1. Introduction
Throughout the world, many industries use dyes in large quantities, such as the cosmetic food and paper industries. Most of these dyes are used in the textile industry[
1] for their chemical stability and ease of synthesis. The global coloring production is worth more than 7×10
5 tons per year, with Azo coloration accounting for 60 to 70% of the total [
2]. But serious environmental problems are the result of the use of these synthetic dyes. These industrial aqueous effluents may include tinctorial effluents, which may contain chemicals that are toxic to microbial populations as well as toxic or carcinogenic to humans or animals [
3].
Methylene blue is not known to be very dangerous, but it can have a variety of side effects. It can cause short periods of fast or difficult breathing if inhaled, Swallowing by mouth causes a burning sensation and may cause gastritis, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting [
4].
Several physical, chemical, and biological methods have been introduced to remove this type of dye, such as flocculation, electro flocculation, membrane filtration, liquid-liquid extraction, Irradiation, coagulation, and ion exchange, advanced oxidation, ozonation, and electrochemical destruction [
5]. But due to the high cost of these processes and their limited capacity to adapt to a wide range of dye wastewater, their use is somewhat limited [
6].
Consequently and due to its advantages and ease of use, adsorption remains the most used method in recent years [
7]. Several materials, including activated carbon and synthetic clay, are used as adsorbents support in this method. The problem with these materials is the high cost of preparation, for this reason, and given the lowering of the preparation cost; several researchers are trying to find new materials.
Because of their abundance in nature and the simplicity of their transformation into effective adsorbents, biosorbents attract a lot of attention [
8]. For instance, lignocellulosic materials (biosorbents) have been proposed for the treatment of colored effluent, such as:
orange peel [
7],
cone of Pinusbrutia [
1],
Stipatenacissima [
2] and its fibers [
9],
cupuassu shell [
10],
Saw dust and
neem bark [
11],
raw pomegranate [
12],
Phragmitesaustralis [
13],
green macro alga [
14],
Acoruscalamus [
15].
Artichoke or Cynarascolymus. Is a vegetable of the Asteraceae family largely consumed in the Mediterranean regions. The edible section of the plant is the yoflowerwers known as the head, which is protected by leaf sheaths called bracts [
16]. The Cynarascolymus canning industry produces solid waste, primarily the stems and external bracts of the flowers, which make up 60–80 percent of the total Cynarascolymus flowers and are unfit for human consumption, and it is generally disposed of as cattle feed or green manure [
17]. Recently, this artichoke residue biomass has been investigated for potential use as a bioactive adsorbent precursor In a few research [
18,
19].
The adsorption of methylene blue onto such adsorbents was estimated using classical models (i.e. Langmuir, Freundlich, Redlich-Peterson (RP), Sips, and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms) at equilibrium; the parameters of these models can provide information on the classification of active sites and elimination capability without inspecting the absorption mechanism of methylene blue [
20,
21].
In this study, we employed novel physical models developed based on the grand canonical ensemble to relate the macroscopic features of molecules with the adsorption properties of materials [
22,
23]. These statistical thermodynamics-based models allow for the estimation of parameters such as the removed amount at saturation (Q
e), the number of adsorbed ions per active site (n), the density of receptor sites (N
m), and the uptake energy (E). All of the parameters were evaluated as a function of the temperature, resulting in a more detailed description of the adsorbate–adsorbent adsorption system [
24].
The physical model parameters collected from the simulation using these models allow us to describe the adsorption process at a molecular level if the adsorbate characteristics, adsorbent porosity, and surface charge are well characterized. Langmuir’s model, for example, indicates that the adsorption site accepts one molecule of adsorbate, while physical models indicate that the acceptor site can accept n molecules of the adsorbate [
25,
26]. In recent years, numerous researchers have employed these physical models to describe the adsorption mechanism of their adsorbent materials such as; organo-sepiolite [
27], Alginate/Carbon-based Films [
28], cocoa shell [
29], bone char [
30], Acorus calamus [
15], Binary Mixture of Forest Waste Biopolymer [
31].
To our knowledge, the mechanism of interaction between Cynarascolymus powder (Cs) and MB ions has not been investigated yet. The purpose of this study was therefore to (a) evaluate the adsorption capacity of Cynarascolymus powder (Cs) for the uptake of MB from aqueous solutions; (b) to investigate the adsorption properties of MB uptake at various temperatures (298, 303, and 313 K) using various equilibrium equations; (c) analysis of the adsorption process considering Langmuir, Freundlich, Redlich-Peterson (RP), Sips, and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms as classical models; (d) obtaining complete information on the mechanism of MB adsorption onto the material (Cs) using statistical physics, and (e) to define the adsorption phenomena in macroscopic terms using thermodynamic functions.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
The Cynarascolymus biomass (external bracts) waste used in this research was collected after consumption. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) with 35% (w/w), Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) with 98,8 % (w/w), chlorure de sodium (NaCl) with 95 % (w/w), and humic acid (HA) with 99,9 % (w/w), were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich.
2.2. Adsorbent preparation
Cynarascolymus residue wastes were passed through several stages of crushing, washing drying, grinding, and sieving to produce the final product powder (Cs) used in this work.
Large quantities of collected Cynarascolymus were ground, washed multiple times with tap water, and then distilled water to remove unwanted impurities, dried in an oven at around 333K, and finally ground to a uniform powder. The particle sizes utilized in the adsorption tests were selectively separated with sieves with mesh widths ranging from 0.3 to 0.5 mm. The finished powder was kept in a desiccator until needed.
2.3. Effluent preparation (MB)
bis- (dimethylamino) - 3.7 phenazathionium chloride or methylene blue as commonly named, and containing an ammonium base, was in the form of a dark green powder. Its crude chemical formula is C16H18ClN3S with a molar mass of 319.85 g•mol-1 and solubility of 4 g•L-1 at 293K. All the MB solutions used in this work were prepared from the stock solution at a concentration of 1 g•L-1. All the glassware was washed with distilled water and dried in an oven at 323K before being used. HCl and NaOH were used to adjust the pH to the desired value. The absorbance of each residual concentration was determined using a UV-vis spectrophotometer SP-8001 from Axiom (Germany. Shimadzu).
2.4. Characterization of the adsorbent
Various characterization techniques were used in this studwhichere is detailed below.
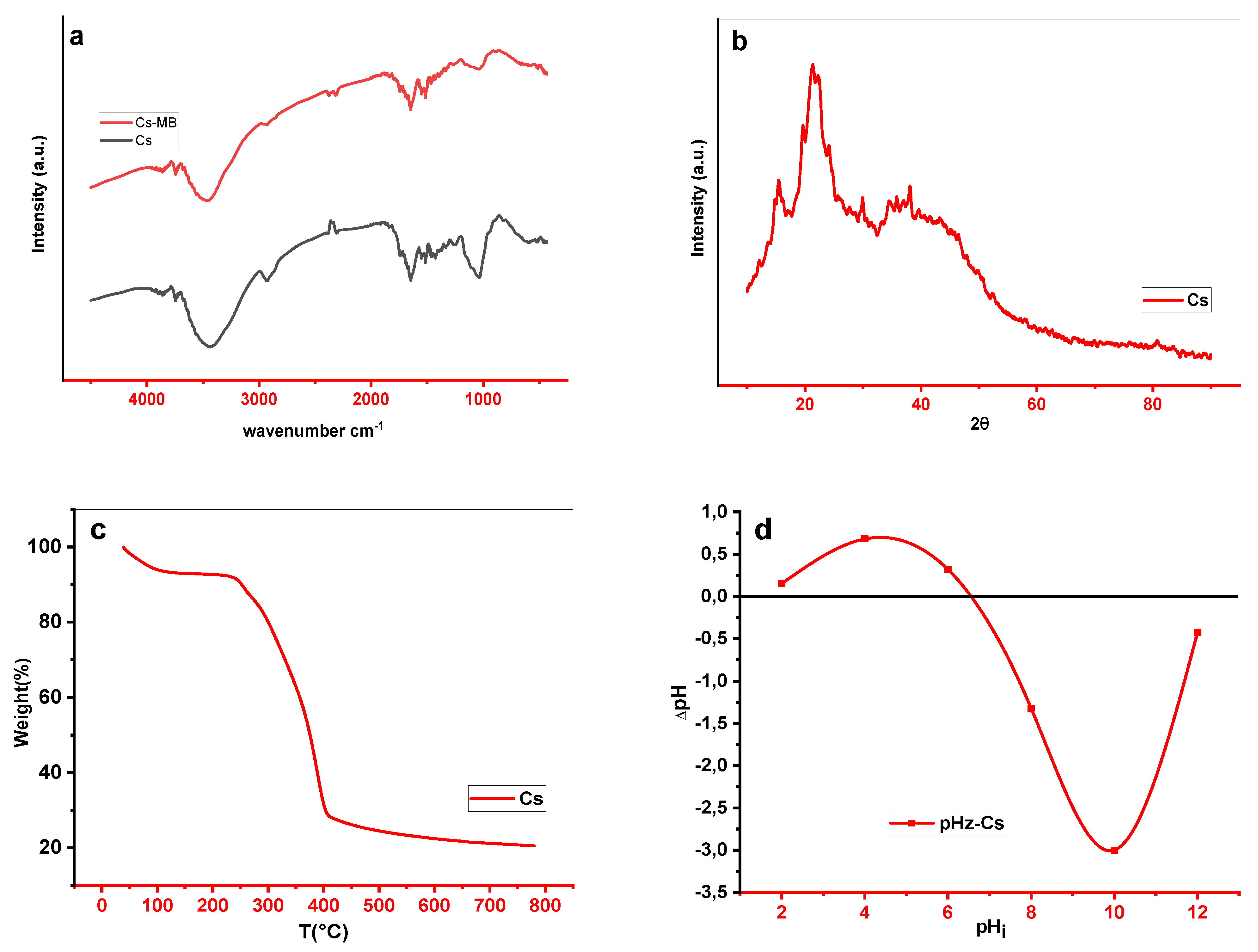
FTIR analysis allows the determination of functional material surface groups. Infra-red spectroscopy was performed on natural and loaded Cs with MB dye (Cs-MB) using the Fourier Transform Infrared spectrometer (FTIR) model IRAffinity-1S.SHIMADZU, employing a high-pressure KBr disc technique in the band of 4000 to 400 cm−1.
