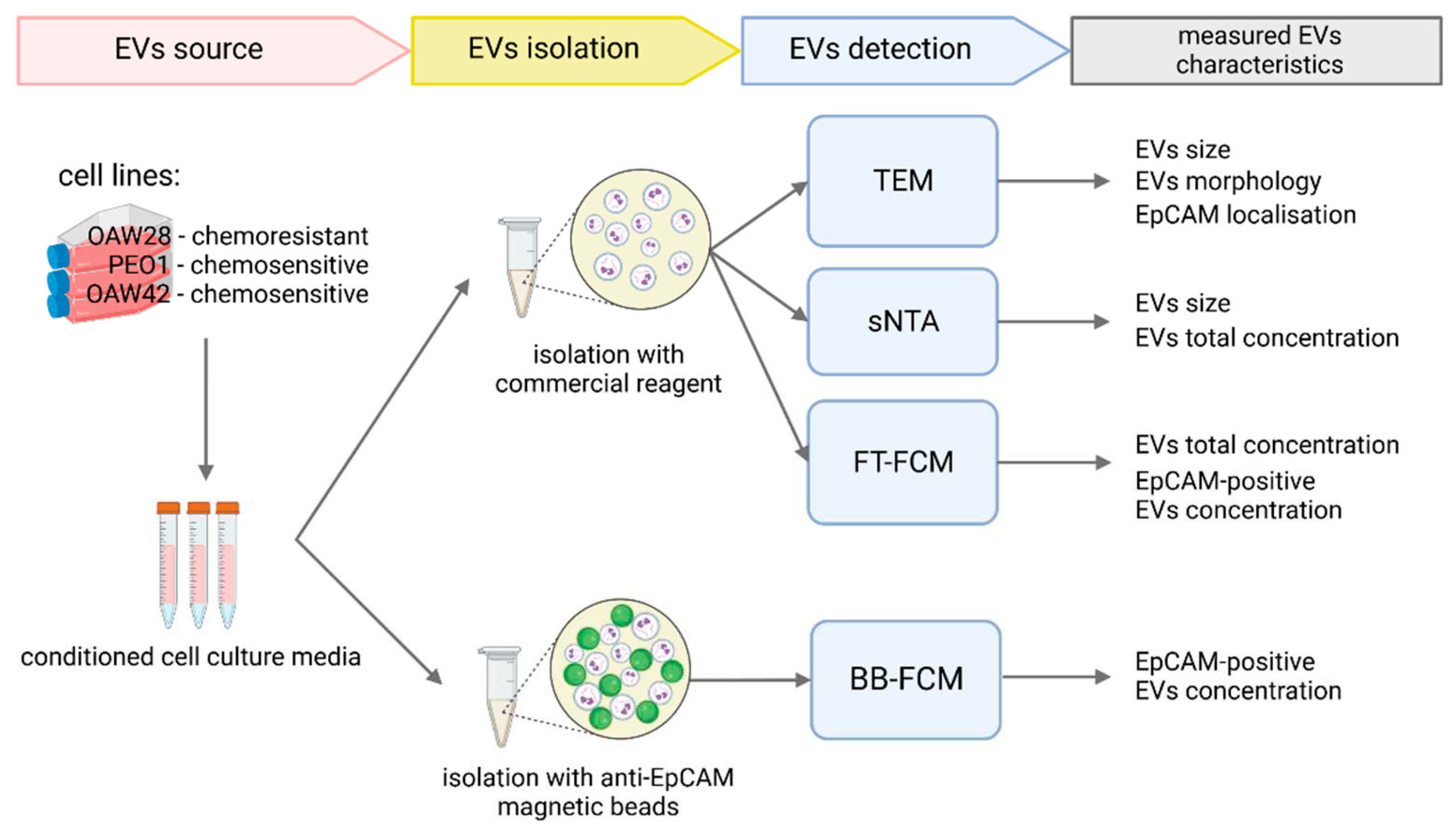
1. Introduction
Ovarian cancer (OC), despite its infrequent incidence, is the most lethal malignancy of the female reproductive system, with most patients presenting with advance stage tumors (FIGO stage III, IV) [
1]. Although there has been an overall decreasing trend of incidence and mortality of OC over the past decade, a substantial increase in incidence has been observed in younger females [
2]. In addition to the late detection of the disease, the main reason for the poor prognosis is resistance to pharmacotherapy. Despite novel targeted drugs such as poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPis), carboplatin with added paclitaxel remains the standard first-line treatment for advanced OC. Moreover, PARPis are indicated for maintenance treatment in the first line and relapsed settings of patients who have responded to platinum-based medicine [
3,
4]. Since platinum-resistant OC is invariably a fatal disease, a central goal in OC research is the development of novel strategies to overcome platinum resistance. Treatment for OC is therefore moving towards personalized therapy. However, selection criteria are not entirely clear, since at present there are no validated molecular predictive biomarkers for platinum resistance [
4].
One of the major challenges in the search for clinical biomarkers for OC is that OC is not a single disease, but rather a myriad of different malignancies with different targets that share a common anatomical location at presentation. In our article, therefore, we have focused on the high-grade serous subtype of ovarian cancer (HGSOC), as the dominant and most lethal subtype of OC [
5].
In recent years, tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) have received significant attention as a promising source of minimally invasive biomarkers, including in OC [
6,
7,
8,
9]. According to the International Society of Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV), the term EVs is appropriate terminology for heterogeneous populations of cell-derived nanoscale vesicles released under physiological and pathological conditions, which can be isolated from cell culture supernatant or body fluids [
10]. Due to their important role in communication between cells [
11], it is not surprising that EVs’ cargo, concentration and size have been shown to be unique in tumor-states. EVs are therefore ideal candidates for aiding prediction of chemoresistance to platinum-based medicines. Although among published studies, those showing that the total concentration of OC-derived EVs has the potential for providing information on diagnosis predominate [
12,
13,
14], the results of some studies do not confirm this [
7,
15], so the question arises as to whether determining the EV concentration alone is sufficient for OC diagnosis. Apart from one preliminary study, the conclusion of which was that determining the EVs’ protein level could be useful in evaluating patients’ response to therapy, we did not find any published study on the importance of determining the total EV concentration as a predictive biomarker in OC [
16].
Among specific EV cargos, particular attention has been paid to the epithelial cellular adhesion molecule (EpCAM) [
6,
7,
14,
17,
18]. Its expression is upregulated in solid epithelial cancer and stem cells. EpCAM can be found in disseminated tumor cells, circulating tumor cells and EVs [
19]. However, (to our surprise), the relevance of analysis of EVs in predicting chemoresistance has been largely unexplored. Research on EpCAM specific EVs might also shed light on the contradictory results of immunohistochemical evaluation of EpCAM overexpression in ovarian tumors in relation to its prognostic value, in terms of overall survival and response to chemotherapy [
20,
21,
22,
23]. Moreover, the determination of EpCAM specific EVs might be helpful in evaluating the potential of therapeutic strategies targeting EpCAM and could explain the disparate results sometimes obtained concerning the effectiveness of EpCAM-based medicine [
24,
25].
