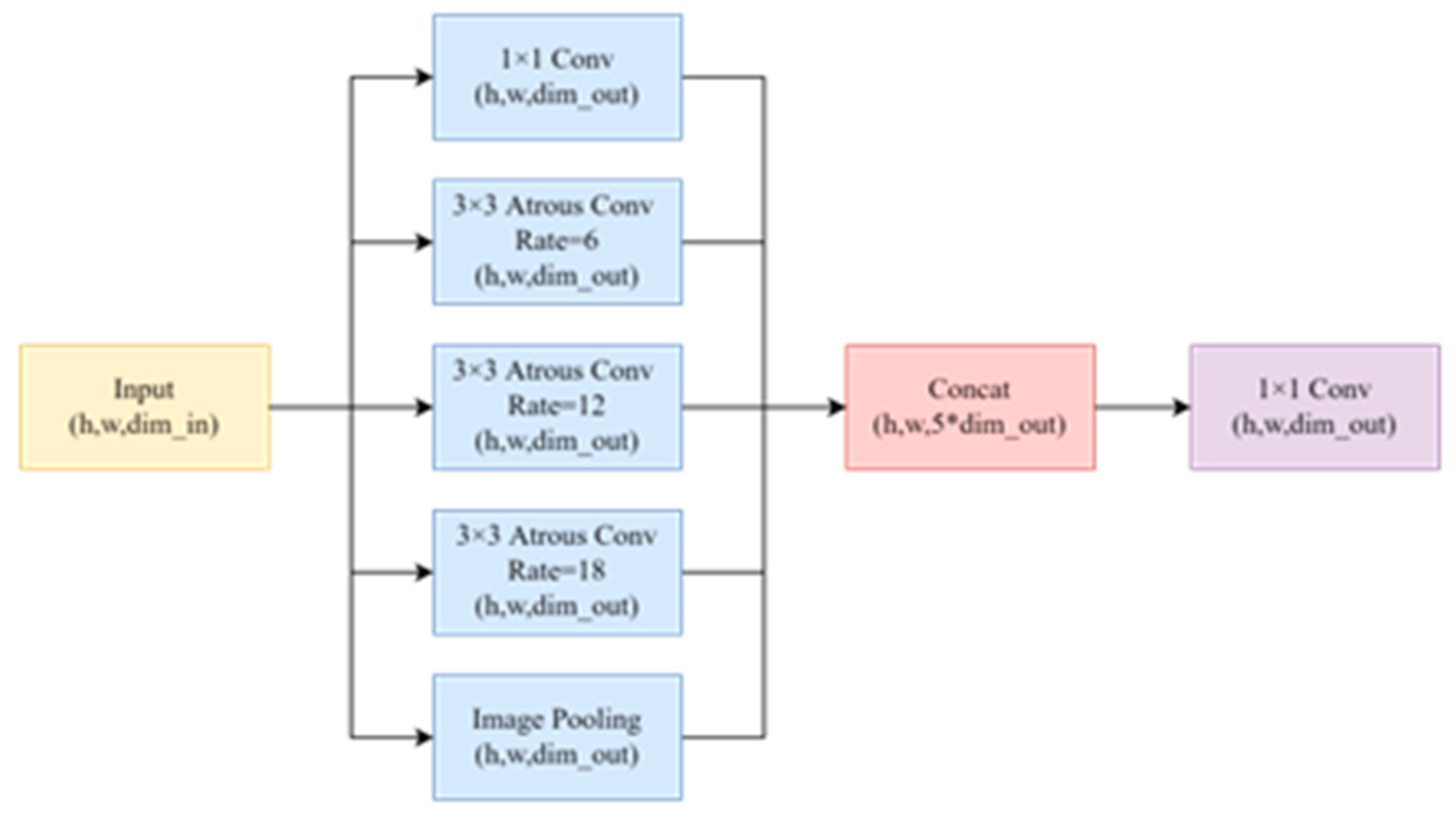
3.3. Neck
3.3. Head
4. Experiment
4.1. Model training
4.2. Dataset
4.3. Comparison Experiment
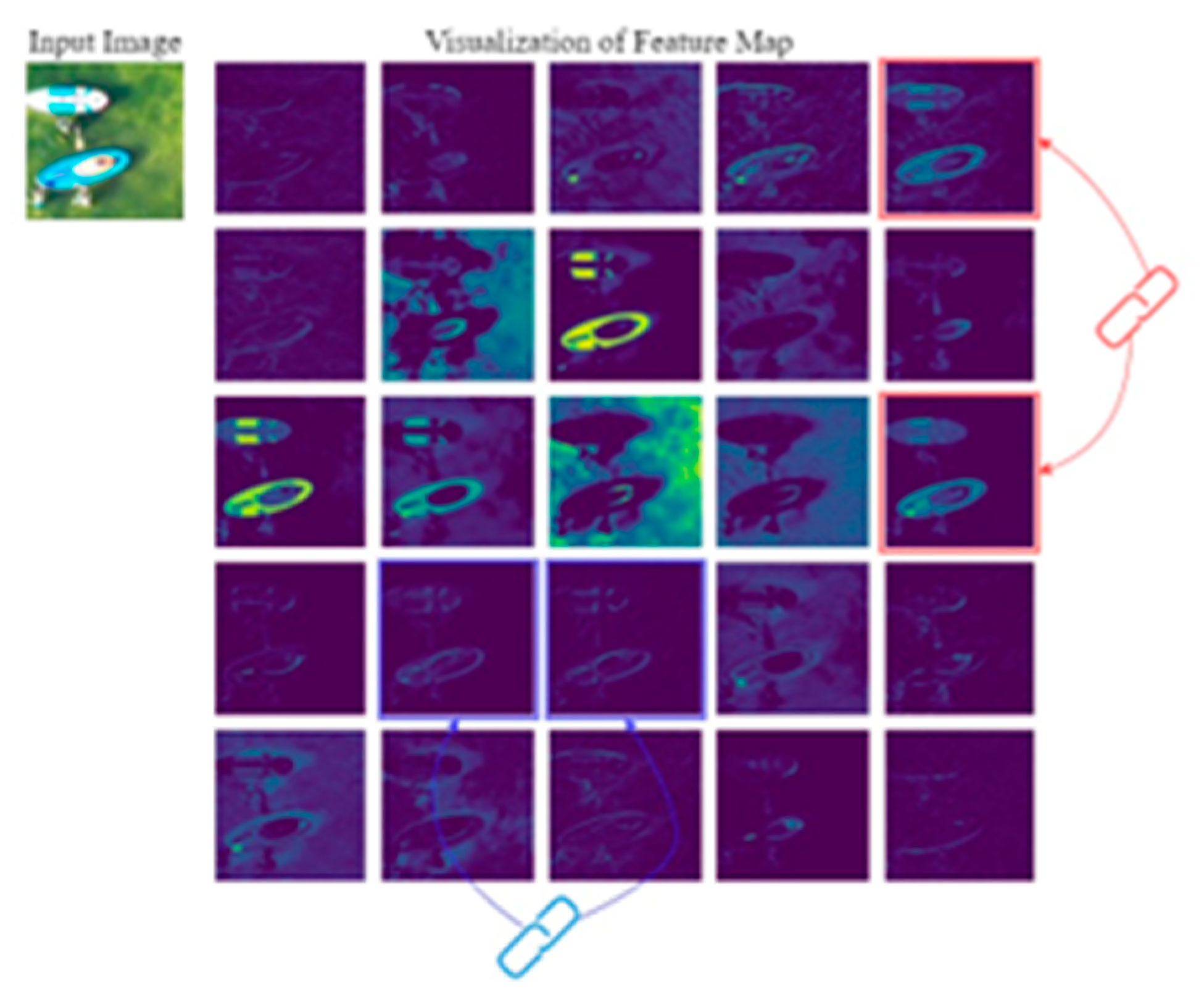
4.4. Ablation Experiment
4. Conclusion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EMSA. Annual overview of marine casualties and incidents[J]. 2018.
- Lin, L.; Goodrich, M.A. UAV intelligent path planning for wilderness search and rescue[C]//2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. IEEE, 2009: 709-714. [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, K.; Deng, Q.; et al. Distributed deep learning model for intelligent video surveillance systems with edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2019. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; et al. Learning to see the hidden part of the vehicle in the autopilot scene. Electronics 2019, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, G.; Ratha, N.; Agarwal, A.; et al. Unravelling robustness of deep learning based face recognition against adversarial attacks[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2018, 32. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X. Unmanned aerial vehicle-based fire detection system: A review. Fire Safety Journal 2020, 113, 103117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W. Application of UAV and computer vision in precision agriculture. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2020, 178, 105782. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.; Im, J.; Son, Y.; Chun, J. Applications of unmanned aerial vehicle-based remote sensing for environmental monitoring. Journal of Environmental Management 2020, 255, 109878. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2014; pp. 580–587.
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2015; pp. 1440-1448.
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; et al. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016; pp. 779–788.
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; et al. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector[C]//European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham, 2016: 21-37. [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Lv, X.; Lian, X.; et al. YOLOv4_Drone: UAV image target detection based on an improved YOLOv4 algorithm. Computers & Electrical Engineering 2021, 93, 107261. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Fan, H.; Chu, P.; et al. Clustered object detection in aerial images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 8311-8320.
- Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Dot distance for tiny object detection in aerial images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2021: 1192-1201.
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; et al. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2020: 1580-1589.
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; et al. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. Efficientdet: Scalable and efficient object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2020: 10781-10790.
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; et al. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and< 0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; et al. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018: 6848-6856.
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017: 2117-2125.
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018: 8759-8768.
- Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.Y.; Le, Q.V. Nas-fpn: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2019: 7036-7045.
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017: 1251-1258.
- Ga̧sienica-Józkowy, J.; Knapik, M.; Cyganek, B. An ensemble deep learning method with optimized weights for drone-based water rescue and surveillance. Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering 2021, 28, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Etten, A. You only look twice: Rapid multi-scale object detection in satellite imagery. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.09512. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; et al. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018: 4510-4520.
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2019: 1314-1324.
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; et al. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design[C]//Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). 2018: 116-131.
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. Scaled-yolov4: Scaling cross stage partial network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/cvf conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2021: 13029-13038.
- Liu, S.; Huang, D. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection[C]//Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). 2018: 385-400.
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). 2018: 3-19.


| Model | Detection Framework | mAP | FPS | GFLOPs | Param |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SqueezeNet MobileNetv2 MobileNetv3 ShuffleNetv2 GhostNet Shuffle-GhostNet |
Faster R-CNN |
84.46% | 24.99 | 33.29G | 29.91M |
| 85.86% | 26.31 | 61.23G | 82.38M | ||
| 82.93% 74.77% 83.15% 84.81% |
27.03 25.64 28.57 30.30 |
21.34G 52.14G 58.37G 21.16G |
33.94M 62.32M 60.49M 14.17M |
| Model | mAP | FPS | GFLOPs | Param |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shuffle-GhostNet + Faster R-CNN YOLOv3-tiny YOLOv4-tiny EfficientDet Our method |
84.81% | 30.30 | 21.16G | 14.17M |
| 79.23% | 29.78 | 5.71G | 9.09M | |
| 81.80% 73.22% 87.48% |
34.75 27.92 31.90 |
6.83G 4.62G 2.34G |
5.89M 3.83M 3.32M |
| Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SqueezeNet MobileNetV2 MobileNetV3 ShuffleNetV2 GhostNet Shuffle-GhostNet YOLOv3-tiny YOLOv4-tiny EfficientDet Our method |
21.1% | 41.1% | 52.9% |
| 19.8% | 47.1% | 58.6% | |
| 12.0% 13.6% 17.8% 18.3% 15.3% 19.1% 13.5% 29.8% |
35.4% 31.2% 38.0% 40.5% 34.9% 32.2% 30.3% 37.2% |
53.7% 45.4% 53.0% 54.9% 50.9% 41.3% 34.9% 52.3% |
| BiFPN-tiny | ASPP | RFB | CBAM | GroupConv (group=4) |
GroupConv (group=2) |
Channel Shuffle |
mAP | FPS | GFLOPs | Param |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ |
78.96% | 27.48 | 1.65G | 2.65M | ||||||
| ✓ | 84.20% | 25.94 | 3.20G | 4.02M | ||||||
|
✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ ✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
83.15% 77.98% 85.67% 85.02% 87.48% |
21.14 25.97 25.54 25.43 31.90 |
1.92G 3.21G 2.68G 2.73G 2.34G |
2.89M 4.03M 3.35M 3.42M 3.32M |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





