1. Introduction
Since the development of cephalometric radiography by Broadbent and Hofrath in 1931 [
1], a multitude of lateral cephalometric analyses have been developed for the purpose of orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. These analyses allow orthodontists to quantify and analyze relationships in the craniofacial region between the skeleton, dentition, and soft tissue. However, an accurate orthodontic diagnosis derived from a cephalometric radiograph requires accurate identification of key landmarks. Current methods of landmark identification include hand tracing with acetate paper or the use of computer software to manually mark digitized cephalometric radiographs, both of which have been shown to be equally reliable [
2].
Regardless of the method of cephalometric tracing, manual identification of anatomical structures presents inherent challenges. Factors such as differences in training and radiograph quality can cause variations in intra-examiner and inter-examiner reliability [
3]. Additionally, reliability varies depending on the landmark being identified. The landmarks condylion, gnathion, orbitale, and anterior nasal spine tended to have the lowest inter-examiner reliability among experienced dental radiologists and orthodontists [
4]. Computing technology demonstrates the potential to automate this process through artificial intelligence (AI).
AI is defined as the ability of computers or machines to mimic the human decision-making process through a series of algorithms [
5]. One area in which AI has been used in orthodontics is automatic lateral cephalometric landmark identification. Pioneered by Cohen in 1984, preliminary attempts to locate landmarks using AI were limited to easily identifiable landmarks such as sella and menton [
6]. Since Cohen’s attempt to automate landmark identification, several AI methods have been developed to increase accuracy and precision. Success rates of these methods, defined as a deviation of less than 2 mm between the distance measured from the AI-marked landmark and the expert-marked landmark, have varied from 35 to 84.7% depending on the methodology [
5]. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), a type of deep-learning algorithm, have demonstrated some of the highest accuracy in automatic lateral cephalometric landmark identification [
7]. The CNN You-Only-Look-Once version 3 (YOLOv3) is a frontrunner in this aspect [
8,
9]. Although cephalometric landmark identification with AI has improved in the last few decades, a few limitations still exist. Most studies have used far below the recommended 2300 images to train the AI in order to achieve the same level of accuracy as human examiners [
10]. Additionally, few studies have used AI trained from multiple types of x-ray machines, which limits real-world clinical application of the software [
11]. A study by Silva et al. addressed these limitations by training a CNN named CEFBOT (RadioMemory Ltd, Belo Horizonte, Brazil) with over 250,000 images from various x-ray sources to automatically perform Arnett’s analysis measurements [
12].
AI-based fully automated decision-making processes put machines in the driver’s seat and aim to replace human decisions. However, can machines and humans work together in making better decisions? This new concept is defined as AI/human augmentation, where the goal is to improve human decision-making by machine insights and recommendations. Although previous studies show a promising future for AI-based automatic cephalometric landmark identification and analysis, machines have not yet shown the ability to outperform humans. Therefore, one may theorize that in the realm of cephalometric landmark identification and analysis, the best decisions can be made by the collaboration of AI and humans. However, the literature lacks studies that evaluate how much clinicians with different experience levels benefit from this collaboration. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to assess the precision and accuracy of cephalometric analyses performed by AI alone and AI/human augmentation. We hypothesized that the least experienced clinicians would benefit the most from the AI/human augmentation in cephalometric analyses.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was reviewed and marked as IRB exempt by Indiana University Institutional Review Board (Protocol:14334) on March 14, 2022.
2.1. Sample Size Justification
Prior to the start of the study, a power analysis was conducted to determine the sample size. With a sample size of 30 images, the width of the 95% confidence interval for the intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) ranged from 0.08 and 0.28 from the estimated ICC, assuming the ICC is between 0.8 and 0.95. In addition, the width of the 95% confidence interval for the percentage of measurements within 1.5 mm of the ideal will range between 20% and 30% from the estimated percentage, assuming the percentage is between 75% and 95%.
