1. Introduction
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is still one of the deadliest cancers in Oncology and due to its increasing incidence and overall five-year survival rate of less than 5% [
1], it is expected to be the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the US by 2030 [
2,
3]. In addition, the annual incidence of PDAC is increasing in people younger than 30 years of age [
4].
Among modifiable risk factors, current cigarette smoking, alcohol use, chronic pancreatitis and obesity has strong association with PDAC [
3].
In most cases PDAC is diagnosed at an advanced stage, locally advanced (30%–35%) or metastatic (50%–55%) [
2], and treated with polychemotherapy regimens, including FOLFIRINOX, Gemcitabine/Nab-Paclitaxel, and nanoliposomal Irinotecan/Fluorouracil, with a survival benefit of 2–6 months compared with a Single-agent Gemcitabine [
3,
5,
6,
7].
Tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a central role in PDAC biology and represents a desmoplastic scaffold characterized by intricate cellular and acellular crosstalk between activated Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), Myeloid-derived suppressive cells (MDSCs), regulatory T cells (Tregs), and bioactive specialized extracellular matrix (ECM), with low numbers of Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). In this scenario, Cell-cell interactions are obstructed by the ECM, which explains not only chemoresistance, but also poor response to immunotherapy.
In the heterogenous mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer KRAS, TP53, SMAD4 and CDKN2A represent major oncogenic events involved in key molecular pathways such as DNA damage repair, cell cycle regulation, TGF-β signalling, chromatin regulation and axonal guidance [
8].
About 30% of all human cancers bear activating Rat sarcoma (RAS) mutations, in particular Kirsten rat sarcoma (KRAS) mutations are considerably more frequent than Harvey rat sarcoma virus oncogene (HRAS) and Neuroblastoma RAS Viral Oncogene Homolog (NRAS) mutations. As for PDAC, more than 90% of patients are KRAS mutated (KRASmu), specifically KRASG12D and KRASG12V are the most common mutations [
9].
The KRAS protein is a molecular switch that cycles between an active, Guanosine-5′-triphosphate (GTP)–bound state and an inactive, Guanosine-5′-diphosphate (GDP)–bound form. In cancer tumorigenesis, KRAS mutations typically increase the Steady-state levels of the active form, driving protumorigenic pathways, such as the Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways.
Mutational activation of KRAS in the earliest precancerous lesions represents the first genetic event leading to invasive pancreatic cancer [
10,
11]. Despite this critical role, its high affinity for nucleotide the lack of viable binding pockets for Small-molecule inhibitors have made direct targeting of the RAS protein extremely difficult over the past four decades [
9,
12]. In this context, understanding PDAC tumorigenesis is crucial for both the identification of early diagnostic markers and the development of multiple alternative modes of intervention.
In this review we explore KRAS-dependency in PDAC and analyse recent data on KRAS signaling inhibitors focusing on how cancer cells establish compensatory escape mechanisms.
2. KRAS-Dependent Tumorigenesis in PDAC
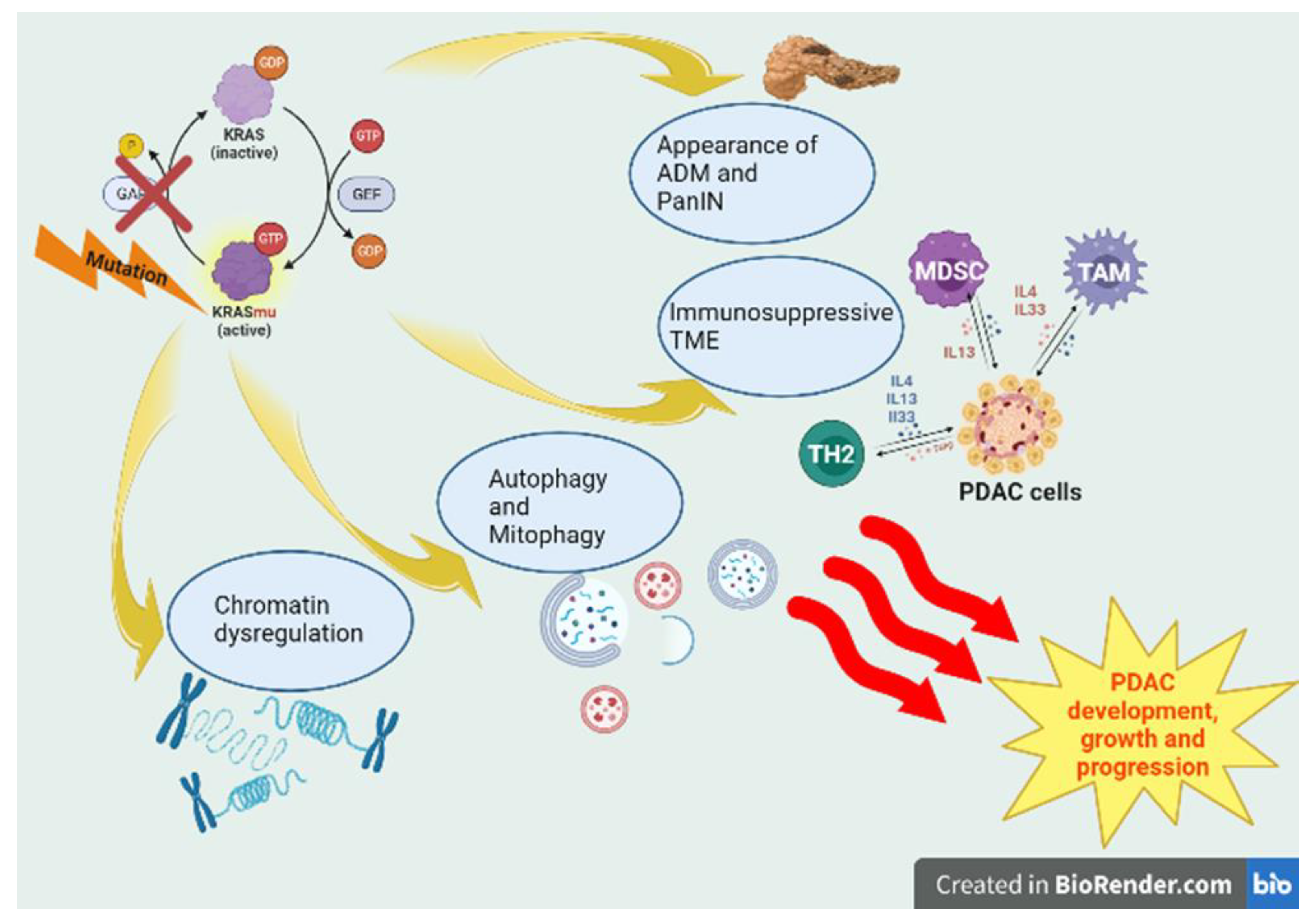
Several studies have demonstrated the strong association between PDAC and inflammation. In the context of chronic pancreatitis, the inflammatory microenvironment can activate survival and proliferation programs and induce chromatin changes in cancer cells, promoting tumor growth. Oncogenic KRAS accelerates this process in pancreatic tissue (
Figure 1.)[
13,
14,
15], inducing, along with inflammatory damage (e.g., cerulean-induced pancreatitis) and other tumor suppressor deficiencies, e.g. protein (p)16INK4a/p14ARF, Tumor Protein p53 (TP53) and/or Suppressor of Mothers against Decapentaplegic 4 (SMAD4) loss, the appearance of neoplastic precursor lesions, such as acinar-to-ductal metaplasia (ADM) and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) [
15].
