1. Introduction
Deaths due to resistance are projected to climb to an estimated 10 million people per year by 2050. [
1] The importance of managing antimicrobial resistance has never been more important. At a local level, annual reports of cumulative pathogen incidence and antibiotic susceptibility data, known as antibiograms, help guide selection of empiric antibiotic therapies. [
2,
3] Antibiograms are utilized for surveillance of resistance rates and potential patterns to highlight trends over time within an institution. There are many methods for compiling and presenting antimicrobial susceptibility data; methodology that can be complex, cumbersome, and produce results that can be difficult to interpret. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) has published multiple guidelines with general recommendations aimed at guiding antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASP) in the development of antibiograms that are both accurate and clinically useful. [
2,
3] However, the guidelines also emphasize some institutions, units, and patient populations may require tailored stratification of the data beyond the standard recommendations to obtain the most reliable results. Several studies have evaluated and found utility of data stratification according to unit, specimen type, and even method of infection acquisition, further termed enhanced antibiograms (EA). [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]
Rule-based technology (RBT) can be used to ease antibiogram creation by automated inclusion and exclusion of cultures and susceptibilities through the triggering of specific rules and criteria. [
9,
10,
11] However, optimization of RBT requires understanding the rules and re-investment. [
12] In one of his many addresses pertaining to quality improvement, Dr. Berwick states what he calls the central law of improvement, “Every system is perfectly designed to achieve exactly the results that it achieves.”[
13] As an example, RBT has been successfully utilized within health informatics to identify and stratify adverse drug events (ADEs).[
14] A study by Jha et al identified ways to improve positive capture by comparing automated ADE collection to those collected manually through chart review and voluntary reporting. [
15] Thanks to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Electronic Health Records Incentive Program, health-systems are all too familiar with the “Out-of-the-Box” misnomer often tagged to software.[
16,
17] Similarly, performance of RBT-generated antibiograms should be subject to performance auditing. Antibiograms should be optimized to best suite their patient populations, which may require revisiting the rules involved in creation.
EA broaden clinical utility and have been successfully deployed in a variety of scenarios. [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23] While the most common utility of the annualized susceptibility report is to guide empiric antimicrobial prescribing decisions, there are further strata that may improve application and prescribing precision. RBT based on guidance of “First culture, per patient” is not without limitations. Based on such rules, a patient acquiring a multi-drug resistant
Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia on day 30 of admission would likely be included in the RBT-generated antibiogram, if it is his/her first culture of the admission. Due to many factors, acute care units treating patients requiring extended lengths of stay are often challenged with exceptionally resistant organisms. [
24,
25,
26,
27] If included, susceptibilities of cultures taken later in admission will heavily skew the antibiograms for these units. These skewed results may overestimate resistance rates for new admissions and lead to overprescribing of broad-spectrum empiric antibiotics. Equally important, antibiograms should not be used to monitor emergence of resistance during antimicrobial treatment, guide treatment later in admission, or after recent antimicrobial exposure. [
2]
