Submitted:
09 May 2023
Posted:
11 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
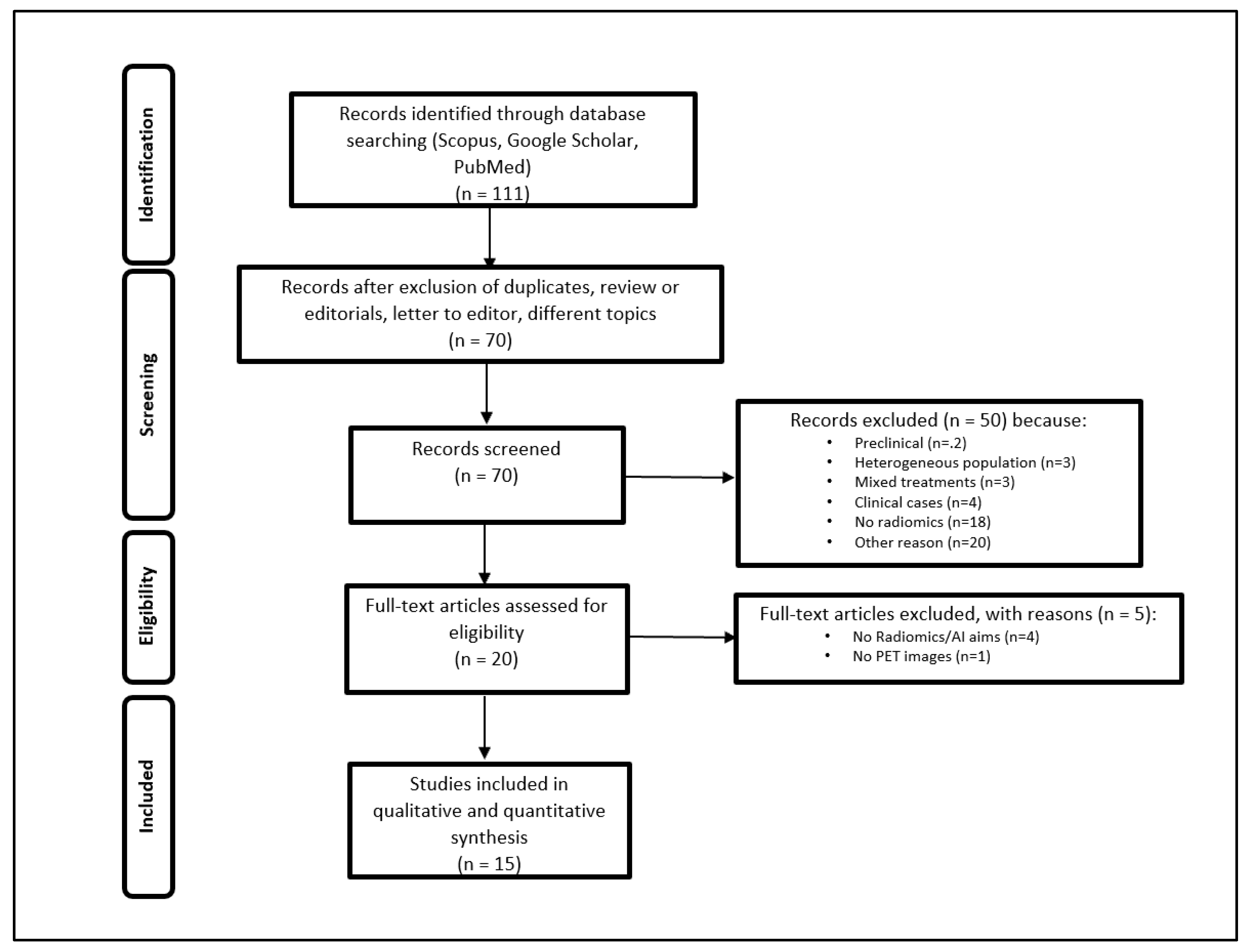
2.1. Research Strategy and Study Selection
2.2. Radiomics Methodology and Study Quality
3. Results
3.1. Radiomics Assessment
3.2. Baseline PET for the Prediction of Biomarker Expression
3.3. The Prediction of Response to Immunotherapy
3.4. The Prediction of Adverse Events Correlated with Immunotherapy by [18F]FDG PET/CT and Radiomics
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Assessment
4.2. Radiomics Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration; Fitzmaurice Ch, Abate D, Abbasi N; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived with Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol 2019, 5, 1749–1768. [CrossRef]
- Revels SL, Lee JM. Anti-angiogenic therapy in nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with tyrosine kinase inhibition (TKI) that targets the VEGF receptor (VEGFR): Perspective on phase III clinical trials. J Thorac Dis. 2018, 10, 617–20. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo Q, Liu L, Chen Z, Fan Y, Zhou Y, Yuan Z; et al. Current treatments for non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2022;12. [CrossRef]
- Mithoowani H, Febbraro M. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in 2022: A Review for General Practitioners in Oncology. Curr Oncol. 2022, 29, 1828–1839. [CrossRef]
- Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crinò L, Eberhardt WEE, Poddubskaya E; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015, 373, 123–35. [CrossRef]
- Onoi K, Chihara Y, Uchino J, Shimamoto T, Morimoto Y, Iwasaku M; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Lung Cancer Treatment: A Review. J Clin Med. 2020, 9, 1362. [CrossRef]
- Melosky B, Cheema PK, Brade A, McLeod D, Liu G, Price PW; et al. Prolonging Survival: The Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Treatment of Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2020, 25, 981–992. [CrossRef]
- Blons H, Garinet S, Laurent-Puig P, Oudart J-B. Molecular markers and prediction of response to immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer, an update. J Thorac Dis. 2019, 11, S25–36. [CrossRef]
- Xu C, Chen Y-P, Du X-J, Liu J-Q, Huang C-L, Chen L; et al. Comparative safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2018;k4226. [CrossRef]
- Rowe SP, Pomper MG. Molecular imaging in oncology: Current impact and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022, 72, 333–52. [CrossRef]
- Evangelista L, Cuppari L, Menis J, Bonanno L, Reccia P, Frega S; et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Nucl Med Commun. 2019, 40, 802–807. [CrossRef]
- Kudura K, Ritz N, Kutzker T, Hoffmann MHK, Templeton AJ, Foerster R; et al. Predictive Value of Baseline FDG-PET/CT for the Durable Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in NSCLC Patients Using the Morphological and Metabolic Features of Primary Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 6095. [CrossRef]
