Submitted:
05 May 2023
Posted:
06 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
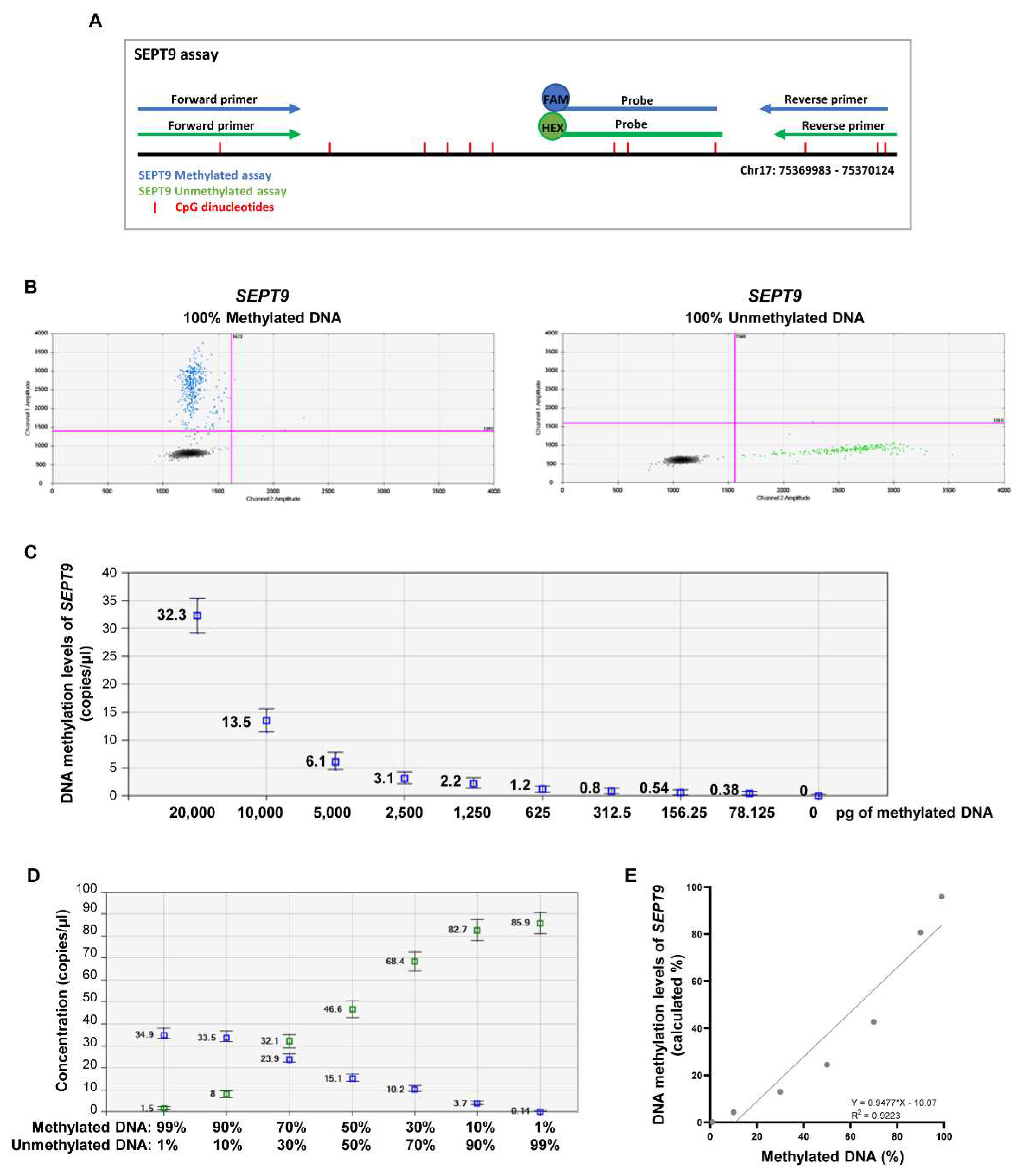
2.1. Establishing the efficiency of MS-ddPCR assays for the detection of SEPT9 DNA methylation
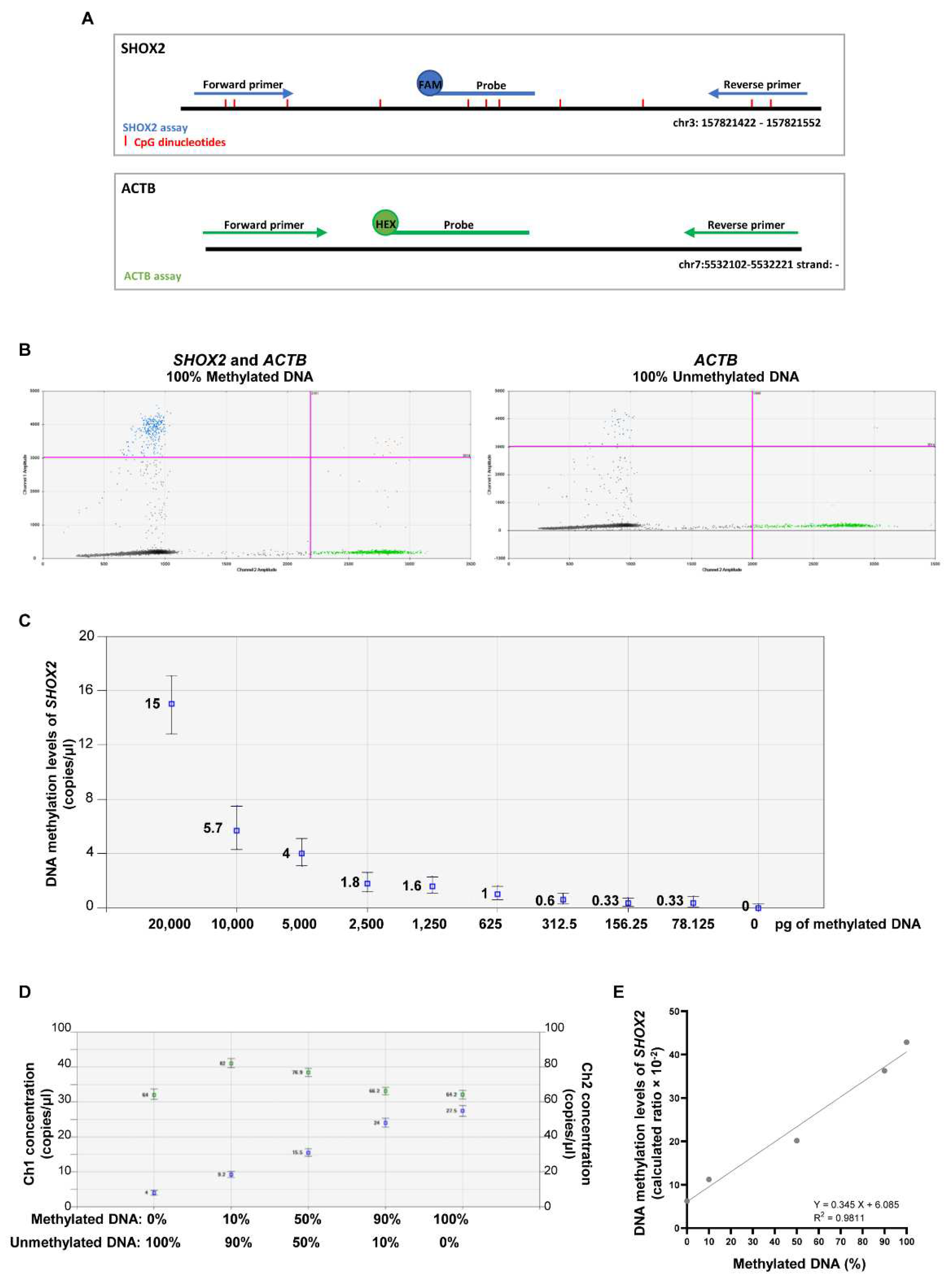
2.2 Establishing the efficiency of MS-ddPCR assays for the detection of SHOX2 DNA methylation
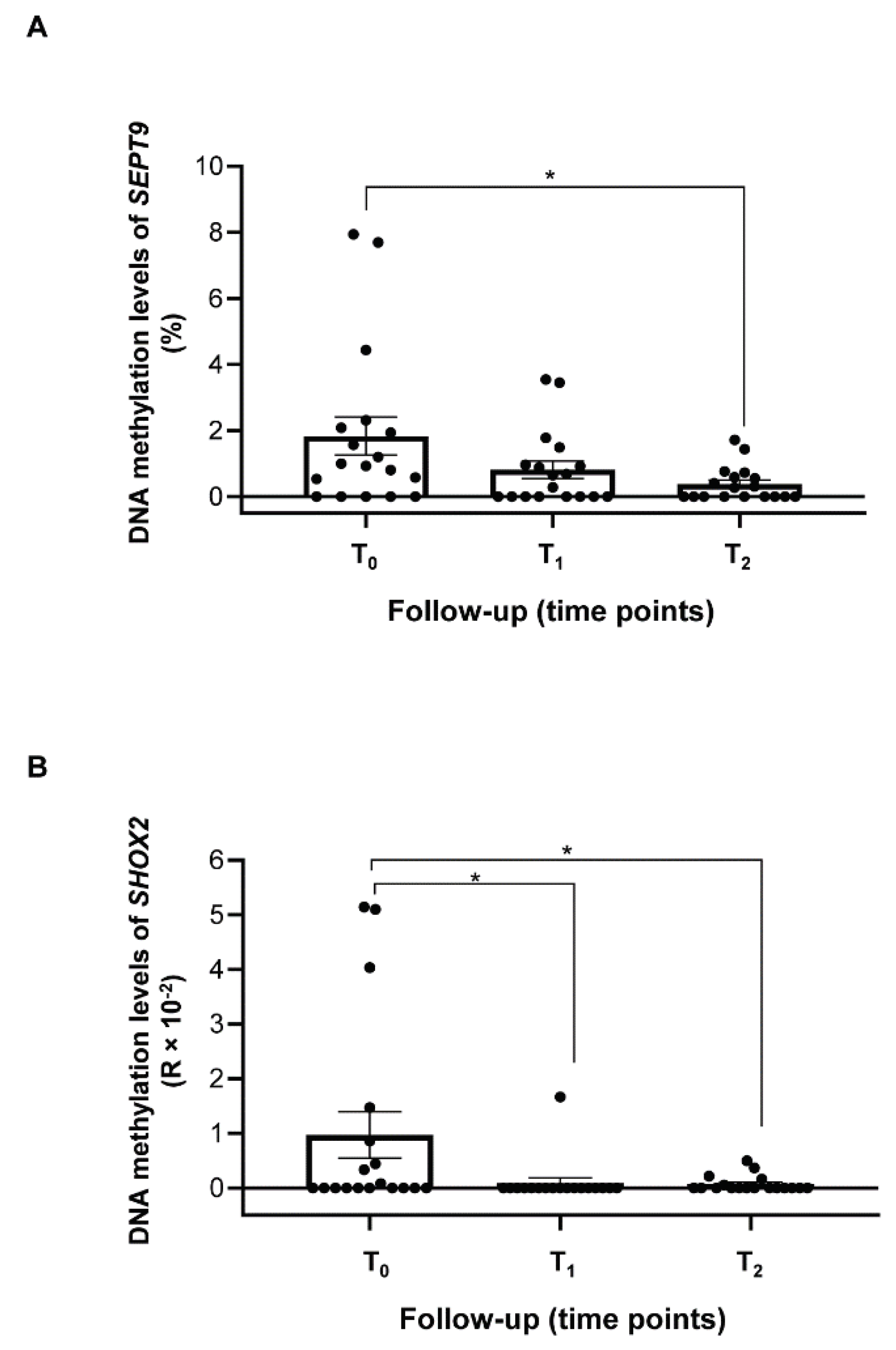
2.3 Methylation levels of SEPT9 and SHOX2 in ccfDNA from plasma of HNSCC patients
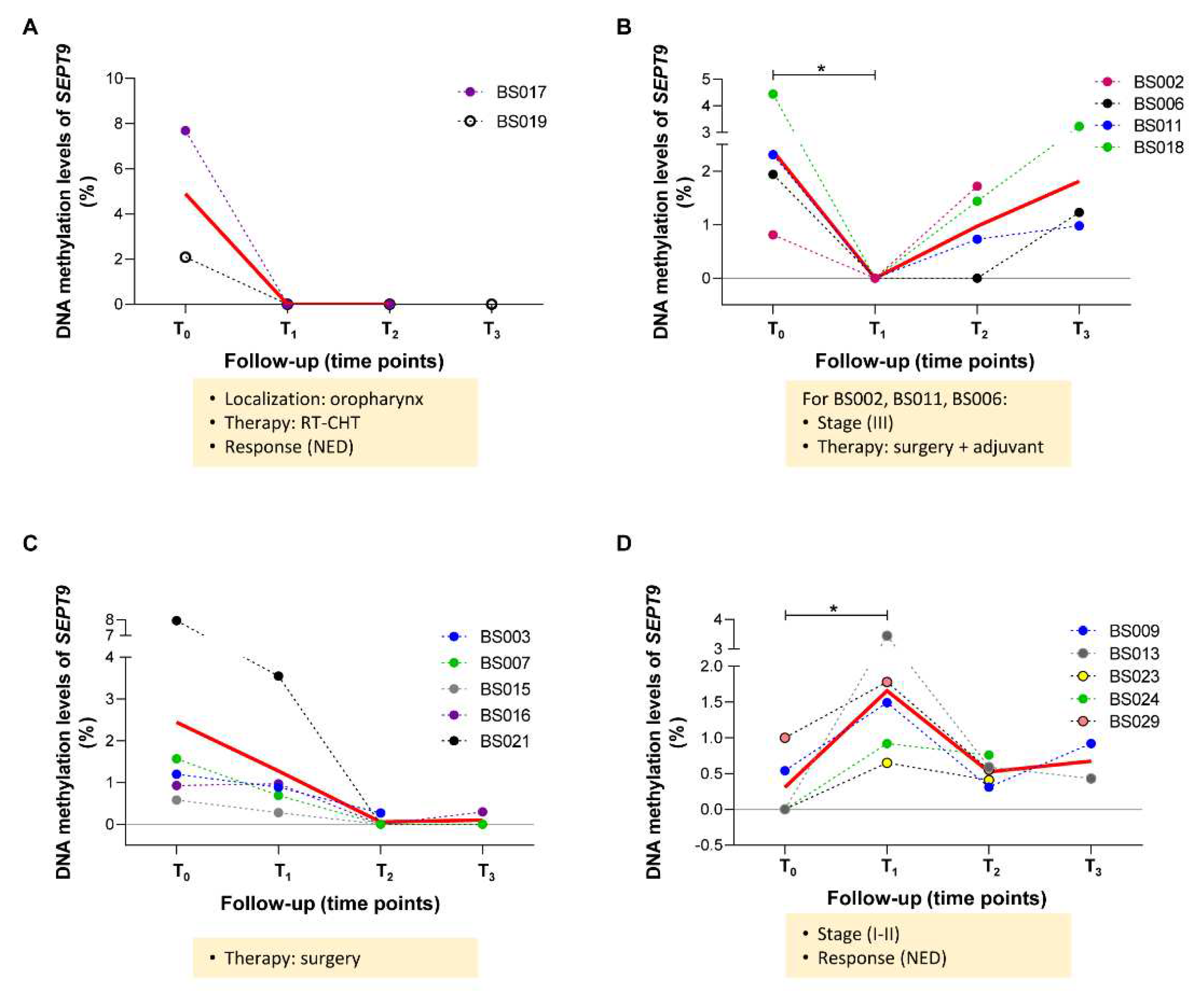
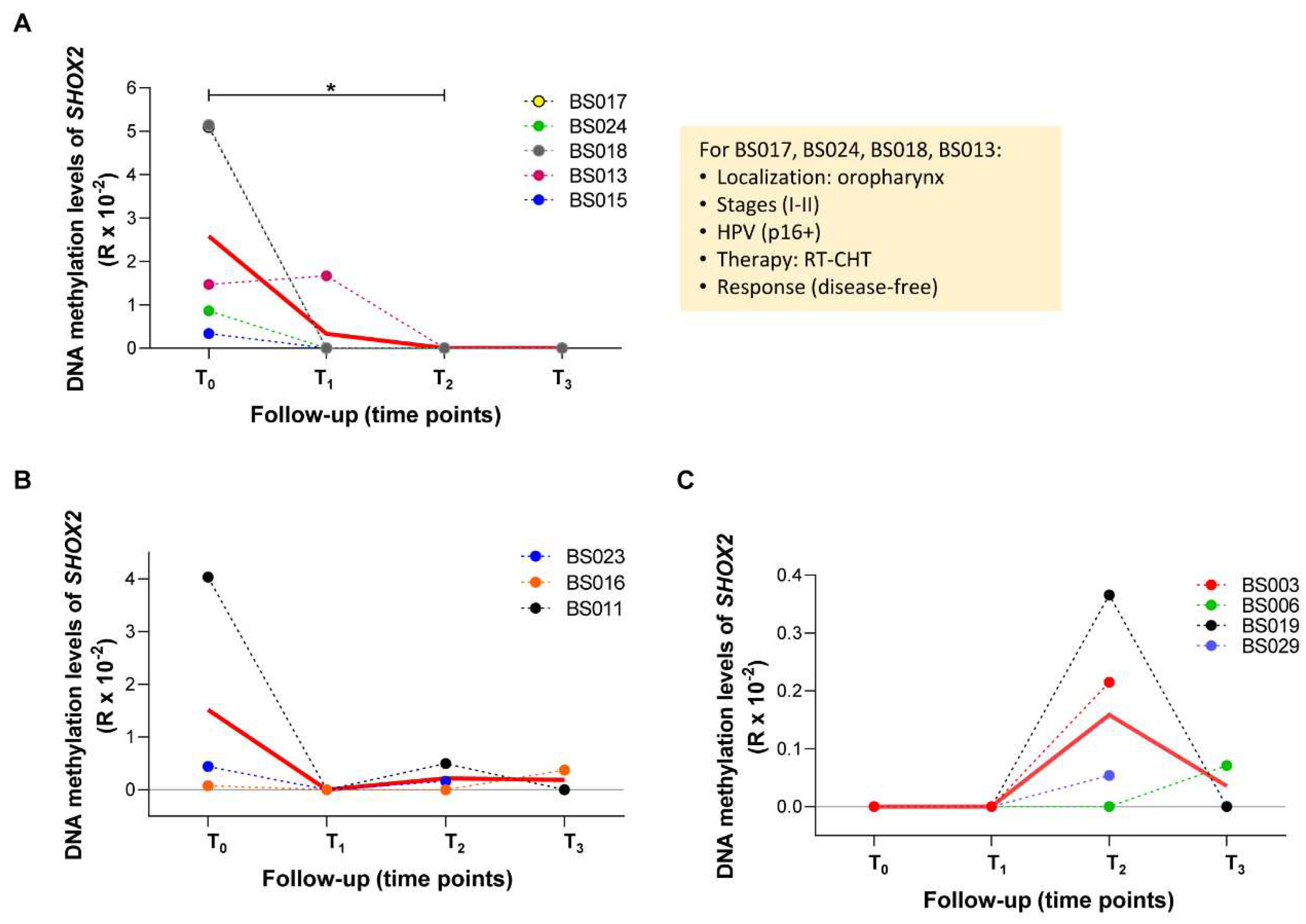
2.4 Longitudinal variations of methylated SEPT9 and SHOX2 in ccfDNA from plasma of HNSCC patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasma samples from HNSCC patients.
4.2. ccfDNA isolation from plasma and bisulfite conversion.
4.3. Methylation specific-droplet digital PCR (MS-ddPCR) assays.
4.4. Establishing the efficiency of MS-ddPCR assays.
4.5. Detection of SEPT9 and SHOX2 methylation levels in ccfDNA of HNSCC patients by MS-ddPCR.
4.6. Statistical analysis.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mody, M.D.; Rocco, J.W.; Yom, S.S.; Haddad, R.I.; Saba, N.F. Head and neck cancer. Lancet (London, England) 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzaffar, J.; Bari, S.; Kirtane, K.; Chung, C.H. Recent Advances and Future Directions in Clinical Management of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Herrero, E.; Serna-Blasco, R.; Robado de Lope, L.; González-Rumayor, V.; Romero, A.; Provencio, M. Circulating Tumor DNA as a