1. Introduction
The concept of autonomous or driverless vehicles refers to vehicles that are intelligent in their operation and are intended to minimize the need for human assistance. Exteroceptive and proprioceptive sensors on these vehicles allow them to monitor their environment and internal states simultaneously [
1,
2]. With heterogeneous sensors, such as cameras, light detection and ranging (LiDAR), radar, global positioning system (GPS), etc., the vehicle is able to learn different tasks and can use its understanding of the context in which it operates [
3]. For autonomous vehicles (AVs) to operate safely and reliably in environments that are complex and dynamic, they must be able to perceive the environment accurately and localize themselves precisely [
4,
5]. It is necessary to acquire and process high-quality, information-rich data obtained from actual environments to accomplish both of these tasks [
6]. Multiple sensors, such as LiDAR and cameras, are used on AVs to capture target context. Digital camera data have traditionally been the most popular source of perception data because they provide two-dimensional (2D) appearance-based representations, are low cost, and are highly efficient [
7]. Due to the lack of three-dimensional (3D) geo-referenced information in image data, the dense, geo-referenced, and accurate 3D point clouds generated by LiDAR are exploited. In addition, LiDAR is not sensitive to changes in lighting conditions and can be used at any time of the day or night, even when glare or shadows are present [
8].
Using LiDAR to generate 3D points can be challenging due to the density of the points. As a result, pre-processing is used to remove noise and extract useful information from the data. It is extremely beneficial to cluster LiDAR data in a wide variety of applications, particularly in those with real-time edge-based data, such as object detection and classification [
9]. Three-dimensional data allow us to determine the shape, size, and other properties of the objects with great precision. However, the task of segmenting 3D point clouds is challenging. It is common for point cloud data to be noisy, sparse, and disorganized. As a result of the scanner’s varying linear and angular rates, the sampling density of points is also typically uneven. Aside from this, the shape of the surface is arbitrary, with sharp features, and the data do not follow a statistical distribution. It is also important to note that, because of the limitations of the 3D sensors, the foreground and background are frequently very entangled. Designing an algorithm to deal with these problems presents a significant challenge [
10].
A further challenge for autonomous vehicles is to perceive their surrounding environment, e.g., when performing complex maneuvers in urban environments for successful navigation [
11]. These maneuvers include merging into or taking out of a lane, following or overtaking the vehicle in front, and crossing an intersection simultaneously with vehicles from other directions. Without the ability to perceive the motion of other objects, it is difficult to manage these situations. Thus, detecting and tracking moving objects on the road is an essential task for intelligent vehicles [
12]. In modern tracking systems, Multi-Target Tracking (MTT) is usually employed, which adopts a single or multiple sensors to produce detections from multiple targets, as well as one or more tracks for the estimation of their states. Prior to updating tracks, MTTs must assign detections to tracks. However, there are a number of challenges in data association that need to be considered by MTT as mentioned in [
13].
The assignment of a target to a detection or a nearby detection becomes ambiguous if they are densely distributed;
Sensors with a small field of view (fov) might not be able to detect the true target during a sensor scan;
It is possible for two targets in close proximity to be detected as a single object if the sensor resolution is low;
The possibility of false alarms increases the complexity of data assignment by introducing additional possible assignments.
There have been several state-of-the-art techniques developed to address the challenges associated with clustering and Multi-Target Tracking. Ref. [
14] provides a complete system for detecting and tracking vehicles based solely on 3D LiDAR information. Using previously mapped LiDAR point clouds to reduce processing time, ref. [
15] describes real-time dynamic object detection algorithms. In [
16], a skeleton-based hierarchical method was proposed, which is capable of automatically detecting pole-like objects using mobile LiDAR point clouds. The authors have proposed a compression approach based on a convolutional long-short-term memory network (LSTM) for multi-line LiDAR point clouds [
17]. These different techniques produce promising results for clustering and tracking multiple objects.
The purpose of this review was to synthesize the existing literature and offer valuable insights into autonomous driving applications through three main contributions. Our first contribution was to classify various clustering and MTT methods based on the findings of other studies. In addition, we identified existing gaps and challenges associated with these methods. Lastly, we reviewed the current state-of-the-art and suggest promising directions for future research. In our review, these findings lay the groundwork for the subsequent discussion.
2. Methodology, Motivation and Contribution
This review study was conducted using a systematic and reproducible methodology to ensure unbiased and comprehensive coverage of the field [
18]. In the context of autonomous driving applications, this methodological rigor is crucial for accurately identifying and classifying the various clustering and Multi-Target Tracking techniques used for LiDAR point clouds. The key objective of this review study was to identify and classify several clustering and Multi-Target Tracking techniques for LiDAR point clouds, working towards autonomous driving solutions. By gaining an understanding of these outcomes, we can identify the main challenges that must be properly addressed to improve the functionality of these techniques.
Methodology: We used the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) methodology to conduct our review [
19]. Research questions focused on challenges and advancements in clustering and Multi-Target Tracking techniques for LiDAR point clouds related to autonomous vehicles. Several major databases were searched to identify relevant studies, including IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, and ACM Digital Library, as well as Google Scholar to find broader coverage. These databases were last searched on 10 December 2022.
A customized search strategy was developed for each database, combining keywords such as “LiDAR”, “autonomous driving”, “clustering”, “Multi-Target Tracking”, and “point clouds”. We used filters to identify publications of relevant types and dates. In databases such as IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, and ACM Digital Library, we searched within abstracts, keywords, and full texts, applying specific filters for different types of articles.