- Bianconi F, Palumbo I, Fravolini ML, Rondini M, Minestrini M, Pascoletti G; et al. Form Factors as Potential Imaging Biomarkers to Differentiate Benign vs. Malignant Lung Lesions on CT Scans. Sensors 2022, 22, 5044. [CrossRef]
- Aide N, Weyts K, Lasnon C. Prediction of the Presence of Targetable Molecular Alteration(s) with Clinico-Metabolic 18 F-FDG PET Radiomics in Non-Asian Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2448. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Hu H-H, Zhou S-H, Xia W-Y, Zhang Y, Zhang J-P; et al. PET-based radiomics visualizes tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cell exhaustion to optimize radiotherapy/immunotherapy combination in mouse models of lung cancer. Biomark Res. 2023, 11, 10. [CrossRef]
- Castello A, Castellani M, Florimonte L, Urso L, Mansi L, Lopci E. The Role of Radiomics in the Era of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A New Protagonist in the Jungle of Response Criteria. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 1740. [CrossRef]
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [CrossRef]
- Hosny A, Aerts HJ, Mak RH. Handcrafted versus deep learning radiomics for prediction of cancer therapy response. Lancet Digit Heal. 2019, 1, e106–e107. [CrossRef]
- Bianconi F, Palumbo I, Spanu A, Nuvoli S, Fravolini ML, Palumbo B. PET/CT Radiomics in Lung Cancer: An Overview. Appl Sci. 2020, 10, 1718. [CrossRef]
- Lambin P, Leijenaar RTH, Deist TM, Peerlings J, de Jong EEC, van Timmeren J; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [CrossRef]
- Mu W, Jiang L, Shi Y, Tunali I, Gray JE, Katsoulakis E; et al. Non-invasive measurement of PD-L1 status and prediction of immunotherapy response using deep learning of PET/CT images. J Immunother cancer. 2021;9. [CrossRef]
- Park C, Na KJ, Choi H, Ock C-Y, Ha S, Kim M; et al. Tumor immune profiles noninvasively estimated by FDG PET with deep learning correlate with immunotherapy response in lung adenocarcinoma. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10838–10848. [CrossRef]
- Valentinuzzi D, Vrankar M, Boc N, Ahac V, Zupancic Z, Unk M; et al. [18F]FDG PET immunotherapy radiomics signature (iRADIOMICS) predicts response of non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with pembrolizumab. Radiol Oncol. 2020, 54, 285–94. [CrossRef]
- Mu W, Katsoulakis E, Whelan CJ, Gage KL, Schabath MB, Gillies RJ. Radiomics predicts risk of cachexia in advanced NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Br J Cancer 2021, 125, 229–239. [CrossRef]
- Doroshow DB, Bhalla S, Beasley MB, Sholl LM, Kerr KM, Gnjatic S; et al. PD-L1 as a biomarker of response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021, 18, 345–62.