Cancer Biomarker: An Overview of Biological Features and Factors That may Impact on ctDNA Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, V.; Ciardiello, F.; Maria, C.; Corte, D.; Martini, G.; Troiani, T.; Napolitano, S. Diagnostic value of liquid biopsy in the era of precision medicine: 10 years of clinical evidence in cancer. [CrossRef]
- Kogo, R.; Manako, T.; Iwaya, T.; Nishizuka, S.; Hiraki, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Idogawa, M.; Tokino, T.; Koide, A.; Komune, N.; et al. Individualized circulating tumor DNA monitoring in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3960–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeni, E.; Grossi, I.; Marchina, E.; Coniglio, A.; Incardona, P.; Cavalli, P.; Zorzi, F.; Chiodera, P.L.; Paties, C.T.; Crosatti, M.; et al. DNA methylation variations in familial female and male breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeni, E.; Salvi, A.; Marchina, E.; Traversa, M.; Arici, B.; De Petro, G. Sorafenib induces variations of the DNA methylome in HA22T/VGH human hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou; Londra, D. ; Tserpeli, V.; Kollias; Tsaroucha, E.; Vamvakaris, I.; Potaris, K.; Pateras, I.; Kotsakis; Georgoulias, V.; et al. DNA methylation analysis of tumor suppressor genes in liquid biopsy components of early stage NSCLC: a promising tool for early detection. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröck, A.; Leisse, A.; De Vos, L.; Gevensleben, H.; Dröge, F.; Franzen, A.; Wachendörfer, M.; Schröck, F.; Ellinger, J.; Teschke, M.; et al. Free-circulating methylated DNA in blood for diagnosis, staging, prognosis, and monitoring of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients: An observational prospective cohort study. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zheng, M.Y.; Li, Y.W.; Zhang, S.W. Structure and function of Septin 9 and its role in human malignant tumors. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, H. Diagnostic performance of SHOX2 promoter methylation as biomarker for lung cancer identification: A meta-analysis update. Thorac. cancer 2021, 12, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semaan, A.; van Ellen, A.; Meller, S.; Bergheim, D.; Branchi, V.; Lingohr, P.; Goltz, D.; Kalff, J.C.; Kristiansen, G.; Matthaei, H.; et al. SEPT9 and SHOX2 DNA methylation status and its utility in the diagnosis of colonic adenomas and colorectal adenocarcinomas. Clin. Epigenetics 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, L.; Gevensleben, H.; Schröck, A.; Franzen, A.; Kristiansen, G.; Bootz, F.; Dietrich, D. Comparison of quantification algorithms for circulating cell-free DNA methylation biomarkers in blood plasma from cancer patients. Clin. Epigenetics 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, J.D.; Xiong, W.; Bunker, A.M.; Vaughn, C.P.; Furtado, L. V.; Roberts, W.L.; Fang, J.C.; Samowitz, W.S.; Heichman, K.A. Septin 9 methylated DNA is a sensitive and specific blood test for colorectal cancer. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanca-Ballester, C.; Rodriguez-Casanova, A.; Torres, S.; Calabuig-Fariñas, S.; Exposito, F.; Serrano, D.; Redin, E.; Valencia, K.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; et al. Cancer epigenetic biomarkers in liquid biopsy for high incidence malignancies. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaga, M.; Chorostowska-Wynimko, J.; Horváth, I.; Tammemagi, M.C.; Shitrit, D.; Eisenberg, V.H.; Liang, H.; Stav, D.; Faber, D.L.; Jansen, M.; et al. Validation of Lung EpiCheck, a novel methylation-based blood assay, for the detection of lung cancer in European and Chinese high-risk individuals. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manganelli, M.; Grossi, I.; Ferracin, M.; Guerriero, P.; Negrini, M.; Ghidini, M.; Senti, C.; Ratti, M.; Pizzo, C.; Passalacqua, R.; et al. Longitudinal circulating levels of mir-23b-3p, mir-126-3p and lncrna gas5 in hcc patients treated with sorafenib. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ginkel, J.H.; Huibers, M.M.H.; van Es, R.J.J.; de Bree, R.; Willems, S.M. Droplet digital PCR for detection and quantification of circulating tumor DNA in plasma of head and neck cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, S.Y.H.; Chan, K.C.A.; Wong, E.W.Y.; Ng, C.W.K.; Cho, R.; Yeung, Z.W.C.; Lam, J.W.K.; Chan, J.Y.K. Droplet digital PCR of tumor suppressor gene methylation in serial oral rinses of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2021, 43, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganelli, M.; Grossi, I.; Corsi, J.; D’agostino, V.G.; Jurikova, K.; Cusanelli, E.; Molfino, S.; Portolani, N.; Salvi, A.; De