Patients’ body fluids, especially blood, as a source of EVs for the study of biomarkers, have several limitations, principally the extremely high heterogeneity of vesicles and low proportion of EVs of tumor origin [
26,
27]. EVs isolated from conditioned media of relevant cultured cells can therefore elucidate these shortcomings. Moreover, the use of well-characterized cancer cell lines to model HGSOC
in vitro can be particularly valuable in the age of personalized therapy. They at least increase the likelihood that the conclusions reached in an
in vitro setting will be transferable to a clinical one. Unfortunately, many of the top cell lines in terms of publication figures poorly recapitulate the genetic features of HGSOC [
28,
29,
30]. In contrast, most suitable cell lines for an HGSOC model (e.g. KURAMOCHI; COV362, OAW28) are rarely used in laboratories [
28]. An additional problem in cell-line models is a lack of patient-derived cell lines of chemoresistant HGSOC. The majority of cell lines used to represent platinum-resistant disease have been generated
in vitro by exposing cells to platinum-based medicines. The type of drug exposure used to elicit the resistant phenotype is therefore unrealistic and, as a consequence, the mechanism is likely to be different from those acting within a patient's body [
5].
In order to identify the characteristics of EVs that have the potential to predict resistance to platinum-based medicine in HGSOC, we compared EVs released from a cell line derived from a clinically confirmed chemoresistant patient and EVs released from two cell lines from tumors sensitive to platinum-based chemotherapy. We showed that the EV concentration did not differ significantly, although a significantly higher concentration of EpCAM specific EVs and a higher proportion of medium/large particles was typical of the chemoresistant HGSOC cell line. A strong correlation between EpCAM specific EV concentration and cell membrane EpCAM expression supports the use of EpCAM specific EVs as cellular surrogates for EpCAM as a biomarker. Although the results of the current study should be validated in clinical samples, they reveal novel characteristics of EVs that may have the potential to aid the prediction of platinum resistant HGSOC and thereby enable the selection of personalized therapy.
3. Discussion
Despite novel targeted drugs, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer remains a fatal disease. Moreover, there are currently no validated molecular predictive biomarkers for platinum resistance. Identification of novel predictive biomarkers to circumvent platinum resistance is thus highly desirable [
4]. Tumour-derived EVs are one promising source of such biomarkers, especially since their cargo, concentration and size have been shown to be unique in tumour-states [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. EV publications in the field of OC chemoresistance are primarily dedicated to research of EV-mediated drug-resistance mechanisms [
39,
40]. The main proposed roles of EVs in this field are drug-export, antigen sink, transfer of resistant phenotype and change in the tumour microenvironment [
37,
39]. However, the potential of EVs for predicting response to platinum-based therapy in OC has been largely unexplored.
In this study, three OC cell lines, OAW28, OAW24 and PEO1, were used as the EV source, in order to examine the characteristics of EVs from a patient who did not respond to cisplatin (OAW28) compared to two patients with a complete response (PEO1, OAW42) [
31,
32]. Since EVs are a promising tool for liquid biopsy, we chose cell lines that had been isolated from patients’ ascites [
31,
32]. We ensured that all three cell lines were well characterized. The OAW28 cell line is among the twelve best candidates for
in vitro studies of HGSOC. Evaluation was made on the basis of correlation of genomic characteristics between tumour samples and cell lines. For this purpose, Domcke
et.al. made a data comparison between The Cancer Genome Atlas, (TCGA) and The Broad-Novartis Cancer Cell Line Encyclopaedia (CCLE) [
28]. Moreover, among 39 OC cell lines tested, the highest concentration of carboplatin causing 50 % growth inhibition was determined for the OAW28 cell line [
29]. In view of novel strategies in the therapy of HGSOC, it is also important that OAW28 is without
BRCA1/2 mutations [
28,
29]. For direct comparison of HGSOC EV characteristics, we chose another HGSOC cell line, PEO1 [
29,
30]. Interestingly, the PEO1 cell line has a reversion of the deleterious
BRCA2 mutation as evidence of selective pressure against
BRCA1/2 mutations. Additionally, loss of heterozygosity (LOH) was detected at both
BRCA1 and
BRCA2 loci [
41]. The third cell line, OAW42, is probably not of the HGSOC subtype, although the original annotation was serous [
28,
29,
32]. However, during culturing, OAW42 cells show ‘epithelial’ morphological characteristics [Beaufort 2014]. We chose this cell line in order to determine whether differences in EV characteristics could be the result of different tumour subtypes. OAW42 shows no
TP53 mutation but a
PIK3CA mutation [
28,
29]. Examination of the
BRCA1 status gave contradictory results; a
BRCA1 mutation was detected in one study but this result was not confirmed in two other studies [
28,
29,
41]. In addition, OAW42 did not show LOH at the
BRCA1/2 locus [
41].
