Submitted:
28 April 2023
Posted:
04 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
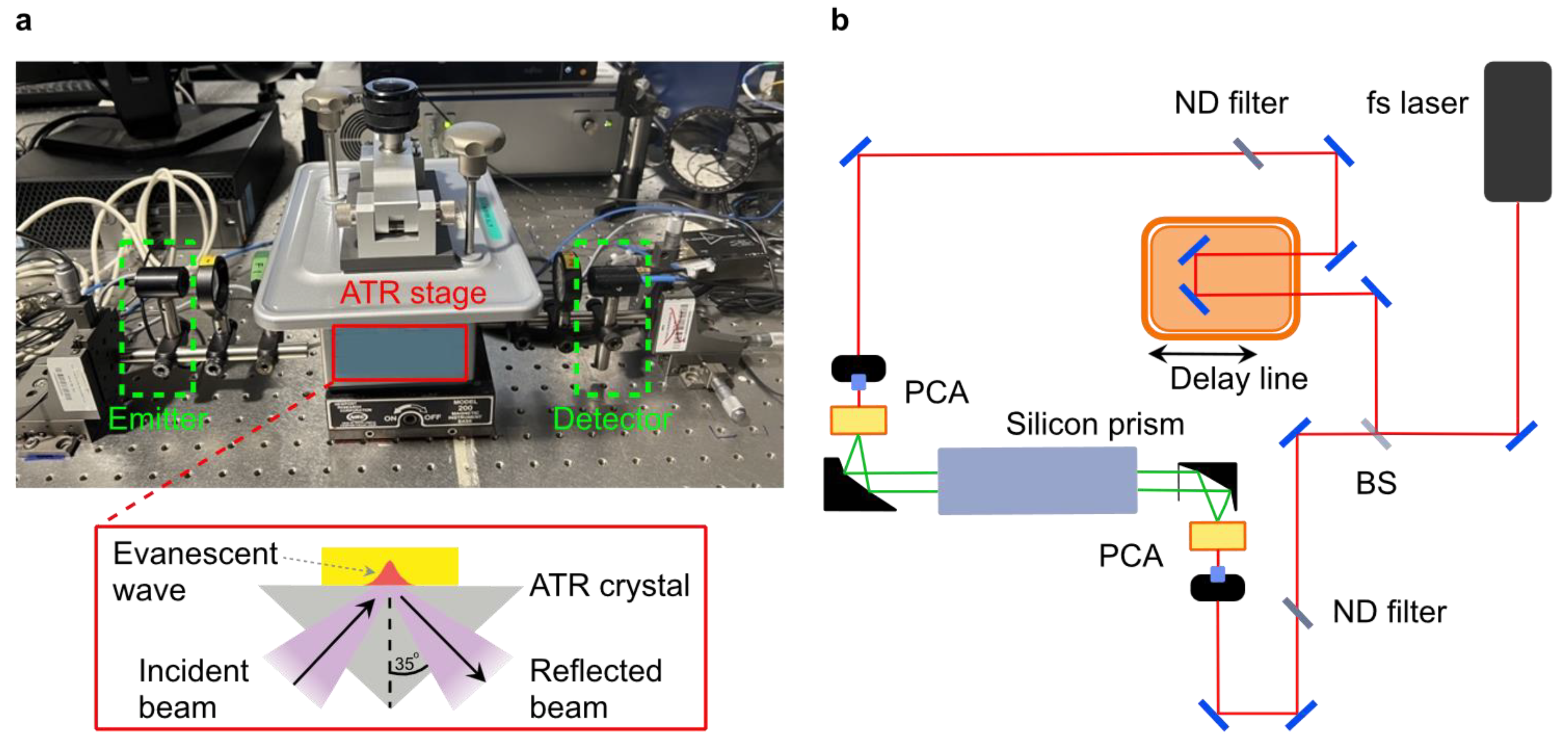
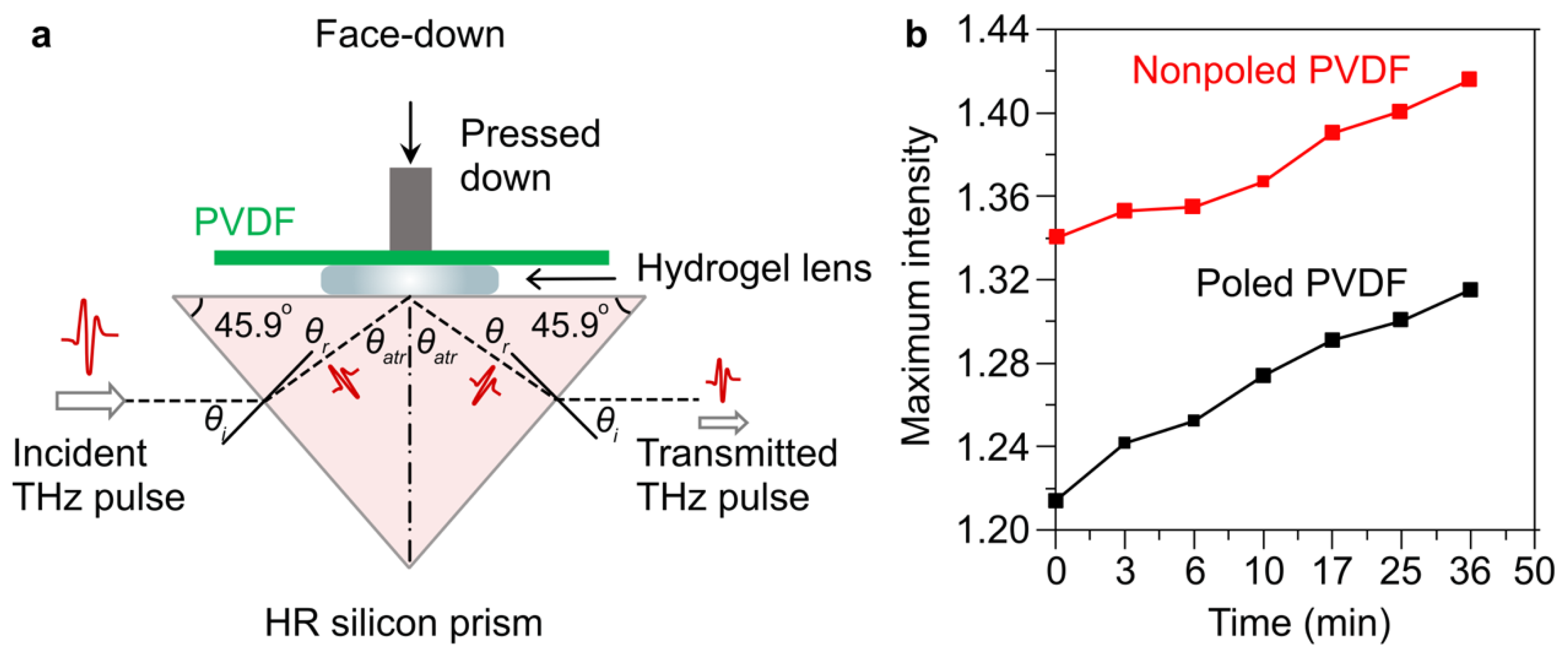
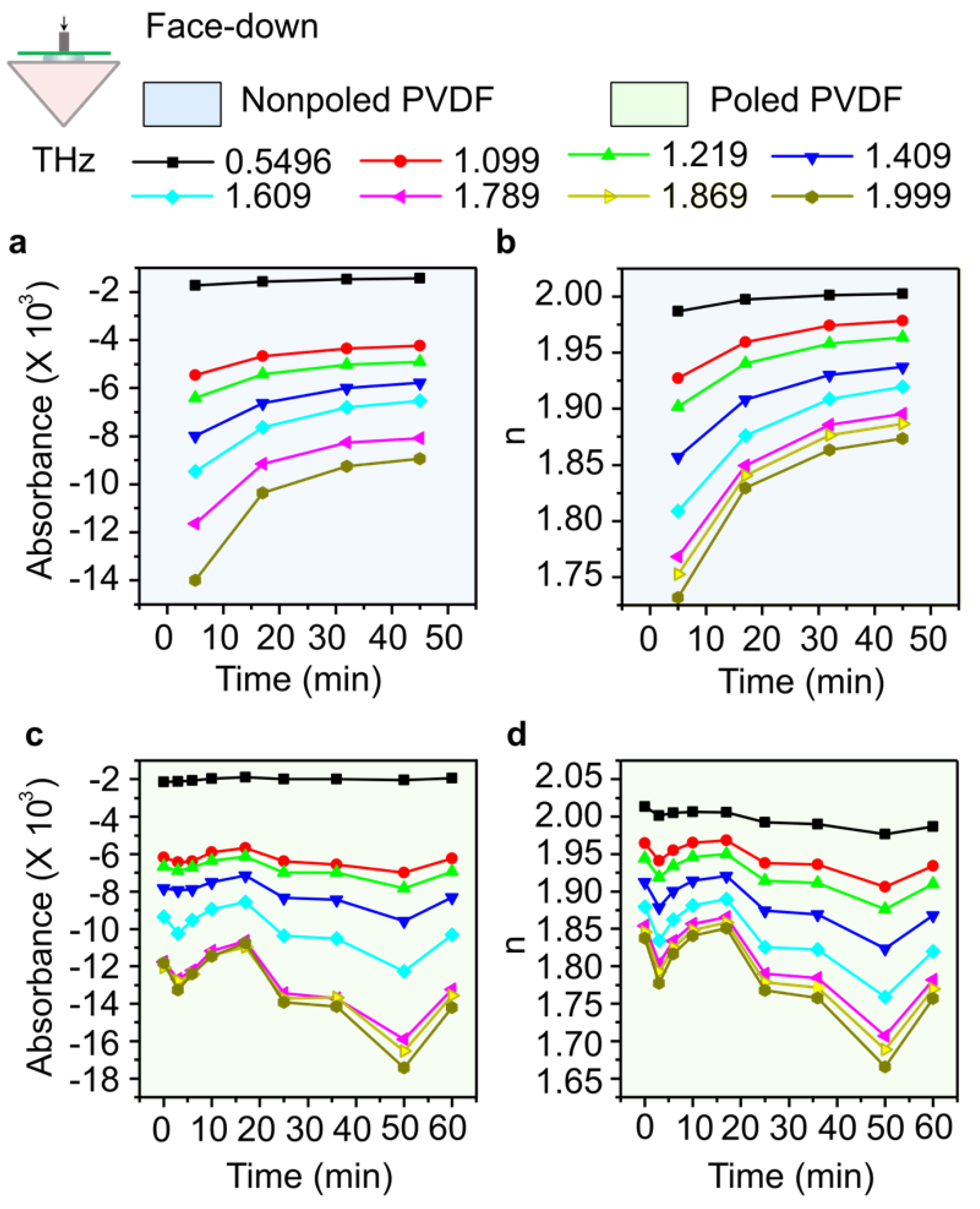
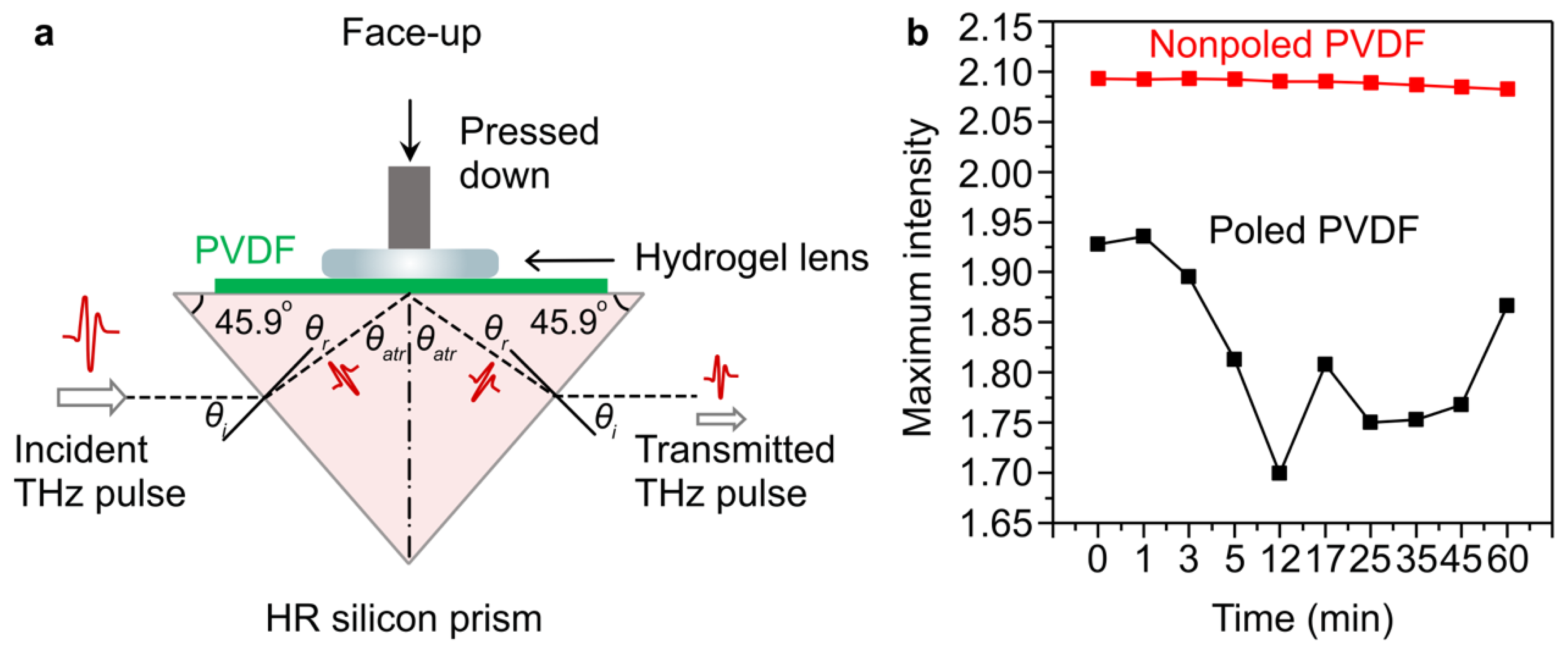
2. Experimental Section
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loh, X.J.; Guerin, W.; Guillaume, S.M. , Sustained delivery of doxorubicin from thermogelling poly (PEG/PPG/PTMC urethane) s for effective eradication of cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21249–21256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, X.J.; Nguyen, V.P.N.; Kuo, N.; Li, J. , Encapsulation of basic fibroblast growth factor in thermogelling copolymers preserves its bioactivity. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chee, P.L.; Owh, C.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Loh, X.J. , Safe and efficient membrane permeabilizing polymers based on PLLA for antibacterial applications. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 28947–28955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Deen, G.R.; Loh, X.; Gan, Y. , New stimuli-responsive copolymers of N-acryloyl-N′-alkyl piperazine and methyl methacrylate and their hydrogels. Polymer 2001, 42, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ong, P.J.; Liu, S.; Thitsartarn, W.; Tan, M.J.B.H.; Suwardi, A.; Zhu, Q.; Loh, X.J. , Recent Advances in Host-Guest Supramolecular Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Chem. –Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metha, A.B.; Crane, A.M.; 3rd, H.G.R.; Thomsen, S.L.; Albrecht, D.G. , Maintaining the Cornea and the General Physiological Environment in Visual Neurophysiology Experiments. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 109, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, A.; Li, H.; Lewittes, D.M.; Dong, B.; Liu, W.; Shu, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, H.F. , Fabricating Customized Hydrogel Contact Lens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnt, N.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.J. , The R-evolution of Contact Lenses: Will Long-term Contact Lens Wearers in the Future be the Same as Now? Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2022, 45, 101557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, X.J. , Poly (DMAEMA-co-PPGMA): Dual-responsive “reversible” micelles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.N.; Kuo, N.; Loh, X.J. , New biocompatible thermogelling copolymers containing ethylene-butylene segments exhibiting very low gelation concentrations. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2150–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Tan, B.H.; Li, Z.; Loh, X.J. , Control of PLA stereoisomers-based polyurethane elastomers as highly efficient shape memory materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, W.Y.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Soo, X.Y.D.; Thitsartarn, W.; Liu, S.; Tan, B.H.; Suwardi, A.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Q. , Responsive hydrogel dressings for intelligent wound management. BMEMat 2023, e12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, X.Y.D.; Png, Z.M.; Wang, X.; Chua, M.H.; Ong, P.J.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Chi, D.; Xu, J.; Loh, X.J. , Rapid UV-curable form-stable polyethylene-glycol-based phase change material. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 2747–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.C.; Sugiarto, S.; Ong, P.J.; Soo, X.Y.D.; Ni, X.; Luo, P.; Hnin, Y.Y.K.; See, J.S.Y.; Wei, F.; Zheng, R. , Lignin-g-polycaprolactone as a form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage application. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Muiruri, J.K.; Soo, X.Y.D.; Liu, S.; Thitsartarn, W.; Tan, B.H.; Suwardi, A.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Loh, X.J. , Bio-Polypropylene and Polypropylene-based Biocomposites: Solutions for a Sustainable Future. Chem. Asian J. 2022, e202200972–e202200972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muiruri, J.K.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Soo, X.Y.D.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Kong, J.; Cao, J.; Tan, B.H.; Suwardi, A.; Li, Z. , Recent Advances of Sustainable Short-chain length Polyhydroxyalkanoates (Scl-PHAs)–Plant Biomass Composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 111882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Png, Z.M.; Wang, C.