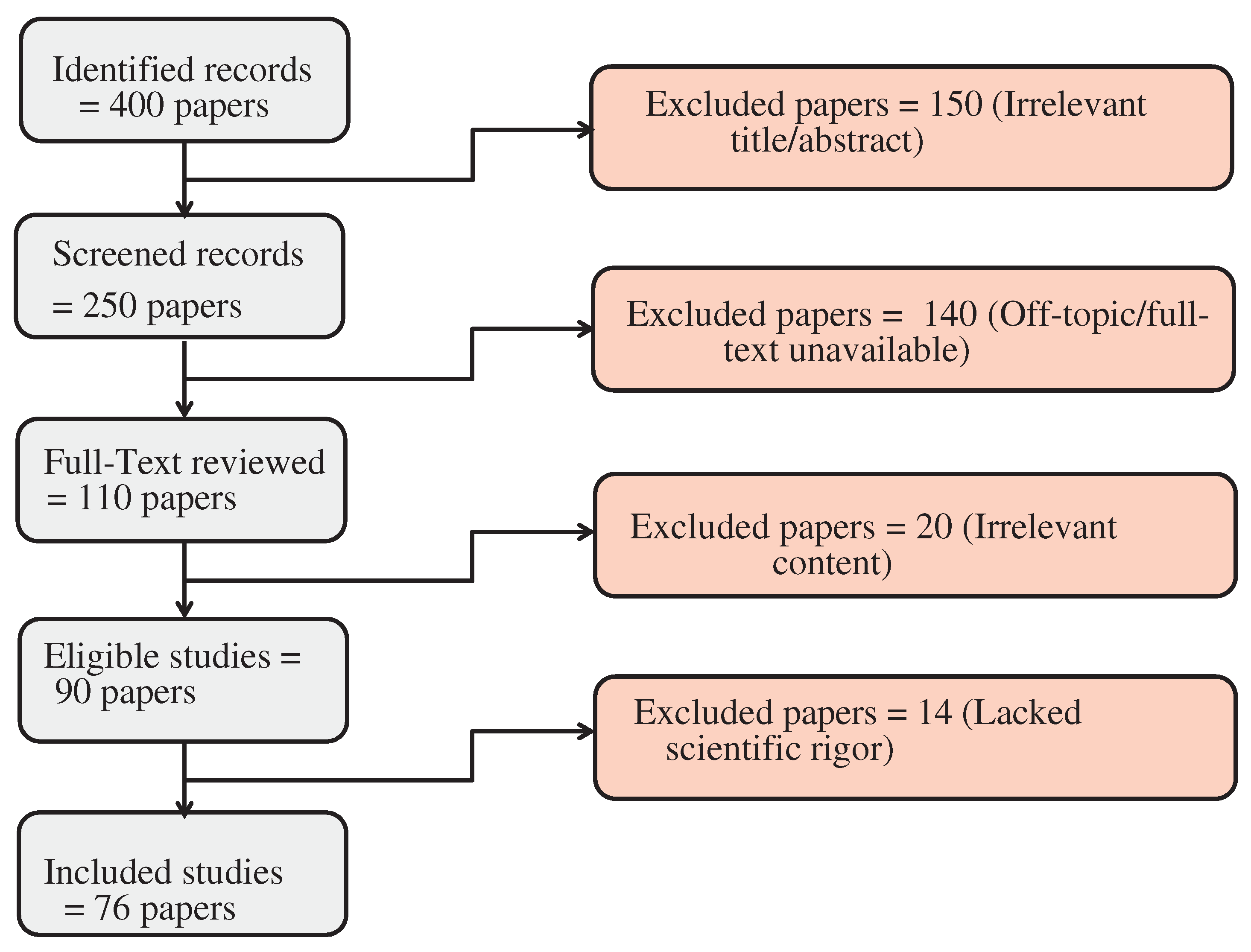
Initially, we identified 400 studies from major databases, including IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, and ACM Digital Library, as well as Google Scholar in order to provide a broader coverage of the literature. There were 150 studies that were excluded at this early stage due to irrelevant titles or abstracts, leaving 250 studies to be screened further. Afterwards, the 250 screened records were further examined. We included studies that examined LiDAR technology in autonomous driving applications, specifically those that addressed clustering and Multi-Target Tracking. We excluded 140 studies due to their off-topic nature or because their full text was not available, thus leaving 110 studies for full-text analysis.
A set of inclusion and exclusion criteria was developed in order to screen the studies [
20]. Each title, abstract, and full text was independently reviewed by two reviewers in order to determine whether it met these criteria for eligibility. Discussions between the reviewers or involvement of a third reviewer were used to resolve disagreements. The screening process was not automated.
A full-text review of 110 studies was conducted by evaluating their methodology, results, and overall contribution to the field. We sought to include studies in our review that presented novel, impactful, and well-supported findings. A total of 90 studies were eligible after 20 were excluded because of irrelevant content.
A further analysis of the scientific rigor of these 90 eligible studies was conducted. It was decided to exclude studies that lacked methodological clarity, presented inconclusive results, or contributed in a significant manner to understanding the topic. As a result, 14 more studies were excluded, leaving 76 studies for detailed analysis.
Multiple authors of this study participated in the extraction process in order to ensure objectivity and minimize bias. Several aspects of each study were considered, such as the methods used for clustering and tracking, the specific challenges addressed, and the effectiveness of the proposed solutions. Our comparative analysis was based on the data collected from this process.