2.1. KRASmu, Inflammation and Precursor Lesions
KRASmu expression is not sufficient to initiate tumorigenesis in pancreas and for ADM induction and development of pancreatic acinar cells, are necessary further subsequent events, such as additional genetic lesions, chronic inflammation, or upregulation of growth factor signaling [
11,
16,
17].
PanIN is considered the major pathological basis of PDAC development with properties of ductal cells as well as tumor cells in PDAC. However, recent data in engineered mouse models (GEMM) of pancreatic cancer have evidenced that acinar cells are the main cellular origin of PDAC. Acinar cells, through ADM, show increased expression of ductal cell markers such as cytokeratin-19 (CK-19) or Sex-determining region Y box 9 (SOX9) and reduced expression of acinar cell markers, such as amylase or MIST-1 [
18,
19,
20]. In presence of KRASmu , the ADM process become irreversible and leads to a change in cellular identity (transdifferentiation) and progression to PanIN. Transcription factors controlling pancreatic duct development, such as SOX9 and hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 (HNF6), or other ones critical for somatic stem cell reprogramming, like Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) have been demonstrated to regulate ADM process [
18]. Ge W and colleagues demonstrated that SOX9 and Phos-SOX9 (S181) levels in acinar cells are both regulated by miR-802, a pancreatic microRNA (miRNA), which controls ADM formation in the presence of oncogenic KRAS [
21]. Costamagna A and colleagues demonstrated that integrin and growth factor receptor signaling converge on p130Cas, an adaptor protein encoded by BRCA1 and a downstream effector of the KRAS pathway, to induce tumorigenesis, and boost acinar to ductal metaplasia and subsequent tumorigenesis through PI3K activation [
11].
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFkB) family of transcription factors is composed by NFkB2 (p100/p52), NFkB1 (p105/p50), RelA/p65, RelB, and Rel. NFkB2 is necessary for KRASG12D-dependent ADM development, PanIN progression and tumor proliferation. In the same way RelB promotes PanIN progression in the KRASG12D PDAC cells [
22].
Recent data have shown that Ring Finger Protein 43 (RNF43) is the most frequently mutated genes in IPMNs together with KRAS RNF43 is a member of the RING finger protein family, and an E3 ubiquitin ligase. It mediates the ubiquitination and degradation of the Wnt receptor complex component Frizzled and chains Transcription Factor 4 (TCF4) to the nuclear membrane by silencing its transcriptional activity. Thus, the loss of RNF43 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [
23].
RNA sequencing analysis of PDAC patients in recent works showed high expression of angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4), which is involved in epidermal differentiation and development of PDAC. Yan HH et al. revealed a Tumor-promoting role of ANGPTL4 through regulation of periostin/integrin signaling during PDAC initiation and maintenance. These data suggested ANGPTL4/periostin axis as a potential molecular target for the prevention of PDAC [
24].
IL-33 has a central role in this program bridging tissue damage with KRAS-dependent epithelial plasticity and accelerating the appearance of early precursor lesions (PanIN) after injury. Additionally, in early neoplasia this cytokine induces an immunosuppressive TME [
25].
2.2. KRASmu and Metabolism
KRASmu PDACs depend on glucose and glutamine for energy production and maintenance of the redox balance and show decreased levels of intracellular amino acid. On the other hand, autophagy is required for the maintenance of KRASmu cells [
26]. Moreover, recent study showed how autophagy increases MHC degradation as escape mechanism from T lymphocytes surveillance and makes tumor cells resistant to im-munomodulatory drugs [
27].
KRASmu pancreatic cancer cells can channel their glucose metabolism away from the mitochondria through programmed mitophagy via the mediator BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19-kDa-interacting protein 3-like (BNIP3L/NIX). NIX ablation in vivo has been shown to delay the progression of PanIN to PDAC. In this context, Viale A et al demonstrated that quiescent KRASmu pancreatic cancer cells that survive oncogene ablation, which are responsible for tumor recurrence, have cancer stem cells characteristics and depend on oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) for survival [
28]. Glutamine metabolism is involved in redox homeostasis and plays a key role in tumor growth [
29].
Previous work in recent years has highlighted the crucial role of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) metabolism in metabolic adaptation in cancer. In particular, BCAA transaminase 1 (BCAT1) or BCAT2 has been shown to be upregulated and important for proliferation in PDAC [
30].
2.3. KRASmu and TME
Mutant KRASG12D upregulates peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-delta (PPARδ) in human and murine PanIN lesions, promoting inflammation-related signaling pathways and pancreatic tumorigenesis. PPARδ hyperactivation recruits TAMs and MDSCs via the CCL2/CCR2 axis, remodeling the immune TME. This process has been demonstrated in mouse model fed with high-fat diet enriched with fatty acids that are natural ligands of PPARδ [
31].
KRASmu upregulates IL2Rγ and IL4R, two members of type I cytokine receptor family, the former of which contributes to PDAC tumorigenesis. In fact, the cytokines IL4 and IL13 signaling via IL4R drive JAK-STAT-cMYC activation, resulting in increased glycolysis and tumor growth [
30]. Previous works have shown that cMYC expression enhances tumor cell proliferation [
32]. In KRASmu PDACs are found higher levels of cytokines IL4, IL13, and, as mentioned in this work, IL-33, secreted by GATA-3+ TH2 polarized CD4+ T cells, resulting in immunosuppressive TME and a self-perpetuating cascade of pro-tumorigenic effects [
31]. In addition, KRASmu is crucial for the crosstalk between PDAC cells and activated cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). CAFs are activated through Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and sonic hedgehog pathways and regulate the tumour stroma, including extracellular matrix, collagen fibres and hyaluronic acid, promoting PDAC cell growth and an immunosuppressive TME [
10].
Moreover, oncogenic KRASG12D suppresses Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression and has the strongest suppressive power compared with other KRAS mutations [
33].
2.4. KRASmu and Chromatin
In the injury-prone pancreas, oncogenic KRAS mutation induces an epigenetic program alternative to physiological regeneration, that leads to PDAC initiation. Alonso-Curbelo D et al. showed in vivo that pancreatic metaplasia is characterized by epigenetic silencing of acinar identity loci that is enhanced by Bromodomain Containing 4 (BRD4) suppression [
25]. The Bromodomain and Extraterminal (BET) family member BRD4 is a chromatin reader which binds acetylated and active chromatin enhancing transcription of Cell-identity genes.
In KRASmu cells, within 48 hours of tissue damage, progression to neoplasia is facilitated by interactions between genetic and environmental insults leading to an ‘Acinar-to-neoplasia’ chromatin switch that alter DNA accessibility. This chromatin remodeling program is present from the early stage of disease to metastasis in advanced PDAC [
25].