-G.; Yeo, J.; Lee, J.J.C.; Surat'man, N.E.B.; Tan, Y.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Tan, M.B.H.; Xu, J. , Stimuli-responsive Structure-Property Switchable Polymer Materials. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, E.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, G.; Tan, T.L.; Xu, J.; Yang, S.-W. , Self-organization of PEDOT: PSS induced by green and water-soluble organic molecules. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 9745–9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yildirim, E.; Wang, X.; Kyaw, A.K.K.; Tang, T.; Soo, X.Y.D.; Wong, Z.M.; Wu, G.; Yang, S.-W.; Xu, J. , Effect of substituents in sulfoxides on the enhancement of thermoelectric properties of PEDOT: PSS: experimental and modelling evidence. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2020, 5, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Kyaw, A.K.K.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, J. , Water-dispersible conducting polyazulene and its application in thermoelectrics. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 9388–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrasko, G. , Hydrogel Dehydration in Various Environments. Int. Contact Lens Clin. 1983, 10, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tranoudis, I.; Efron, N. , Water Properties of Soft Contact Lens Materials. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2004, 27, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, N.; Efron, N.; Bruce, A.; Duldig, D.; Russo, N. , Dehydration of Hydrogel Lenses: Environmental Influences During Normal Wear. Am. J. Optom. Physiol. Opt. 1988, 65, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, P.; Ors, J. , New Materials Demand More Accurate Measurements of Performance. Spectrum 1997, 12, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimov, P.; Yokoi, N.; Peev, N.; Georgiev, G.A. , Impact of Air Exposure Time on the Water Contact Angles of Daily Disposable Silicone Hydrogels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. , Biomedical Applications of Hydrogels: A Review of Patents and