- Jiang M, Sun D, Guo Y, Guo Y, Xiao J, Wang L; et al. Assessing PD-L1 Expression Level by Radiomic Features From PET/CT in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Patients: An Initial Result. Acad Radiol. 2020, 27, 171–179. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Ge S, Sang S, Hu C, Deng S. Evaluation of PD-L1 Expression Level in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by 18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics and Clinicopathological Characteristics. Front Oncol. 2021;11. [CrossRef]
- Zhao X, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Liu L, Zhao X. Predicting PD-L1 expression status in patients with non-small cell lung cancer using [18F]FDG PET/CT radiomics. EJNMMI Res. 2023, 13, 4. [CrossRef]
- Kim H, Kwon HJ, Han YB, Park SY, Kim ES, Kim SH; et al. Increased CD3+ T cells with a low FOXP3+/CD8+ T cell ratio can predict anti-PD-1 therapeutic response in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Mod Pathol. 2019, 32, 367–375. [CrossRef]
- Geng Y, Shao Y, He W, Hu W, Xu Y, Chen J; et al. Prognostic Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015, 37, 1560–1571. [CrossRef]
- Tong H, Sun J, Fang J, Zhang M, Liu H, Xia R; et al. A Machine Learning Model Based on PET/CT Radiomics and Clinical Characteristics Predicts Tumor Immune Profiles in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Multicohort Study. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 859323. [CrossRef]
- Polverari G, Ceci F, Bertaglia V, Reale ML, Rampado O, Gallio E; et al. 18F-FDG Pet Parameters and Radiomics Features Analysis in Advanced Nsclc Treated with Immunotherapy as Predictors of Therapy Response and Survival. Cancers 2020;12. [CrossRef]
- Tankyevych O, Trousset F, Latappy C, Berraho M, Dutilh J, Tasu JP; et al. Development of Radiomic-Based Model to Predict Clinical Outcomes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy. Cancers 2022;14. [CrossRef]
- Cui Y, Lin Y, Zhao Z, Long H, Zheng L, Lin X. Comprehensive 18F-FDG PET-based radiomics in elevating the pathological response to neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy for resectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: A pilot study. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 994917. [CrossRef]
- Wang D, Zhang X, Liu H, Qiu B, Liu S, Zheng C; et al. Assessing dynamic metabolic heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer patients via ultra-high sensitivity total-body [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging: Quantitative analysis of [18F]FDG uptake in primary tumors and metastatic lymph nodes. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022, 49, 4692–4704. [CrossRef]
- Mu W, Tunali I, Qi J, Schabath MB, Gillies RJ. Radiomics of 18 F Fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT Images Predicts Severe Immune-related Adverse Events in Patients with NSCLC. Radiol Artif Intell. 2020, 2, e190063. [CrossRef]
- Tisdale, MJ. Cachexia in cancer patients. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002, 2, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitroulas P, Brocki L, Christopher Chung N, Marchadour W, Vermet F, Gaubert L; et al. Artificial intelligence: Deep learning in oncological radiomics and challenges of interpretability and data harmonization. Phys Medica. 2021, 83, 108–121. [CrossRef]