Cells release a heterogeneous population of EVs with different sizes (30–10,000 nm) [
42]. EVs are a mixture of exosomes and ectosomes (microparticles/microvesicles), which differ in size and biogenesis. Exosomes are released on the exocytosis of multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Ectosomes, on the other hand, bud directly outwards from the plasma membrane and tend to be larger in size. Due to overlapping size ranges, current EV isolation methods are not able to differentiate precisely between subtypes of EVs and so assigning an EV to a particular biogenesis pathway remains difficult. We therefore refer to “small EVs” (sEVs) and “medium/large EVs” (m/lEVs) based on the size range: < 200 nm [small] and > 200 nm [large and medium], respectively, as recommended by the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles [
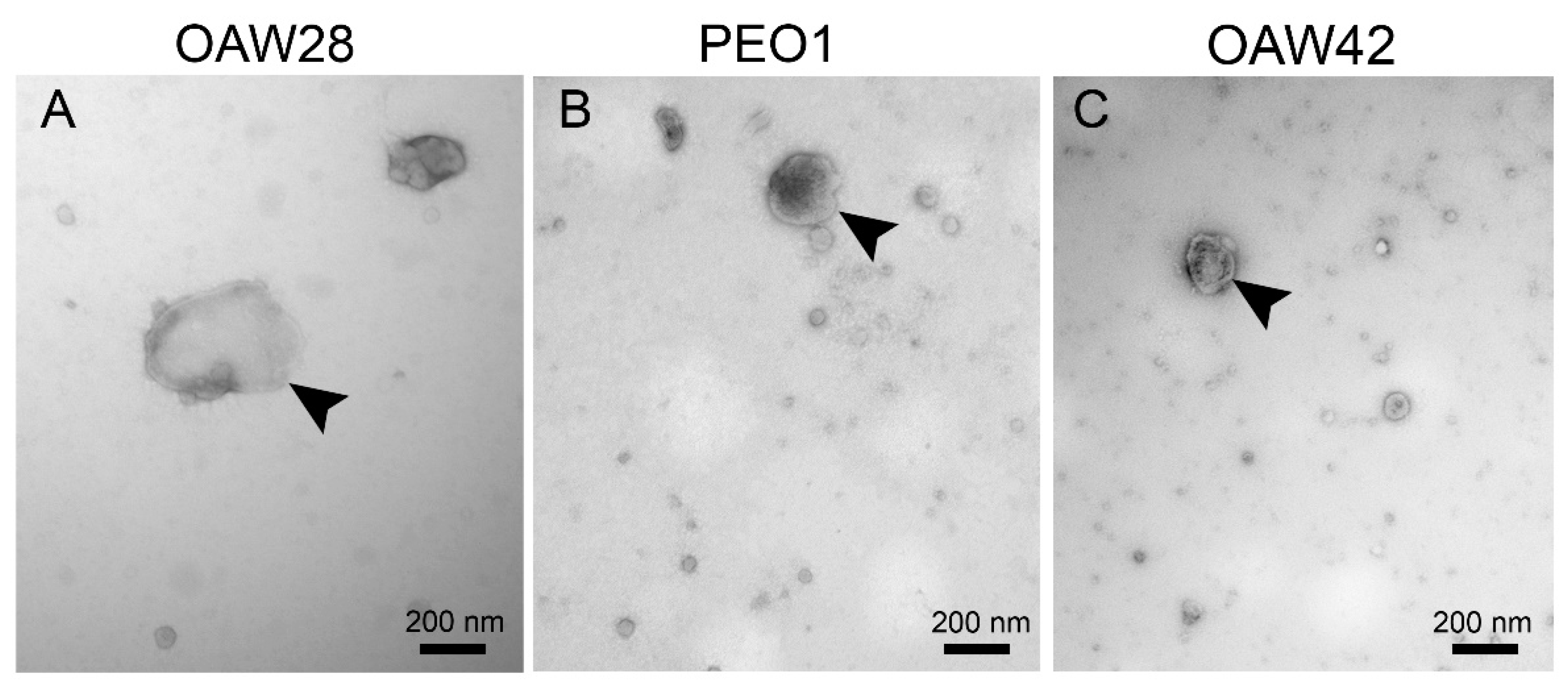
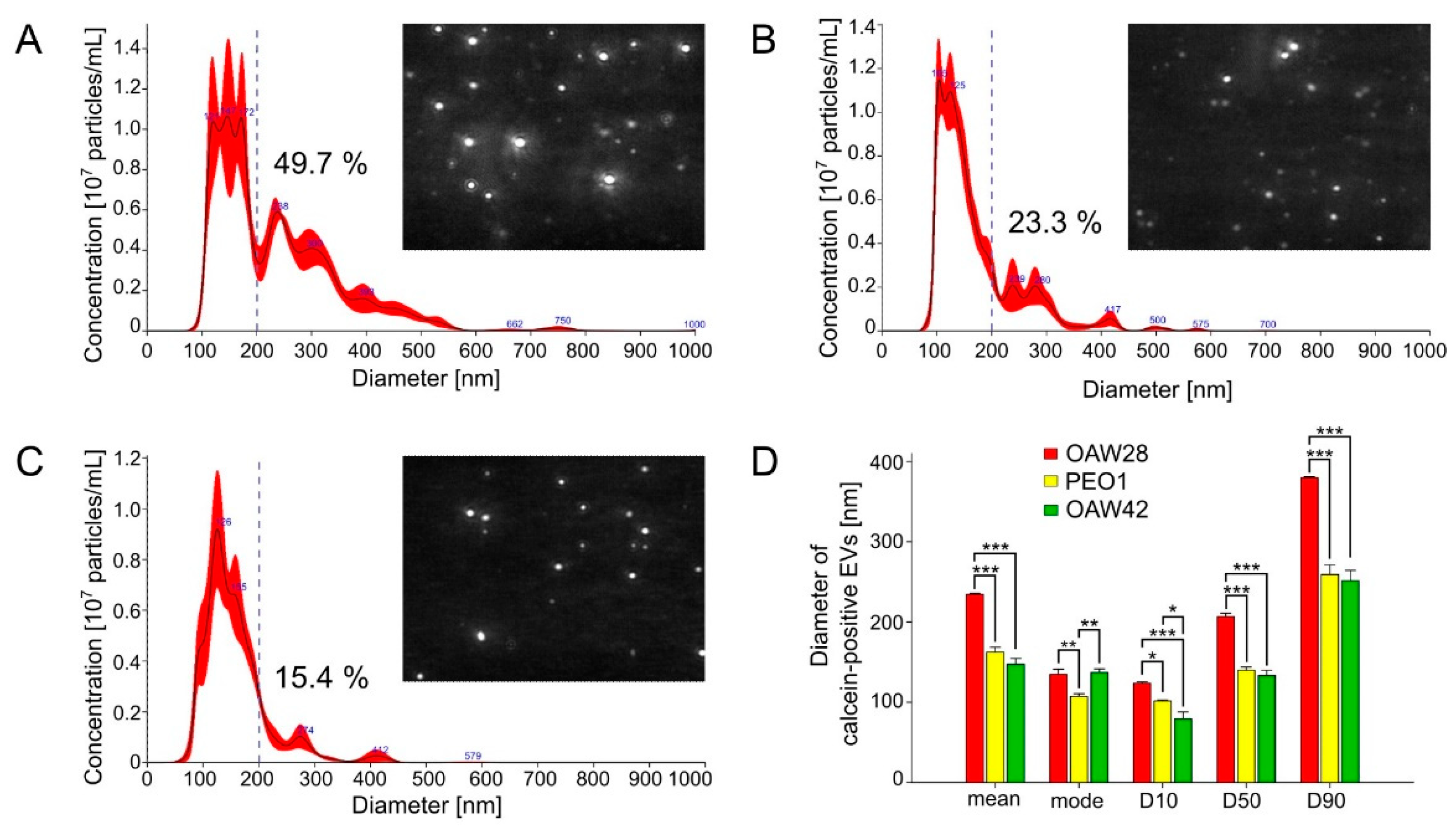
34]. TEM analysis revealed that all three cell lines released spherical EVs with different sizes, although a more heterogeneous size distribution and higher proportion of m/lEVs was observed among EVs released from OAW28 cells, which was confirmed by the results of S-NTA. On the other hand, the EVs from all three cell lines were most commonly found in the size range from 100 to 140 nm, which falls within the size range of sEVs. This result is comparable with a previously published study obtained with an OVCAR3 cell line, as another cell line of the HGSOC subtype, and analysed with S-NTA [
17,
29]. However, the most commonly found size of EVs released from OAW28 cells was larger than that from PEO1-derived EVs, while OAW42-derived and OAW28-derived EVs did not differ. This observation indicates that the size of the major peak of EVs depends on other factors, such as different histological subtype [
17]. On the other hand, a higher proportion of m/lEVs released from OAW28 was observed compared to PEO1-derived and OAW42-derived EVs. Therefore, this result is probably not due to differences between EVs released from different histological subtypes but may indicate an association of a higher number of m/lEVs with resistance to chemotherapy. The difference in the size distribution of EVs is probably a very early sign of a changed state in the cell, which is reflected in the biogenesis of EVs. It was observed that the proportion of EVs of different sizes released from HeLa cells was modified on silencing of some cell components involved in EV formation [
35]. One problem with determining the significance of the modified size distribution is that its analysis also depends on the method of EV isolation. Although the size distribution determined by S-NTA showed a major EV peak independently of the isolation method, we still do not know which subpopulations are lost during the isolation process [
42]. This problem is even greater when EVs are isolated from a patient’s body fluid. Although studies on the association of a larger size of EVs with a worse prognosis already exist for EVs from the blood of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [
43,
44], such research in the field of HGOSC is still lacking. Despite problems with EVs analysis, tumour-derived large EVs have progressively received increasing interest due to their peculiar content and function [
45].