Commercial Products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatt, I.; Chaston, J. , The Effect of Temperature on Refractive Index, Water Content and Central Thickness of Hydrogel Contact Lenses. Int. Contact Lens Clin. 1980, 7, 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, S.; Sickenberger, W. , A Novel In-Vitro Method for Assessing Contact Lens Surface Dewetting: Noninvasive Keratograph Dry-up Time (NIK-DUT). Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2017, 40, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weed, K.; Fonn, D.; Potvin, R. , Discontinuation of Contact Lens Wear. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1993, 70, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Liu, Y.; Gilbert, J.L. , Micromechanical Measurement of Adhesion of Dehydrating Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lenses to Corneal Tissue. Acta Biomater. 2021, 127, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, B.; Sweeney, D.; Seger, R. , Epithelial Erosions Caused by Thin High Water Content Lenses. Clin Exp Optom 1986, 69, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Cho, H.; Yeh, Y.; Yang, M. , Improvement of the Surface Wettability of Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lenses via Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly Technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranoudis, I.; Efron, N. , In-eye Performance of Soft Contact Lenses Made from Different Materials. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2004, 27, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajchel, D.; Krysztofiak, K.; Szyczewski, A. , Influence of Sodium Hyaluronate on Dehydration and Water Distribution in Soft Contact Lenses. Opt. Appl. 2016, 46, 483–496. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, N.; Morgan, P.B. , Hydrogel Contact Lens Dehydration and Oxygen Transmissibility. Clao. J. 1999, 25, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Efron, N.; Brennan, N.; Bruce, A.; Duldig, D.; Russo, N. , Dehydration of Hydrogel Lenses under Normal Wearing Conditions. CLAO J. 1987, 13, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mousa, G.; Callender, M.; Sivak, J.; Egan, D. , The Effect of the