1. Introduction
Oxidation and oxidative phosphorylation are essential processes in our body for metabolism and energy formation, but oxidative stresses are negative reaction of the imbalance between oxidation and antioxidation caused by over-production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Excessive ROS could attack the cellular proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, leading to cellular dysfunction, immune reaction, and inflammation [
1,
2].
Inflammation is a part of the complex biological responses of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as erythema and edema, which are induced by increased blood flow to the site of injury as well as enhanced vascular permeability resulting in extravasation of macromolecules [
3]. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process [
4]. However, if the host fails to eliminate the stimuli early enough or undergoes an improper recovery process, the unresolved inflammation can cause organ dysfunction and become detrimental to the host [
5]. Inflammation underlies a wide variety of physiological and pathological processes [
6]. Previous reports have provided evidence that inflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of acute and chronic diseases [
7,
8]. Thus, considering that inflammation is the cornerstone of many acute and chronic pathological processes, anti-inflammatory therapy is essential to increase patients’ survival rate and to improve their quality of life.
As an in vitro inflammation model, RAW 264.7 cells, a macrophage cell line, stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) are commonly used [
9,
10]. Since during activation of the cells, dual pathways of inflammation, that is, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) ― nitric oxide (NO) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) ― prostaglandin E
2 (PGE
2), are activated [
11]. For the screening of anti-inflammatory compounds, the mRNA expression of iNOS and COX-2 as well as the production of NO and PGE
2 can be analyzed.
Among many in vivo skin inflammation models, λ-carrageenan-induced air-pouch inflammation is recommended, in which exudate can be easily collected for the analysis of inflammatory cells and mediators in the exudate. Carrageenans are high molecular weight sulphated polygalactans obtained from marine algae [
12]. Air pouch is formed by subcutaneous injection of sterile air into the backside of rats or mice, which can be later injected with λ-carrageenan to produce inflammation [
13,
14]. The pathogenic agent λ-carrageenan induces inflammatory responses in the lining tissue of the pouch wall [
15], leading to extravasation of blood cells and fluid into the pouch. Investigators have shown the accumulation of inflammatory cells such as macrophages, white blood cells (WBCs), and lymphocytes, cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), as well as mediators such as NO and PGE
2 [
8,
16,
17]. These endpoints can be quantified and used to determine the degree of inflammation, resolution of inflammation, or anti-inflammatory and antioxidative activities of test compounds [
18].
The TNF-α ― iNOS ― NO and arachidonic acid ― COX-2 ― PGE
2 inflammatory pathways are blocked by steroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), respectively [
19]. However, severe adverse effects of such drugs are easily developed [20-22]. Indeed, it is well known that high doses and/or long-term use of synthetic steroids cause tolerance, glaucoma, cataracts, diabetes, osteoporosis, and muscle weakness [
22]. NSAIDS can induce gastrointestinal bleeding, congestive heart failure, chronic kidney diseases with renal papillary necrosis, and allergic reactions. Thus, consumers are interested in natural ingredients that are effective, but not come with the side effects of synthetic drugs [
23,
24].
Roses are dicotyledons belonging to the genus Rosa in the family Rosacea. Plants from the Rosacea family are rich in natural molecules with beneficial biological properties, and they are widely appreciated and used in the food industry, perfumery, and cosmetics [
25]. Rose has been confirmed to contain a large amount of antioxidants, and is used as an edible flower in many countries, as well as being used as a cosmetic ingredient [
26]. It was found that rose petals contained antioxidant ingredients including vitamins, polyphenols, anthocyanins, flavonoids, and lactones, and thus displaying antioxidative activity higher than other plants [
27,
28] and comparable to that of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), a representative synthetic antioxidant [29-31]. Related to effectiveness, anthocyanins of rose flowers have been reported to be effective in preventing cardiovascular diseases, cancers, and diabetes [
32]. In many our studies, it has been confirmed that rosebud extracts have strong antimicrobial potential [
33,
34], and exhibit anti-allergic, anti-atopic and anti-inflammatory activities [
35,
36], and antioxidation and anyi-inflammation-related neuroprotective effects [
37,
38].
Therefore, the purpose of this study is screening of novel functional materials with high antioxdative and anti-inflammatory activities. In this context, polyphenol contents and antioxidative activities of 24 rosebud extracts from newly-crossbred roses were assessed first, and the anti-inflammatory effects of a selected candidate were confirmed in vitro and in vivo using RAW 264.7 macrophages and a λ-carrageenan-induced air-pouch inflammation model, respectively.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of Rosebuds
Dried rosebuds from 24 newly-crossbred Korean roses (Rosa hybrida) were from Gumi Floriculture Research Institute (Gumi, Korea) in 2021, which are 1) Lover Shy, 2) Lovely Scarlet, 3) Loving Heart, 4) Red Perfume, 5) Luminus, 6) Mirinae Gold, 7) Betty, 8) Bichina, 9) Aileen, 10) Onnuri, 11) Yunina, 12) Jaemina Red, 13) Jinseonmi, 14) Chilbaegri, 15) Tamina, 16) Tamnari, 17) Pretty Velvet, 18) Peach Grace, 19) Pink Love, 20) Pink Perfume, 21) Hanaro, 22) Hanaram, 23) Hanggina, and 24) Ice Wing.
The dried rosebuds were pulverized in a rotor mill (Laval Lab Inc., Laval, QC, Canada), immersed in 80% ethanol in an ultrasonic water bath, heated at 60~70°C for 2 hours, and then ultrasonic-extracted for 1 hour. Actually, the extraction solvent : solid ratio was set to 49 : 1 (980 mL 80% ethanol : 20 g dried rosebuds). After extraction, the mixture was cooled at room temperature, filtered, and then concentrated under a reduced pressure to 50 brix using a vacuum evaporator (Rotary Vacuum Evaporator N-N series; Eyela, Tokyo, Japan), and then used as a test sample.
2.2. Analysis of Antioxidant Ingredients
Total polyphenols as a major antioxidant component of plants were measured according to the method of Dewanto et al. (2002) [
39]. That is, the contents of polyphenol were measured by the principle that Folin-Ciocalteu's phenol reagent is reduced by the polyphenolic compounds to develop a color of molybdenum. The sample concentration was adjusted to 1 mg/mL. Into 100 μL sample solution, 2 mL of 2% Na
2CO
3 was added, and reacted for 3 min. After adding 100 μL of 50% Folin-Ciocalteu's phenol reagent and reacting for 30 min, the absorbance was measured at 750 nm using a spectrophotometer (UV-1650; Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan). A standard calibration curve was prepared with gallic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) as a standard material diluted 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 times, and the polyphenol contents were expressed as mg gallic acid equivalent (GAE) in 1 g of extract.