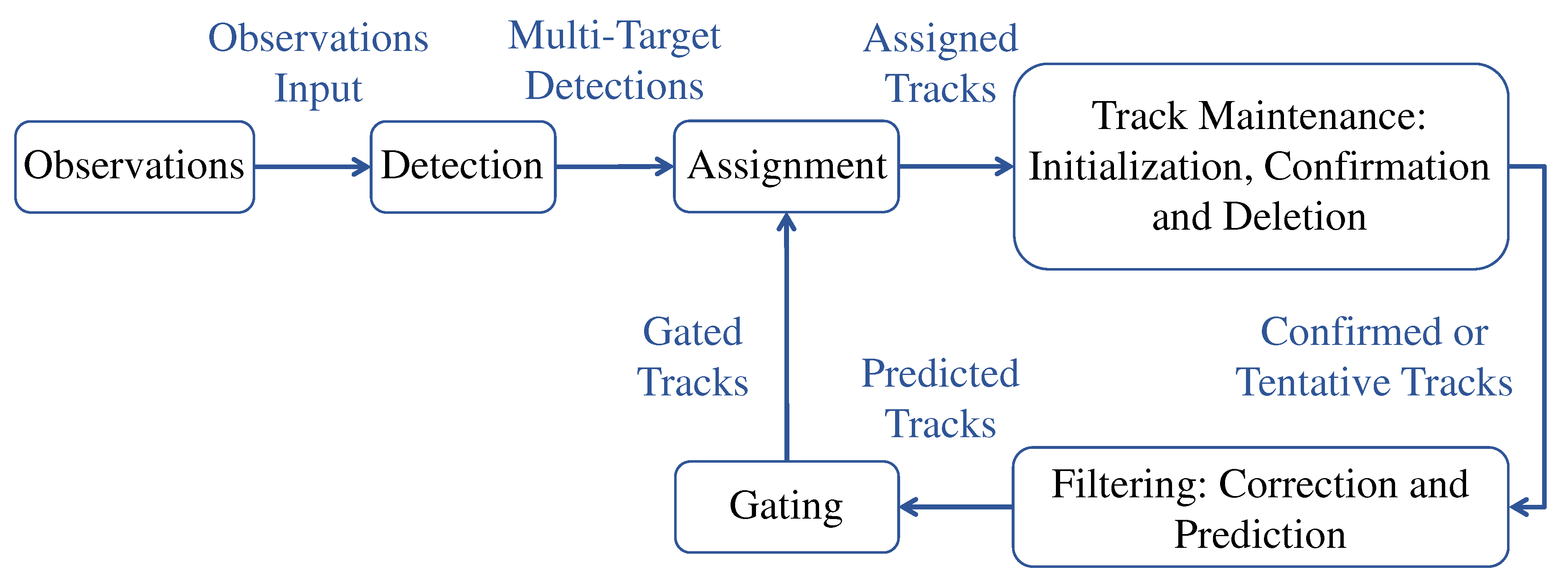
Figure 1 illustrates the methodological process. Our clear and systematic approach allows other researchers to reproduce our review process, ensuring its transparency and reproducibility.
Figure 1 illustrates the methodological process. Our clear and systematic approach allows other researchers to reproduce our review process, ensuring its transparency and reproducibility.
Below we outline our motivation, key objectives, and contributions.
Motivation: Several reviews [
8,
10,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31] have been conducted in the context of LiDAR point clouds, but a literature review examining these emerging techniques for clustering and multi-object tracking within the context of autonomous driving is currently lacking. As part of this literature review study, we aimed to address this gap for both researchers and practitioners.
As shown in
Table 1, we provide a summary of the literature review and a comparison with recent research studies. In this table, it can be seen that we have covered those disciplines not covered in detail in other surveys. The table indicates that very limited research has been conducted on the concept of tracking and clustering combined. In the next paragraphs, we analyze the available reviews in the state-of-the-art and compare them with our survey.
The article [
10] classified and summarized segmentation and clustering methods for point clouds. It does not mention MTT nor autonomous driving. Challenges of working on point cloud data were only briefly introduced, whereas in our paper we describe them more in detail.
The three surveys [
22,
26,
29] cover several topics in deep learning for point cloud data, briefly discussing either clustering or MTT. In our survey, instead, we cite both traditional and deep learning methods. To be more precise, ref. [
22] offers a review of recent deep learning methods for point clouds. It is divided into three core theoretical sections, dedicated, respectively, to: (i) 3D shape classification, (ii) 3D object detection, tracking, and scene flow estimation, and (iii) 3D point cloud segmentation. However, the second section only briefly discusses tracking and mostly focuses on object detection. Various papers in the first and third sections also adopt clustering in their pipeline; however, clustering is not one of the main topics of the survey. Several AV papers are cited, but autonomous driving is not the fulcrum of the article. Instead, ref. [
26] focuses on deep learning methods for fusing camera and LiDAR in the AV context. One page is dedicated to tracking but only considers works combining camera and LiDAR data. Finally, ref. [
29] is a review of unsupervised point cloud representation learning using deep neural networks (DNNs). While discussing unsupervised point cloud representation learning, the authors mention in a paragraph how clustering has been adopted in a few papers in conjunction with other unsupervised learning approaches. Two examples are given, but no further analysis of clustering methods is provided.
Whereas the above-mentioned three surveys focus on deep learning, ref. [
23] advocates the use of traditional geometry-based clustering methods as an asset for point cloud panoptic segmentation. This article provides a survey of point cloud clustering methods and at the same time proposes a general pipeline for panoptic segmentation. The proposed pipeline contemplates the use of a semantic segmentation network to extract the semantic information followed by a traditional clustering method to separate object instances. However, the focus of this article was on panoptic segmentation, and MTT is not mentioned.
In
Table 1, we also report the total number of papers referenced in each survey (third column), how many of these papers use clustering in their main method (fifth column), how many use MTT (seventh column) and how many use both clustering and MTT (eighth column). We examined, one by one, each paper cited by the surveys in the table. A standard paper was counted in the column “# clustering-related refs” when clustering was a step of the main pipeline of the method or was defined as one of the final objectives of the method. Even if clustering was not the focus of the paper, the paper was counted. Consequently, many clustering-related papers appear for survey [
22], which briefly notes its use as a step in some methods (hence the `briefly covered’ classification), and in [
26], which does not tackle clustering as one of its topics and only mentions it three times while describing cited papers (hence the `not covered’ classification). The same rule applies to MTT. Survey papers were also counted, but papers that do not discuss methods were not counted in the fifth, seventh, and eighth columns of the table (e.g., dataset papers). From this analysis, we can observe how MTT in particular is a topic that has been very rarely examined and reviewed for point cloud data. This applies even more to papers combining clustering and MTT, a case that has never been jointly covered in a survey.
