1. Introduction
Epigenetics refer to reversible alterations on the gene expressions that do not modify the DNA sequence [
1]. Post translational modifications such as methylation, acetylation and others make changes of the N-terminal tails of histones [
2]. Histone acetylation and deacetylation modifications are controlled by different class of enzymes, histone acetyltransferases (HAT) and histone deacetylases (HDAC) [
3,
4]. Thus, the chemical modification is reversible [
5,
6].
To date, 18 human HDACs have been characterized. HDACs are separated into two groups and four classes depending on sequence similarity to yeast HDAC [
7]. Zinc dependent HDACs are class I, class II and class IV HDACs, while nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) dependent enzymes are class III HDACs which are also known as sirtuins [
8,
9,
10]. Class I HDACs (HDAC1, 2, 3 and 8) are located in the nucleus [
11]. HDAC1 and HDAC2 interact with the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase complex (NuRD), transcriptional regulatory protein sin3A, corepressor of REST (CoREST) and mitotic deacetylase complex (MIDAC) [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16], while HDAC3 form a complex only with the silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid receptors (SMRT) and nuclear receptor corepressor (NCoR) [
17,
18]. HDAC8 does not need to form a complex and works alone [
19,
20].
HDACs are involved in signal transduction, cell growth and cell death [
21]. So far, several inhibitors including SAHA, FK228, belinostat and panobinostat have been approved by the FDA against T-cell lymphoma [
22,
23,
24,
25]. However, due to reported side effects and unfavorable pharmacokinetics, much effort is made to develop novel selective and better bioavailable HDAC inhibitors against several diseases such as cancer, parasitic diseases, inflammation, and others [
26,
27,
28,
29].
The majority of HDAC inhibitors consists of three pharmacophoric features: a zinc binding group (ZBG) which chelates the zinc ion at the bottom of the catalytic pocket, a linker group which is located at the substrate binding tunnel, and a cap group which is solvent-exposed at the rim of the pocket [
7,
30]. Some HDACs can be selectively inhibited by compounds addressing available subpockets of HDACs such as side-pockets, lower-pocket and foot-pocket (FP) [
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. For example, class I HDACs show an additional foot pocket [
40]. Targeting this foot pocket resulted in class I HDAC-selective inhibitors [
31,
34,
35,
41,
42,
43,
44]. However, the development of selective inhibitors for the class I members of HDACs, particularly HDAC1-3, remains a critical challenge to overcome. The zinc binding group is part of most of the HDAC inhibitors. Till now, hydroxamic acid, 2-aminobenzamide, 2-substituted benzamide, alky/arylketone and thiol groups are often used as warheads for inhibitors of class I HDACs [
35,
37,
38,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45]. Recently, the alkylhydrazide scaffold attracted attention for the development of HDAC3 inhibitors due to its high potency, selectivity and good bioavailability [
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52]. Their general structure has been represented in
Figure 1.
Interestingly, by varying the length of the alkyl group (from
n-propyl to
n-hexyl) resulted in a shift of the selectivity towards HDAC8 and provided substrate competitive and highly potent inhibitors [
53].
In the current study, we performed docking and molecular dynamics studies of alkylhydrazides as HDAC3 inhibitors. Available data were compiled to apply ligand-based and structure-based methods to understand the structure-activity relationship of this class of inhibitors. Various quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) methods were evaluated for this purpose, including pharmacophore models, atom-based 3D QSAR models, and binding free energy-based QSAR models. In addition, we tested the models on novel designed alkylhydrazides.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Diversity analysis of the datasets
A dataset containing 63 compounds having an
N-monosubstituted hydrazide scaffold were collected from the literature [
46,
48,
50]. The 2D structures and IC
50 values of all alkylhydrazides are shown in
Table S1 (Supplement). The selected compounds cover a reasonable biological activity range (
Table 1). All compounds were measured in vitro using recombinant human HDAC3 and the peptidic substrate (Boc-Lys(acetyl)-AMC) [
46,
48,
50].
We first grouped the compounds into three activity classes according to their HDAC3 data (
Table 1,
Table S1 Supplement);
Highly active inhibitors showing pIC50 > 7
Moderately active inhibitors showing pIC50 between 5.30 and 7
Inactive inhibitors showing pIC50 < 5.30
The compounds were randomly divided into a training set (70 %; 39 compounds) and test set (30 %; 17 compounds) using the “RAND” function in MOE program (MOE – Molecular database calculator – RAND) [
54]. The compounds either having no exact IC
50 values or showing an IC
50 value higher than 5 µM were classed as inactives (
Table 1). The same training and test sets were used for the ligand and structure based model development studies. The training set was used to generate the models, while the independent test set was utilized to evaluate the predictive accuracy of the selected best models. The inactive set was only utilized for the validation of the pharmacophore models by calculating the inactive-survival score (detail in
Section 2.2).
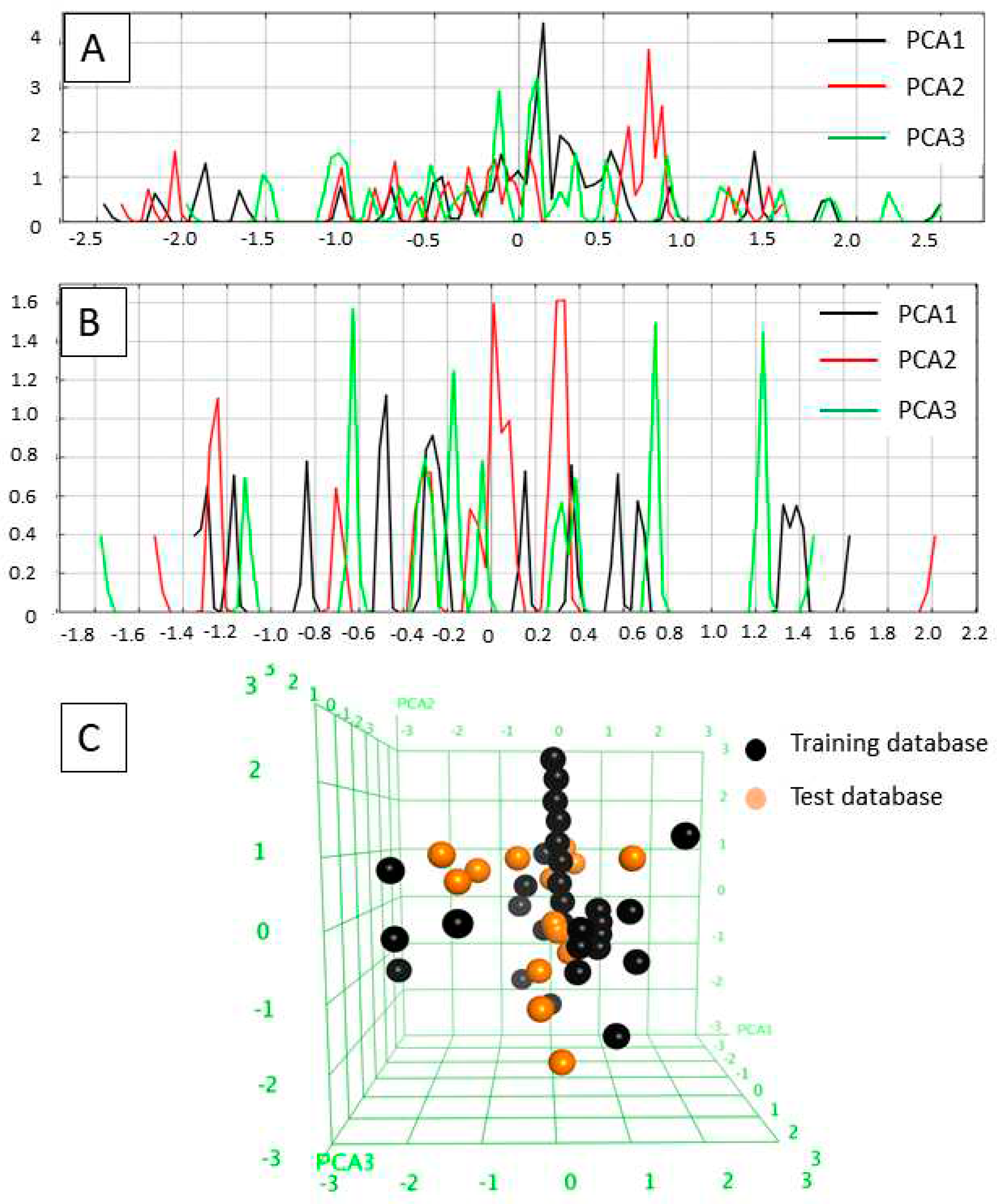
The applicability domains of the training and external test sets were analyzed by plotting the three most important principal components (PCA1, PCA2, and PCA3) [
55,
56] of the calculated descriptors (PEOE_VSA_HYD, GCUT_SLOGP_0, TPSA, b_single, lip_acc, lip_don, vsa_hyd - explained in
Table 2). The most important PCA of the molecular descriptors can explain about 100 % of the original space. The PCA analysis showed that the training set and external test set were homogeneously distributed in the chemical space (
Figure 2).
2.2. Analysis of the pharmacophore model
An important step in establishing a 3D-QSAR model is the development of the correct alignment, usually based on a generated pharmacophore model. In the current work, the pharmacophore model was generated using the Phase module implemented in Schrödinger considering 30 active compounds (pIC
50 > 7) [
57]. Then, seven inactive compounds were used to analyze the ability of the generated models for discriminating the actives from inactives.
The pharmacophore model shows the 3D (three dimensional) structural features which might be essential for the biological activity [
58,
59]. Hence, the pharmacophores that are common to the 30 active compounds showing pIC
50 more than 7 were obtained. In total, 38 pharmacophore hypothesis were generated. Then, the generated pharmacophore hypotheses were scored according to the survival score. The survival score was generated by evaluating how well the selected pharmacophore hypothesis fits to the most active inhibitors. Additionally, the Phase module penalizes the generated pharmacophore hypothesis that cannot discriminate the actives from inactives. Thus, the developed hypotheses were mapped onto the inactive compounds and scored as inactive-survival score. If the inactive score is better than the survival score, it means that the pharmacophore hypothesis does not discriminate the actives from inactives. For the selected pharmacophore hypothesis, all inactive compounds should show low fitness to the pharmacophores.
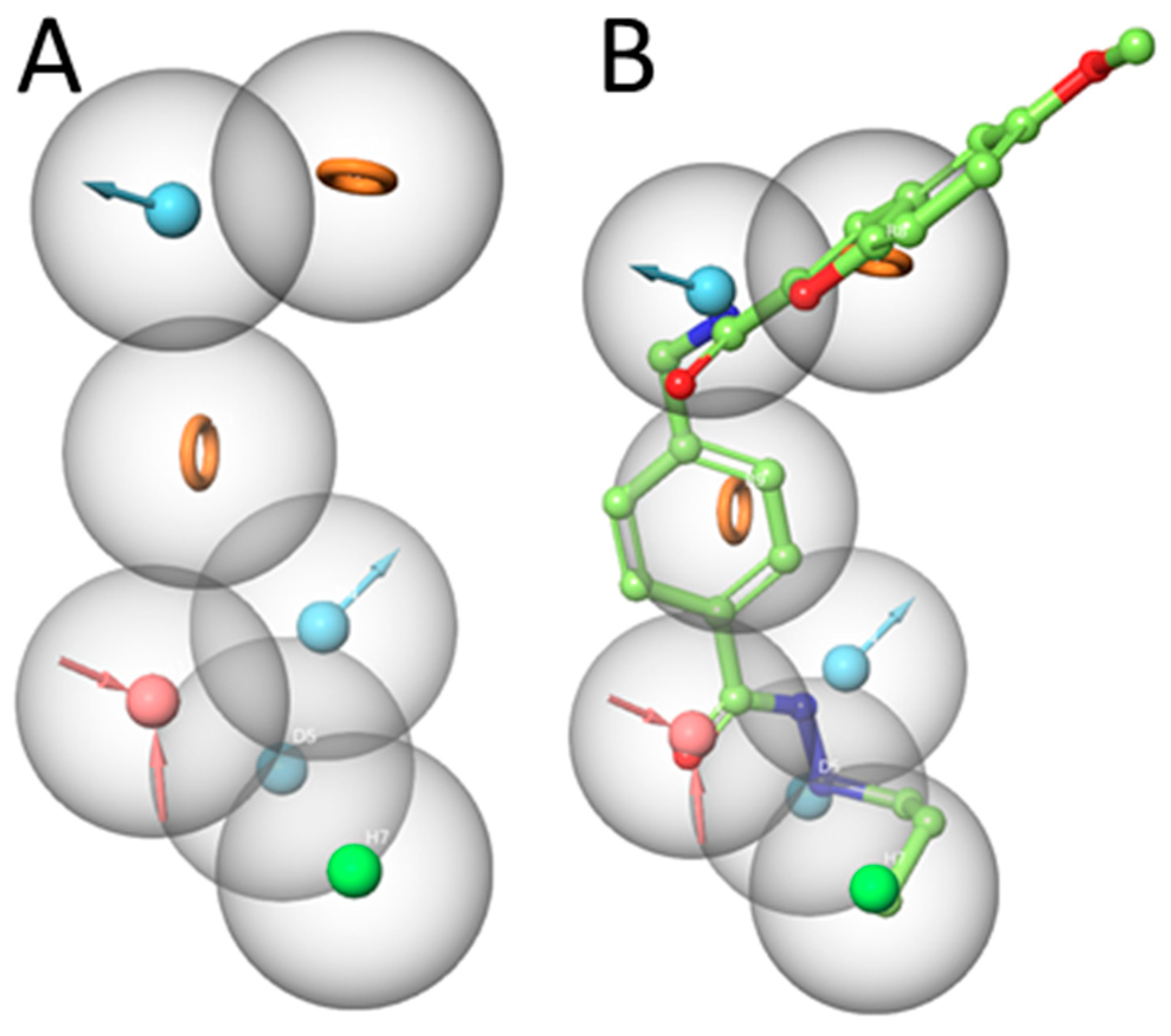
After scoring the generated pharmacophore hypothesis, the best-scored pharmacophore model consisting of seven pharmacophoric features (ADDDHRR –
Figure 3A) were selected. The survival score (6.923) and the inactive score (1.688) of the hypothesis were shown in
Table 3. The survival score is higher than the inactive-survival score meaning that the selected pharmacophore hypothesis can discriminate actives and inactives. Pharmacophore features were specified as hydrogen-bond acceptor (A), hydrogen bond donor (D), hydrophobic (H), negative ionic (N), positive ionic (P) and aromatic ring (R).