Additionally, the Cs material fine powder was analyzed using a PW3071/xx diffractometer operating at 45 KV and 35mA with a copper anticathode emitting Ka radiation (λ=1.5405 A). The XRD graphs were made with a step of 0.02° and a time step of 6.985 s/step throughout a 2θ angle range of 4 to 90°.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of the Cs product before biosorption was visualized using the JCM-5000 NeoScope TM to examine the morphological features of the Cs biosorbent.
To evaluate the thermal characteristics of the Cs material, a thermogravimetric examination was performed in the temperature range of 303 to 1053 K using an SDT Q600 V20.9 Build 20 thermal gravimetric.
Finally, electrostatic interactions with a material surface are among the most important factors in deciding on the functionality and compatibility between the adsorbent and the adsorbate to give an idea of the adsorption mechanism. To determine the phpzc of our materials, a very simple protocol was considered. A series of suspensions: biosorbent (10 mg) / distilled water (10 ml) stirred for 24 hours, each with a different initial pH (range 2 to 12), and the final ph vawaswere measured. The results are graphically represented (when Δph=0, the pHpzc point equals the phi).
2.5. Effect of the initial pH
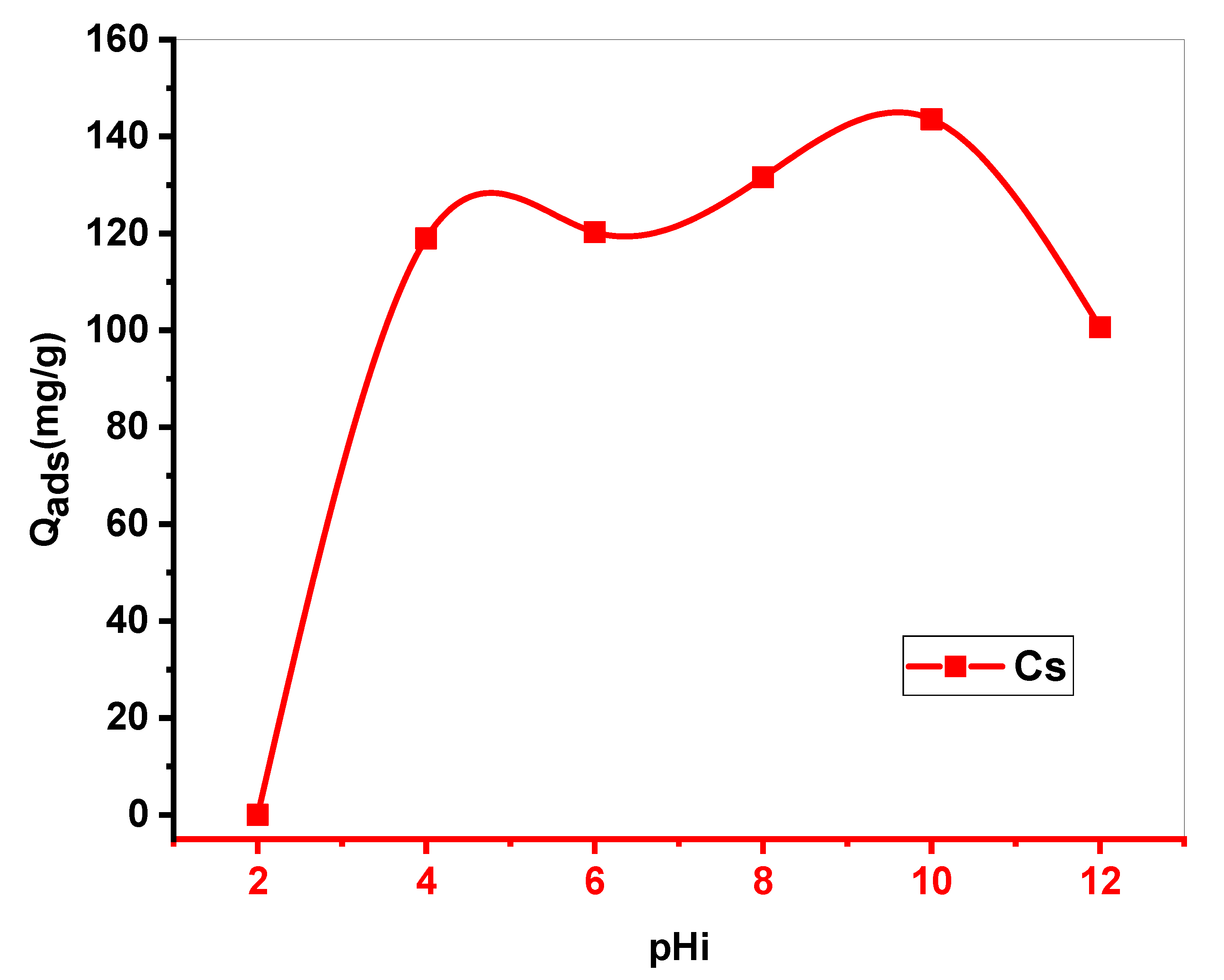
A factor that plays a very important role in the adsorption phenomenon is ph; it can alter the surface function and the distribution of anions and cations of any materials.
To test the effect of this parameter, in each 25 ml Erlenmeyer flask, 10 ml of a methylene blue solution at 250 mg•L-1was mixed with 10 mg of Cs. Every suspension was adjusted to a given initial pH (range of 2.4 to 12).
At room temperature, the mixture was stirred for 24 hours at a speed of 250 ppm. The suspension was centrifuged and the final concentration of the filter was measured by UV.
