Submitted:
26 April 2023
Posted:
11 May 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Extreme Events, Climate Stressors, and Nearshore Problems (Storms and Sea Level Rise, Waves, Storms Surge, Tsunamis, Marine Georisk)
3. Threat of Climate Change, SLR, and Threat to Sustainable Development
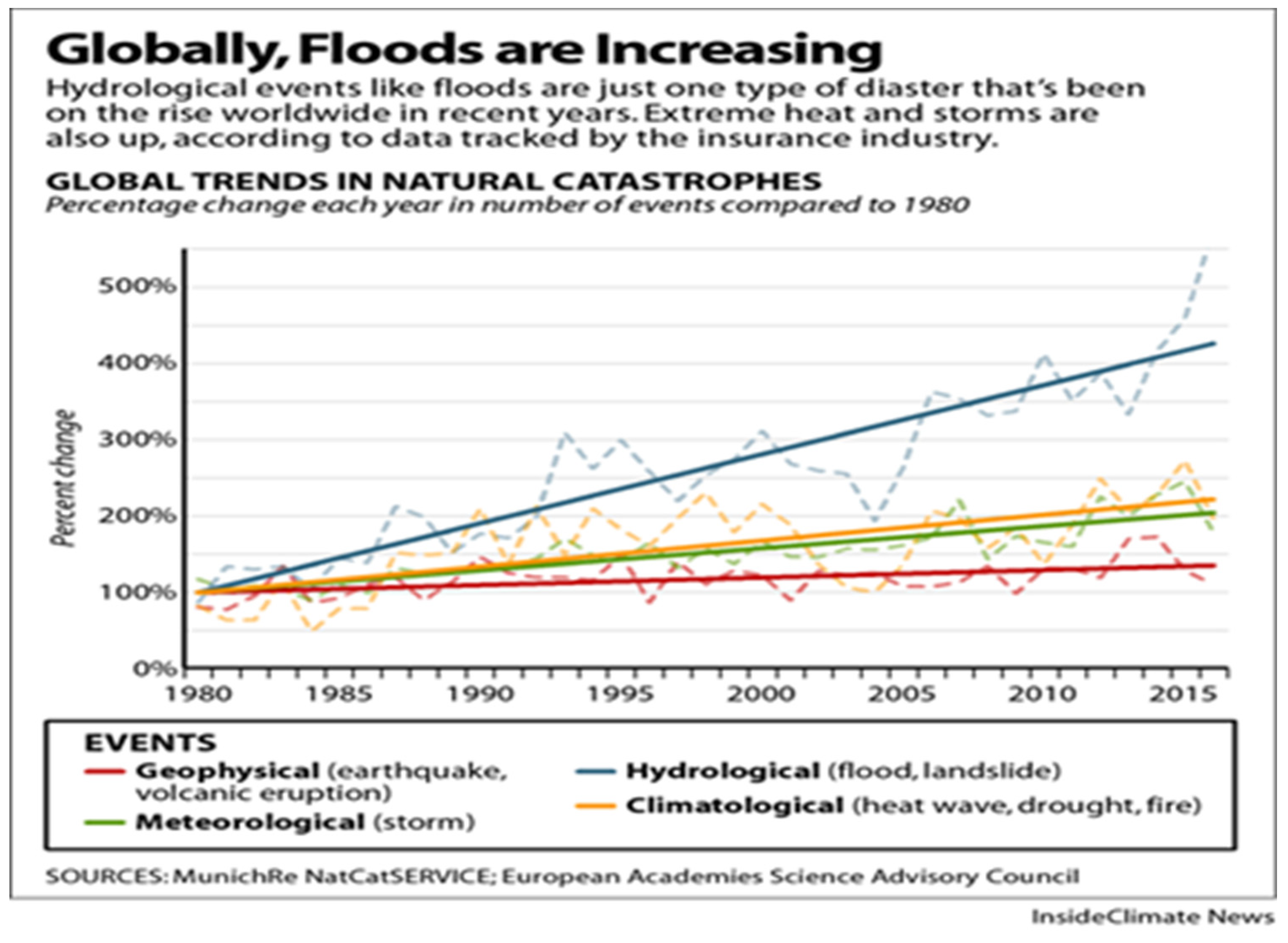
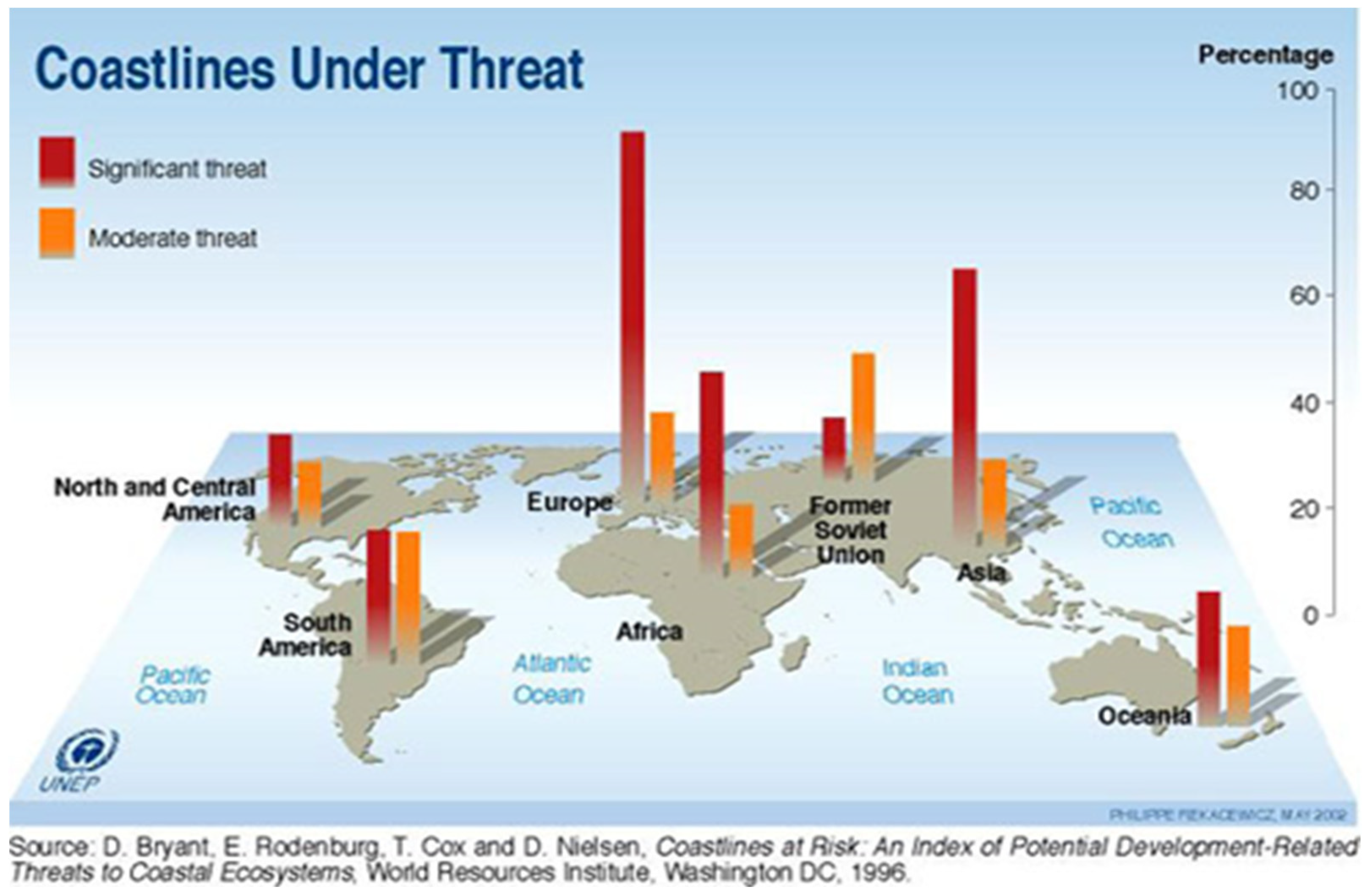
4. Ecosystem and Biodiversity Degradation
5. Wave Propagation and Dynamic