The generated pharmacophore model mapped onto the most active compound 1. This pharmacophore model shows the importance of the hydrogen bond donor and acceptor functions of the hydrazide moiety (
Figure 3B). The carbonyl oxygen of the hydrazide serves as acceptor, while the two nitrogen atoms serve as donor groups. The alkylchain shows hydrophobic features. The two ring systems are able to exhibit aromatic interactions. The amide scaffold between linker and cap group donates the hydrogen of nitrogen (details shown in the docking part). Accordingly, the selected ADDDHRR pharmacophore model shows the important structural features which can interact with the HDAC3 pocket.
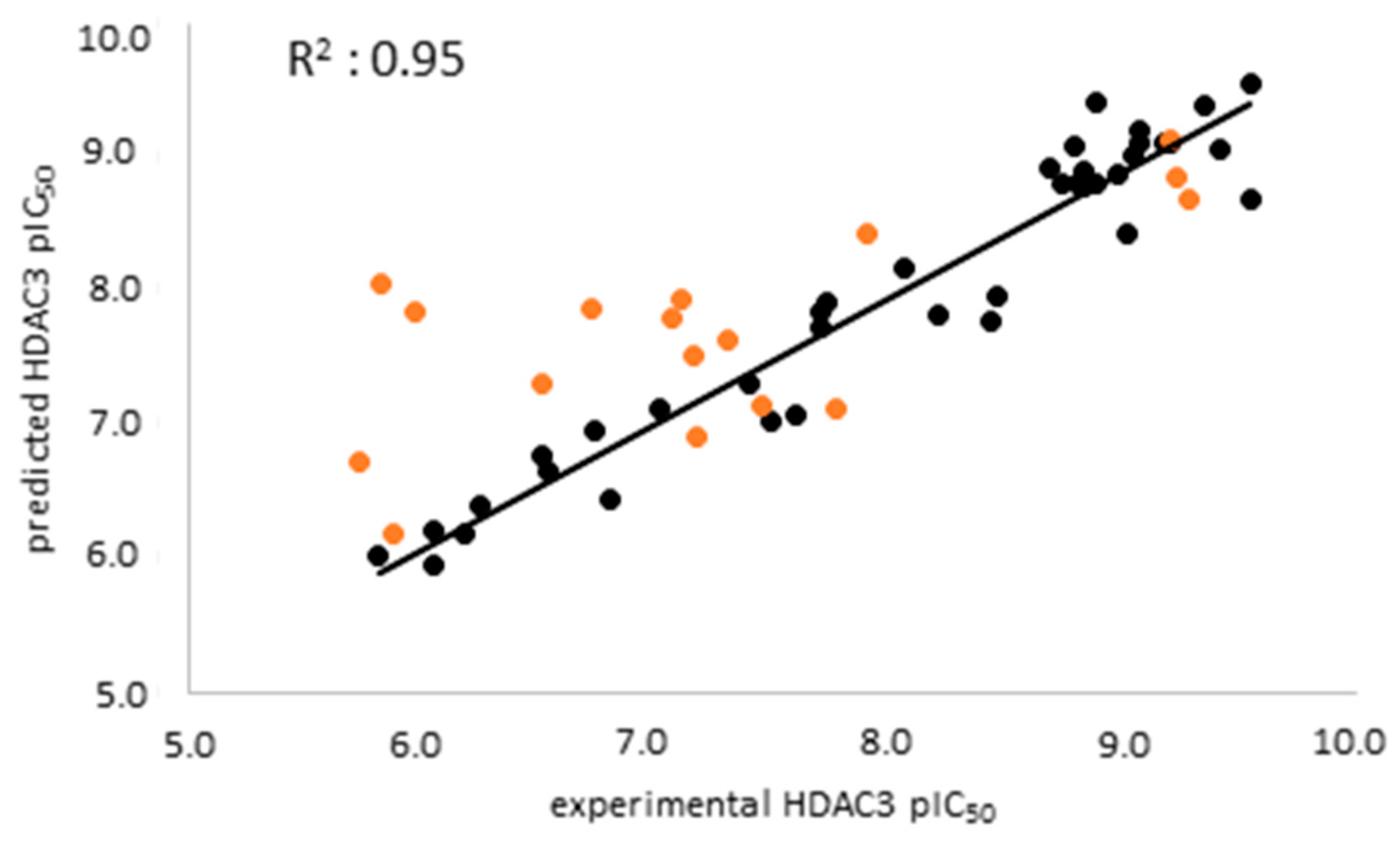
2.3. Analysis of atom-based 3D-QSAR model
The atom-based 3D-QSAR model was built in Schrödinger19 using the 39 compounds in the training set [
57,
58,
59]. The 3D-QSAR model enable us to consider all relevant structural features such as steric clashes as well as pharmacophores for HDAC3 activity. In this step, the previously selected seven-featured pharmacophore model (ADDDHRR) was used as an alignment rule for the generation of an atom-based QSAR model. First, 39 compounds were aligned by the pharmacophore model and then, the atom based 3D-QSAR models were generated, and these models were cross-validated. The best atom-based 3D-QSAR model was obtained with a good correlation coefficient (R
2: 0.95), and cross-validated correlation coefficient (Q
2: 0.88) (
Table 4).
The atom-based 3D-QSAR techniques visualize the compounds as 3D (three-dimensional) based on the non-covalent protein-ligand interactions such as hydrogen bond acceptor and donor, hydrophobic, positive and negative ionic bonds. The model marks the favorable structural features with green cubes showing and unfavorable structural features with red cubes showing. To understand the most favorable and less favorable interactions, we have analyzed the all compounds from the training set. As examples, three compounds having low activity (Compounds 35, 36, 38) and three compounds having good activity (Compounds 1, 2, 3) from the training set were chosen to analyze the atom-based QSAR model (
Figure S1, Supplement). According to the atom-based QSAR model, compound 35 exhibited poor activity due to its heptyl alkyl chain (
Figure S1A, Supplement). In
Figure S1B (Supplement), the meta-substituent on the phenyl linker group as exemplified with compound 36 showed unfavorable effect on the HDAC3 activity. In case of compound 38, the thiophene ring showed unfavorable structural features decreasing the HDAC3 activity (
Figure S1C, Supplement). On the other hand, the propyl alkyl chain attached to the hydrazide is favored for three active compounds (
Figure S1D–F, Supplement). In addition to that, para-substituted cap groups are also favored and covered by green cubes. According to the model visualization, the least active compounds (
Figure S1A–C, Supplement) are mainly covered by red cubes, while the more active compounds especially the cap groups (
Figure S1D–F, Supplement) are mostly covered by green cubes.
The external validation was performed using a test set which was not used for model generation, with the aim of evaluating the predictive accuracy and reliability of the generated atom-based QSAR model. The scatter plot of the training and test set was shown in
Figure 4. The prediction results of the training, test and inactive databases are shown in
Table S2.
Analysis of the test set revealed that the atom-based QSAR model well predicts the active inhibitors with differences less than 1 log unit. However, several of the moderately active inhibitors (compounds 51, 53, 55, 56) in the external test set as well as the seven inactive compounds were predicted with differences more than 1 log unit (
Table 5,
Table S2 Supplement). The atom-based QSAR model classified most of the moderately active and inactive inhibitors into the active class. Due to limited accuracy of the ligand-based models in correctly predicting the inactives/weakly actives, we tried to overcome this by generating structure-based prediction models. For this we applied docking and binding free energy calculation techniques discussed in the next section.
