Submitted:
08 May 2023
Posted:
09 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Arame and Nori Seaweeds Extract
2.3. Cell Lines Cultures
2.4. Inhibition of Enzyme HMG-CoA Reductase (HMGR)
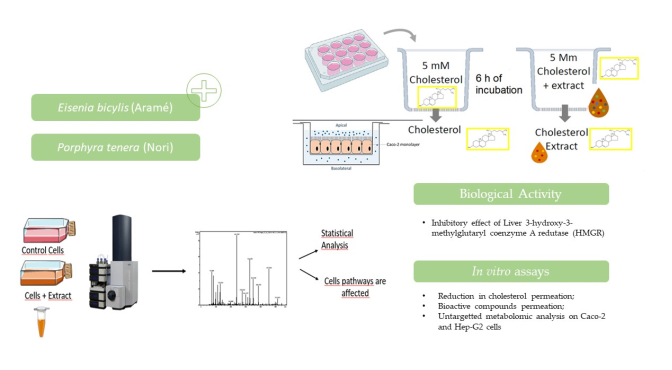
2.5. In Vitro Studies in Caco-2 Cells Monolayers Simulating the Intestinal Lining
2.5.1. Cholesterol Permeation Assay
2.5.2. Seaweeds Compounds Permeation Assay
2.7. Metabolomic Analysis of Caco-2 and Hep-G2 Cells Treated with Seaweeds Extract
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Seaweeds Extracts Anti-Hypercholesterolemia Effects
3.1.1. Inhibitory Effect on HMG-CoA Reductase (HMGR)
3.1.2. Effects on Cholesterol Permeation In Vitro through Human Caco-2 Cells
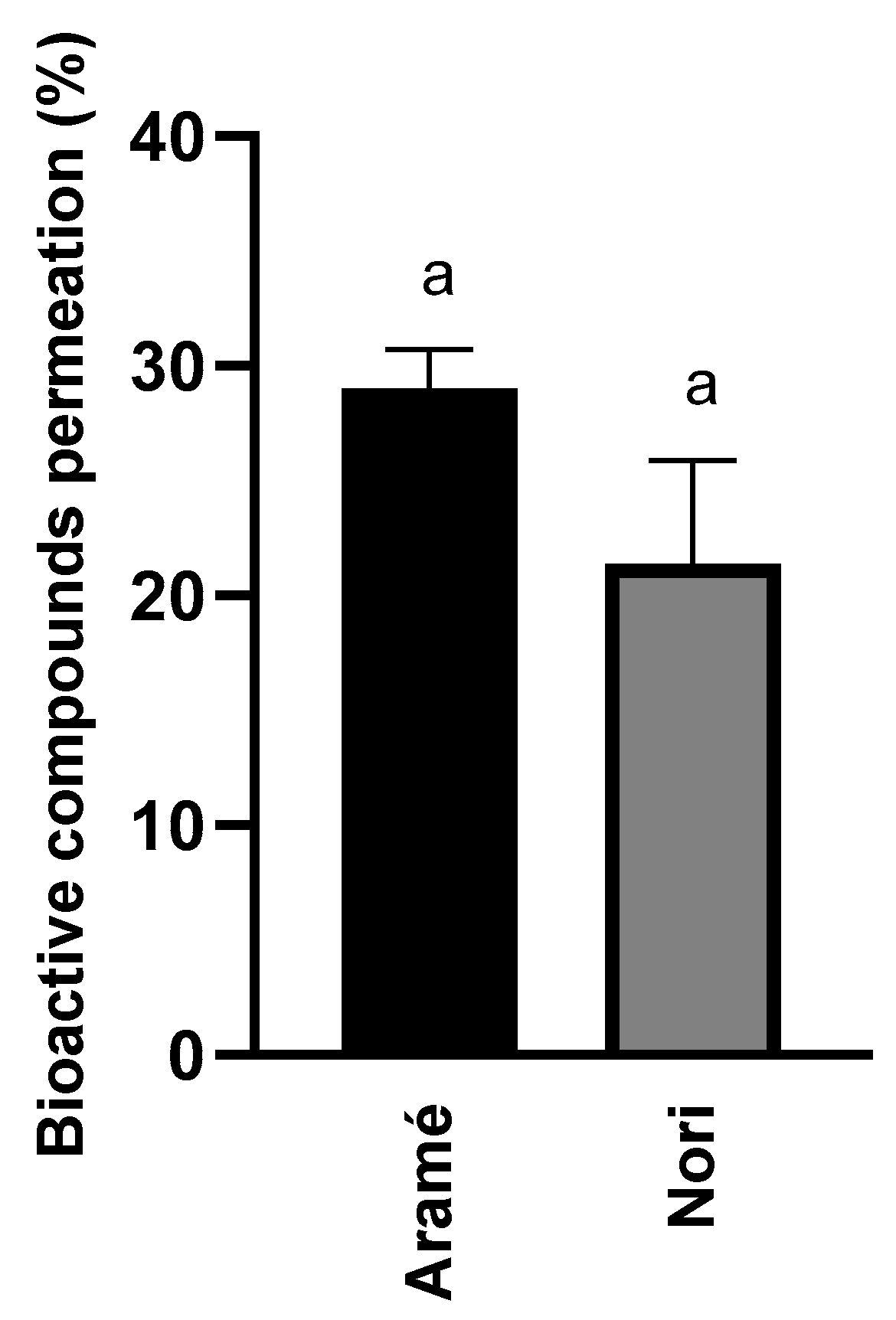