- Astaraki M, Yang G, Zakko Y, Toma-Dasu I, Smedby Ö, Wang C. A Comparative Study of Radiomics and Deep-Learning Based Methods for Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy Prediction in Low Dose CT Images. Front Oncol. 2021;11. [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg A, Vallières M, Abdalah MA, Aerts HJWL, Andrearczyk V, Apte A; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [CrossRef]
- Mu W, Tunali I, Gray JE, Qi J, Schabath MB, Gillies RJ. Radiomics of 18F-FDG PET/CT images predicts clinical benefit of advanced NSCLC patients to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2020, 47, 1168–1182. [CrossRef]
- Fiz F, Viganò L, Gennaro N, Costa G, La Bella L, Boichuk A; et al. Radiomics of Liver Metastases: A Systematic Review. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12. [CrossRef]
- Dercle L, McGale J, Sun S, Marabelle A, Yeh R, Deutsch E; et al. Artificial intelligence and radiomics: Fundamentals, applications, and challenges in immunotherapy. J Immunother cancer. 2022;10. [CrossRef]
- van Timmeren JE, Cester D, Tanadini-Lang S, Alkadhi H, Baessler B. Radiomics in medical imaging-”how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging. 2020, 11, 91. [CrossRef]
- Laudicella R, Comelli A, Liberini V, Vento A, Stefano A, Spataro A; et al. [68Ga]DOTATOC PET/CT Radiomics to Predict the Response in GEP-NETs Undergoing [177Lu]DOTATOC PRRT: The “Theragnomics” Concept. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14. [CrossRef]
- Binczyk F, Prazuch W, Bozek P, Polanska J. Radiomics and artificial intelligence in lung cancer screening. Transl lung cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1186–1199. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B. Understanding Sources of Variation to Improve the Reproducibility of Radiomics. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 633176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao S-X, Lambregts DM, Schnerr RS, Beckers RC, Maas M, Albarello F; et al. CT texture analysis in colorectal liver metastases: A better way than size and volume measurements to assess response to chemotherapy? United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2016, 4, 257–263. [CrossRef]
- Zhou J, Zou S, Kuang D, Yan J, Zhao J, Zhu X. A Novel Approach Using FDG-PET/CT-Based Radiomics to Assess Tumor Immune Phenotypes in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 769272. [CrossRef]
| Author, ref | Year of pub. | Design | Sample size | Histology | Type of ICIs | Histopathology correlation | Software | Model | External validation cohort | Outcome measures | Relevant radiomics indexes | RQS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiang et al. [26] | 2019 | R | 399 | NSCLC (SCC and Adenocarcinoma) | Atezolizumab and Nivolumab | Yes | ITK V. 3.6.1 | Logistic regression and random forest | Na | PD-L1 expression | Shape, IQR, GLCM_JointAverage, median, NGTDM_contrast | 22 (33,3%) |
| Polverari et al. [32] | 2020 | R | 57 | mixed histologies | Mixed | Yes | LifeX | Univariate analysis | Na | PD-L1 expression; progression status | Coarseness, GLZLM_ZLNU, Kurtosis, Skewness, GLZLM_LZE, GLRLM_RP/SRE/HGRE, GLCM_Homogeneity | 13 (19,7%) |
| Mu et al. [36] |
2020 | R/P | 146 (R), 48 (P) | NSCLC (123 ADC and 71 SCC) | N/S | Yes | In-house software | Logistic regression and Cox multivariate regression | Na | Durable clinical benefit, PFS, and OS | P/R radiomics signatures | 28 (42,4%) |
| Mu et al. [41] | 2020 | R/P | 146 (R), 48 (P) | NSCLC (123 ADC and 71 SCC) | Multiple | Na | In-house software | Multivariable regression analysis | Na | Immune-related adverse events | Radiomic signature (KLD_SZLGE and KLD_SRLGE) | 26 (39,39%) |