2.2. Data Collection
Thirty lateral cephalograms were randomly selected from a pool of adult (age 18 or older) orthodontic patients treated in the Indiana University School of Dentistry (IUSD). Inclusion criteria included patients with class I skeletal relationship (defined as ANB between 0.5 to 5.0˚) and Angle class I dental relationship. Patients were excluded if they had craniofacial anomalies, missing or unerupted permanent incisors, missing or unerupted permanent molars, or poor quality initial cephalometric radiographs. The cephalometric radiographs were saved as JPEG files at a resolution of 200 dpi.
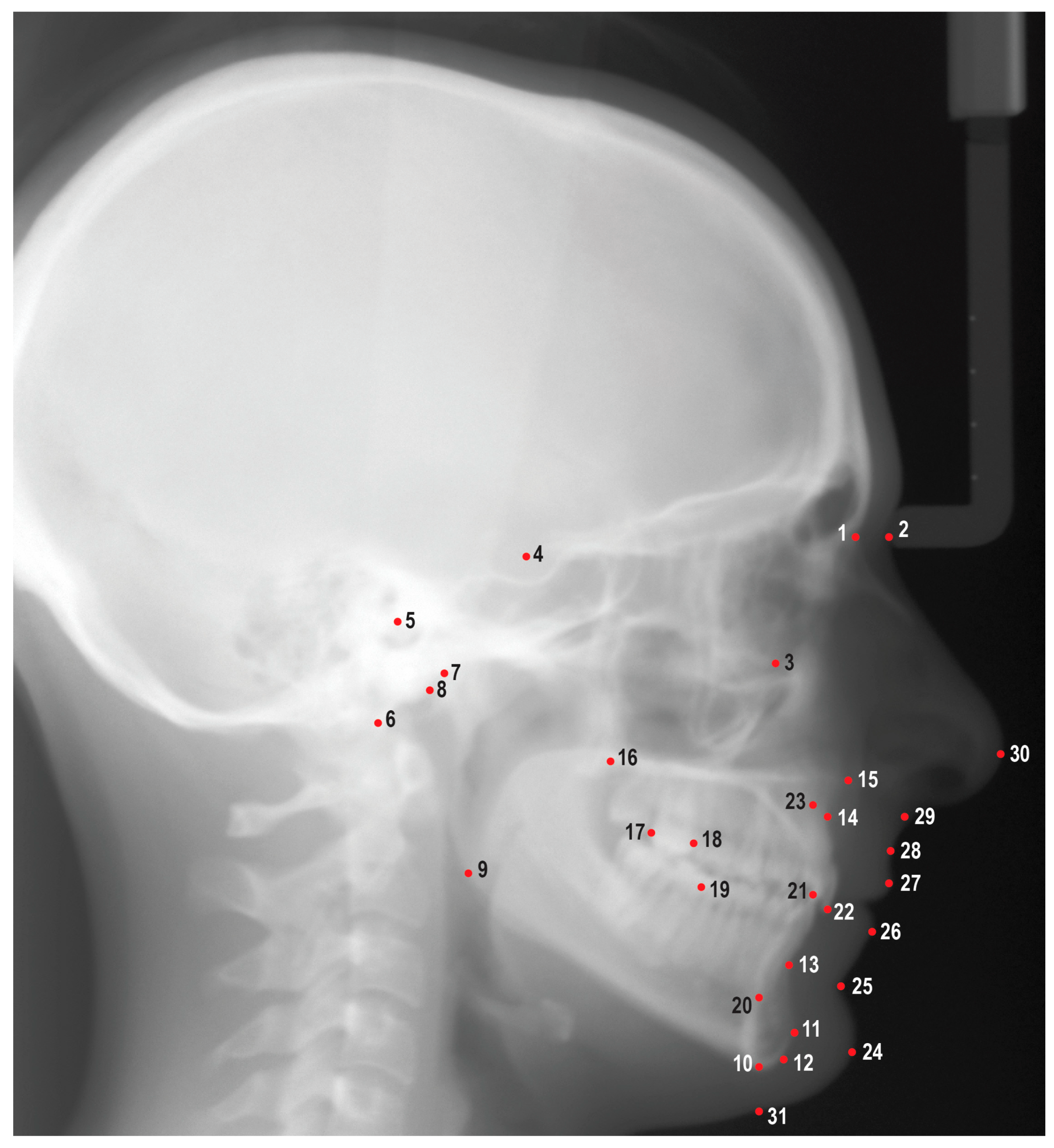
A calibration session led by an orthodontist with 25 years of experience was conducted to clarify the cephalometric landmark identification process and to define each of the landmarks. Four examiners, including an orthodontist with two years of experience, a second-year orthodontics resident, a fourth-year dental student, and a general dentist with one year of experience, each separately and manually identified 31 cephalometric landmarks on the 30 radiographs (
Figure 1). The same examiners retraced all radiographs after a period of one week in a randomized order. After completion of the manual tracings, the examiners traced the same cephalometric radiographs with the aid of a deep-learning AI (AI/human augmentation method). For these tracings, AI first located all the landmarks, and the examiners later adjusted points as needed. The AI/human augmentation method tracings were completed again after one week in a randomized order. Additionally, AI alone identified each of the landmarks without any adjustments and repeated the process one week later.
The gold standard for landmark positions were identified with the collaboration of an orthodontist and dental radiologist, each with 25 years of experience within their respective fields. Any disagreements resulted in the point being located at the midpoint both vertically and horizontally of the two points.