Petro, G. Expression of Cellular and Extracellular TERRA, TERC and TERT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, I.; Schiavone, M.; Cannone, E.; Grejdan, O.A.; Tobia, C.; Bonomini, F.; Rezzani, R.; Salvi, A.; De Petro, G. Lasp1 Expression Is Implicated in Embryonic Development of Zebrafish. Genes (Basel). 2022, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armakolas, A.; Kotsari, M.; Koskinas, J. Liquid Biopsies, Novel Approaches and Future Directions. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vos, L.; Jung, M.; Koerber, R.M.; Bawden, E.G.; Holderried, T.A.W.; Dietrich, J.; Bootz, F.; Brossart, P.; Kristiansen, G.; Dietrich, D. Treatment Response Monitoring in Patients with Advanced Malignancies Using Cell-Free SHOX2 and SEPT9 DNA Methylation in Blood: An Observational Prospective Study. J. Mol. Diagnostics 2020, 22, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergheim, J.; Semaan, A.; Gevensleben, H.; Groening, S.; Knoblich, A.; Dietrich, J.; Weber, J.; Kalff, J.C.; Bootz, F.; Kristiansen, G.; et al. Potential of quantitative SEPT9 and SHOX2 methylation in plasmatic circulating cell-free DNA as auxiliary staging parameter in colorectal cancer: a prospective observational cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stejskal, P.; Goodarzi, H.; Srovnal, J.; Hajdúch, M.; van ’t Veer, L.J.; Magbanua, M.J.M. Circulating tumor nucleic acids: biology, release mechanisms, and clinical relevance. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Carter, K.T.; Makar, K.W.; Vickers, K.; Ulrich, C.M.; Schoen, R.E.; Brenner, D.; Markowitz, S.D.; Grady, W.M. Methylight droplet digital PCR for detection and absolute quantification of infrequently methylated alleles. Epigenetics 2015, 10, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postel, M.; Roosen, A.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Taly, V.; Wang-Renault, S.F. Droplet-based digital PCR and next generation sequencing for monitoring circulating tumor DNA: a cancer diagnostic perspective. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 18, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausewitz, P.; Kluemper, N.; Richter, A.P.; Büttner, T.; Kristiansen, G.; Ritter, M.; Ellinger, J. Early Dynamics of Quantitative SEPT9 and SHOX2 Methylation in Circulating Cell-Free Plasma DNA during Prostate Biopsy for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ID patient | Tumor Site | Staging (VIII ed. AJCC) | HPV (SCC Oropharynx) |
Treatment Type | Status of Disease (at last FU) |
Time point of FU with blood sample collected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS002 | Larynx | III | Surgery + adj | Right neck lymph nodes recurrence + pulmonary metastasis at 6 months of FU | 6 months (T2) | |
| BS003 | Oral cavity | II | Surgery + adj | Local recurrence at 8 months of FU | 6 months (T2) | |
| BS006 | Oral cavity | III | Surgery + adj | NED (FU 18 months) |
12 months (T3) | |
| BS007 | Oral cavity | II | Surgery | NED (FU 18 months) |
