Submitted:
13 May 2023
Posted:
15 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introductory overview
1.1. Insulin
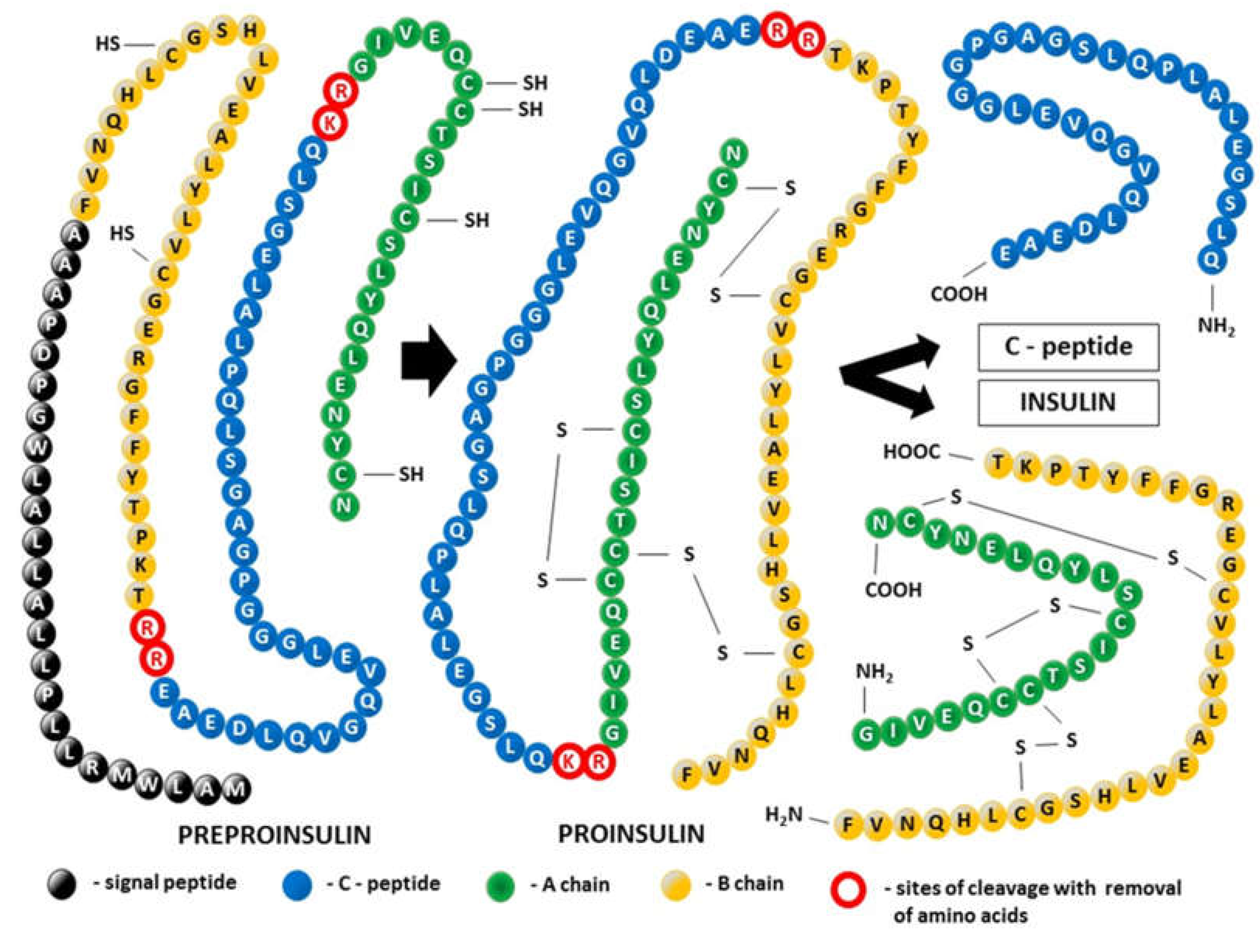
1.1.1. Posttranslational modification of the tertiary structure of insulin (Figure 1)
1.2. Insulin receptor (INSR)
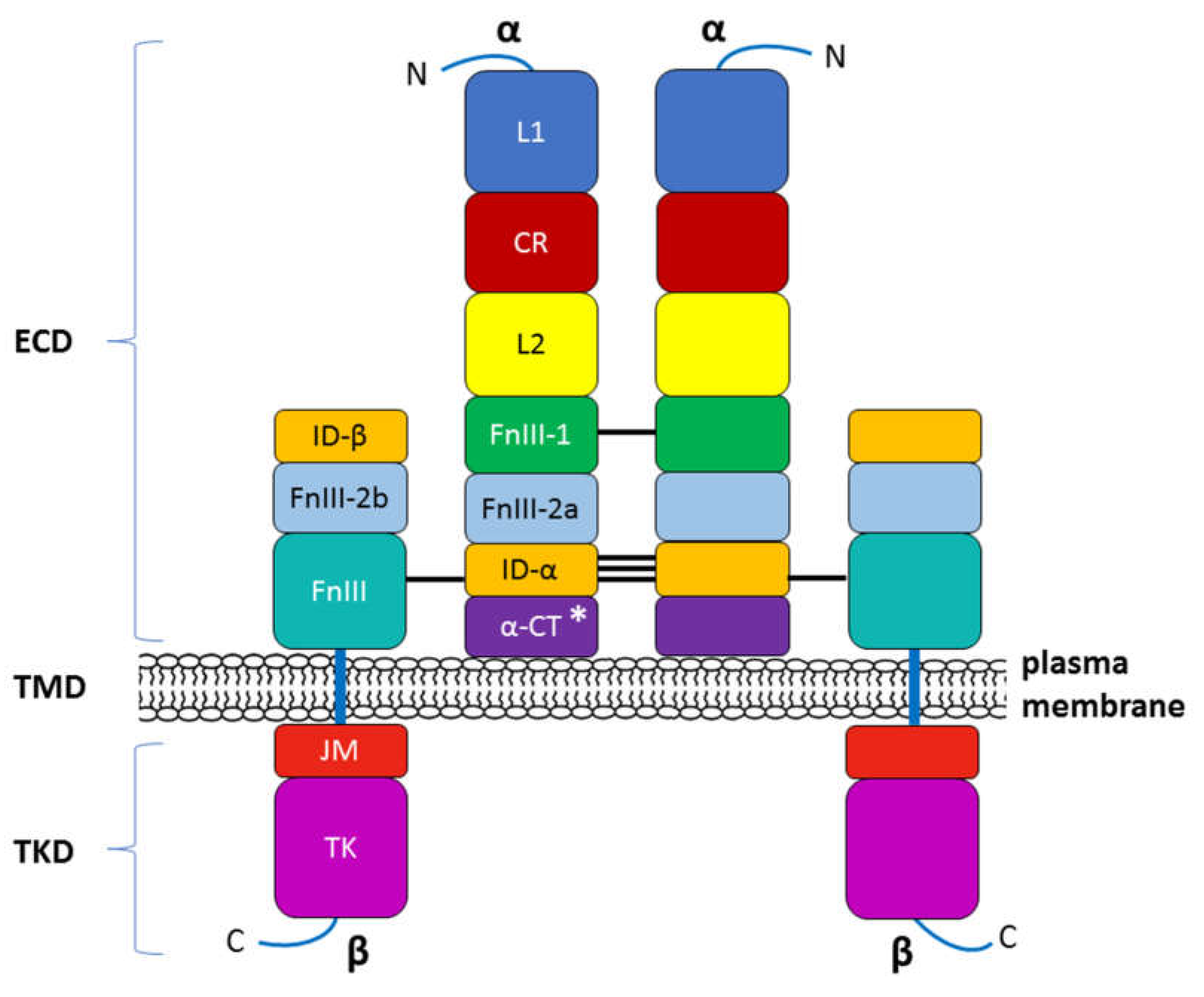
1.2.1. INSR structure
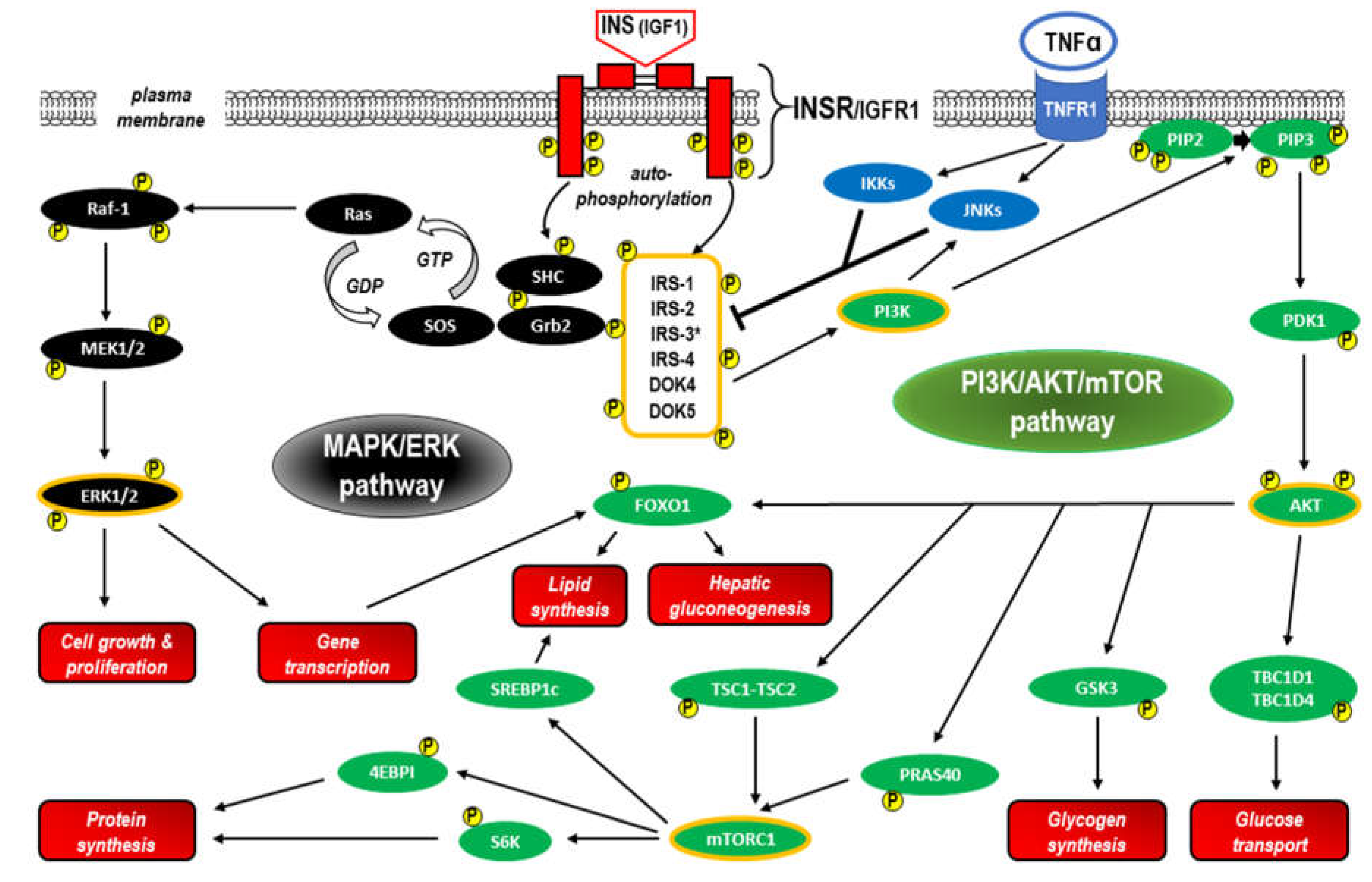
1.2.2. INSR signaling
- IRS proteins
2. Insulin resistance (IR)
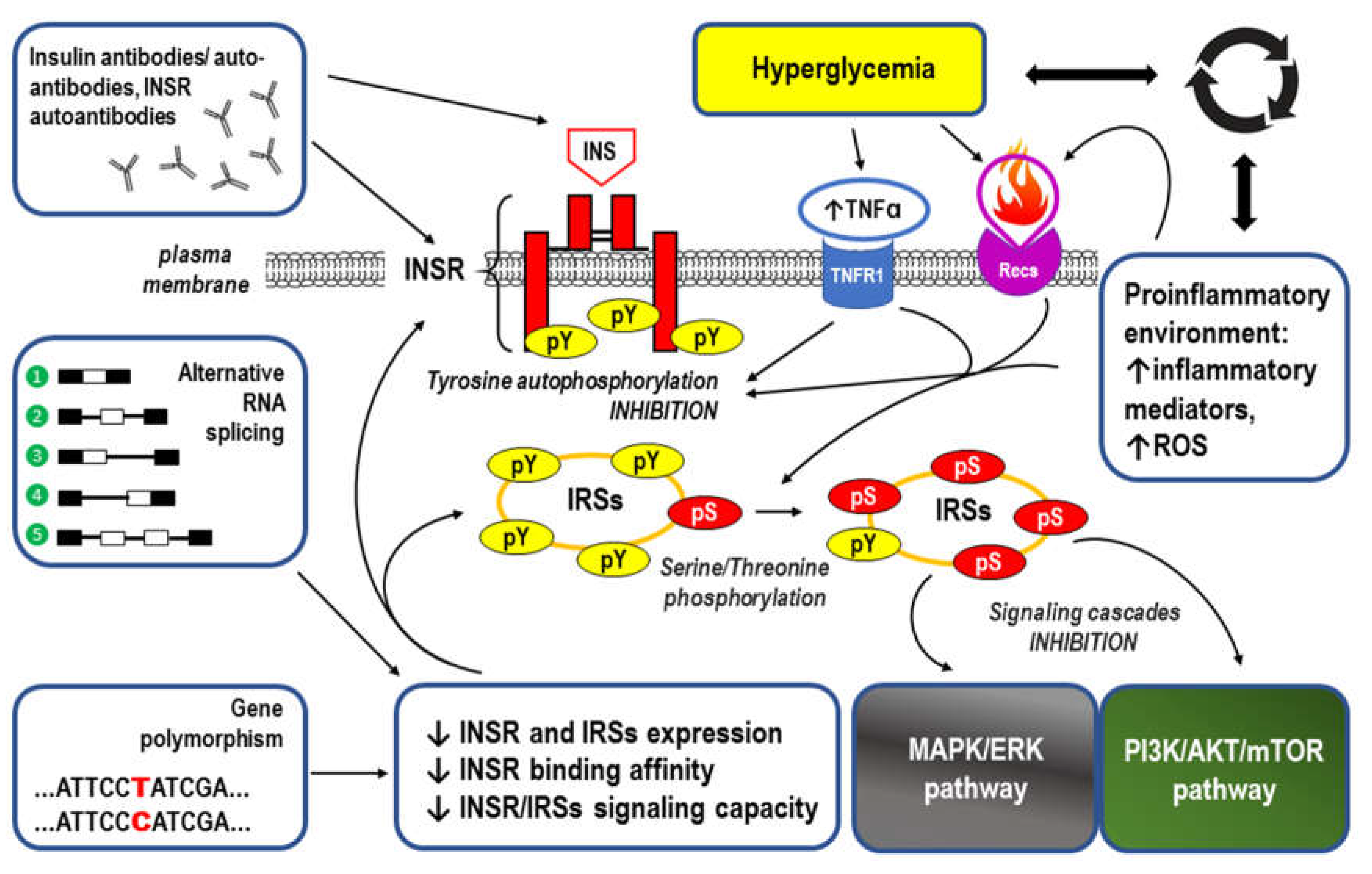
3. Inflammatory response and IR (see also the summary in Figure 5 at the end of this chapter)
3.1. Innate immune system and pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
3.1.1. TLR activation
3.1.2. NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) activation
3.2. Inflammatory response related to B cells and T cells
3.2.1. B cells
3.2.2. T cells
- Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and T cells
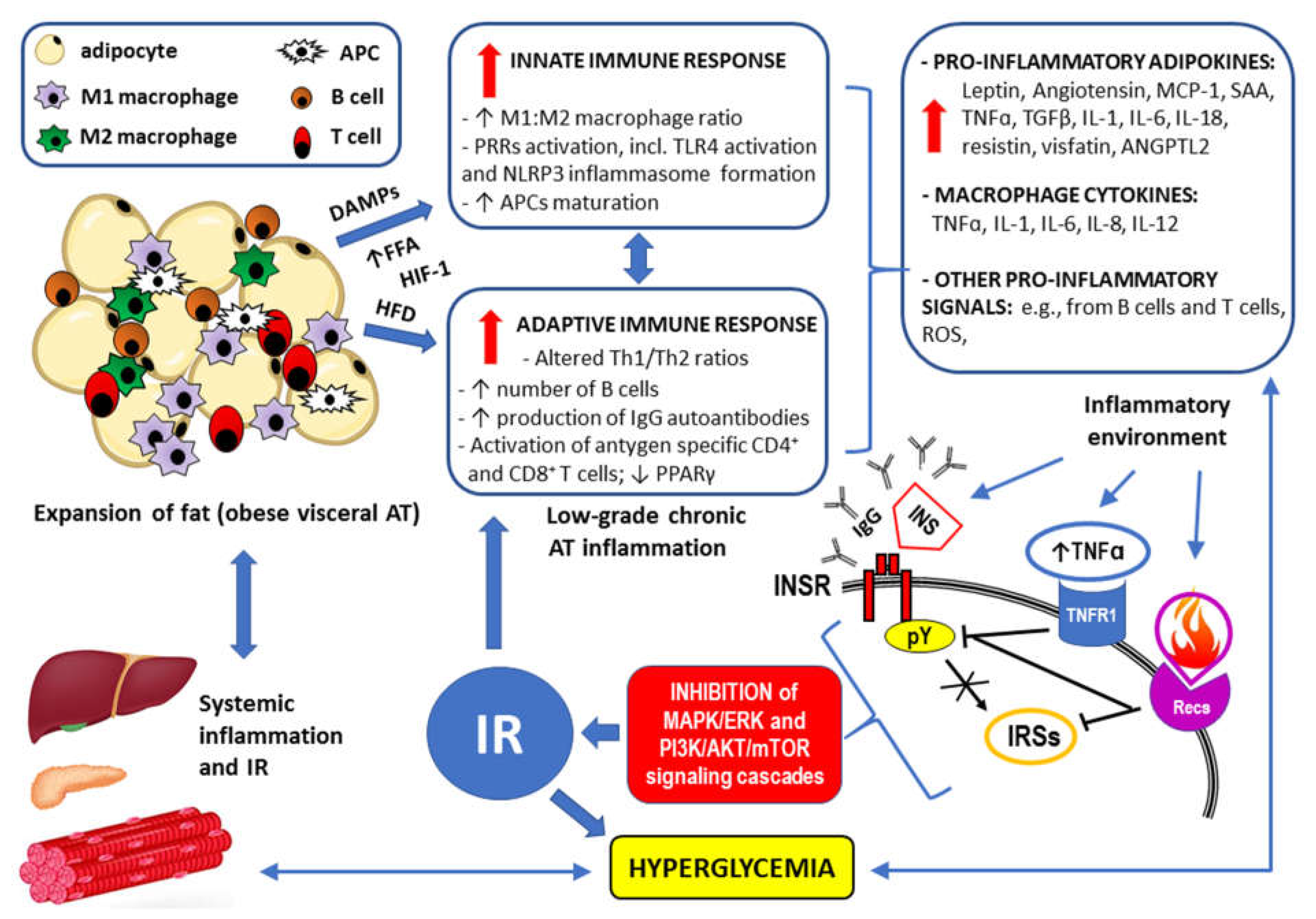
4. Concluding remarks
Funding Statement
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCs | age-associated B cells |
| acetyl-CoA | acetyl coenzyme A |
| AD | Alzheimer's disease |
| AF-1 | activation function 1 |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| Ang II | angiotensin II |
| AP-1 | activator protein 1 |
| APCs | antigen-presenting cells |
| ASC | apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing caspase recruitment domain (also PYCARD – PYD and CARD domain) |
| AT | adipose tissue |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| BCL-6 | corepressor B-cell lymphoma 6 |
| BMI | body mass index |
| Breg | regulatory B cells |
| CLRs | C-type lecithin receptors |
| Crk | adapter protein (also known as proto-oncogene c-Crk) |
| CXCR3 | chemokine receptor CXCR3 |
| CXCL10, CXCL11, and CXCL12 | chemokines – C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10, 11, and 12, respectively |
| DAMPs | damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DCs | dendritic cells |
| DIO mice | diet-induced obese mice |
| DOK4, DOK5 | docking proteins 4 and 5 (also known as IRS-5, IRS-6 – insulin receptor substrates 5 and 6, respectively) |
| DUBs | deubiquitinating enzymes (also known as deubiquitinating peptidases) |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EDCs | endocrine disrupting compounds |
| EPIL | early placenta insulin-like peptide (also known as INSL4 – insulin-like growth factor 4) |
| ERα, ERβ | estrogen receptor alpha, beta, respectively |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FFAs | free fatty acids |
| G-6-P | glucose-6-phosphate |
| Gab | Grb2-associated binder family proteins |
| GLUT4 | glucose transporter type 4 |
| GRB2 | growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 |
| HIF-1 | hypoxia-induced factor 1 |
| HOMA-IR | homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) of insulin resistance (IR) |
| IFN-γ | interferon gamma |
| IGF-1, IGF-2 | insulin-like growth factor 1 and 2 |