2.3. Measurement of Antioxidative Activities
2.3.1. Analysis of ABTS-scavenging activity
The antioxidant efficacy of rosebud extracts was measured by the scavenging potential of 2,2-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline 6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS; Sigma-Aldrich) [
40]. A stock ABTS radical cation solution (7 mM) was added to a 2.45 mM potassium and sulfate solution, stirred well for 12 to 16 hours in the dark at room temperature. The solution was diluted with distilled water to obtain an absorbance of 1.4 to 1.5 at 735 nm. A diluted 1 mL ABTS radical cation solution was added to 50 μL of the test substance or distilled water (blank) to adjust to 0.5 mg/mL. After 1 hour, the absorbance was measured at 735 nm. ABTS radical scavenging activity, i.e., electron-donating ability, was expressed as mg ascorbic acid equivalent (AAE) in 1 g of extract with the difference in absorbance according to the addition and non-addition (distilled water) of the test substance.
2.3.2. Analysis of DPPH-scavenging activity
Additional antioxidant efficacy of the rosebud extracts was measured according to the method of Hwang et al. (2006) [
41], based on the scavenging potential of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Sigma-Aldrich). That is, into 0.8 mL of 0.2 mM DPPH solution, 0.2 mL of the extract or distilled water (blank) was added to adjust to 0.1 mg/mL concentration. After 30-min incubation at room temperature, absorbance was measured at 520 nm. DPPH radical-scavenging activity, i.e., electron-donating ability, was expressed as mg AAE in 1 g of extract with the difference in absorbance according to the addition and non-addition (distilled water) of the test substance.
2.3.3. Analysis of correlation between antioxidant contents and antioxidative activities
The correlations between antioxidant (polyphenol) contents and antioxidative activities were analyzed. Linear regression coefficients were calculated for the estimation of relationship.
2.4. Measurement of Anti-inflammatory Activities
2.4.1. Analysis of NO-inhibitory activity
RAW 264.7 cells were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). Cells were cultivated with Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; Biowest, Kansas City, MO, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Biowest).
RAW 264.7 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate in a density of 5 × 105 cells/mL (0.1 mL/well). The cells were incubated with LPS (Sigma-Aldrich; 1 μg/mL) and 100 μg/mL of 24 each rosebud extract for 24 hours. The cell culture supernatants were harvested, and the concentrations of NO were measured by Griess reagent system (Promega, Madison, WI, USA).
2.4.2. Analysis of correlation between antioxidant contents and NO-inhibitory activities
The correlation between antioxidant (polyphenol) contents and NO-inhibitory activity of 24 rosebud extracts was analyzed. Linear regression coefficient was calculated for the estimation of relationship.
Based on the antioxidant contents, antioxidative activities and NO-inhibitory potentials of 24 rosebud extracts, Pretty Velvet rosebud extract (PVRE) was selected as a candidate for further studies on anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in vivo, and underlying mechanisms.
2.5. Measurement of In Vitro Anti-inflammatory Activity of PVRE
2.5.1. MTT assay for cytotoxicity
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (98% purity). Briefly, MTT powder was dissolved in Dulbecco’s phosphate- buffered saline (D-PBS; Biowest) to a final concentration of 5 mg/mL (MTT stock solution).
RAW 264.7 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate at a density of 5 × 105 cells/mL (0.1 mL/well). The cells were incubated with various concentrations (10, 30 or 100 μg/mL) of PVRE for 24 hours. Into each cell culture well (0.1 mL/well), 100 μL of DMEM medium containing 10% MTT stock solution (MTT medium) was added, and incubated under 5% CO2 at 37°C for further 1 hour. The MTT medium was then discarded, and the formazan produced in the cells was extracted with 100 μL of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The absorbance was read at 540 nm.
2.5.2. qPCR analysis of mRNA expressions of iNOS and COX-II
RAW 264.7 cells were seeded into a 24-well plate (5 × 10
5 cells/mL) and incubated under 5% CO
2 at 37°C overnight. The cells were incubated with LPS (1 μg/mL) and various concentrations (10, 30 or 100 μg/mL) of PVRE for 24 hours. Total RNA was extracted using 1 mL of RNAiso PLUS (TaKaRa, Shiga, Japan). Then, 1 μg of total RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA. Real-time qPCR samples were prepared with a PrimeScript
TM RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa). The primer sequences for iNOS, COX-II, and GAPDH are described in
Table 1. qPCR was performed with a AriaMx Real-Time PCR system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) using a two-step protocol (40 cycles of 95°C for 30 sec followed by 60°C for 30 sec).
2.5.3. Chemical analysis of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2
After collection of RAW 264.7 cells for the analysis of mRNA expression, the culture supernatant was harvested. The concentrations of NO and PGE2 were measured using the Griess reagent and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), respectively.
2.6. Measurement of In Vivo Anti-inflammatory Activity of PVRE
2.6.1. Animals
Six-week-old male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were purchased from DBL (Eumsung, Korea). The animals were housed at a room with a constant temperature (23 ± 2°C), relative humidity of 55 ± 10%, and 12-hour light/dark cycle, and fed with standard rodent chow and purified water ad libitum
All animal experimental procedures were approved and carried out in accordance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Laboratory Animal Research Center at Chungbuk National University, Korea (Approval No. CBNUR-1629-21).
2.6.2. Experimental design using an air-pouch inflammation model
A λ-carrageenan-induced air-pouch model of acute inflammation was established in rats. Briefly, rats were anesthetized with isoflurane. Then, 20 mL of sterile air was injected subcutaneously into the mid-back side using a syringe. On the 5th and 6th days, 10 mL of sterile air was re-injected at the same site to maintain the size of the air pouch. Twenty four hours later, inflammation was induced by injecting 1 mL of λ-carrageenan solution (2% in D-PBS) into the pouch. Test sample (PVRE; 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg), dexamethasone (Sigma-Aldrich; 2 mg/kg) or indomethacin (Sigma-Aldrich; 2 mg/kg) were administrated intraperitoneally 30 min before λ-carrageenan injection. Six hours after λ-carrageenan injection, the exudate in the pouch was collected. An aliquot of the exudate was analyzed for inflammatory cells. Remaining exudate was centrifuged at 10,000 g at 4°C for 10 min, and the supernatant was used for the analysis of inflammatory mediators. The centrally-positioned skin tissues of the pouches were excised for Image-J analysis and histopathological examination.
2.6.3. Analysis of exudate volume and inflammation cells
After sacrifice of the rats, the air-pouch exudate was collected. Briefly, 2 mL of cold saline (0.9% NaCl) was injected into the pouch and the pouch was gently massaged. All the fluid was harvested using a syringe, the volume was recorded, and net exudate was calculated by subtracting 2 mL saline injected.
The exudate was analyzed for total white blood cells (WBCs), neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes with a hematology analyzer (IDEXX Procyte Dx, Westbrook, CT, USA).
2.6.4. ELISA analysis of inflammatory cytokines
The levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in air-pouch exudate were measured using ELISA kits (R&D Systems) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.6.5. Chemical analysis of NO and PGE2
The concentrations of NO and PGE2 in air-pouch exudate were measured using the Griess reagent (Sigma-Aldrich) and ELISA kit (R&D Systems), respectively, as described above.