Sangrador I et al demonstrated that the transcriptional repressor Zinc finger E-box binding homebox 1 (ZEB1) is a key mediator of KRAS-dependent oncogenesis in vivo; indeed, in the presence of a KRAS mutation, ZEB1 haploinsufficiency delays PDAC development. Notably, ZEB1 is predominantly expressed in stromal myofibroblasts associated with PanIN and PDAC [
34]. Genovese G et al highlight the crucial tumour-suppressive role of SWI/SNF Related, Matrix Associated, Actin Dependent Regulator Of Chromatin, Subfamily B, Member 1 (SMARCB1) as a differentiation checkpoint and a gatekeeper of Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. This is a novel mechanism of KRAS-dependent tumorigenesis of PDAC cells that fail to activate downstream KRAS singaling (e.g., through MAPK) [
35]. SMARCB1 is a Switch/Sucrose Non-Fermentable (SWI/SNF) chromatin remodeling factor whose activity restrains growth and metabolic programs by MYC activation [
35].
3. KRAS Signaling Inhibitors in PDAC
3.1. KRASG12C Inhibition
The frequency of KRASG12C mutations in PDAC patients is abnormally high in some regions like Japan, while its frequency in PDAC patients worldwide is quite low. However, none of the KRASG12C inhibitors, such as sotorasib or adagrasib, have been approved as a treatment for PDAC [
36]. A previous work has demonstrated the growth inhibition power of Adagrasib (MRTX849) in a pancreatic cancer cell line [
37,
38] and it is undergoing clinical trials for patients with KRASG12C mutant pancreatic cancer (NCT03785249) (
Table 1). Also, a confirmed partial response has been reported in the phase I/Ib cohort in a patient with PDAC (NCT03785249). Ostrem et al. pinpointed the druggable switch-II pocket in KRASG12C through X-ray crystallography and mass spectrometry [
38]. Anyway, only a small percentage of PDAC patients harbors G12C mutation, on the other hand, as previous mentioned in this review, G12D is the most prevalent KRAS mutation in PDAC.
3.2. KRASG12D Inhibition
Various groups have shown that it is possible to pharmacologize GTP-bound KRASG12D: KD2 is a cyclic peptide that can selectively target the switch-II groove in mutant GTP-bound KRASG12D; both in vitro and in vivo KS-58, a bicyclic peptide, has shown activity against KRASG12D mutated pancreatic cancer [
39]; MRTX1133 is a small molecule that selectively targets KRASG12D by blocking downstream pathways through inhibition of nucleotide exchange and binding of effector Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma 1 (RAF1), in vivo MRTX1133 reduced phosphorylation of Extracellular Signal-regulated kinase (ERK) resulting in tumor regression [
33]. Using a medicinal chemistry approach, other compounds were discovered: TH-Z827 and TH-Z835 are two inhibitors that bind with Asp12 inside the switch-II pocket specifically inhibiting KRAS signaling, and not KRASG12C or WT, in G12D mutant PDAC in vitro and in vivo; in vitro KD-8 is another inhibitor of KRASG12D PDAC tumor growth [
33]. These works provide proof of concept evidence that the KRASG12D mutation could potentially be targeted, benefiting a larger number of PDAC patients [
38].
3.3. Other Inhibitors
RNA interference (RNAi) has been demonstrated to suppress KRASmu expression in pancreatic cancer cells inhibiting Anchorage-independent growth and tumorigenic proliferation. These effects suggest RNAi as a potential drug for KRASmu PDAC [
10]. Messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-5671/V941 is a novel mRNA vaccine encoding mutant KRAS which is being studied in patients with KRASmu cancers in phase I clinical trial (NCT03948763) with or without Pembrolizumab. Similarly, dendritic cell vaccines (NCT03592888) and peptide vaccines (NCT04117087) for KRASmu patients are in clinical trials (
Table 1) [
38].
Engineering patient lymphocytes to express receptors that specifically target tumor neoantigens is known as adoptive cell therapy [
40]. A previous work has generated murine T cells that can recognize KRASG12D PDAC in an HLA-A*11:01 restricted manner and inhibit tumor growth in vivo [
41]. Two ongoing phase I/II clinical trials are investigating the transfer of such cells engineered to express the murine T-cell receptor (TCR) specific for KRASG12D (NCT03745326) or KRASG12V (NCT03190941) (
Table 1) in an HLA-restricted manner, in patients with solid tumors, including KRASG12D PDAC [
33,
38].
Tricomplex inhibitors bind Cyclophilin A, a chaperone protein ubiquitously present inside the cell [
42], which in turn binds the target protein, creating a Target-inhibitor-Cyclophilin-A complex. RMC-9805 is a novel specific tricomplex inhibitor of KRASG12D which suppresses tumor growth in xenograft PDAC [
33]. RMC-6236, on the other hand, is a Multi-RAS inhibitor tricomplex, capable of targeting multiple different mutations of KRAS, like KRASG12V [
38].
For KRAS to localize on membrane and become active giving rise to signal transduction, its Post-translational prenylation catalyzed by farnesyl transferases (FTases) is required [
43]. For this reason, a number of FTase inhibitors (FTIs), e.g. lonafarnib and tipifarnib, have been designed and clinically studied [
44], reaching phase III clinical trials for various cancer types, with disappointing results in PDAC [
38].
4. Mechanisms of Escaping in Resistance to KRAS Inhibitors
Despite promising results in preclinical and clinical studies of several inhibitors outlined in this paper, there are still few studies on mechanisms of escaping in resistance to KRASG12D inhibitors. So far, even MRTX1133, a KRASG12D inhibitor, has not entered clinical trials yet. Thus, most of the data about mechanisms of escaping in resistance to KRASG12D need to be translated from studies on the application in the clinic of KRASG12C inhibitors.
Pre and Post-treatment comparison of samples from patients treated with the KRASG12C inhibitor sotorasib showed multiple genetic escape mutations after treatment in 63% of patients, including KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, EGFR, FGFR2, and MYC [
36]. Further exploration revealed that the inhibitory effect of sotorasib was reduced after the occurrence of KRASG12V, NRASQ61K or MRASQ71R (a small GTPase regulating the dimerization and activation of CRAF, a RAF family protein in KRAS downstream of the MAPK-ERK pathway [
36]). The binding site for a series of KRASG12C inhibitors, like sotorasib, is the cysteine 12 residue of the KRASG12C protein, which is located near the switch-II pocket [
45]. Mutations at this site, like KRASY96D found in a patient after treatment with the KRASG12C inhibitor MRTX849, disrupt the hydrogen bond between the binding site and KRASG12C inhibitor [
36]. In the development of resistance, other acquired genetic mutations in KRAS are G12D/R/W, G13D, Q61H, R68S, H95D/Q/R, Y96C, and KRASG12C allele amplification, as well as genetic changes such as MET (also known as the N-methyl-N0-nitroso-guanidine human osteosarcoma transforming gene) amplification, mutational activation of Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MAP2K1) also known as MEK and Rearranged during Transfection (RET), oncogene fusion of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), RET, B-RAF, RAF1, and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), Loss-of-function mutations in Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) and Phosphatase and Tensin homolog (PTEN) [
12,
38]. These mutations increase the levels of active GTP-bound KRAS protein preventing drug binding [
46]. It has been demonstrated that KRASmu inhibitors, such as sotorasib, or MEK inhibitors, such as trametinib, to induce escape mechanisms in PDAC, causing activation of the Mechanistic target of rapamycin 2 (mTORC2) molecule Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mammalian target of rapamycin (RICTOR) and phosphorylation of AKT at Ser-473 by integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in several PDAC mouse models and human tumors [
38]. After these results, it was shown that inhibition of mTORC2 alone stimulates ERK activation [
47] promoting cell survival. On the other hand, mTORC2 signaling has an important role in the development of resistance in PDAC; in fact, its inhibitors have Anti-tumor activity in PDAC cells when combined with an inhibitor of KRASmu or MEK [
38]. Because PDAC is characterized by high cell heterogeneity, it is highly likely that future use of KRASG12D inhibitors in PDAC may lead to the same result by increasing mutational burden with the previously mentioned mutations and genetic changes [
36].