| IGFR1 | insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 |
| IκB | inhibitor of NF-κB |
| IKKs | inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) kinases |
| IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-17E(IL-25), IL-18 | interleukins |
| INSL3 | mammalian Leydig cell-specific insulin-like peptide |
| INSL4 | insulin-like peptide 4 (also known as EPIL – early placenta insulin-like peptide), |
| INSL5, INSL6 | insulin-like peptides 5 and 6 |
| INSR | insulin receptor |
| IR | insulin resistance |
| IRAK1, IRAK2, IRAK4 | IL-1 receptor-associated kinases 1, 2, and 4, respectively |
| IRS-5, IRS-6 | insulin receptor substrates 5 and 6 (also known as DOK4, DOK5 – docking proteins 4 and 5, respectively) |
| IRSs | insulin receptor substrates |
| ISIOGTT | insulin sensitivity index (ISI) obtained from oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) |
| JAK2 | Janus kinase 2 |
| JNKs | c-Jun-N-terminal kinases |
| LAT | linker for the activation of T cell |
| LIRP | locust insulin-related peptide |
| lncRNAs | long non-coding RNAs |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| LRR | leucine-rich-repeat motifs |
| LTB4 | chemokine leukotriene B4 |
| LTB4R1 | leukotriene B4 receptor 1 (also known as BLT1) |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCs | mast cells |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| MHO | metabolically healthy obesity |
| MIG | monokine induced by IFN-γ or chemokine CXCL9 |
| MIP | molluscan insulin-related peptides |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| MW | molecular weight |
| ncRNAs | non-coding RNAs |
| NEK7 | serine-threonine kinase NEK7 (NIMA "never in mitosis gene a"-related kinase 7) |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NK cells | natural killer cells |
| NLRP3 inflammasome | leucine-rich repeat (LRR)-containing proteins (NLR) family member 3 inflammasome |
| NLRs | nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors |
| NLSs | nuclear localization signals |
| NOD | nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain |
| NPXY (Asn-Pro-x-Tyr) motif (also known as the juxtamembrane Tyr960) | a conserved tyrosine phosphorylation motif in the activated insulin receptor (INSR) |
| OcaB | Oct coactivator B |
| OXPHOS | oxidative phosphorylation |
| PCOS | polycystic ovary syndrome |
| PDH | pyruvate dehydrogenase |
| PDK | pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase |
| PH | pleckstrin homology (also known as IH1) domain of the insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PLCγ1 | phospholipase-C-γ1 |
| PPARs | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors |
| pMHC-I | immunogenic peptide – MHC class I |
| PPARα, PPARβ, and PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, beta and gamma, respectively |
| PRRs | pattern recognition receptors |
| PTB | phosphotyrosine binding (also known as IH2) domain of the insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) |