At the time of the study design, empiric antimicrobial therapy was source specific; however, most patients were empirically started on vancomycin and cefepime, despite the local, unit-specific antibiogram recommending empiric coverage with vancomycin and double coverage for potential Gram-negative pathogens. Anecdotal practice did not align with the automated RBT antibiogram. A quick pull of the source data for the Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates utilized to generate the RBT antibiogram found several isolates included that were drawn many weeks after admission. It was hypothesized manual review of the data and creation of EA may have potential big implications for prescribing recommendations and future ASP practices. While the current antibiogram of study is already an EA (e.g. burn unit-specific), thought was given to common bedside prescribing practices when considering which additional rules to consider in the further stratified EA. The primary objective of this study was to compare the pathogens and susceptibilities of the current automated RBT antibiogram with EA manually collected through chart review with additional rules accounting for days since admission, risk factors for hospital-acquired infections, and initial courses of antibiotic therapy.
2. Results
2.1. Patient Demographics and Injury Characteristics
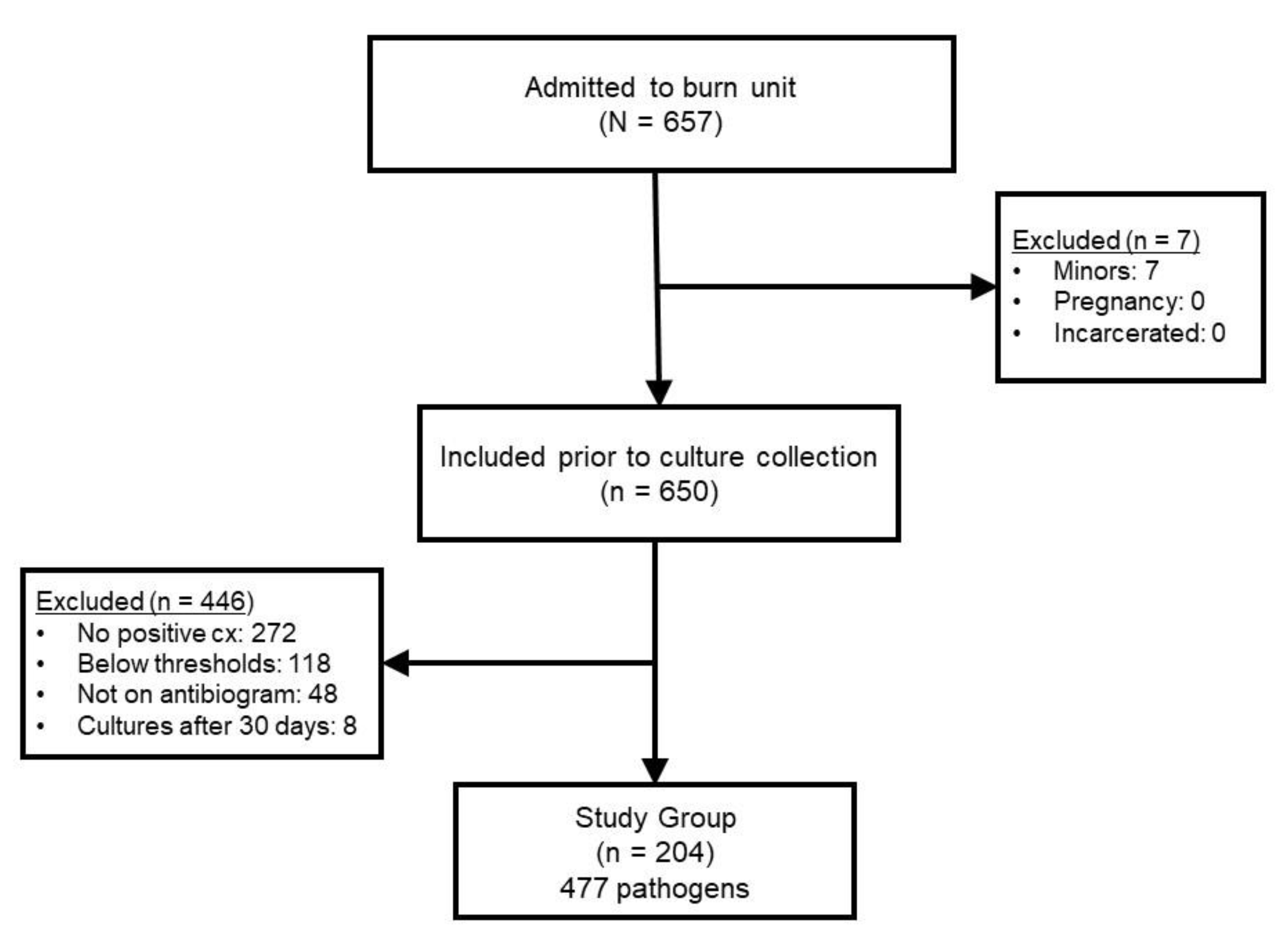
During the two year study period, 657 patients were admitted. Reasons for exclusion in the retrospective cohort can be seen in
Figure 1. The most common reason for exclusion was lack of positive culture (n = 272) or a result that was not considered clinically significant enough to prescribe systemic antimicrobial therapy (n = 118). The final sample included 204 patients in which 477 pathogens were utilized to construct the different antibiogram versions for comparison.
Demographic results and injury characteristics for the patient population are displayed in
Table 1. The mean age of the cohort was 50.6 ± 16.5 years with most being male (66%). Nearly all patients were either African American or Caucasian, which were evenly distributed. The majority (72%) of patients were admitted for acute burn injury; half of which were attributed to direct flame (54%). The median percent total body surface area (TBSA) burned was 10 (3, 21) and 10% of patients sustained an inhalation injury. Inhalation injury was confirmed via bronchoscopic examination. A large percentage of patients (59%) had at least one risk factor for hospital-acquired infection at admission.
2.2. Pathogens
The most common culture source was a tissue sample from a wound, representing 52% of pathogens. Pathogens isolated from blood (14%) and lungs (14%) were comparable. Few were collected from urine (7%), bone (6%), or other sites (7%). Considering only bacteria, Gram-negative (57%) pathogens were more common than Gram-positive (43%). Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (n = 90) was the most common Gram-positive, followed by methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (n = 57), Enterococcus faecalis (n = 41), and E. faecium (n = 16). The two most commonly isolated Gram-negatives were Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n = 70) and Enterobacter spp. (n = 69), followed by Klebsiella spp. (n = 32), Acinetobacter baumannii (n = 26), Escherichia coli (n = 24), Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (n = 24), Proteus spp. (n = 21), Serratia marcescens (n = 6), and Haemophilus influenza (n = 1).
2.2.1. Gram-positive pathogens
Looking just at Gram-positive infections in the three manually-derived models, vancomycin (or an equivalent) will still be a necessary component of empiric therapy. For the antibiogram considering cultures taken within 7 days of admission, Gram-positives were slightly more common (54%), but 42% were resistant to standard β-lactam antibiotics (e.g. ampicillin, cefazolin, ceftriaxone, etc). The second model built on the first (e.g. within 7 days of admission) by removing patients with risk factors for healthcare-associated infection (HAI), but did not change the inference and resultant recommendation. Although 47% were Gram-positive, 44% were still resistant to standard β-lactam antibiotics. The third model compared patients being prescribed their first course of antibiotics versus those receiving antibiotics after at least 7 days of a previous course, which also did not change the recommendation. Prior to the first course of antibiotics, 54% were Gram-positive, but 46% were resistant to standard β-lactam antibiotics.