6. Coastal Process and Wave Impact
7. Coastal System Breaking Wave and Impact
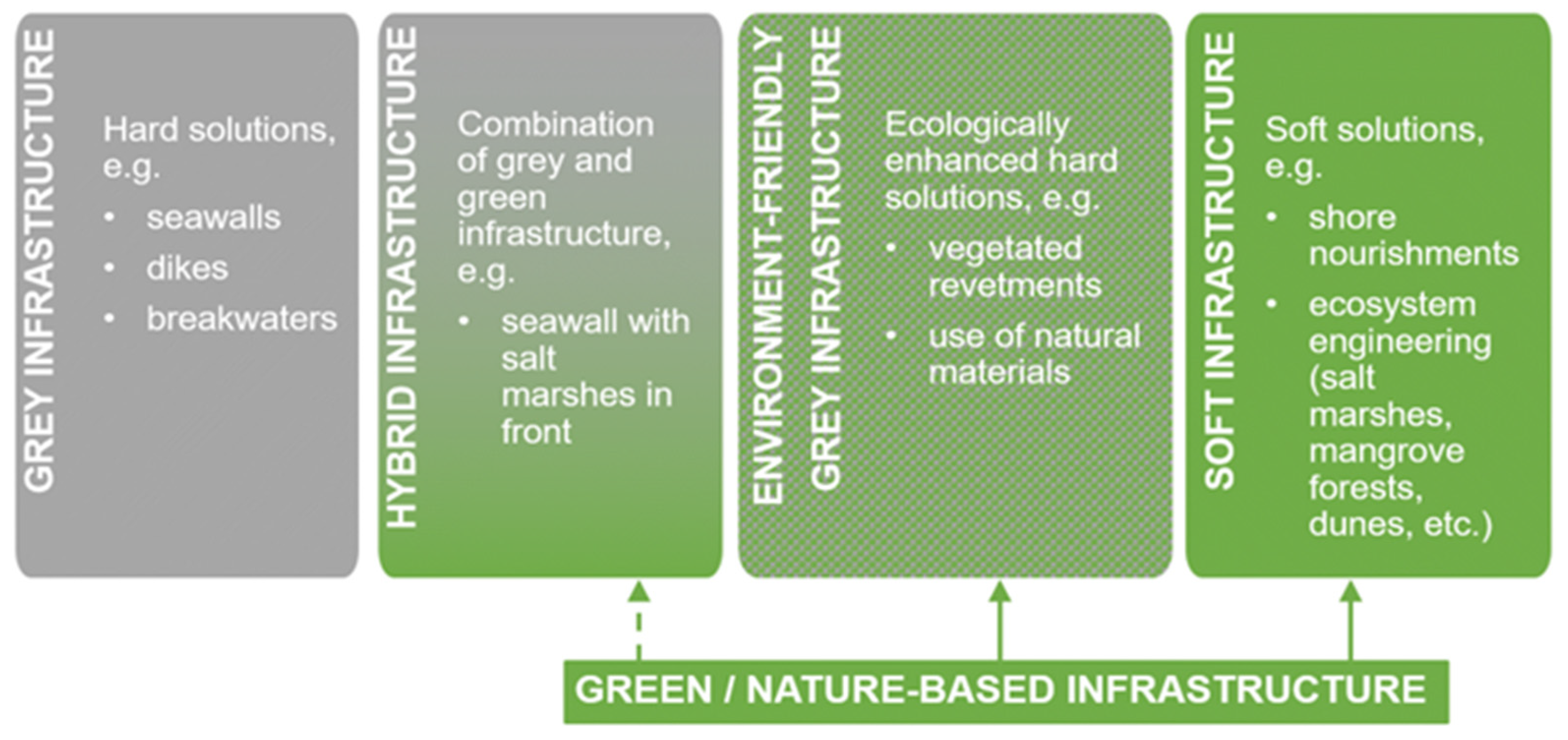
8. Combining Coastal Protection and Biodiversity Restoration–Hard Coastal Structures vs. Nature-based Solutions
9. Conclusions and Recommendation
Acknowledgment
References
- EASAC. Trends in extreme weather events in Europe: Implications for national and European Union adaptation strategies. 2013. Policy report 22.