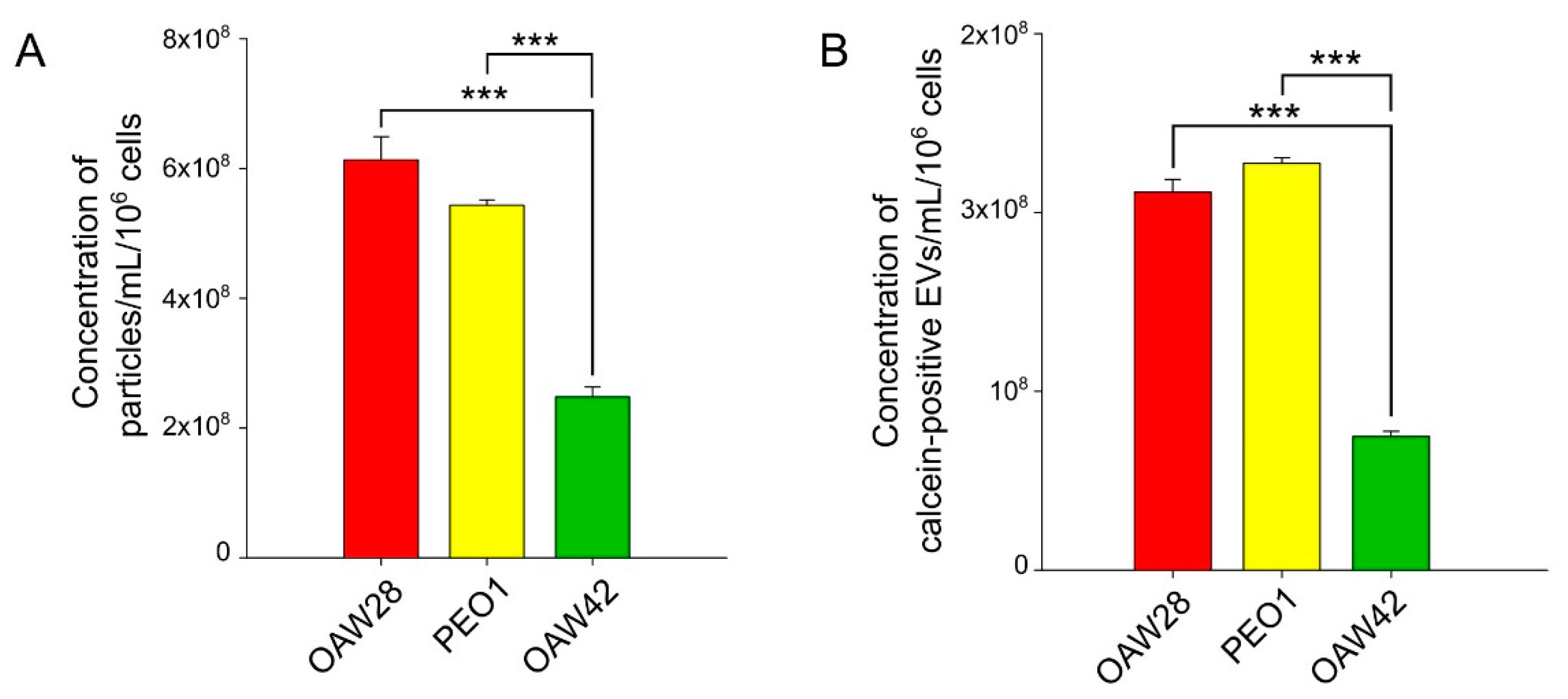
Since quantification of EVs is difficult, we used two methods to confirm our results: S-NTA and FT-FCM. Particle counting by S-NTA may result in overestimation of EV counts since the technique is not specific to EVs and also registers co-isolated particles. On the other hand, FT-FCM, due to the detection limit, registers larger particles than S-NTA. We used calcein as a generic fluorescent marker for detecting EVs by FT-FCM. The advantage of calcein is differentiation of intact EVs from membrane fragments, while the disadvantage is that it requires the presence of enzyme in the EVs. For both reasons, particle counting by FT-FCM may result in underestimation of EV counts. However, the results of S-NTA and FT-FCM were in excellent correlation (r = 0.95, p < 0.001), despite the lower particle number detected by FT-FCM, which is a logical consequence of the above explanation.
In the present study, in which the results were obtained using the two methods mentioned above, we showed that the EV concentration between OAW28-derived EVs and PEO1-derived EVs did not differ significantly, which indicates that HGSOC cells from patient resistant to platinum-based therapy do not release more EVs than cells from tumours sensitive to platinum-based therapy. The detected concentration of EVs from OAW28 and PEO1 cell lines analysed by S-NTA in our study were in accordance with previous reports on EV concentration released from another HGSOC cell line (OVCAR3) in the same period of time and analysed with the same method [
17,
29]. Intriguingly, the concentration of EVs produced by OAW42 cells was lower than the concentration of EVs produced by OAW28 and PEO1 cells. This difference in the production of EVs between two cell lines from tumours sensitive to platinum-based therapy might be attributable to different histological OC subtypes. However, detected EVs released from OAW42 were much smaller when compared with the results of a previous study. Zhang
et al. measured the concentration of EVs released from cell lines with HGSOC, endometrioid and clear cell histology, but the numbers of EVs produced by cells from different histological OC subtypes did not differ [
17]. The lower EV concentration produced by the OAW42 cell line might therefore be a consequence of its special genomic profile or some other unknown factor [
28,
29]. Szajnik
et al. investigated the association between plasma EV level (measured as protein level) and response to primary therapy with carboplatin/paclitaxel in 12 OC patients with different types of histology. The levels of EV proteins varied greatly among patients but the response to therapy was not associated with the level of plasma EV proteins before treatment started, which is in agreement with the results of our study. However, the clinical response to therapy in the majority of patients was associated with a decrease in EV protein levels. These results, while preliminary and performed with only few patients, should be further evaluated [
16].