Apart from the surveys in
Table 1, other recent reviews have tackled the use of LiDAR point clouds for AVs but deal with neither clustering nor MTT. Instead, they reviewed object detection [
8,
24,
25,
28], classification [
8,
24] and semantic segmentation [
8,
24]. The surveys [
21,
30,
31] discuss 3D object detection with either LiDAR data, other sensory data (e.g., camera, radar), or a multi-modal fusion. In [
27], LiDAR basic concepts were analyzed, as well as commercial solutions and LiDAR challenges. We do not report these surveys in
Table 1.
Finally, several other surveys exist on the separate general topics of clustering (e.g., [
32,
33,
34]) and MTT (e.g., [
35]). However, they neither examine the additional challenges of using these algorithms on point cloud data nor do they specifically review papers dealing with this data type nor do they focus on the autonomous driving context. We do not report these surveys in
Table 1 either.
To summarize, in our survey, we reviewed clustering and Multi-Target Tracking solutions for LiDAR point clouds in an AV context. To the best of our knowledge, these subjects were never extensively and jointly tackled before in a survey.
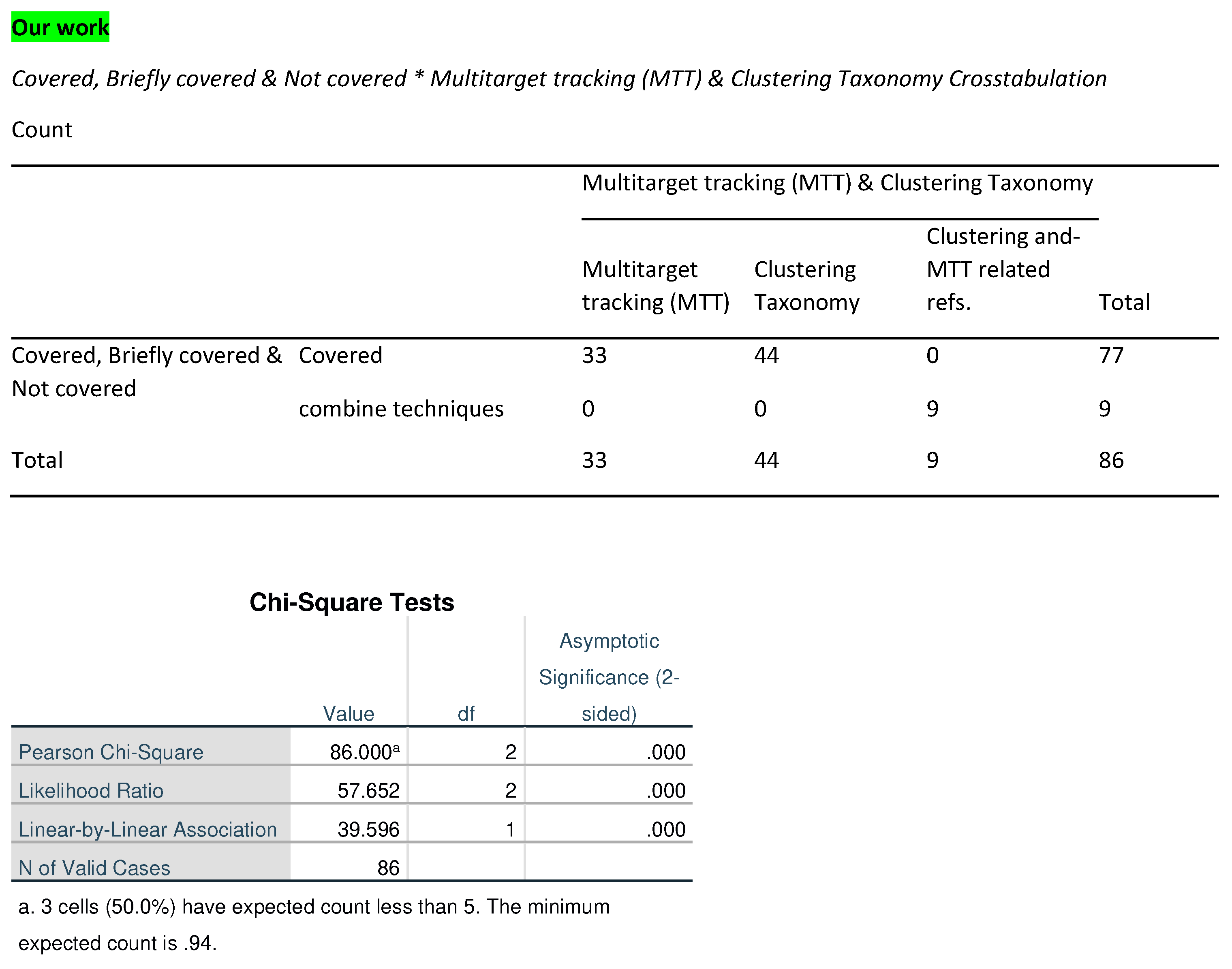
In comparison with our study, a frequency
Table 2 based on