- UNISDR. Annual Report, Geneva, Switzerland. 2017. 2016. 17. Biennium Work Programme. Final Report.
- Devlin, A.T., Jay, D.A., Talke, S.A. et al. Coupling of sea level and tidal range changes, with implications for future water levels. Sci Rep. 2017. 7, 17021. [CrossRef]
- Rebecca, Andreucci, R., & Aktas, C. B. Vulnerability of coastal Connecticut to sea level rise: Land inundation and impacts to residential property. Civil Engineering and Environmental Systems, 2017 34(2), 89-103. [CrossRef]
- Mark Denny and Brian Gaylord. The mechanics of wave-swept algae. Journal of Experimental biology. 2002. [CrossRef]
- Sondak, C.F., Ang, P.O., Beardall, J., Bellgrove, A., Boo, S.M., Gerung, G.S., Hepburn, C.D., Hong, D.D., Hu, Z., and Kawai, H. (2017). Carbon dioxide mitigation potential of seaweed aquaculture beds (SABs). J. Appl. Phycol. 2017. Vol. 29, pg. 2363–2373. [CrossRef]
- Oladokun S. O. Study of Macro Algae as Marine Biomass Energy Source, Journal of Aquaculture & Marine Biology, 2015. Volume 2. Issue 1. [CrossRef]
- Mortensen L.M. Remediation of nutrient-rich, brackish fjord water through the production of protein-rich kelp S. latissima and L. digitata. Journal of Applied Phycology. 2017. Vol. 28: Pg.3089–3096. [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Marine and coastal ecosystems and human well-being: A syn1269 thesis report based on the findings of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. UNEP. 2006. (p. 76). URL: https://www.millenniumassessment.org/ 1271 documents/Document.799.aspx.pdf.
- UNISDR. Technical guidance for monitoring and reporting on progress in achieving the global targets of the Sendai framework for disaster risk reduction (New ed.). 2017a. Geneva: United Nations.
- UNISDR.). Terminology. United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction, 2017b Geneva. Retrieved from https://www.unisdr. org/we/inform/terminology.
- Klaus Reicherter and Gösta Hoffmann.Geohazards: Coastal Disasters, Springer reference. 2015.
- Slangen, A. B. A. et al. A review of recent updates of sea-level projections at global and regional scales. Surveys in Geophysics. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Holthuijsen, L. Linear wave theory (coastal waters). In Waves in Oceanic and Coastal Waters. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2007. pp. 197-243. [CrossRef]
- Church JA; et al. Climate change: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press. 2013. New York.
- SOER. Knowledge for transition to a sustainable Europe. The European environment, state and outlook 2020, Copenhagen, Denmark.
- IPBES. Global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. E. S. Brondizio, J. Settele, S. Díaz, and H. T. Ngo (editors). IPBES secretariat, Bonn, Germany. 2019 1148 pages. [CrossRef]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). (2 The European environment, state and outlook, IPCC, Fifth Assessment Report (AR4). 2020.
- Robbie Andrew et al. Global CO2 emissions from cement production (Version 220516) [Data set]. Zenodo. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Clark. R. J. Designing Information Strategies for Coastal Zone Management, CRC Press, USA. 1995.
- Alizadeh et al. Effect of river flow on the quality of estuarine and coastal waters using machine learning models. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics. 2018. Vol. 12. [CrossRef]
- Halpern BS, et.al. Spatial and temporal changes in cumulative human impacts on the world's ocean. Nat Commun. 2015. J Vol 6 pg7615. PMID: 26172980; PMCID: PMC4510691. [CrossRef]
- Fredston-Hermann et al., Where Does River Runoff Matter for Coastal Marine Conservation? Sec. Marine Affairs and Policy, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Rabelais et al., Global Change and Eutrophication of Coastal Waters. – ICES Journal of Marine Science. 2002. 66. 0-0. [CrossRef]
- Katharina E. Fabricius. Effects of terrestrial runoff on the ecology of corals and coral reefs: Review and synthesis. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2005. Volume 50, Issue 2, Pages 125-146, ISSN 0025-326X. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025326X04004497). [CrossRef]
- Espey, W.H. & Ward G.H. Estuarine Water Quality Models,Water Research, 1972. Volume 6, Issue 10, Pages 1117-1131. ISSN 0043-1354. [CrossRef]
- Adriano Madonna, Agostino Balzano, Dea Rabbito, Mustapha Hasnaoui, Abdelraouf A. Moustafa, Nourredine Guezgouz, Alessia Vittorioso, Fatima-Zara Majdoubi, Oladokun Sulaiman Olanrewaju, Giulia Guerriero. Assessment of the biological effects of biofouling and antibiofouling EDCs: Gaeta Harbor (South Italy) benthic communities' analysis by biodiversity indices and quantitative gpx4 expression. Proceedings of the Zoological Society. 74, 591?604. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C. A.; Arancon, N. Q.; Sherman, R. Vermiculture technology: Earthworms, organic wastes, and environmental management. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Macready, P.I., Anton, A., Raven, J.A.; et al. The future of Blue Carbon science. Nat Commun 2019. 10, 3998. [CrossRef]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC, 2017 Fourth Assessment Report (AR4). [CrossRef]
- Morris A Bender, Thomas R Knutson, Robert E. Tuleya, Modelled Impact of Anthropogenic Warming on the Frequency of Intense Atlantic Hurricanes, Science. 2010 Vol. 327, Issue 5964, pp. 454-458.