Cheng DK et al. demonstrated that oncogenic KRASmu inhibits wild type (WT) RAS signaling through NF1/Ribosomal S6 kinase 1 (RSK1). In fact, the inhibition of this negative feedback pathway with KRAS inhibitors activates WT RAS signaling and promotes adaptive resistance, as evidenced in PDAC cells survived after treatment with KRASG12V inhibitor. In addition, inhibition of both WT RAS, through son of sevenless 1 (SOS1) inhibition, and KRASG12C mutation, through AMG 510, showed the best response in vitro, demonstrating a synergy between KRASG12C inhibitors and upstream effectors (SOS1) inhibitors. These data strengthen the idea of WT RAS as a central actor in the acquired resistance to KRASmu inhibitors [
49].
Alterations of multiple Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-RAS-MAPK pathways contribute to the resistance to KRASG12C inhibitor adagrasib, and the combination of inhibitors of RTK, Src homology region 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 (SHP2) and KRASmu is the subject of ongoing clinical trials (NCT04330664, NCT04185883) (
Table 1) [
12,
38].
Moreover, KRASmu tumors have another intrinsic mechanism of resistance; in fact in the presence of FTIs described above, KRAS is prenylated by geranylgeranyl transferase 1 (GGTase1), the so-called alternative prenylation [
38].
As previous said in this paper, TME is composed of various types of cells and plays a central role in chemoresistance and immunoresistance in PDAC. CAFs have been shown to contribute to resistance to therapies such as KRASmu inhibitors and to express vitamin D receptor which plays an important role in the development of resistance; confirming this, a work has shown how calcipotriol, a vitamin D receptor agonist, can override the influence of CAFs in murine model [
38]. As said above, autophagy is necessary for the maintenance of KRASmu cells, in fact cancer cells utilize several metabolites derived from autophagic degradation of CAFs resulting in resistance to different therapies including KRAS inhibitors [
50]. As well as CAFs, neurons present in the TME release amino acid serine, promoting PDAC growth [
38].
5. Alternative Targets in KRAS Signaling Pathways and Future Perspectives
5.1. Alternative Targets in KRAS Signaling Pathway
An effective strategy to overcome resistance to KRAS inhibitors is combining different types of therapies, e.g. combination of KRASG12C inhibitors with SHP2 (an upstream effector of RAS) inhibitors has been shown to surpass resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors alone and remodel TME in PDAC models reducing the number of activated CAFs [
49]. On the other hand, the combination of KRAS inhibitors with downstream target therapies, such as MAPK-ERK and PI3K-AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways inhibitors, showed disappointing results in pancreatic cancer models. Nevertheless, the inhibitory effect of histone deacetylase (HDAC) synergizes with the combined targeting of the MAPK-ERK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathways [
36]. Promising new combinations include KRASG12C inhibitors with cell cycle checkpoints or immune checkpoints inhibitors (ICIs) [
37,
45] or the triple inhibition of KRASG12C/ SHP2/PD-L1 tested in PDAC murine models [
51]. Recent data suggest nuclear export protein exportin 1 (XPO1), which transports protein cargo from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, as an important factor in relieving tumor cells from resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors [
36].
Another promising factor in resistance to KRAS inhibition is the deubiquitinase Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 21 (USP21), which at is amplified and overexpressed in about 20% of PDAC patient samples. Its nuclear activity promotes pancreatic tumor growth and tumor stem cell properties by deubiquitinating the Transcription factor 7 (TCF7) and amplifying canonical Wnt signaling [
52]. Further explorations are needed to test USP21 inhibitors with or without KRAS inhibitors as possible therapies in PDAC [
53].
Different molecules that prevent the interaction between Son of Sevenless (SOS1) and KRAS have been identified [
38]. SOS1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that binds GDP-bound KRAS and catalyzes the switch of GDP for GTP activating KRAS [
54]. Its low levels result in inhibition of growth tumor. BI-3406 is a SOS1 inhibitor active only in KRASmu cells with Anti-tumoral activity synergistic with MEK inhibitors. BI-1701963 is another SOS1 inhibitor which is being studied in an ongoing phase I clinical trial (NCT04111458) with or without MEK inhibitor (trametinib) in patients with KRASmu cancers (
Table 2) [
38].
SHP2 is a tyrosine phosphatase protein encoded by the gene PTPN11 with an intrinsic regulatory mechanism, [
38] its role in KRAS signaling seems to be linked to other proteins such as SOS1 and Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2) and it is involved in various pathways such as KRAS-MAPK signaling [
55]. SHP2 plays a central role in cancer development in KRASmu PDAC and NSCLC models, and its inhibition has been seen as synergistic with MEK inhibition stopping tumor growth in PDAC and NSCLC models in vivo [
38]. SHP099 is a compound that lock SHP2 in its inactive autoinhibited state and able to inhibit tumor growth via MAPK pathway in vivo [
56]. Several potential inhibitors of SHP2 are in different ongoing cilinical trial [
57]: RMC-4630 is currently in phase I/Ib clinical trials with or without an ERK inhibitor (NCT03634982, NCT04916236); RMC-4550 has shown to inhibit KRASmu cells proliferation in preclinical models [
58]; TNO155, an allosteric inhibitor of SHP2 with demonstrated Anti-tumoral activity through MAPK, is in several ongoing phase I and II clinical trials with or without several synergistic targeted therapies (NCT04000529, NCT04330664, NCT03114319) (
Table 1,
Table 2) [
59]; other SHP2 inhibitors are in clinical trials, such as ERAS-601 (NCT04670679), JAB-3312 (NCT04121286), BBP-398 (NCT04528836), and RLY-1971 (NCT04252339) (
Table 2) [
38].
5.2. Future Perspectives
Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) consist of two peptides, one that binds the target protein linked to another peptide that recruits an E3 ubiquitin ligase for proteasomal degradation of the target protein [
60]. LC-2 is a PROTAC that targets KRASG12C composed of MRTX849 bound to a von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) recruiter peptide; the former binds covalently to KRASmu, and the latter induces sustained proteasomal degradation of KRASmu and subsequent MAPK inhibition. The compound 17f is a PROTAC that targets phosphodiesterase 6 (PDEδ), an important prenylation factor [
38].