3.1.3. Seaweed Extracts Permeation In Vitro through Human Caco-2 Cells
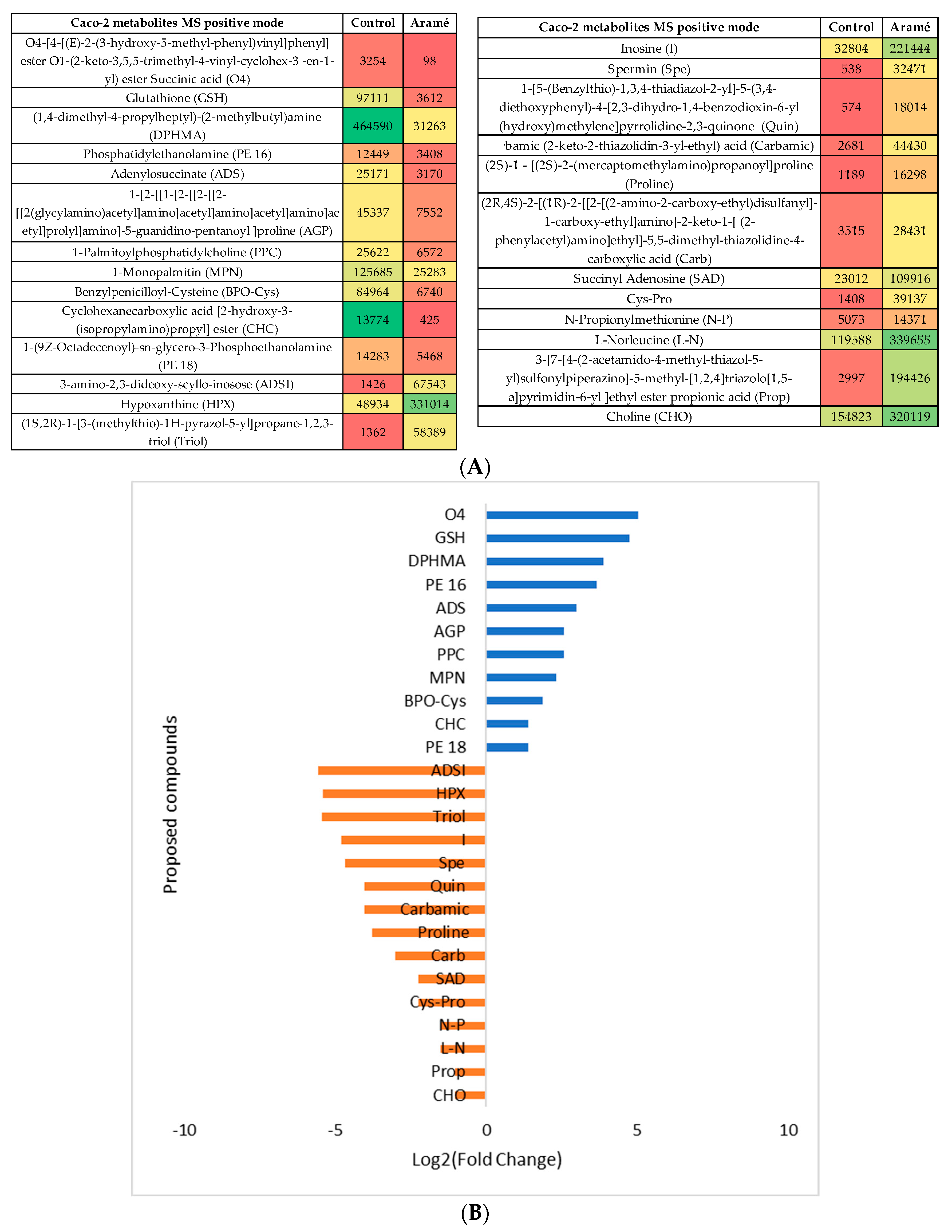
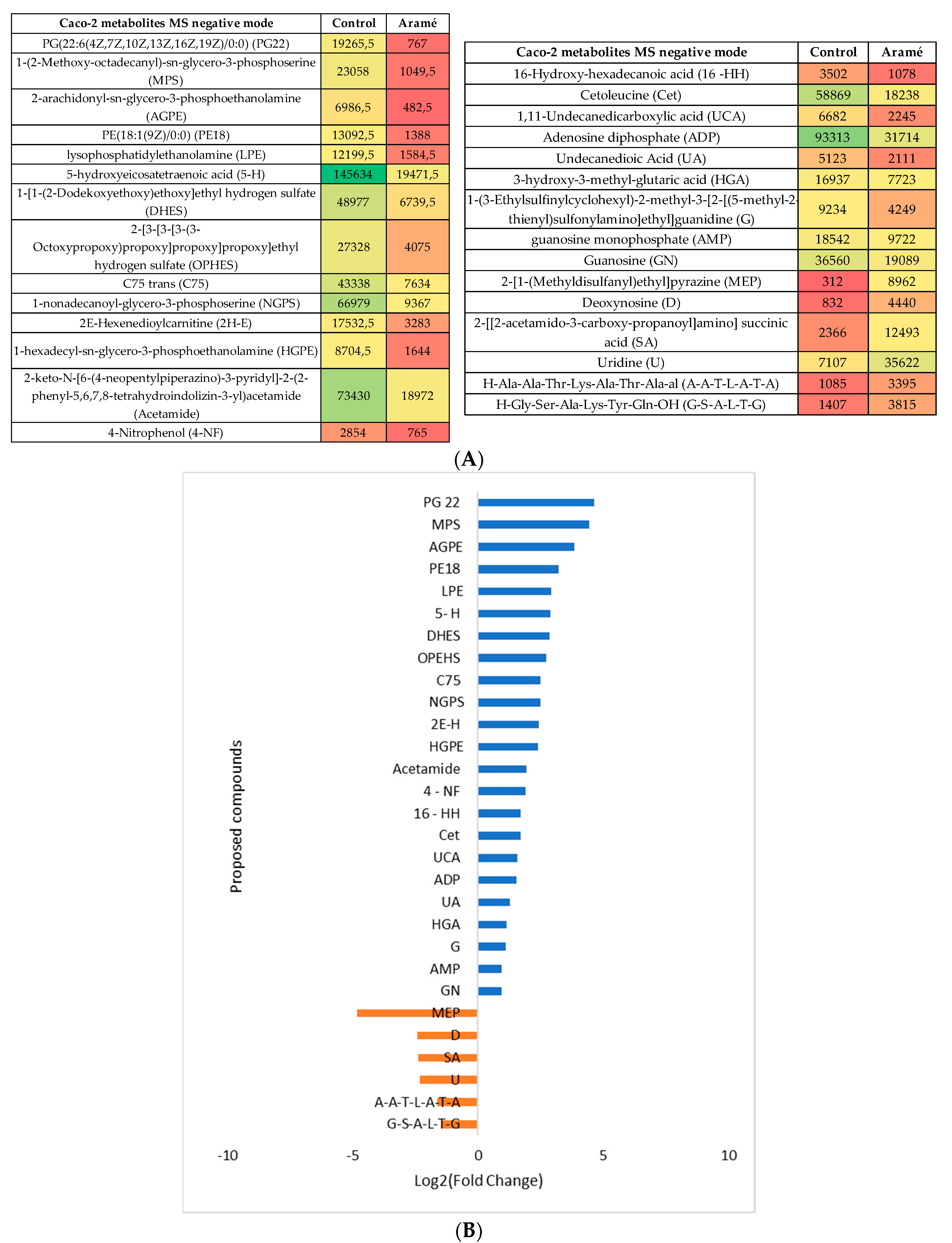
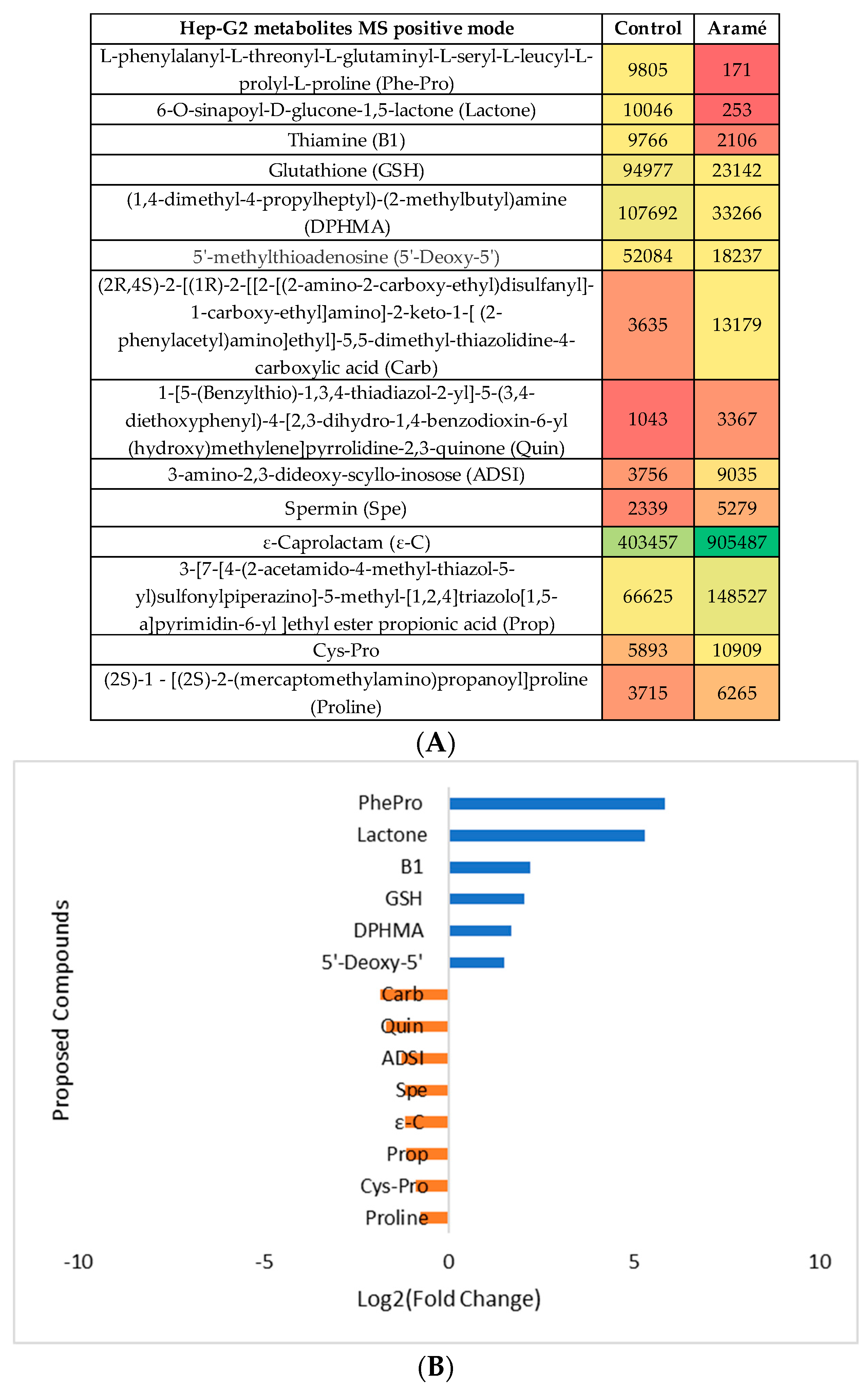
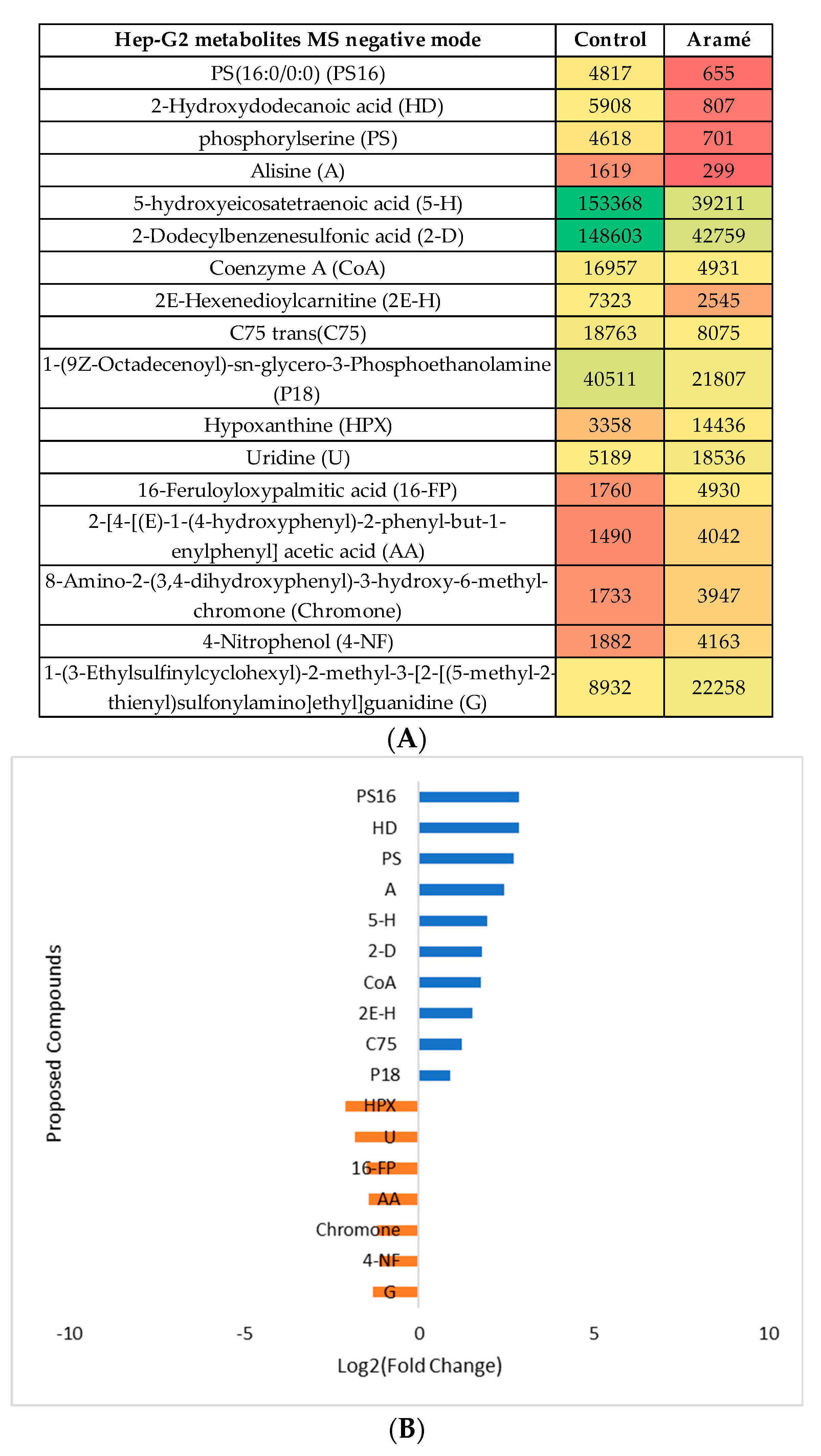
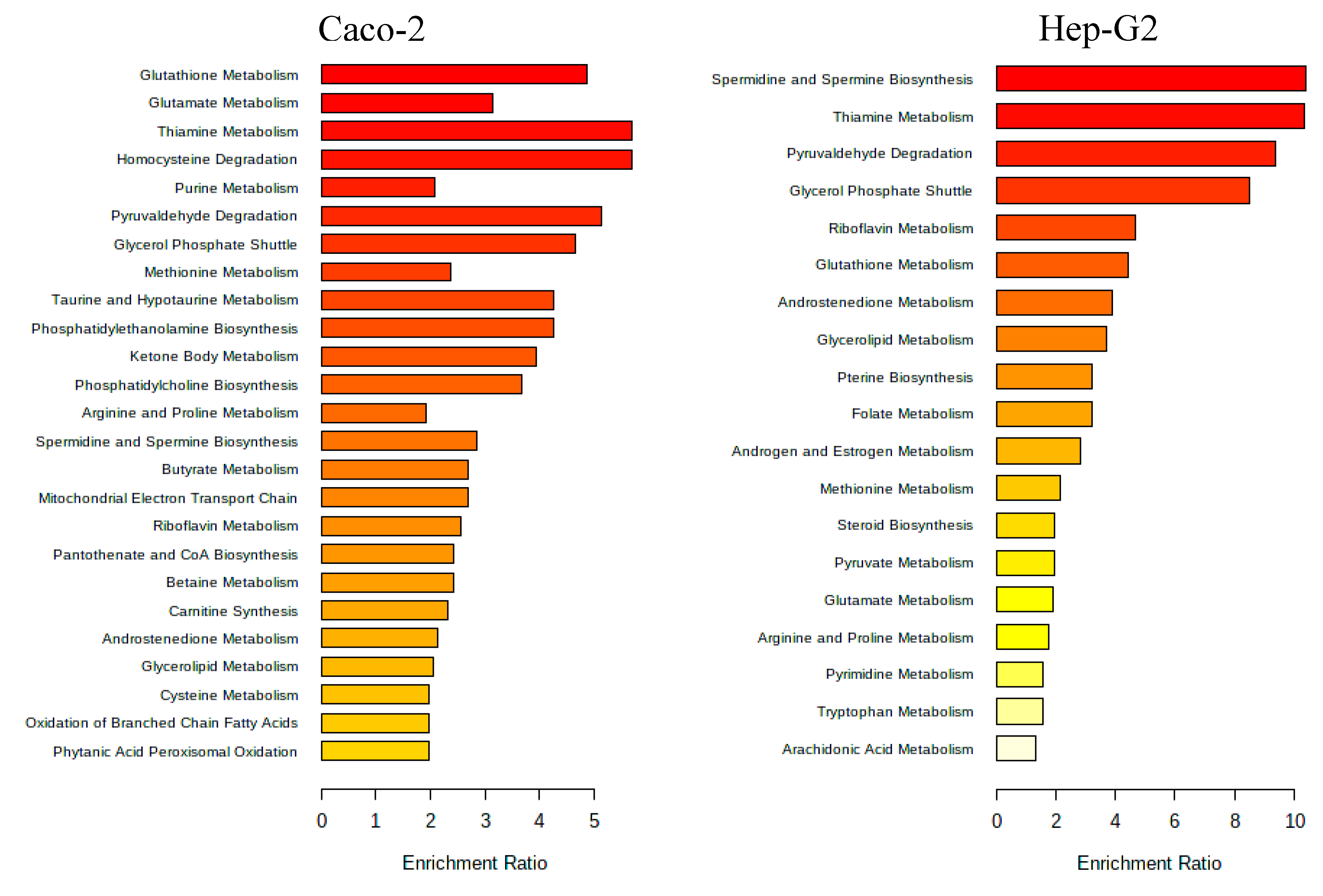
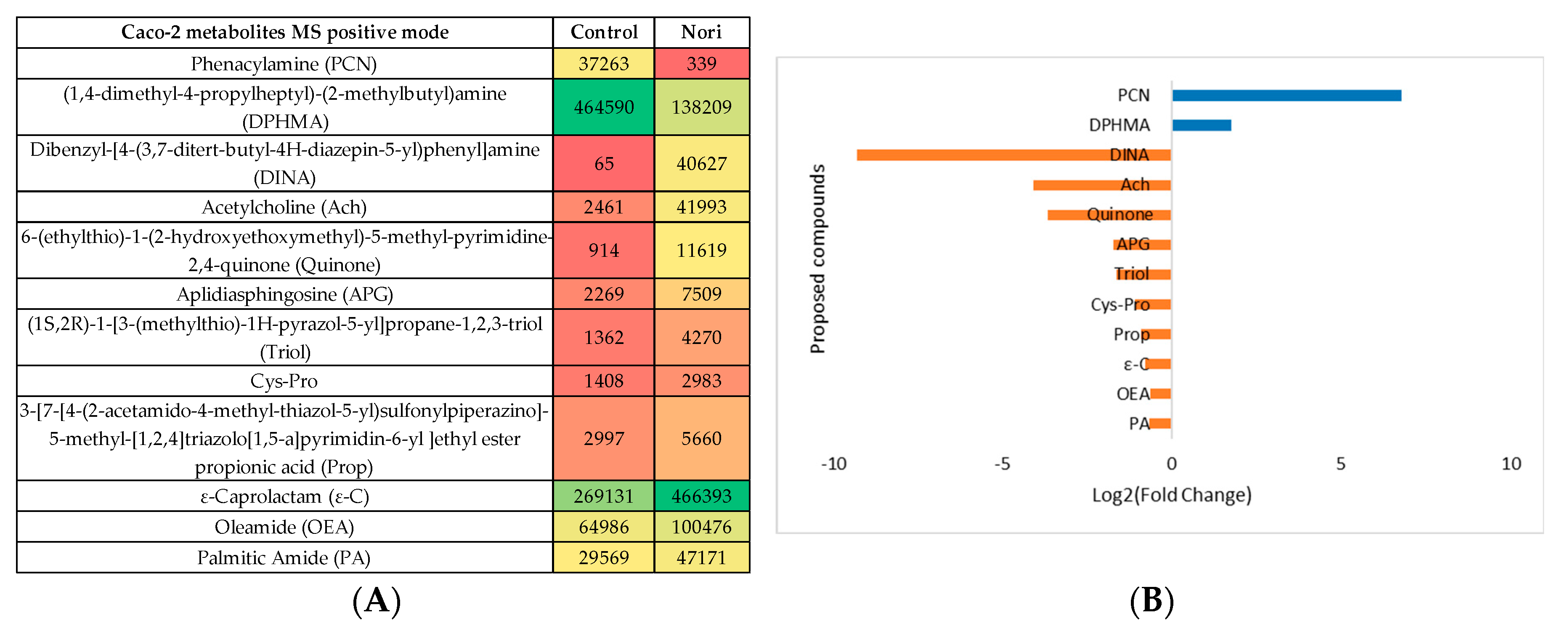
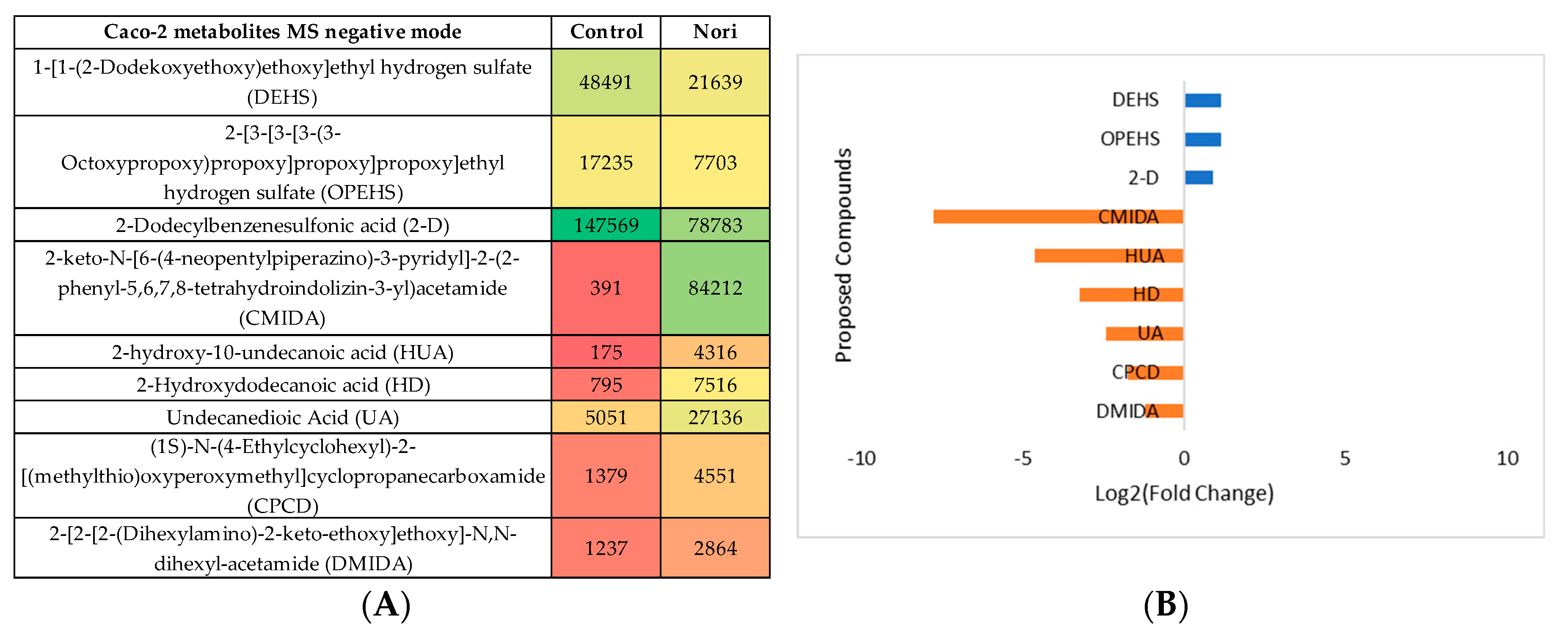
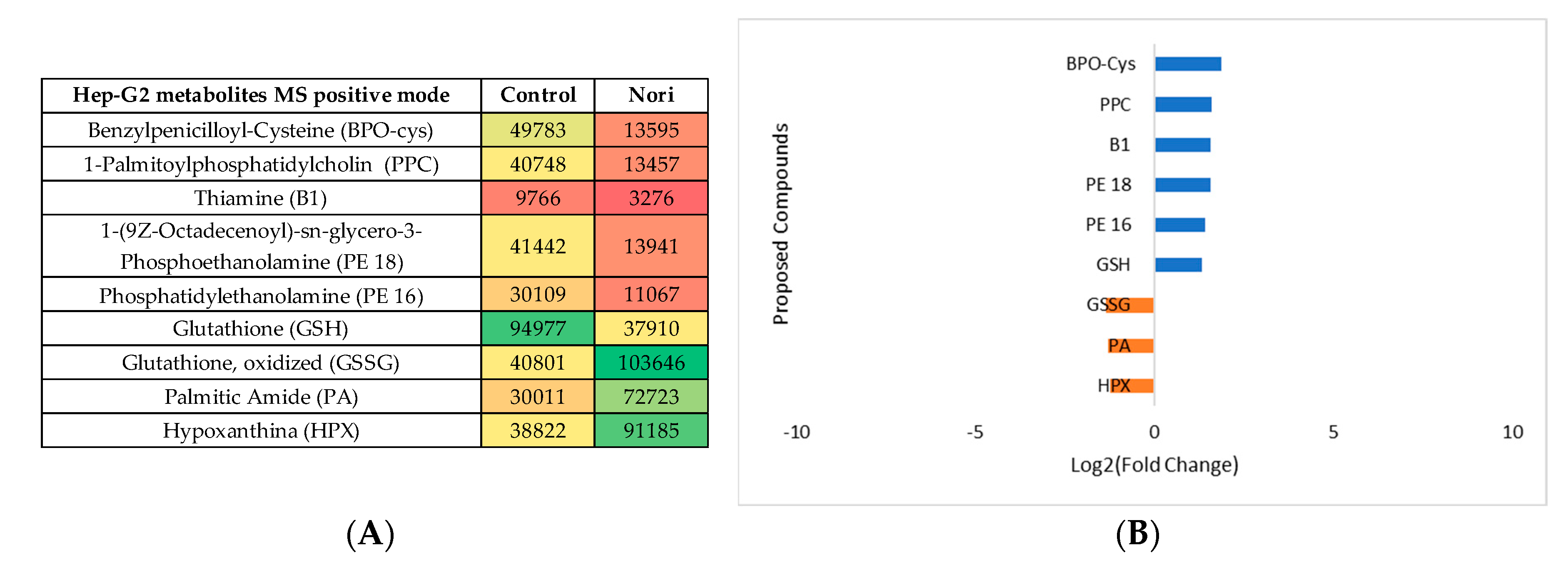
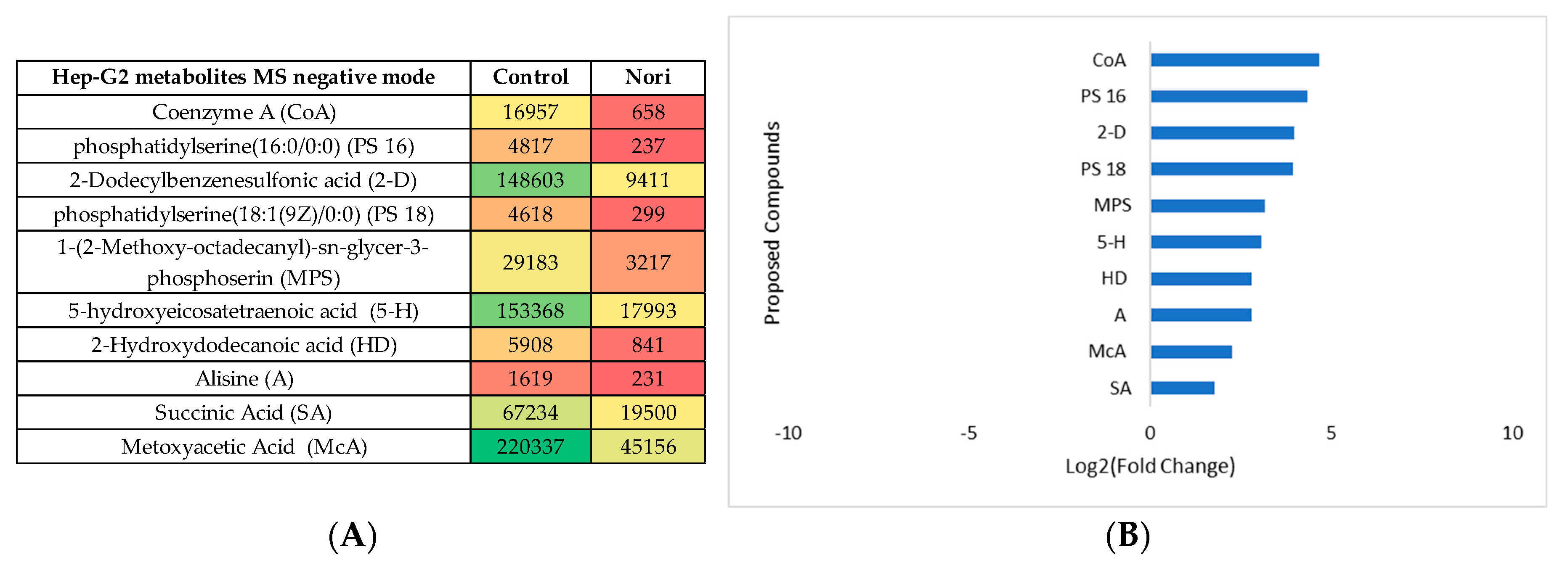
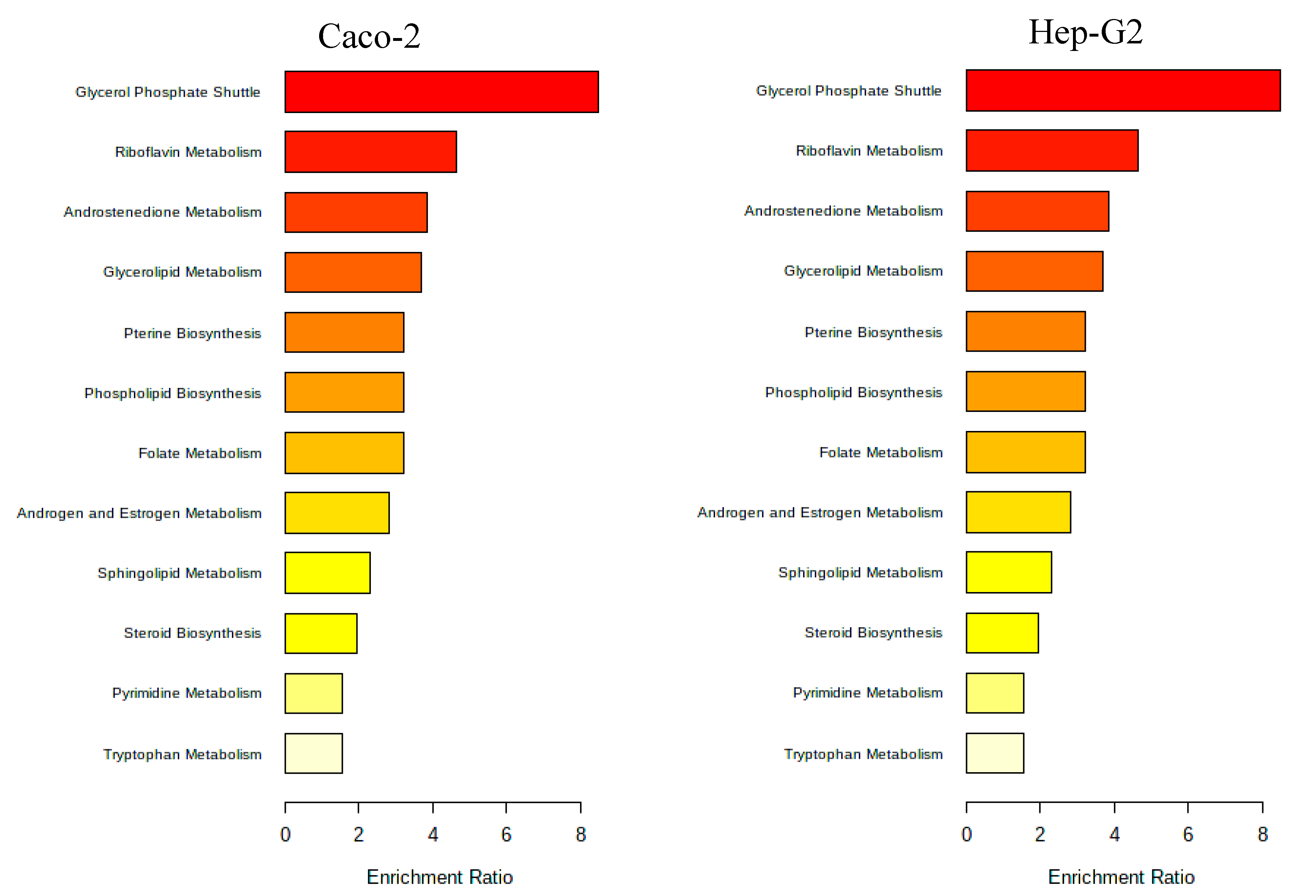
3.2.3. Metabolomic Effect of Seaweed Extract on Caco-2 and Hep-G2
- Aramé extract
- Nori extract
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amante, C.; Esposito, T.; Luccheo, G.; Luccheo, L.; Russo, P.; Del Gaudio, P. Life 2022, 12. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization, W.H. Cardiovascular Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/about_cvd/en/. (accessed on 12 march 2023).
- Martinez-Hervas, S.; Ascaso, J.F. Hypercholesterolemia. In Encyclopedia of Endocrine Diseases (Second Edition), Huhtaniemi, I., Martini, L., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2019; pp. 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Civeira, F.; Arca, M.; Cenarro, A.; Hegele, R.A. A mechanism-based operational definition and classification of hypercholesterolemia. Journal of Clinical Lipidology 2022, 16, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, R.; Pacheco, R.; Bourbon, M.; Serralheiro, M.L. Brown Algae Potential as a Functional Food against Hypercholesterolemia: Review. Foods 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordestgaard, B.G.; Nicholls, S.J.; Langsted, A.; Ray, K.K.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A. Advances in lipid-lowering therapy through gene-silencing technologies. Nat Rev Cardiol 2018, 15, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.; Shi, M.; Ren, X.; Ge, J. Efficacy and Tolerability of Ezetimibe/Atorvastatin Fixed-dose Combination Versus Atorvastatin Monotherapy in Hypercholesterolemia: A Phase III, Randomized, Active-controlled Study in Chinese Patients. Clinical Therapeutics 2022, 44, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Database, H.M. Cholesterol. Available online: (accessed on.