2.2.2. Gram-negative pathogens
Suggested Gram-negative coverage was significantly altered after manual data collection and application of the additional rules. (
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4)
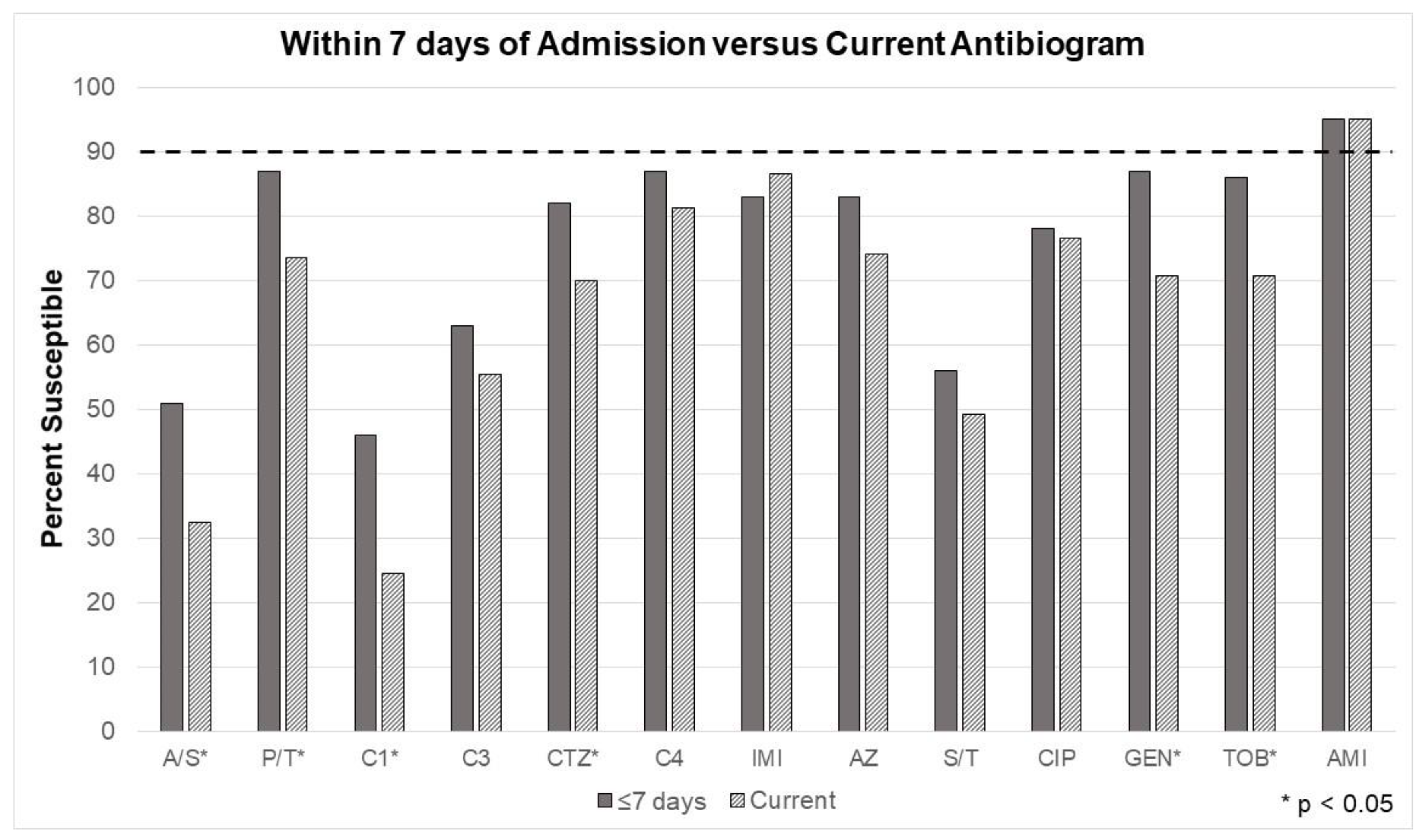
Figure 2 demonstrates changes in the antibiogram susceptibilities with the addition of the 7-day rule, where cultures taken after the first 7 days of admission were not considered in the EA. Susceptibilities significantly improved for ampicillin/sulbactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, cefazolin, ceftriaxone, gentamicin, and tobramycin. Amikacin in vitro activity remained excellent. While improved, the unit’s current empiric Gram-negative coverage (cefepime) still fell below the minimum susceptibility goal (90%).
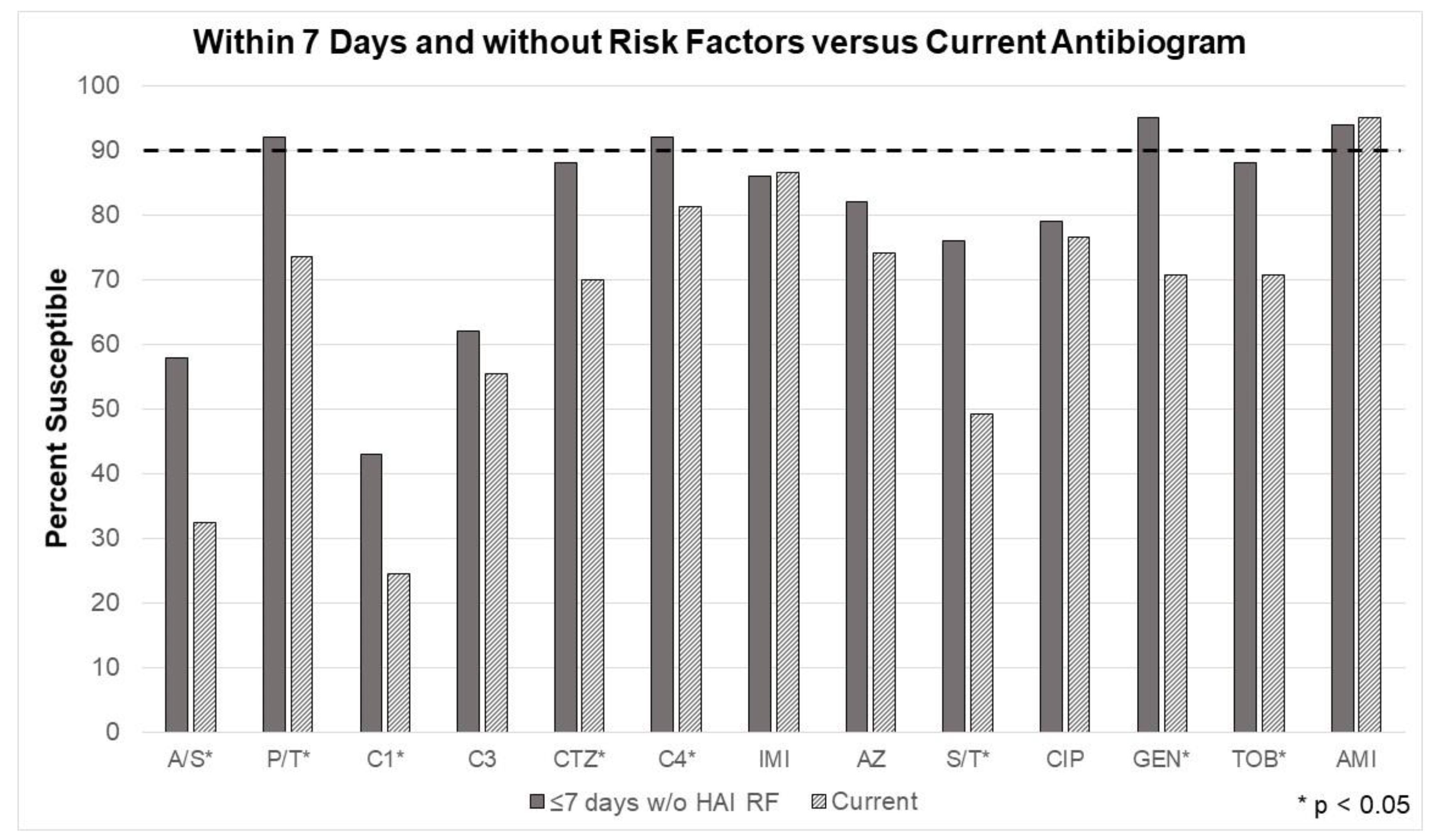