2.6.6. Image-J analysis of dermal blood vessel area
After the rats were sacrificed, the back skin was cut off in the same area and photographed, and the area of blood vessels on the back skin were observed and calculated by Image-J software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
2.6.7. Microscopic examination of tissue inflammation
Skin tissues obtained from the pouches were fixed with 10% neutral formalin, followed by tissue processing and paraffin embedding. Paraffin blocks were sectioned (4 μm in thickness) and stained with hematoxylin-eosin. Histopathological examination was then performed under a light microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The data were described as mean ± standard error. Statistical significance between the groups was analyzed by one-way analysis of variance using the SPSS statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). P-values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
4. Discussion
Most of the animals consuming oxygen for metabolism suffer from tissue damage, called oxidative stress, and aging due to the generation of ROS [
42]. Organisms synthesize or ingest antioxidants in the body to block cell and tissue damages caused by ROS. If oxidative stress in the body goes beyond the antioxidant defense capacity that counteracts it, theoretically, supplementation with antioxidants can limit oxidative damage. As such, the search for a compound capable of scavenging ROS or a substance that inhibits the formation of oxides is being actively conducted. Such compounds mainly containing a polyphenol structure are rich in plants, called phytochemicals which are largely divided into phenolics, carotenoids, alkaloids, organosulfur derivatives, and nitrogen-containing compounds [
30].
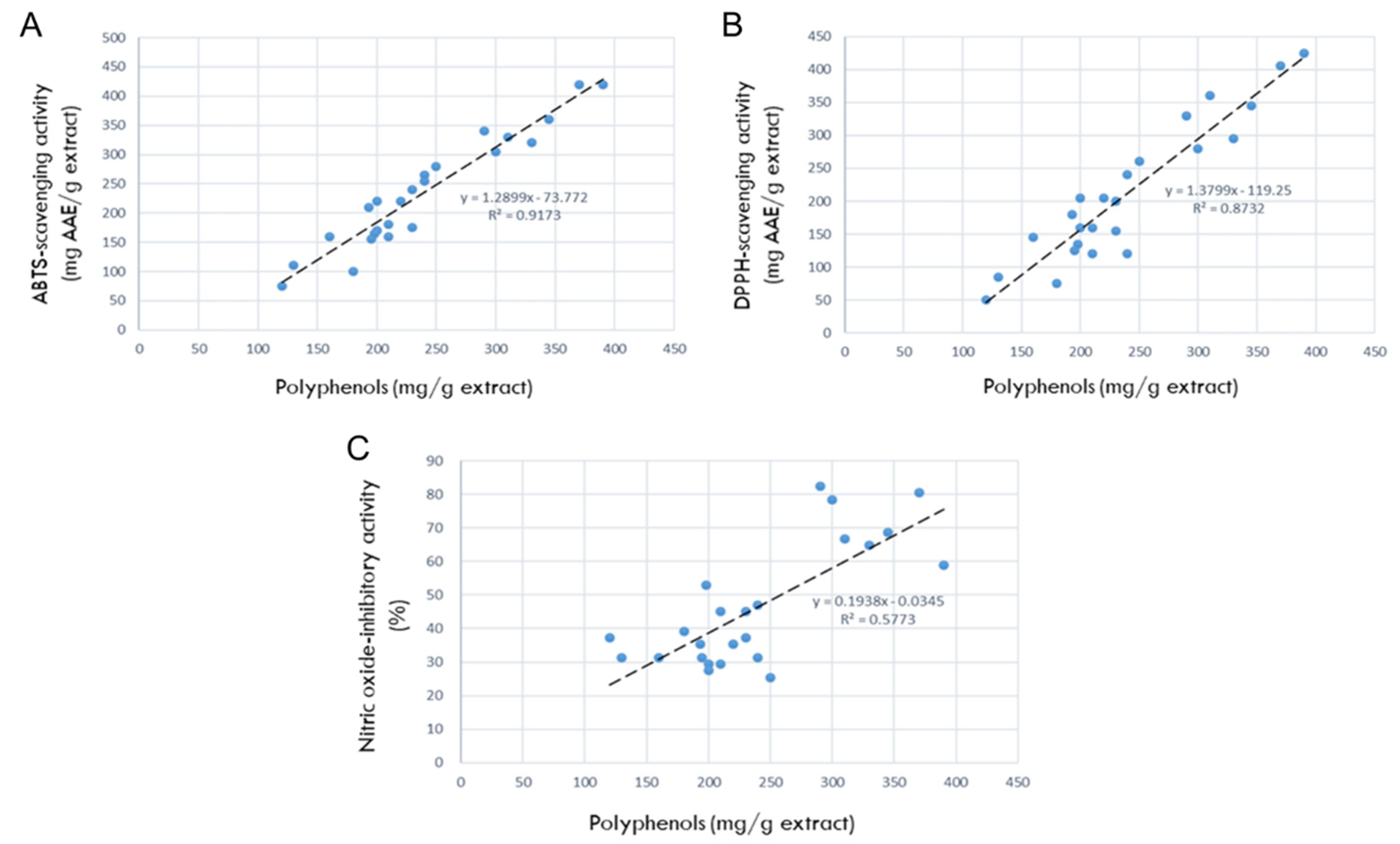
ABTS and DPPH radical-scavenging activities are common tools for the rapid assessment of antioxidative potentials of diverse natural products [
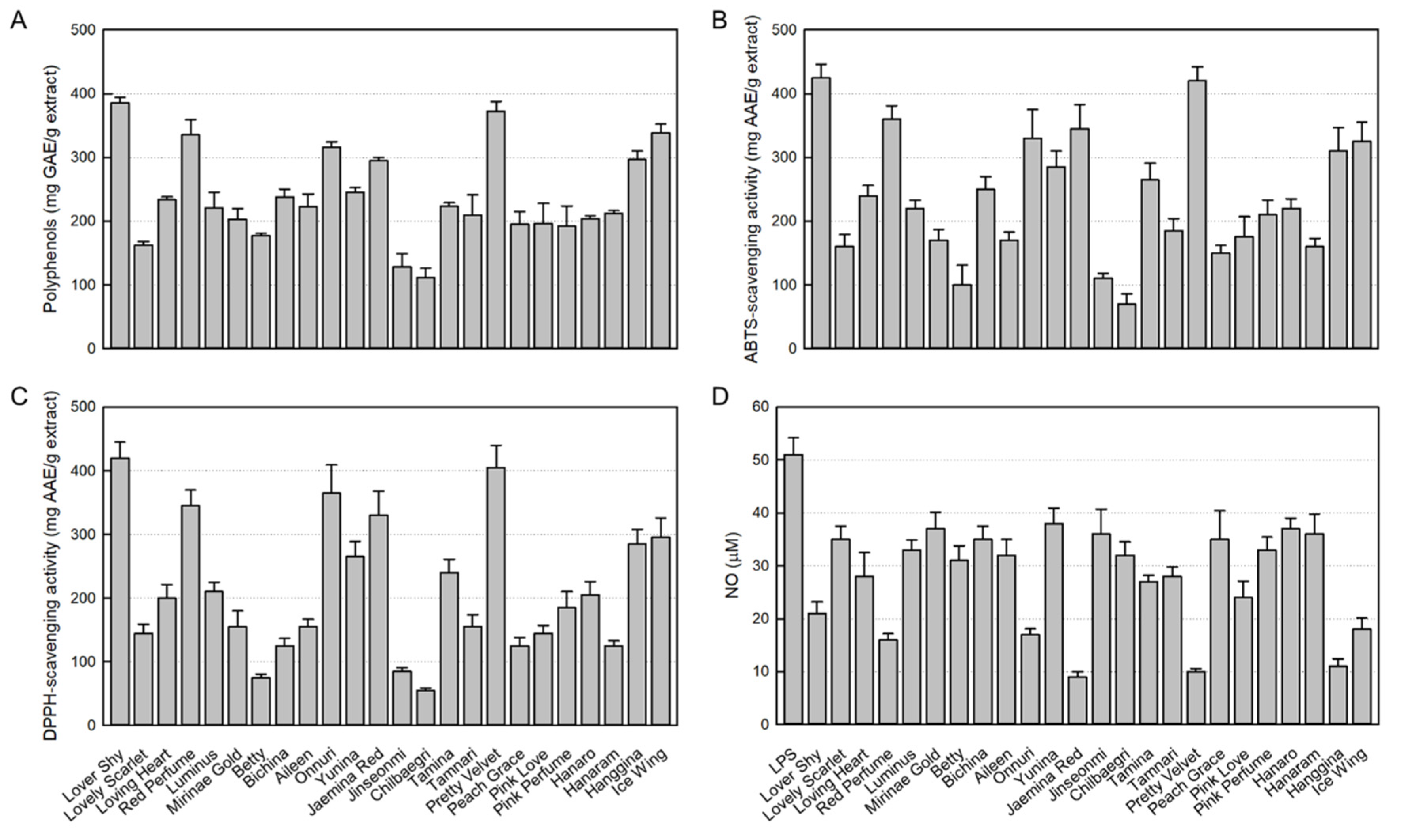
43]. In the present study, the polyphenol contents and antioxidant activities of 24 rosebud extracts showed high relationships, and among them, Lover Shy and Pretty Velvet were found to be the highest in both antioxidant ingredients and their activities.