NS-1 is a monobody inhibitor of RAS dimerization that targets the α4–α5 interface of KRAS able to prevent the development and progression of pancreatic cancer in murine model. The unique problem with this potential new strategy is the size of the molecule NS-1 which makes its intracellular localization difficult [
38].
Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNAs) are synthetic nucleotide analogs capable of binding to specific complementary DNA and RNA sequences [
36] or to the mRNA of the target gene inhibiting its translation process [
61]. In a previous work, PNAs significantly inhibited tumor cell activity and reduced the the KRASG12D gene expression in the human metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line AsPC-1 [
36].
As previous mentioned in this paper, WT KRAS can induce resistance to KRAS inhibitors with its compensatory effect and in this setting Pan-RAS inhibitors could overcome this mechanism. Jin Wang et al. have developed several small-molecule Pan-RAS inhibitors that stabilize the “open non-signaling intermediate conformation” of RAS [
62]: NSC290956 (also called Spiclomazine or APY606) inhibited the proliferation of KRAS-dependent pancreatic cancer cell lines CFPAC-1 (KRASG12V), MIA PaCa-2 (KRASG12C), Capan-1 (KRASG12V), SW1990 (KRASG12T) and BxPC-3 (WT KRAS) [
36]; NSC48160 showed similar effect on CPFAC-1 (KRASG12V) and BxPC-3 (WT KRAS) [
63] and induced apoptosis in MIA PaCa-2 (KRASG12C) [
64]; inhibitory effects of NSC48693 on KRAS-dependent cancer cells were superior to those of NSC48160 on CFPAC-1(KRASG12V), MIA PaCa-2 (KRASG12C) and BxPC-3 (WT KRAS) cells [
36].
We have already mentioned a class of tricomplex inhibitors that has shown promising results; another similar class of compounds is the tricomplex RAS-ON (RASON) inhibitors, comprehending KRASG12C, G12D, and G13C inhibitors, and a G12X inhibitor which targets multiple different G12 mutations, which are currently being studied after initial preclinical data [
65].
As mentioned earlier in this review, IL4/IL13 cytokines play a central role in TME remodeling via the IL4-IL4R-Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins (STAT) signaling cascade. However, trials with JAK1/2 inhibitors have yielded disheartening results [
66]. Further explorations are necessary to study interactions between cancer cells and TME cells.
We have already discussed RNAi which still poses a challenge a challenge because of enzymatic breakdown, renal clearance and precise targeting of the tissue of interest. Loaded siRNAs targeting KRAS into Local Drug Eluter (LODER), a biodegradable polymetric matrix that protects siRNA allowing constant local release of siRNA inside tumour tissues, have shown Anti-tumoral activity towards human pancreatic tumour cells by increasing survival of murine models. In an open-label phase I–IIa study with 15 patients enrolled, LODER siRNAs in combination with FOLFIRINOX showed a median overall survival rate of 15 months and an 18-month survival rate of 38.5%. A phase II study of patients with locally advanced PDAC is ongoing to test siRNAG12D LODER in combination with standard therapy [
10]. Another approach for siRNAs delivery against KRASmu is represented by exosomes, also termed inhibitory exosomes (iExosomes), which have shown efficacy in several preclinical models of pancreatic cancer [
10]. In addition, CD47, a ‘do not eat me’ signal present on iExosomes, enables them to enter cells via micropinocytosis that is enhanced by KRASmu-dependent tumorigenesis. A clinical trial is pending to address the feasibility, safety and efficacy of iExosomes in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer [
10,
67]. One,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (DOPC) is the major component of a promising nanoliposomal platform used in vivo for KRAS-targeting siRNA delivery [
10].
Recent data have already challenged conventional knowledge that KRAS mutations (e.g. G12C, G12D, G12V or G12S) cannot hydrolyze GTP and return to the GDP-bound state and have demonstrated that these mutations are still able to hydrolyze GTP, suggesting a further Fine-tuning regulation of RAS. The aforementioned mentioned RASON, a novel protein encoded by the long Non-protein intergenic coding RNA 00673 (LINC00673), is the first identified positive regulator of KRAS that binds directly to it stabilizing its hyperactive state in a way that differs from guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) or GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) [
9].
As we said above, the BET family member BRD4 is a chromatin reader which binds acetylated and active chromatin enhancing transcription of Cell-identity genes with a Tumor-permissive role. Principe et al. have developed XP-524, a promising BET inhibitor that has shown encouraging results in combination with gemcitabine or PARP inhibitors by restraining the effects of KRAS activating mutations. In addition, XP-524 increases CD4+ and CD8+ T cell populations [
68], suggesting a possible strategy to sensitize KRASmu PDAC to immune checkpoint inhibition.
Jonghwa Jin et al explored glutamine metabolism in PDAC targeting glutamine transporters as a promising strategy for advanced or drug-resistant cancers[
29].
Dixon defined ferroptosis as a type of Iron-dependent Non-apoptotic cell death in KRASmu cancer cells in 2012 [
69], however oncogenic KRAS makes cells more resistant to ferroptosis through upregulation of ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1). Basing on these data Müller F and colleagues suggested ferroptosis induction combined with FSP1 inhibition as a new therapeutic strategy against KRASmu cancers [
70].
6. KRAS Dependency in PDAC
KRAS regulates development, cell growth, Epigenetically-dysregulated differentiation, and survival in PDAC through activation of key downstream pathways, such as MAPK-ERK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling, in a KRAS-dependent manner [
71]. Previous works showed as some pancreatic cancer cell lines survive to KRASmu silencing and then depend on PI3K which induces overexpression of Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1), an important transcriptional Co-activator of Hippo pathway, escaping KRAS inhibition [
36]. Furthermore, higher dosage of the mutant allele of KRAS than its WT counterpart has been associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients. This phenomenon is called “Mutant allele-specific imbalance” (MASI) [
71]. In addition, recent data have shown that restoration of WT KRAS in pancreatic cancer cells induces inhibition of nuclear translocation of YAP1 [
71,
72] which associated with poor prognosis in PDAC patients [
73]. In mouse models, after KRAS inactivation, One-third of spontaneous tumour recurrences that escape KRASG12D dependency shows deficit of KRAS expression and YAP1 amplification, resulting in an aggressive Quasi-mesenchymal phenotype with the activation of cell cycle and DNA repair pathways through cooperation of the transcription factor E2F [
10].
Chen et al. observed that murine PDAC cells, when KRAS is sustainedly silenced, undergo a reversible cell state without mutational or transcriptional alterations and characterized by morphological changes, Tumor-promoting activity with activation of the focal adhesion pathway, suggesting that the latter is a possible manifestation of acquired KRAS independency [
38].
USP21 ability to bypass KRAS dependency occurs in the cytoplasm with a novel mechanism different from the previously mentioned KRAS escape mechanisms, such as activation of MEK/ERK signaling or YAP1 upregulation. Hou et al. evidenced that USP21 reduces autophagy and increases amino acid levels, resulting in upregulation of MTOR-associated signaling [
74]. Further analysis demonstrated that Microtubule Affinity Regulating Kinase 3 (MARK3), a Microtubule-binding kinase and regulator of microtubule dynamics, is directly deubiquitinated by USP21, leading to KRAS-independent growth, cancer development and macropinocytosis, a key metabolism mechanism for KRASmu PDAC cell survival.