2.6. Effect of humic acid and NaCl
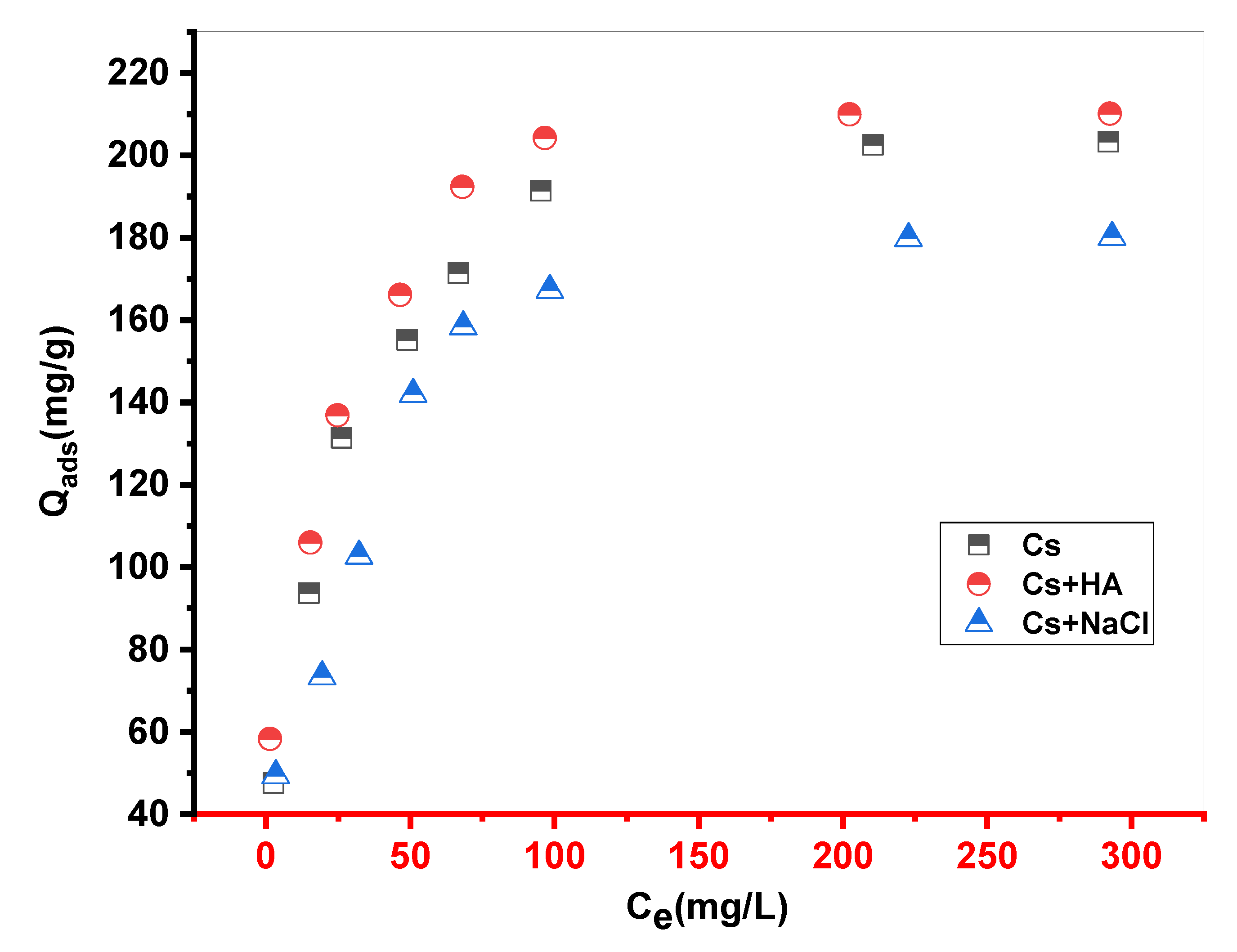
Textile wastewater is known to contain inorganic and organic ions in varying concentrations, mainly catio, ns, and anions such as chlorides, nitrates, hydrogen, sulfates, and carbonates. Consequently, and to get information on the effect of these ions on the retention process of MB dye by the Cs material, NaCl and humic acid (HA) have been considered as test ions.
A small amount of NaCl (0.1 M) was added to 10 ml of MB and 10 mg of biosorbent for different concentrations of MB dye (from 50 to 800 mg•L-1); the mixture was stirred until the equilibrium time, then the suspension was separated and analyzed. The same protocol was repeated with the second HA ion (0.1 M).
2.7. Study of adsorption
2.7.1. Adsorption kinetics
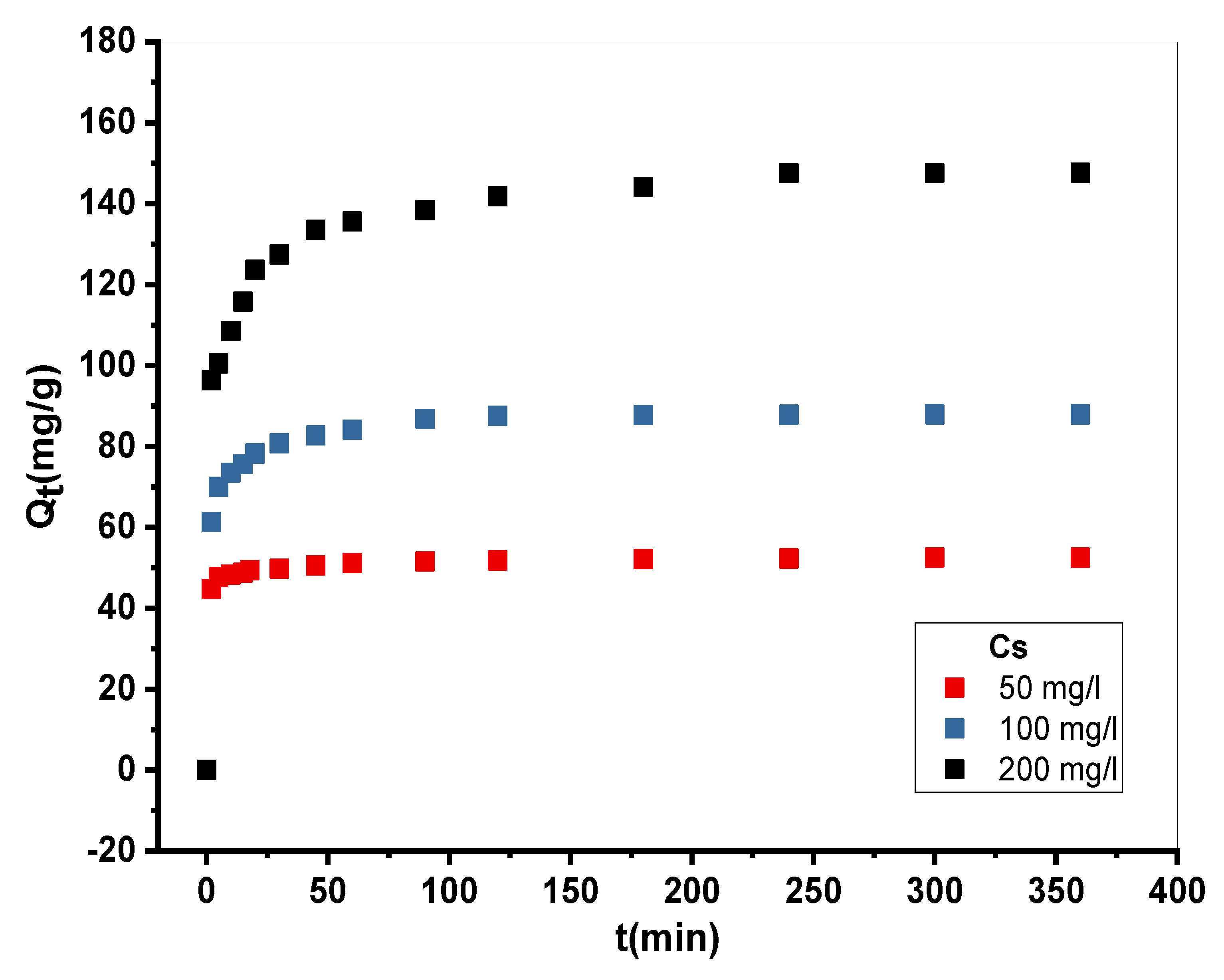
The following experiment was performed on three different MB concentrations (50. 100, and 200 mg•L
-1). In a 50 ml Erlenemayer series, at optimal pH (pH chosen in the section: pH Influence) and ambient temperature, 20 mg of adsorbent was introduced into 20 ml of MB dye solution. The mixture was stirred for a given time at a speed of 250 rpm on stir plates. Then, the centrifugation of each suspension was centrifuged and the absorbance was measured to determine the residual BM. The adsorbed quantity was calculated using the following relation:
With Qt: the quantity adsorbed, C0: the initial concentration of MB, and Ct: the final concentration of MB. V: the volume of the mixture, m: the mass of the mixture.
2.7.2. Kinetic modeling
Some kinetic models such as pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order [
32], and Pseudo-n
th orde zr [
33] were used. Their equation and parameter are listed in
Table 1.
The intraparticle diffusion model and the Boyd model were considered to evaluate the diffusion mechanism and the rate control step.