- Piñeiro-Corbeira, C., Barreiro, R., Cremades, J. et al. Seaweed assemblages under a climate change scenario: Functional responses to temperature of eight intertidal seaweeds match recent abundance shifts. Sci Rep 2018. 12978. [CrossRef]
- Porter-Smith, R., McKinlay, J., Fraser, A. D., and Massom, R. A. Coastal complexity of the Antarctic continent, Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2021. 13, 3103–3114. [CrossRef]
- Gretchen Grebe, Adam St. Gelais, and Carrie J. Byron. An Ecosystem Approach to the Culture of Seaweed, Northeast Fisheries Science Center. 2019.
- Roy Haines-Young and Marion Potschin. The links between biodiversity, ecosystem services and human well-being. Ecosystem Ecology. 2010.
- Michael Y. Roleda, &Catriona L. Hurd, (2019), Seaweed nutrient physiology: Application of concepts to aquaculture and bioremediation. 2019. P552-562.
- Iona Campbell, Adrian Macleod, Christian Sahlmann, Luiza Neves, Jon Funderud, Margareth Øverland, Adam D. Hughes, and Michele Stanley. The Environmental Risks Associated with the Development of Seaweed Farming in Europe - Prioritizing Key Knowledge Gaps, Blue Economy. The Scottish Association for Marine Science, Oban, United Kingdom. 2019.
- Carlos M. Duarte, Jiaping Wu, Xi Xiao, Annette Bruhn, and Dorte Krause-Jensen. (2017). Can Seaweed Farming Play a Role in Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation? Frontier Development. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Chung, I. K. & Oak, Jung Hyun & Lee, Jin & Shin, Jong & Kim, Jong & Park, Kwang-Seok. (2013). Installing kelp forests/seaweed beds for mitigation and adaptation against global warming: Korean Project Overview. ICES Journal of Marine Science. 2013. 70. 1038-1044. [CrossRef]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), ICCP. The Physical Science Basis. Working Group, I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change-Abstract for decision-makers. Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., & Wuebbles, D. (eds.). 2013. [CrossRef]
- MunichRE NatCatService. NatCatSERVICE-Tool – Service – Methodology. http://natcatservice.munichre.com. 2019.
- Gornitz, V. (1991). Global coastal hazards from future sea level rise. Global and Planetary Change. 1991. 3(4), 379-398.
- Talbot, C.J., Bennett, E.M., Cassell, K. et al. The impact of flooding on aquatic ecosystem services. Biogeochemistry. 2018. 141, 439–461. [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mateos D, Power ME, Comin FA, Yockteng R. Structural and functional loss in restored wetland ecosystems. PLoS Biol. 2012. 10(1): e1001247. [CrossRef]
- IUCN Global Standard for Nature-based Solutions: A user-friendly framework for the verification, design, and scaling up of NbS. First edition. Gland, Switzerland: International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). 2020. [CrossRef]
- EurOtop. Manual on wave overtopping of sea defenses and related structures. An overtopping manual largely based on European research, but for worldwide application. van der Meer, J. W.; Allsop, N. 2018.
- Global Footprint Network, Global Footprint Networ. The business case for one-planet prosperity, Oklahoma. 2019.
- Cambridge et al., (1986), Cambridge ML, Chiffings AW, Brittan C, Moore L, McComb AJ, (1986) The loss of seagrass in Cockburn Sound, Western Australia. II. Possible causes of seagrass decline. Aquat Bot. 1986. 24:269–285.
- Short and Wyllie-Echeverria, Global seagrass declines and effects of climate change. C. Sheppard (Ed.), Seas at the Millennium: An Environmental Evaluation, vol. 3, Elsevier Science, Amsterdam 2000, pp. 10-11.
- Paling, E.I., van Keulen, M., Wheeler, K., Walker, C., 2000. Effects of depth on manual transplantation of the seagrass, Western Australia. Pacific Conservation Biology 2000. 5, 314–320.