| RACK1 | receptor for activated C kinase 1 |
| RLRs | retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors |
| RORγt | retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor γt (also known as RORγ2) |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SAT | subcutaneous adipose tissues |
| SFAs | saturated fatty acids |
| SH2B | adapter protein containing a SH2 (Src homology 2) and a PH (pleckstrin homology) domains |
| SHP2 | protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 of the Src homology region 2 (SH2) |
| siRNAs | small interfering RNAs (also known as silencing RNAs) |
| SOCS-3 | suppressor of cytokine signaling protein 3 |
| SREBP-1 | sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (also known as SREBF1 – sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1) |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| STKs | serine/threonine protein kinases |
| T1D, T2D | type 1, type 2 diabetes mellitus, respectively |
| TAK1 | transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-activated kinase 1 |
| T-bet | transcription factor T-bet (also known as Tbx21) |
| TCR | T-cell receptor |
| Th1, Th2 cells | T helper 1, T helper 2 lymphocytes, respectively |
| TIR | toll/interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor homology domain |
| TLRs, TLR1-10 | toll-like receptors |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TNFR1 | tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) receptor 1 |
| TRAF6 | tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor associated factor 6 |
| TRAPα, TRAPβ, TRAPγ, TRAPδ | translocation-associated protein complexes α, β, γ, and δ (also known as SSR1, SSR2, SSR3, and SSR3 – signal sequence receptors, respectively) |
| Treg | regulatory T cells |
| TRIF | toll/interleukin 1 receptor (IL-1R) domain-containing adaptor-inducing interferon beta (IFN-β) |
| TZDs | thiazolidinediones |
| ZAP-70 | zeta-associated protein of 70,000 molecular weight |
References
- Magkos, F.; Wang, X.; Mittendorfer, B. Metabolic actions of insulin in men and women. Nutrition 2010, 26, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Li, J.; Gao, F. New insights into insulin: The anti-inflammatory effect and its clinical relevance. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: how are they interlinked? J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldrum, D.R.; Morris, M.A.; Gambone, J.C. Obesity pandemic: causes, consequences, and solutions—but do we have the will? Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramana, K.V.; Plowman, T.J.; Shah, M.H.; Fernandez, E.; Christensen, H.; Aiges, M. Role of innate immune and inflammatory responses in the development of secondary diabetic complications. Curr. Mol. Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banting FG, Best CH, Collip JB, Campbell WR, Fletcher AA, MacLeod JJR, Noble EC. The effect produced on diabetes by extracts of pancreas. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1922; 37:337-347.