Tissue damage caused by ROS is involved in the most inflammatory responses. Inflammation is the basic mechanism available for tissue repair after an injury and consists of a cascade of cellular and microvascular reactions. Therefore, the anti-inflammatory effects of the 24 rosebud extracts were evaluated in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, from which Pretty Velvet, Jaemina Red, and Hanggina displayed the highest NO-inhibitory activities. Thus, PVRE possessing the highest antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potentials was selected as a candidate for further studies on therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms in vitro and in vivo.
The process of inflammation is accompanied by exudation, infiltration of inflammatory cells, and production of cytokines and inflammatory mediators. The accumulation of circulating leukocytes and monocytes, followed by lymphocytes, is one of the most visible signs of inflammation [
6,
44]. In this process, an important role has been attributed to the release of chemo-attractants by resident cells inducing the inflammatory cell recruitment to the inflammatory focus [
45]. Inflammatory cytokines are produced predominantly by activated macrophages, and mediate upregulation of inflammatory reactions [
46]. Especially, certain inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β are involved in the process of pathologic pain [
47,
48]. Although NO produced by constitutive NOS (cNOS) is an important cellular signaling molecule that participates in diverse physiological functions in mammals, excessive production of NO from cytokine- or bacterial endotoxin-activated iNOS cause acute pain, edema, and even shock [
49,
50]. It has been well defined that TNF-α ― iNOS ― NO pathway is controlled by steroids [
9,
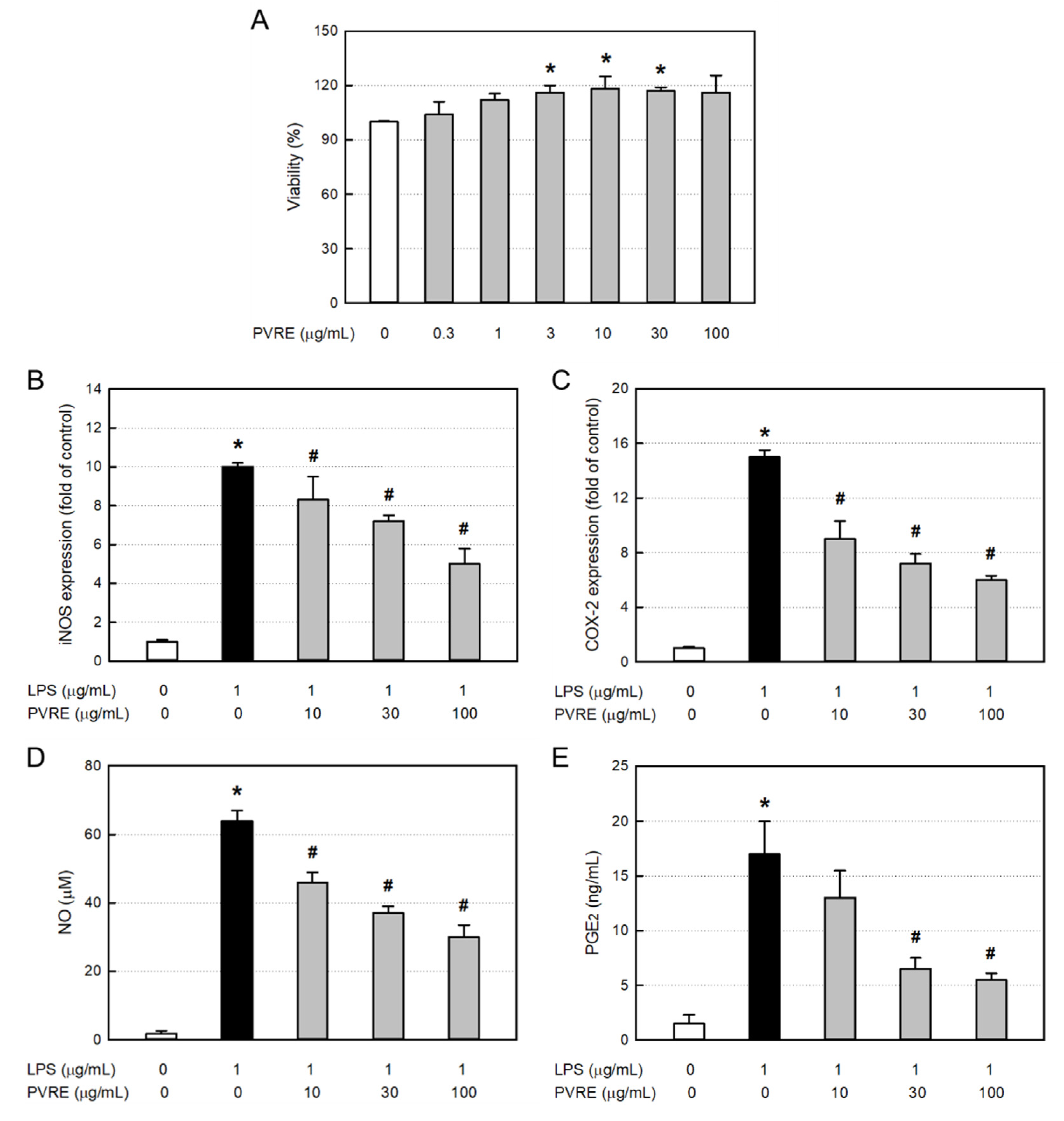
10]. Interestingly, PVRE strongly inhibited the iNOS mRNA expression, and ensuing NO production in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. From such phenomena, it is inferred that PVRE has steroid-like action mechanism.