The changes in susceptibilities for the second model, considering the 7-day rule and excluding patients with risk factors for HAI. Susceptibilities significantly improved for nearly every tested antibiotic (ampicillin/sulbactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, cefazolin, ceftriaxone, cefepime, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, gentamicin, and tobramycin). (
Figure 3) Most notably, the unit’s current Gram-negative agent, cefepime, was shown adequate for monotherapy coverage. Piperacillin/tazobactam, cefepime, gentamicin, and amikacin were the only antimicrobials that surpassed the minimum 90% threshold, according to in vitro testing.
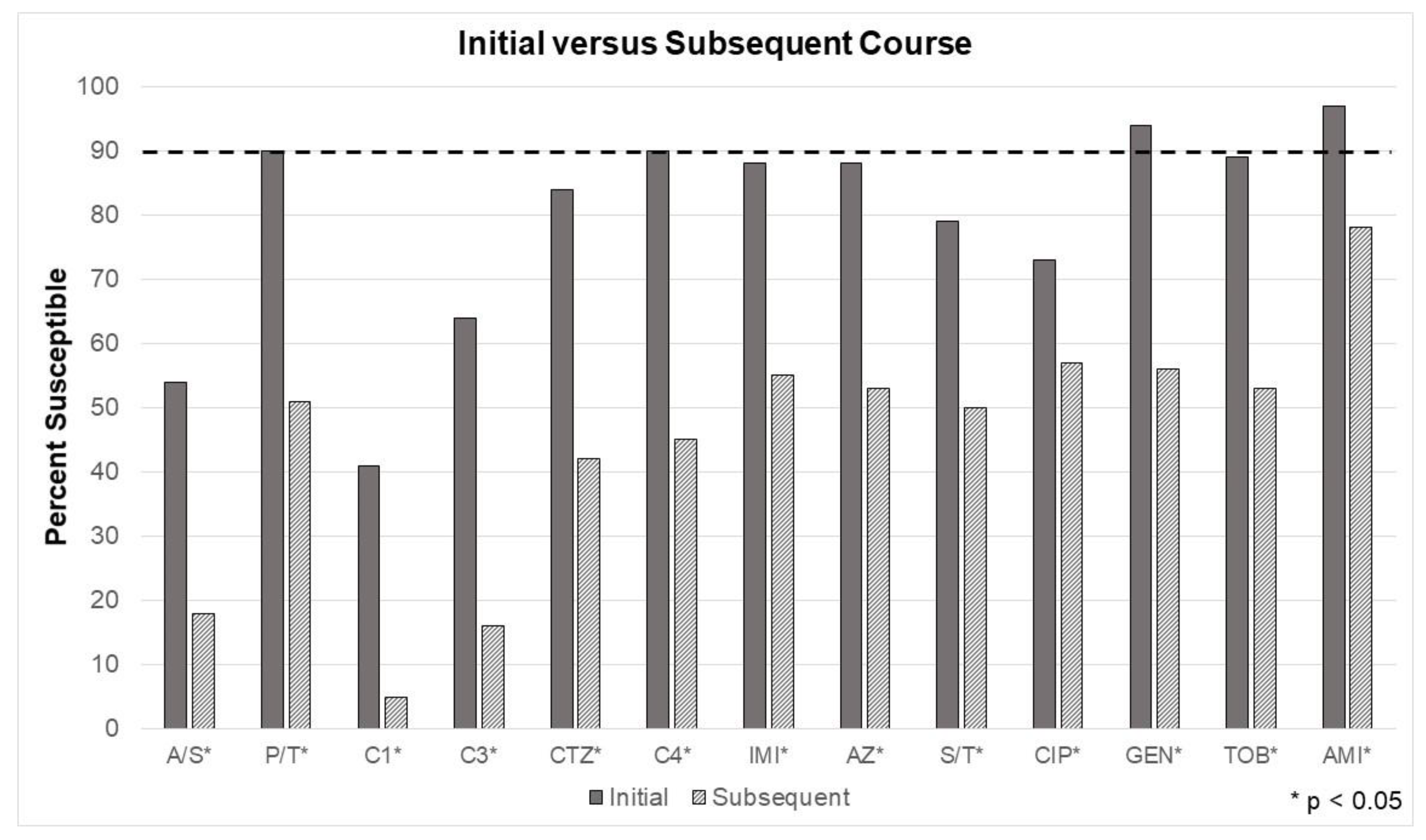
Recall, the third model tested another common bedside prescribing consideration. Has the patient recently received a course of antibiotics? Susceptibilities were significantly different between every tested antibiotic when comparing initial treatment versus culture results taken after exposure to at least 7 days of an antibiotic (e.g. subsequent treatment).