- Hobbs R. J. & Norton D. A. (1996) Toward a conceptual framework for restoration ecology. Restoration Ecology 1996. 4: 93–110. [CrossRef]
- Eijgenraam, Carel, Jarl Kind, Carlijn Bak, Ruud Brekelmans, Dick den Hertog, Matthijs Duits, Kees Roos, Pieter Vermeer, and Wim Kuijken. “Economically Efficient Standards to Protect the Netherlands Against Flooding.” Interfaces. 2014. 44, no. 1. 7–21. http://www.jstor.org/stable/43699372. [CrossRef]
- Bouma, T. J., M. B. De Vries, and P. M. J. Herman. “Comparing Ecosystem Engineering Efficiency of Two Plant Species with Contrasting Growth Strategies.” Ecology 2010. 91, no. 9. 2696–2704. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27860846. [CrossRef]
- Bos, IJ. Architecture and facies distribution of organic-clastic lake fills in the fluvio-deltaic Rhine–Meuse system, the Netherlands. Journal of Sedimentary Research 2010. 80: 339–356. [CrossRef]
- Van der Heide, T., E. H. van Nes, G. W. Geerling, A. J. P.Smolders, T. J. Bouma, and M. M. van Katwijk.. Positive feedbacks in seagrass ecosystems: Implications for success in conservation and restoration. Ecosystems. 2010 10:1311–1322. [CrossRef]
- Byers JE, Cuddington K, Jones CG, Talley TS, Hastings A, Lambrinos JG, Crooks JA, Wilson WG. (2006) Using ecosystem engineers to restore ecological systems. Trends Ecol Evol. 2006. 21(9):493-500. Epub 2006 Jun 30. PMID: 16806576. [CrossRef]
- Shanley, P., and C. López, (2009): Out of the loop: Why research rarely reaches policy makers and the public and what can be done. Biotropica, 2009. 41, 535–544. [CrossRef]
- P.G. King, A.R. McGregor, J.D. Whittet. Can California coastal managers plan for sea-level rise in a cost-effective way? J. Environ. Plan. Manag.. 2016. 59, pp. 98-119. [CrossRef]
- S. Díaz, J. et. al... Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Secretariat of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, Bonn, Germany. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G., D. Cumming, and C. Redman. Scale mismatches in social-ecological systems: Causes, consequences, and solutions. Ecology and Society. 2006.11(1): 14. [online] URL: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol11/iss1/art14/.
- William E. Rees (2020), Ecological economics for humanity’s plague phase. University of British Columbia, School of Community and Regional Planning, 6333 Memorial Rd, Vancouver, BC, V6T 1Z2, Canada. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Levin (1999) Fragile Dominion: Complexity and the Commons. S. Levin (1999). Journal of Ecology. 2019. 88.1. 181-181. Pp. xii+250. Perseus Books, Massachusetts. ISBN 0-7382-0111-1. [CrossRef]
- Selby, K. A. and Smith, D. E. Late Devensian and Holocene relative sea-level changes on the Isle of Skye, Scotland, UK. J. Quaternary Sci., 2006.Vol.22 pp. 119–139. ISSN 0267–8179.
- Brand, R., & Karvonen, A. The ecosystem of expertise: Complementary knowledges for sustainable development. Sustainability: Science, Practice, & Policy. 2007. 3(1), 21. [CrossRef]
- Van Bavel, B, Berrang Ford, L, Harper, SL et al. (4 more authors). Contributions of scale: What we stand to gain from Indigenous and local inclusion in climate-health monitoring and surveillance systems. Environmental Research Letters. ISSN 1748-9326.2020. [CrossRef]
- Kushans, K. A., Okamoto, D. K., Rassweiler, A., Novak, M., Bolton, J. J., Cavanaugh, K. C., ... Byrnes, J. E. K. (2016). Global patterns of kelp forest change over the past half-century. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113, 13785–13790. 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Waycott, C.M. Duarte, T.J.B. Carruthers, R.J. Orth, W.C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J.W. Fourqurean, K.L. Heck, A.R. Hughes, G.A. Kendrick, W.J. Kenworthy, F.T. Short, S.L. Williams. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106. 2009. pp. 12377-12381.
- Christensen V, Walters CJ. Ecopath with Ecosim: Methods, capabilities and limitations. Ecol Model. 2004. 172:109–139 . [CrossRef]
- Frieler, K., Meinshausen, M., Golly, A., Mengel, M., Lebek, K., Donner, S.D., HoeghGuldberg, O., Limiting global warming to 2 °C is unlikely to save most coral reefs. Nat. Clim. Change. 2013. 3, 165–170. [CrossRef]
- Erb, K.-H. et al. Biomass turnover time in terrestrial ecosystems halved by land use. Nat. Geosci. .2014. 9, 674–678 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Davidson, N. Loss of intertidal habitat through landclaim in Asia. In ‘The State of the World’s Birds. 2013. p 14. (BirdLife International: Cambridge, UK). [CrossRef]
- Oladokun S. O., A. Saman. A. Kader, Allan Magee. Risk Analysis of Offshore Aquaculture Ocean Plantation System, Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2013. 7(14). Pages: 380-395.
- WWF (2020) Living Planet Report. Bending the curve of biodiversity loss. Almond, R.E.A., Grooten M. and Petersen, T. (Eds). WWF, Gland, Switzerland. 2020.
- Bar-On, Y.M., Phillips, R., and Milo, R. The biomass distribution on Earth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci... 2018. 115, 6506–6511. USA.
- Antonelli et. al…State of the World’s Plants and Fungi. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mora C, Tittensor DP, Adl S, Simpson AGB, Worm B (2011) How Many Species Are There on Earth and in the Ocean? PLoS Biol. 2011. 9(8): e1001127. [CrossRef]
- Alleway, H. K., Gillies, C. L., Bishop, M. J., Gentry, R. R., & Theuerkauf, S. J. The ecosystem services of marine aquaculture: Valuing benefits to people and nature. BioScience, 69(1). 2019. 59-68. [CrossRef]
- [A. Tan, A. Chilvery, M. Dokhanian, and S. Crutcher, "Tsunami Propagation Models Based on First Principles", in Tsunami - Analysis of a Hazard - From Physical Interpretation to Human Impact. London, United Kingdom: IntechOpen, 2012 [Online]. Available: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/41064. [CrossRef]
- Santos, N. Fonseca, J. L. Zêzere. Tsunami risk assessment at Figueira da Foz, Portugal. Tsunami risk assessment at Figueira da Foz , Portugal. 2012.