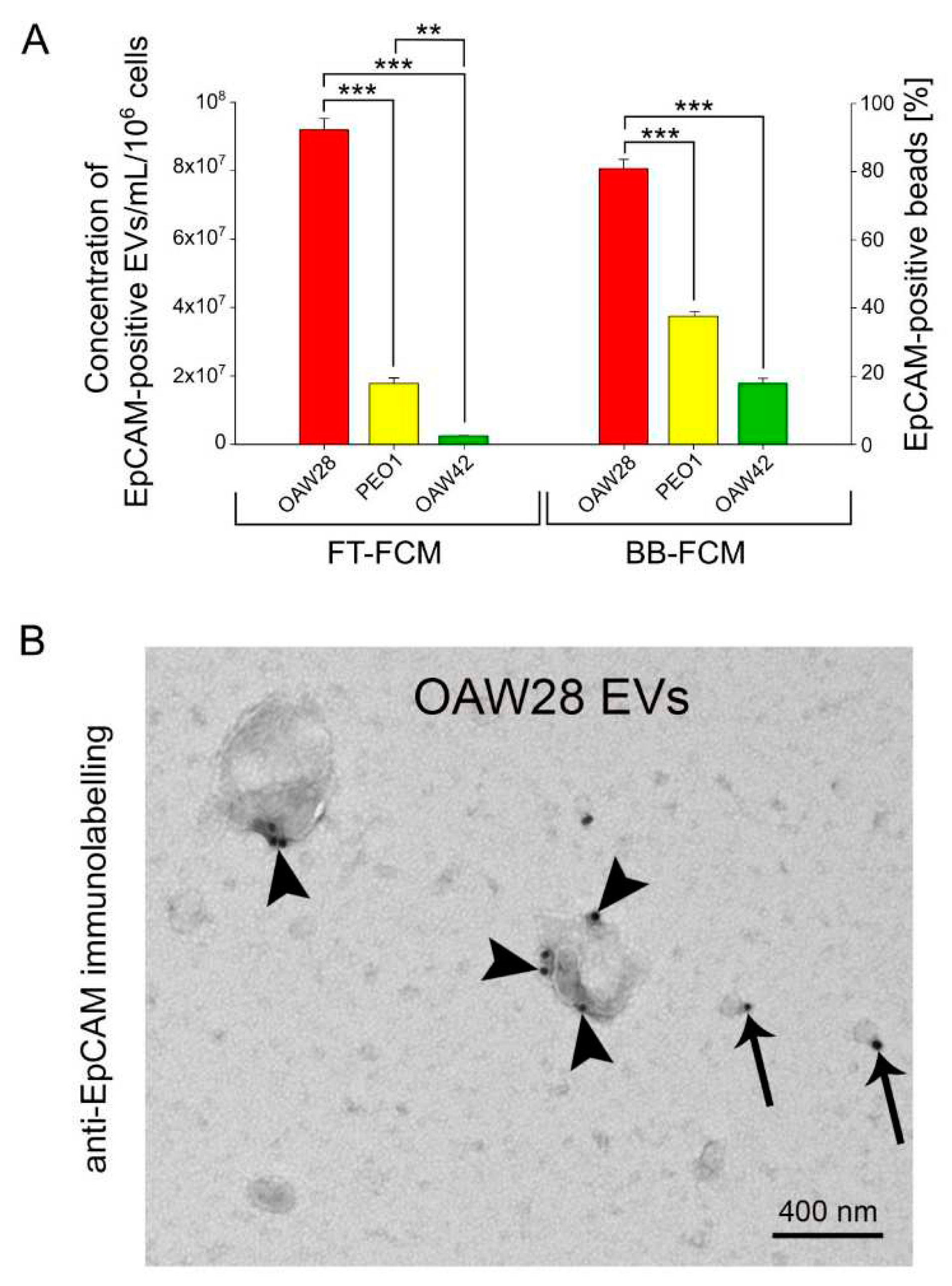
It is likely that specific EVs might be more informative in predicting the response to therapy than total EV levels. Among specific cargoes of EVs, we chose EpCAM as a marker of epithelium-derived cells. EpCAM-positive vesicles were detected in plasma, ascites and pleural effusion of OC patients, as well as in conditioned media of OC cell lines [
6,
7,
14,
17,
18]. However, the relevance of analysis of EpCAM-positive EVs in predicting chemoresistance has been largely unexplored. The results of our study, obtained by two methods, FT-FCM and BB-FCM, showed that cells derived from the patient resistant to platinum-based therapy (OAW28) released a much larger number of EpCAM-positive EVs than cells from tumours sensitive to platinum-based therapy, regardless of the histological subtype. EpCAM-positive vesicles released from OAW28 cells accounted for 43 % of total EVs as detected by FT-FCM. A previous study reported a lower percentage of EpCAM-positive EVs released from another HGSOC cell line (~24 %, OVCAR-3), an endometrioid cell line (~18 %, ES-2) and a clear cell carcinoma cell line (~15 %, IGROV) detected by fluorescent-NTA [
17,
29].
EpCAM-positive vesicles showed the clinical usefulness of monitoring the clinical response to platinum-based therapy. The EVs' EpCAM levels decreased among responding patients, whereas increased levels were associated with non-responding patients as detected by nano-plasmonic sensor. However, the difference was not significant since the study was performed in 8 OC patients with different types of histology. The levels of the EVs' EpCAM before therapy varied greatly among patients, but the relation of the response to therapy with these levels was not assessed [
7]. EpCAM was also included in the EV signature (a weight sum of eight EV protein markers), which provides a complementary approach for monitoring treatment response in metastatic breast cancer [
39].
An interesting question that arises is what is the content of EpCAM-positive EVs? Taylor
et.al. isolated EpCAM-positive EVs from the sera of 50 patients with HGSOC and detected 8 microRNA (miR-21, miR-141, miR-200a, miR-200b, mir200c, miR-203, miR-205 and miR-214) in EVs whose levels were increased compared to those with benign disease [
6]. Although the purpose of this study was to discover diagnostic biomarkers, there are other published studies that have examined the presence of noncoding RNA (microRNA and circular RNA) in EVs and their utility as biomarkers of response to chemotherapy [
39,
46,
47,
48]. Moreover, in prostate cancer, miR-200c and miR-205 were shown to induce expression of EpCAM mRNA and protein [
49].
We discovered that cells from the chemoresistant patient released EpCAM-positive EVs of different sizes (sEVs and m/lEVs). However, a higher proportion of m/lEVs was observed compared to those from cells from the tumours sensitive to chemotherapy. Additionally, immunogold labelling predominated in EVs that were ≥ 400 nm in size and a higher number of EpCAM molecules was found on larger EVs. Gercel-Taylor
et al. also observed the presence of EpCAM in various size ranges of vesicles derived from sera of advanced HGSOC patients [
13].