2.7.3. Isotherm Adsorption
The capacity of adsorbents to adsorb the different components of a mixture is the most critical factor in the efficiency of most adsorption processes. Therefore, it is important to have a clear understanding of the properties of the adsorbent-adsorbate equilibrium, for planning and scaling precisely the adsorption process, Three isotherms were performed at the three temperatures (T = 298, 303.313K) by the protocol outlined below.
For each Erlenemayer (25 ml), 10 g of adsorbent was added to 10 ml of MB of variable concentration solution at the optimal pH. The mixture was stirred at 250 ppm up to equilibrium. A wide range of
MB concentrations was used (from 50 to 800 mg • L-1).
The adsorbed quantity was determined using Relation 8.
With Qe: the quantity adsorbed, C0: the initial concentration of BM, Ce: the final concentration of MB in the solution, V: the volume of the mixture, and m: the mass of the mixture.
2.7.4. Isothermmodeling
Mathematical simulations were considered to evaluate accurately the interaction between the Cs and the MB dye.
2.7.4.1. Classical models
three models with a two-parameter equation, Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin–Radushkevich [
34], and two models with a three-parameter equation, Redlich-Peterson [
35] and Sips [
36], are the most widely used models in the literature to describe the non-linear equilibrium at a constant temperature between the adsorbed pollutant (Q
e) and the rest of the pollutant in solution (C
e).
Table 2 shows the equations and parameters of such models.
2.7.4.2. Description of advanced statistical physics models used to analyze the experimental results of adsorption isotherm of MB on Cs
To better understand the mechanism of MB adsorption on Cs, advanced adsorption models were considered to confirm the results obtained using classical models, as well as to provide more information on the behavior of the adsorbent-adsorbate system [
37].
Five advanced models were selected for this analysis. These models are briefly represented in
Table 3.
2.8. Statistical assessment of equilibrium parameters
The average percentage errors APE (%) function represented by Eq.19, was used to evaluate nonlinear adsorption curves of kinetics and isotherms. This function allows comparing experimental data to the adjusted model’s results point by point. The models with the lowest APE (%) values are the best for describing the experimental behavior.
Where Qi.mod is the model’s adsorption capacity, Qi.exp is the experimental adsorption capacity, and N is the number of experimental points performed [
40].
4. Conclusion