Figure 4 depicts a simple measure of just how much a single course of antibiotics can impact microbiota. For the group receiving antibiotics for an initial course, piperacillin/tazobactam, cefepime, and the aminoglycosides were at or above the minimum required susceptibility threshold (e.g. 90%), based on the in vitro data.
3. Discussion
This study has many implications for current and future antimicrobial susceptibility reporting, interpretation, and antimicrobial prescribing. The goal of antibiograms is to provide regularly updated data as a means to guide antimicrobial selection for empiric treatment of initial infections. In this study, an EA specific to the institution’s burn center was further enhanced by additional manually-applied rules. Each rule selected was based on typical decision trees utilized in bedside differentiation in empiric antibiotic determination. Each rule provided a unique depiction of sensitivity alterations, especially compared to the current EA. While patient outcomes were not considered, this report is the first to offer analysis on additional diverse strata applied to burn specific EA. In a population at high risk for multi-drug resistant pathogens, any means to minimize exposure to unnecessarily broad spectra of antimicrobials has large downstream implications for the patient and the unit.
The “call” is clear for further research exploring the true impact of clinical decision support systems and antibiograms on ASP. [
2,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32] In their summary, Hindler and Stelling outlined the necessity for future researchers to look more critically at the produced antibiograms to best optimize performance and improve prudent prescribing. [
2] Treatment outcome was not directly measured in this study. However, the analysis provides clear evidence how prescribing recommendations of empiric antibiotics are altered with additional EA considerations. Consider the results in perspective of a case example, where a patient may be admitted with acute severe burns to 50 percent of his/her body. Using national averages, he/she will require more than 10 acute surgical procedures and be in the hospital around 70 days. [
33,
34] Sepsis remains the most common reason for mortality in patients with burn injuries surviving the initial 48 hours and wound infection the most common source. [
24,
35] At some point in the stay, the patient will likely require systemic antibiotics; likely multiple courses. If on hospital day 6 cefepime, amikacin, and vancomycin are prescribed empirically for suspected sepsis, the subsequent infection (or perhaps during treatment) will likely be highly resistant. Traditionally, international burn-specific data is strongly correlated and suggests
Pseudomonas sp., Acinetobacter sp., Stenotrophomonas, or
carbapenem-resistant Enterbacteriales sp will soon follow. [
36,
37,
38]
Figure 4 demonstrates multi-drug resistance is highly prevalent, even after a single course (or 7 days of exposure) of antibiotics. In some cases, empiric antibiotics are initiated without attainment of cultures. Despite recommendations, some patients receive antibiotics without cultures to guide definitive treatment. This is obvious from the study results, as the current antibiogram reflecting “first culture, per patient” would have more closely resembled the “initial” EA in
Figure 4.
Recall during the time of analysis, empiric antimicrobial prescribing did not abide the RBT EA and instead followed anecdotal evidence. There is potential for great error with recall bias and relying solely on anecdotes should be discouraged. The study hypothesis was created with this in mind. It is noteworthy, anecdotal evidence proved to be more reliable than the RBT utilized for past iterations of the EA antibiogram. CLSI recommends avoiding empiric monotherapy prescriptions for serious infection when susceptibility patterns indicate the chosen agent has less than 90% susceptibility for the likely pathogen(s). [
2,
3] In the same recommendations, there is latitude given for susceptibilities down to 80% for certain infections and populations. The additional rules applied to the EA supported the use of a single antipseudomonal beta-lactam antibiotic plus an agent with activity against methicillin-resistant S
taphylococcus aureus (MRSA), instead of two Gram-negative antibiotics.
Unfortunately, early empiric recommendations still indicate an antipseudomonal agent is necessary. Globally,
Pseudomonas sp.,
Acinetobacter sp., and
Enterbacteriales sp remain common pathogens following burn injury [
36,
37,
38,
39] Additionally, the prevalence of community-onset MRSA is growing (unpublished institutional data), which parallels statewide and national reports. [
40] While a single antipseudomonal beta-lactam antibiotic will typically cover methicillin-sensitive
Staphylococcus aureus, it is a poor choice for MRSA. Even in the best EA model scenario produced during the study, using only a single beta-lactam without a MRSA active agent would have resulted in 44% of patients inadequately covered. Fortunately, a previous unpublished, internal analysis noted few isolates with minimum inhibitory concentration in excess of 1 μg/mL, which improves likelihood of treatment response.
Reflecting Dr. Berwick’s remarks, continuous investment in process improvement (PI) is imperative. In fact, it is a necessary to demonstrate an adequate PI program for burn center verification through the American Burn Association. Infection prevention and stewardship practices should be a cornerstone of PI, as iatrogenic-acquisition of multidrug resistant bacteria carries with it proud morbidity and mortality. An easy method of preventing the creep of early multidrug resistant pathogen prevalence is reducing iatrogenic spread. Attention must stretch beyond contact isolation and proper donning of personal protective equipment. An often-overlooked aspect of infection prevention are the various components of environmental cleanliness, especially for units caring for patients with burn injuries. Microbes are called such for a reason. Any small break in the infection prevention chain affords a massive opportunity for opportunistic pathogenesis. Mattresses are havens for microbes. While top covers are formulated with coatings marketed to resist fluid penetrance, there are caveats. The materials are not completely impervious, especially as normal wear and tear and time accumulates. Especially related to patients with large acute burns, mattresses are not designed to withstand the 3+ Liters per day of exudate seen for the weeks prior to wound closure. And consider the material within. There is no recovery of a foam mattress once impregnated with the microbe-rich exudate. Air mattresses can be disassembled and internal components can be sterilized. As such, air mattresses should be considered like dressings. While it is not feasible to do so twice daily, air mattresses should be periodically exchanged to allow proper cleaning to reduce microbial burden on top and within the baffles. Think in a different mindset: When patients with burn injuries go to the operating room for burn wound excision, it would be extreme mal-practice to rewrap the cleanly excised wounds in the same exudate-soiled dressings they were in preoperatively. When patients are moved from their room or discharged (e.g. terminal cleans), rooms should be mechanically wiped with antimicrobial solutions from ceiling to floor. Everything should be cleaned and removed. Floors should be stripped and resurfaced. High touch surfaces should be routinely audited (i.e. cultures or bioluminescence testing). Units sufficiently monitoring culture data will see fluctuations and timing of “their unit-specific pathogens”, which will indicate when reinvestment in infection prevention audits may be indicated.