2.4. Analyzing the binding mode of alkylhydrazides at HDAC3
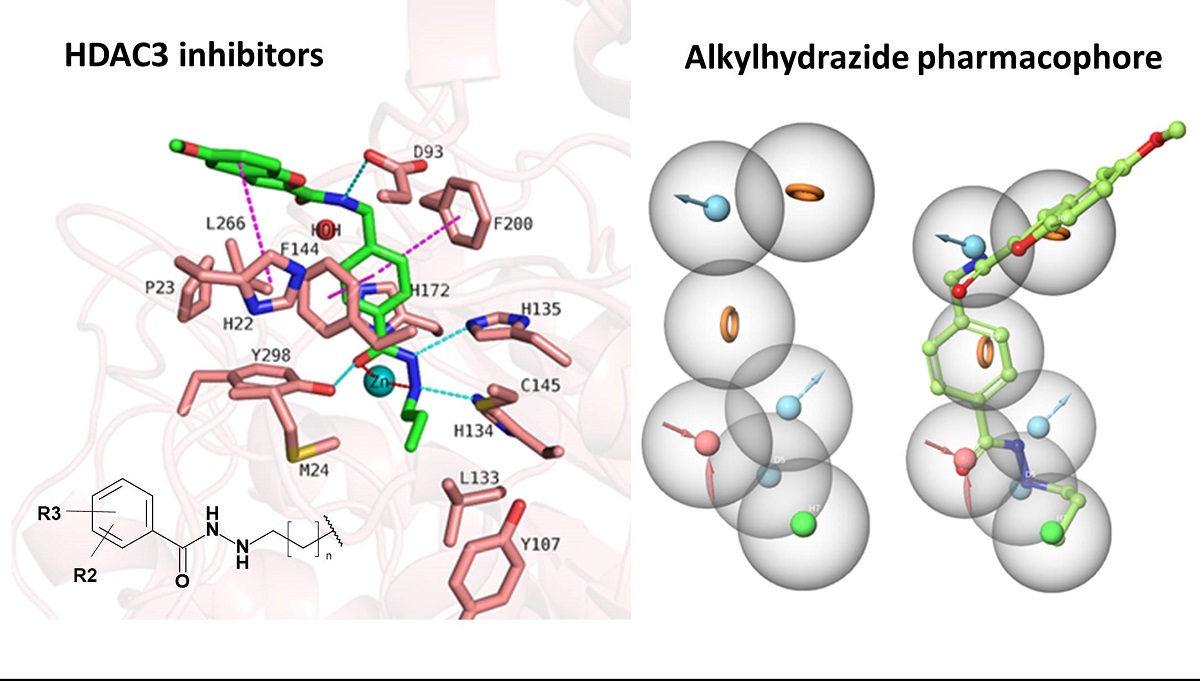
We started with docking of all inhibitors to HDAC3 (PDB ID: 4A69 [
60]) (
Figure S2, Supplement). We used a docking setup in Glide that we previously validated for HDAC inhibitors from different chemical series [
31,
34,
53]. To date, there is no crystal structure of an HDAC in complex with an alkylhydrazide but we could recently show that alkylhydrazides similar to inhibitors 1 and 47 (
Table S1, Supplement) [
46,
50] are reversible and substrate competitive inhibitors of HDACs [
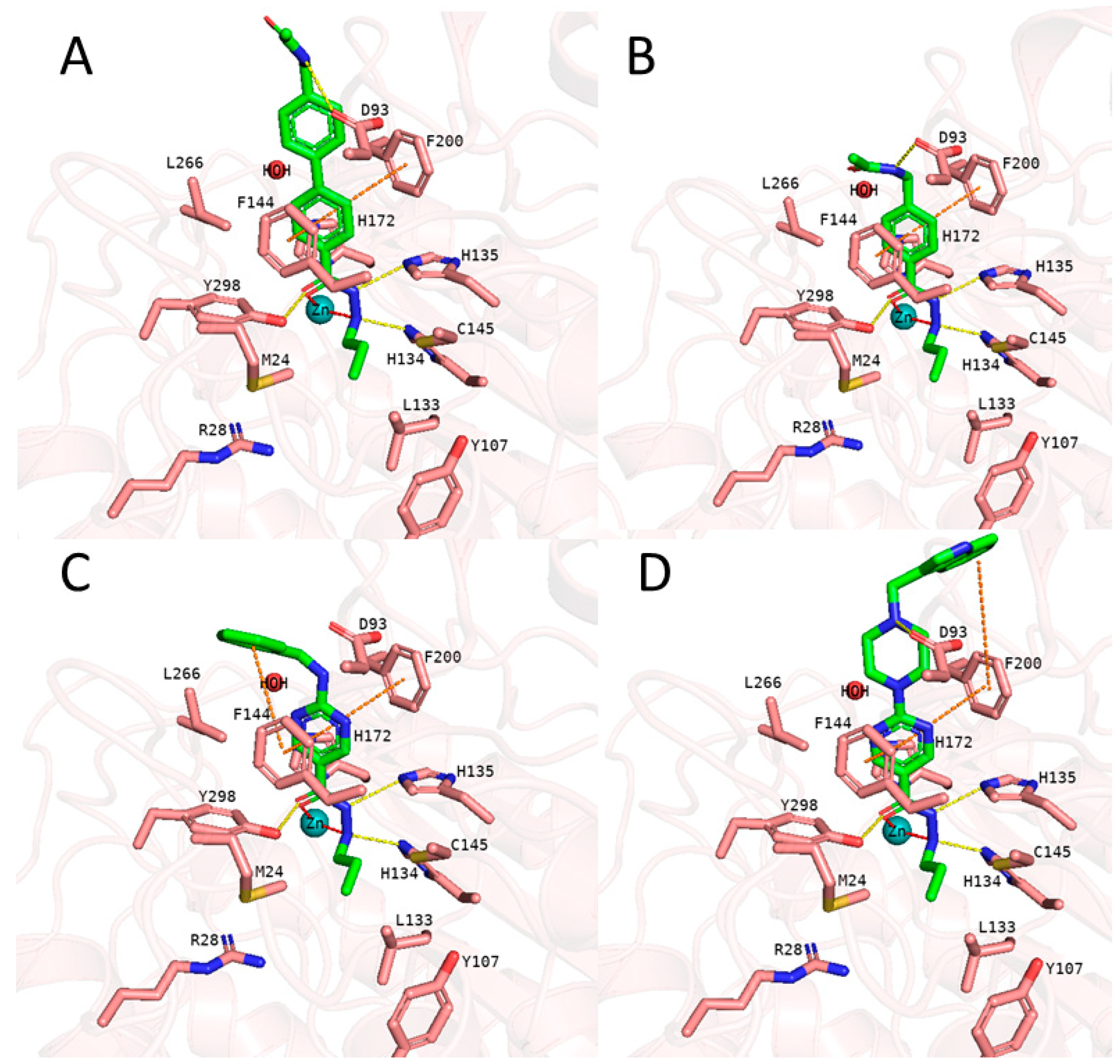
53]. Thus, we docked the alkylhydrazides into the catalytic pocket of HDAC3 and analyzed whether they are able to chelate the catalytic zinc ion. The analysis of the docking results of active inhibitors, as exemplified by compounds 1 and 2 from the training set (
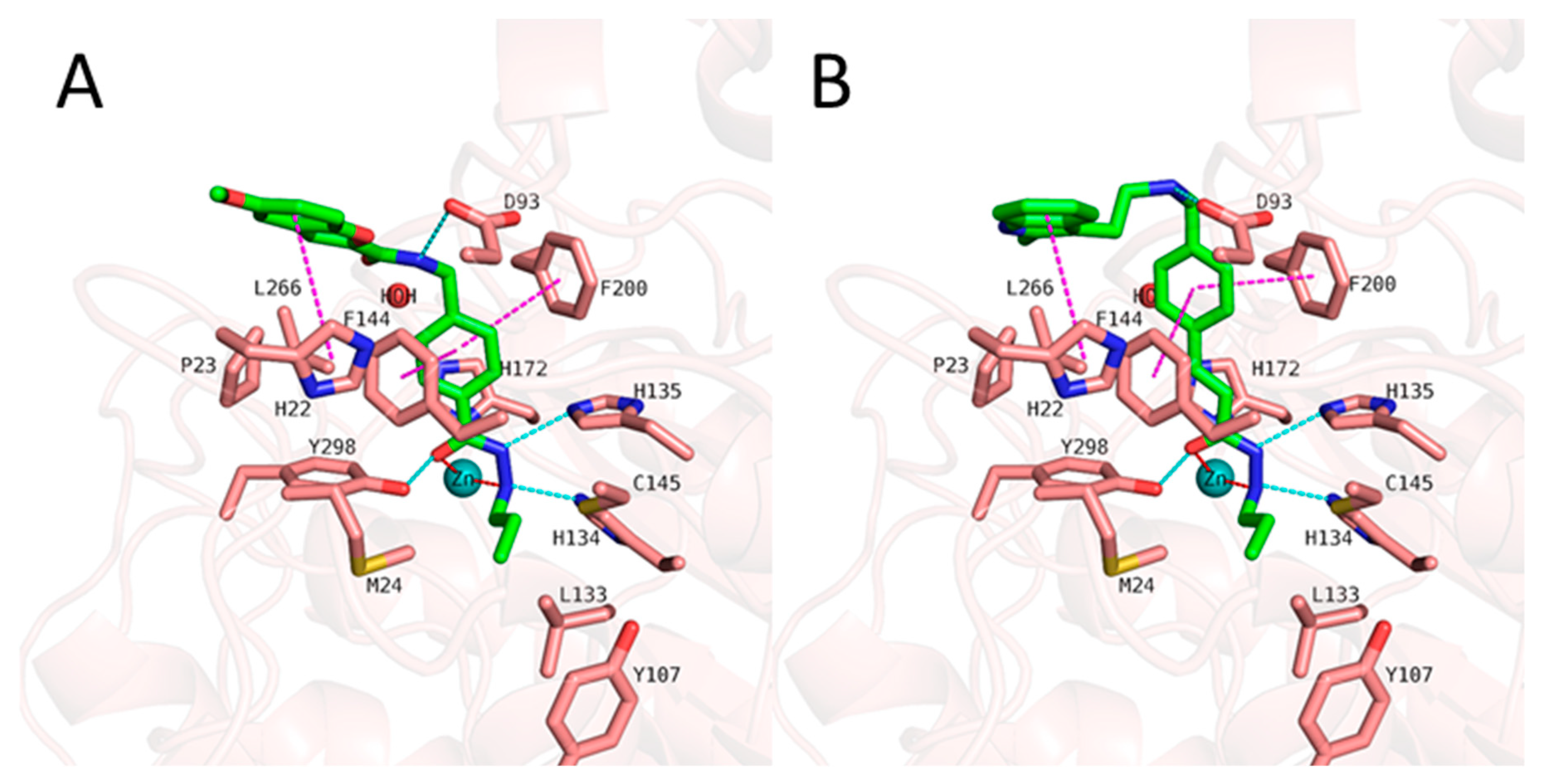
Figure 5), showed that the hydrazide moiety chelates the zinc ion in a bidentate manner through its nitrogen and carbonyl oxygen and exhibits conserved hydrogen bond interactions with H134, H135 and Y298 at the bottom of the catalytic pocket. The aromatic linker group were placed into the hydrophobic tunnel consisting of F144, H172, F200, L266, where it makes aromatic pi-pi interactions with F144 and F200. The cap group is interacting with residues at the surface by forming hydrogen bond interaction with D93 as well as occupies the hydrophobic pocket comprised of H22, P23 in HDAC3. A structural difference which influences the potency and selectivity on HDAC3 is observed in the foot pocket region. According to the docking results, propyl and butyl chains of the alkylhydrazides fit well into the foot pocket of HDAC3. However, replacing the propyl or butyl chains by pentyl or longer side chains resulted in dramatic decrease in the HDAC3 activity due to the steric hindrance observed in HDAC3. The Y107 residue pushes L133 resulting in a narrower foot pocket region [
31,
34]. The pentyl and longer alkyl chains in the foot pocket region show steric clashing with M24 and L133 causing a decrease or loss in the HDAC3 activity.
Although the docking poses show reasonable binding in the HDAC3 active site, the correlation between docking scores and pIC50 was poor (R2 = 0.28 for HDAC3). Thus, we rescored the docking poses by calculating binding free energies.
In addition to the docking results, we have checked the interaction of the potent inhibitors 1 and 2 using 50 ns MD simulation (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6,
Figures S3 and S4, Supplement). MD simulation analysis of compound 1 and 2 revealed that the
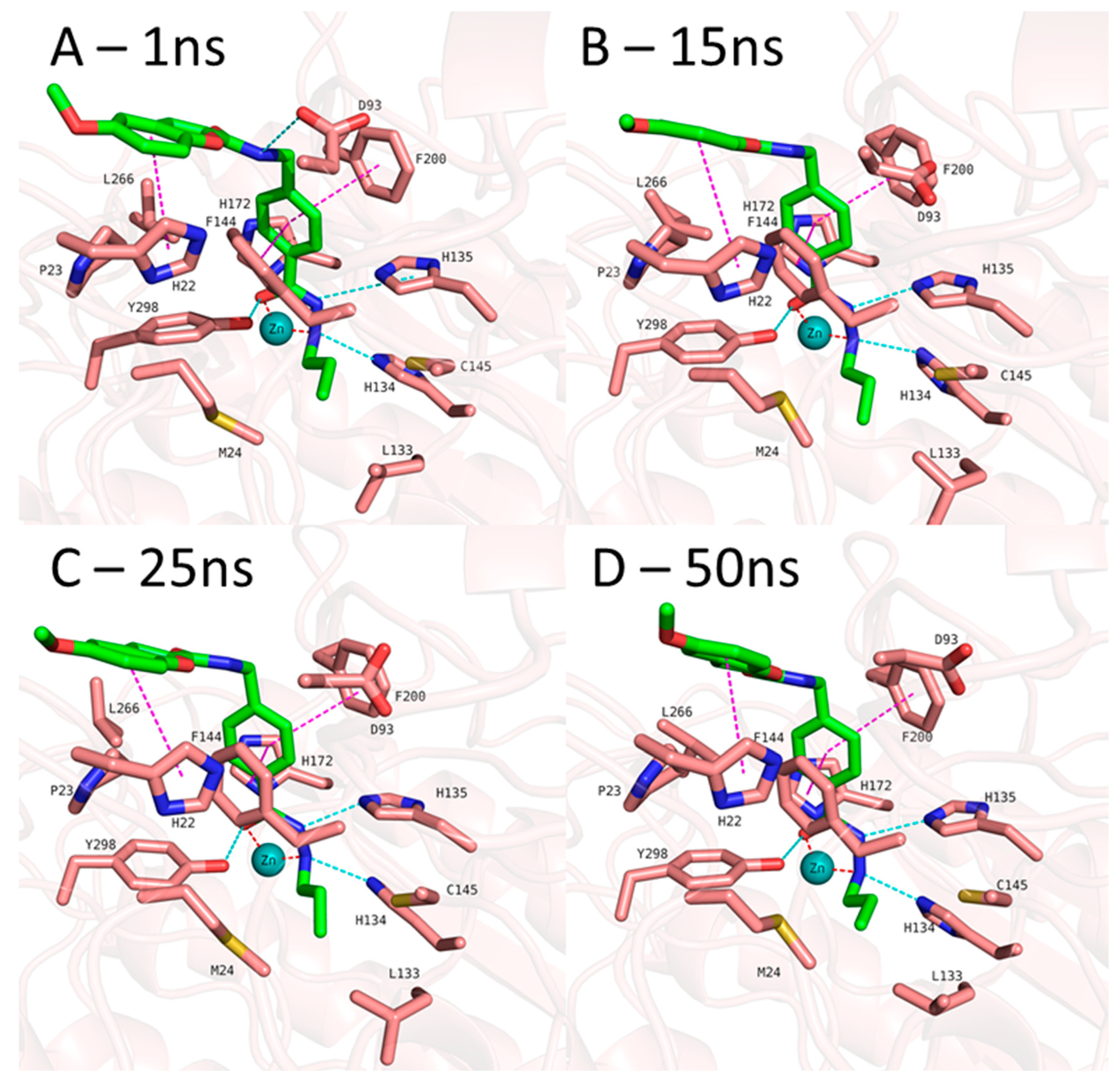
n-propyl chain attached to the hydrazide fit into the foot pocket consisting of M24 and L133. Notably, M24 and L133 play a key role as a gate keeper in the foot pocket region of HDAC3. M24 and L133 closed the foot pocket and make the volume narrower which only propyl or butyl side chain favorably fit. This conformational changes of M24 and L133 might explain the decrease or loss of the HDAC3 activity of the compounds having longer alkyl chain than butyl and propyl. The zinc binding group which is the common part of the compounds 1 and 2 preserves its bidentate coordination and makes hydrogen bond interactions with H134, H135 and Y298 throughout the MD simulation. Furthermore, the linker groups of compounds 1 and 2 are sandwiched between F144 and F200. In addition to these similar protein-ligand interactions of compounds 1 and 2, MD simulation analysis exerted some differences in the cap region of compounds 1 and 2.
According to the MD simulation of compound 1, the selected docking pose as well as the HDAC3-inhibitor complex are stable during the 50 ns MD simulation (
Figure 6 and
Figure S3, Supplement). In case of the compound 1 (
Figure 5), the amide group lost its hydrogen bond interaction with D93, although the ligand maintained the binding conformation. The D93 side chain which is located at the surface of the protein moved away from the compound 1. The benzofuran cap group of compound 1 is occupying the hydrophobic pocket by making aromatic interaction with H22 at the surface of the protein.