Table 1 was constructed to assess the coverage extent of Multitarget Tracking (MTT) and Clustering Taxonomy across reviewed studies. This table elucidates the counts for various combinations of MTT, Clustering Taxonomy, and Clustering and MTT-related references jointly. The “our work” category encapsulates 77 observations, with 33 labeled as Covered for MTT, 44 for Clustering Taxonomy, and nine for Clustering and MTT. This category also includes a subgroup, “Combine Covered”, which counts nine and pertains to the nine papers in our review discusses that have examined MTT and clustering jointly. For the [
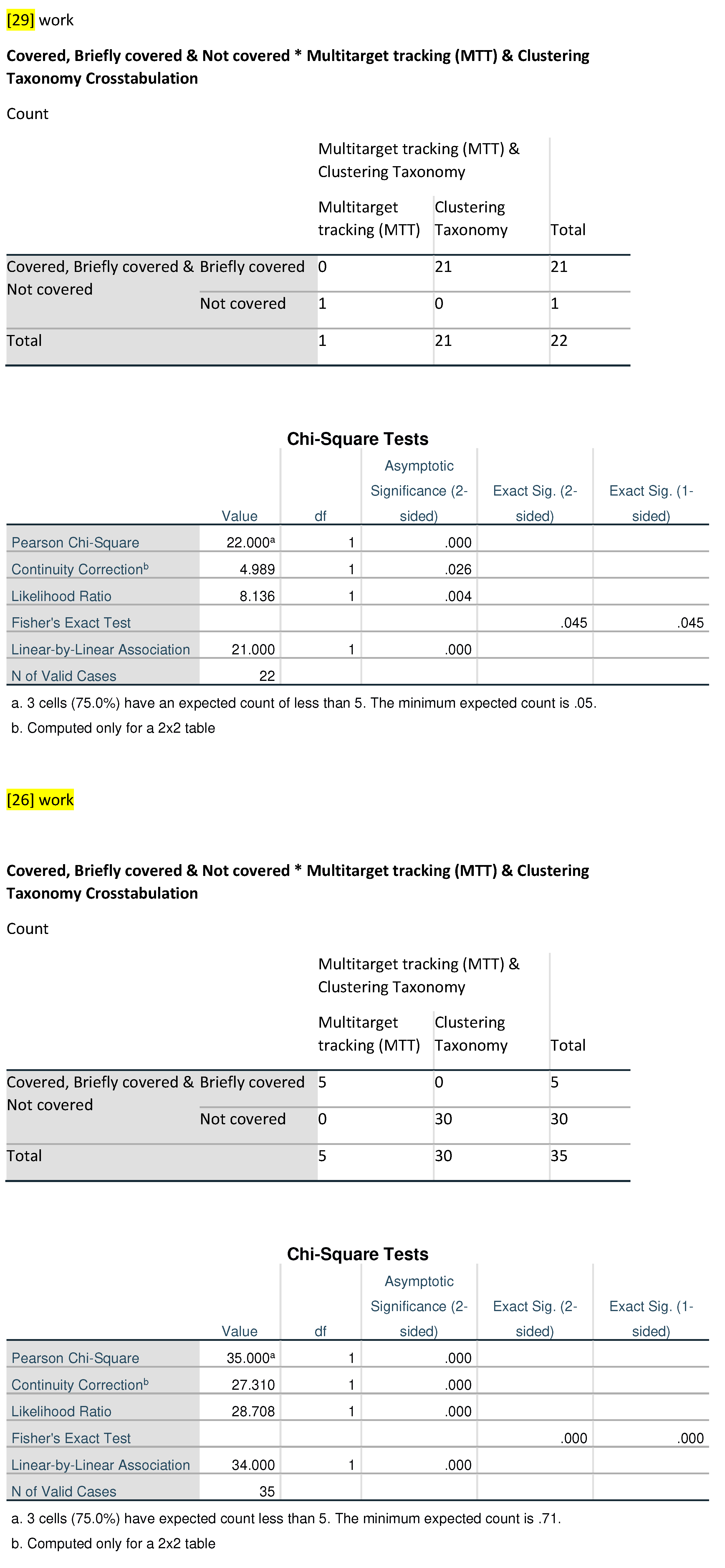
29] category, 21 out of 22 observations are briefly covered for Clustering Taxonomy, with 1 designated as Covered for MTT. The [
26] category holds 35 observations, including five briefly covered for MTT and 30 covered for Clustering Taxonomy, with no Clustering Taxonomy or Clustering and MTT-related references jointly.
Table 1.
Our survey and recent research on point cloud data are summarized and compared. `#’ stands for `number’ and `refs.’ for `references’.
Table 1.
Our survey and recent research on point cloud data are summarized and compared. `#’ stands for `number’ and `refs.’ for `references’.
| Survey |
Year |
Total # of Refs. |
Clustering Taxonomy |