Knowing RBT or laboratory-based susceptibility reports may not present the clinically-relevant data is certainly not a novel concept. [
2,
41,
42] It is important to understand not all bacteria are pathogens. Most of the infections seen in burn centers involve the wound. However, it is critical to understand a common misnomer, wounds do not have to be sterile to heal. In fact, evidence is growing, especially as our ability to detect and biobank species, some bacteria promote wound healing. [
43,
44] Over-targeting bacteria or exposing patients to a broad spectrum of antimicrobials could be more detrimental than previous depictions. It is imperative to not include surveillance data in antibiograms.
A major limitation of this study is the reproducibility. While the hypothesis was supported, the amount of man hours required for the chart review and data collection could provide a sufficient workload to support an entire full-time equivalent (e.g. FTE), especially when considering the other EA needed for the multiple different hospital units. Each hospital unit typically houses patients from a single (or a small number) subspecialty and presents a unique environment/microbiota. Recall, the demographic and clinical data for each admitted patient was reviewed in hopes of creating the additional EA and only including clinically relevant pathogens (e.g. reduce chances of reporting surveillance cultures). The evidence presented supports the need to invest in software development and integration. The point of RBT is to substantially improve efficiency and accuracy. We are not there yet. Due to wide confidence intervals and potential misrepresentation of the larger population (e.g. all patients admitted to the unit), it is recommended samples (e.g. pathogens) be either excluded or pooled with additional cohorts or in a multiyear fashion, when analyzed at a drug-pathogen level. In this analysis, power was dramatically improved over individual drug-pathogen analysis by including 1) two years of laboratory and clinical data and 2) pooling all the pathogens. Antibiograms displaying sensitivities per individual pathogen have advantages when source is known and likely pathogen can be narrowed. However, this is disadvantageous when source is not known and the pooled analysis was a better method to answer the hypothesis questioned in the study.
4. Materials and methods
4.1. Study Design and Patient Population
This dual IRB approved study (20-07615-XP) was an observational case series of patients admitted to a single verified burn center between January 1, 2018 and December 31, 2019. Patients were excluded for any of the following: 1) no positive bacterial cultures obtained, 2) less than 18 years of age, 3) incarcerated, 4) pregnant, 5) cultures collected after 30 days of admission, 6) culture results below quantitative thresholds, or 7) isolates not reported on the automated antibiogram (e.g., no comparison could be made). Patients were screened initially by reviewing burn center admission logs during the study period and exclusion criteria applied to generate a final sample of patients and cultures.
Computer generated, rule-based antibiograms were compared to the manually-collected antibiograms over the two-year period. The study period was chosen to ensure an adequate sample after application of inclusion and exclusion criteria and ability to compare the last two annual antibiograms. [
2,
45] A priori estimates accounted for an estimated 750 admissions with half being cultured for a potential infection and goal of at least 30 isolates for the most common reported pathogens (
Staphylococcus aureus,
Enterococcus spp.,
Enterobacter spp., and
Pseudomonas spp.).
The hypotheses driving this study attempted to capture bedside considerations when initiating new courses of antibiotics. The primary hypothesis of this study was including days since admission, as a rule, will significantly alter the antibiogram and associated sensitivities. The aim was to compare each pathogen from the autogenerated antibiogram to a manually collected version with an additional rule applied of within 7 days of admission. A second hypothesis was excluding patients with risk factors for hospital-acquired infections will significantly alter the ideal choice for empiric antimicrobial therapy. The second aim compared the automated version to a manually collected antibiogram with two additional rules applied: 1) within 7 days of admission and 2) patients without risk factors for hospital-acquired infections. The third hypothesis was susceptibilities significantly decrease after a single course of antimicrobials. To test this hypothesis, susceptibilities were compared between patients with a prior history of antibiotic exposure.
4.2. Data Collection
Data was manually collected from the electronic medical record during individual chart review. Demographic data included: age, sex, race, comorbidities, date of arrival and risk factors for hospital-acquired infections (e.g., intravenous access, history of chemotherapy, positive urine drug screen or reported social history, resident in nursing home or long-term acute care hospital, or admission to the hospital in the last 90 days). Burn injury characteristics included: etiology, presence of inhalation injury, percent total body surface area burned, and percent partial thickness and full thickness injury. Treatment data during the first 30 days of admission included: dressings utilized, topical and systemic antimicrobial agents and dates utilized, systemic antimicrobial indication, and systemic steroid use and dates. Based on the aims, outcome data included pathogens and sensitivities.
Every attempt was made to include only those considered pathogens (e.g., limit inclusion of surveillance cultures). Positive bacterial cultures were defined as pathogens meeting the positivity threshold for the source of culture or deemed to require therapeutic courses of antibiotics. Positivity thresholds were dependent on source: wounds (105 or semiquantitative tissue or exudate results treated with systemic therapy), bronchoalveolar lavage (105), blood (any growth that resulted in treatment with systemic therapy), urine (105), bone (any growth resulting in treatment with systemic therapy), other (typically semiquantitative results of drainage). Susceptible pathogens were defined as strains whose minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were interpreted to be susceptible to a given antibiotic. Non-susceptible pathogens were defined as strains whose MICs were interpreted to be resistant or intermediate to a given antibiotic. During this study period, the institution’s microbiology laboratory utilized the Vitek 2 system to determine bacterial susceptibilities. Therefore, choice of which antibiotic susceptibilities to test and report were determined based on the Vitek 2 standard panels for each specimen. Similarly, bacterial isolates were chosen based on the hospital’s laboratory’s identification abilities and frequencies.