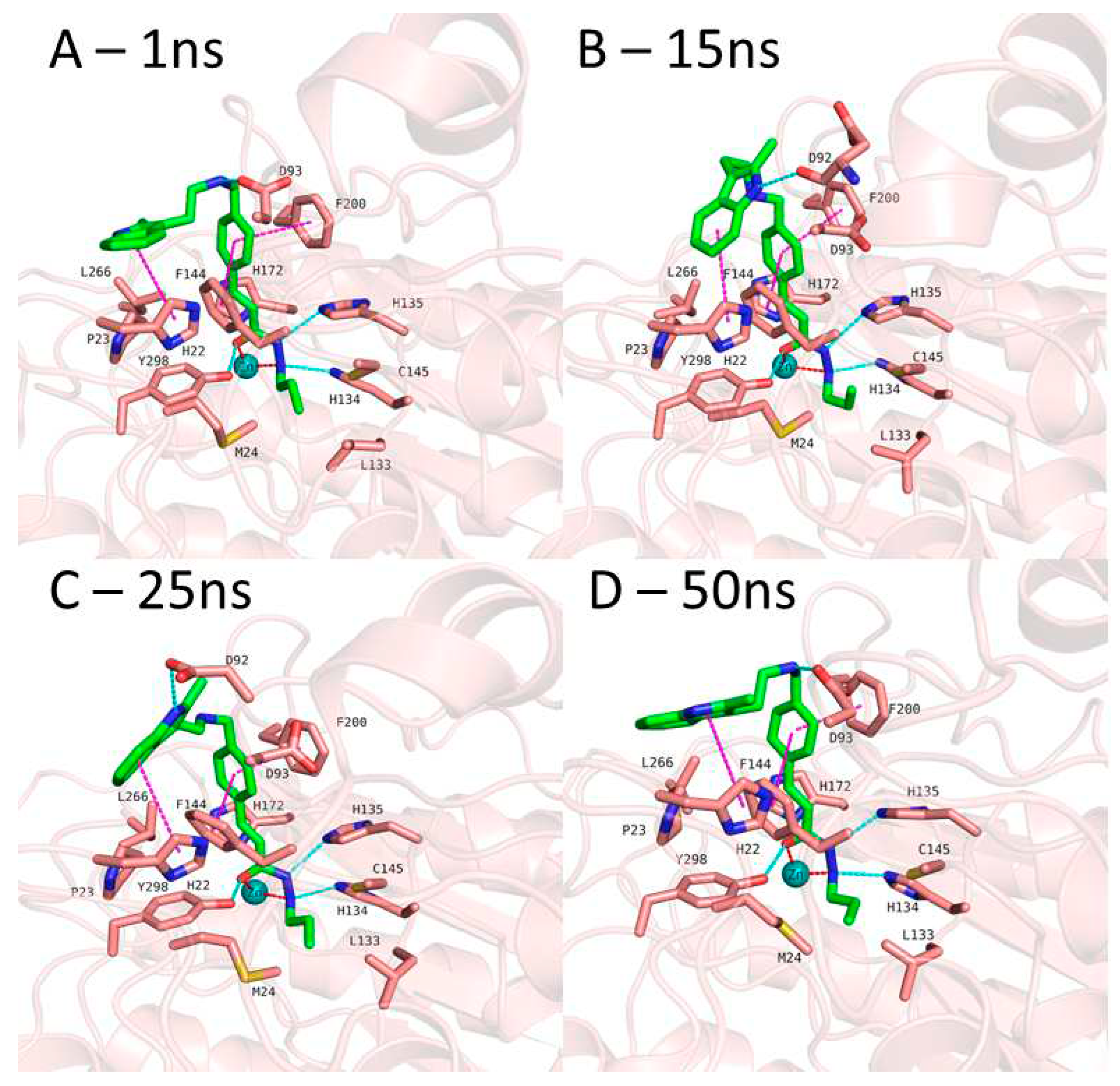
In case of compound 2 (
Figure 7), the flexible 2-methyl-1
H-indole attached to phenyl via (ethylamino)methyl group showed some conformational changes. Hence, the ligand RMSD of compound 2 showed higher fluctuations (
Figure S4, Supplement). The 2-methyl-1
H-indole group changed its conformation and turned down and, then, directed towards D92 and D93 at the surface of the HDAC3. Throughout 50 ns MD simulation, the indole group kept its hydrophobic interactions with H22. The zinc bind group (alkylhydrazide) and the linker group ((prop-1-en-1yl)benzene) of the compound 2 showed a stable binding during the 50 ns MD simulation.
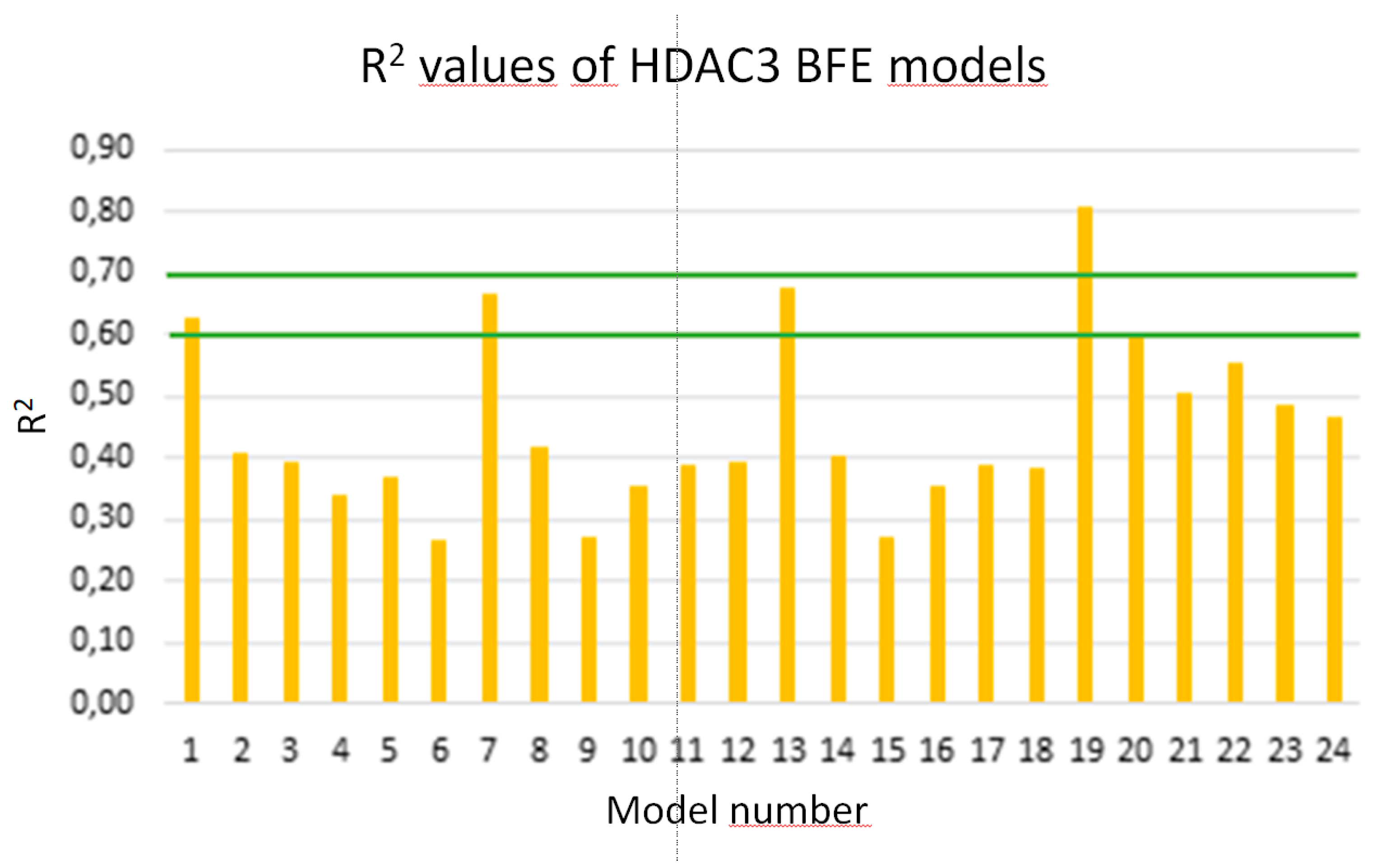
2.5. Binding free energy calculation
Due to the low correlation between docking scores and pIC
50 values, rescoring of the selected docking poses was performed using the MM/GBSA method in AMBER16 [
61]. The total energies of HDAC3-inhibitor complexes were calculated using four different parameter settings (solvation models) and six different frame settings (see Methods part for details). The training set including the 39 compounds was used again for model generation. In total, 24 models were generated. The models were assessed based on the correlation coefficients (Q2, R2) between biological data and calculated energy values (
Figure 8). The prediction results of the training, test set and inactive compounds are shown in
Table S3 (Supplement).
Four models showing an R
2 value > 0.6 were considered for further statistical analysis MODEL1, 7, 13, 19). Interestingly, the selected four models are all based on the protein-ligand complex obtained with one minimization step (Emin1,
Table 6).
Among the selected four models, Model 19 based on the GB8 solvation model showed the lowest RMSE and QMSE values with 0.49 and 0.52, respectively (
Figure 9 and
Table 6). In addition, we tested whether the inclusion a 2D descriptor describing the shape/electronic properties of the inhibitors could improve the models. 2D descriptors were computed for all compounds in MOE [
54]. All available 2D descriptors were tried to assess if they improve the model. The total hydrophobic van der Waals surface area (PEOE_VSA_HYD) gave the best improvement. The combination of the 2D descriptor and selected energy term improved R
2 from 0.81 to 0.87 and Q
2 from 0.78 to 0.84. In addition, MODEL19_1 exhibits lower RMSE and QMSE values compared to MODEL19 (
Table 6).
The test was used to evaluate the accuracy of the best generated model (Model19_1). In the test set (
Table 7), all of the compounds were predicted with less than 1 log unit differences. Additionally, the prediction of the inactive compounds was more satisfying compared to the ligand-based QSAR models, with less than 1 log unit except compound 61 (
Table S3, Supplement). For compound 61, the docking poses could not explain the incorrect prediction. The scatter plot and prediction results were shown in
Figure 7,
Table 7 and
Table S3 (Supplement), respectively.