2.3. Software
RadioCef software (RadioMemory Ltd, Belo Horizonte, Brazil) with CEFBOT module was used for automated cephalometric landmark identification. This software uses four subsystems to locate cephalometric landmarks. Subsystem 1 is a convolutional neural network (CNN) that processes radiographs into probability maps of cephalometric landmark positions. Subsystem 2 is also a CNN that partitions radiographs by vectorizing skeletal and soft tissue borders and estimates the positions of cranial landmarks. Subsystem 3 combines the two CNN subsystems to estimate the position of landmarks, whereas subsystem 4 acts as a quality check to validate the previous results [
12]. CEFBOT has been trained with substantial cephalometric data with over 250,000 cephalometric images from multiple x-ray sources and providers [
12].
2.4. Data Analyses
Using the traced landmarks, 26 cephalometric measurements were measured for each of the traced radiographs (
Supplementary Table S1). Precision was evaluated by comparing the initial tracing to the final tracing completed after a period of one week for each of the examiners, with and without the aid of AI. The accuracy of each of these measurements was evaluated by comparing each examiners’ values, with and without the aid of AI, to the gold standard values through mean absolute error (MAE). MAEs were expressed as millimeters or degrees depending on if it was a linear or angular measurement.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
For both precision and accuracy analyses, MAEs with 95% confidence intervals were provided for differences between the gold standard and each initial measurement. For precision analysis, ICCs and Bland Altman plots were used to measure the agreement between initial and final measurements. All the analyses were done using SAS 9.4 (NC, Cary) software.