The natural powder of Cynarascolymus (Cs) was used as an adsorbent in this investigation to remove methylene blue ions (MB). The ideal pH for removing MB color was determined to be 10, which resulted in the greatest amount of adsorption. Modeling the adsorption kinetics data showed that the pseudo-nth-order kinetic model (PNO) gave the most accurate fit of the experimental results. According to the Boyd and Intraparticle models, film diffusion was the limiting step controlling the adsorption process.
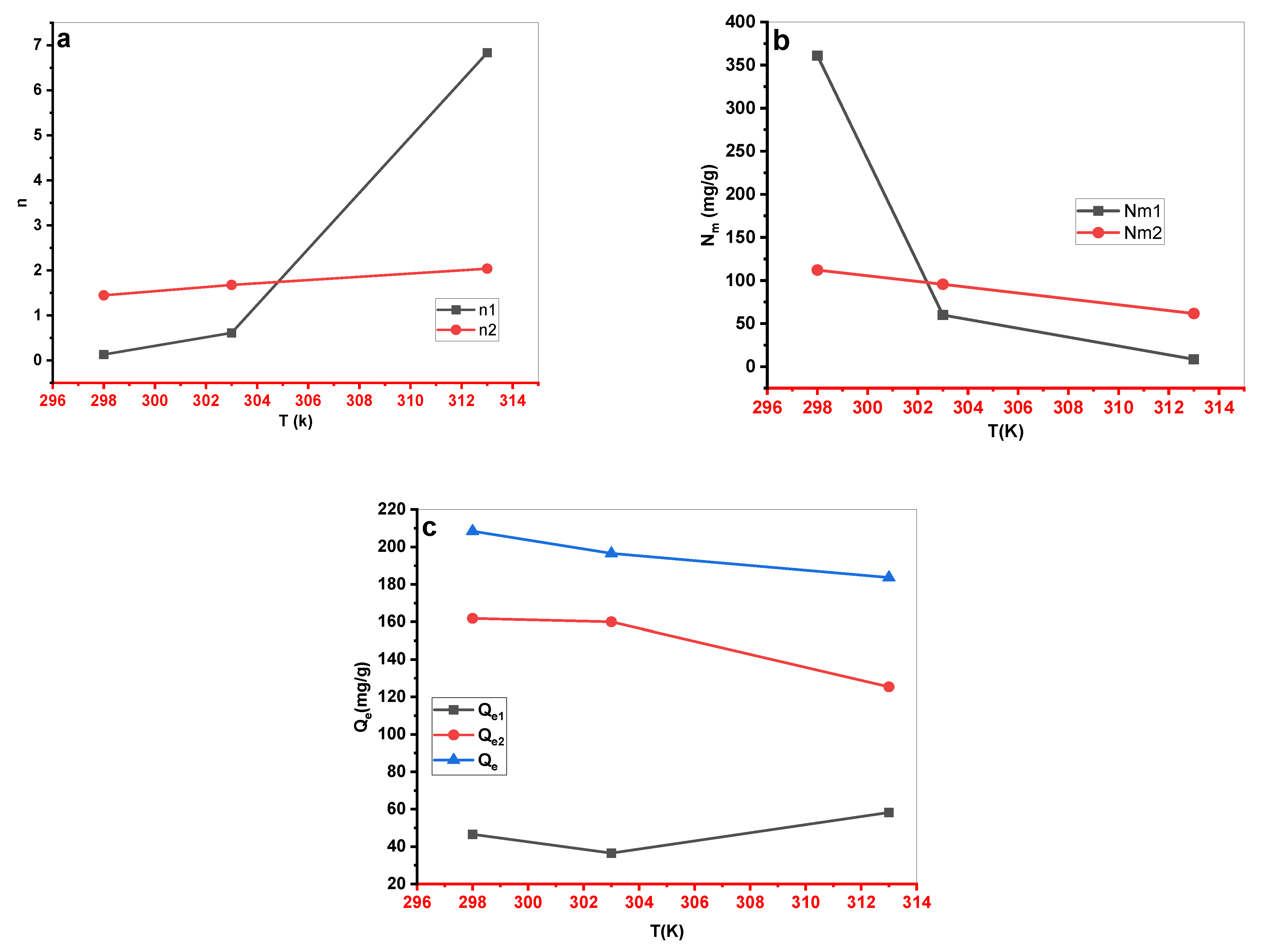
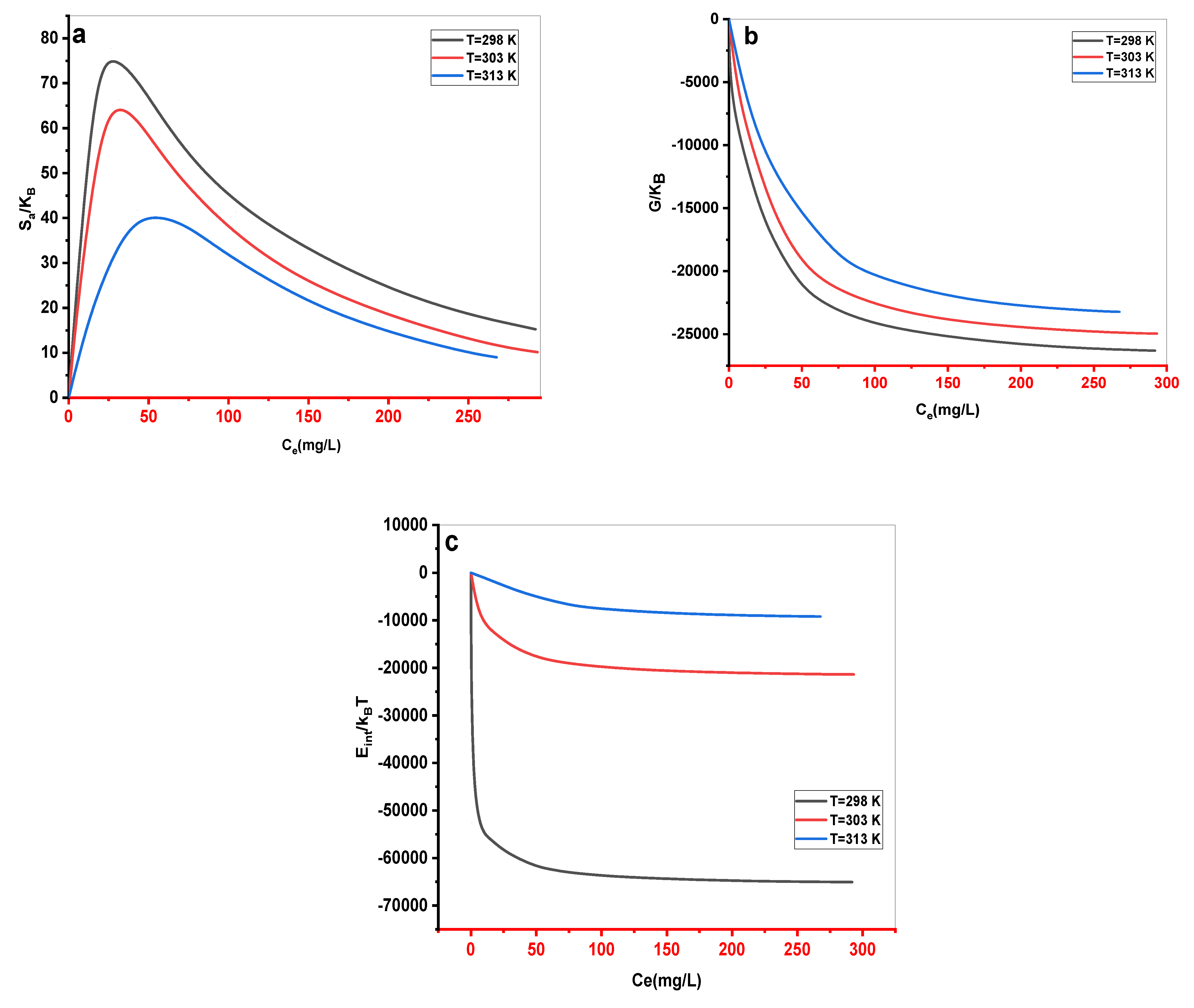
The Cs material had a maximum experimental adsorption capacity of 203.333, 192.187, and 179.380 mg•g-1 at 298, 303, and 313 K, respectively. Langmuir, Freundlich, Redlich-Peterson (R-P), Sips, and Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R) were used as classical models to describe experimental results. The Redlich-Peterson (R-P) equation provided the best fit for the adsorption data without elucidating the process of MB absorption. Five statistical physics models (AM1, AM2, AM3, AM4, and AM5) were considered to better explain the interaction between the MB ions and the Cs active sites. The steric, energetic, and thermodynamic parameters resulting from the double-energy single-layer model that gave the appropriate fit of the MB–Cs interaction were thoroughly interpreted. The MB adsorption on the Cs composite was mediated by multi–docking and multimolecular modes. The receptor’s site density (Nm) decreased with increasing solution temperature for both Nm1 and Nm2. Adsorption energies were estimated to be negative and < 40 kJ•mol-1, indicating exothermic and physical processes. As the temperature dropped, Qe increased, confirming the exothermic nature of the uptake processes. Entropy, Gibbs free enthalpy, and internal energy indicated that MB adsorption onto the novel Cs adsorbent was possible and spontaneous.
Figure 1.
Cynarascolymus (Cs) Characterization (a) FTIR spectrum, (b) XRD shape, (c) Thermogravimetric analysis, (d) isoelectric point.
Figure 1.
Cynarascolymus (Cs) Characterization (a) FTIR spectrum, (b) XRD shape, (c) Thermogravimetric analysis, (d) isoelectric point.
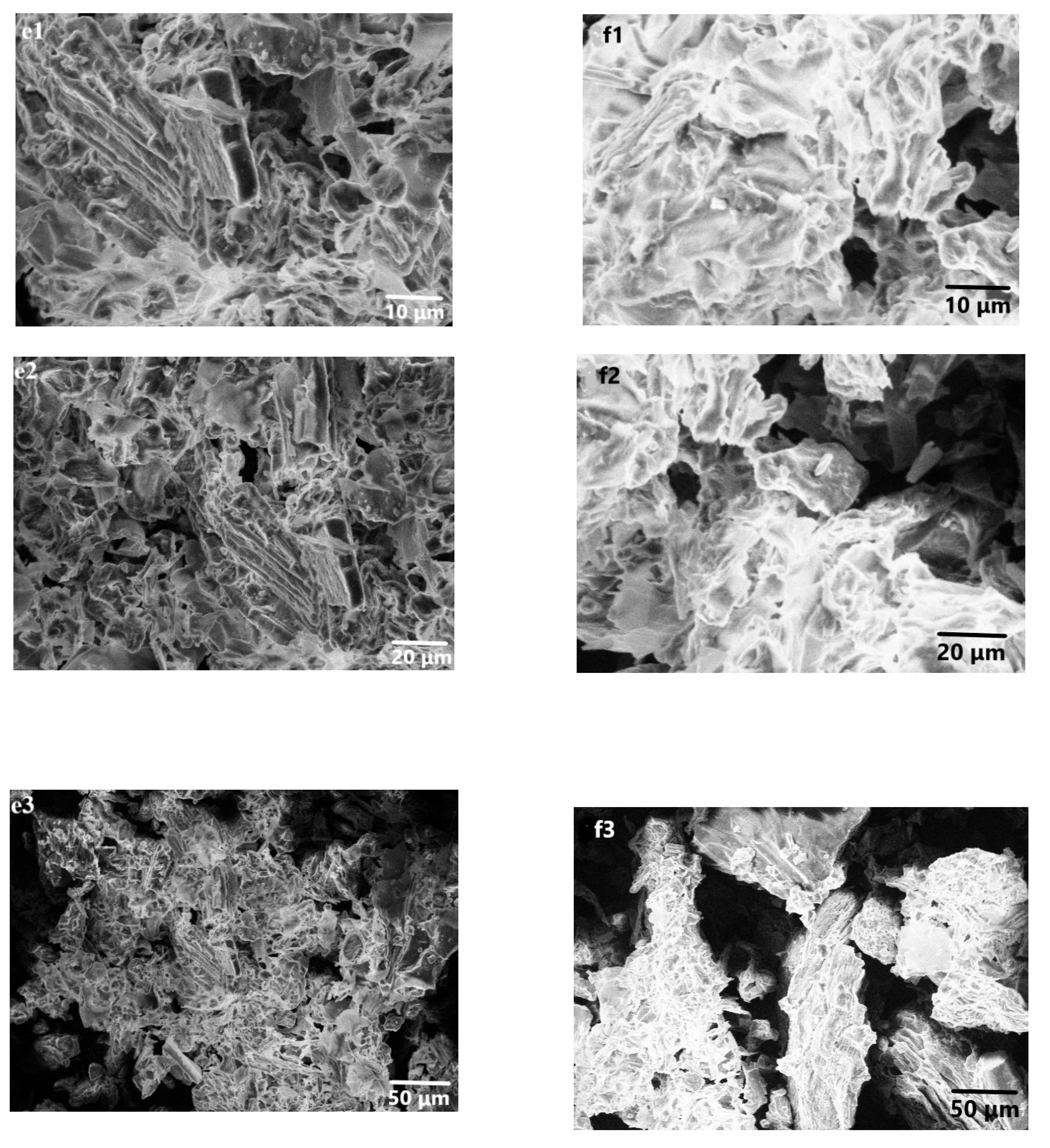
Figure 2.
SEM images (e) before and (f) after adsorption.
Figure 2.
SEM images (e) before and (f) after adsorption.
Figure 3.
The effect of initial pH on adsorption of MB with Cs (m = 10 mg.V = 10 ml. pH=10.stirring = 250 ppm. Tambient).
Figure 3.
The effect of initial pH on adsorption of MB with Cs (m = 10 mg.V = 10 ml. pH=10.stirring = 250 ppm. Tambient).
Figure 4.
Influence of NaCl and humic acid (HA) on the discoloration of MB solutions by Cs (m = 10 mg.V = 10 ml. stirring = 250 ppm.pH=10.Tambient).
Figure 4.
Influence of NaCl and humic acid (HA) on the discoloration of MB solutions by Cs (m = 10 mg.V = 10 ml. stirring = 250 ppm.pH=10.Tambient).