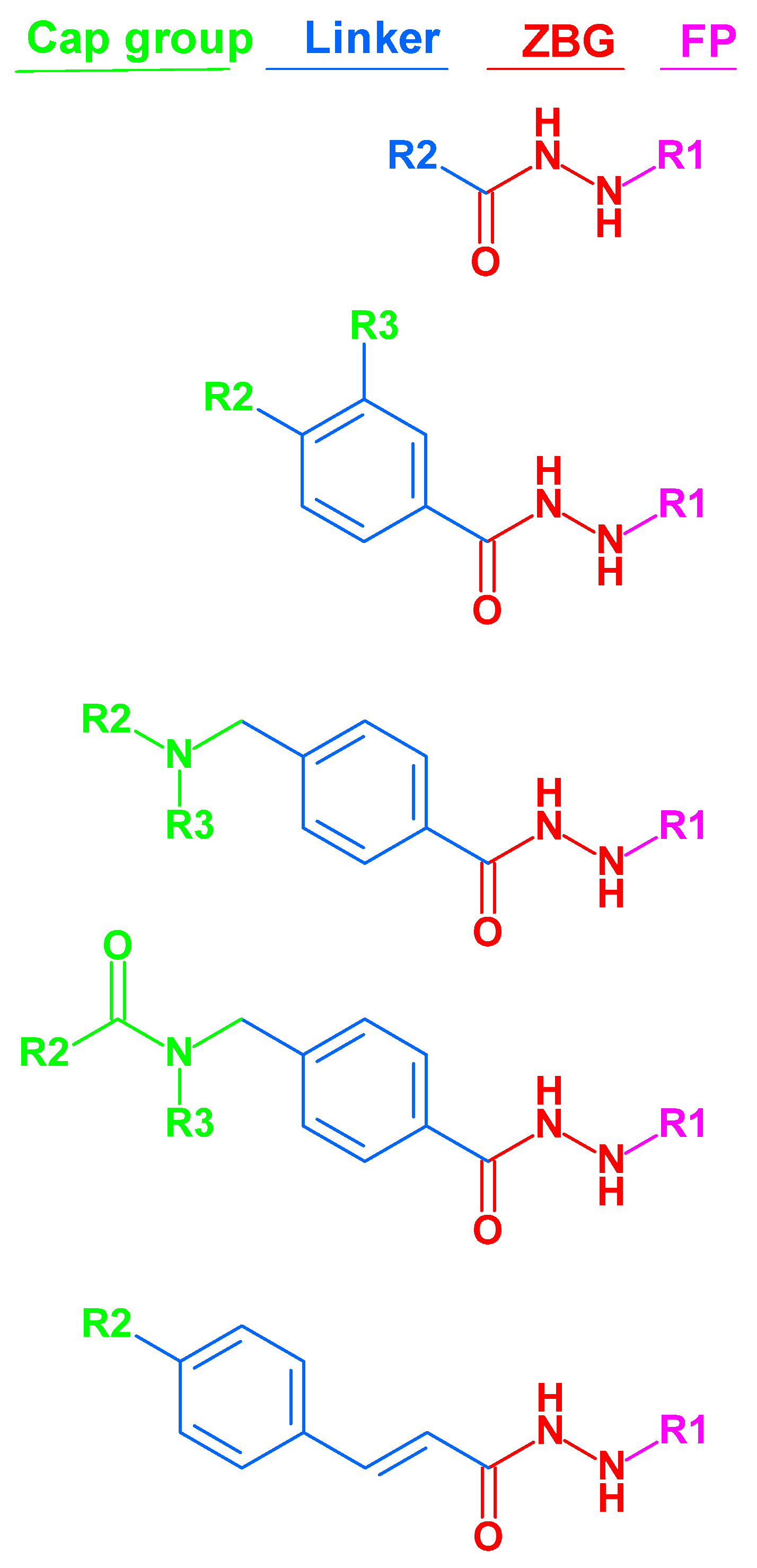
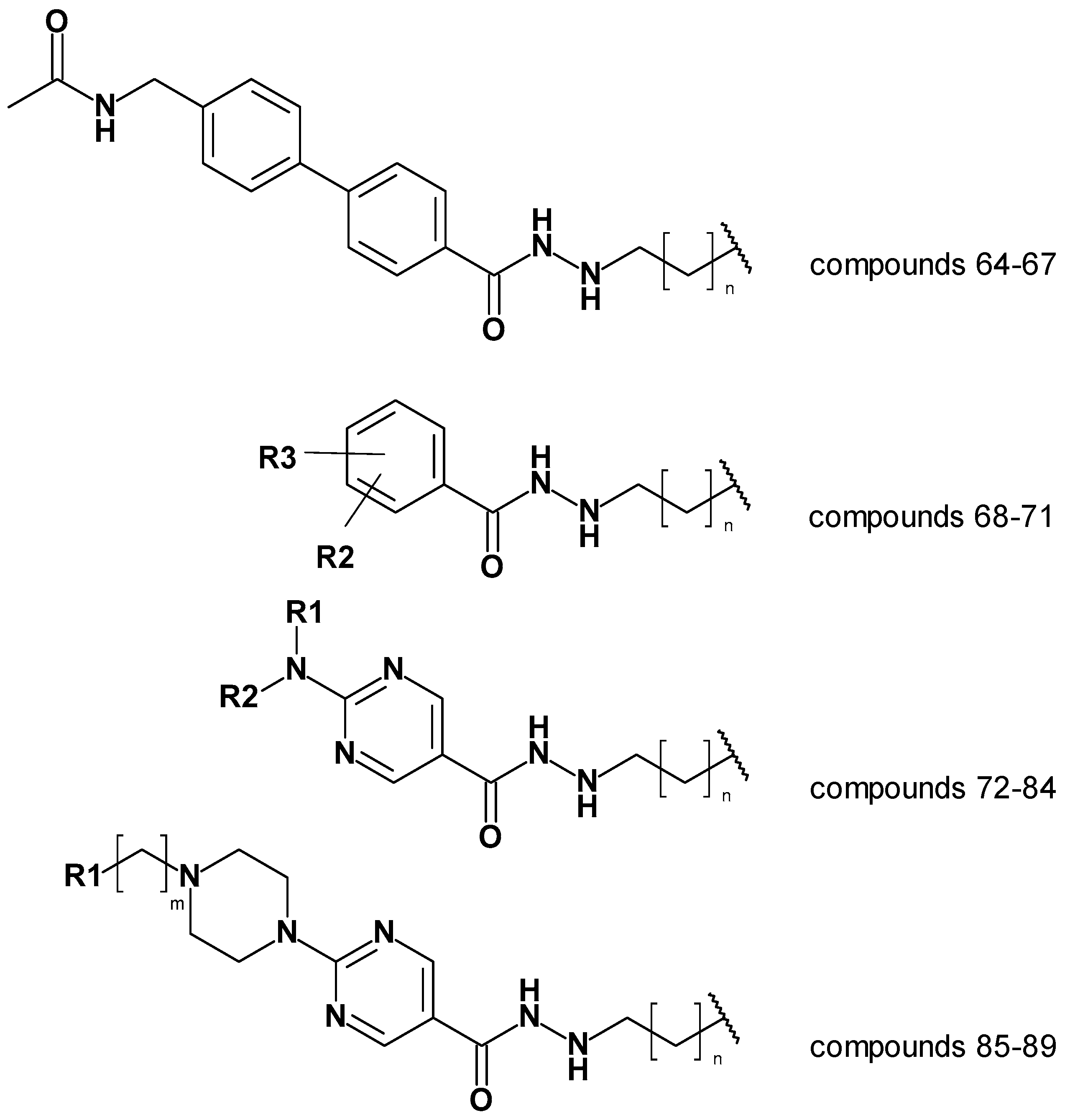
2.6. Evaluation of the generated models on newly designed compounds.
The created models; atom-based 3D QSAR model, Model 19_1, and generated docking poses were then used to predict alkyl hydrazides with other linkers and capping groups that we synthesized (chemistry and in vitro testing has been published elsewhere [
53]. The compounds have been designed starting from compound 47 (
Table S1). Several structural modifications have been carried out to extend the SAR on this series of HDAC inhibitors. In the first series of compounds, the effect of a different length of the alkyl side chain has been evaluated. In the second series of compounds, different substitutions on position 3 or 4 of the phenyl ring have been analyzed. In the next series of compounds, the aminopyrimidine linker group with different
N-arylmethyl,
N-arylethyl, or
N-ethylpiperazynl moieties has been evaluated. In the last series of compounds, piperazynl-piperidine linker group has been attached to the phenylalkylhydrazide core of the compounds. The general structures of the new inhibitors are summarized in
Figure 10. The experimental HDAC3 IC
50 values and the prediction results are shown in
Table 8 and
Tables S5 and S6 (Supplement, all 2D structures are summarized in
Table S4 Supplement).
First, the ligand based models; pharmacophore models and 3D_atom-based QSAR models, were tested. The developed pharmacophore model was used to align the 26 new compounds to apply the atom-based QSAR model.
Analyzing the atom-based prediction results of the 26 new compounds revealed interesting results (
Table 8). Based on the atom-based QSAR model prediction results, the difference between experimental and predicted pIC50 of 9 compounds, which are moderate or inactive compounds, was more than >1 log unit. This is a weak point of the atom-based QSAR model. Although atom-based QSAR prediction has correctly worked for most of the active and highly compounds, this model showed weakness to discriminate the moderate or inactive compounds from active inhibitors.
Then we evaluated the binding free energy based prediction results (
Table 8). Initially, the 26 compounds have been docked to the HDAC3 using the same protocol as for the training set. Similar HDAC3 docking poses as obtained for compound 1 and 2 has been obtained for the new 26 compounds (exemplified in
Figure 11). Among the 26 compounds, the common parts; alkylhydrazide moiety and various aromatic linker groups, exhibited similar interactions as observed for compound 1 and 2. A bidentate chelation between zinc ion and hydrazide moiety was observed for all compounds. In addition, the hydrazide moiety showed hydrogen bonds with H134, H135 and Y298 in the zinc binding region of the HDAC3 catalytic pocket. The aromatic linker groups are accommodated into the hydrophobic tunnel and interact with F144 and F200 showing pi-pi interactions. Besides, the cap groups and foot pocket targeting groups showed significant differences which has an impact on the HDAC3 activity.
In the first series exemplified by compound 64 (
Figure 11), the acetoamidomethyl cap group was placed at the entrance of the pocket and showed hydrogen bond interaction with D93. The different length of the hydrazide alkyl side chain resulted in a crucial difference on HDAC3 activity. Compound 64 possessing a propyl side chain has been predicted as having better pIC50 than 65, 66, and 67. The difference between experimental and predicted values is less than < 1 log unit in this series. Moreover, compound 67 having a hexyl side chain has been predicted to be inactive. This result confirms that the BFE model is sensible to the side chain effects on this dataset.
In the second series, only compound 68 (
Figure 11) bearing the acetamidomethyl cap group and propyl side chain in foot pocket targeting region showed moderate activity on HDAC3. The other compounds 69, 70 and 71 having a hexyl side chain, did not show significant activity on HDAC3. Similar to the experimental activity, the BFE model also predicted the compound 68 as moderate inhibitor, while 69, 70 and 71 have been predicted as inactive compounds.
In the third series of compounds bearing an aminopyrimidine group as linker group, different
N-arylmethyl,
N-arylethyl, or
N-methylpiperaziniyl moieties as capping groups have been tested. This series have been exemplified by compound 72 (
Figure 11). All compounds bearing a propyl side chain except compound 74 have been predicted with less than <1 log unit compared to experimental activities. Interestingly, compound 74 bearing a
N-arylethyl cap group did not show significant inhibitory activity (41%@1µM) on HDAC3. Flexible cap group could cause for the reduced activity on HDAC3. However, the model predicted compound 74 as active inhibitor. Besides, compounds 81-84 possessing a hexyl side chain have been predicted as inactive inhibitors.
The last series of compounds bearing indole or
N-methylindole groups attached via methyl or ethyl bridge to the piperazinylpyrimidine scaffold were predicted close to the experimental activities. The difference between experimental and predicted values is less than <1 log unit. The docking poses of this series have been exemplified by compound 85 (
Figure 11).
In conclusion we applied the validated BFE models to the further development of the alkylhydrazide based class I HDAC inhibitors. The best inhibitors from this series were also tested for their immunmodulatory effects in Jurkat cells and showed promising cellular effects [
53]. As we have recently demonstrated potent T cell memory response by combined class I HDAC inhibition and immune-checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) therapy the new alkylhydrazides represent an interesting class of inhibitors to explore their potential for cancer therapy.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Ligand database preparation
A ligand data set of 63 compounds having hydrazide as zinc binding group (ZBG) was collected from the literature [
46,
48,
50]. Only compounds having an
N-monosubstituted hydrazide scaffold were considered. The IC
50 values of the selected compounds were retrieved from three publications and they all were determined against HDAC3 using the same fluorogenic substrate (Boc-Lys(acetyl)-AMC (amino methyl coumarin)). The same human recombinant HDAC3 enzyme was used for the in vitro studies [
46,
48,
50]. The compounds were prepared in ligprep tool using the OPLS3e forcefield in Schrödinger suite [
62]. Subsequently, the output of the ligprep step was submitted the Confgen to generate 64 conformers per ligand while minimizing the output conformers using the OPLS3e forcefield [
62,
63]. The compounds were automatically divided into training (70 %) and external test set (30 %) using the “RAND” function in MOE program (MOE – Molecular database calculator- RAND) [
54]. The same training set and external test set were used for the model development studies. The compounds having no exact IC
50 values were considered as inactive. The QSAR models were built using the most active and moderate inhibitors for which exact IC
50 values were available.
The diversity analysis of the compounds was performed by analyzing the three most important principal components using the principal component analysis (PCA) implemented in MOE [
54,
55,
56]. The 2D descriptors were computed in MOE [
54]. Several 2D descriptors were selected using the Contingency tool in MOE. The three most important principal components (PCA1, PCA2, PCA3) were calculated using the selected 2D descriptors. These principal components were used to check the diversity of the compounds.
The 26 compounds have been collected from the article published by our group to evaluate the established models and check their reliability on different dataset [
53]. The ligands have been prepared using the same protocol with validation set.
3.2. Pharmacophore Model
The pharmacophore model was established using 30 inhibitors having IC
50 values lower than 100 nM in the training set and the 7 inactive compounds in Phase module of Schrödinger [
57]. The compounds were prepared in ligprep using OPLS3e forcefield in the previous step [
62,
63]. The conformational search was performed in phase module by adjusting 64 conformers per compound and minimizing the output conformers using the “Develop Pharmacophore model” module in Schrödinger [
57]. The common pharmacophore hypotheses were developed, scored and ranked. The selected pharmacophore model was used as an alignment rule for atom-based 3D-QSAR model.
3.3. Atom-based 3D-QSAR model
The ligand-based 3D-QSAR model was generated using the training data set in Phase module of Schrödinger [
57]. The 39 compounds in the training database were aligned using the selected pharmacophore hypothesis from the previous step. The QSAR models were built with four latent factor and 1.0 Å grid spacing as well as leave-one-out-cross-validation approach. The generated models were evaluated by means of standard deviation of the regression (SD), R
2 (correlation coefficient of regression), RMSE (root mean square error of test set prediction), Q
2 (cross-training of test set prediction).
3.4. Docking study
The hydroxamic acid scaffold and hydrazide scaffold are structurally similar groups. Therefore, X-ray crystal structures of HDAC2 (PDB ID: 4LXZ [
35]) and HDAC3 (PDB ID: 4A69 [
60]) were retrieved from the Protein Data Bank (PDB,
rcsb.org [
64]) and analyzed in MOE [
54]. SAHA having hydroxamic acid scaffold in complex with HDAC2 protein (PDB ID: 4LXZ) was defined as pan-HDAC inhibitor and shows activity on HDAC3 [
35]. First, the HDAC2 (PDB ID: 4LXZ) and HDAC3 (PDB ID: 4A69) were superposed in MOE [
54]. Then, SAHA was transferred from the HDAC2 protein (PDB ID: 4LXZ) to HDAC3 to mimic the induced fit effect of the zinc binding group.