3. Results
3.1. Precision Analysis
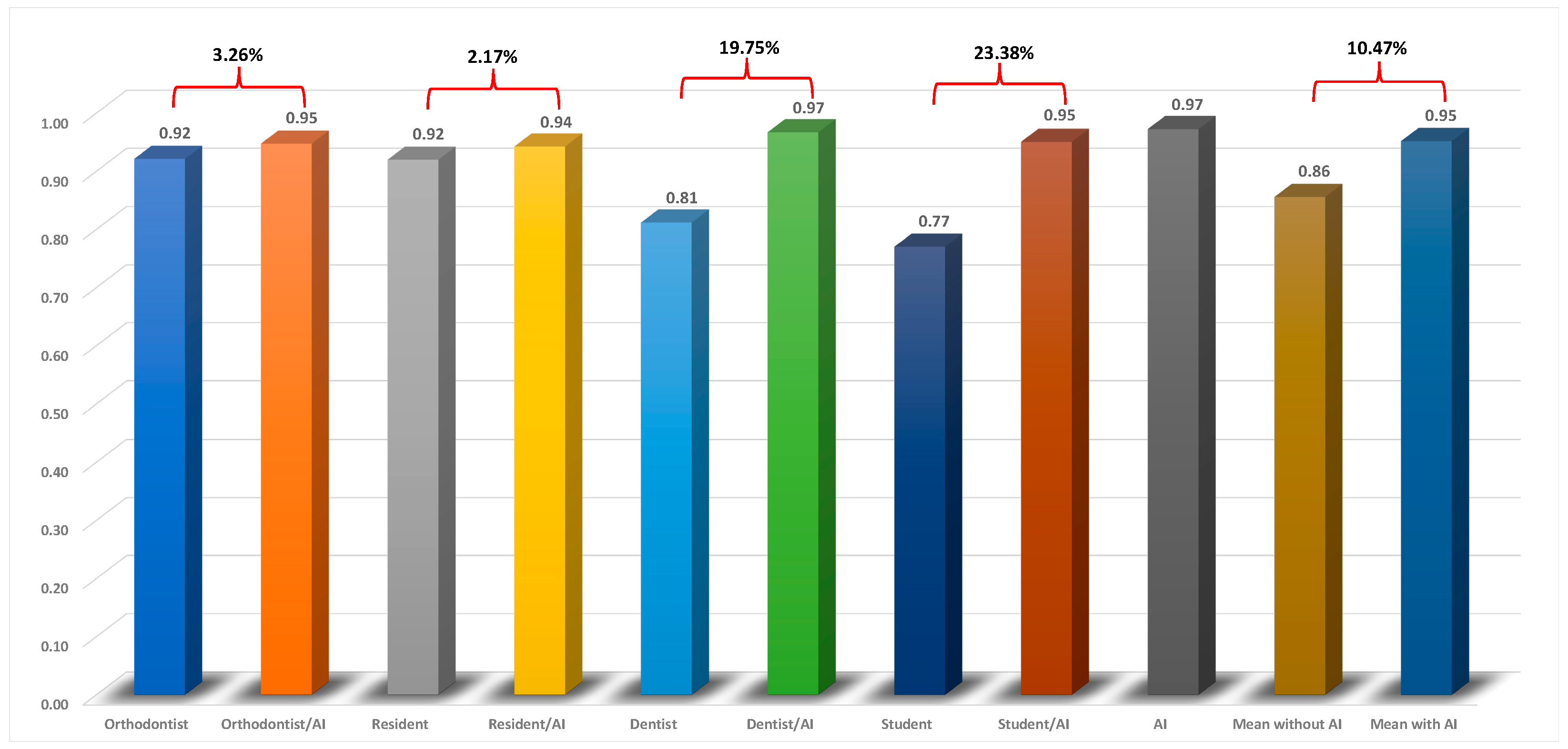
Table 1 shows the ICCs of the cephalometric measurements for each group. Mean ICC values were also calculated for all groups of examiners by averaging the individual cephalometric measurement ICC values. According to the results, AI showed excellent precision (ICCs>0.90). The precision of the examiners without the aid of AI generally followed their level of experience and exposure to the cephalometric analyses. The orthodontist, resident, dentist, and dental student had a mean ICC of 0.92, 0.92, 0.81, and 0.77, respectively. With the aid of AI, the precision of the orthodontist, resident, dentist, and dental student improved by 3.26%, 2.17%, 19.75%, and 23.38%, respectively (
Figure 2). Overall, the precision of the examiners improved by 10.47% with the aid of AI. As we expected, the least experienced clinicians benefitted the most from the help of AI.