PGs produced from arachidonic acid by enzyme COX-1 are important physiological intrinsic regulators for blood blow, gastric mucosal protection, and renal and uterine functions. Among diverse PGs, PGE
2 synthesis is affected by the expression of COX-2, levels of which are highly inducible in many tissues by inflammatory factors including cytokines and growth factors. Thus, PGE
2 is an important lipid mediator of inflammatory and immune responses during acute and chronic infections [
51]. By comparison with the TNF-α ― iNOS ― NO pathway, arachidonic acid ― COX-2 ― PGE
2 pathway is regulated by NSAIDs. In the present study, the COX-2 expression and PGE
2 production were markedly inhibited by PVRE, indicative of an NSAID-like activity of PVRE. Based on the dual effects of PVRE on NO and PGE
2 regulation, it was expected that PVRE could be a potential candidate for anti-inflammation. So, further studies in vivo were conducted.
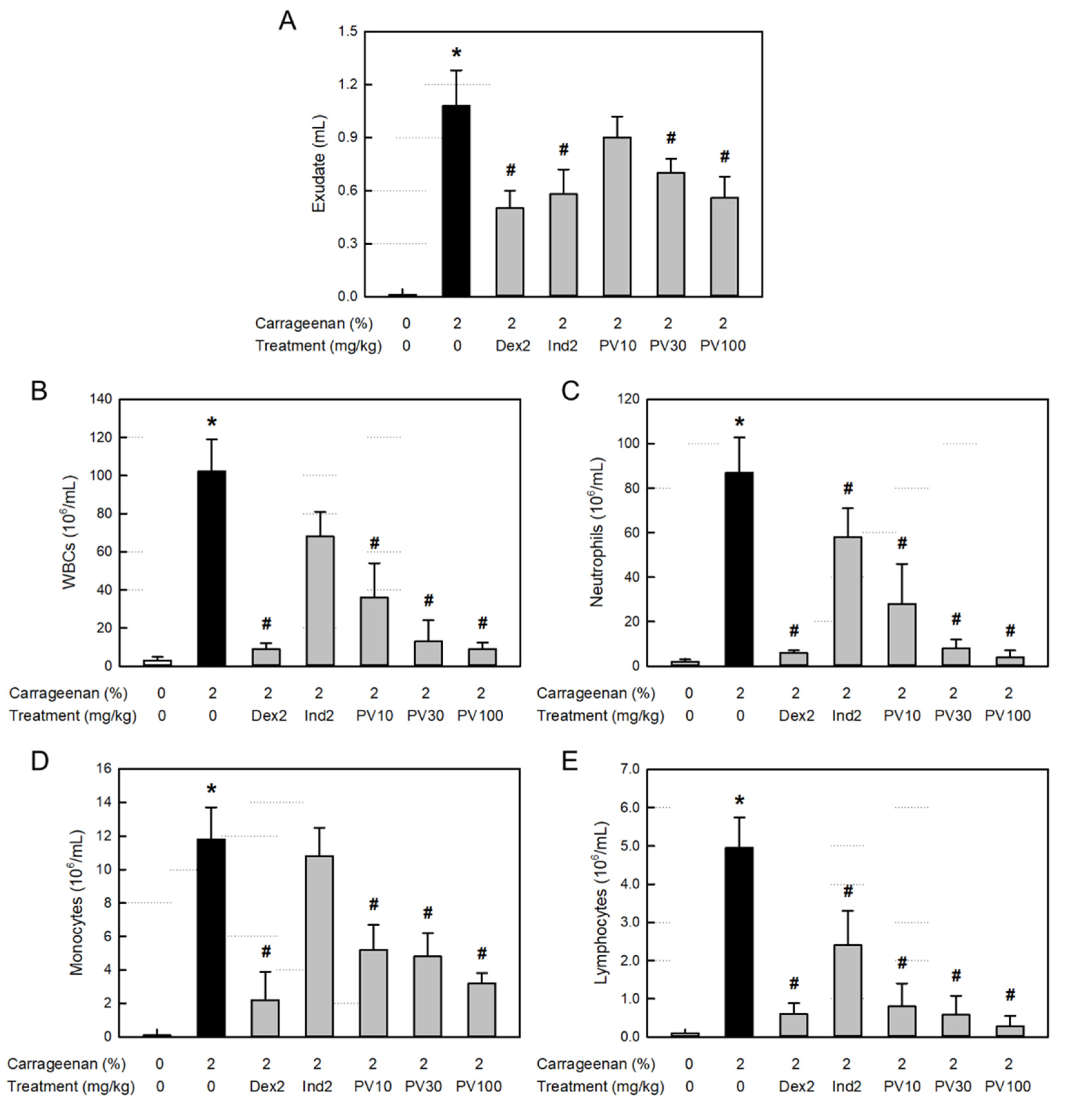
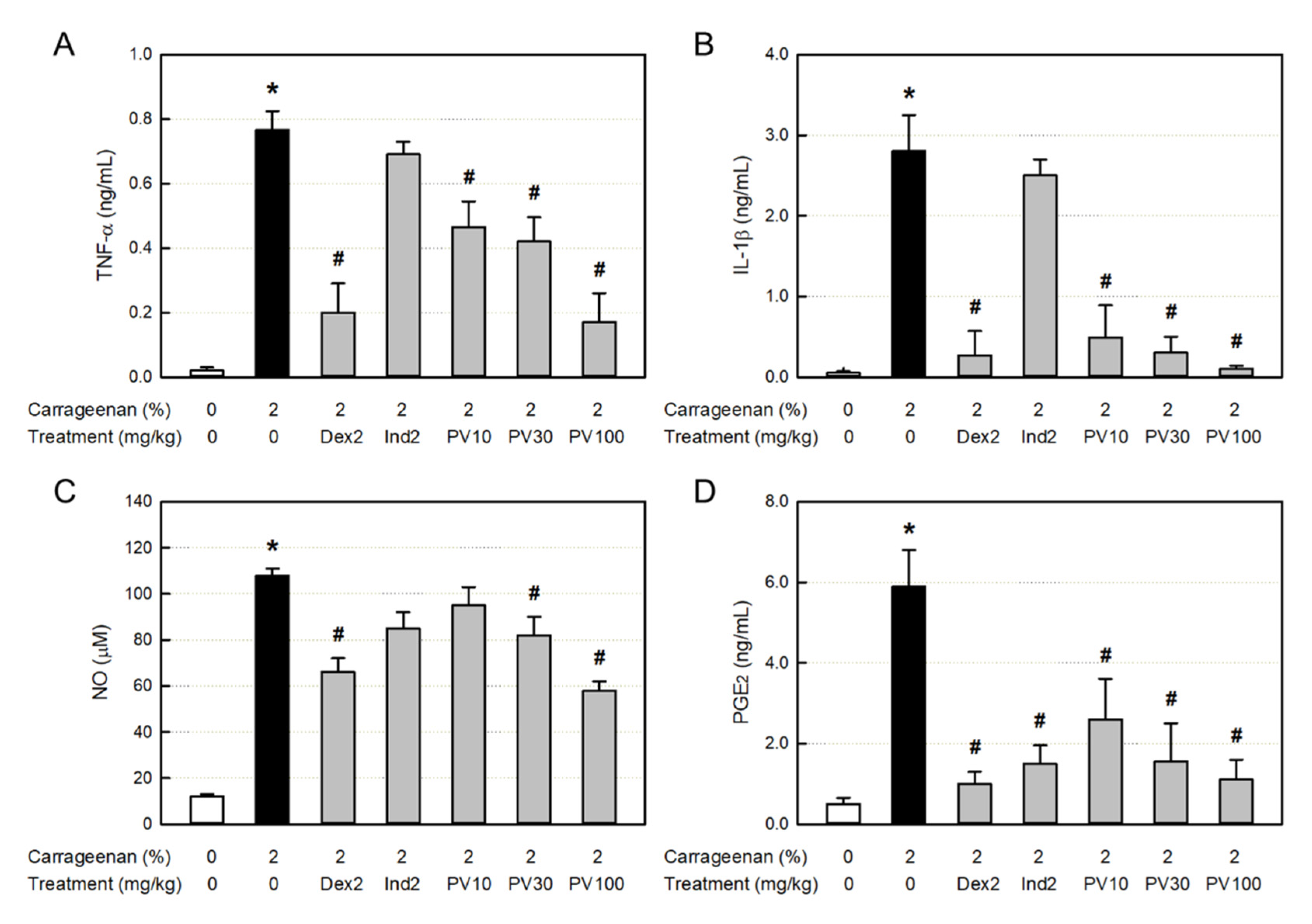
In vivo air-pouch inflammation, λ-carrageenan caused vascular dilatation (erythema) and dermal edema, resulting in the great increase in exudate volume, which are indicative of vascular leakage of serum components [
52]. The vasodilatation and exudation were effectively attenuated by dexamethasone (a steroid), indomethacin (an NSAID), and PVRE. In addition, the huge increases in inflammatory cells (WBCs, neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes), cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β), and NO in the exudate was also markedly