Submitted:
12 May 2023
Posted:
12 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Compliance and Total Dosage
3.3. Perceived Difficulty of the Exercises
3.4. Losses of Follow-Ups and Evaluations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Institute For Health and Care Excellence. Cerebral palsy in under 25s: assessment and management. NICE Guidel 2017; 47.
- Wimalasundera, N.; Stevenson, V.L. Cerebral palsy. Pr. Neurol. 2016, 16, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waikato District Health Board. Cerebral Palsy Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2014.
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health: Children & Youth Version: ICF-CY. 2017; 91: 399–404.
- Klingels, K.; Demeyere, I.; Jaspers, E.; De Cock, P.; Molenaers, G.; Boyd, R.; Feys, H. Upper limb impairments and their impact on activity measures in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaleat-Valayer, E.; Bard-Pondarre, R.; Ganne, C.; Roumenoff, F.; Combey, A.; Bernard, J. Relation between unimanual capacities and bimanual performance in hemiplegic cerebral-palsied children: Impact of synkinesis. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakzewski, L.; Ziviani, J.; Boyd, R. The relationship between unimanual capacity and bimanual performance in children with congenital hemiplegia. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, M.L.; Boyd, R.; Moseley, G.L.; Ware, R.; Johnston, L.M. Tactile function in children with unilateral cerebral palsy compared to typically developing children. Disabil. Rehabilitation 2012, 34, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, M.L.; Boyd, R.N.; Moseley, G.L.; Ware, R.S.; Johnston, L.M. Impact of Tactile Dysfunction on Upper-Limb Motor Performance in Children With Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2012, 93, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnould, C.; Bleyenheuft, Y.; Thonnard, J.-L. Hand Functioning in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, F.; Cretual, A.; Cordillet, S.; Le Cornec, C.; Gonthier, C.; Bouvier, B.; Heyman, R.; Marleix, S.; Bonan, I.; Rauscent, H. Kinematic motion abnormalities and bimanual performance in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.; Ziviani, J.; Ware, R.S.; Boyd, R.N. Relationships between activities of daily living, upper limb function, and visual perception in children and adolescents with unilateral cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Rha, D.W.; Park, J.H.; Park, D.H.; Sim, E.G. Relation among the Gross Motor Function, Manual Performance and Upper Limb Functional Measures in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Yonsei Med J. 2013, 54, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klevberg, G.L.; Østensjø, S.; Elkjær, S.; Kjeken, I.; Jahnsen, R.B. Hand Function in Young Children with Cerebral Palsy: Current Practice and Parent-Reported Benefits. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2016, 37, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrhaug, H.T.; Østensjø, S.; Larun, L.; Odgaard-Jensen, J.; Jahnsen, R. Intensive training of motor function and functional skills among young children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Fahey, M.; Finch-Edmondson, M.; Galea, C.; Hines, A.; Langdon, K.; Mc Namara, M.; Paton, M.C.; Popat, H.; et al. State of the Evidence Traffic Lights 2019: Systematic Review of Interventions for Preventing and Treating Children with Cerebral Palsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre, C.L.; Brandão, M.; Surana, B.; Dew, A.P.; Moreau, N.G.; Gordon, A.M. Caregiver-directed home-based intensive bimanual training in young children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy: a randomized trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 59, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, A.; Haas, T.; Shierk, A. Review of Therapeutic Interventions for the Upper Limb Classified by Manual Ability in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2016, 30, 014–023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepper, S.E.; Krasinski, D.C.; Gilb, M.C.; Khalil, N. Comparing Unimanual and Bimanual Training in Upper Extremity Function in Children With Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2017, 29, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.; Chiarello, L. Family-Centered Care for Children With Cerebral Palsy. J. Child Neurol. 2014, 29, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Beckers, L.W.M.; E Geijen, M.M.; Kleijnen, J.; A A Rameckers, E.; Schnackers, M.L.A.P.; Smeets, R.J.E.M.; Janssen-Potten, Y.J.M. Feasibility and effectiveness of home-based therapy programmes for children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Scher, M.S.; Tilton, A. Cerebral Palsy and Rehabilitative Care: The Role of Home-Based Care and Family-Centered Approach. Indian Pediatr. 2021, 58, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, H.; Mehrholz, J.; Pohl, M.; Behrens, J.; Dohle, C. Mirror therapy for improving motor function after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD008449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gygax, M.J.; Schneider, P.; Newman, C.J. Mirror therapy in children with hemiplegia: a pilot study. 2011, 53, 473–476. [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Sierra, M.; Ríos-León, M.; Abuín-Porras, V.; Martín-Casas, P. Effectiveness of mirror therapy and action observation therapy in infantile cerebral palsy: a systematic review. An. del Sist. Sanit. de Navar. 2022, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narimani, A.; Kalantari, M.; Dalvand, H.; Tabatabaee, S.M. Effect of Mirror Therapy on Dexterity and Hand Grasp in Children Aged 9-14 Years with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. 2019, 13, 135–142.