Without the aid of AI, the cephalometric measurements which yielded the moderate precision were maxillary length, U1-NA (mm), SNA, ANB, and convexity angles. With AI/human augmentation method, 23 out of 26 measurements showed excellent precision, while U1-NA (mm), ANB, and convexity angles improved to good precision (
Table 1).
3.2. Accuracy Analysis
To compare each examiner
’s overall accuracy with and without AI
’s aid, an average of the MAEs was calculated for each group (
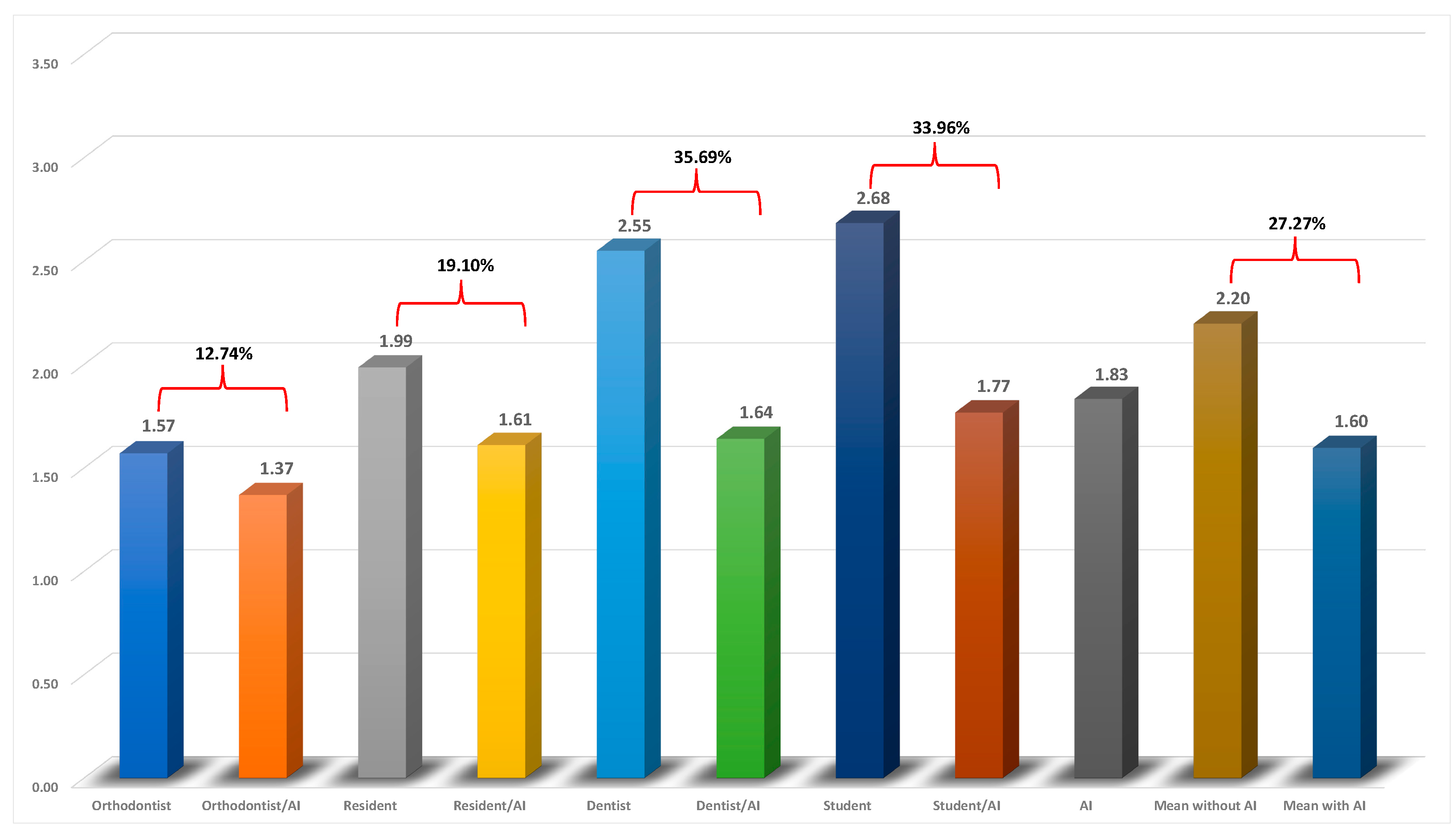
Table 2). The average MAE of CEFBOT was 1.83 (in mm/˚) which was within the clinically acceptable range (MAEs<2 mm/˚). The examiners
’ accuracy without AI generally followed their level of experience and exposure to the cephalometric analyses. The orthodontist and resident both had MAEs within the clinically acceptable range (1.57 and 1.99 mm/˚, respectively) while the accuracy of the dentist and dental student were out of the range with MAEs of 2.55 and 2.68 mm/˚, respectively. With the aid of AI, the accuracy of the orthodontist, resident, dentist, and dental student improved by 12.74%, 19.10%, 35.69%, and 33.96%, respectively (
Figure 3). AI/human augmentation method revealed clinically acceptable accuracies for all the examiner groups. Although the examiners
’ accuracy improved by 27.27% with the aid of AI, the least experienced clinicians benefitted the most from the AI/human augmentation method of cephalometric landmark identification.
Without the aid of AI, 13 out of 26 cephalometric measurements (maxillary and mandibular lengths, posterior face height, SNA, FMA, cranial base, U1-SN, L1-MP, L1-NB, interincisal, convexity and facial angles) yielded MAEs out of the clinically acceptable range (
Table 2). With AI/human augmentation method, 5 of these measurements (SNA, maxillary and mandibular lengths, convexity and facial angles) improved to be in the clinically acceptable range, while others remained out of the range although they showed some improvement in their accuracies (
Table 2).
4. Discussion
The precision of AI alone obtained in this study was similar to the levels of precision reported in other studies [
9,