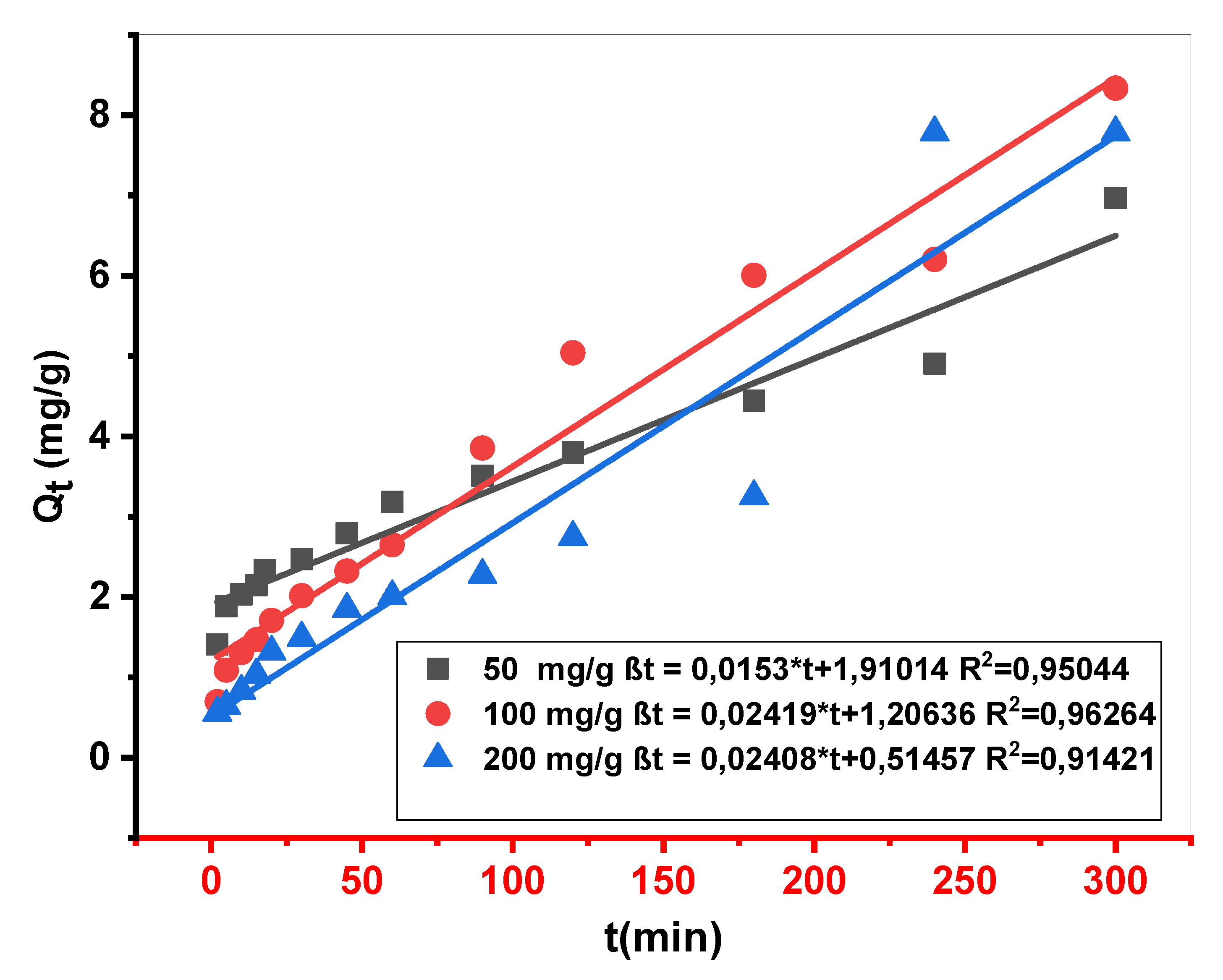
Figure 5.
Representative curve of experimental adsorption kinetics of BM on Cs material (m = 10 mg.V = 10 ml.stirring = 250 ppm.pH=10.Tambient ).
Figure 5.
Representative curve of experimental adsorption kinetics of BM on Cs material (m = 10 mg.V = 10 ml.stirring = 250 ppm.pH=10.Tambient ).
Figure 6.
The curves representative of linear simulation of MB adsorption on Cs using boyd model.
Figure 6.
The curves representative of linear simulation of MB adsorption on Cs using boyd model.
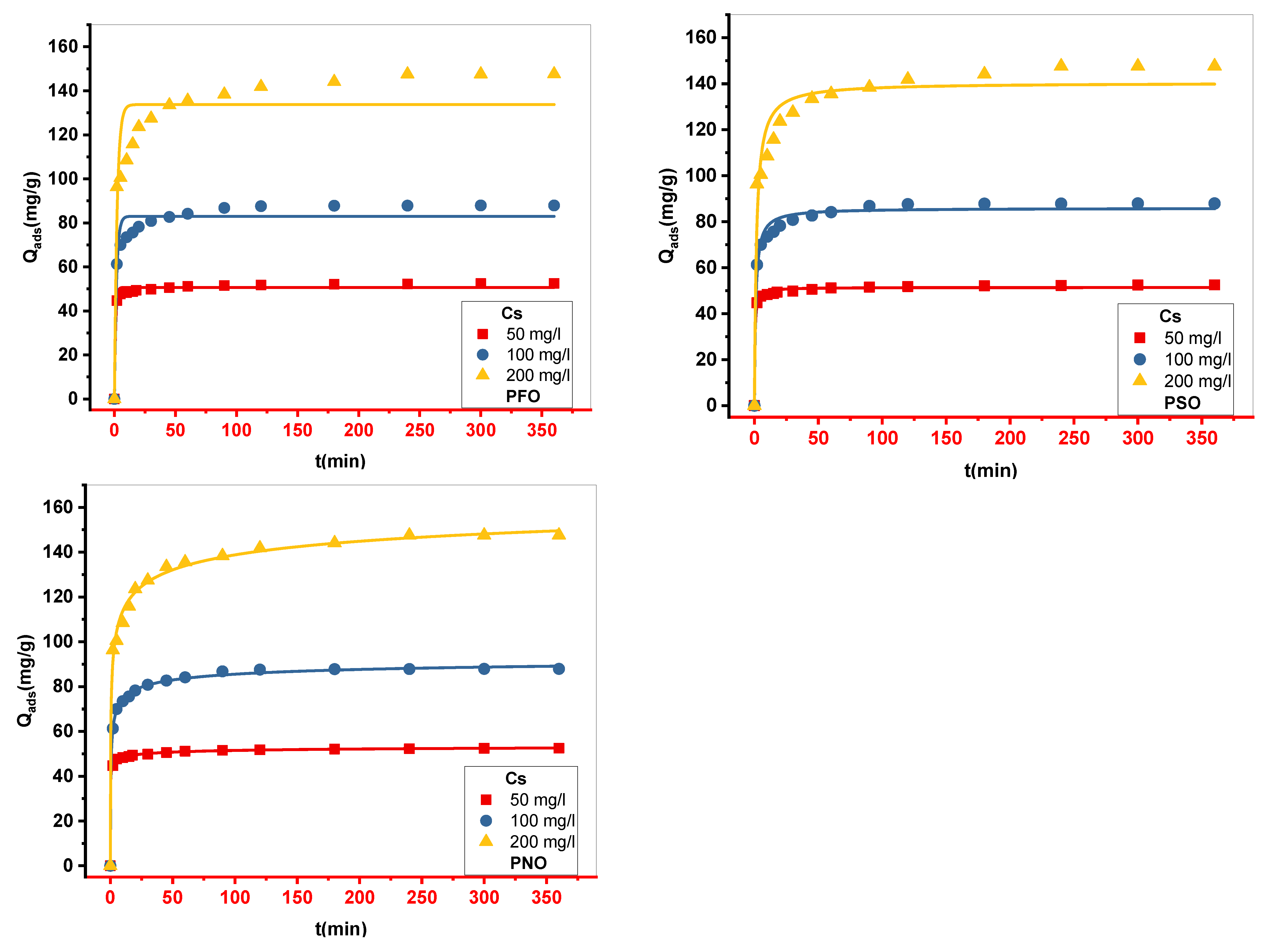
Figure 7.
The curves representative of Nonlinear simulation of the pseudo-first-order (PFO), pseudo-second-order(PSO), and pseudo-nth-order kinetic models(PNO).
Figure 7.
The curves representative of Nonlinear simulation of the pseudo-first-order (PFO), pseudo-second-order(PSO), and pseudo-nth-order kinetic models(PNO).