12 months (T3) | |
| BS008 | Oral cavity | II |
p16+, HPV DNA+ | RT-CHT | Tumor persistence at T1 | Pre-treatment (T0) |
| BS009 | Oral cavity | II | Surgery + adj | NED (FU 18 months) |
12 months (T3) | |
| BS010 | Larynx | II | CHT neo + RT | NED (FU 12 months) |
6 months (T2) | |
| BS011 | Oral cavity | III | Surgery + adj | Second primary tumor (SCC of the right tonsil) at 15 months of FU | 12 months (T3) | |
| BS013 | Oropharynx | II | p16+ | RT-CHT | NED (FU 18 months) |
12 months (T3) |
| BS014 | Larynx | III | Surgery + adj | Progressive disease with pulmonary metastasis at 4 months of FU | Pre-treatment (T0) | |
| BS015 | Hypopharynx | III | Surgery + adj | Pulmonary metastasis at 9 months of FU | 6 months (T2) | |
| BS016 | Larynx | II | Surgery + adj | NED (FU 18 months) |
12 months (T3) | |
| BS017 | Oropharynx | I | p16+ | RT-CHT | NED (FU 15 months) |
12 months (T3) |
| BS018 | Oropharynx | II | p16+ | RT-CHT | NED (FU 15 months) |
12 months (T3) |
| BS019 | Oropharynx | IV | NEG | RT-CHT | NED (FU 15 months) |
12 months (T3) |
| BS020 | Oropharynx | II | p16+ | RT-CHT | NED until T2, then lost at FU | 6 months (T2) |
| BS021 | Oral cavity | III | Surgery + adj | NED (FU 18 months) |
12 months (T3) | |
| BS029 | Larynx | II | Surgery | NED (FU 15 months) |
6 months (T2) | |
| BS023 | Oropharynx | I | p16+, HPV DNA+ | RT-CHT | NED (FU 12 months) |
6 months (T2) |
| BS024 | Oropharynx | I | p16+ | RT-CHT | NED (FU 12 months) |
6 months (T2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