Hydration Characteristics of Hydrogel Lenses on the Refractive Index. Int. Contact Lens Clin. 1983, 10, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, N. , A Simple Instrument for Measuring the Water Content of Hydrogel Lenses. Int. Contact Lens Clin. 1983, 10, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Galas, S.; Enns, J. , Humidity-conditioned Gravimetric Method to Measure the Water Content of Hydrogel Contact Lens Materials. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1993, 70, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helton, D., W. L., Hydrogel Contact Lens Dehydration Rates Determined by Thermogravimetric Analysis. CLAO J. 1991, 17, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mirejovsky, D.; Patel, A.; Young, G. , Water Properties of Hydrogel Contact Lens Materials: A Possible Predictive Model for Corneal Desiccation Staining. Biomaterials 1993, 14, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConville, P.; Pope, J.M. , Diffusion Limited Evaporation Rates in Hydrogel Contact Lenses. CLAO J. 2001, 27, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.; May, C.; Nazar, L.; Simpson, T. , In Vitro Evaluation of the Dehydration Characteristics of Silicone Hydrogel and Conventional Hydrogel Contact Lens Materials. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2002, 25, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-M.; Lee, H.-L. , Sorption/desorption properties of water vapour in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate): 1. Experimental and preliminary analysis. Polymer 1996, 37, 3815–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.W.; Huff, J.W.; Holden, B.A. , Proton NMR Relaxation in Hydrogel Contact Lenses: Correlation with In Vivo Lens Dehydration Data. Curr. Eye Res. 1990, 9, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConville, P.; Pope, J.M. , 1H NMR T2 Relaxation in Contact Lens Hydrogels as a Probe of Water Mobility. Polymer 2001, 42, 3559–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y.; Ikeda-Fukazawa, T. , Structural Changes of Water in a Hydrogel During Dehydration. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 034501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ding, J.; Cui, F.