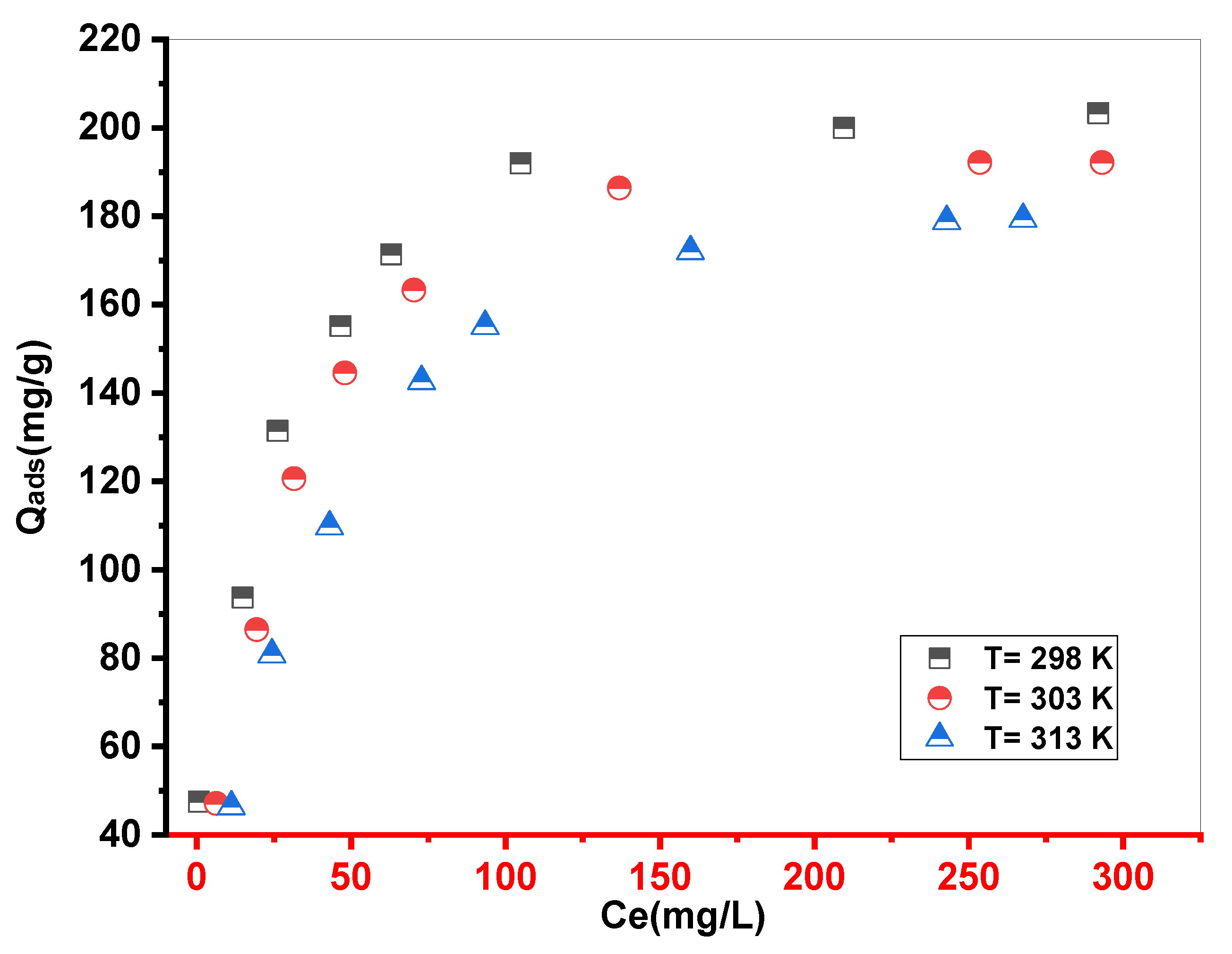
Figure 8.
Experimental isotherms of MB adsorption onto Cs. (m = 10 mg.V = 10 ml. stirring = 250 ppm. pH=10. T ambient).
Figure 8.
Experimental isotherms of MB adsorption onto Cs. (m = 10 mg.V = 10 ml. stirring = 250 ppm. pH=10. T ambient).
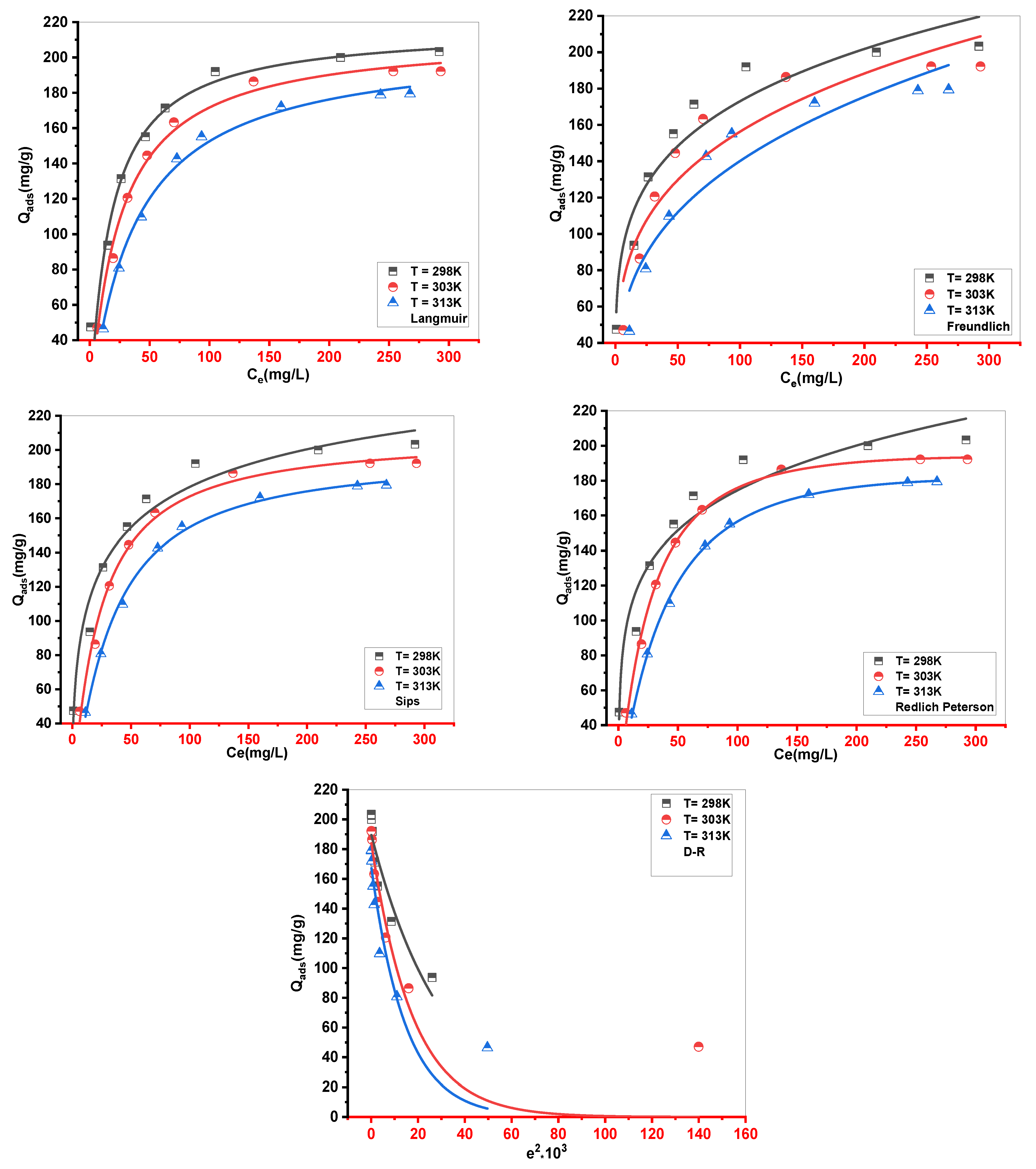
Figure 9.
Result of fitting isotherms data of MB adsorption onto Cs with Langmuir, Freundlich, D−R, Redlich-Peterson(R-P) and Sips.
Figure 9.
Result of fitting isotherms data of MB adsorption onto Cs with Langmuir, Freundlich, D−R, Redlich-Peterson(R-P) and Sips.
Figure 10.