4.3. Sample and Statistical Analysis
4.3.1. Sample size determination
The primary objective was to compare resultant antibiograms between an automated, rule-based software and a manually derived antibiogram to include standard rules plus days since admission. Given rarity of some pathogens, the two year period of admissions were reviewed to ensure at least 30 of the most commonly reported pathogens were included in the study sample.
4.3.2. Statistical analysis
Patient demographic data and injury characteristics were reported using descriptive statistics. Nominal data was reported with n (%). The Shapiro-Wilk test was utilized to test for normality of continuous data. Non-parametric data was reported as median (interquartile range). Normally distributed data was reported as mean ± standard deviation. Differences in sensitivities for pathogen and antibiotic was compared using Fisher’s exact test. Statistical analysis was performed in SigmaPlot 11.2.
5. Conclusions
Hospitals with specialized care units should regard the term “specialized care.” Policies and practices (even software) are built with the greater majority in mind. Many practices of specialized units fall well outside of the normal distribution. There must be institutional understanding and investment to customize tools and practices necessary to optimize care provided by specialized care units. This study of enhanced antibiograms is just a single example of the potential downstream implications.
Author Contributions
D.H. was responsible for study design, data analysis and compilation, and manuscript drafting.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by dual Institutional Review Board (University and Hospital).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the design. The research presented no more than minimal risk of harm to participants and involved no procedures for which written consent is normally required.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available.
Acknowledgements
Sam Bowker, PharmD for assistance with data collection. Lorraine Todor, PharmD for editing expertise.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Razzaque, M.S. Implementation of antimicrobial stewardship to reduce antimicrobial drug resistance. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 2021, 19, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindler, J.F.; Stelling, J. Analysis and Presentation of Cumulative Antibiograms: A New Consensus Guideline from the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simner, P.J.; Hindler, J.A.; Bhowmick, T.; Das, S.; Johnson, J.K.; Lubers, B.V.; Redell, M.A.; Stelling, J.; Erdman, S.M. What’s New in Antibiograms? Updating CLSI M39 Guidance with Current Trends. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0221021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, S.P.; et al. Correlation between case mix index and antibiotic use in hospitals. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2008, 62, 837–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, S.P.; et al. Quantitative antibiotic use in hospitals: comparison of measurements, literature review, and recommendations for a standard of reporting. Infection, 2008, 36, 549–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, S.P.; et al. Stratification of cumulative antibiograms in hospitals for hospital unit, specimen type, isolate sequence and duration of hospital stay. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2008, 62, 1451–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmann, R.; Gatermann, S.G. Analysis and Presentation of Cumulative Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Data – The Influence of Different Parameters in a Routine Clinical Microbiology Laboratory. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0147965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campigotto, A.; et al. Cumulative Antimicrobial Susceptibility Data from Intensive Care Units at One Institution: Should Data Be Combined? J Clin Microbiol, 2016, 54, 956–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, W.R.; Hidayat, L.; A Bolaris, M.; Nguyen, L.; Yamaki, J. The antibiogram: key considerations for its development and utilization. JAC-Antimicrobial Resist. 2021, 3, dlab060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Kapila, K.; Kumar, S. WHONET Software for the Surveillance of Antimicrobial Susceptibility. Med J. Armed Forces India 2009, 65, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpao, A.F.; Ahumada, L.M.; Martinez, B.L.; Cardenas, A.M.; Metjian, T.A.; Sullivan, K.V.; Gálvez, J.A.; Desai, B.R.; Rehman, M.A.; Gerber, J.S. Design and Implementation of a Visual Analytics Electronic Antibiogram within an Electronic Health Record System at a Tertiary Pediatric Hospital. Appl. Clin. Informatics 2018, 9, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.; Badarudeen, S.; Godwin, A. Real-time validation and presentation of the cumulative antibiogram and implications of presenting a standard format using a novel in-house software: ABSOFT. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2010, 38, e25–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berwick, D.M. A primer on leading the improvement of systems. BMJ 1996, 312, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, D.C.; Pestotnik, S.L.; Evans, R.S.; Burke, J.P. Description of a computerized adverse drug event monitor using a hospital information system. . 1992, 27, 774–776. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, A.K.; Kuperman, G.J.; Teich, J.M.; Leape, L.; Shea, B.; Rittenberg, E.; Burdick, E.; Seger, D.L.; Vliet, M.V.; Bates, D.W. Identifying Adverse Drug Events: Development of a Computer-based Monitor and Comparison with Chart Review and Stimulated Voluntary Report. J. Am. Med Informatics Assoc. 1998, 5, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for, M. and H.H.S. Medicaid Services. Medicare and Medicaid programs; electronic health record incentive program. Final rule. Fed Regist 2010, 75, 44313–44588. [Google Scholar]