inhibited by dexamethasone and PVRE, but not by indomethacin. It is of interest to note that λ-carrageenan induces inflammatory cell infiltration and activation to release cytokines, iNOS expression, and NO production, and that PVRE blocks the cell chemo-attraction, activation, and iNOS expression similarly to the steroids’ activity.
λ-Carrageenan greatly increased the PGE
2 concentration in the exudate indicating the activation of COX-2 inflammatory pathway, which was inhibited by indomethacin as well as PVRE. Therefore, it was confirmed that PVRE has both steroid- and NSAID-like activities. Separately, the PGE
2-reducing activity of dexamethasone may be due to the inhibitory effect of steroids on the arachidonic acid-degrading phospholipase A
2 (PLA
2) [
53].
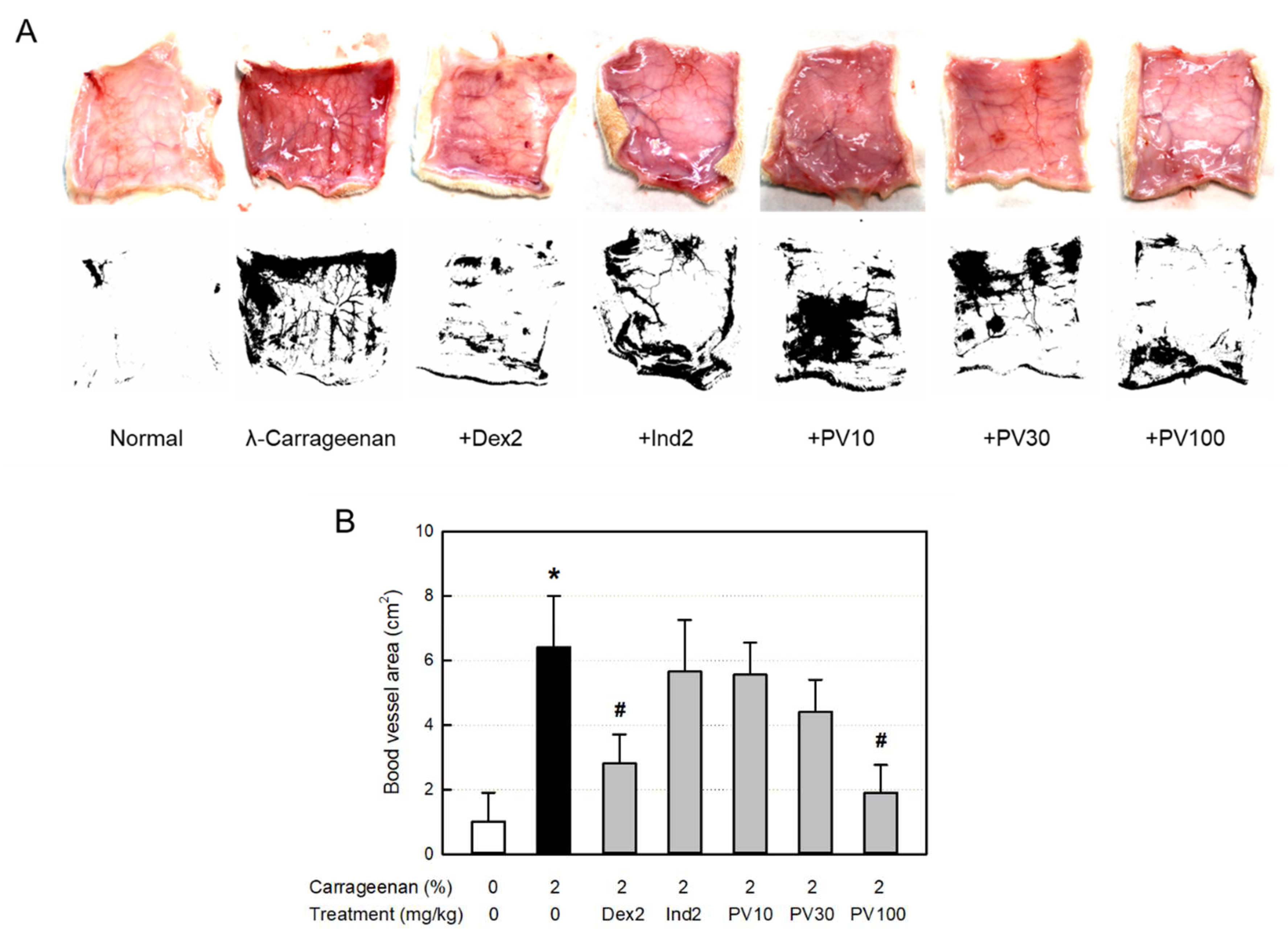
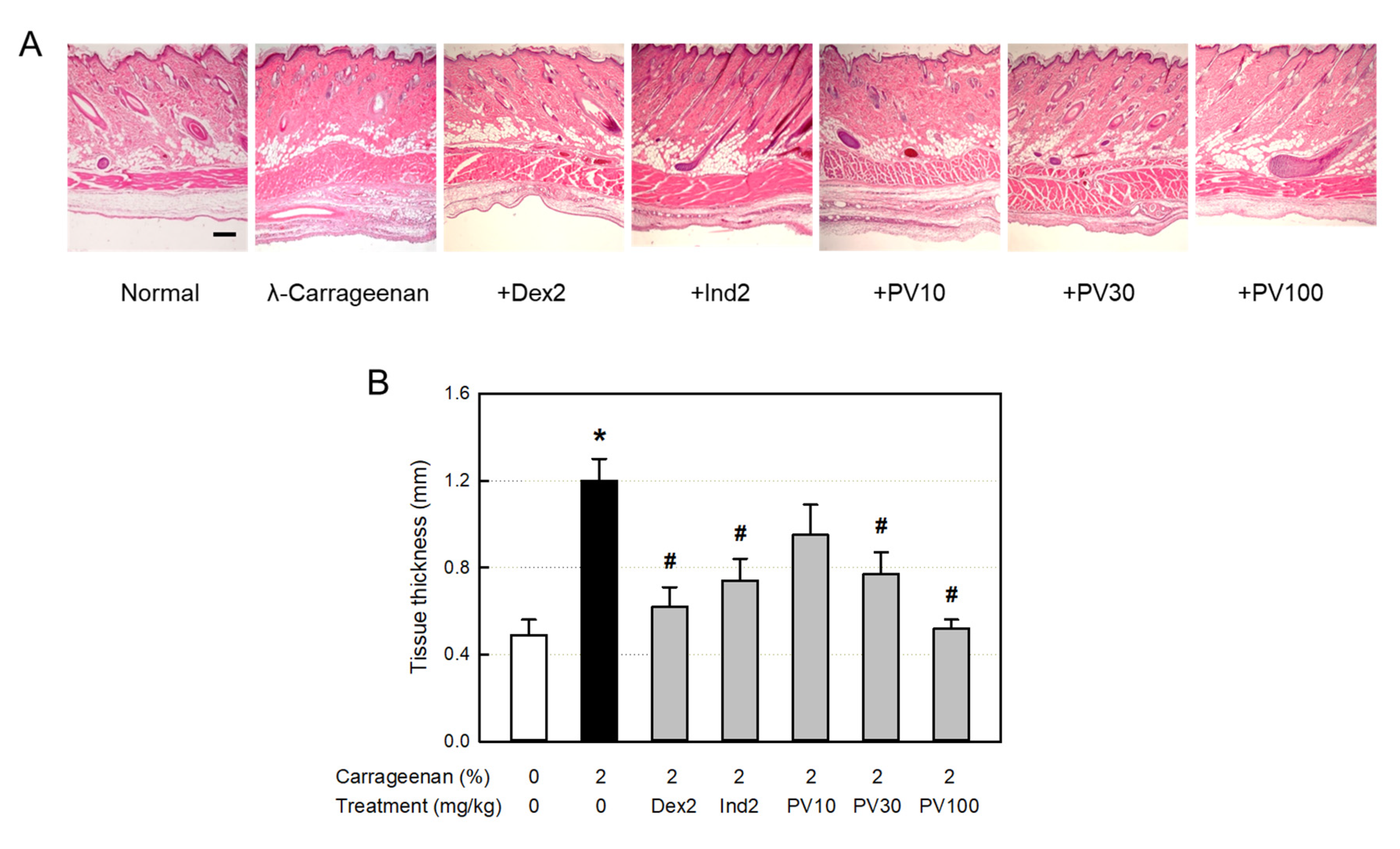
The anti-inflammatory effects of PVRE on vascular exudation, edema, and inflammatory cell infiltration were confirmed in microscopic examinations. The dermal tissues exposed to λ-carrageenan exhibited severe vasodilatation, increasing the blood vessel area under Image-J analysis, as well as tissue edema, increasing the dermal and muscular layer thickening. In addition, severe infiltration of inflammatory cells was observed in the dermal and subcutaneous tissues. Interestingly, such inflammation was substantially suppressed by PVRE and dexamethasone, which were superior to indomethacin. Such phenomena indicate that λ-carrageenan-induced vascular response and inflammatory cell infiltration are mainly mediated by TNF-α ― iNOS ― NO pathway.