# Clustering-Related Refs. |
Multi-Target Tracking (MTT) |
# MTT-Related Refs. |
# Clustering-and-MTT-Related Refs. |
| Our work |
2023 |
101 |
Covered |
44 |
Covered |
33 |
9 |
| [29] |
2022 |
150 |
Briefly covered |
21 |
Not covered |
1 |
0 |
| [26] |
2021 |
138 |
Not covered |
30 |
Briefly covered |
5 |
0 |
| [23] |
2021 |
47 |
Covered |
24 |
Not covered |
0 |
0 |
| [22] |
2020 |
256 |
Briefly covered |
45 |
Briefly covered |
9 |
1 |
| [10] |
2013 |
46 |
Covered |
29 |
Not covered |
0 |
0 |
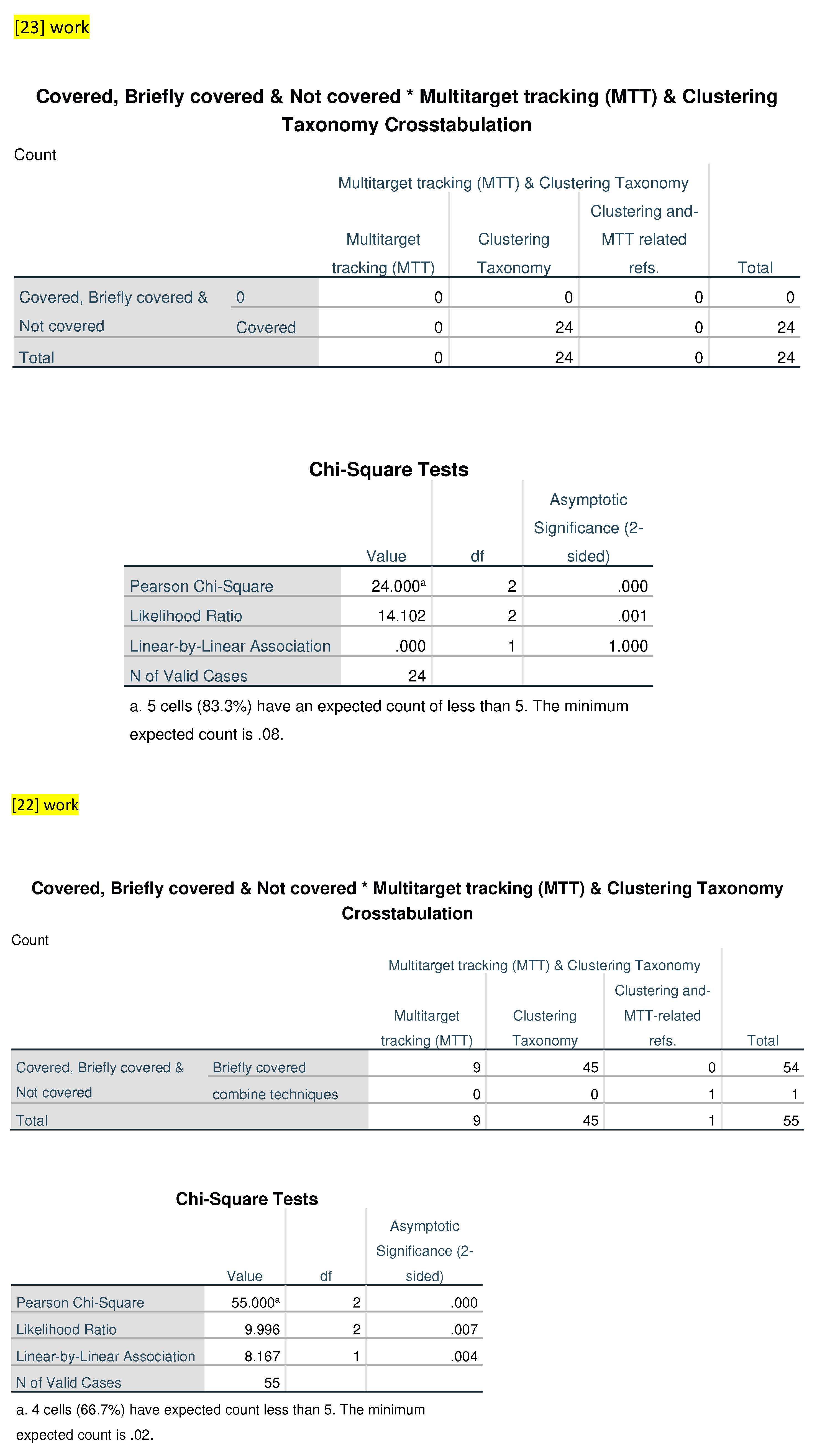
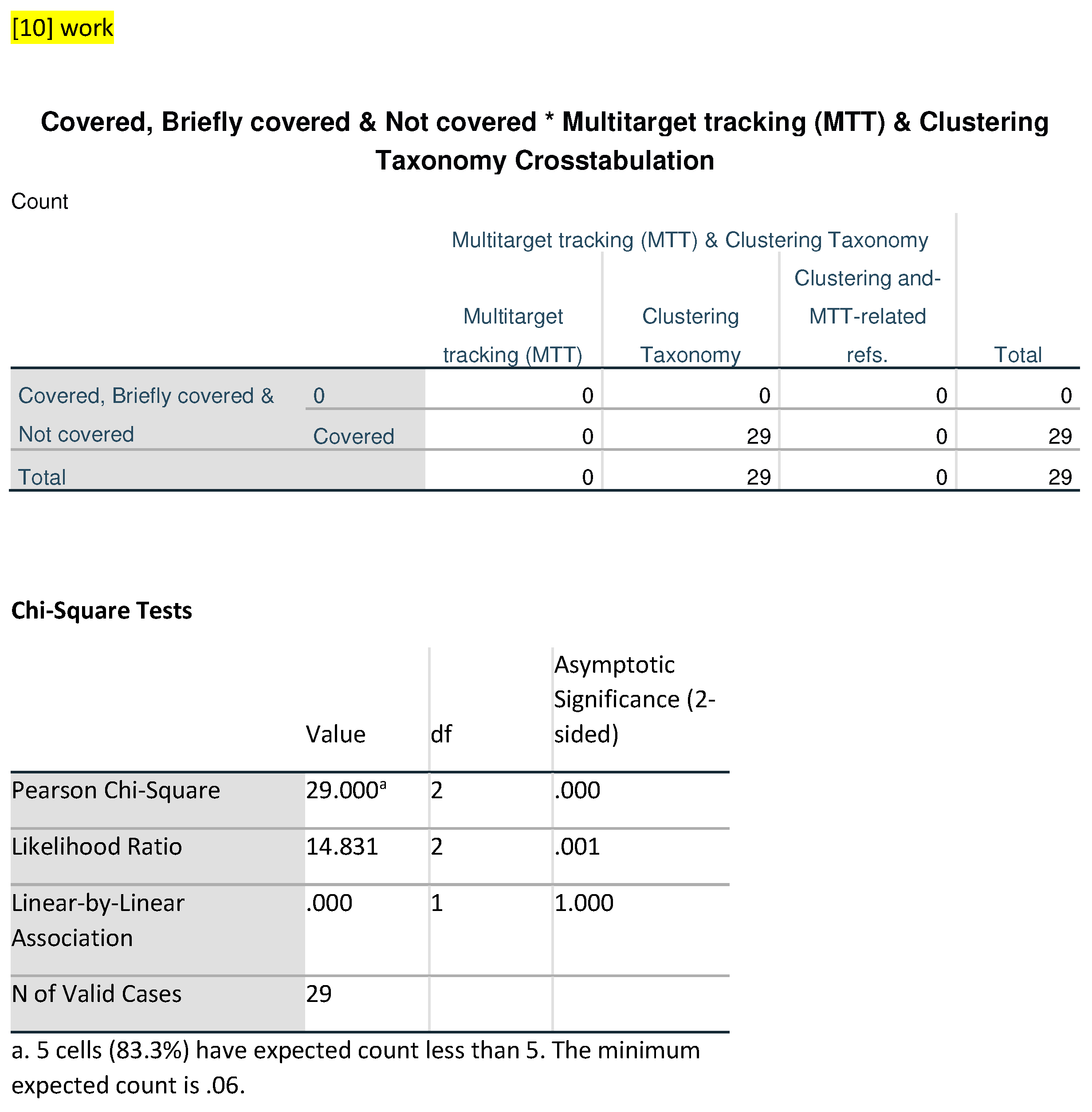
In the [
23] category, none out of 24 observations are labeled as MTT and 24 number of references are covered in the paper of Clustering Taxonomy. Again, there are no references to Clustering and MTT. Category jointly. Ref. [
22] presents 55 observations, with nine briefly covered for MTT, 45 Covered for Clustering Taxonomy, nine references are related to the MTT and one tagged as “combine techniques” where, in this one reference, combinations of both techniques such as MTT and Clustering are discussed in the paper. Lastly, the [
10] category comprises 29 observations with none labeled as MTT, 29 reference are used of clustering and there are no references have been reported in the paper about MTT and Clustering techniques combinely.