- Luo, J.; Yang, H.; Song, B.L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020, 21, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ressaissi, A.; Attia, N.; Pacheco, R.; Falé, P.L.; Serralheiro, M.L.M. Cholesterol transporter proteins in HepG2 cells can be modulated by phenolic compounds present in Opuntia ficus-indica aqueous solutions. Journal of Functional Foods 2020, 64, 103674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmaoglu, S.; Yilmaz, A.O.; Taslimi, P.; Algul, O.; Kilic, D.; Gulcin, I. Synthesis and biological evaluation of phloroglucinol derivatives possessing α-glycosidase, acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activity. Archiv der Pharmazie 2018, 351, 1700314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, B.A.; Dayspring, T.D.; Toth, P.P. Ezetimibe therapy: mechanism of action and clinical update. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2012, 8, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaggia, A.; Donzelli, A.; Font, M.; Molteni, D.; Galvano, A. Clinical efficacy and safety of Ezetimibe on major cardiovascular endpoints: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0124587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiology, A.C.o. Cardiology, A.C.o. Ezetimibe: The lower the LDL-C, the better (even for total cardiovascular events). Available online: Ezetimibe: The Lower the LDL-C, the Better (Even for Total Cardiovascular Events) - American College of Cardiology (acc.org) (accessed on 1st March).