From the present study results, several rosebud extracts were found to contain high concentrations of antioxidant ingredients, and exhibited close relationships with antioxidative and NO-inhibitory activities. At the same time, PVRE inhibited inflammatory reactions in RAW 264.7 macrophages by down-regulating iNOS and COX-2 mRNA expression. In addition, PVRE decreased the λ-carrageenan-induced air-pouch inflammation in vivo: i.e., it blocked vascular leakage, inflammatory cell infiltration, and inflammatory cytokine and mediator production in dual mechanisms on TNF-α ― iNOS ― NO and arachidonic acid ― COX-2 ― PGE2 pathways, which are controlled by steroids and NSAIDs, respectively.
Therefore, the results indicate that rosebud extracts containing large amounts of antioxidants, including PVRE, from newly-crossbred roses could be candidates for the development of antioxidative and anti-inflammatory functional products. In addition, it is expected that novel medicinal plants through cross-breeding could be produced in the near future.
Figure 1.
Antioxidant contents in 24 rosebud extracts and their antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities (100 μg/mL). (A) Polyphenol contents. (B) 2,2-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline 6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical-scavenging activity. (C) 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical- scavenging activity. (D) Inhibitory activity on nitric oxide (NO) production from RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1 μg/mL).
Figure 1.