- Julian, P., Gerber, S., Bhomia, R.K. et al. Understanding stoichiometric mechanisms of nutrient retention in wetland macrophytes: Stoichiometric homeostasis along a nutrient gradient in a subtropical wetland. Oecologia. 2020.193, 969–980. [CrossRef]
- Theide Wöffler, Holger Schüttrumpf, Arne Arns, Malte Schindler. Development of Coastal Protection Measures for Small Islands in The Wadden Sea Using a Risk-Based Approach, Coastal Engineering. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Masselink, G., and M.G. Hughes. Introduction to Coastal Processes and Geomorphology. Routledge. 2003. 354pp.
- Wright, L.D., and A.D. Short. Morphodynamic variability of surf zones and beaches: A synthesis. Marine Geology. 1984. 56(1), 93-118. Coasts Form, Process and Evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- Nobuko Fukui, Adi Prasetyo, Nobuhito, Mori. Numerical Modeling of Tsunami Inundation Using Subgrid Scale Urban Roughness Parameterization, Coastal Engineering. 2018. 1(36):86. [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, A., & Bruno, M. Coastal Extreme Events: The Risks and the Responses. In the Urban Ocean: The Interaction of Cities with Water. 2018. pp. 147-166. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [CrossRef]
- Thom, B.G. and Hall, W. The behavior of beach profiles during accretion and erosion-dominated periods. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. 1991. 16(2).. pp.113-127. [CrossRef]
- GODA. The Coast, 73 Eurotop (2007), 1-178; https://izw.baw.de › die-kueste .1980.
- Ashton, A., A.B. Murray, and O. Arnault. Formation of coastline features by large-scale instabilities induced by high-angle waves. Nature. 2001. 414(6861) 296-300. [CrossRef]
- Dietze, M., Cook, K.L., Illien, L., Rach, O., Puffpaff, S., Stodian, I., Hovius, N. Impact of nested moisture cycles on coastal chalk cliff failure revealed by multi-seasonal seismic and topographic surveys. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Dietze et al, Impact of Nested Moisture Cycles on Coastal Chalk Cliff Failure Revealed by Multiseasonal Seismic and Topographic Surveys, Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface (2020). [CrossRef]