Similarly, Hou et al. showed that an upregulation of HDAC5 enhances the recruitment of TAMs into the TME, promoting resistance to KRAS inhibitors through the activation of the C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 (CCL2)/ C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 2 (CCR2) axis and of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) in a SMAD-4 dependent manner bypassing KRAS-dependency [
38,
75].
Several clinical studies have shown that KRAS inhibition blocks both PI3K-AKT-MTOR and MAPK signaling in KRAS-dependent tumors [
76]. On the other hand, inhibition of the MAPK pathway alone leads to hyperactivation of the PI3K-AKT-MTOR pathway via different RTKs such as AXL and Platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRa), and activation of several escape circuits, such as recruitment of insulin receptor kinase by MTORC1 and MEK Inhibition-mediated hyperactivation of the ERBB receptors Epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and ERBB3. However, RTK activation after MEK inhibition has been demonstrated in both RASmu and WT RAS tumor models and recent data have evidenced that combinations of inhibitors are highly toxic [
76].
Thus, KRAS dependency is so strong and essential in KRASmu PDAC that cancer cells have secured several compensatory escape mechanisms to counteract the effectiveness of KRAS inhibitors [
77].
7. Conclusions
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma remains a real challenge in oncology. We reviewed all the efforts spent in the recent years. A lot of new possibilities are now actual therapies, but more studies are needed to refine these new strategies.
KRAS dependency is probably the key in fighting these kinds of tumors. There are several oncogenic mutations of KRAS and we focused on the more frequent ones in PDAC. KRAS dependency is evident in each different developmental stages of PDAC and its precursor lesions.
We reviewed all types of direct and undirect inhibitors of KRAS signaling, its upstream effectors and also downstream effectors, analysing what is now affirmed as reality and current therapies. We showed how these new strategies are limited by several mechanisms of escaping, highlighting the necessity of much more studies to understand how to overcome these limitations.
ADM and much more PanIN represent the critical elements in the establishment of oncogenic KRAS dependency and further effects. In this setting, PPARδ is a potential target to prevent PanIN cancerization [
31].
Chromatin remodeling plays a central role in identity changes of ADM in the inflamed and injured pancreas, suggesting a tool for early detection of Epigenetically-dysregulated programs in PDAC development [
25]. These changes often lead to cancer stem cells characteristics and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) for cancer survival, showing other new viable targets [
28]. Often the PDAC phenotype changes to aggressive mesenchymal type, showing how SWI/SNF-controlled proteostasis with its chromatin remodeler SMARCB1 need to be further explored to better understand Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in PDAC [
35].
Several emerging therapies use inhibitors of different players in KRAS signaling, such as p130Cas [
11] or dual inhibition of FTase and GGTase activity [
38] or RASON [
9] in KRASmu PDAC.
However, the endless combination possibilities of inhibitors lead to infinite possibilities of mechanisms of escaping and resistance that we have yet to fully understand and overcome in order to definitely win against PDAC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, supervision, E.G., G.G., L.P., A.A., G.P., C.C. and G.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
is work was supported by the AIRC IG grant number 26330 to G.T., My First AIRC Grant “Luigi Bonatti e Anna Maria Bonatti Rocca” grant number 23681 to C.C., Convenzione Gemelli-FIMP Progetto CUP J38D19000690001 to G.T. and Ministry of Health CO 2019-12369662 to G.T.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ha, C.S.R.; Müller-Nurasyid, M.; Petrera, A.; Hauck, S.M.; Marini, F.; Bartsch, D.K.; Slater, E.P.; Strauch, K. Proteomics Biomarker Discovery for Individualized Prevention of Familial Pancreatic Cancer Using Statistical Learning. PloS One 2023, 18, e0280399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Siegel, R.L.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Jemal, A. Emerging Cancer Trends among Young Adults in the USA: Analysis of a Population-Based Cancer Registry. Lancet Public Health 2019, 4, e137–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouché, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Bécouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; de la Fouchardière, C.; et al. FOLFIRINOX versus Gemcitabine for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Ma, W.W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased Survival in Pancreatic Cancer with Nab-Paclitaxel plus Gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang-Gillam, A.; Li, C.-P.; Bodoky, G.; Dean, A.; Shan, Y.-S.; Jameson, G.; Macarulla, T.; Lee, K.-H.; Cunningham, D.; Blanc, J.F.; et al. Nanoliposomal Irinotecan with Fluorouracil and Folinic Acid in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer after Previous Gemcitabine-Based Therapy (NAPOLI-1): A Global, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2016, 387, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Nones, K.; Johns, A.L.; Patch, A.-M.; Gingras, M.-C.; Miller, D.K.; Christ, A.N.; Bruxner, T.J.C.; Quinn, M.C.; et al. Genomic Analyses Identify Molecular Subtypes of Pancreatic Cancer. Nature 2016, 531, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Li, F.; Zhang, M.; Xia, X.; Wu, J.; Gao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; et al. A Novel Protein RASON Encoded by a LncRNA Controls Oncogenic RAS Signaling in KRAS Mutant Cancers. Cell Res. 2023, 33, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscail, L.; Bournet, B.; Cordelier, P. Role of Oncogenic KRAS in the Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamagna, A.; Natalini, D.; Camacho Leal, M.D.P.; Simoni, M.; Gozzelino, L.; Cappello, P.; Novelli, F.; Ambrogio, C.; Defilippi, P.; Turco, E.; et al. Docking Protein P130Cas Regulates Acinar to Ductal Metaplasia During Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Development and Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Liu, S.; Rybkin, I.I.; Arbour, K.C.; Dilly, J.; Zhu, V.W.; Johnson, M.L.; Heist, R.S.; Patil, T.; Riely, G.J.; et al. Acquired Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2382–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidekel Friedlander, S.Y.; Chu, G.C.; Snyder, E.L.; Girnius, N.; Dibelius, G.; Crowley, D.; Vasile, E.; DePinho, R.A.; Jacks, T. Context-Dependent Transformation of Adult Pancreatic Cells by Oncogenic K-Ras. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.; Collado, M.; Navas, C.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Hernández-Porras, I.; Cañamero, M.; Rodriguez-Justo, M.; Serrano, M.; Barbacid, M. Pancreatitis-Induced Inflammation Contributes to Pancreatic Cancer by Inhibiting Oncogene-Induced Senescence. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Poggetto, E.; Ho, I.-L.; Balestrieri, C.; Yen, E.-Y.; Zhang, S.; Citron, F.; Shah, R.; Corti, D.; Diaferia, G.R.; Li, C.