- Carrión, R.P.; Escobar, J.C.Z.; Guerra, M.C.; Martínez, P.B.; Cepa, C.B.M. Terapia en espejo y de observación de la acción en niños con parálisis cerebral espástica unilateral: estudio de viabilidad. 2022, 75, 325–332. [CrossRef]
- Farzamfar, P.; Heirani, A.; Sedighi, M. The Effect of Motor Training in Mirror Therapy on Gross Motor Skills of the Affected Hand in Children With Hemiplegia. Iran. Rehabilitation J. 2017, 15, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, O.K.; Yardimci, B.N.; Sahin, S.; Orhan, C.; Livanelioglu, A.; Soylu, A.R. Combined Effects of Mirror Therapy and Exercises on the Upper Extremities in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2019, 23, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchez, R.; Gygax, M.J.; Roches, S.; Fluss, J.; Jacquier, D.; Ballabeni, P.; Grunt, S.; Newman, C.J. Mirror therapy in children with hemiparesis: a randomized observer-blinded trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, M.L.; Johnston, L.M.; Russo, R.N.; Moseley, G.L. A Single Session of Mirror-based Tactile and Motor Training Improves Tactile Dysfunction in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Replicated Randomized Controlled Case Series. Physiother. Res. Int. 2016, 22, e1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smorenburg, A.R.; Ledebt, A.; Deconinck, F.J.; Savelsbergh, G.J. Matching accuracy in hemiparetic cerebral palsy during unimanual and bimanual movements with (mirror) visual feedback. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2012, 33, 2088–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, M.L.; Johnston, L.M. Perspectives on tactile intervention for children with cerebral palsy: a framework to guide clinical reasoning and future research. Disabil. Rehabilitation 2017, 40, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakzewski, L.; Ziviani, J.; Boyd, R.N. Efficacy of Upper Limb Therapies for Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Meta-analysis. PEDIATRICS 2014, 133, e175–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auld, M.L.; Russo, R.; Moseley, G.L.; Johnston, L.M. Determination of interventions for upper extremity tactile impairment in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 815–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo-Carrión, R.; Zuil-Escobar, J.C.; Cabrera-Guerra, M.; Barreda-Martínez, P.; Martínez-Cepa, C.B. Mirror Therapy and Action Observation Therapy to Increase the Affected Upper Limb Functionality in Children with Hemiplegia: A Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2021, 18, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuro Orthopaedic Institute. NOI Group. 2023; Im Internet. Available online: https://www.noigroup.com/.
- Karolinska Institutet. Children’s Hand-use Experience Questionnaire 2.0. 2011; Im Internet. Available online: https://www.cheq.se/questionnaire.
- Amer, A.; Eliasson, A.; Peny-Dahlstrand, M.; Hermansson, L. Validity and test–retest reliability of Children’s Hand-use Experience Questionnaire in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 58, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sköld, A.; Hermansson, L.N.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Eliasson, A.-C. Development and evidence of validity for the Children’s Hand-use Experience Questionnaire (CHEQ). Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, M.L.; Ware, R.S.; Boyd, R.N.; Moseley, G.L.; Johnston, L.M. Reproducibility of Tactile Assessments for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2012, 32, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, M.L.; Boyd, R.N.; Moseley, G.L.; Johnston, L.M. Tactile Assessment in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Clinimetric Review. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2011, 31, 413–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell-Krotoski, J.; Tomancik, E. The repeatability of testing with Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments. J. Hand Surg. 1987, 12, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, A.L.; Mackinnon, S.E.; Crosby, P.M. Reliability of two-point discrimination measurements. J. Hand Surg. 1987, 12, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varni JW, MAPI. PedsQL TM Módulo de Parálisis Cerebral. Versión 3.0 - Spanish (Spain).