12]. Silva and his colleagues found that the ICC of AI ranged from 0.768 to 0.997 for the 10 Arnett’s measurements. Excluding the lowest ICC measurement of Frankfort plane to true horizontal line (ICC = 0.768), the remaining ICC values were greater than 0.94, indicating excellent precision [
12]. This is similar to our study in that the ICC values of AI traced cephalometric measurements ranged from 0.890 to 1.00 across the 26 cephalometric measurements and demonstrated the greatest precision of all examiners. Hwang had also found that the YOLOv3 deep-learning software had excellent precision and marked each landmark at the exact same position compared to the human inter-examiner reliability of 0.97 mm [
9]. The accuracy of AI derived cephalometric measurements differed from Silva’s study which found that there were no statistically significant differences in accuracy of 9 of the 10 Arnett’s measurements used, and AI was unable to measure the 10th measurement [
9]. In this study, 10 out of 26 AI derived measurements revealed accuracies out of the clinically acceptable range. An interesting note was that of the 4 of these measurements involved the gonion landmark (posterior face height, FMA, SN-MP, and L1-MP). Posterior face height and L1-MP were significantly underestimated, whereas SN-MP and FMA were overestimated. These errors were consistent with AI software identifying gonion too superiorly relative to the gold standard, which is a likely source contributing to the mean error. This error was not limited to our study, as Hwang found that the mean error of YOLOv3 was 2.9 mm in the identification of the gonion landmark [
9].
Of the five cephalometric measurements that demonstrated moderate precision without the aid of AI, 4 of them (U1-NA distance, SNA, ANB, and convexity angles) involved “Point A” landmark. This suggests “Point A” may pose significant challenges in terms of reproducibility. Possibilities for this include the proximity of this point to the maxillary incisor root, superimposition of nearby structures, blurriness of the curvature in the anterior maxilla, and proximity of the canine fossa. Subspinale, also known as Point A, has shown good reliability in the x-axis but significant variation in the y-axis [
13].