Table 2.
Frequency Distribution of Coverage for Multitarget Tracking (MTT), Clustering Taxonomy, and Clustering-MTT Related References in Reviewed Works. Cov. = Covered, Com. Cov. = Combine Covered, Br. Cov. = Briefly Covered, Not Cov. = Not Covered, Com. Tech. = Combine Techniques, MTT = Multitarget Tracking.
Table 2.
Frequency Distribution of Coverage for Multitarget Tracking (MTT), Clustering Taxonomy, and Clustering-MTT Related References in Reviewed Works. Cov. = Covered, Com. Cov. = Combine Covered, Br. Cov. = Briefly Covered, Not Cov. = Not Covered, Com. Tech. = Combine Techniques, MTT = Multitarget Tracking.
| |
MTT |
Clustering |
Clustering-MTT |
Total |
| Our work |
|
|
|
|
| Cov. |
33 |
44 |
0 |
77 |
| Com. Cov. |
0 |
0 |
9 |
9 |
| Total |
33 |
44 |
9 |
86 |
| [29] |
|
|
|
|
| Br. Cov. |
1 |
21 |
0 |
21 |
| Not Cov. |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Total |
1 |
21 |
0 |
22 |
| [26] |
|
|
|
|
| Br. Cov. |
5 |
30 |
0 |
35 |
| Not Cov. |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Total |
5 |
30 |
0 |
35 |
| [23] |
|
|
|
|
| Not Cov. |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Cov. |
0 |
24 |
0 |
24 |
| Total |
0 |
24 |
0 |
24 |
| [22] |
|
|
|
|
| Br. Cov. |
9 |
45 |
0 |
54 |
| Com. Tech. |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
| Total |
9 |
45 |
1 |
55 |
| [10] |
|
|
|
|
| Not Cov. |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Cov. |
0 |
29 |
0 |
29 |
| Total |
0 |
29 |
0 |
29 |
Table 3, as detailed below, presents the outcomes of the Pearson Chi-square tests [
36] executed on the observed frequencies for each category: “our work,” and the works represented by the references [
10,
22,
23,
26,
29]. The results of these tests included the test statistic, degrees of freedom, and the
p-value for each category.
Notably, a p-value of 0.000 is observed uniformly across all categories. This score indicates a highly significant statistical correlation within each category. It is worth emphasizing that a p-value of 0.000 is compelling evidence against the null hypothesis, as it suggests there’s almost no chance that the observed differences occurred by random chance alone.
In terms of the test statistic or Chi-square value, “our work” posts a figure of 86.000, which is superior to the other works, including ref. [
29] with 22.000, ref. [
26] with 35.000, ref. [
23] with 24.000, ref. [
22] with 55.000, and ref. [
10] with 29.000. This greater test statistic underlines the enhanced efficacy and strength of “Our Work” in comparison to the other research works represented.
The degrees of freedom, another critical statistical measure, ranges between 1 and 2 depending on the category. The degree of freedom can greatly influence the Chi-square test as it impacts the expected frequencies. It also determines the distribution used to find the critical value or cut-off for deciding when to reject the null hypothesis. Although there is variation in the degrees of freedom among the categories, the consistent p-value of 0.000 across all categories confirms the statistical significance of each one.
In summary, the results from
Table 3 affirm the superior statistical validity of “Our Work” compared to the other studies referenced. The stronger Pearson Chi-square test statistic coupled with a consistent
p-value of 0.000 presents a compelling case for the superiority of our results.
Table 3.
Pearson Chi-square test results for observed frequencies in each category.
Table 3.
Pearson Chi-square test results for observed frequencies in each category.
| |
Pearson Chi-Square |
Value |
df |
Significance (2-Sided) |
| Our Work |
|
86.000 |
2 |
0.000 |
| [29] |
|
22.000 |
1 |
0.000 |
| [26] |
|
35.000 |
1 |
0.000 |
| [23] |
|
24.000 |
2 |
0.000 |
| [22] |
|
55.000 |
2 |
0.000 |
| [10] |
|
29.000 |
2 |
0.000 |
For further reference and consideration,
Appendix A contains the comprehensive figures resulting from the statistical evaluation using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software.
Key Objectives:
RQ1: What are the most effective clustering and Multi-Target Tracking (MTT) methods employed in existing studies for processing LiDAR point clouds in the context of autonomous driving?
RQ2: What are the key challenges in the state-of-the-art clustering and MTT methods for autonomous driving applications?
RQ3: What are the methods used to assess the performance of clustering and MTT algorithms in the state-of-the-art? How are these methods used for evaluation on the point clouds dataset? What is the performance of the reported methods?
Contributions:
Contribution 1: The categorization and identification of various clustering and MTT methods used in autonomous driving applications for point clouds.
Contribution 2: Assessing the research gaps and challenges associated with clustering and MTT methods in autonomous driving applications.
Contribution 3: Analyzing the state-of-the-art and identifying challenges to distinguish promising future research directions in the field of clustering and Multi-Target Tracking for LiDAR point clouds used in autonomous driving applications.
Tables and Graphs: To facilitate a better understanding of the terminology used throughout this review paper, we have provided a table of key terms and abbreviations. The table serves as a quick reference for readers and provides clarification of the concepts discussed. Detailed descriptions and definitions of each term can be found in
Table 4.