- Varni, J.W.; Burwinkle, T.M.; Berrin, S.J.; A Sherman, S.; Artavia, K.; Malcarne, V.L.; Chambers, H.G. The PedsQL in pediatric cerebral palsy: reliability, validity, and sensitivity of the Generic Core Scales and Cerebral Palsy Module. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, L.; van der Burg, J.; Janssen-Potten, Y.; Rameckers, E.; Aarts, P.; Smeets, R. Process evaluation of two home-based bimanual training programs in children with unilateral cerebral palsy (the COAD-study): protocol for a mixed methods study. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo-Carrión, R.; Romay-Barrero, H.; Lirio-Romero, C.; Arroyo-Fernádez, R.; M-Guijarro-Herraiz, M.; Ferri-Morales, A. Feasibility of family-directed home-based bimanual intensive therapy combined with modified constraint induced movement therapy (h-BITmCI) in very low and low bimanual functional level: A brief report. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2022, 26, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beani, E.; Menici, V.; Ferrari, A.; Cioni, G.; Sgandurra, G. Feasibility of a Home-Based Action Observation Training for Children With Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: An Explorative Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasri, N.A.; An, M.; Palisano, R.J. Parents’ Perception of Receiving Family-Centered Care for Their Children with Physical Disabilities: A Meta-Analysis. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2017, 38, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, L.; Rameckers, E.; Aarts, P.; van der Burg, J.; Smeets, R.; Schnackers, M.; Steenbergen, B.; de Groot, I.; Geurts, A.; Janssen-Potten, Y. Effect of Home-based Bimanual Training in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy (The COAD-study): A Case Series. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2021, 24, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnackers, M.; Beckers, L.; Janssen-Potten, Y.; Aarts, P.; Rameckers, E.; van der Burg, J.; de Groot, I.; Smeets, R.; Geurts, S.; et al.; COAD Focus Group Home-based bimanual training based on motor learning principles in children with unilateral cerebral palsy and their parents (the COAD-study): rationale and protocols. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Pazi, H.; Beni-Adani, L.; Lamdan, R. Accelerating Telemedicine for Cerebral Palsy During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ardanaz, B.; Morales-Asencio, J.M.; León-Campos, A.; Kaknani-Uttumchandani, S.; López-Leiva, I.; Garcia-Piñero, J.M.; Martí-García, C.; García-Mayor, S. Quality of Life and Health Services Utilization for Spanish Children With Cerebral Palsy. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2020, 53, e121–e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, E.S.; Ravanbakhsh, M.; Torabipour, A.; Amiri, E.; Haghighyzade, M. Home-based versus center-based care in children with cerebral palsy: a cost-effectiveness analysis. 2015, 8, 245–251.
- Majnemer, A.; Shikako-Thomas, K.; Lach, L.; Shevell, M.; Law, M.; Schmitz, N.; Poulin, C. ; QUALA Group Rehabilitation service utilization in children and youth with cerebral palsy. Child: Care, Heal. Dev. 2013, 40, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Participants’ Characteristics | MT Group (n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|
| n | % | |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 2 | 33.3 |
| Female | 4 | 66.7 |
| MACS1 level | ||
| I | 3 | 50.0 |
| II | 3 | 50.0 |
| Affected side | ||
| Left | 1 | 16.7 |
| Right | 5 | 83.3 |
| Participant | Total minutes of MT |
|---|---|
| 1 | 600.0 |
| 2 | 651.0 |
| 3 | 717.0 |
| 4 | 720.0 |
| 5 | 603.3 |
| 6 | 600.0 |
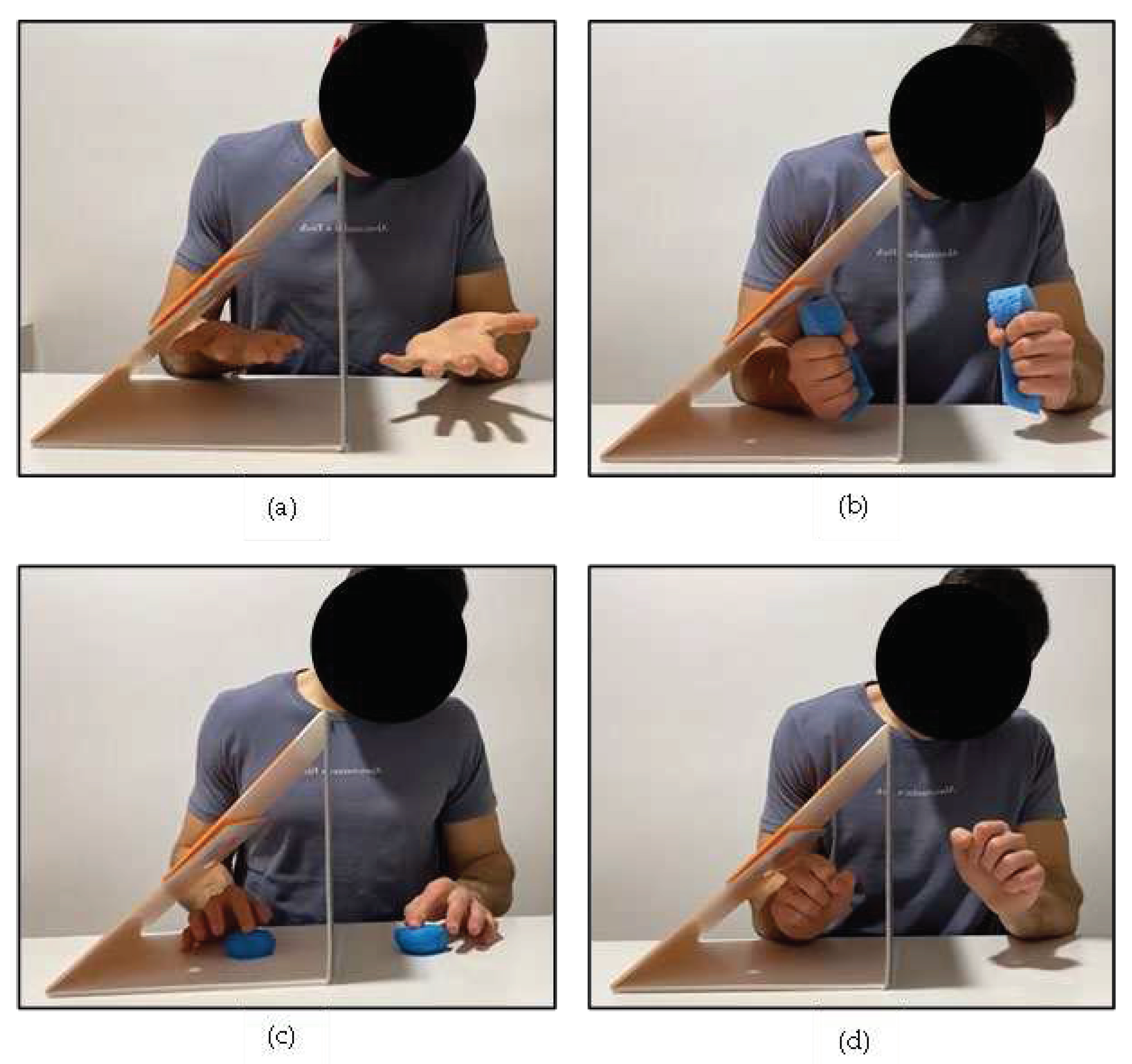
| Data (n = 5) | Forearm Pronosupination | Sponge Squeezing | Finger-by-Finger Pressing | Wrist Spins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | 3.17 (2.51) | 2.91 (1.44) | 4.41 (2.49) | 4.51 (1.81) |
| Week 2 | 2.38 (2.23) | 3.19 (2.24) | 4.46 (2.57) | 4.32 (1.62) |
| Week 3 | 2.55 (2.32) | 2.56 (2.38) | 3.66 (2.59) | 3.80 (1.41) |
| Week 4 | 2.37 (2.15) | 2.82 (1.91) | 3.23 (2.04) | 4.07 (1.71) |
| Week 5 | 2.60 (2.71) | 2.68 (1.90) | 2.94 (2.04) | 3.91 (1.98) |
| Differences between week 1 and week 5 (p value) | 0.345 | 0.715 | 0.225 | 0.068 |
| Evaluations | Participants | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| E01 | CHEQ 2.0 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SF4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| C-PedsQL5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| P-PedsQL6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| E12 | CHEQ 2.0 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SF4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| C-PedsQL5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| P-PedsQL6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| E23 | CHEQ 2.0 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SF4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| C-PedsQL5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| P-PedsQL6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