In terms of accuracy averaged among all the examiners, 13 of the 26 measurements demonstrated MAEs greater than 2 mm or degrees without the use of AI. The increased MAEs of FMA and posterior face height may be due to the difficulty of identification of the gonion landmark. Gonion is a constructed point that relies on accurate identification of other landmarks, such as articulare and menton, to create tangent lines to the inferior body of the mandible and posterior border of the ramus. Slight inaccuracies in the tangent lines can dramatically affect the location of gonion. Among the 16 landmarks evaluated by Baumrind and Frantz, Gonion was found to be the least reliable landmark in both the x and y-axes in lateral cephalometric films [
14]. Additionally, in the case of FMA, it is possible the orbitale landmark was not accurately identified by all examiners. Orbitale has been shown to have significant variability in lateral cephalometric identification, especially in the y-axis [
15]. Inaccuracy of the maxillary length measurement may be due to difficulty of identification of the posterior nasal spine landmark, as it is often superimposed with the 3rd molar germ. Condylion and basion landmarks are also challenging to identify due to the superimposition of other craniofacial structures and thus may explain the higher MAEs of mandibular length and cranial base angle. Basion has shown significant variation in identification in both the x and y-coordinates [
15]. The incisor angulation measurements (U1-SN, U1-NA, L1-MP, L1-NB, and interincisal angle) also demonstrated increased MAEs. This could be due to difficulty in the identification of upper and lower incisor apices. Stabrun and Danielson found that upper and lower incisor apices were not reproducibly identified in 75% of cases [
16]. Misidentification of the incisor root apices results in alterations of the long axis of the upper and lower incisors, which affects the accuracy of U1-SN, U1-NA, L1-MP, L1-NB, and interincisal angles.
The AI/human augmentation method was a novel aspect of this study. This method demonstrated an increase in precision and accuracy of all examiner groups compared to the manual landmark identification technique, especially with the less experienced student and dentist examiners. This is likely due to the inherent ability of the AI to predictably locate each landmark in a nearly identical position [
9]. The less experienced examiners may not have changed the position of landmarks unless there was a significant discrepancy due to a lack of skill in tracing lateral cephalometric radiographs. Most measurements that showed clinical significance overlapped between AI alone and the AI/human augmentation method (posterior face height, FMA, L1-MP, L1-NB, and interincisal angles). This reinforces the idea that the location of difficult to locate landmarks, such as gonion and incisor apices, may not have been modified by examiners.
One limitation of this study is that a single examiner represented an entire dental professional group. Ideally, each experience level would comprise of multiple examiners. Additionally, we were unable to compare the accuracy or precision of individual landmarks. Future studies with multiple examiners and evaluation of the precision and accuracy of individual landmarks are recommended. Despite significant improvements in computing technology and AI in automatic lateral cephalometric landmark identification, AI alone cannot fully replace experienced clinicians. However, AI can serve as an educational tool and aid in landmark identification through the human/AI augmentation method, especially for less experienced clinicians.