We hypothesised that larger EpCAM-positive EVs with a higher number of EpCAM molecules can bind more effectively to tumour-reactive autoantibodies and to therapeutic EpCAM antibodies and thereby reduce the binding of antibodies to tumour cells. It has been discovered that ectopic overexpression of EpCAM and HER2 on cancer cells induces humoral immune responses in patients. Both antigens are also targets for a number of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. In the first situation, this will impair antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADDC), which is a major immune effector function toward tumour cells [
50]. EpCAM specific autoantibodies have been found in sera of OC patients [
51]. This phenomenon may be an additional explanation for the contradictory results of EpCAM overexpression in ovarian tumours in relation to its prognostic value [
20,
21,
22,
23]. In the second situation, this may contribute to therapeutic failure of EpCAM monoclonal antibodies. This has been suggested in the case of the HER-2 specific therapeutic antibody trastuzumab [
50]. A higher level of HER2-specific autoantibodies was found in sera from patients with HER2-expressing mammary carcinoma [
52]. It has been proposed that the antibody has a higher binding affinity to full-sized HER2 than to soluble HER2 extracellular domains generated by proteolytic cleavage [
53]. It would therefore be worth exploring the role of this indirect mechanism of EpCAM on EVs in therapeutic failure.
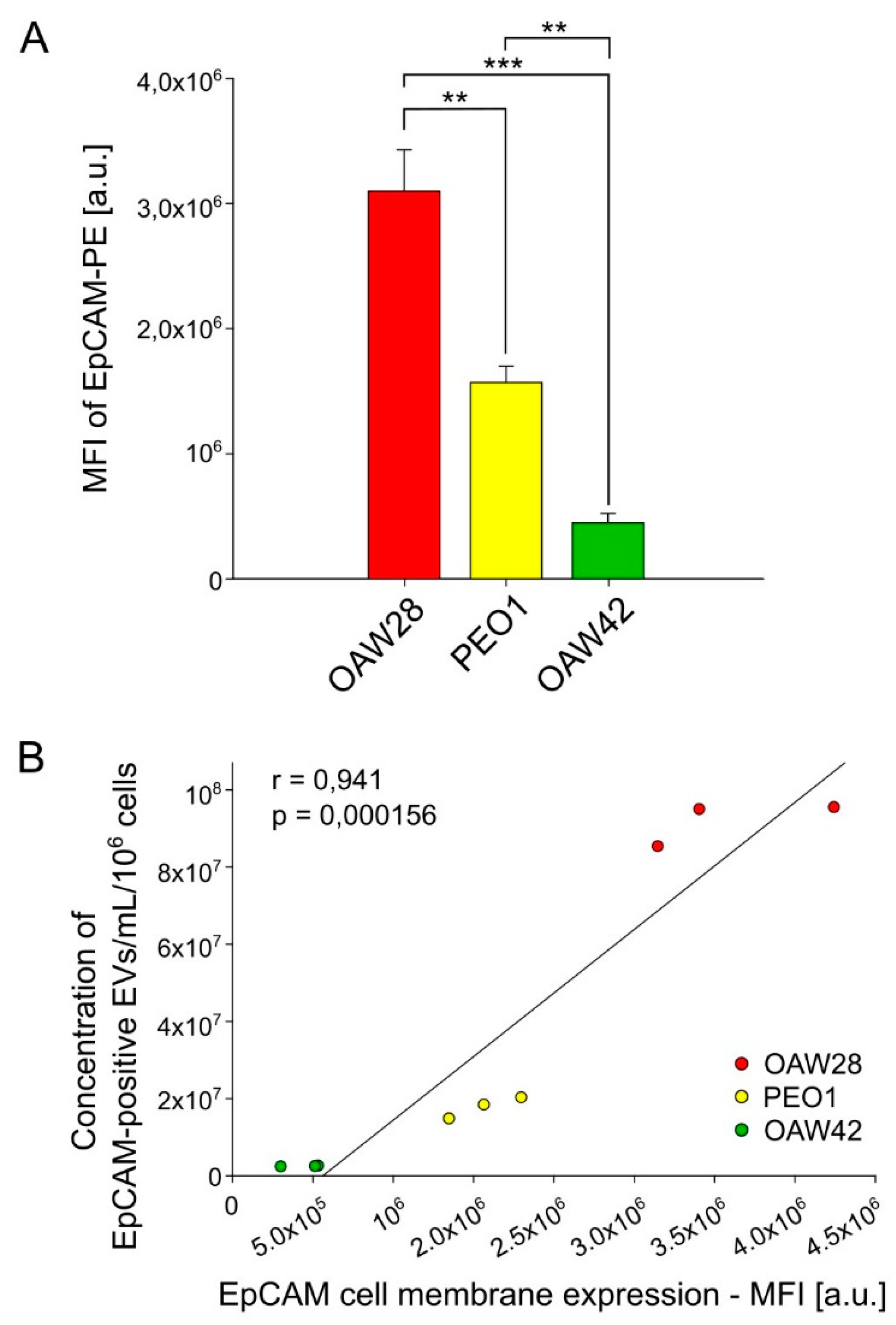
The results of the present study showed a strong positive correlation between the concentration EpCAM-positive EVs and expression of EpCAM on the cell membrane. This finding supports the use of EpCAM specific EVs as cellular surrogates for EpCAM and could therefore be included in liquid biopsy to shed light on the contradictory results of immunohistochemical evaluation of EpCAM overexpression in ovarian tumours as a biomarker for predicting response to chemotherapy. Moreover, it would be interesting to examine in a future study the clinical usefulness of EpCAM-specific EVs in combination with other promising molecular biomarkers or other innovative approaches for the prediction of platinum resistant HGSOC.
In conclusion, we showed for the first time that a more heterogeneous size distribution, with a higher proportion of larger EVs, is characteristic of EVs released from the HGSOC cell line of a clinically confirmed resistant patient, which may reflect the changed state of the cell, reflected in the biogenesis of EVs. In addition, these cells released a higher number of EpCAM specific EVs of different sizes, although expression of EpCAM predominated on larger EVs, especially on those larger than 400 nm. The association of a higher concentration of EpCAM specific EVs with a higher expression of EpCAM on cell membranes demonstrates the feasibility of applying EpCAM specific EVs as a biomarker for cellular EpCAM. Although the results of the current study should be validated in clinical samples, they reveal novel characteristics of EVs that may have the potential to aid the prediction of platinum resistant HGSOC and thereby enable the selection of personalized therapy.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell culture
We included in this study three well characterized ovarian cancer cell lines purchased from the European collection of cell culture (ECACC via Sigma): OAW28 (ECACC 85101601), PEO1 (ECACC 10032308) and OAW42 (ECACC 85073102).