- Ward, N.C.; Watts, G.F.; Eckel, R.H. Statin Toxicity. Circulation Research 2019, 124, 328–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, F.; Ray, K.K.; Wiklund, O.; Corsini, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Bruckert, E.; De Backer, G.; Hegele, R.A.; Hovingh, G.K.; Jacobson, T.A.; et al. Adverse effects of statin therapy: perception vs. the evidence - focus on glucose homeostasis, cognitive, renal and hepatic function, haemorrhagic stroke and cataract. Eur Heart J 2018, 39, 2526–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.; Reith, C.; Emberson, J.; Armitage, J.; Baigent, C.; Blackwell, L.; Blumenthal, R.; Danesh, J.; Smith, G.D.; DeMets, D.; et al. Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of statin therapy. Lancet 2016, 388, 2532–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Gong, K.; Xu, S.; Zhang, F.; Meng, X.; Han, J. Regulation of cholesterol homeostasis in health and diseases: from mechanisms to targeted therapeutics. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2022, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, S.; Gaspar, M.M.; Ascensão, L.; Faísca, P.; Reis, C.P.; Pacheco, R. Nanoformulation of Seaweed Eisenia bicyclis in Albumin Nanoparticles Targeting Cardiovascular Diseases: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Marine Drugs 2022, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tantawy, W.H.; Temraz, A. Natural products for controlling hyperlipidemia: review. Arch Physiol Biochem 2019, 125, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, P.M.; Hegele, R.A. Functional foods and dietary supplements for the management of dyslipidaemia. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2017, 13, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Sairazi, N.S.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S. Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds: Neuroprotective Potentials against Neurodegenerative Diseases. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020, 2020, 6565396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, A.; Novellino, E. Nutraceuticals in hypercholesterolaemia: an overview. Br J Pharmacol 2017, 174, 1450–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigogliuso, S.; Campora, S.; Notarbartolo, M.; Ghersi, G. Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Marine Organisms: Focus on the Future Perspectives for Pharmacological, Biomedical and Regenerative Medicine Applications of Marine Collagen. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.; Duarte, A.P.; Pinto, S.; Botelho, H.M.; Reis, C.P.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Pacheco, R. Edible Seaweeds Extracts: Characterization and Functional Properties for Health Conditions. Antioxidants 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Gálvez, J. Potential Role of Seaweed Polyphenols in Cardiovascular-Associated Disorders. Mar Drugs 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagata, K. Prevention of cardiovascular disease through modulation of endothelial cell function by dietary seaweed intake. Phytomedicine Plus 2021, 1, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinita, M.D.; Harwanto, D.; Choi, J.-S. Seaweed Exhibits Therapeutic Properties against Chronic Diseases: An Overview. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.G.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. Looking Beyond the Terrestrial: The Potential of Seaweed Derived Bioactives to Treat Non-Communicable Diseases. Mar Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, A.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Seaweed’s Bioactive Candidate Compounds to Food Industry and Global Food Security. Life (Basel) 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, B.; Chauhan, O.P.; Mishra, A. Edible Seaweeds: A Potential Novel Source of Bioactive Metabolites and Nutraceuticals With Human Health Benefits. Frontiers in Marine Science 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, K. Seaweeds: A sustainable food source. 2015; pp. 347–364.
- Peñalver, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Ros, G.; Amarowicz, R.; Pateiro, M.; Nieto, G. Seaweeds as a Functional Ingredient for a Healthy Diet. Mar Drugs 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Roy, A.; Jung, J.H.; Choi, J.S. Evaluation of the inhibitory effects of eckol and dieckol isolated from edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis on human monoamine oxidases A and B. Arch Pharm Res 2017, 40, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Dasagrandhi, C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, B.G.; Eom, S.H.; Kim, Y.M. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Phlorotannins from Edible Brown Algae, Eisenia bicyclis Against Streptomycin-Resistant Listeria monocytogenes. Indian J Microbiol 2018, 58, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.A.; Kim, S.M.; Kang, S.W.; Jeon, S.I.; Um, B.H.; Jung, S.H. Edible seaweed, Eisenia bicyclis, protects retinal ganglion cells death caused by oxidative stress. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 2012, 14, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, K.L.; Mehta, A. Health Benefits and Pharmacological Effects of Porphyra Species. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 2019, 74, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichihara, T.; Wanibuchi, H.; Taniyama, T.; Okai, Y.; Yano, Y.; Otani, S.; Imaoka, S.; Funae, Y.; Fukushima, S. Inhibition of liver glutathione S-transferase placental form-positive foci development in the rat hepatocarcinogenesis by Porphyra tenera (Asakusa-nori). Cancer Lett 1999, 141, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arantes, A.A. Inhibition of HMG-CoA redutase activity and cholesterol permeation through Caco-2 cells by caffeoylquinic acids from Vernonia condensata leaves. 2016, 26, 738–743.
- Theodoridis, G.A.; Gika, H.G.; Want, E.J.; Wilson, I.D. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based global metabolite profiling: a review. Anal Chim Acta 2012, 711, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr Metabolomics 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climent, E.; Benaiges, D.; Pedro-Botet, J. Hydrophilic or Lipophilic Statins? Front Cardiovasc Med 2021, 8, 687585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Cao, Q.; Xing, M.; Xiao, H.; Cheng, Z.; Song, S.; Ji, A. Advances in the Study of Marine Products with Lipid-Lowering Properties. Mar Drugs 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, N.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Chung, H.Y.; Choi, J.S. Anti-hyperlipidemic effect of an edible brown algae, Ecklonia stolonifera, and its constituents on poloxamer 407-induced hyperlipidemic and cholesterol-fed rats. Arch Pharm Res 2008, 31, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Ohlsson, L.; Duan, R.D. Curcumin inhibits cholesterol uptake in Caco-2 cells by down-regulation of NPC1L1 expression. Lipids Health Dis 2010, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larregieu, C.A.; Benet, L.Z. Drug discovery and regulatory considerations for improving in silico and in vitro predictions that use Caco-2 as a surrogate for human intestinal permeability measurements. Aaps j 2013, 15, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.A.; Almeida, T.; Lima, B.; Rocha, E. Cytotoxic activity of the seaweed compound fucosterol, alone and in combination with 5-fluorouracil, in colon cells using 2D and 3D culturing. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2019, 82, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, S.Y.; Althubiti, M.A.; Abdallah, M.E.; Wink, M.; El-Readi, M.Z. The carotenoid fucoxanthin can sensitize multidrug resistant cancer cells to doxorubicin via induction of apoptosis, inhibition of multidrug resistance proteins and metabolic enzymes. Phytomedicine 2020, 77, 153280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, N.; Keitoku, S.; Miyake, H.; Tanaka, R.; Shibata, T. Evaluation on Intestinal Permeability of Phlorotannins Using Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Natural Product Communications 2022, 17, 1934578X211070415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Ji, Y.; Anegboonlap, P.; Hotchkiss, S.; Gill, C.; Yaqoob, P.; Spencer, J.P.; Rowland, I. Gastrointestinal modifications and bioavailability of brown seaweed phlorotannins and effects on inflammatory markers. Br J Nutr 2016, 115, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, M.C.; Thomas, R.L.; Pavisic, J.; James, S.J.; Ulrich, C.M.; Nijhout, H.F. A mathematical model of glutathione metabolism. Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling 2008, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hira, H.S.; Samal, P.; Kaur, A.; Kapoor, S. Plasma level of hypoxanthine/xanthine as markers of oxidative stress with different stages of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Ann Saudi Med 2014, 34, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blachier, F.; Andriamihaja, M.; Blais, A. Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids and Lipid Metabolism. J Nutr 2020, 150, 2524s–2531s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KEGG. Glutathione. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/pathway/map00480 (accessed on 16th July).
- KEGG. Alanine, aspartate and.
- glutamate metabolism Available online: glutamate metabolism - Reference pathway (genome.jp) (accessed on 16th July).
- KEGG. Taurine and hypotaurine.
- metabolism Available online: metabolism - Reference pathway (genome.jp) (accessed on 16th July).
- Stipanuk, M.H.; Ueki, I. Dealing with methionine/homocysteine sulfur: cysteine metabolism to taurine and inorganic sulfur. J Inherit Metab Dis 2011, 34, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, R.; Guedes, R.; López, J.; Serralheiro, M.L. Untargeted metabolomic study of HepG2 cells under the effect of Fucus vesiculosus aqueous extract. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2021, 35, e9197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, T.; Shabbir, M.A.; Inam-Ur-Raheem, M.; Manzoor, M.F.; Ahmad, N.; Liu, Z.W.; Ahmad, M.H.; Siddeeg, A.; Abid, M.; Aadil, R.M. Cysteine and homocysteine as biomarker of various diseases. Food Sci Nutr 2020, 8, 4696–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Agellon, L.B.; Allen, T.M.; Umeda, M.; Jewell, L.; Mason, A.; Vance, D.E. The ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine influences membrane integrity and steatohepatitis. Cell Metab 2006, 3, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, C.L.; Connors, K.E.; Klein, M.S.; Johnsen, V.L.; Shearer, J.; Vogel, H.J.; Devaney, J.M.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Many, G.M.; Barfield, W.; et al. The ACTN3 R577X Polymorphism Is Associated with Cardiometabolic Fitness in Healthy Young Adults. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0130644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Exogenous spermine inhibits high glucose/oxidized LDL-induced oxidative stress and macrophage pyroptosis by activating the Nrf2 pathway. Exp Ther Med 2022, 23, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Yuan, W.; Guo, H.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, L. Effect of Serum Spermidine on the Prognosis in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hong, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Peng, J.; Hong, L. Targeting purine metabolism in ovarian cancer. Journal of Ovarian Research 2022, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, H.M.; Reidling, J.C.; Ortiz, A. Cellular and molecular aspects of thiamin uptake by human liver cells: studies with cultured HepG2 cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2002, 1567, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.P.; Macedo-Júnior, S.J.; Lapa-Costa, F.R.; Cezar-dos-Santos, F.; Santos, A.R.S. Inosine as a Tool to Understand and Treat Central Nervous System Disorders: A Neglected Actor? Frontiers in Neuroscience 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshak, E.S.; Arafa, A.E. Thiamine deficiency and cardiovascular disorders. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2018, 28, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc-Ozdemir, M.; Miller, G.; Song, L.; Kim, J.; Sodek, A.; Koussevitzky, S.; Misra, A.N.; Mittler, R.; Shintani, D. Thiamin confers enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 2009, 151, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.L.; Dunlap, T. Formation and Biological Targets of Quinones: Cytotoxic versus Cytoprotective Effects. Chem Res Toxicol 2017, 30, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
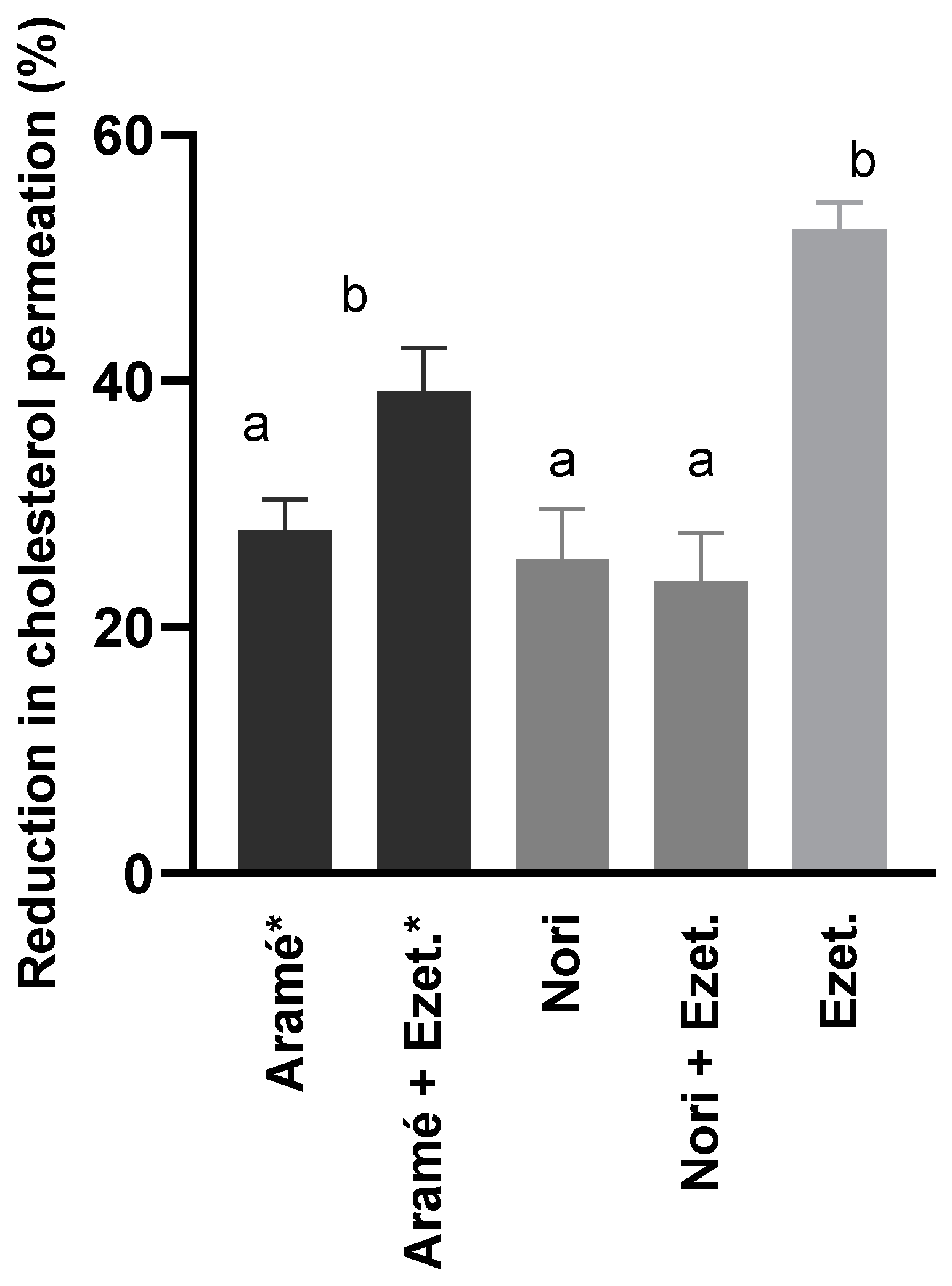
| HMGR inhibitory activitywyxwyx(%) | |
|---|---|
| Nori | 41 ± 3a |
| pravastatin | 95 ± 1b |
| Aramé [19] | 79 ± 7c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