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. , Polymer-Protein Interaction, Water Retention, and Biocompatibility of a Stimuli-sensitive Superporous Hydrogel Containing Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. J. Appl. Poly. Sci. 2008, 108, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbudayanidhi, S.; Nayak, S.K.; Mohanty, S. , Synthesis and Water State Characterization of Polysodium Acrylate/Cellulose Microfibril Hydrogels. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2014, 27, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munćan, J.; Mileusnić, I.; Rosić, J.Š.; Vasić-Milovanović, A.; Matija, L. , Water Properties of Soft Contact Lenses: A Comparative Near-Infrared Study of Two Hydrogel Materials. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 3737916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Fernández, F.J.; Guaus, E.; Martínez, C.; Vilaseca, M. , Terahertz-based System for Dehydration Analysis of Hydrogel Contact Lenses. Opt. Appl. 2019, 49, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fu, W.; Luo, Y. , Biomedical Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirga, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kondo, N.; Tanaka, K.; Ogawa, Y. , Hydration State Inside HeLa Cell Monolayer Investigated with Terahertz Spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 253701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gente, R.; Koch, M. , Monitoring Leaf Water Content with THz and sub-THz Waves. Plant Methods 2015, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.-C. , Terahertz Sensor for Noncontact and Non-destructive Inspection of Automotive Paints. Int. J. Sens. Netw. Data Commun. 2014, 4, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Rahman, A.K.; Rao, B. , Early Detection of Skin Cancer via Terahertz Spectral Profiling and 3D Imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 82, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guo, T.; Zhang, X.; Cao, S.; Ding, X. , Toxic Chemical Compound Detection by Terahertz Spectroscopy: A Review. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 37, 20170021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