- CIRIA. The International Levee Handbook. CIRIA: C731. London, UK: Construction Industry Research and Information Association (CIRIA). 2013.
- USACE. Coastal Engineering Manual. Washington, DC, USA. 2002.
- Schoonees, T., Gijón Mancheño, A., Scheres, B., Bouma, T. J., Silva, R., Schlurmann, T., & Schüttrumpf, H. Hard structures for coastal protection, towards greener designs. Estuaries and Coasts. 2019. 42(7), 1709–1729. [CrossRef]
- Bouma, T. J., van Belzen, J., Balke, T., Zhu, Z., Airoldi, L., Blight, A. J., Davies, A. J., Galvan, C., Hawkins, S. J., Hoggart, S. P.G., Lara, J. L., Losada, I. J., Maza, M., Ondiviela, B., Skov, M. W., Strain, E. M., Thompson, R. C., Yang, S., Zanuttigh, B., Zhang, L., & Herman, P. M.J. Identifying knowledge gaps hampering application of intertidal habitats in coastal protection: Opportunities & steps to take. Coastal Engineering. 2014. 87. 147–157. [CrossRef]
- Scheres, B., & Schüttrumpf, H. Nature-Based Solutions in Coastal Research – A New Challenge for Coastal Engineers? In N. Trung Viet, D. Xiping, & T. Thanh Tung (Eds.). APAC. Springer Singapore. 2019. Vol. 76, pp. 1383–1389. [CrossRef]
- Mahy M., Ameen, Abdelraouf A. Moustafa, Jelan Mofeed, Mustapha Hasnaoui, Oladokun S. Olanrewaju, Umberto Lazzaro, and Giulia Guerriero. Factors Affecting Efficiency of Biosorption of Fe (III) and Zn (II) by Ulva lactuca and Corallina officinalis and Their Activated Carbons. Water, 13, 3421. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Tramice, Annabella, Marco Trifuoggi, Mohammad F. Ahmad, Su S. Lam, Carmine Iodice, Gennaro Velotto, Antonella Giarra, Sara Inglese, Adelaide Cupo, Giulia Guerriero*, and Giuseppina Tommonaro*. Comparative fatty acid profiling of edible fishes in Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia. Foods, 10 (10), 2456. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Oladokun Sulaiman Olanrewaju, Giuseppina Tommonaro, Giulia Guerriero, Chiara Fogliano, Carmine Iodice, Gennaro Velotto, Annabella Tramice. New Insight into Marine Biotechnology: Carrageenans Chemical eatures and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Inhibition Activity of Two Edible Seaweeds of the Genus Kappaphycus. In: Ksibi M. et al. (eds) Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition). EMCEI 2019. Environmental Science and Engineering. pp 2203-2207. Springer, Cham. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Oladokun Sulaiman Olanrewaju, Anna De Maio, Eva Lionetti, Anna Rita Bianchi, Dea Rabbito, Andrea Ariano, Fatima-Zahra Majdoubi, and Giulia Guerriero. Sea Farms as a Safe and Sustainable Food Source: An Investigation on Use of Seaweeds for Liver Detoxification and Reduced DNA Damage in Lates calcarifer (Bloch, 1790). In: Ksibi M. et al. (eds) Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition). EMCEI 2019. Environmental Science and Engineering. pp 671-675. Springer, Cham. 2021. [CrossRef]
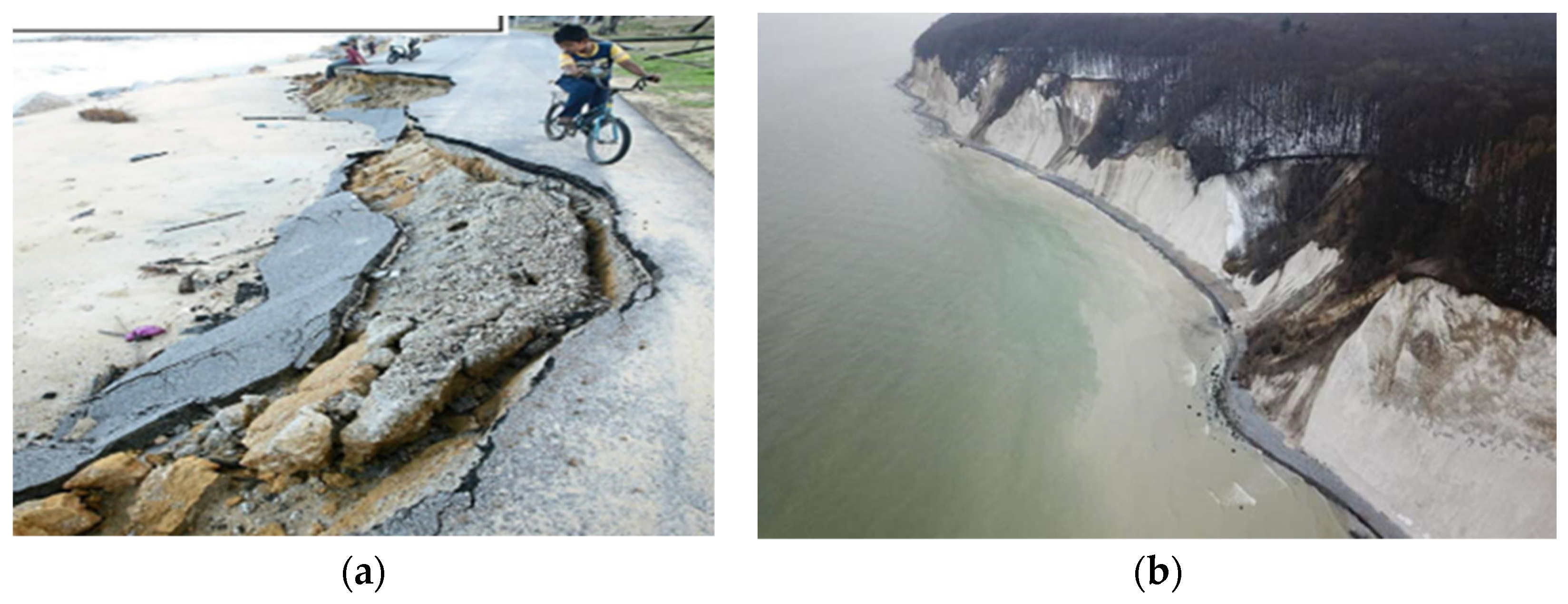
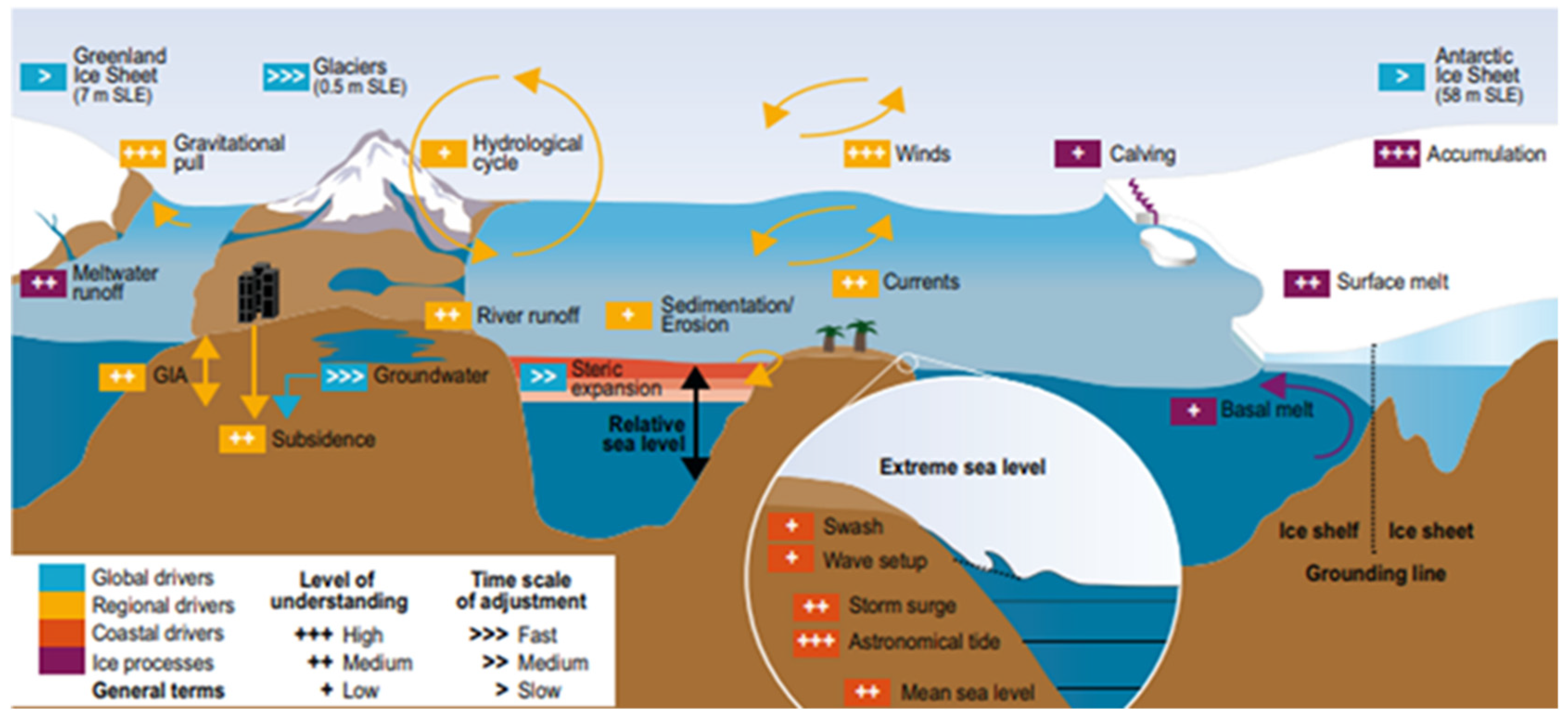


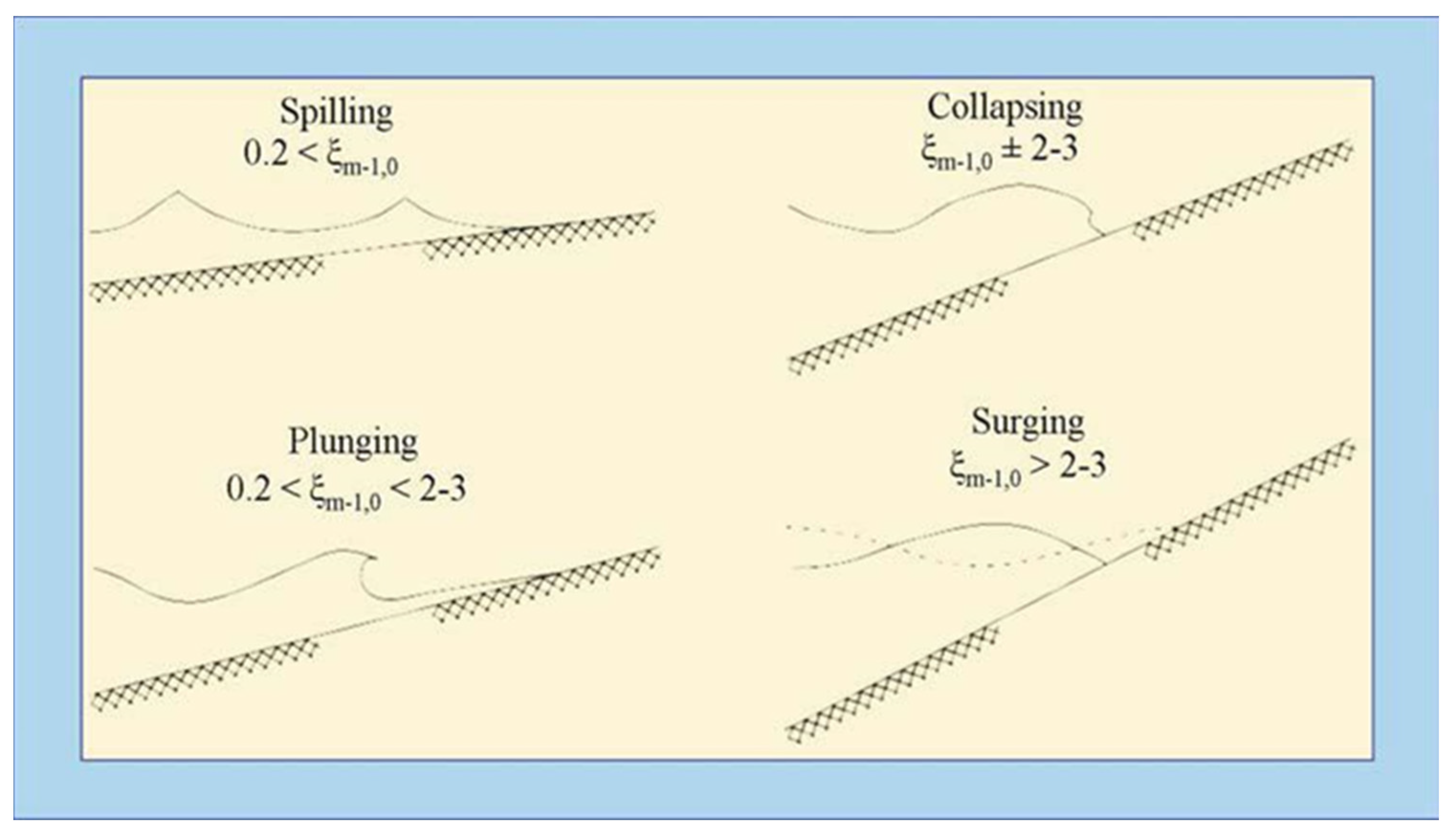


| Author | Issues |
| [57], [58,122] |
The current socio-political processes are delaying effective action |
| [59] | There are many solutions |
| [60] | the current scale of solution implementation does not match the pace of biodiversity loss |
| [61] | There are other existential threats tied to the expansion of enterprise development |
| [18] | Time delays between ecological deterioration and socio-economic, climate disruption impede recognition of the magnitude of the challenge |
| [62] | Disciplinary specialization and insularity encourage unfamiliarity with the complex adaptive systems |
| [63],[64] | The problems and their potential solutions are embedded |
| [65] | Widespread ignorance of human behavior |
| [17],[22] | Earth surface and ocean |
| [66],[67] | Kept and seagrass, corals, |
| [59],[68],[69] | Fish and terrestrial biodiversity |
| [70],[71],[72] |
Terrestrial vegetation, wetland, rivers |
| [73],[74],[75],[76]. |
Vertebrate population, wild animals, endangered plants, threatened species |
| [77] . |
The ecosystem services of marine aquaculture: valuing benefits to people and nature. Bioscience |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