| Park et al. [22] | 2020 | R | 29 | NSCLC (ADC) | Pembrolizumab (10) Nivolumab (18) Atezolizumab (1) |
Yes | LifeX v 4 | Deep Learning | Yes | Cytolitic activity; tumour response, PFS, and OS | N/S | 16 (26,23%)* |
| Valentinuzzi et al. [23] | 2020 | P | 30 | NSCLC (17 ADC, 8 SCC, and 5 other) | Pembrolizumab | Na | In-house software | Univariate analysis and Cox regression model | Na | OS | GLRLM_SRE | 22 (33,3%) |
| Li et al. [27] | 2021 | R | 255 | NSCLC (SCC and Adenocarcinoma) | N/S | Yes | LifeX v 7 | Logistic regression | Na | PD-L1 expression (>1% and >50%) | N/S (12 and 3 feature for >1% and >50%, respectively) | 20 (30,3%) |
| Mu et al. [24] | 2021 | R | 210 | NSCLC (109 ADC and 66 SCC) | N/S (anti PD-1 and anti PD-L1) | N | MatLab 2020.a | Uni/multivariable regression analysis | Y | Caxhexia; Durable clinical benefit, PFS, and OS | Radiomic signature (SRHGE and LZLGE) | 26 (39,39%) |
| Mu et al. [21] | 2021 | R/P | 648 (R), 49 (P) | NSCLC (531 ADC and 166 SCC) | N/S | Y | ITK | Small residual convolutional network (SResCNN) | Y | PD-L1 expression; Durable clinical benefit, PFS, and OS | N/S | 26 (42,6%) |
| Zhou et al. [49] | 2021 | R | 103 | 28 SCC and 75 other | N/S | Y | LifeX v 5.1 | Univariate analysis and logistic regression | N | PD-L1 and CD8 expression | GLRLM_LRHGE, GLZLM_SZE, SUVmax, NGLDM_Contrast | 23 (34,85%) |
| Tankyevych et al. [33] | 2022 | R | 83 | mixed histologies | Mixed | Y | PyRadiomics | Multivariate model | N | Survival, Progression, durable clinical benefit | Skewness, median, NGTDM_Complexity, GLCM_Autocorrelation and GLCM_imc1 | 25 (37,9%) |
| Tong et al. [31] | 2022 | R | 221 | NSCLC (N/S) | N/S | Y | ITK V. 3.8 | Clinical-radiomics models; machine learning | N | CD-8 expression | GLCM_IMC1, GLSZM_SZLGE, GLTDM_LGE, Histogram Energy, GLTDM_Entropy | 24 (36,36%) |
| Cui et al. [34] | 2022 | P | 29 | NSCLC (mixed histologies) | Toripalimab | Y | Pyradiomics | Logistic regression | N | Pathological response of the primary | Delta SUV-indices; EOT SUV indices; EOT MTV/TLG, EOT uniformity and EOT GLDM_LDHGLE | 21 (31,82%) |
| Wang et al. [35] | 2022 | P | 30 | NSCLC (16 ADC, 12 SCC, and 2 other) | None** | Y | N/S | Univariate analysis | Y | Heterogeneity, immune infiltrate | Entropy | 16 (24,24%) |
| Zhao et al. [28] | 2023 | R | 334 | NSCLC (163 ADC, 59 SCC, and 112 other) | Pembrolizumab | Y | LifeX v 7 | Univariate analysis and logistic regression | N | PD-L1 expression | GLRLM_RP | 20 (30,30%) |
| Authors (PMID) | Rater | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB | FF | LM | Consensus | |
| Jiang et al. [26] | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Polverari et al. [32] | 13 | 13 | 15 | 13 |
| Mu et al. [36] | 23 | 26 | 26 | 28 |
| Mu et al. [41] * | 24 | 25 | 23 | 26 |
| Park et al. [22] | 14 | 16 | 15 | 16 |
| Valentinuzzi et al. [23] | 26 | 27 | 27 | 22 |
| Li et al. [27] | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mu et al. [24] | 27 | 25 | 25 | 26 |
| Mu et al. [21] | 27 | 27 | 26 | 26 |
| Zhou et al. [49] | 20 | 24 | 20 | 23 |
| Tankyevych et al. [33] | 24 | 25 | 23 | 25 |
| Tong et al. [31] | 33 | 21 | 30 | 24 |
| Cui et al. [34] | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 |
| Wang et al. [35] | 23 | 18 | 18 | 16 |
| Zhao et al. [28] | 27 | 22 | 22 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