In vitro cultured OAW28, OAW24 and PEO1 cells were used as the EV source for this study, in order to examine the characteristics of EVs from a patient who did not respond to cisplatin (OAW28) compared to EVs from two patients with a complete response (PEO1, OAW42) [
31,
32]. OAW28 and PEO1 are representatives of HGSOC, while OAW42 cells were described to be of serous origin without mutation in the
TP53 gene [
28,
29]. Cell lines were cultured according to the manufacturer’s instructions. OAW28 and OAW42 cells were grown in DMEM medium (Sigma-Aldrich, #D6546) and supplemented with 2 mM glutamine, 20 UI/l bovine insulin purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 10 % FBS [Gibco/Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc.; #10500-037, Lot 08G1094K], 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin and 50 µg/ml gentamycin purchased from Gibco/Invitrogene. PEO1 cells were grown in RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco, #A10491-01), supplemented with 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 10 % FBS [#10500-037, Lot 08G1094K], 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin and 50 µg/ml gentamycin purchased from Gibco/Invitrogene. The cell lines were maintained at 37 °C in an incubator with humidified air with 5 % CO
2. For EV isolation, cells were seeded at a density of 1.5 × 10
6 and grown in a 175 cm
2 flask until ~80 % confluence, rinsed three times with Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS, without Ca
2+ and Mg
2+; Gibco/Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc., #14190-94) and grown in 30 ml serum-free medium. After 24 h of incubation, the conditioned medium was collected and centrifuged for 30 min at 2000 ×
g, RT to eliminate cell and cell debris contamination. Supernatant 10 mm above the pellet was transferred into a plastic tube and mixed gently before proceeding with isolation of EVs. For analysis of expression of EpCAM on the cell membrane and for cell/viability counts, attached cells were fully disaggregated by TripLE
TM select enzyme (Gibco/ Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc.; #12563-029). Cell lines were used from passages 4–7.
4.2. Cell counts and viability measurement
To normalize the amount of released EVs, we chose a number of live cells [
34]. For viability measurement, the cell suspension was mixed with an equal volume of 0.4 % trypan blue solution (Invitrogen/Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc.; #T102882) to count live and dead cells using an image-based automated cell counter (Countess II FL; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, USA) The required viability was
> 90 %.
4.3. EV enrichment (isolation)
The cell culture conditioned medium sample (7 ml) was transferred to a fresh tube and 3.5 ml of Exosome Isolation Reagent (Invitrogen/Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc., #4478359) was added and mixed thoroughly by pipetting up and down. The solution was incubated overnight at 4 °C. The following day, the samples were centrifuged at 10,000 x g for 60 min. The pellet was then resuspended in 200 µl DPBS and stored at 2–8 °C for a maximum of up to seven days before downstream analysis or further purification by the immunomagnetic bead method.
4.4. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
A 10 µl drop of EVs was loaded onto a glow-discharged formvar/carbon-coated grid, adsorbed vesicles were fixed with 2 % paraformaldehyde (in PBS), washed in distilled water, stained by negative contrast with 1 % aqueous uranyl acetate, briefly washed in distilled water and air-dried. Samples were examined with a Philips CM100 transmission electron microscope operated at 80 kV. Images were captured with an AMT camera (Advanced Microscopy Techniques Corp., Woburn, USA).
For EpCAM immunolabelling, a 10 µl drop of extracellular vesicles was loaded onto a glow-discharged formvar/carbon-coated grid. Adsorbed vesicles were fixed with 2 % paraformaldehyde (in PBS), blocked in 0.5 % BSA and incubated with mouse monoclonal anti-EpCAM (CD326) primary antibodies, clone 1B7 (Invitrogen/ Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, USA; #12-9326-42), diluted to 1:100 (1 % BSA in PBS), for 30 min at room temperature. Vesicles were washed in PBS and incubated with 18 nm colloidal gold goat anti-mouse IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch, Cambridgeshire, CB7 4EX United Kingdom; #115-215-146) secondary antibodies, washed in distilled water and stained with 1 % aqueous uranyl acetate. Air-dried samples were examined with a Philips CM100 transmission electron microscope operated at 80 kV and equipped with an AMT camera.
4.5. Nanoparticle tracking analysis in scatter mode (S-NTA)
Isolated EVs from conditioned media were diluted in filtered DPBS (without Ca2+ and Mg2+) and analysed for particle size distribution and concentration by S-NTA using a NanoSight NS300 instrument (488 nm laser) connected to an automated sample assistant (both Malvern Panalytical, Worcestershire, UK). The samples were diluted to a concentration allowing accurate particle tracking (according to the manufacturer, app. 20–100 particles in the field of view). Each sample was measured (recorded) 4 times with 80 s acquisitions at 25 °C and processed using NTA software (version 3.3). The camera level was adjusted according to the sample. Analysis settings were maintained for all readings: detection threshold 5, water viscosity, automatic blur size and automatic (10.2–15.7 pix) maximum jump distance. Data obtained were particle concentration (number of particles/ml of cell cultured conditioned media), mode (nm), mean (nm) and percentile values: D10, D50, D90. Particle size values indicating that 10, 50 and 90 %, respectively, of the distribution was below this value. To calculate the number of particles for each sample, the dilution factor during sample preparation was taken into account. Reference nanospheres (100 nm polystyrene, Malvern Pananalytical, #LT3100A) were analysed on the same day to compensate for day-to-day variation in instrument performance. Raw data were analysed by NanoSight NTA 3.3 software (Malvern Panalytical, Worcestershire, UK).
4.6. Fluorescence-triggered flow cytometry (FT-FCM) of EVs
A flow cytometer (CytoFLEX, Beckman Coulter, Brea, USA) was used to determine the concentration of EpCAM-positive and calcein-positive EVs in the conditioned media of OC cell lines. Fluorescence-based detection of EVs using FCM was employed to better resolve EVs from the background noise and because it is independent of size and refractive index [
54]. Calcein-acetoxymethyl ester (AM) green (referred to as calcein) (Thermo Fischer Scientific; #C3100MP) was used as the generic fluorescent marker for detection of EVs. Calcein AM is non-fluorescent until it passively enters EVs, after which the lipophilic blocking groups are cleaved by non-specific esterase. As a result, calcein is trapped inside the EVs and emits a green fluorescent signal (emission max. 516 nm) following excitation with a blue (488 nm) laser [
33,
34,
55]. For sample preparation, antibodies were centrifuged at 20,000 ×
g for 30 minutes at RT to remove any fluorescent antibody aggregates, as described elsewhere [
56]. To stain, 20 µl of sample was incubated with 1.25 µl PE-conjugated anti-EpCAM (CD326) primary antibodies, clone 1B7 (Invitrogen/ Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, ZDA; #12-9326-42) or PE-conjugated isotype antibody, mouse IgG1 kappa (Invitrogen/ Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, ZDA; #12-1714-42) and kept in the dark for 2 h at room temperature. Due to some overlap between the emission spectra of PE and calcein, which could lead to a false positive signal, a separate sample was stained with calcein [
57]. One hundred µl of calcein (10 µM) was added to 20 µl of sample and incubated for 30 minutes in the dark on ice. After incubation, we diluted samples in DPBS to a count rate below 2000 events/s to prevent swarm detection [
58].