Antioxidant contents in 24 rosebud extracts and their antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities (100 μg/mL). (A) Polyphenol contents. (B) 2,2-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline 6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical-scavenging activity. (C) 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical- scavenging activity. (D) Inhibitory activity on nitric oxide (NO) production from RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1 μg/mL).
Figure 2.
Correlations between antioxidant ingredients in 24 rosebud extracts and their antioxidative or anti-inflammatory activities (100 μg/mL). (A) Correlation between polyphenols and 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline 6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical-scavenging activity. (B) Correlation between polyphenols and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical- scavenging activity. (C) Correlation between polyphenols and nitric oxide (NO)-inhibitory activities.
Figure 2.
Correlations between antioxidant ingredients in 24 rosebud extracts and their antioxidative or anti-inflammatory activities (100 μg/mL). (A) Correlation between polyphenols and 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline 6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical-scavenging activity. (B) Correlation between polyphenols and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical- scavenging activity. (C) Correlation between polyphenols and nitric oxide (NO)-inhibitory activities.
Figure 3.
Cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of Pretty Velvet rosebud extract (PVRE) in RAW 264.7 cells. (A) Cytotoxicity of PVRE. (B-E) Inhibitory activities on inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression (B), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression (C), nitric oxide (NO) production (D), and prostaglandin 2 (PGE2) production from RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from LPS alone (P<0.05).
Figure 3.
Cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of Pretty Velvet rosebud extract (PVRE) in RAW 264.7 cells. (A) Cytotoxicity of PVRE. (B-E) Inhibitory activities on inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression (B), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression (C), nitric oxide (NO) production (D), and prostaglandin 2 (PGE2) production from RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from LPS alone (P<0.05).
Figure 4.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Pretty Velvet (PV) rosebud extract (PVRE) in a dermatitis animal model. (A) Effects on λ-carrageenan-induced exudation. (B-E) Effects on the infiltration of white blood cells (WBCs, B), neutrophils (C), monocytes (D), and lymphocytes (E) in the exudate. Dex2: 2 mg/kg dexamethasone, Ind2: 2 mg/kg indomethacin, PV10: 10 mg/kg PVRE, PV30: 30 mg/kg PVRE, PV100: 100 mg/kg PVRE. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from λ-carrageenan alone (P<0.05).
Figure 4.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Pretty Velvet (PV) rosebud extract (PVRE) in a dermatitis animal model. (A) Effects on λ-carrageenan-induced exudation. (B-E) Effects on the infiltration of white blood cells (WBCs, B), neutrophils (C), monocytes (D), and lymphocytes (E) in the exudate. Dex2: 2 mg/kg dexamethasone, Ind2: 2 mg/kg indomethacin, PV10: 10 mg/kg PVRE, PV30: 30 mg/kg PVRE, PV100: 100 mg/kg PVRE. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from λ-carrageenan alone (P<0.05).
Figure 5.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Pretty Velvet (PV) rosebud extract (PVRE) in a dermatitis animal model. (A & B) Effects on the λ-carrageenan-induced accumulation of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α, A) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β, B). (C & D) Effects on the accumulation of nitric oxide (NO, C) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2, D). Dex2: 2 mg/kg dexamethasone, Ind2: 2 mg/kg indomethacin, PV10: 10 mg/kg PVRE, PV30: 30 mg/kg PVRE, PV100: 100 mg/kg PVRE. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from λ-carrageenan alone (P<0.05).
Figure 5.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Pretty Velvet (PV) rosebud extract (PVRE) in a dermatitis animal model. (A & B) Effects on the λ-carrageenan-induced accumulation of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α, A) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β, B). (C & D) Effects on the accumulation of nitric oxide (NO, C) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2, D). Dex2: 2 mg/kg dexamethasone, Ind2: 2 mg/kg indomethacin, PV10: 10 mg/kg PVRE, PV30: 30 mg/kg PVRE, PV100: 100 mg/kg PVRE. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from λ-carrageenan alone (P<0.05).
Figure 6.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Pretty Velvet (PV) rosebud extract (PVRE) in a dermatitis animal model. (A) Representative findings of λ-carrageenan-induced erythema (vascular swelling) in the skin (Upper: gross findings, Lower: Image-J findings). (B) Blood vessel area analyzed with Image-J. Dex2: 2 mg/kg dexamethasone, Ind2: 2 mg/kg indomethacin, PV10: 10 mg/kg PVRE, PV30: 30 mg/kg PVRE, PV100: 100 mg/kg PVRE. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from λ-carrageenan alone (P<0.05).
Figure 6.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Pretty Velvet (PV) rosebud extract (PVRE) in a dermatitis animal model. (A) Representative findings of λ-carrageenan-induced erythema (vascular swelling) in the skin (Upper: gross findings, Lower: Image-J findings). (B) Blood vessel area analyzed with Image-J. Dex2: 2 mg/kg dexamethasone, Ind2: 2 mg/kg indomethacin, PV10: 10 mg/kg PVRE, PV30: 30 mg/kg PVRE, PV100: 100 mg/kg PVRE. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from λ-carrageenan alone (P<0.05).
Figure 7.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Pretty Velvet (PV) rosebud extract (PVRE) in a dermatitis animal model. (A) Representative microscopic findings of λ-carrageenan-induced edema (tissue thickening) and inflammatory cell infiltration in the skin. (B) The thickness of air-pouch lining tissue. Dex2: 2 mg/kg dexamethasone, Ind2: 2 mg/kg indomethacin, PV10: 10 mg/kg PVRE, PV30: 30 mg/kg PVRE, PV100: 100 mg/kg PVRE. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from λ-carrageenan alone (P<0.05). Scale bar = 200 μm.
Figure 7.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Pretty Velvet (PV) rosebud extract (PVRE) in a dermatitis animal model. (A) Representative microscopic findings of λ-carrageenan-induced edema (tissue thickening) and inflammatory cell infiltration in the skin. (B) The thickness of air-pouch lining tissue. Dex2: 2 mg/kg dexamethasone, Ind2: 2 mg/kg indomethacin, PV10: 10 mg/kg PVRE, PV30: 30 mg/kg PVRE, PV100: 100 mg/kg PVRE. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05). #Significantly different from λ-carrageenan alone (P<0.05). Scale bar = 200 μm.
Table 1.
Primer sequences used in this study.
Table 1.
Primer sequences used in this study.
| Genes |
Sequence 5’-3’ |
Temperature |
| iNOS |
Forward: CAGGATCCAGTGGTCCAACC
Reverse: CGTACCGGATGAGCTGTGAA |
60°C59°C |
| COX-2 |
Forward: GTACAAGCAGTGGCAAAGGC
Reverse: ACGAGGTTTTTCCACCAGCA |
60°C60°C |
| GAPDH |
Forward: GACCTCATGGCCTACATGGC
Reverse: GCCCCTCCTGTTATTATGGGG |
60°C59°C |