5. Conclusions
Deep learning AI software demonstrated excellent precision and good accuracy in automated cephalometric analysis. Overall, precision and accuracy of the examiners with the aid of AI improved by 10.47% and 27.27%, respectively. The AI/human augmentation method significantly improved the precision and accuracy of less experienced dental professionals and students to that of an experienced orthodontist. These groups benefited the most from the approach.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
Preprints.org, Table S1: Cephalometric measurements and their definitions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Sumer Panesar and Hakan Turkkahraman; Data curation, Sumer Panesar, Alyssa Zhao, Eric Hollensbe, Ariel Wong, Vinicius Dutra and Hakan Turkkahraman; Formal analysis, Sumer Panesar, Surya Bhamidipalli, George Eckert, Vinicius Dutra and Hakan Turkkahraman; Investigation, Sumer Panesar, Vinicius Dutra and Hakan Turkkahraman; Methodology, Sumer Panesar, Alyssa Zhao, Eric Hollensbe, Ariel Wong and Vinicius Dutra; Project administration, Hakan Turkkahraman; Software, Hakan Turkkahraman; Supervision, Hakan Turkkahraman; Validation, Sumer Panesar; Writing – original draft, Sumer Panesar and Hakan Turkkahraman; Writing – review & editing, Sumer Panesar, Ariel Wong, Vinicius Dutra and Hakan Turkkahraman.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was reviewed and marked as IRB exempt by Indiana University Institutional Review Board (Protocol:14334) on March 14, 2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying this article are available in the article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Craig Eberhardt, EHR systems engineer, for help in filtering patient data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Leonardi, R.; Giordano, D.; Maiorana, F.; Spampinato, C. Automatic cephalometric analysis. Angle Orthod 2008, 78, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarakati, S.F.; Kula, K.S.; Ghoneima, A.A. The reliability and reproducibility of cephalometric measurements: a comparison of conventional and digital methods. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2012, 41, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.K.; Chen, Y.T.; Cheng, K.S. Accuracy of computerized automatic identification of cephalometric landmarks. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2000, 118, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durão, A.P.; Morosolli, A.; Pittayapat, P.; Bolstad, N.; Ferreira, A.P.; Jacobs, R. Cephalometric landmark variability among orthodontists and dentomaxillofacial radiologists: a comparative study. Imaging Sci Dent 2015, 45, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.; Montalvao, C.; Tanaka, R.; Kawai, T.; Bornstein, M.M. The use and performance of artificial intelligence applications in dental and maxillofacial radiology: A systematic review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2020, 49, 20190107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.M.; Ip, H.H.; Linney, A.D. A preliminary study of computer recognition and identification of skeletal landmarks as a new method of cephalometric analysis. Br J Orthod 1984, 11, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Luo, H.; Su, C.; Yao, Y.; Liao, W. Machine learning in dental, oral and craniofacial imaging: a review of recent progress. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Hwang, H.W.; Moon, J.H.; Yu, Y.; Kim, H.; Her, S.B.; Srinivasan, G.; Aljanabi, M.N.A.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.J. Automated identification of cephalometric landmarks: Part 1-Comparisons between the latest deep-learning methods YOLOV3 and SSD. Angle Orthod 2019, 89, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-W.; Park, J.-H.; Moon, J.-H.; Yu, Y.; Kim, H.; Her, S.-B.; Srinivasan, G.; Aljanabi, M.N.A.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.-J. Automated Identification of Cephalometric Landmarks: Part 2-Might It Be Better Than human? The Angle Orthodontist 2019, 90, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.H.; Hwang, H.W.; Yu, Y.; Kim, M.G.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.J. How much deep learning is enough for automatic identification to be reliable? Angle Orthod 2020, 90, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, I.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, M.; Cho, J.-H.; Hong, M.; Kang, K.-H.; Lim, S.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. Accuracy of automated identification of lateral cephalometric landmarks using cascade convolutional neural networks on lateral cephalograms from nationwide multi-centres. Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research 2021, 24, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.P.; Hughes, M.M.; Menezes, L.D.S.; de Melo, M.F.B.; Takeshita, W.M.; Freitas, P.H.L. Artificial intelligence-based cephalometric landmark annotation and measurements according to Arnett’s analysis: can we trust a bot to do that? Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2022, 20200548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broch, J.; Slagsvold, O.; Røsler, M. Error in landmark identification in lateral radiographic headplates. European Journal of Orthodontics 1981, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumrind, S.; Frantz, R.C. The reliability of head film measurements. 1. Landmark identification. Am J Orthod 1971, 60, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trpkova, B.; Major, P.; Prasad, N.; Nebbe, B. Cephalometric landmarks identification and reproducibility: a meta analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1997, 112, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabrun, A.E.; Danielsen, K. Precision in cephalometric landmark identification. Eur J Orthod 1982, 4, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).