-Y.; et al. Epithelial Memory of Inflammation Limits Tissue Damage While Promoting Pancreatic Tumorigenesis. Science 2021, 373, eabj0486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storz, P.; Crawford, H.C. Carcinogenesis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2072–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Cañamero, M.; Grippo, P.J.; Verdaguer, L.; Pérez-Gallego, L.; Dubus, P.; Sandgren, E.P.; Barbacid, M. Chronic Pancreatitis Is Essential for Induction of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by K-Ras Oncogenes in Adult Mice. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xie, D.; Wei, D. Pancreatic Acinar-to-Ductal Metaplasia and Pancreatic Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2019, 1882, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, O.; Dor, Y.; Alsina, J.; Stirman, A.; Lauwers, G.; Trainor, A.; Castillo, C.F.-D.; Warshaw, A.L.; Thayer, S.P. In Vivo Lineage Tracing Defines the Role of Acinar-to-Ductal Transdifferentiation in Inflammatory Ductal Metaplasia. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; DiRenzo, D.; Qu, C.; Barney, D.; Miley, D.; Konieczny, S.F. Maintenance of Acinar Cell Organization Is Critical to Preventing Kras-Induced Acinar-Ductal Metaplasia. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Goga, A.; He, Y.; Silva, P.N.; Hirt, C.K.; Herrmanns, K.; Guccini, I.; Godbersen, S.; Schwank, G.; Stoffel, M. MiR-802 Suppresses Acinar-to-Ductal Reprogramming During Early Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.; Schneeweis, C.; Wirth, M.; Müller, S.; Geismann, C.; Neuß, T.; Steiger, K.; Krämer, O.H.; Schmid, R.M.; Rad, R.; et al. Important Role of Nfkb2 in the KrasG12D-Driven Carcinogenesis in the Pancreas. Pancreatol. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Pancreatol. IAP Al 2021, 21, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Qu, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Jing, Y.; Li, L.; Deng, W.; Liu, F.; et al. Deficient Rnf43 Potentiates Hyperactive Kras-Mediated Pancreatic Preneoplasia Initiation and Malignant Transformation. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2022, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.H.; Jung, K.H.; Lee, J.E.; Son, M.K.; Fang, Z.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lim, J.H.; Hong, S.-S. ANGPTL4 Accelerates KRASG12D-Induced Acinar to Ductal Metaplasia and Pancreatic Carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 519, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Curbelo, D.; Ho, Y.-J.; Burdziak, C.; Maag, J.L.V.; Morris, J.P.; Chandwani, R.; Chen, H.-A.; Tsanov, K.M.; Barriga, F.M.; Luan, W.; et al. A Gene-Environment-Induced Epigenetic Program Initiates Tumorigenesis. Nature 2021, 590, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeldt, M.T.; O’Prey, J.; Morton, J.P.; Nixon, C.; MacKay, G.; Mrowinska, A.; Au, A.; Rai, T.S.; Zheng, L.; Ridgway, R.; et al. P53 Status Determines the Role of Autophagy in Pancreatic Tumour Development. Nature 2013, 504, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, C.; Piro, G.; Agostini, A.; Delfino, P.; De Sanctis, F.; Nasca, V.; Spallotta, F.; Sette, C.; Martini, M.; Ugel, S.; Corbo, V.; Cappello, P.; Bria, E.; Scarpa, A.; Tortora, G. Intratumoral Injection of TLR9 Agonist Promotes an Immunopermissive Microenvironment Transition and Causes Cooperative Antitumor Activity in Combination with Anti-PD1 in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, A.; Pettazzoni, P.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Ying, H.; Sánchez, N.; Marchesini, M.; Carugo, A.; Green, T.; Seth, S.; Giuliani, V.; et al. Oncogene Ablation-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells Depend on Mitochondrial Function. Nature 2014, 514, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Byun, J.-K.; Choi, Y.-K.; Park, K.-G. Targeting Glutamine Metabolism as a Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, P.; Baddour, J.; Muller, F.; Wu, C.C.; Wang, H.; Liao, W.-T.; Lan, Z.; Chen, A.; Gutschner, T.; Kang, Y.; et al. Genomic Deletion of Malic Enzyme 2 Confers Collateral Lethality in Pancreatic Cancer. Nature 2017, 542, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deguchi, Y.; Wei, D.; Liu, F.; Moussalli, M.J.; Deguchi, E.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Valentin, L.A.; Colby, J.K.; et al. Rapid Acceleration of KRAS-Mutant Pancreatic Carcinogenesis via Remodeling of Tumor Immune Microenvironment by PPARδ. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, M.A.; Baker, C.M.; Cottle, D.L.; Watt, F.M. Dose and Context Dependent Effects of Myc on Epidermal Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannoura, S.F.; Khan, H.Y.; Azmi, A.S. KRAS G12D Targeted Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer: Has the Fortress Been Conquered? Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1013902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangrador, I.; Molero, X.; Campbell, F.; Franch-Expósito, S.; Rovira-Rigau, M.; Samper, E.; Domínguez-Fraile, M.; Fillat, C.; Castells, A.; Vaquero, E.C. Zeb1 in Stromal Myofibroblasts Promotes Kras-Driven Development of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2624–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, G.; Carugo, A.; Tepper, J.; Robinson, F.S.; Li, L.; Svelto, M.; Nezi, L.; Corti, D.; Minelli, R.; Pettazzoni, P.; et al. Synthetic Vulnerabilities of Mesenchymal Subpopulations in Pancreatic Cancer. Nature 2017, 542, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Targeting KRAS in PDAC: A New Way to Cure It? Cancers 2022, 14, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallin, J.; Engstrom, L.D.; Hargis, L.; Calinisan, A.; Aranda, R.; Briere, D.M.; Sudhakar, N.; Bowcut, V.; Baer, B.R.; Ballard, J.A.; et al. The KRASG12C Inhibitor MRTX849 Provides Insight toward Therapeutic Susceptibility of KRAS-Mutant Cancers in Mouse Models and Patients. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannoura, S.F.; Uddin, M.H.; Nagasaka, M.; Fazili, F.; Al-Hallak, M.N.; Philip, P.A.; El-Rayes, B.; Azmi, A.S. Targeting KRAS in Pancreatic Cancer: New Drugs on the Horizon. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Masutani, T.; Hirokawa, T. Generation of KS-58 as the First K-Ras(G12D)-Inhibitory Peptide Presenting Anti-Cancer Activity in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, Y.J. Adoptive Cell Therapy Targeting Neoantigens: A Frontier for Cancer Research. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Yu, Z.; Griffith, K.; Hanada, K.; Restifo, N.P.; Yang, J.C. Identification of T-Cell Receptors Targeting KRAS-Mutated Human Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Heitman, J. The Cyclophilins. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahearn, I.M.; Haigis, K.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Philips, M.R. Regulating the Regulator: Post-Translational Modification of RAS. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-H.; Yuan, T.; Qian, M.-J.; Yan, F.-J.; Yang, L.; He, Q.-J.; Yang, B.; Lu, J.-J.; Zhu, H. Post-Translational Modification of KRAS: Potential Targets for Cancer Therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canon, J.; Rex, K.; Saiki, A.Y.; Mohr, C.; Cooke, K.; Bagal, D.; Gaida, K.; Holt, T.; Knutson, C.G.; Koppada, N.; et al. The Clinical KRAS(G12C) Inhibitor AMG 510 Drives Anti-Tumour Immunity. Nature 2019, 575, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lito, P.; Solomon, M.; Li, L.