- Tsapepas, D.S.; McKeen, J.T.; Martin, S.T.; Walker-McDermott, J.K.; Yang, A.; Hirsch, J.; Mohan, S.; Tiwari, R. Risk evaluation and mitigation strategy programs in solid organ transplantation: the promises of information technology. J. Am. Med Informatics Assoc. 2014, 21, e358–e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguio-Vila, M.; Staicu, M.L.; Brundige, M.L.; Alcantara, J.; Yang, H.; Lautenbach, E.; Dumyati, G. Urinary tract infection stewardship: A urinary antibiogram and electronic medical record alert nudging narrower-spectrum antibiotics for urinary tract infections. Antimicrob. Steward. Heal. Epidemiology 2021, 1, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, C.K.; et al. Personalized antibiograms for machine learning driven antibiotic selection. Commun Med 2022, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, H.M.; Chan, B.P.; Zimmermann, C.R.; Talbot, E.A.; Calderwood, M.S.; Dave, A.R.; Santos, P.; Hansen, K.E. Creation of State Antibiogram and Subsequent Launch of Public Health–Coordinated Antibiotic Stewardship in New Hampshire: Small State, Big Collaboration. Public Heal. Rep. 2021, 137, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wheeler, J.S.; Blanchette, L.M. Impact of Combination Antibiogram and Related Education on Inpatient Fluoroquinolone Prescribing Patterns for Patients With Health Care–Associated Pneumonia. Ann. Pharmacother. 2016, 50, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.L. Selection of an Empiric Antibiotic Regimen for Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia Using a Unit and Culture-Type Specific Antibiogram. J. Intensiv. Care Med. 2005, 20, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.R.; Tajchman, S.K.; Dee, B.M.; Bruno, J.J.; Qiao, W.; Tverdek, F.P. Development of a combination antibiogram for Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia in an oncology population. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pr. 2015, 22, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.M.; Sinclair, S.E.; Hickerson, W.L. Rational Selection and Use of Antimicrobials in Patients with Burn Injuries. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2017, 44, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.E.; Thomas, B.C. Reducing Biofilm Infections in Burn Patients' Wounds and Biofilms on Surfaces in Hospitals, Medical Facilities and Medical Equipment to Improve Burn Care: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, H.; Tracy, L.M.; Padiglione, A.; Stewardson, A.J. Patterns of multidrug resistant organism acquisition in an adult specialist burns service: a retrospective review. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2022, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escandón-Vargas, K.; Tangua, A.R.; Medina, P.; Zorrilla-Vaca, A.; Briceño, E.; Clavijo-Martínez, T.; Tróchez, J.P. Healthcare-associated infections in burn patients: Timeline and risk factors. Burn. 2020, 46, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermsen, E.D.; VanSchooneveld, T.C.; Sayles, H.; Rupp, M.E. Implementation of a Clinical Decision Support System for Antimicrobial Stewardship. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiology 2012, 33, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremmer, D.N.; Trienski, T.L.; Walsh, T.L.; Moffa, M.A. Role of Technology in Antimicrobial Stewardship. Med Clin. North Am. 2018, 102, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, G.N.; Van Schooneveld, T.C.; Kullar, R.; Schulz, L.T.; Duong, P.; Postelnick, M. Use of Electronic Health Records and Clinical Decision Support Systems for Antimicrobial Stewardship. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, S122–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S. Hospital antibiogram: A necessity. Indian J. Med Microbiol. 2010, 28, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakyz, A.L. The Utility of Hospital Antibiograms as Tools for Guiding Empiric Therapy and Tracking Resistance: Insights from the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2007, 27, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Carter, J.; Amani, H.; Carter, D.; Foster, K.N.; A Griswold, J.; Hickerson, W.L.; Holmes, J.H.; Jones, S.; Khandelwal, A.; Kopari, N.; et al. Evaluating Real-World National and Regional Trends in Definitive Closure in U.S. Burn Care: A Survey of U.S. Burn Centers. J. Burn. Care Res. 2021, 43, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, S.; Kruger, E.; Bilir, P.; Holmes, J.H.; Hickerson, W.; Foster, K.; Nystrom, S.; Sparks, J.; Iyer, N.; Bush, K.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness of the Use of Autologous Cell Harvesting Device Compared to Standard of Care for Treatment of Severe Burns in the United States. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 1715–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.M.; Percy, M.D.; Velamuri, S.R.; Lanfranco, J.; Legro, I.R.; E Sinclair, S.; Hickerson, W.L. Predictors for Identifying Burn Sepsis and Performance vs Existing Criteria. J. Burn. Care Res. 2018, 39, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.C.; et al. Emergence of resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter species after the use of antimicrobials for burned patients. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol, 2004, 25, 868–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahemia, I.; Muganza, A.; Moore, R.; Sahid, F.; Menezes, C. Microbiology and antibiotic resistance in severe burns patients: A 5 year review in an adult burns unit. Burns 2015, 41, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Yu, P.; Zheng-Li, C.; Hao, L.; Ze-Jing, W.; Shao-Shuo, Y.; Yu, S.; Guang-Yi, W.; Shi-Hui, Z.; Bing, M.; et al. Epidemiological retrospective analysis in major burn patients: single centre medical records from 2009 to 2019. Updat. Surg. 2022, 74, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branski, L.K.; Al-Mousawi, A.; Rivero, H.; Jeschke, M.G.; Sanford, A.P.; Herndon, D.N.; Graça, M.G.; van der Heijden, I.M.; Perdigão, L.; Taira, C.; et al. Emerging Infections in Burns. Surg. Infect. 2009, 10, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, M.P.; Octaria, R.; Kainer, M.A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections and Injection Drug Use, Tennessee, USA, 2015-2017. Emerg Infect Dis, 2020, 26, 446–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantar, C.; et al. Are laboratory-based antibiograms reliable to guide the selection of empirical antimicrobial treatment in patients with hospital-acquired infections? J Antimicrob Chemother, 2007, 59, 140–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Bosso, J.; Sieg, A.; Mauldin, P.D. Comparison of Hospitalwide and Custom Antibiograms for Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. . 2013, 48, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.R.; Gómez, B.I.; McIntyre, M.K.; Dubick, M.A.; Christy, R.J.; Nicholson, S.E.; Burmeister, D.M. The Cutaneous Microbiome and Wounds: New Molecular Targets to Promote Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, K.M.; Davis, R.R.; Liu, S.Y.; Greenhalgh, D.G.; Tran, N.K. Longitudinal profiling of the burn patient cutaneous and gastrointestinal microbiota: a pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Hargy, J.; Hess, B.; Pettengill, M.A. Estimated Impact of Low Isolate Numbers on the Reliability of Cumulative Antibiogram Data. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0393922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).