- Banting, F.G.; Best, C.H.; Collip, J.B.; Campbell, W.R.; Fletcher, A. Pancreatic Extracts in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: Preliminary Report. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1922, 12, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.W.; Lawrence, M.C. Landmarks in Insulin Research. Front. Endocrinol. 2011, 2, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stretton, A.O.W. The First Sequence: Fred Sanger and Insulin. Genetics 2002, 162, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2004-. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 118984375, Insulin Human; [cited 2023 Mar. 21]. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Insulin-Human.
- Hua, Q. Insulin: a small protein with a long journey. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halban, P.A. Structural domains and molecular lifestyles of insulin and its precursors in the pancreatic Beta cell. Diabetologia 1991, 34, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss M, Steiner DF, Philipson LH. Insulin Biosynthesis, Secretion, Structure, and Structure-Activity Relationships. 2014 Feb 1. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, New M, Purnell J, Sahay R, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. 2: PMID, 2590.
- Yegorov, S.; Bogerd, J.; Good, S.V. The relaxin family peptide receptors and their ligands: New developments and paradigms in the evolution from jawless fish to mammals. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 209, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, L.; Streiner, N.; Webster, L.; Yamamoto, S.; Okabe, R.; Kawamata, T.; Shimoda, J.; Büllesbach, E.; Schwabe, C.; Bryant-Greenwood, G. Early placental insulin-like protein (INSL4 or EPIL) in placental and fetal membrane growth. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwa, V.; Oh, Y.; Rosenfeld, R. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: a proposed superfamily. Acta Paediatr. 1999, 88, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nistor, M.; Schmidt, M.; Schiffner, R. The relaxin peptide family – potential future hope for neuroprotective therapy? A short review. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Kawano, T. The C. elegans insulin-like peptides (ILPs). AIMS Biophys. 2018, 5, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.W.; Geraerts, W.P.; Ebberink, R.H.; Joosse, J. Purification and sequencing of molluscan insulin-related peptide I (MIP I) from the neuroendocrine light green cells of Lymnaea stagnalis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1992, 85, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Hatanaka, H.; Kohda, D.; Kataoka, H.; Nagasawa, H.; Isogai, A.; Ishizaki, H.; Suzuki, A.; Inagaki, F. Three-dimensional Solution Structure of Bombyxin-II an Insulin-like Peptide of the SilkmothBombyx mori: Structural Comparison with Insulin and Relaxin. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 253, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.-Y.; Qiao, Z.-S.; Feng, Y.-M. TheIn VitroOxidative Folding of the Insulin Superfamily. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wright, J.; Guo, H.; Xiong, Y.; Arvan, P. Proinsulin Entry and Transit Through the Endoplasmic Reticulum in Pancreatic Beta Cells. 2014, 95, 35–62. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Arvan, P.; Liu, M. The Role of TRAPγ/SSR3 in Preproinsulin Translocation Into the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Diabetes 2021, 71, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Rohli, K.; Boyer, C.K.; Bearrows, S.C.; Moyer, M.R.; Elison, W.S.; Bauchle, C.J.; E Blom, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Stephens, S.B. ER Redox Homeostasis Regulates Proinsulin Trafficking and Insulin Granule Formation in the Pancreatic Islet β-Cell. Function 2022, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisho, Y.; Arai, T. Postprandial C-Peptide to Glucose Ratio as a Marker of β Cell Function: Implication for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddaloni, E.; Bolli, G.B.; Frier, B.M.; Little, R.R.; Leslie, R.D.; Pozzilli, P.; Buzzetti, R. C-peptide determination in the diagnosis of type of diabetes and its management: A clinical perspective. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1912–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, R.G.; Fontaine, M.J.; Rogers, J. C-Peptide. Pancreas 2004, 29, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahren, J.; Ekberg, K.; Johansson, J.; Henriksson, M.; Pramanik, A.; Johansson, B.-L.; Rigler, R.; Jörnvall, H. Role of C-peptide in human physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2000, 278, E759–E768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejrazkova, D.; Vankova, M.; Lukasova, P.; Vcelak, J.; Bendlova, B. Insights Into the Physiology of C-peptide. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, S237–S243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ido, Y.; Vindigni, A.; Chang, K.; Stramm, L.; Chance, R.; Heath, W.F.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Di Cera, E.; Williamson, J.R. Prevention of Vascular and Neural Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats by C-Peptide. Science 1997, 277, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallerath, T.; Kunt, T.; Forst, T.; I Closs, E.; Lehmann, R.; Flohr, T.; Gabriel, M.; Schäfer, D.; Göpfert, A.; Pfützner, A.; et al. Stimulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by proinsulin C-peptide. Nitric Oxide 2003, 9, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, S.B.; Campos, J.R.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Silva, A.M.; Cicero, N.; Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Multiple Cell Signalling Pathways of Human Proinsulin C-Peptide in Vasculopathy Protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, R.L.; Mueller, K.; Kaur, G.; Moreno, T.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Ramalingam, L.; Dufour, J.M. C-Peptide as a Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.; De Meyts, P. Chapter 3 Molecular Mechanisms of Differential Intracellular Signaling From the Insulin Receptor. 2009, 80, 51–75. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Bi, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, L. The Insulin Receptor: An Important Target for the Development of Novel Medicines and Pesticides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.L.; Park, K.; Li, Q. Selective Insulin Resistance and the Development of Cardiovascular Diseases in Diabetes: The 2015 Edwin Bierman Award Lecture. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Yu, M.G.; Li, Q.; Park, K.; King, G.L. Insulin's actions on vascular tissues: Physiological effects and pathophysiological contributions to vascular complications of diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szukiewicz, D.; Trojanowski, S.; Kociszewska, A.; Szewczyk, G. Modulation of the Inflammatory Response in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)—Searching for Epigenetic Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, K. Role of insulin action in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Diabetol. Int. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, G.G.; Huerta, M.; A González-Usigli, H.; Torres-Sánchez, E.D.; Delgado-Lara, D.L.; Pacheco-Moisés, F.P.; A Mireles-Ramírez, M.; Torres-Mendoza, B.M.; I Moreno-Cih, R.; E Velázquez-Brizuela, I. Cognitive disorder and dementia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2022, 13, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezkurdia, A.; Ramírez, M.J.; Solas, M. Metabolic Syndrome as a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Focus on Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Obesity and endocrine-related cancer: The important role of IGF-1. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Alex, J.M.; Bast, F. Insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) signaling systems: novel treatment strategies for cancer. Med Oncol. 2013, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Pilch, P.F. The insulin receptor: structure, function, and signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1994, 266, C319–C334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, S.R. The Insulin Receptor: Both a Prototypical and Atypical Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008946–a008946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Maji, S.; Sanghera, N.; Gopalasingam, P.; Gorbunov, E.; Tarasov, S.; Epstein, O.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. Structure and dynamics of the insulin receptor: implications for receptor activation and drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapin, G.; Dandey, V.P.; Zhang, Z.; Prosise, W.; Hruza, A.; Kelly, T.; Mayhood, T.; Strickland, C.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B. Structure of the insulin receptor–insulin complex by single-particle cryo-EM analysis. Nature 2018, 556, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payankaulam, S.; Raicu, A.-M.; Arnosti, D.N. Transcriptional Regulation of INSR, the Insulin Receptor Gene. Genes 2019, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorden, P.; Arakaki, R.; Collier, E.; Carpentier, J.L. Biosynthesis and regulation of the insulin receptor. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1989, 62, 521–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Westermeier, F.; Sáez, T.; Arroyo, P.; Toledo, F.; Gutiérrez, J.; Sanhueza, C.; Pardo, F.; Leiva, A.; Sobrevia, L. Insulin receptor isoforms: an integrated view focused on gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2015, 32, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Vella, V.; Lawrence, M.; Sciacca, L.; Frasca, F.; Morrione, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Physiology and Disease: An Updated View. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 379–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Scalia, P.; Sciacca, L.; Mineo, R.; Costantino, A.; Goldfine, I.D.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin Receptor Isoform A, a Newly Recognized, High-Affinity Insulin-Like Growth Factor II Receptor in Fetal and Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 3278–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, B.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Ermel, B.; Ullrich, A.; Häring, H.-U. The two isotypes of the human insulin receptor (HIR-A and HIR-B) follow different internalization kinetics. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 177, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneit, N.; Fernández-García, C.E.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Perdomo, L.; Escribano. ; Michel, J.B.; García-Gómez, G.; Fernández, S.; Díaz-Castroverde, S.; Egido, J.; et al. Expression of insulin receptor (IR) A and B isoforms, IGF-IR, and IR/IGF-IR hybrid receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells and their role in cell migration in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, A.; Joost, H. Insulin Receptor. 2008, 632–636. [CrossRef]
- De Meyts, P. The Insulin Receptor and Its Signal Transduction Network. 2016 Apr 27. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, New M, Purnell J, Sahay R, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–.
- Tatulian, S.A. Structural Dynamics of Insulin Receptor and Transmembrane Signaling. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 5523–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.S.; Zamaletdinov, M.F.; Bershatsky, Y.V.; Urban, A.S.; Bocharova, O.V.; Bennasroune, A.; Maurice, P.; Bocharov, E.V.; Efremov, R.G. Dimeric states of transmembrane domains of insulin and IGF-1R receptors: Structures and possible role in activation. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Biomembr. 2020, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddle, K. Signalling by insulin and IGF receptors: supporting acts and new players. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, R1–R10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Guglielmo GM, Drake PG, Baass PC, Authier F, Posner BI, Bergeron JJ. Insulin receptor internalization and signalling. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;182(1-2):59-63.