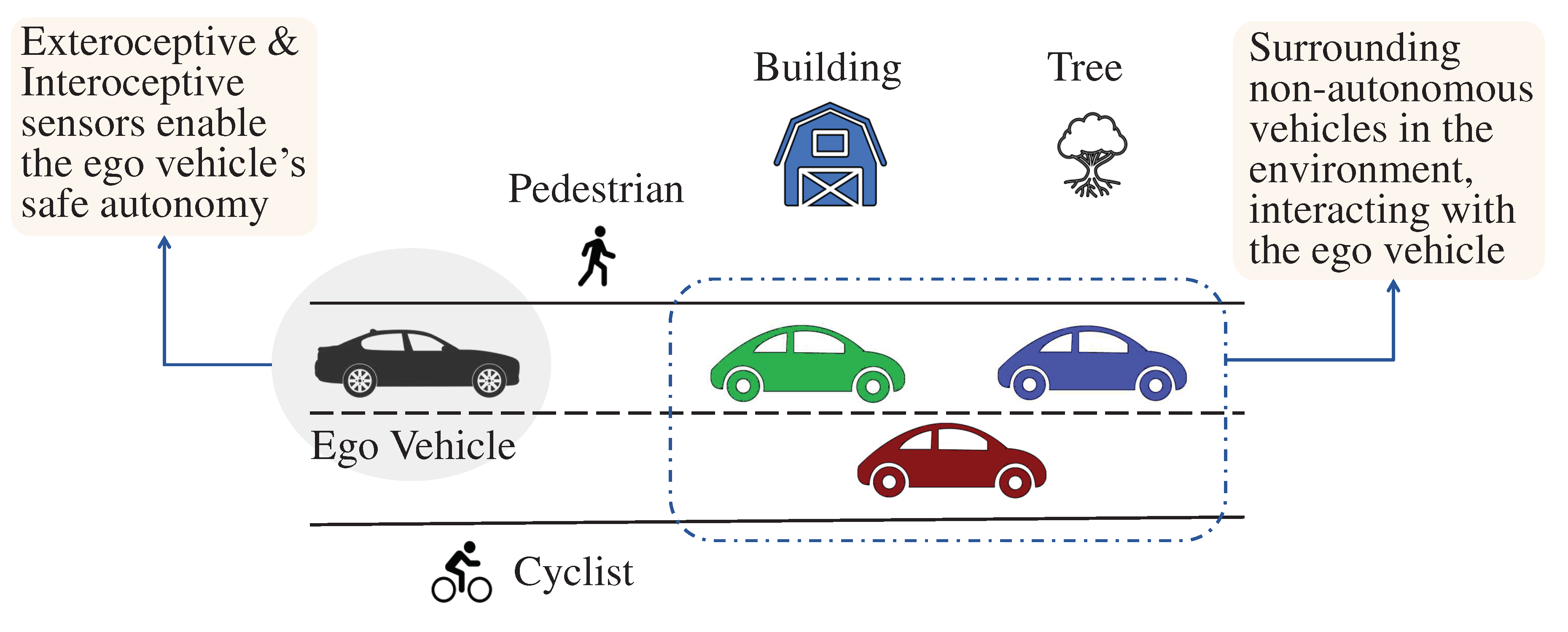
We present in
Figure 2 a graphic representation of a general scenario in which an ego vehicle navigates a complex environment equipped with both interoceptive and exteroceptive sensors. In addition to the ego vehicle, there are non-ego vehicles, trees, buildings, and a cyclist that must be accurately perceived and tracked using LiDAR point clouds.
Table 4.
List of important words and abbreviations.
Table 4.
List of important words and abbreviations.
| Term/Abbreviation |
Definition/Explanation |
| MTT |
Multi-target tracking |
| LiDAR |
Light Detection and Ranging |
| AVs |
Autonomous Vehicles |
| FoV |
Field of View |
| LSTM |
Long-Short-Term Memory |
| MOT |
Multi-Object-Tracking |
| DBSCAN |
Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise |
| DNN |
Deep Neural Network |
| DAC |
DBSCAN-based adaptive clustering method |
| ROI |
Region of Interest |
| WBLC |
Window Based LiDAR Clustering |
| HEVC |
High Efficiency Video Coding |
| CA |
Constant Acceleration |
| MHT |
Multiple Hypothesis Tracking |
| ICP |
Iterative Closest Points |
| ADAS |
Advanced Driver Assisted Systems |
| ACKF |
Adaptive Cubature Kalman Filter |
| SRTs |
Scale-Rotation-Translation score |
| DPCR |
Dynamic Point Cloud Registration |
| EKF |
Extended Kalman Filter |
| UKF |
Unscented Kalman Filter |
| PF |
Particle Filter |
| VLP-16 |
Velodyne LiDAR Pucks |
| MAR |
Minimum Area Rectangle |
| JPDA |
Joint Probabilistic Data Association |
| IMM |
Interactive Multiple Model |
| PRISMA |
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| TLG |
Two-Layer-Graph |
Paper structure: The rest of the paper is divided into four core sections.
Section 3 focuses on clustering: first, we provide a general overview of clustering techniques (
Section 3.1), then we analyzed their application on LiDAR point clouds for autonomous driving (
Section 3.2), and finally we discuss the major challenges in this context (
Section 3.3).
Section 4 follows the same division in three parts, but tackles the topic of MTT. More specifically, MTT is introduced in
Section 4.1 and its applications on LiDAR point clouds for autonomous driving are discussed in
Section 4.2. In
Section 4.3, we highlight the challenges associated with tracking multiple targets within the context of autonomous vehicles.
Section 5 presents an integrated discussion of clustering and MTT: future research directions are envisioned in the area of clustering and Multi-Target Tracking in autonomous vehicles (
Section 5.1) and our findings are discussed (
Section 5.2). Finally,
Section 6 concludes the paper by summarizing the key insights and contributions presented in this study.