The HDAC3-SAHA complex was prepared in the protein preparation wizard of Schrödinger’s suite by adding hydrogen bonds and missing side chains and assigning the bond orders [
62]. The water molecules (except W2083) and ions (except Zn
+2 ion) were deleted. The protonation states and tautomers were optimized at pH 7.4 using PROPKA tool. The optimized complex was minimized using the OPLS3e force field to remove the steric clashes [
63].
Molecular docking studies were done applying the standard precision (SP) mode in Glide implemented in Schrödinger Suite [
62]. The grid box including the information of active site coordinates of the proteins was defined with 10 Å radius around the ligand. Ten docking poses were employed for further post-docking minimization. The other settings were kept as default. The docking results were visually analyzed in MOE program [
54].
3.5. Molecular dynamics simulation
The selected docking poses of the compound 1 and 2 in complex with HDAC3 (PDB ID: 4A69) was subjected to a 50 ns MD simulation in AMBER16 [
61]. Antechamber package was used to prepare the topologies, force field parameters, atom types and bond types by applying the semi-empirical Austin Model1 with bond charge correction (AM1-BCC) [
65,
66]. Then, the tLEaP module was employed to prepare the protein-ligand complexes. General amber force field (GAFF), the Duan force field (ff03.r1) and 12-6-4LJ ionic model were used for ligand, protein and zinc, respectively [
67,
68,
69,
70]. The system was solvated by TIP3P water model, and a margin of 10 Å. Two minimization steps including the two sub-steps in each minimization were carried out. In the first step, 4000 iterations (2000 cycles of steepest descent and then 2000 conjugate gradient) were performed, while the protein residues, ligand and zinc ion were restrained to their initial geometries (force constant of 10 kcal*mol
-1* Å
-2) to relieve the bad contacts. In the second step, 4000 iterations (2000 cycles of steepest descent and then 2000 conjugate gradient) were performed to remove the steric clashes in the entire complex. The restraint on the protein, ligand and zinc were removed during the second minimization. Then, the system was heated at 300 K through 100 ps of MD. The protein-ligand complex was restrained to prevent large structural deviations (force constant of 10 kcal*mol
-1* Å
-2). The SHAKE algorithm was activated to constrain bonds involving hydrogens [
71]. Finally, the system was equilibrated within a period of 200 ps. Langevin dynamics was applied to keep the temperature of 300 K with a collision frequency of 2 ps [
72]. The pressure was kept at 1 bar using isotropic position scaling with a relaxation time of 2 ps. Afterwards, a 50 ns MD simulation was run with a time step of 2 fs using the same conditions as in the equilibration step. A non-bonded cut-off distance was 10 Å was used. The electrostatic interactions were calculated by applying the particle mesh Ewald (PME) method. After the MD simulation, CPPTRAJ module of AMBER was used to analyze the MD snapshots.
3.6. Binding free energy calculation
Binding free energies (BFE) of the prepared protein-ligand complexes were calculated using the AMBER16 program [
61]. The MMPBSA.py script was utilized for calculations [
73]. Different implicit solvent models (GB
HCT (igb = 1), GB
OBC (igb = 2), GB
OBC2 (igb = 5), and GBn (igb = 8) were tested [
74,
75,
76]. Molecular mechanics (MM) and solvent models were combined for the MMGBSA calculations [
77,
78,
79]. The results of BFE were analyzed using the following six different methods: 1) single frame at the first minimization step (Emin1), 2) single frame at the second minimization step (Emin2), 3) single frame at the third minimization after MD (Emin3), 4) 1-50 frames during MD (MD-1) with an interval of 5, 5) 51-100 frames during MD (MD-2) with an interval of 5, 6) 101-500 frames during MD (MD-3) with an interval of 5. The correlation between biological activity and the energy results was measured by using the QSAR tool in MOE program [
54].
4. Conclusion
In the current study, we have evaluated several QSAR models including ligand-based and structure-based techniques to understand the structure-activity relationship of alkylhydrazides developed as HDAC3 inhibitors. Additionally, the binding modes of the most potent two HDAC3 inhibitors (compounds 1 and 2) were verified through 50 ns MD simulation, since there is no X-ray structure crystallized with a alkylhydrazide derivative.
The ligand based models enabled us to obtain a general overview of the binding of the compounds in HDAC3 protein. Established pharmacophore model and atom-based 3D-QSAR model can be used to filter the big databases. However, the predictive power of the ligand-based models was not satisfactory. These models predicted moderate inhibitors and inactive compounds as active compounds, although they predict the actives as actives. Thus, these methods should be used to reduce the number of compounds in the big database.
The weakness of the ligand-based methods directed us to generate the structure-based methods. The binding mode of the alkylhydrazide predicted by docking. The selected binding modes from the validation set (compounds 1 and 2) were verified by the short 50 ns MD simulation. The analysis of the MD simulation revealed that the M24 and L133 are gatekeepers in the foot pocket of HDAC3. Additionally, the alkylhydrazides kept their bidentate chelation to zinc ion during the 50 ns MD simulation. The compounds were rescored by means of BFE calculations. The binding free energies were correlated with experimental derived inhibitory activities. The established binding free energy based QSAR model predicted the all compounds in the test set with less than 1 log differences. Additionally, we have tested the established model on a new dataset containing 26 molecules which have been designed, synthesized, tested taking knowledge of the developed BFE models [
53]. The structure based model was able to predict these novel compounds with less than 1 log unit error and showed its value for the chemical optimization. For the different test sets, the structure based model showed better accuracy than the ligand based models.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org., Figure S1: Visualization of Atom-based 3D-QSAR model in training set; Figure S2: Docking poses of training set, external test set and inactive set; Figure S3: 50ns MD results for the HDAC3-1 complex; Figure S4: 50ns MD results for the HDAC3-2 complex; Table S1: 2D chemical structures and biological data of compounds in training set, external test set and inactive set; Table S2: Prediction values of the best atom-based QSAR model generated for training set, test set and inactive set in HDAC3; Table S3: Prediction values of the best BFE model generated for training set, test set and inactive set in HDAC3; Table S4: 2D chemical structures and biological data of test set; Table S5: Prediction values of the best atom-based QSAR model generated for test set in HDAC3 ; Table S6: Prediction values of the best BFE model generated for test set in HDAC3.
Author Contributions
EFB and DR did the computational studies and wrote the manuscript. JM and DR supervised the MD simulations and revised the manuscript. PS, FM and MZ carried out the data correction and statistical tests and wrote part of the manuscript. MS and WS supervised the experiments and revised the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) SI868/22-1 project number 46995445 (to W.S.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Weinhold, B. Epigenetics: the science of change. Environ Health Perspect 2006, 114, A160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraczek, J.; van Grunsven, L.A.; Vinken, M.; Snykers, S.; Deleu, S.; Vanderkerken, K.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. Histone deacetylase inhibition and the regulation of cell growth with particular reference to liver pathobiology. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 2009, 13, 2990–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.J.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Li, J. Epigenetic modifications by histone deacetylases: Biological implications and therapeutic potential in liver fibrosis. Biochimie 2015, 116, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: implications for disease and therapy. Nature Reviews Genetics 2009, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of Histone Acetylation: The Histone Deacetylase Enzymes. Csh Perspect Biol 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melesina, J.; Simoben, C.V.; Praetorius, L.; Bulbul, E.F.; Robaa, D.; Sippl, W. Strategies To Design Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Chemmedchem 2021, 16, 1336–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolden, J.E.; Peart, M.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006, 5, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoretti, I.V.; Lee, Y.M.; Goodson, H.V. Molecular evolution of the histone deacetylase family: Functional implications of phylogenetic analysis. Journal of Molecular Biology 2004, 338, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildmann, C.; Riester, D.; Schwienhorst, A. Histone deacetylases--an important class of cellular regulators with a variety of functions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2007, 75, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barneda-Zahonero, B.; Parra, M. Histone deacetylases and cancer. Mol Oncol 2012, 6, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denslow, S.A.; Wade, P.A. The human Mi-2/NuRD complex and gene regulation. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5433–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozinger, C.M.; Schreiber, S.L. Deacetylase enzymes: biological functions and the use of small-molecule inhibitors. Chemistry & Biology 2002, 9, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laherty, C.D.; Yang, W.M.; Sun, J.M.; Davie, J.R.; Seto, E.; Eisenman, R.N. Histone deacetylases associated with the mSin3 corepressor mediate Mad transcriptional repression. Cell 1997, 89, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, R.E.; Fairall, L.; Saleh, A.; Kelsall, E.; Morris, K.L.; Ragan, T.J.; Savva, C.G.; Chandru, A.; Millard, C.J.; Makarova, O.V.; et al. The MiDAC histone deacetylase complex is essential for embryonic development and has a unique multivalent structure. Nature Communications 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.T.; Wong, J.M.; Moreno, G.T.; Young, M.K.; Cote, J.; Wang, W.D. NURD, a novel complex with both ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling and histone deacetylase activities. Molecular Cell 1998, 2, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.W.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.X.; Nawaz, Z.; Liu, J.M.; Qin, J.; Wong, J.M. Both corepressor proteins SMRT and N-CoR exist in large protein complexes containing HDAC3. Embo Journal 2000, 19, 4342–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberoi, J.; Fairall, L.; Watson, P.J.; Yang, J.C.; Czimmerer, Z.; Kampmann, T.; Goult, B.T.; Greenwood, J.A.; Gooch, J.T.; Kallenberger, B.C.; et al. Structural basis for the assembly of the SMRT/NCoR core transcriptional repression machinery. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2011, 18, 177–U239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Chen, Z.X.; Fredrickson, T.; Zhu, Y.; Kirkpatrick, R.; Zhang, G.F.; Johanson, K.; Sung, C.M.; Liu, R.G.; Winkler, J. Cloning and characterization of a novel human. Class I histone deacetylase that functions as a transcription repressor. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2000, 275, 15254–15264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.S. A short guide to histone deacetylases including recent progress on class II enzymes. Experimental and Molecular Medicine 2020, 52, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, F.; Zand, H.; Nosrat-Mirshekarlou, E.; Najafi, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. The role dietary of bioactive compounds on the regulation of histone acetylases and deacetylases: A review. Gene 2015, 562, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, W.W.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, Y.; Wuensche, P.; Alvarez, R.; Wen, D.L.; Aribi, A.M.; Thean, S.M.; Doan, N.B.; Said, J.W.; et al. Growth Inhibition of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Belinostat Through Suppression of Multiple Pathways Including HIF, NFkB, and mTOR Signaling In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol Carcinogen 2014, 53, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furumai, R.; Matsuyama, A.; Kobashi, N.; Lee, K.H.; Nishiyama, N.; Nakajima, I.; Tanaka, A.; Komatsu, Y.; Nishino, N.; Yoshida, M.; et al. FK228 (depsipeptide) as a natural prodrug that inhibits class I histone deacetylases. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 4916–4921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mann, B.S.; Johnson, J.R.; He, K.; Sridhara, R.; Abraham, S.; Booth, B.P.; Verbois, L.; Morse, D.E.; Jee, J.M.; Pope, S.; et al. Vorinostat for treatment of cutaneous manifestations of advanced primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Clinical Cancer Research 2007, 13, 2318–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraj, D.; Green, M.M.; Gasparetto, C. Panobinostat for the management of multiple myeloma. Future Oncol 2017, 13, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, M.F.; Ballestar, E.; Villar-Garea, A.; Boix-Chornet, M.; Espada, J.; Schotta, G.; Bonaldi, T.; Haydon, C.; Ropero, S.; Petrie, K.; et al. Loss of acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Nat Genet 2005, 37, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryder, B.E. Targeted cancer therapy: giving histone deacetylase inhibitors all they need to succeed (vol 4, pg 505, 2012). Future Med Chem 2012, 4, 1369–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, G.S.; Robaa, D.; Forgione, M.; Sippl, W.; Rotili, D.; Mai, A. Lysine Deacetylase Inhibitors in Parasites: Past, Present, and Future Perspectives. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2017, 60, 4780–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, K.; Peixoto, E.; Richard, S.; Gradilone, S.A. Role of Histone Deacetylases in Carcinogenesis: Potential Role in Cholangiocarcinoma. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Brosch, G.; Kolle, D.; Scherf, H.; Gerhauser, C.; Loidl, P. Amide analogues of trichostatin A as inhibitors of histone deacetylase and inducers of terminal cell differentiation. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 1999, 42, 4669–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, E.F.; Melesina, J.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Abdelsalam, M.; Vecchio, A.; Robaa, D.; Zessin, M.; Schutkowski, M.; Sippl, W. Docking, Binding Free Energy Calculations and In Vitro Characterization of Pyrazine Linked 2-Aminobenzamides as Novel Class I Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burli, R.W.; Luckhurst, C.A.; Aziz, O.; Matthews, K.L.; Yates, D.; Lyons, K.A.; Beconi, M.; McAllister, G.; Breccia, P.; Stott, A.J.