- Chang, L.; Chiang, S.-H.; Saltiel, A.R. Insulin Signaling and the Regulation of Glucose Transport. Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posner, B.I. Insulin Signalling: The Inside Story. Can. J. Diabetes 2016, 41, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Neto, J.A.; Fenerich, B.A.; Alves, A.P.N.R.; Fernandes, J.C.; Scopim-Ribeiro, R.; Coelho-Silva, J.L.; Traina, F. Insulin Substrate Receptor (IRS) proteins in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Clinics 2018, 73, e566s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, L.M. The insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.J.; Rothenberg, P.; Kahn, C.R.; Backer, J.M.; Araki, E.; A Wilden, P.; A Cahill, D.; Goldstein, B.J.; White, M.F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature 1991, 352, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.F. IRS proteins and the common path to diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2002, 283, E413–E422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. , B.; A., H.; A., A.; S., L.; S., L.; G., L.; S., T.; P., A.; J., Z.; Björnholm, M.; et al. Absence of functional insulin receptor substrate-3 ( IRS-3 ) gene in humans. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavan, B.E.; Fantin, V.R.; Chang, E.T.; Lane, W.S.; Keller, S.R.; Lienhard, G.E. A Novel 160-kDa Phosphotyrosine Protein in Insulin-treated Embryonic Kidney Cells Is a New Member of the Insulin Receptor Substrate Family. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21403–21407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardilovich, K.; Pankratz, S.L.; Shaw, L.M. Expression and function of the insulin receptor substrate proteins in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 7, 14–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Melendez, P.A.; Lee, J.; Shoelson, S.E. Two New Substrates in Insulin Signaling, IRS5/DOK4 and IRS6/DOK5. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25323–25330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, J.; Sachs, M.; Britsch, S.; Di Cesare, S.; Schwarz-Romond, T.; Alitalo, K.; Birchmeier, W. Novel p62dok family members, dok-4 and dok-5, are substrates of the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase and mediate neuronal differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favre, C.; Gérard, A.; Clauzier, E.; Pontarotti, P.; Olive, D.; A Nunès, J. DOK4 and DOK5: new dok-related genes expressed in human T cells. Genes Immun. 2003, 4, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, S.; Mann, M. The Phosphotyrosine Interactome of the Insulin Receptor Family and Its Substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voliovitch, H.; Schindler, D.G.; Hadari, Y.R.; Taylor, S.I.; Accili, D.; Zick, Y. Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 in Vivo Depends upon the Presence of Its Pleckstrin Homology Region. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 18083–18087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenush, L.; Makati, K.J.; Smith-Hall, J.; Ishibashi, O.; Myers, M.G.; White, M.F. The Pleckstrin Homology Domain Is the Principle Link between the Insulin Receptor and IRS-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 24300–24306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawka-Verhelle, D.; Tartare-Deckert, S.; White, M.F.; Van Obberghen, E. Insulin Receptor Substrate-2 Binds to the Insulin Receptor through Its Phosphotyrosine-binding Domain and through a Newly Identified Domain Comprising Amino Acids 591–786. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5980–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.A.; Jablonowski, K.; Shah, E.E.; Engelmann, B.W.; Jones, R.B.; Nash, P.D. SH2 Domains Recognize Contextual Peptide Sequence Information to Determine Selectivity. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2391–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, C.M.; Emanuelli, B.; Kahn, C.R. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, G.; Kumaran, S.; Lubman, O. SH2 domains: role, structure and implications for molecular medicine. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2004, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.J.; Wang, L.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Yenush, L.; Jr, M.G.M.; Glasheen, E.; Lane, W.S.; Pierce, J.H.; White, M.F. Role of IRS-2 in insulin and cytokine signalling. Nature 1995, 377, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatani, T.; Shirakawa, J.; Shibue, K.; Gupta, M.K.; Kim, H.; Lu, S.; Hu, J.; White, M.F.; Kennedy, R.T.; Kulkarni, R.N. Insulin receptor substrate 1, but not IRS2, plays a dominant role in regulating pancreatic alpha cell function in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde. M.; González-Rodríguez,. IRS2 and PTP1B: Two opposite modulators of hepatic insulin signalling. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 117, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.T.-Y.; Lee, A.V. Insulin Receptor Substrates (IRSs) and Breast Tumorigenesis. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2008, 13, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Du, T.; Li, C.; Yang, G. STAT3 phosphorylation in central leptin resistance. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giani, J.F.; Gironacci, M.M.; Muñoz, M.C.; Peña, C.; Turyn, D.; Dominici, F.P. Angiotensin-(1–7) stimulates the phosphorylation of JAK2, IRS-1 and Akt in rat heart in vivo: role of the AT1 and Mas receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H1154–H1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassak, A.; Del Valle, L.; Peruzzi, F.; Wang, J.Y.; Enam, S.; Croul, S.; Khalili, K.; Reiss, K. Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 Translocation to the Nucleus by the Human JC Virus T-antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 17231–17238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisco, M.; Santini, F.; Baffa, R.; Liu, M.; Drakas, R.; Wu, A.; Baserga, R. Nuclear Translocation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 by the Simian Virus 40 T Antigen and the Activated Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32078–32085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuori, K.; Ruoslahti, E. Association of insulin receptor substrate-1 with integrins. Science 1994, 266, 1576–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanska, K.; Pannizzo, P.; Lassak, A.; Gualco, E.; Surmacz, E.; Croul, S.; Del Valle, L.; Khalili, K.; Reiss, K. Estrogen receptor β-mediated nuclear interaction between IRS-1 and Rad51 inhibits homologous recombination directed DNA repair in medulloblastoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 219, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Batta, P.; Innocent, N.; Prisco, M.; Casaburi, I.; Belletti, B.; Baserga, R. Nuclear Translocation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 by Oncogenes And Igf-I. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44357–44365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, H.; Cai, W.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Steger, M.; Batista, T.M.; Pan, H.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Mann, M.; Kahn, C.R. Distinct signaling by insulin and IGF-1 receptors and their extra- and intracellular domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakuno, F.; Fukushima, T.; Yoneyama, Y.; Kamei, H.; Ozoe, A.; Yoshihara, H.; Yamanaka, D.; Shibano, T.; Sone-Yonezawa, M.; Yu, B.-C.; et al. The Novel Functions of High-Molecular-Mass Complexes Containing Insulin Receptor Substrates in Mediation and Modulation of Insulin-Like Activities: Emerging Concept of Diverse Functions by IRS-Associated Proteins. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Ahmad, Y.; Oknin-Vaisman, A.; Bitman-Lotan, E.; Orian, A. From the Evasion of Degradation to Ubiquitin-Dependent Protein Stabilization. Cells 2021, 10, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girnita, L.; Girnita, A.; Larsson, O. Mdm2-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 8247–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zick, Y. Ser/Thr Phosphorylation of IRS Proteins: A Molecular Basis for Insulin Resistance. Sci. STKE 2005, 2005, pe4–pe4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, J.K.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Metabolic Messengers: tumour necrosis factor. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G. Mechanisms of TNF-α-induced insulin resistance. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 1999, 107, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, R.M.; Neves, K.B.; Mestriner, F.L.; Louzada-Junior, P.; Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Tostes, R.C. TNF-α induces vascular insulin resistance via positive modulation of PTEN and decreased Akt/eNOS/NO signaling in high fat diet-fed mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, D.P.; White, M.F.; Brazil, D.P. IRS proteins and diabetic complications. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2280–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Oh, A.S.; Fagan, D.H.; Byron, S.; Sarver, A.L.; Lee, A.V.; Shaw, L.M.; Fan, C.; Perou, C.; et al. Insulin Receptor Substrate Adaptor Proteins Mediate Prognostic Gene Expression Profiles in Breast Cancer. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0150564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebovitz, H.E. Insulin resistance: definition and consequences. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2001, 109, S135–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman AM, Pennings N. Insulin Resistance. 2022 Sep 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. 2: PMID, 2993.
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, T.J.; Haines, S.T. Treatment Approach to Patients With Severe Insulin Resistance. Clin. Diabetes 2016, 34, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.R.; Matta, S.T.; Haymond, M.W.; Chung, S.T. Measuring Insulin Resistance in Humans. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2020, 93, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; Kempf, K.; Röhling, M.; Martin, S. Insulin: too much of a good thing is bad. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; Stumvoll, M.; Kramer, W.; Kempf, K.; Martin, S. Insulin translates unfavourable lifestyle into obesity. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidi, A.M.; Filippaios, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Severe insulin resistance syndromes. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHaan KN, Preszler J, Hansen K. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: A Narrative Review. S D Med. 4: 2022;75(9), 2022.