-S.; Hansen, R.; Rosen, N. Allele-Specific Inhibitors Inactivate Mutant KRAS G12C by a Trapping Mechanism. Science 2016, 351, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, H.P.; Ming, M.; Mellon, M.; Young, S.H.; Han, L.; Sinnet-Smith, J.; Rozengurt, E. Dual PI3K/MTOR Inhibitors Induce Rapid Overactivation of the MEK/ERK Pathway in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Suppression of MTORC2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncogenic KRAS Engages an RSK1/NF1 Pathway to Inhibit Wild-Type RAS Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer – PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34021083/ (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Fedele, C.; Li, S.; Teng, K.W.; Foster, C.J.R.; Peng, D.; Ran, H.; Mita, P.; Geer, M.J.; Hattori, T.; Koide, A.; et al. SHP2 Inhibition Diminishes KRASG12C Cycling and Promotes Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; Baddour, J.; Achreja, A.; Bernard, V.; Moss, T.; Marini, J.C.; Tudawe, T.; Seviour, E.G.; San Lucas, F.A.; et al. Tumor Microenvironment Derived Exosomes Pleiotropically Modulate Cancer Cell Metabolism. eLife 2016, 5, e10250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, C.; Ran, H.; Diskin, B.; Wei, W.; Jen, J.; Geer, M.J.; Araki, K.; Ozerdem, U.; Simeone, D.M.; Miller, G.; et al. SHP2 Inhibition Prevents Adaptive Resistance to MEK Inhibitors in Multiple Cancer Models. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.-J.; Liao, W.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Guan, C.; et al. USP21 Deubiquitinase Promotes Pancreas Cancer Cell Stemness via Wnt Pathway Activation. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, H.C. Anticipating Resistance to KRAS Inhibition: A Novel Role for USP21 in Macropinocytosis Regulation. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 1325–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, A.; Markwart, R.; Esparza-Franco, M.A.; Ladds, G.; Rubio, I. Ras Activation Revisited: Role of GEF and GAP Systems. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Nishimura, R.; Kashishian, A.; Batzer, A.G.; Kim, W.J.; Cooper, J.A.; Schlessinger, J. A New Function for a Phosphotyrosine Phosphatase: Linking GRB2-Sos to a Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-N.P.; LaMarche, M.J.; Chan, H.M.; Fekkes, P.; Garcia-Fortanet, J.; Acker, M.G.; Antonakos, B.; Chen, C.H.-T.; Chen, Z.; Cooke, V.G.; et al. Allosteric Inhibition of SHP2 Phosphatase Inhibits Cancers Driven by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Nature 2016, 535, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D.L.; Haderk, F.; Bivona, T.G. Allosteric SHP2 Inhibitors in Cancer: Targeting the Intersection of RAS, Resistance, and the Immune Microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.J.; Haderk, F.; Stahlhut, C.; Schulze, C.J.; Hemmati, G.; Wildes, D.; Tzitzilonis, C.; Mordec, K.; Marquez, A.; Romero, J.; et al. RAS Nucleotide Cycling Underlies the SHP2 Phosphatase Dependence of Mutant BRAF-, NF1- and RAS-Driven Cancers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Loo, A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Kowal, C.; Delach, S.; Wang, Y.; Goldoni, S.; et al. Combinations with Allosteric SHP2 Inhibitor TNO155 to Block Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, P.P.; Hamann, L.G. Development of Targeted Protein Degradation Therapeutics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarantini, L.; Cerasi, A.; Fraternale, A.; Millo, E.; Benatti, U.; Sparnacci, K.; Laus, M.; Ballestri, M.; Tondelli, L. Comparison of Novel Delivery Systems for Antisense Peptide Nucleic Acids. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2005, 109, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, E.; Wang, J. Rational Drug Design: The Search for Ras Protein Hydrolysis Intermediate Conformation Inhibitors with Both Affinity and Specificity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 2246–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, E. A Small-Molecule Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses Metastasis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Zheng, X.; Wang, E.; Wang, J. Selective Induction of Apoptosis: Promising Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.Y.; Nagasaka, M.; Li, Y.; Aboukameel, A.; Uddin, M.H.; Sexton, R.; Bannoura, S.; Mzannar, Y.; Al-Hallak, M.N.; Kim, S.; et al. Inhibitor of the Nuclear Transport Protein XPO1 Enhances the Anticancer Efficacy of KRAS G12C Inhibitors in Preclinical Models of KRAS G12C-Mutant Cancers. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chaurasiya, S.; Strom, A.; Wang, H.; Liao, W.-T.; Cavallaro, F.; Denz, P.; Bernard, V.; et al. Oncogenic KRAS-Driven Metabolic Reprogramming in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Utilizes Cytokines from the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 608–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Phase I Study of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells-Derived Exosomes With KrasG12D SiRNA for Metastatic Pancreas Cancer Patients Harboring KrasG12D Mutation; clinicaltrials.gov, 2023.
- XP-524 Is a Dual-BET/EP300 Inhibitor That Represses Oncogenic KRAS and Potentiates Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Pancreatic Cancer – PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35064087/ (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An Iron-Dependent Form of Nonapoptotic Cell Death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, F.; Lim, J.K.M.; Bebber, C.M.; Seidel, E.; Tishina, S.; Dahlhaus, A.; Stroh, J.; Beck, J.; Yapici, F.I.; Nakayama, K.; et al. Elevated FSP1 Protects KRAS-Mutated Cells from Ferroptosis during Tumor Initiation. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Yu, C.-C.; Fine, S.A.; Youssof, A.L.; Yang, Y.-R.; Yan, J.; Karg, D.C.; Cheung, E.C.; Friedman, R.A.; Ying, H.; et al. Loss of the Wild-Type KRAS Allele Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression through Functional Activation of YAP1. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6759–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordenonsi, M.; Zanconato, F.; Azzolin, L.; Forcato, M.; Rosato, A.; Frasson, C.; Inui, M.; Montagner, M.; Parenti, A.R.; Poletti, A.; et al. The Hippo Transducer TAZ Confers Cancer Stem Cell-Related Traits on Breast Cancer Cells. Cell 2011, 147, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo Allende, M.T.; Zeron-Medina, J.; Hernandez, J.; Macarulla, T.; Balsells, J.; Merino, X.; Allende, H.; Tabernero, J.; Ramon Y Cajal, S. Overexpression of Yes Associated Protein 1, an Independent Prognostic Marker in Patients With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma, Correlated With Liver Metastasis and Poor Prognosis. Pancreas 2017, 46, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.-J.; Li, J.; Tan, L.; Yao, W.; Yan, L.; Zhou, X.; et al. USP21 Deubiquitinase Elevates Macropinocytosis to Enable Oncogenic KRAS Bypass in Pancreatic Cancer. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.; Kapoor, A.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Wu, C.-J.; Li, J.; Lan, Z.; Tang, M.; Ma, X.; Ackroyd, J.J.; et al. Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling Enables Bypass of Oncogenic KRAS Dependency in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1058–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettazzoni, P.; Viale, A.; Shah, P.; Carugo, A.; Ying, H.; Wang, H.; Genovese, G.; Seth, S.; Minelli, R.; Green, T.; et al. Genetic Events That Limit the Efficacy of MEK and RTK Inhibitor Therapies in a Mouse Model of KRAS-Driven Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, A.M.; Der, C.J. KRAS: The Critical Driver and Therapeutic Target for Pancreatic Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a031435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).