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Potent and Selective Class IIa Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Potential Therapy for Huntington's Disease. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2013, 56, 9934–9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimburg, T.; Chakrabarti, A.; Lancelot, J.; Marek, M.; Melesina, J.; Hauser, A.T.; Shaik, T.B.; Duclaud, S.; Robaa, D.; Erdmann, F.; et al. Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of Novel Inhibitors Targeting HDAC8 from Schistosoma mansoni for the Treatment of Schistosomiasis. J Med Chem 2016, 59, 2423–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.S.; Abdelsalam, M.; Zeyn, Y.; Zessin, M.; Mustafa, A.M.; Fischer, M.A.; Zeyen, P.; Sun, P.; Bulbul, E.F.; Vecchio, A.; et al. Synthesis, Molecular Docking and Biological Characterization of Pyrazine Linked 2-Aminobenzamides as New Class I Selective Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors with Anti-Leukemic Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauffer, B.E.; Mintzer, R.; Fong, R.; Mukund, S.; Tam, C.; Zilberleyb, I.; Flicke, B.; Ritscher, A.; Fedorowicz, G.; Vallero, R.; et al. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor kinetic rate constants correlate with cellular histone acetylation but not transcription and cell viability. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 26926–26943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckhurst, C.A.; Breccia, P.; Stott, A.J.; Aziz, O.; Birch, H.L.; Burli, R.W.; Hughes, S.J.; Jarvis, R.E.; Lamers, M.; Leonard, P.M.; et al. Potent, Selective, and CNS-Penetrant Tetrasubstituted Cyclopropane Class Ila Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors. Acs Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2016, 7, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, M.; Ramos-Morales, E.; Picchi-Constante, G.F.A.; Bayer, T.; Norstrom, C.; Herp, D.; Sales, P.A.; Guerra-Slompo, E.P.; Hausmann, K.; Chakrabarti, A.; et al. Species-selective targeting of pathogens revealed by the atypical structure and active site of Trypanosoma cruzi histone deacetylase DAC2. Cell Rep 2021, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, M.; Shaik, T.B.; Heimburg, T.; Chakrabarti, A.; Lancelot, J.; Ramos-Morales, E.; Da Veiga, C.; Kalinin, D.; Melesina, J.; Robaa, D.; et al. Characterization of Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) Selective Inhibition Reveals Specific Active Site Structural and Functional Determinants. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2018, 61, 10000–10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoben, C.V.; Robaa, D.; Chakrabarti, A.; Schmidtkunz, K.; Marek, M.; Lancelot, J.; Kannan, S.; Melesina, J.; Shaik, T.B.; Pierce, R.J.; et al. A Novel Class of Schistosoma mansoni Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) Inhibitors Identified by Structure-Based Virtual Screening and In Vitro Testing. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.F.; Wiest, O.; Helquist, P.; Lan-Hargest, H.Y.; Wiech, N.L. On the function of the 14 angstrom long internal cavity of histone deacetylase-like protein: Implications for the design of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2004, 47, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, J.C.; Jennings, A.J.; Skene, R.; Wu, Y.Q.; Melkus, R.; De Jong, R.; O'Connell, S.; Grimshaw, C.E.; Navre, M.; Gangloff, A.R. Exploration of the HDAC2 foot pocket: Synthesis and SAR of substituted N-(2-aminophenyl)benzamides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2010, 20, 3142–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Kelly, J.; Yu, W.S.; Clausen, D.; Yu, Y.N.; Kim, H.; Duffy, J.L.; Chung, C.C.; Myers, R.W.; Carroll, S.; et al. Selective Class I HDAC Inhibitors Based on Aryl Ketone Zinc Binding Induce HIV-1 Protein for Clearance. Acs Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2020, 11, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, F.F.; Weiwer, M.; Steinbacher, S.; Schomburg, A.; Reinemer, P.; Gale, J.P.; Campbell, A.J.; Fisher, S.L.; Zhao, W.N.; Reis, S.A.; et al. Kinetic and structural insights into the binding of histone deacetylase 1 and 2 (HDAC1, 2) inhibitors. Bioorgan Med Chem 2016, 24, 4008–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.S.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.N.; Zhang, V.; Clausen, D.; Kelly, J.; Wolkenberg, S.; Beshore, D.; Duffy, J.L.; Chung, C.C.; et al. Discovery of ethyl ketone-based HDACs 1, 2, and 3 selective inhibitors for HIV latency reactivation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.N.; Kelly, J.; Sha, D.Y.; Alhassan, A.B.; Yu, W.S.; Maletic, M.M.; Duffy, J.L.; Klein, D.J.; Holloway, M.K.; et al. Discovery of Highly Selective and Potent HDAC3 Inhibitors Based on a 2-Substituted Benzamide Zinc Binding Group. Acs Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2020, 11, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Xu, J.; Yue, K.R.; Huang, C.; Qin, M.T.; Chi, D.Y.; Yu, Q.X.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, X.H.; Xu, T.Q.; et al. Potent Hydrazide-Based HDAC Inhibitors with a Superior Pharmacokinetic Profile for Efficient Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia In Vivo. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2022, 65, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, M.V.; Konduktorov, K.A.; Shcherbakova, A.S.; Kochetkov, S.N. Synthesis of N '-propylhydrazide analogs of hydroxamic inhibitors of histone deacetylases (HDACs) and evaluation of their impact on activities of HDACs and replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2019, 29, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Peterson, Y.K.; Xu, T.Q.; Himes, R.A.; Luo, X.; Yin, G.L.; Inks, E.S.; Dolloff, N.; Halene, S.; et al. Design of Hydrazide-Bearing HDACIs Based on Panobinostat and Their p53 and FLT3-ITD Dependency in Antileukemia Activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 63, 5501–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Peterson, Y.K.; Inks, E.S.; Himes, R.A.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Kong, X.J.; Chou, C.J. Class I HDAC Inhibitors Display Different Antitumor Mechanism in Leukemia and Prostatic Cancer Cells Depending on Their p53 Status. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2018, 61, 2589–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Inks, E.S.; Peterson, Y.K.; Li, J.Y.; Chou, C.J. Development of Allosteric Hydrazide-Containing Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors for Use in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 59, 9942–9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Stowe, R.L.; Pinello, C.E.; Tian, G.M.; Madoux, F.; Li, D.W.; Zhao, L.S.Y.; Li, J.L.; Wang, Y.R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Benzoylhydrazide Scaffold that Selectively Inhibit Class I Histone Deacetylases. Chemistry & Biology 2015, 22, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.S.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Zheng, G.R.; Zhang, X.; Liao, D.Q. Discovery of histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3)-specific PROTACs. Chem Commun 2020, 56, 9866–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping Sun, J.W. , Khadija Shahed Khan, Weiqin Yang, Wai-Lung Ng, Nikita Ilment,, Matthes Zessin, Emre F. Bülbül, Dina Robaa, Frank Erdmann,Matthias Schmidt, Christophe Romier, Mike Schutkowski, Alfred Sze-Lok Cheng, Wolfgang Sippl. Development of alkylated hydrazides as highly potent and selective class I HDAC inhibitors with T cell modulatory properties. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2022, 65, 16313–16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
Molecular operating Environment (MOE), 2019.01, Chemical Computing Group (CCG): 1010 Sherbooke St. West, Suite 910, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3A 2R7, 2019.
- Carey, R.N.; Wold, S.; Westgard, J.O. Principal component analysis: an alternative to "referee" methods in method comparison studies. Anal Chem 1975, 47, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: a review and recent developments. Philos T R Soc A 2016, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
Schrödinger Release 2019-1: Phase, Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY (USA), 2019.
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Knoll, E.H.; Rao, S.N.; Shaw, D.E.; Friesner, R.A. PHASE: a new engine for pharmacophore perception, 3D QSAR model development, and 3D database screening: 1. Methodology and preliminary results. J Comput Aid Mol Des 2006, 20, 647–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Rao, S.N. PHASE: A novel approach to pharmacophore modeling and 3D database searching. Chem Biol Drug Des 2006, 67, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.J.; Fairall, L.; Santos, G.M.; Schwabe, J.W.R. Structure of HDAC3 bound to co-repressor and inositol tetraphosphate. Nature 2012, 481, 335–U114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D.A. Case, R.M.B., D. D.A. Case, R.M.B., D.S. Cerutti, T.E. Cheatham, III, T.A. Darden, R.E. Duke, T.J. Giese, H. Gohlke, A.W. Goetz, N. Homeyer, S. Izadi, P. Janowski, J. Kaus, A. Kovalenko, T.S. Lee, S. LeGrand, P. Li, C. Lin, T. Luchko, R. Luo, B. Madej, D. Mermelstein, K.M. Merz, G. Monard, H. Nguyen, H.T. Nguyen, I. Omelyan, A. Onufriev, D.R. Roe, A. Roitberg, C. Sagui, C.L. Simmerling, W.M. Botello-Smith, J. Swails, R.C. Walker, J. Wang, R.M. Wolf, X. Wu, L. Xiao and P.A. Kollman. AMBER2016, University of Claiforni, San Francisco. 2016.
-
Schrödinger Release 2019-1: Maestro, Protein Preparation Wizard, prime, Epik, Ligprep, Confgen, Glide, Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY (USA), 2019.
- Harder, E.; Damm, W.; Maple, J.; Wu, C.J.; Reboul, M.; Xiang, J.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Lupyan, D.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Knight, J.L.; et al. OPLS3: A Force Field Providing Broad Coverage of Drug-like Small Molecules and Proteins. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 2016, 12, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Research 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakalian, A.; Jack, D.B.; Bayly, C.I. Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2002, 23, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakalian, A.; Bush, B.L.; Jack, D.B.; Bayly, C.I. Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic Charges. AM1-BCC model: I. Method. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2000, 21, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.F.; Song, L.F.; Merz, K.M. Parameterization of Highly Charged Metal Ions Using the 12-6-4 LJ-Type Nonbonded Model in Explicit Water. Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2015, 119, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Duan, Y. Distinguish protein decoys by using a scoring function based on a new AMBER force field, short molecular dynamics simulations, and the generalized born solvent model. Proteins-Structure Function and Bioinformatics 2004, 55, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wu, C.; Chowdhury, S.; Lee, M.C.; Xiong, G.M.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Cieplak, P.; Luo, R.; Lee, T.; et al. A point-charge force field for molecular mechanics simulations of proteins based on condensed-phase quantum mechanical calculations. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2003, 24, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Paul Ryckaert, G.C. , Herman J. C. Berendsen. Numerical integration of the cartesan equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. Journal of Computational Physics 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, R.W.; Brooks, B.R.; Szabo, A. An analysis of the accuracy of Langevin and molecular dynamics algorithms. Molecular Physics 1988, 65, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.R., 3rd; McGee, T.D., Jr.; Swails, J.M.; Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H.; Roitberg, A.E. MMPBSA.py: An Efficient Program for End-State Free Energy Calculations. J Chem Theory Comput 2012, 8, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onufriev, A.; Bashford, D.; Case, D.A. Exploring protein native states and large-scale conformational changes with a modified generalized born model. Proteins-Structure Function and Bioinformatics 2004, 55, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, G.D.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Parametrized models of aqueous free energies of solvation based on pairwise descreening of solute atomic charges from a dielectric medium. J Phys Chem-Us 1996, 100, 19824–19839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, M.; Onufriev, A.; Lee, M.S.; Im, W.; Case, D.A.; Brooks, C.L. Performance comparison of generalized born and Poisson methods in the calculation of electrostatic solvation energies for protein structures. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2004, 25, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, B.; Sippl, W. Docking and binding free energy calculations of sirtuin inhibitors. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 93, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods to estimate ligand-binding affinities. Expert Opin Drug Dis 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cournia, Z.; Allen, B.; Sherman, W. Relative Binding Free Energy Calculations in Drug Discovery: Recent Advances and Practical Considerations. J Chem Inf Model 2017, 57, 2911–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Structures of alkylated hydrazide based HDAC inhibitors that have been used in this article. (The molecular structures of all compounds under study are shown in
Table S1, Supplement.) FP: Foot pocket.
Figure 1.
Structures of alkylated hydrazide based HDAC inhibitors that have been used in this article. (The molecular structures of all compounds under study are shown in
Table S1, Supplement.) FP: Foot pocket.
Figure 2.
A) Field histogram to visualize the variation of the three most important principal components for the training set. B) Field histogram to visualize the variation of the three most important principal components for the test set. C) 3D plot of the first tree PCAs. Training set is colored as black, test set is colored orange.
Figure 2.
A) Field histogram to visualize the variation of the three most important principal components for the training set. B) Field histogram to visualize the variation of the three most important principal components for the test set. C) 3D plot of the first tree PCAs. Training set is colored as black, test set is colored orange.
Figure 3.
A) Developed pharmacophore model (ADDDHRR) for HDAC3 inhibitors. B) Superposition of compound 1 and the pharmacophore hypothesis (acceptor –red color, donor – cyan color, hydrophobic – green color, ring orange color).
Figure 3.
A) Developed pharmacophore model (ADDDHRR) for HDAC3 inhibitors. B) Superposition of compound 1 and the pharmacophore hypothesis (acceptor –red color, donor – cyan color, hydrophobic – green color, ring orange color).
Figure 4.
Scatter plot of the best ligand-based QSAR model for training set (black) and test set (orange).
Figure 4.
Scatter plot of the best ligand-based QSAR model for training set (black) and test set (orange).
Figure 5.
Docking poses of 1 (A, green colored sticks), 2 (B, orange colored sticks) in HDAC3 (PDB ID: 4A69). Hydrogen bonds (cyan dashed lines), hydrophobic interactions (magenta dashed lines) and metal coordination (red dashed lines) between inhibitors and the protein are shown. Relevant residues are shown in stick representation with salmon carbon atoms in HDAC3. The zinc ion is shown as cyan colored sphere. The conserved water molecule is shown as red sphere.
Figure 5.
Docking poses of 1 (A, green colored sticks), 2 (B, orange colored sticks) in HDAC3 (PDB ID: 4A69). Hydrogen bonds (cyan dashed lines), hydrophobic interactions (magenta dashed lines) and metal coordination (red dashed lines) between inhibitors and the protein are shown. Relevant residues are shown in stick representation with salmon carbon atoms in HDAC3. The zinc ion is shown as cyan colored sphere. The conserved water molecule is shown as red sphere.
Figure 6.
MD frames of HDAC3-1 complex. A) Frame at 1ns MD simulation, B) Frame at 15ns MD simulation, C) Frame at 25ns MD simulation, D) Frame at 50ns MD simulation, Hydrogen bonds (cyan dashed lines), hydrophobic interactions (magenta dashed lines) and metal coordination (red dashed lines) between inhibitors and the protein are shown. Relevant residues are shown in stick representation with salmon carbon atoms in HDAC3. Ligand is shown in stick representation with green carbon atoms. The zinc ion is shown as cyan colored sphere.
Figure 6.
MD frames of HDAC3-1 complex. A) Frame at 1ns MD simulation, B) Frame at 15ns MD simulation, C) Frame at 25ns MD simulation, D) Frame at 50ns MD simulation, Hydrogen bonds (cyan dashed lines), hydrophobic interactions (magenta dashed lines) and metal coordination (red dashed lines) between inhibitors and the protein are shown. Relevant residues are shown in stick representation with salmon carbon atoms in HDAC3. Ligand is shown in stick representation with green carbon atoms. The zinc ion is shown as cyan colored sphere.
Figure 7.
MD frames of HDAC3-2 complex. A) Frame at 1ns MD simulation, B) Frame at 15ns MD simulation, C) Frame at 25ns MD simulation, D) Frame at 50ns MD simulation, Hydrogen bonds (cyan dashed lines), hydrophobic interactions (magenta dashed lines) and metal coordination (red dashed lines) between inhibitors and the protein are shown. Relevant residues are shown in stick representation with salmon carbon atoms in HDAC3. Ligand is shown in stick representation with green carbon atoms. The zinc ion is shown as cyan colored sphere.
Figure 7.
MD frames of HDAC3-2 complex. A) Frame at 1ns MD simulation, B) Frame at 15ns MD simulation, C) Frame at 25ns MD simulation, D) Frame at 50ns MD simulation, Hydrogen bonds (cyan dashed lines), hydrophobic interactions (magenta dashed lines) and metal coordination (red dashed lines) between inhibitors and the protein are shown. Relevant residues are shown in stick representation with salmon carbon atoms in HDAC3. Ligand is shown in stick representation with green carbon atoms. The zinc ion is shown as cyan colored sphere.
Figure 8.
Calculated R2 values of the established models for alkylhydrazides (training set, orange bars).
Figure 8.
Calculated R2 values of the established models for alkylhydrazides (training set, orange bars).
Figure 9.
Correlation plots of the A) MODEL19 and B) MODEL19_1 showing correlation between the predicted data and experimental data for HDAC3. Training set (black), external test set (orange).
Figure 9.
Correlation plots of the A) MODEL19 and B) MODEL19_1 showing correlation between the predicted data and experimental data for HDAC3. Training set (black), external test set (orange).
Figure 10.
General structures of the tested compounds [
53].
Figure 10.
General structures of the tested compounds [
53].
Figure 11.
A) Docking pose of compound 64, B) Docking pose of compound 68, C) Docking pose of compound 72, D) Docking pose of compound 85. Hydrogen bonds (yellow dashed lines), hydrophobic interactions (orange dashed lines) and metal coordination (red dashed lines) between inhibitors and the protein are shown. Relevant residues are shown in stick representation with salmon carbon atoms in HDAC3. Ligand is shown in stick representation with green carbon atoms. The zinc ion is shown as cyan colored sphere.
Figure 11.
A) Docking pose of compound 64, B) Docking pose of compound 68, C) Docking pose of compound 72, D) Docking pose of compound 85. Hydrogen bonds (yellow dashed lines), hydrophobic interactions (orange dashed lines) and metal coordination (red dashed lines) between inhibitors and the protein are shown. Relevant residues are shown in stick representation with salmon carbon atoms in HDAC3. Ligand is shown in stick representation with green carbon atoms. The zinc ion is shown as cyan colored sphere.
Table 1.
Distribution of inhibitors in training and test set according to their HDAC3 IC50 values.
Table 1.
Distribution of inhibitors in training and test set according to their HDAC3 IC50 values.
| HDAC3 dataset |
Number of compounds |
7 < pIC50
Highly active |
5.3< pIC50 < 7
Moderately active |
pIC50 < 5.3
Inactive |
| Training |
39 |
30 |
9 |
- |
| Test |
17 |
11 |
6 |
- |
| Inactive |
7 |
- |
- |
7 |
| Total |
63 |
41 |
15 |
7 |
Table 2.
List of selected molecular descriptors for PCA analysis.
Table 2.
List of selected molecular descriptors for PCA analysis.
| Abbreviations |
Molecular descriptors |
| PEOE_VSA_HYD |
The partial equalization of orbital electronegativity (PEOE). Total hydrophobic van der Waals surface area |
| GCUT_SLOGP_0 |
The GCUT descriptors using atomic contribution to logP |
| TPSA |
Polar surface area |
| b_single |
Number of single bonds (including implicit hydrogens). Aromatic bonds are not considered to be single bonds. |
| lip_acc |
The number of O and N atoms |
| lip_don |
The number of OH and NH atoms |
| vsa_hyd |
Approximation of the sum of VDW surface areas of hydrophobic atoms. |
Table 3.
Calculated values of the best performing pharmacophore hypothesis.
Table 3.
Calculated values of the best performing pharmacophore hypothesis.
| HYPO ID |
Survival Score |
Inactive Score |
| ADDDHRR |
6.923 |
1.688 |
Table 4.
The best performing ligand-based 3D_QSAR model.
Table 4.
The best performing ligand-based 3D_QSAR model.
| HDAC3 model |
N |
SD |
R2
|
RMSE |
Q2
|
| 1 |
39 |
0.27 |
0.95 |
0.39 |
0.88 |
Table 5.
Prediction results of the test set compounds (atom-based QSAR model).
Table 5.
Prediction results of the test set compounds (atom-based QSAR model).
| Compound number |
pIC50 HDAC3 |
Prediction by atom-based QSAR |
Difference (experimental – predicted activity) atom-based |
References |
| 40 |
9.29 |
8.69 |
0.60 |
[46] |
| 41 |
9.24 |
8.87 |
0.37 |
[46] |
| 42 |
9.21 |
9.14 |
0.07 |
[46] |
| 43 |
7.90 |
8.43 |
0.53 |
[48] |
| 44 |
7.78 |
7.13 |
0.64 |
[48] |
| 45 |
7.46 |
7.17 |
0.29 |
[48] |
| 46 |
7.31 |
7.65 |
0.34 |
[48] |
| 47 |
7.17 |
6.92 |
0.24 |
[50] |
| 48 |
7.16 |
7.54 |
0.38 |
[50] |
| 49 |
7.11 |
7.96 |
0.85 |
[48] |
| 50 |
7.07 |
7.81 |
0.74 |
[50] |
| 51 |
6.73 |
7.88 |
1.16 |
[50] |
| 52 |
6.51 |
7.32 |
0.81 |
[50] |
| 53 |
5.96 |
7.85 |
1.89 |
[50] |
| 54 |
5.87 |
6.19 |
0.33 |
[50] |
| 55 |
5.81 |
8.08 |
2.26 |
[50] |
| 56 |
5.72 |
6.74 |
1.01 |
[50] |
Table 6.
Best performing BFE models.
Table 6.
Best performing BFE models.
| Model number |
N |
Method |
Frame |
2D
Descriptor |
R2
|
RMSE |
Q2LOO
|
QMSE |
| MODEL1 |
39 |
GB1 |
Emin1 |
- |
0.63 |
0.69 |
0.58 |
0.73 |
| MODEL7 |
39 |
GB2 |
Emin1 |
- |
0.66 |
0.65 |
0.63 |
0.69 |
| MODEL13 |
39 |
GB5 |
Emin1 |
- |
0.67 |
0.65 |
0.64 |
0.68 |
| MODEL19 |
39 |
GB8 |
Emin1 |
- |
0.81 |
0.49 |
0.78 |
0.52 |
| MODEL19_1 |
39 |
GB8 |
Emin1 |
PEOE_VSA_HYD |
0.87 |
0.40 |
0.84 |
0.44 |
Table 7.
Prediction results of the test set compounds using the BFE model (MODEL19_1).
Table 7.
Prediction results of the test set compounds using the BFE model (MODEL19_1).
| Compound number |
pIC50 HDAC3 |
Prediction of BFE |
Difference (experimental – predicted activity) |
References |
| 40 |
9.29 |
8.60 |
0.70 |
[46] |
| 41 |
9.24 |
9.75 |
0.51 |
[46] |
| 42 |
9.21 |
9.37 |
0.17 |
[46] |
| 43 |
7.90 |
8.53 |
0.63 |
[48] |
| 44 |
7.78 |
8.10 |
0.33 |
[48] |
| 45 |
7.46 |
7.42 |
0.03 |
[48] |
| 46 |
7.31 |
8.06 |
0.75 |
[48] |
| 47 |
7.17 |
7.85 |
0.68 |
[50] |
| 48 |
7.16 |
8.12 |
0.96 |
[50] |
| 49 |
7.11 |
6.30 |
0.81 |
[48] |
| 50 |
7.07 |
7.32 |
0.25 |
[50] |
| 51 |
6.73 |
7.56 |
0.83 |
[50] |
| 52 |
6.51 |
6.89 |
0.38 |
[50] |
| 53 |
5.96 |
6.19 |
0.22 |
[50] |
| 54 |
5.87 |
6.41 |
0.55 |
[50] |
| 55 |
5.81 |
6.27 |
0.46 |
[50] |
| 56 |
5.72 |
6.42 |
0.69 |
[50] |
Table 8.
Experimental and predicted activities by BFE-based and atom-based models.
Table 8.
Experimental and predicted activities by BFE-based and atom-based models.
| Compound number |
pIC50 HDAC3 |
Prediction by atom-based QSAR |
Difference (experimental – predicted activity) atom-based |
Prediction by BFE model |
Difference (experimental – predicted activity) BFE |
| 64 |
7.04 |
7.03 |
0.01 |
7.16 |
-0.12 |
| 65 |
6.46 |
6.59 |
-0.13 |
6.89 |
-0.43 |
| 66 |
5.82 |
6.57 |
-0.75 |
6.36 |
-0.54 |
| 67 |
<5.00 |
6.43 |
- |
5.41 |
- |
| 68 |
5.80 |
7.25 |
-1.46 |
6.69 |
-0.89 |
| 69 |
<5.00 |
7.05 |
- |
5.07 |
- |
| 70 |
<5.00 |
6.98 |
- |
3.92 |
- |
| 71 |
9%@1uM |
6.82 |
- |
0.24 |
- |
| 72 |
7.37 |
7.85 |
-0.49 |
7.60 |
-0.23 |
| 73 |
6.70 |
7.29 |
-0.59 |
6.68 |
0.02 |
| 74 |
41%@1uM |
7.39 |
- |
7.29 |
- |
| 75 |
7.09 |
7.82 |
-0.73 |
8.06 |
-0.97 |
| 76 |
7.22 |
7.12 |
0.10 |
6.86 |
0.36 |
| 77 |
7.43 |
7.96 |
-0.53 |
7.06 |
0.38 |
| 78 |
7.24 |
7.03 |
0.20 |
7.98 |
-0.75 |
| 79 |
6.92 |
6.80 |
0.12 |
6.32 |
0.60 |
| 80 |
6.96 |
8.10 |
-1.14 |
7.42 |
-0.46 |
| 81 |
<5.00 |
6.54 |
- |
1.65 |
- |
| 82 |
<5.00 |
6.86 |
- |
1.61 |
- |
| 83 |
5.52 |
7.25 |
-1.73 |
3.26 |
2.26 |
| 84 |
<5.00 |
7.61 |
- |
2.69 |
- |
| 85 |
7.52 |
7.63 |
-0.10 |
7.64 |
-0.11 |
| 86 |
7.00 |
7.18 |
-0.18 |
7.29 |
-0.29 |
| 87 |
6.52 |
6.52 |
0.00 |
6.86 |
-0.33 |
| 88 |
6.00 |
7.40 |
-1.40 |
6.13 |
-0.13 |
| 89 |
5.85 |
7.13 |
-1.28 |
6.11 |
-0.26 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).