- Yoon, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Son, S.U.; Choi, J.; You, S.-W.; Park, H.; Cha, S.-Y.; Maeng, S. How Can Insulin Resistance Cause Alzheimer’s Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; An, X.; Yang, C.; Sun, W.; Ji, H.; Lian, F. The crucial role and mechanism of insulin resistance in metabolic disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1149239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lause, M.; Kamboj, A.; Faith, E.F. Dermatologic manifestations of endocrine disorders. Transl. Pediatr. 2017, 6, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady MF, Rawla P. Acanthosis Nigricans. [Updated 2022 Oct 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. 4310.
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin Receptor Signaling in Normal and Insulin-Resistant States. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191–a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wei, T. Inputs and outputs of insulin receptor. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, K.J.; Maddux, B.A.; Szary, J.; Youngren, J.F.; Goldfine, I.D.; Schaufele, F. Insulin Resistance Induced by Hyperinsulinemia Coincides with a Persistent Alteration at the Insulin Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Domain. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Corbin, J.; Bhaskar, V.; Goldfine, I.D.; Issafras, H.; Bedinger, D.H.; Lau, A.; Michelson, K.; Gross, L.M.; A Maddux, B.; Kuan, H.F.; et al. Inhibition of insulin receptor function by a human, allosteric monoclonal antibody. mAbs 2013, 6, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, D. Current Studies on Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, M.; Hosseini, H.; ArabSadeghabadi, Z.; Babaei-Khorzoughi, R.; Gorgani-Firuzjaee, S.; Meshkani, R. The role of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 78, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, A.; Tanokashira, D.; Fukuokaya, W. Involvement of insulin receptor substrates in cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.-S. The Role of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) in Insulin Signaling. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Haque, M. Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Ultimatum to Renal Physiology. Cureus 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.L.; Ikeda, Y.; Olsen, G.S.; Busch, A.K.; Mosthaf, L. Insulin Signaling Is Inhibited by Micromolar Concentrations of H2O2. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25078–25084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, C.M.O.; Villar-Delfino, P.H.; Dos Anjos, P.M.F.; Nogueira-Machado, J.A. Cellular death, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and diabetic complications. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, D.L.; Stevenson, M.; Steenkamp, D. Type B insulin resistance syndrome. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2016, 23, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anna, A.; Monika, G. Splicing mutations in human genetic disorders: examples, detection, and confirmation. J. Appl. Genet. 2018, 59, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, O.; Ugi, S.; Takayoshi, T.; Omura, Y.; Yonishi, M.; Sato, D.; Fujita, Y.; Fuke, T.; Hirota, Y.; Ogawa, W.; et al. A family with type A insulin resistance syndrome caused by a novel insulin receptor mutation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-Q.; Wang, B.-A.; Zhao, W.-R.; Gu, W.-J.; Lui, Z.-H.; Dou, J.-T.; Mu, Y.-M.; Lu, J.-M. Clinical and genetic analysis of the insulin receptor gene in a Chinese patient with extreme insulin resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2010, 89, e56–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, S.U.A.; Nabi, M.; Ashraf, S.; Amin, S. Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 Gly972Arg (rs1801278) Polymorphism Is Associated with Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Kashmiri Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Genes 2022, 13, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehart, H.; Kumpf, S.; Ittner, A.; Ricci, R. MAPK signalling in cellular metabolism: stress or wellness? EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakyan, G.; Vejux, A.; Sahakyan, N. The Role of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Inflammation in the Development of T2DM-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy: Possible Preventive Action of Tannins and Other Oligomeric Polyphenols. Molecules 2022, 27, 9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, V.F.; Merce, A.P.; Hâncu, I.M.; Bătrân, A.D.; Kennedy, G.; Rosca, M.G.; Muntean, D.M. Impairment of Mitochondrial Respiration in Metabolic Diseases: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Mechanistic Insight into Oxidative Stress-Triggered Signaling Pathways and Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules 2022, 27, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, H.S. A Synopsis of the Associations of Oxidative Stress, ROS, and Antioxidants with Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N. Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Normal Weight and Obesity. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 35, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, B.A.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Krishnamurthy, P.T.; Wadhwani, A.; Mohankumar, S.K. Cytosolic lipid excess-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is the cause or effect of high fat diet-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance: a molecular insight. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 46, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshmoghadam, J.; Omidifar, A.; Dilmaghani, N.A.; Karimi, Z.; Emamgholipour, S.; Shanaki, M. The gene expression of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs): MEG3 and H19 in adipose tissues from obese women and its association with insulin resistance and obesity indices. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, L.; Taegtmeyer, H. The Randle cycle revisited: a new head for an old hat. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2009, 297, E578–E591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z. Pyruvate dehydrogenase, Randle cycle, and skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, 201505398–E2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camastra, S.; Ferrannini, E. Role of anatomical location, cellular phenotype and perfusion of adipose tissue in intermediary metabolism: A narrative review. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Loof, M.; Renguet, E.; Ginion, A.; Bouzin, C.; Horman, S.; Beauloye, C.; Bertrand, L.; Bultot, L. Enhanced protein acetylation initiates fatty acid-mediated inhibition of cardiac glucose transport. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2023, 324, H305–H317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, W.; Shi, J.; Shen, J.; Gao, T.; Zhang, J.; Xi, F.; Li, J.; Li, N. Insulin alleviates the inflammatory response and oxidative stress injury in cerebral tissues in septic rats. J. Inflamm. 2014, 11, 18–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-T.; Lue, J.-H.; Cheng, T.-H.; Tsai, Y.-J. Glycemic control with insulin attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by inhibiting glial activation via the suppression of the nuclear factor kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in septic rats. Brain Res. 2020, 1738, 146822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-W.; Hung, L.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, W.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tzeng, H.-H.; Suen, J.-L.; Chen, Y.-H. Insulin Reduces Inflammation by Regulating the Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Khanna, S.; Khanna, P.; Kahar, P.; Patel, B.M. Obesity: A Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation and Its Markers. Cureus 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillana, N.; Astudillo-Guerrero, C.; D’espessailles, A.; Cruz, G. White Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Emergent Measurements. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daryabor, G.; Kabelitz, D.; Kalantar, K. An update on immune dysregulation in obesity-related insulin resistance. Scand. J. Immunol. 2018, 89, e12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Rodelo, C.; Arellano-Plancarte, A.; Hernandez-Aranda, J.; Landa-Galvan, H.V.; Parra-Mercado, G.K.; Moreno-Licona, N.J.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, K.D.; Catt, K.J.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. Angiotensin II Inhibits Insulin Receptor Signaling in Adipose Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Liaqat, A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha: Role in Development of Insulin Resistance and Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 119, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, J.; Grémeaux, T.; Cormont, M.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Tanti, J.-F. Interleukin-1β-Induced Insulin Resistance in Adipocytes through Down-Regulation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Expression. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H.; Liaqat, A.; Kamal, S.; Qadir, M.I.; Rasul, A. Role of Interleukin-6 in Development of Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2017, 27, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Kai, Y.; Ono, M.; Ezaki, O. Overexpression of Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor γ Coactivator-1α Down-regulates GLUT4 mRNA in Skeletal Muscles. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31385–31390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, P.; Van Obberghen, E. SOCS proteins causing trouble in insulin action. Acta Physiol. 2007, 192, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, S.B.; O’neill, H.M.; Sylow, L.; Honeyman, J.; Hewitt, K.A.; Palanivel, R.; Fullerton, M.D.; Öberg, L.; Balendran, A.; Galic, S.; et al. Deletion of Skeletal Muscle SOCS3 Prevents Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Diabetes 2012, 62, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X. Research Advances on Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 (SOCS3) in Animal Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism Processes. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 25, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, T.; Ackerman, S.E.; Shen, L.; Engleman, E. Role of innate and adaptive immunity in obesity-associated metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Xia, P.; Liu, X.; Cai, X.; Yang, P.; Ling, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Advances in T Cells Based on Inflammation in Metabolic Diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Bris, R.; Saez, A.; Herrero-Fernandez, B.; Rius, C.; Sanchez-Martinez, H.; Gonzalez-Granado, J.M. CD4 T-Cell Subsets and the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H. Obese visceral fat tissue inflammation: from protective to detrimental? . 2022, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, K.M.; Takeuchi, O. Innate immune sensing of pathogens and its post-transcriptional regulations by RNA-binding proteins. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2023, 46, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Adjemian, S.; Branco, L.M.; Zanetti, L.C.; Weinlich, R.; Bortoluci, K.R. Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Host Cell Death Molecular Machinery. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.; Cai, S.-Y.; Shao, J.-Z.; Chen, J. Toll-Like Receptors, Associated Biological Roles, and Signaling Networks in Non-Mammals. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannoy, V.; Côté-Biron, A.; Asselin, C.; Rivard, N. TIRAP, TRAM, and Toll-Like Receptors: The Untold Story. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, R.; Mosser, D.M. Pattern recognition receptors in innate immunity, host defense, and immunopathology. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2013, 37, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinini, A.M.; Midwood, K.S. DAMPening Inflammation by Modulating TLR Signalling. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 672395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, T.; Du, Y.; Xing, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.-F. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling and Its Role in Cell-Mediated Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botos, I.; Segal, D.M.; Davies, D.R. The Structural Biology of Toll-like Receptors. Structure 2011, 19, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, W. Structures and recognition modes of toll-like receptors. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2016, 85, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landström, M. The TAK1–TRAF6 signalling pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, B.M.; Billiar, T.R.; Bauer, A.J. Dominant role of the MyD88-dependent signaling pathway in mediating early endotoxin-induced murine ileus. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G531–G538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguine, J.; Barton, G.M. MyD88: a central player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 97–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, M.O.; Sweet, M.J.; Mansell, A.; Kellie, S.; Kobe, B. TRIF-dependent TLR signaling, its functions in host defense and inflammation, and its potential as a therapeutic target. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daryabor, G.; Kabelitz, D.; Kalantar, K. An update on immune dysregulation in obesity-related insulin resistance. Scand. J. Immunol. 2018, 89, e12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochando, J.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Madsen, J.C.; Netea, M.G.; Duivenvoorden, R. Trained immunity — basic concepts and contributions to immunopathology. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 19, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Barreiro, L.B.; Chavakis, T.; Divangahi, M.; Fuchs, E.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Van Der Meer, J.W.M.; Mhlanga, M.M.; Mulder, W.J.M.; et al. Defining trained immunity and its role in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Sears, D.D. TLR4 and Insulin Resistance. Gastroenterol. Res. Pr. 2010, 2010, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieronymaki, E.; Daskalaki, M.G.; Lyroni, K.; Tsatsanis, C. Insulin Signaling and Insulin Resistance Facilitate Trained Immunity in Macrophages Through Metabolic and Epigenetic Changes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobayashi, M.; Albert, V.; Wölnerhanssen, B.; Frei, I.C.; Weissenberger, D.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Clement, N.; Moes, S.; Colombi, M.; Meier, J.A.; et al. Insulin resistance causes inflammation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Ye, X.-J.; He, X.-H.; Ouyang, D.-Y. The Signaling Pathways Regulating NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Inflammation 2021, 44, 1229–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blevins, H.M.; Xu, Y.; Biby, S.; Zhang, S. The NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway: A Review of Mechanisms and Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Xu, S.; Ma, Y.; Liu, G.; Jang, H.; Fang, J. Modulatory Mechanisms of the NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Diabetes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronkite, D.A.; Strutt, T.M. The Regulation of Inflammation by Innate and Adaptive Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1467538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Bosselut, R. CD4–CD8 differentiation in the thymus: connecting circuits and building memories. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O, E.; Lee, Y.-T.; Ko, E.-J.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-N.; Song, J.-M.; Kwon, Y.-M.; Kim, M.-C.; Perez, D.R.; Kang, S.-M. Roles of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II in Inducing Protective Immune Responses to Influenza Vaccination. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7764–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, I.; Jeon, D.; Moseman, J.E.; Muralidhar, A.; Potluri, H.K.; McNeel, D.G. Role of B cells as antigen presenting cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.S.; Warrington, R.; Watson, W.; Kim, H.L. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy, Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, H.S.; Prakken, B.; Kalkhoven, E.; Boes, M. Adipose tissue-resident immune cells: key players in immunometabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, J.; Meng, H.; Zhang, X. Adipose Tissue-Resident Immune Cells in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, M.; Haluzik, M. The role of adipose tissue immune cells in obesity and low-grade inflammation. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 222, R113–R127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutens, L.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Dhingra, S.; Cramer, R.A.; Netea, M.G.; Stienstra, R. Unique metabolic activation of adipose tissue macrophages in obesity promotes inflammatory responses. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, C.; Kinnunen, T. B-cell helper T cells and type 1 diabetes. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolosowicz, M.; Lukaszuk, B.; Chabowski, A. The Causes of Insulin Resistance in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Is There a Place for Quaternary Prevention? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, I.; Wei, C.; Jenks, S.A.; Cashman, K.S.; Tipton, C.; Woodruff, M.C.; Hom, J.; Lee, F.E.-H. Challenges and Opportunities for Consistent Classification of Human B Cell and Plasma Cell Populations. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikakulapu, P.; McNamara, C.A. B Lymphocytes and Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffaut, C.; Galitzky, J.; Lafontan, M.; Bouloumié, A. Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the adipose tissue during the onset of obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 384, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Winer, D.; Winer, S.; Shen, L.; Wadia, P.P.; Yantha, J.; Paltser, G.; Tsui, H.; Wu, P.; Davidson, M.G.; Alonso, M.N.; et al. B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, S.W.; Stockley, R.A. Leukotriene B4. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 30, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahara, M.; Ito, N.; Hoshino, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Yokomizo, T.; Nakamura, M.; Shimizu, T.; Yamada, Y. Role of leukotriene B4 (LTB4)-LTB4 receptor 1 signaling in post-incisional nociceptive sensitization and local inflammation in mice. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0276135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Q. The role of the LTB4-BLT1 axis in health and disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrillo, R.; González-Périz, A.; Martínez-Clemente, M.; López-Parra, M.; Ferré, N.; Titos, E.; Morán-Salvador, E.; Deulofeu, R.; Arroyo, V.; Clària, J. 5-Lipoxygenase Activating Protein Signals Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Lipid Dysfunction in Experimental Obesity. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3978–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Oh, D.Y.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Lagakos, W.S.; Talukdar, S.; Osborn, O.; Johnson, A.; Chung, H.; Mayoral, R.; Maris, M.; et al. LTB4 promotes insulin resistance in obese mice by acting on macrophages, hepatocytes and myocytes. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mothe-Satney, I.; Filloux, C.; Amghar, H.; Pons, C.; Bourlier, V.; Galitzky, J.; Grimaldi, P.A.; Féral, C.C.; Bouloumié, A.; Van Obberghen, E.; et al. Adipocytes Secrete Leukotrienes. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, W.; Wollam, J.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; El Ouarrat, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Oh, D.Y.; Li, P.; Osborn, O.; Olefsky, J.M. Adipose tissue B2 cells promote insulin resistance through leukotriene LTB4/LTB4R1 signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFuria, J.; Belkina, A.C.; Jagannathan-Bogdan, M.; Snyder-Cappione, J.; Carr, J.D.; Nersesova, Y.R.; Markham, D.; Strissel, K.J.; Watkins, A.A.; Zhu, M.; et al. B cells promote inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes through regulation of T-cell function and an inflammatory cytokine profile. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 5133–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Chng, M.H.Y.; Alonso, M.N.; Yuan, R.; Winer, D.A.; Engleman, E.G. B-1a Lymphocytes Attenuate Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2014, 64, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, D.B.; Srikakulapu, P.; Kaplan, J.L.; Oldham, S.N.; McSkimming, C.; Garmey, J.C.; Perry, H.M.; Kirby, J.L.; Prohaska, T.A.; Gonen, A.; et al. Protective Role for B-1b B Cells and IgM in Obesity-Associated Inflammation, Glucose Intolerance, and Insulin Resistance. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Manabe, I.; Takaki, S.; Nagasaki, M.; Otsu, M.; Yamashita, H.; Sugita, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Eto, K.; Komuro, I.; et al. Adipose Natural Regulatory B Cells Negatively Control Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Hao, Y. B Cell Dysfunction Associated With Aging and Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachinidis, A.; Xanthopoulos, K.; Garyfallos, A. Age-Associated B Cells (ABCs) in the Prognosis, Diagnosis and Therapy of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 31, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.; Miard, S.; Caron, A.; Sallé-Lefort, S.; St-Pierre, P.; Anhê, F.F.; Lavoie-Charland, E.; Blais-Lecours, P.; Drolet, M.-C.; Lefebvre, J.S.; et al. Loss of OcaB Prevents Age-Induced Fat Accretion and Insulin Resistance by Altering B-Lymphocyte Transition and Promoting Energy Expenditure. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, D.; Garcia, D.; Diaz, A.; Romero, M.; Thaller, S.; Blomberg, B.B. Phenotypic and functional features of B cells from two different human subcutaneous adipose depots. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0285025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, N. CXCR3 Ligands in Cancer and Autoimmunity, Chemoattraction of Effector T Cells, and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolarczyk, E.; Lord, G.M.; Howard, J.K. The immune cell transcription factor T-bet: A novel metabolic regulator. Adipocyte 2013, 3, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Exley, M.; Hand, L.; O'Shea, D.; Lynch, L. Interplay between the immune system and adipose tissue in obesity. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, R41–R48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Calderón, J.R.; Cuéllar, R.X.; Gonzalez, M.R.R.; Rubio-Infante, N.; Castillo, E.C.; Elizondo-Montemayor, L.; García-Rivas, G. Interplay between the Adaptive Immune System and Insulin Resistance in Weight Loss Induced by Bariatric Surgery. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensussen, A.; Torres-Magallanes, J.A.; de Álvarez-Buylla, E.R. Molecular tracking of insulin resistance and inflammation development on visceral adipose tissue. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbierski-Kind, J.; Goldeck, D.; Buchmann, N.; Spranger, J.; Volk, H.-D.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Pawelec, G.; Demuth, I.; Spira, D. T cell phenotypes associated with insulin resistance: results from the Berlin Aging Study II. Immun. Ageing 2020, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotoarivelo, V.; Lacraz, G.; Mayhue, M.; Brown, C.; Rottembourg, D.; Fradette, J.; Ilangumaran, S.; Menendez, A.; Langlois, M.-F.; Ramanathan, S. Inflammatory Cytokine Profiles in Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissues of Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery Reveal Lack of Correlation With Obesity or Diabetes. Ebiomedicine 2018, 30, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frikke-Schmidt, H.; O'Rourke, R.W.; Lumeng, C.N.; Sandoval, D.A.; Seeley, R.J. Does bariatric surgery improve adipose tissue function? Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Conles. ; Vidal, J.; de Hollanda, A. Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Adipose Tissue Biology. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, G.T.; Fomin, D.S.; Rizzo, L.V. Human follicular helper T lymphocytes critical players in antibody responses. 2021, 19, eRB6077. [CrossRef]
- Altara, R.; Manca, M.; Brandão, R.D.; Zeidan, A.; Booz, G.W.; Zouein, F.A. Emerging importance of chemokine receptor CXCR3 and its ligands in cardiovascular diseases. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, X. Role of Chemokine (C–X–C Motif) Ligand 10 (CXCL10) in Renal Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billottet, C.; Quemener, C.; Bikfalvi, A. CXCR3, a double-edged sword in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Rev. Cancer 2013, 1836, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huen, A.C.; Wells, A. The Beginning of the End: CXCR3 Signaling in Late-Stage Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2012, 1, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, W.A.; Knechtle, S.J. CXCR3-mediated T-cell chemotaxis involves ZAP-70 and is regulated by signalling through the T-cell receptor. Immunology 2007, 120, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kadlecek, T.A.; Au-Yeung, B.B.; Goodfellow, H.E.S.; Hsu, L.-Y.; Freedman, T.S.; Weiss, A. ZAP-70: An Essential Kinase in T-cell Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a002279–a002279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarczyk, E.; Vong, C.T.; Perucha, E.; Jackson, I.; Cawthorne, M.A.; Wargent, E.T.; Powell, N.; Canavan, J.B.; Lord, G.; Howard, J.K. Improved Insulin Sensitivity despite Increased Visceral Adiposity in Mice Deficient for the Immune Cell Transcription Factor T-bet. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, T.; Czimmerer, Z.; Nagy, L. PPARs are a unique set of fatty acid regulated transcription factors controlling both lipid metabolism and inflammation. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.; Wagner, K.-D. The Role of PPARs in Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofides, A.; Konstantinidou, E.; Jani, C.; Boussiotis, V.A. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in immune responses. Metabolism 2020, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricote, M.; Glass, C.K. PPARs and molecular mechanisms of transrepression. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2007, 1771, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Menn, G.; Neels, J.G. Regulation of Immune Cell Function by PPARs and the Connection with Metabolic and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maculewicz, E.; Mastalerz, A.; Maciejewska-Skrendo, A.; Cięszczyk, P.; Cywińska, A.; Borecka, A.; Garbacz, A.; Szarska, E.; Dziuda. ; Lorenz, K.; et al. Association between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha, -delta and -gamma gene (PPARA, PPARD, PPARG) polymorphisms and overweight parameters in physically active men. Biol. Sport 2021, 38, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, I.; Gurnell, M.; Crowley, V.E.F.; Agostini, M.; Schwabe, J.W.; Soos, M.A.; Maslen, G.L.; Williams, T.D.M.; Lewis, H.; Schafer, A.J.; et al. Dominant negative mutations in human PPARγ associated with severe insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Nature 1999, 402, 880–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.A.; Rego, D.; Moshkova, M.; Kebir, H.; Chruscinski, A.; Nguyen, H.; Akkermann, R.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Prat, A.; Steinman, L.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)α and -γ regulate IFNγ and IL-17A production by human T cells in a sex-specific way. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 9505–9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-M.; Bothwell, A.L.M. The nuclear receptor PPARs as important regulators of T-cell functions and autoimmune diseases. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, L.; Burgdorf, S.; Dani, I.; Saijo, K.; Flossdorf, J.; Hucke, S.; Alferink, J.; Novak, N.; Beyer, M.; Mayer, G.; et al. The nuclear receptor PPARγ selectively inhibits Th17 differentiation in a T cell–intrinsic fashion and suppresses CNS autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angela, M.; Endo, Y.; Asou, H.K.; Yamamoto, T.; Tumes, D.J.; Tokuyama, H.; Yokote, K.; Nakayama, T. Fatty acid metabolic reprogramming via mTOR-mediated inductions of PPARγ directs early activation of T cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ren, L.; Ye, P.; Cheng, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xie, A.; Xia, J. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Deficiency in T Cells Accelerates Chronic Rejection by Influencing the Differentiation of CD4+ T Cells and Alternatively Activated Macrophages. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e112953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolletta, D.; Feuerer, M.; Li, A.; Kamei, N.; Lee, J.; Shoelson, S.E.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. PPAR-γ is a major driver of the accumulation and phenotype of adipose tissue Treg cells. Nature 2012, 486, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuerer, M.; Herrero, L.; Cipolletta, D.; Naaz, A.; Wong, J.; Nayer, A.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B.; Benoist, C.; Shoelson, S.; et al. Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolletta, D.; Cohen, P.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Appearance and disappearance of the mRNA signature characteristic of T reg cells in visceral adipose tissue: Age, diet, and PPARγ effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 112, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalek, R.D.; Gerriets, V.A.; Jacobs, S.R.; Macintyre, A.N.; MacIver, N.J.; Mason, E.F.; Sullivan, S.A.; Nichols, A.G.; Rathmell, J.C. Cutting Edge: Distinct Glycolytic and Lipid Oxidative Metabolic Programs Are Essential for Effector and Regulatory CD4+ T Cell Subsets. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3299–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peraldi, P.; Xu, M.; Spiegelman, B.M. Thiazolidinediones block tumor necrosis factor-α-induced inhibition of insulin signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardini, A.; Laviola, L.; Perrini, S.; Natalicchio, A.; Giorgino, F. Cross-Talk between PPAR�and Insulin Signaling and Modulation of Insulin Sensitivity. PPAR Res. 2009, 2009, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frkic, R.L.; Richter, K.; Bruning, J.B. The therapeutic potential of inhibiting PPARγ phosphorylation to treat type 2 diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, S.; Zhan, Y.; Lu, Q. The roles of PPARγ and its agonists in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 113, 102510–102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, P.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Medina-Gómez, G. PPARs and Metabolic Disorders Associated with Challenged Adipose Tissue Plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, N.J.A.; Zabihi-Mahmoudabadi, H.; Ebrahimi, R.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Hashemnia, S.M.R.; Meshkani, R.; Emamgholipour, S. Principal component analysis of adipose tissue gene expression of lipogenic and adipogenic factors in obesity. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haluzík, M. PPAR-alpha and insulin sensitivity. Physiol. Res. 2006, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jokelainen, J.; Auvinen, J.; Puukka, K.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Järvelin, M.-R.; Kettunen, J.; Mäkinen, V.-P.; Ala-Korpela, M. Insulin resistance and systemic metabolic changes in oral glucose tolerance test in 5340 individuals: an interventional study. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998;15(7):539-53. [CrossRef]
- Groop, L.; Orho-Melander, M. The dysmetabolic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2001, 250, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaenisch, R.; Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, A.; Giovenzana, A.; Insalaco, V.; Phillips, B.E.; Pietropaolo, M.; Giannoukakis, N. Autoimmune Inflammation and Insulin Resistance: Hallmarks So Far and Yet So Close to Explain Diabetes Endotypes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szukiewicz, D. Epigenetic regulation and T-cell responses in endometriosis – something other than autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohil, A.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Al-Shafai, M.; Terranegra, A. The Interplay Between Diet and the Epigenome in the Pathogenesis of Type-1 Diabetes. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M. An Overview of Epigenetics in Obesity: The Role of Lifestyle and Therapeutic Interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biobaku, F.; Ghanim, H.; Monte, S.V.; A Caruana, J.; Dandona, P. Bariatric Surgery: Remission of Inflammation, Cardiometabolic Benefits, and Common Adverse Effects. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvaa049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, R.; Chapela, S.P.; Álvarez-Córdova, L.; Bautista-Valarezo, E.; Sarmiento-Andrade, Y.; Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Sarno, G. Epigenetics in Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus: New Insights. Nutrients 2023, 15, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Olsen, T.; Vinknes, K.J.; Refsum, H.; Gulseth, H.L.; Birkeland, K.I.; Drevon, C.A. Plasma Sulphur-Containing Amino Acids, Physical Exercise and Insulin Sensitivity in Overweight Dysglycemic and Normal Weight Normoglycemic Men. Nutrients 2018, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.K.; Jang, Y.J.; Park, H.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Hong, J.P.; Lee, Y.J.; Heo, Y.-S. Enhanced ANGPTL2 expression in adipose tissues and its association with insulin resistance in obese women. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