Result of fitting isotherms data of MB adsorption onto Cs with AM1, AM2, AM3, AM4, and AM5 models.
Figure 10.
Result of fitting isotherms data of MB adsorption onto Cs with AM1, AM2, AM3, AM4, and AM5 models.
Figure 11.
The evolution of (a) n, (b) Nm, and (c) Qe as a function of temperature for MB-Cs adsorption.
Figure 11.
The evolution of (a) n, (b) Nm, and (c) Qe as a function of temperature for MB-Cs adsorption.
Figure 12.
(a) Entropy, (b) free enthalpy, and (c) internal energy evolution as a function of concentration for MB absorption by Cs adsorbent at various temperatures.
Figure 12.
(a) Entropy, (b) free enthalpy, and (c) internal energy evolution as a function of concentration for MB absorption by Cs adsorbent at various temperatures.
Table 1.
Equations of PFO, PSO, and PNO models for nonlinear regression of Kinetic adsorption data.
Table 1.
Equations of PFO, PSO, and PNO models for nonlinear regression of Kinetic adsorption data.
| Kinetics model |
number |
Equation |
| Pseudo-first order |
2 |
|
| Pseudo-second order |
3 |
|
| Pseudo-nthorder |
4 |
|
| Intraparticle diffusion |
5 |
|
| Boyd |
67 |
|
Table 2.
Langmuir, Freundlich, Dubinin–Radushkevich, Redlich-Peterson (R-P), and Sips equations and Equation.
Table 2.
Langmuir, Freundlich, Dubinin–Radushkevich, Redlich-Peterson (R-P), and Sips equations and Equation.
| Isotherme model |
number |
Equation |
| Langmuir |
9 |
|
| Freundlich |
10 |
|
| Sips |
11 |
|
| Redlich-Peterson |
12 |
|
| Dubinin–Radushkevich |
13 |
|
Table 3.
The Advanced statistical physics models AM1, AM2, AM3, AM4, and AM5.
Table 3.
The Advanced statistical physics models AM1, AM2, AM3, AM4, and AM5.
| Model |
num |
Equation |
Ref |
| Single-energy single-layer model(AM1) |
14 |
|
[38] |
| Double-energy single-layer model(AM 2) |
15 |
|
[39] |
| Single-energy -double layer model(AM 3) |
16 |
|
[20] |
| Double-energy -double layer model(AM 4) |
17 |
|
[21] |
| Finitemultilayer(AM 5) |
18 |
With :
|
[39] |
Table 4.
Parameters of Kinetic for nonlinear regression of PFO, PSO, and PNO models for the adsorption of MB on Cs.
Table 4.
Parameters of Kinetic for nonlinear regression of PFO, PSO, and PNO models for the adsorption of MB on Cs.
| models |
Parameters |
50 mg•L-1
|
100 mg•L-1
|
150 mg•L-1
|
| PFO |
Qexp |
52.5 |
87.92 |
147.61 |
| Qe |
50.68 |
82.98 |
133.75 |
| K1
|
1.044 |
0.58 |
0.461 |
| R2
|
0.985 |
0.939 |
0.865 |
| |
APE(%) |
2.664 |
5.973 |
9.474 |
| PSO |
Qe |
51.43 |
85.88 |
140.42 |
| K2*10+4
|
0.055 |
0.011 |
0.0046 |
| R2
|
0.994 |
0.982 |
0.947 |
| APE(%) |
1.657 |
5.714 |
5.795 |
| PNO |
Qe |
55.46 |
96.89 |
203.56 |
| kn
|
1.073*10-5
|
8.38*10-7
|
2.49*10-16
|
| no |
4.97 |
4.365 |
8.04 |
| R2
|
0.999 |
0.998 |
0.994 |
| APE(%) |
0.328 |
0.889 |
1.851 |
Table 5.
Langmuir, Freundlich,D−R,Redlich-Peterson(R-P),and Sips parametres for the adsorption of MB onto Cs.
Table 5.
Langmuir, Freundlich,D−R,Redlich-Peterson(R-P),and Sips parametres for the adsorption of MB onto Cs.
| Models |
Parameters |
298K |
303k |
313K |
| Langmuir |
Qe(mg•g-1) |
203.333 |
192.187 |
179.380 |
| Qm(mg•g-1) |
217.075 |
213.012 |
208.577 |
| KL (L•mg-1) |
0.0579 |
0.04155 |
0.0272 |
| R2
|
0.911 |
0.990 |
0.994 |
| APE(%) |
12.143 |
3.506 |
2.707 |
| Freundlich |
nf |
4.499 |
3.7136 |
3.078 |
| KF(mg•g-1)(L/mg)1/n
|
62.16 |
45.219 |
31.38 |
| R2
|
0.926 |
0.866 |
0.899 |
| APE(%) |
9.569 |
15.586 |
12.618 |
| Sips |
Qm(mg•g-1) |
294.691 |
208.441 |
197.356 |
| KS (L•mg-1) |
0.0248 |
0.04314 |
0.031 |
| ms |
0.4714 |
1.0793 |
1.1606 |
| R2
|
0.949 |
0.989 |
0.996 |
| APE(%) |
7.645 |
3.908 |
1.994 |
| Redlishpeterson |
kR(L•g-1) |
181.46 |
7.294 |
4.637 |
| R
|
2.496 |
0.022 |
0.011 |
| R2
|
0.926 |
0.993 |
0.999 |
| APE(%) |
7.544 |
3.187 |
1.224 |
| D−R |
Qm(mg•g-1) |
189.969 |
184.75 |
168.348 |
| E(kJ•mol-1) |
3.927 |
2.967 |
2.7048 |
| R2
|
0.869 |
0.832 |
0.819 |
| APE(%) |
10.614 |
18.477 |
17.246 |
Table 6.
Values of the estimated parameters of models AM1, AM2, AM3, AM4, and AM5 of the MB-Cs adsorption process.
Table 6.
Values of the estimated parameters of models AM1, AM2, AM3, AM4, and AM5 of the MB-Cs adsorption process.
| Models |
Parameters |
T = 298 K |
T = 303 K |
T = 313 K |
| AM1 |
n |
0.471 |
1.079 |
1.161 |
| Nm
|
624.728 |
193.109 |
170.044 |
| C1/2
|
40.359 |
23.182 |
32.839 |
| R2
|
0.949 |
0.989 |
0.996 |
| APE(%) |
7.646 |
3.908 |
1.995 |
| AM2 |
n1
|
0.129 |
0.610 |
6.833 |
| n2
|
1.444 |
1.676 |
2.036 |
| Nm1
|
360.902 |
59.874 |
8.5241 |
| Nm2
|
112.073 |
95.507 |
61.579 |
| C1
|
2.419*10-35
|
9.807*10-13
|
9.851 |
| C2
|
26.414 |
30.566 |
51.191 |
| R2
|
0.99218 |
0.99781 |
0.99994 |
| APE(%) |
1.354960 |
0.766527 |
0.096792 |
| AM3 |
n |
0.374 |
0.811 |
0.867 |
| Nm
|
382.960 |
130.008 |
115.298 |
| C1/2
|
35.781 |
23.896 |
33.782 |
| R2
|
0.95233 |
0.99038 |
0.99675 |
| APE(%) |
7.527145 |
3.706916 |
1.792957 |
| AM4 |
n |
0.363 |
0.76608 |
0.81213 |
| Nm
|
394.458 |
137.7444 |
123.15063 |
| C1
|
45.7492 |
30.3144 |
43.7831 |
| C2
|
35.848 |
23.911 |
33.791 |
| R2
|
0.94044 |
0.98802 |
0.99596 |
| APE(%) |
7.519079 |
3.701431 |
1.805403 |
| AM5 |
n |
0.717 |
0.779 |
1.986 |
| N2
|
3.842 |
4.176 |
1.334 |
| C1
|
1.229*10-11
|
0.835 |
9.879 |
| C2
|
27.059 |
31.696 |
58.628 |
| Nm |
61,556 |
49,993 |
39,537 |
| R2
|
0.99421 |
0.99812 |
0.9999 |
| APE(%) |
1.405965 |
0.8529428 |
0.17386 |
Table 7.
Entropy, free enthalpy, and internal energy function according to the AM2 model.
Table 7.
Entropy, free enthalpy, and internal energy function according to the AM2 model.
| fonction |
num |
Equation |
| Entropy |
22 |
|
| Gibbs free enthalpy |
23 |
With:
|
| Internal energy |
24 |
|