The stained samples were measured by flow cytometry within 1.5 hour, using fluorescence triggering, timed at a slow flow rate for 120 s. Enumeration of EVs was performed using volumetric measurement (events/mL). Calibrating the sample flow rate was conducted following the CytoFLEX instructions by water weight difference during 18-min acquisition with a slow flow rate. To set up VSSC detection, we replaced the 450 nm filter with a 405 nm filter, and appropriately labelled the detector as VSSC. For daily verification of the flow cytometer's optical alignment and fluidics system, we used CytoFLEX Daily QC Fluorospheres (Beckman Coulter, #B53230) with settings optimized for EV detection. The upper size limit for the EV gate was set by detecting 1000 nm fluorescent-green silica beads (Kisker-biotech, #PSI-G1.0] using VSSC triggering [
56]. The threshold for fluorescence-triggering of calcein-positive events was set by the plain cell culture medium samples, which were treated with calcein in the same way as the EVs in the culture conditioned medium samples. The fluorescence signal from PE was used to trigger detection of EVs labelled with anti PE-conjugated antibodies. The gate for PE was derived by measuring corresponding isotype control bodies. Another negative control was performed using anti-EpCAM-PE in DPB and unstained EV samples. The addition of 0.2% Triton 100 (Sigma, #T8787) to EV samples for 20 minutes at room temperature was accompanied by a near total disappearance of the EVs. Analysis of the acquired data was performed using CytExpert 2.3 software (Beckman Coulter, Brea, USA). To calculate the number of events for each sample, the dilution factor during sample preparation and staining was taken into account. Due to the detection limit of our flow cytometer, the EVs measured in this study predominantly correspond to ectosomes (microparticles), not to exosomes.
4.7. Anti-human EpCAM antibody-coated magnetic bead-based EV isolation
EpCAM-positive EV subsets from a pre-enriched EV sample were isolated using Exosome - Human EpCAM Flow Detection (Invitrogen/ Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc., #10624D) following the manufacturer’s instructions. DynabeadsTM are magnetic polystyrene beads (2.7 µm diameter) coated with primary monoclonal antibody specific for the EpCAM membrane antigen expressed on the EVs. The assay buffer was prepared from DPBS with added 0.1 % BSA as the blocking agent and 0.2 µm filtered. Dynabeads were resuspended by vortexing for 30 seconds, 20 µl was withdrawn and transferred to a tube with 1 ml of assay buffer. The tube was placed in a DynaMag™-2 magnetic separator (Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc., #12321D) for 2 minutes. After the buffer had been carefully removed, 90 µl of fresh assay buffer and 10 µl of pre-enriched EV sample were added and incubated at 2–8 °C overnight on a HulaMixer (Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc., #15920D). The next day, the assay buffer was added and the tube placed in a magnetic separator for 1–2 min before removing all supernatants. The procedure with the magnetic separator was repeated 3-times to wash the bead-bound EVs. For analysis with bead-based flow cytometry, the sample was finally diluted in 300 µl of assay buffer.
4.8. Bead-based flow cytometry (BB-FCM) of EpCAM-positve EVs
EVs were also analysed by bead-based flow cytometry (BB-FCM) as a semi quantitative method for assessing approximate EpCAM-positive concentrations [
59]. Because of the size of the Dynabeads™ magnetic beads, EVs are easily detected by flow cytometry while bound to the surface of the beads, enabling the detection of EpCAM on the EV membrane. A total of 100 µl of bead-bound EV sample was stained using 20 µl (0.06 µg) of RPE-conjugated anti-EpCAM (CD326) primary antibodies, clone EBA (Biosciences/Becton Dickinson, #347198). After 45 min of incubation in the dark on an orbital shaker (RT, 1000 rpm), 300 µl of assay buffer was added to each tube and the tubes placed in a magnetic separator for 1–2 min before removing the buffer. We repeated the procedure with the magnetic separator once more. The final EV sample for flow cytometry was diluted in 300 µl DPBS. Flow cytometry was performed using a CytoFLEX flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Brea, USA). Isotype control antibodies (Mouse IgG1-RPE isotype control, Biosciences/Becton Dickinson; #559320) and an unstained EV sample were used as negative control. Gating of bead-bound EVs was performed based on FSC/SSC parameters, so that non-bead events and bead doublets were excluded from the analysis, and beads were selected using the corresponding channels of fluorescence. Results were expressed as EpCAM-positive beads. Analysis of the acquired data was performed using CytExpert 2.3 software (Beckman Coulter, Brea, USA).
4.9. Flow cytometry of EpCAM cell membrane expression
Expression of EpCAM on the cell membrane was analysed using a CytoFLEX flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Brea, USA). For analysis with the flow cytometer, 2 × 105 cells were needed for each sample, which were resuspended in 100 µl of DPBS. 1.25 µl PE-conjugated anti-EpCAM (CD326) primary antibodies, clone 1B7 (Invitrogen/ Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, ZDA; #12-9326-42) were added to the first sample. The second sample was an isotype control, so 1.25 µl of PE-conjugated isotype antibody, mouse IgG1 kappa (Invitrogen/ Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, ZDA; #12-1714-42) was added to the cells. The third sample consisted of unstained cells. The samples were incubated in the dark for 45 minutes at 4 °C. They were then washed three times by centrifugation (3 minutes, 200 × g, at room temperature) and resuspended in between in 500 µl DPBS. Final cell samples for analysis were resuspended in 200 µl DPBS. Fluorescence gating parameters were established using antibody isotype controls, and values above a 99 % negative staining threshold were considered positive. Using isotype antibodies, we confirmed that the binding of primary antibodies was specific. Unstained cells were used to control cellular autofluorescence. The concentration of the isotype antibodies should be the same as the concentration of the primary antibodies. We set up the instrument appropriately with the help of this control, which also allowed us to set up the gate appropriately to capture the events we wanted to analyse. A total of 5000 cells was measured. Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) was used to compare expression of EpCAM between different cell lines. Analysis of the acquired data was performed using CytExpert 2.3 software (Beckman Coulter, Brea, USA).
5.0. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SigmaPlot v.12.5 (Systat Software, Palo Alto, USA). All quantitative measurements were conducted as three independent measurements, which were made in duplicate. One-way ANOVA was used as an appropriate method to test for significant differences between more than two normally distributed samples, followed by Holm-Sidak's multiple comparison test. Person’s correlation coefficient was used to calculate the direction and strength of the relationship between variables. A p value of < 0.05 was considered significant. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM).