Submitted:
30 April 2023
Posted:
01 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
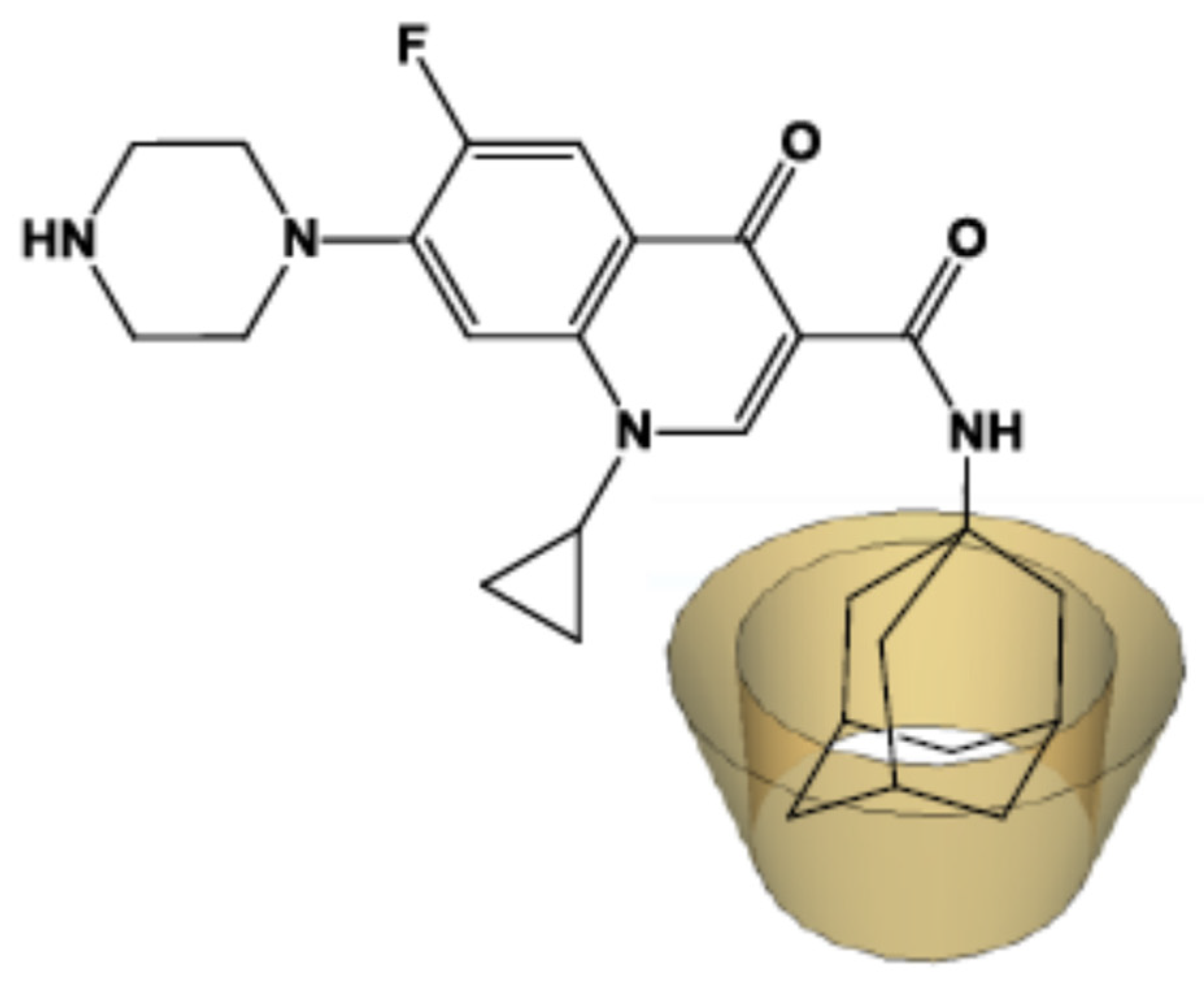
2.1. NMR Study
2.2. ITC studies
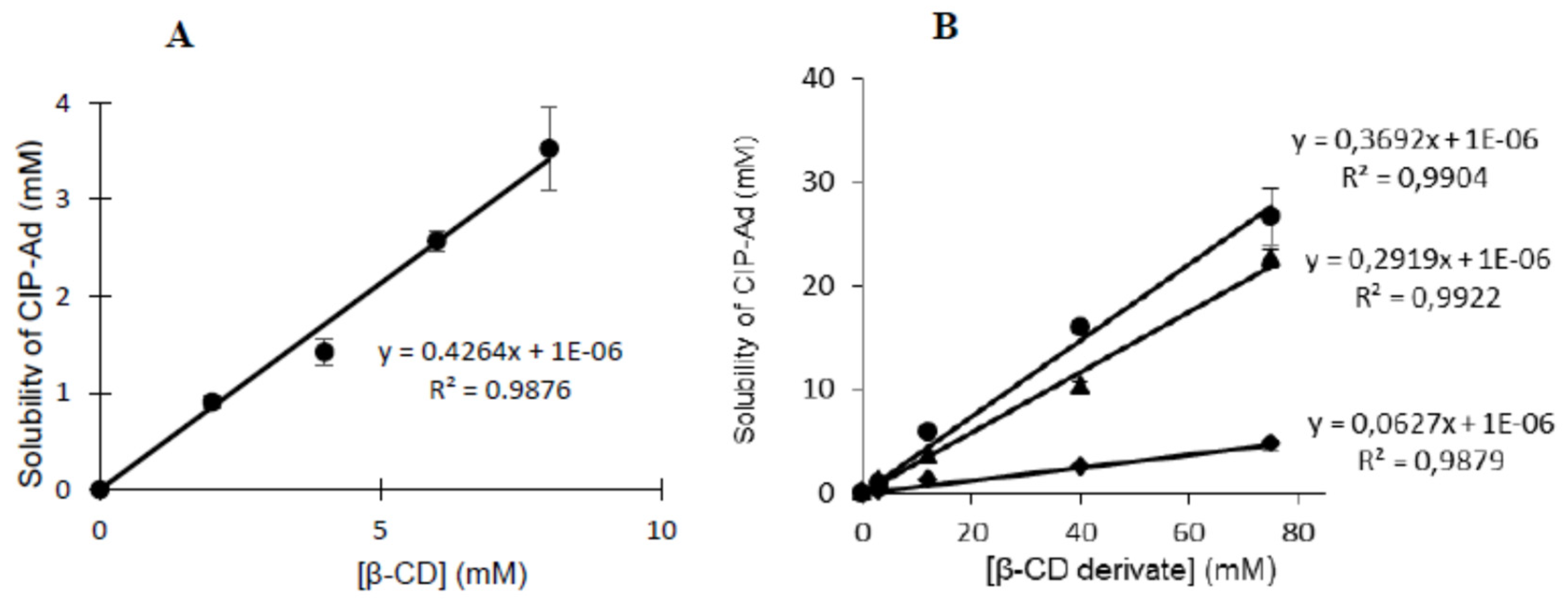
2.3. Solubility studies
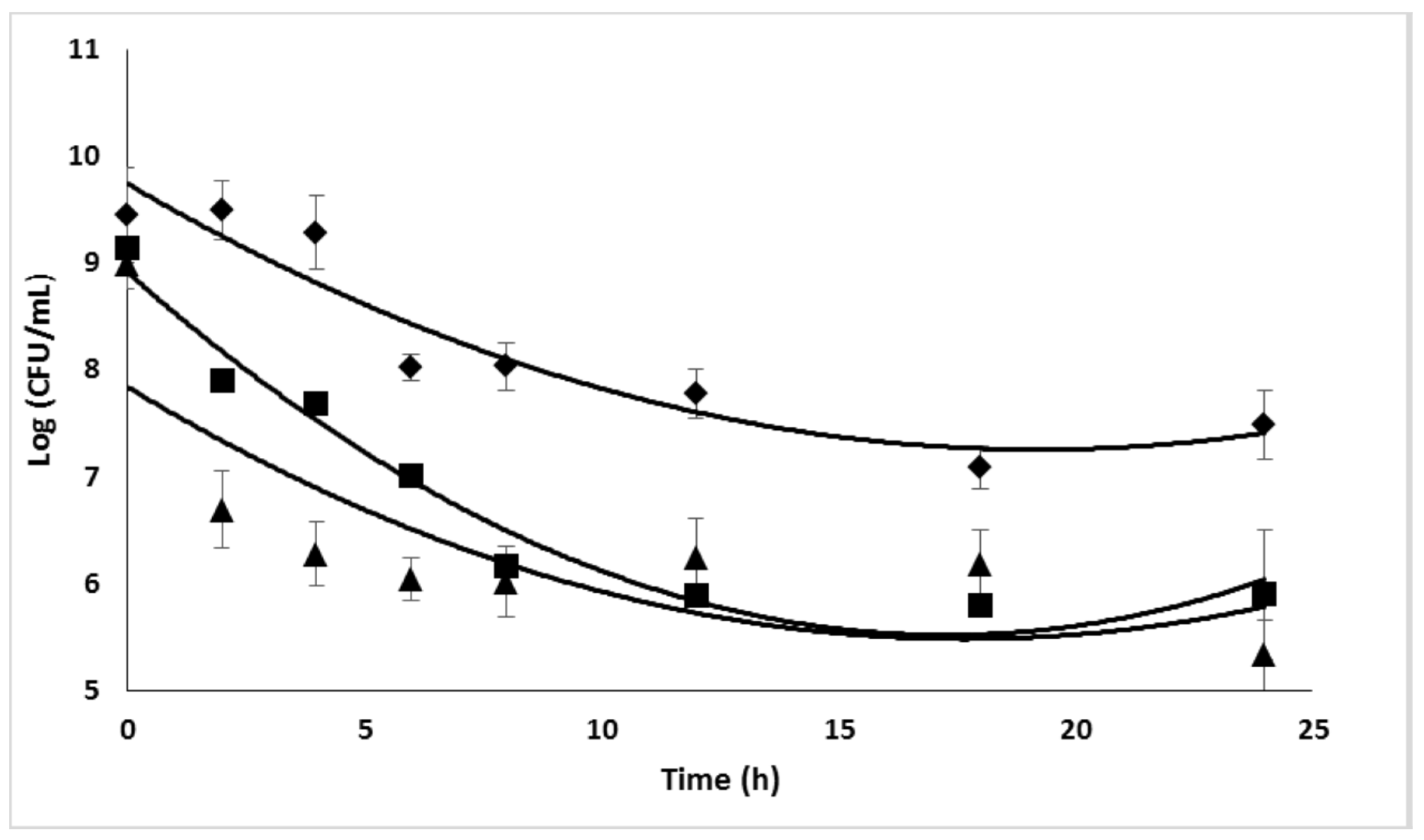
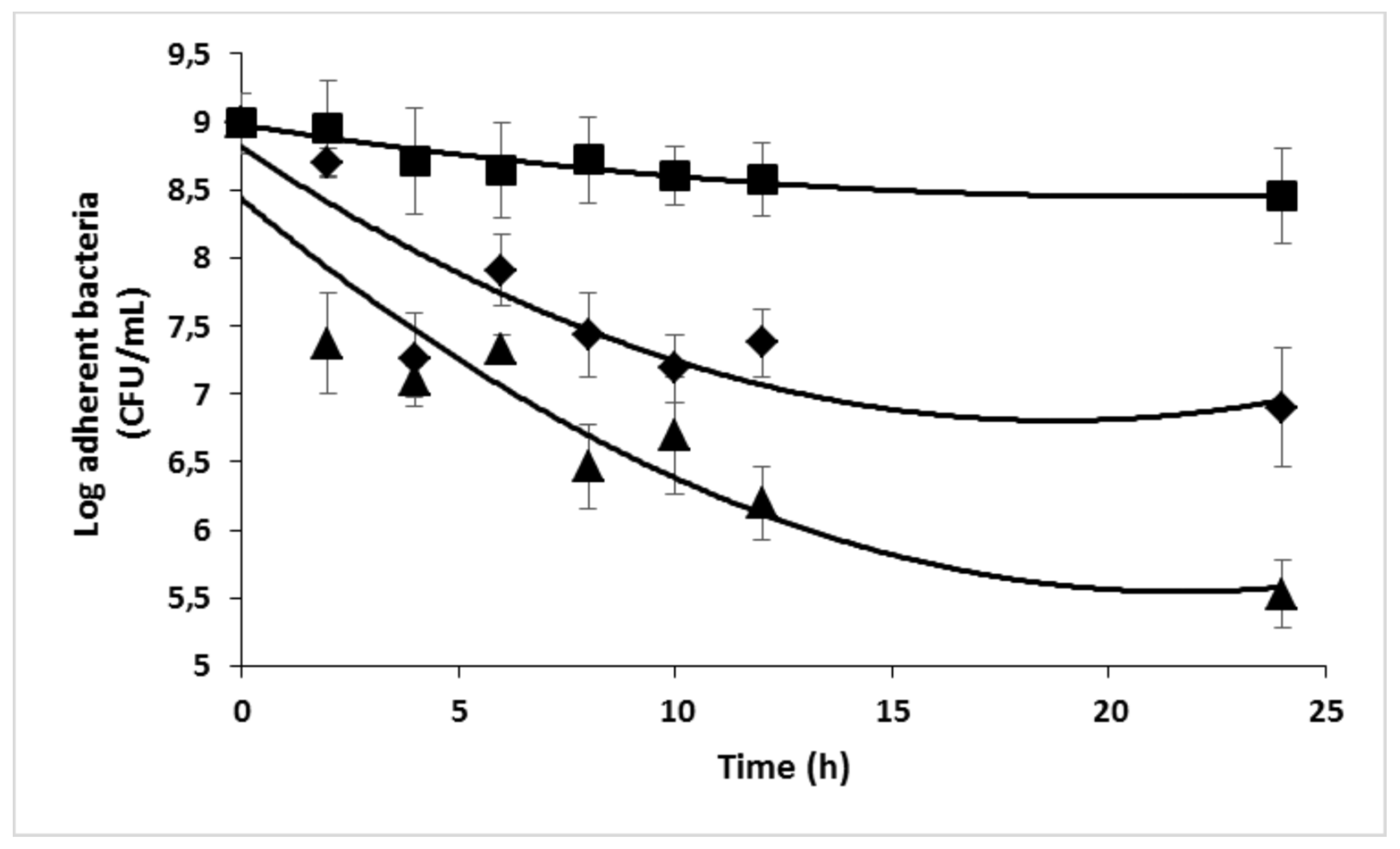
2.4. Antimicrobial efficacy of Ciprofloxacin
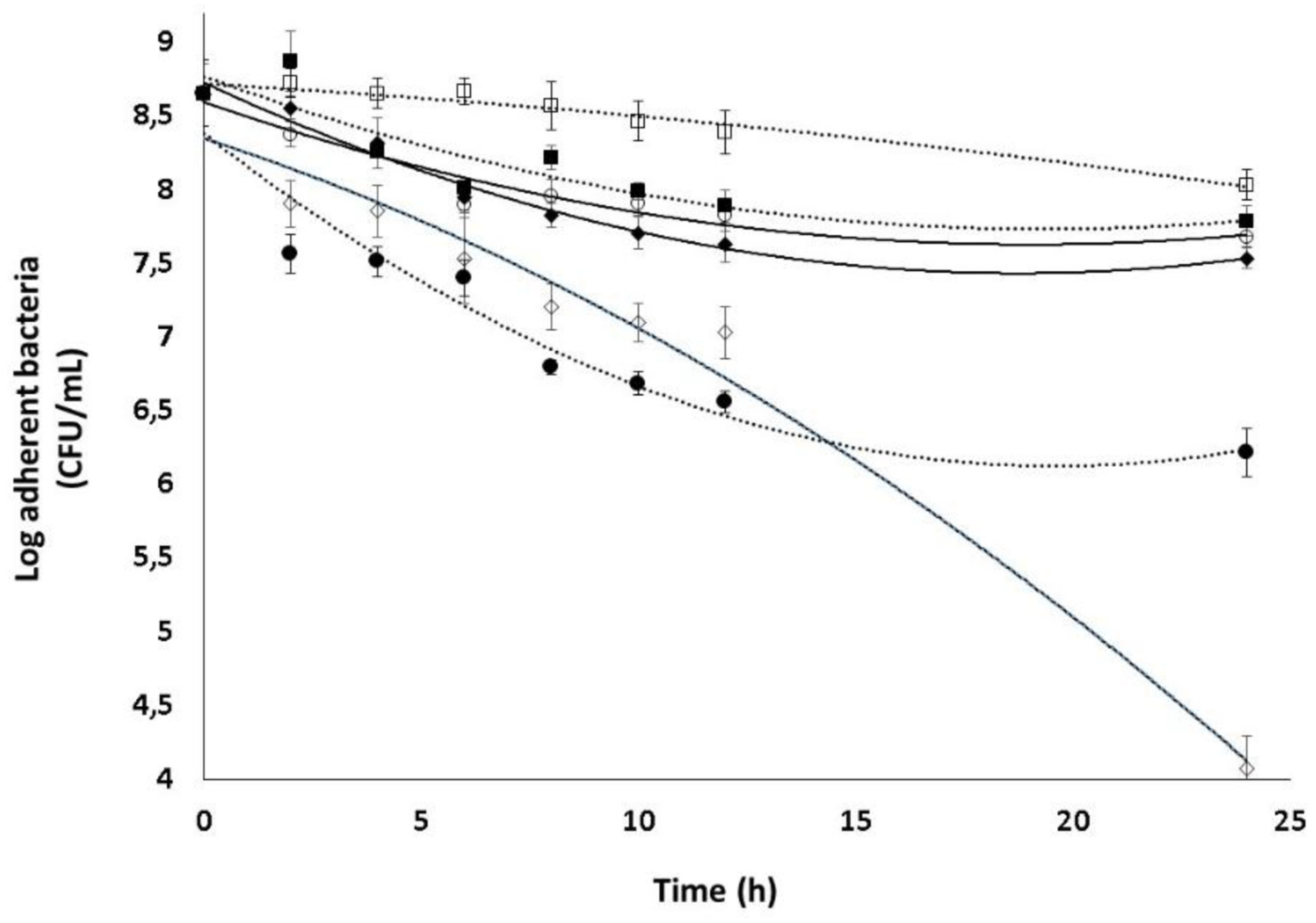
2.5. Combined effect of Dsp B and β-CD II/CIP-Ad complex against biofilms
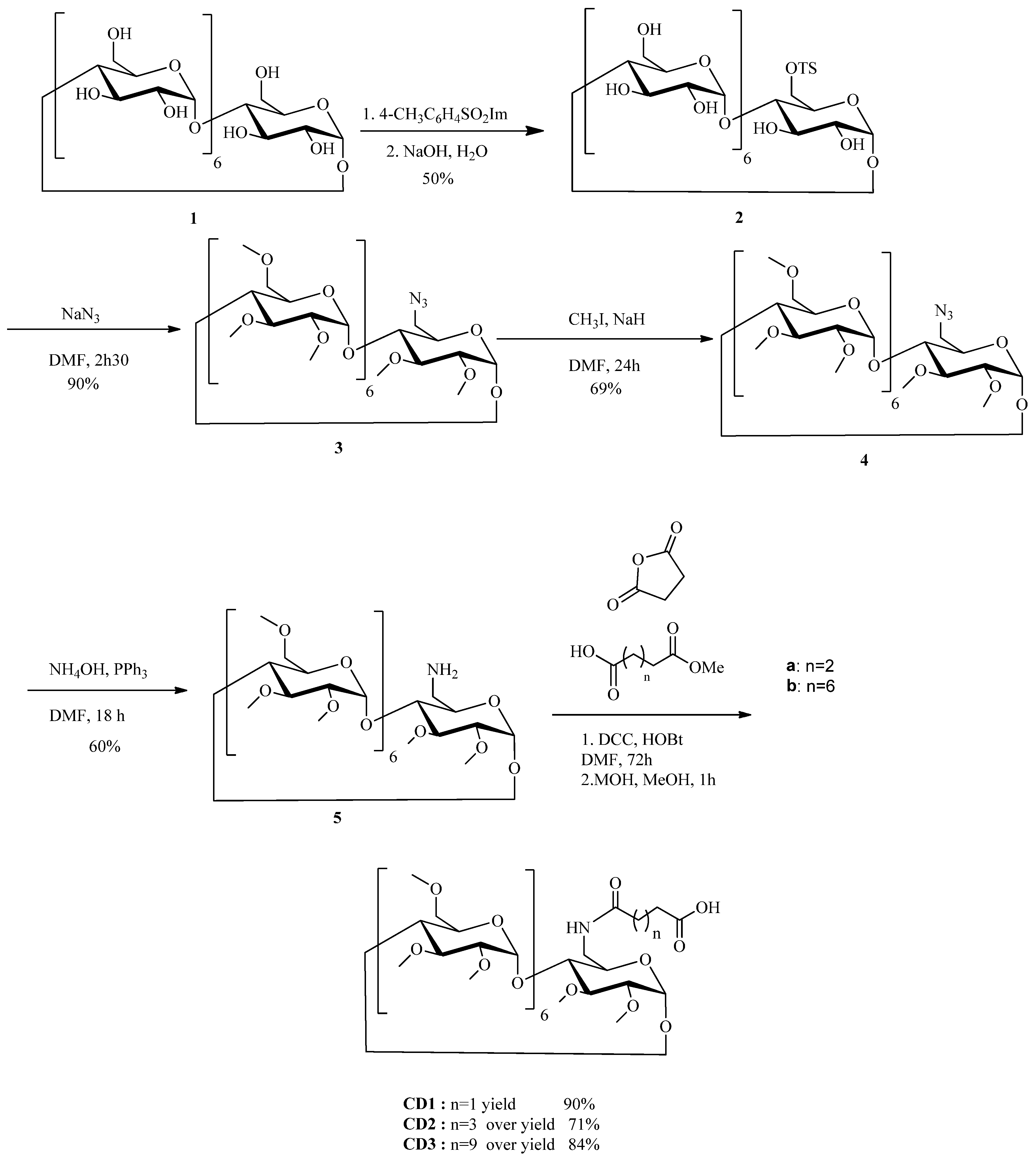
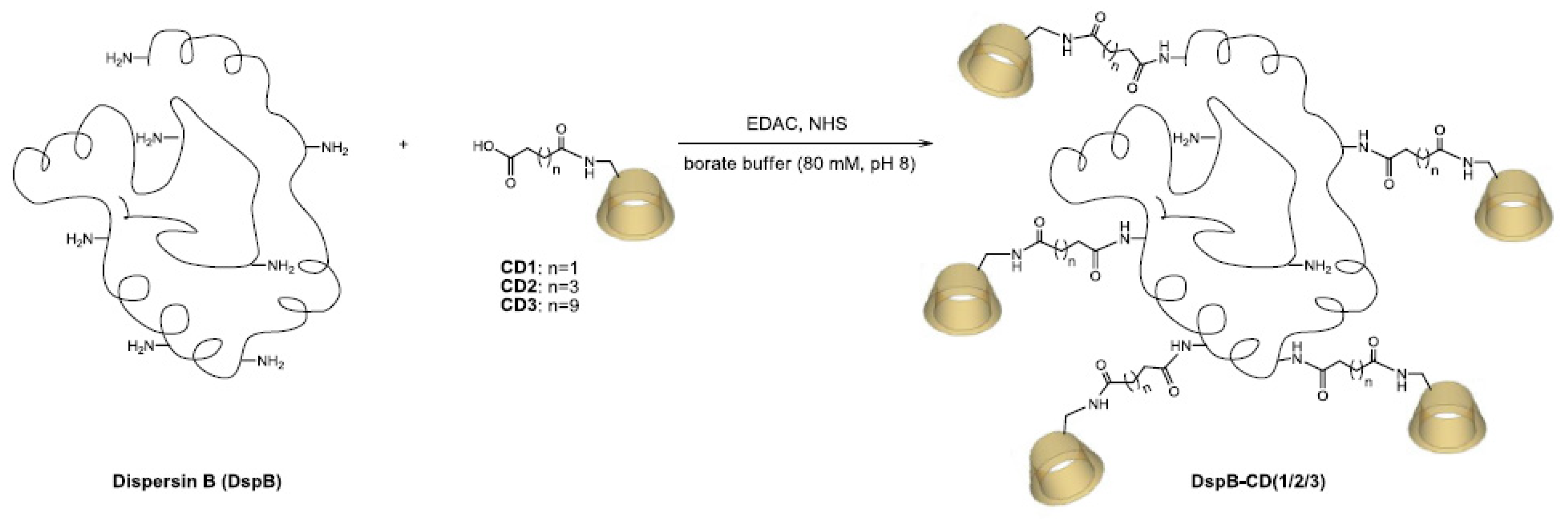
2.6. Synthesis of CD derivatives CD1-3
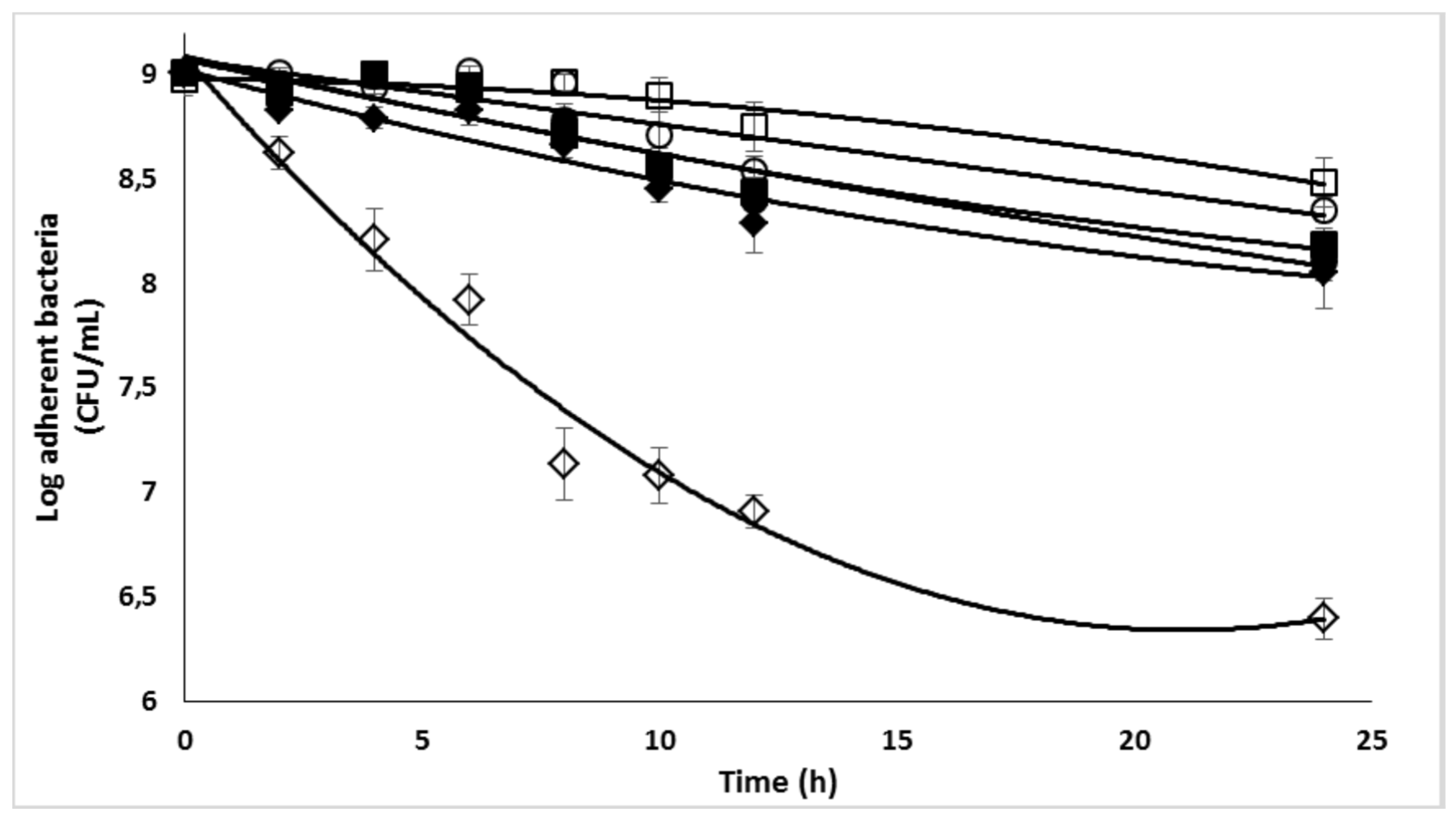
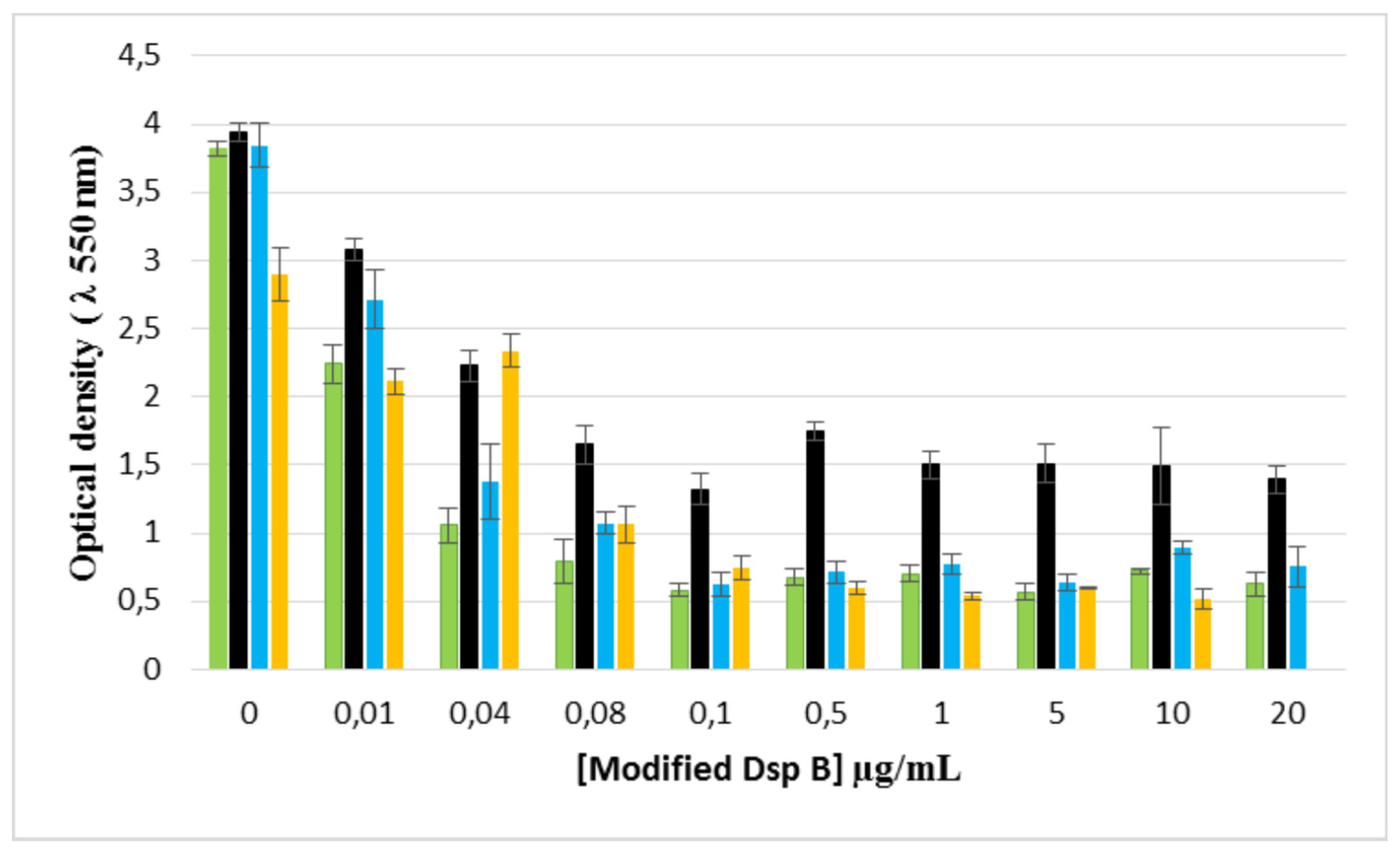
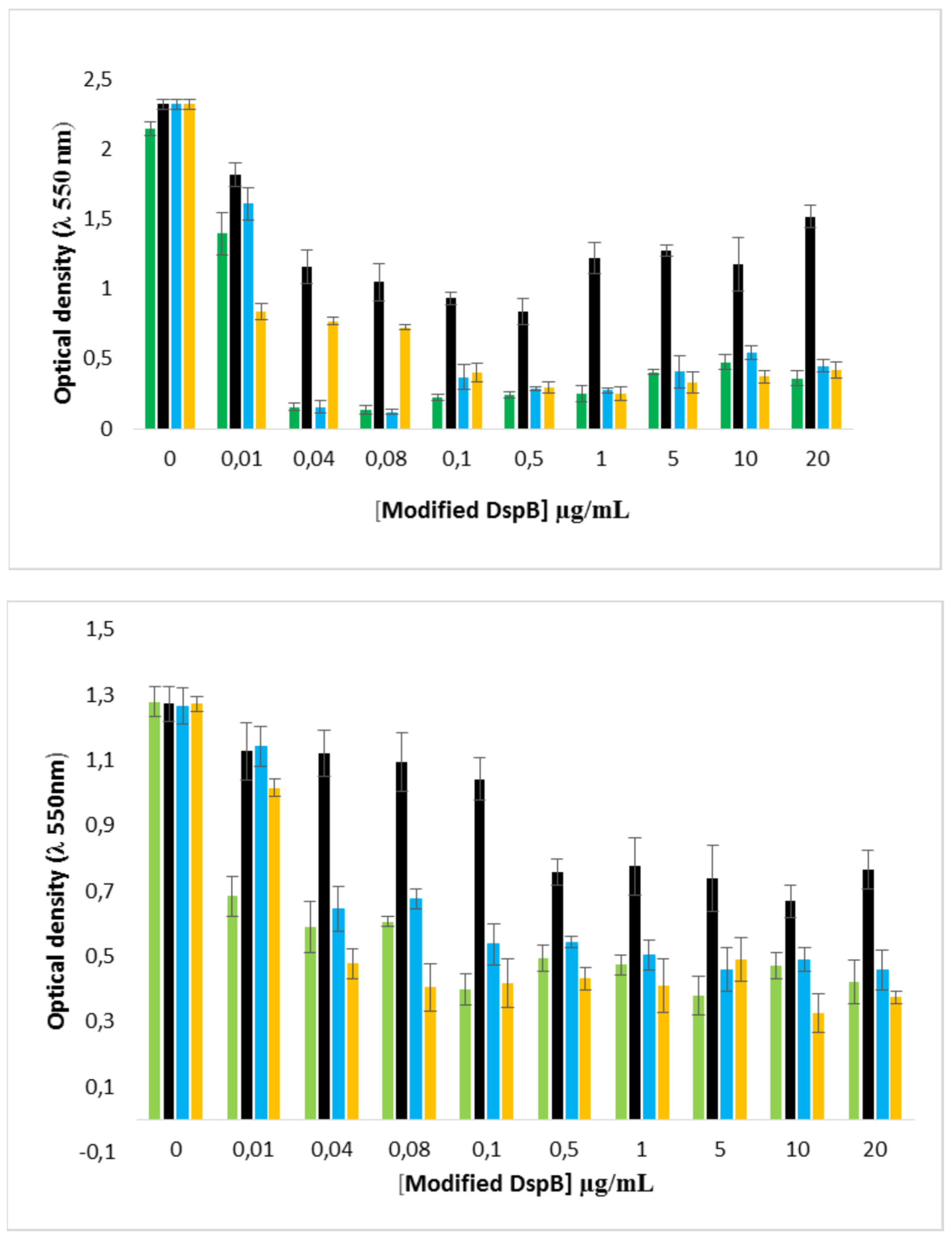
2.7. Enzymatic biofilm dispersion assays by DspB-β-CDs conjugates
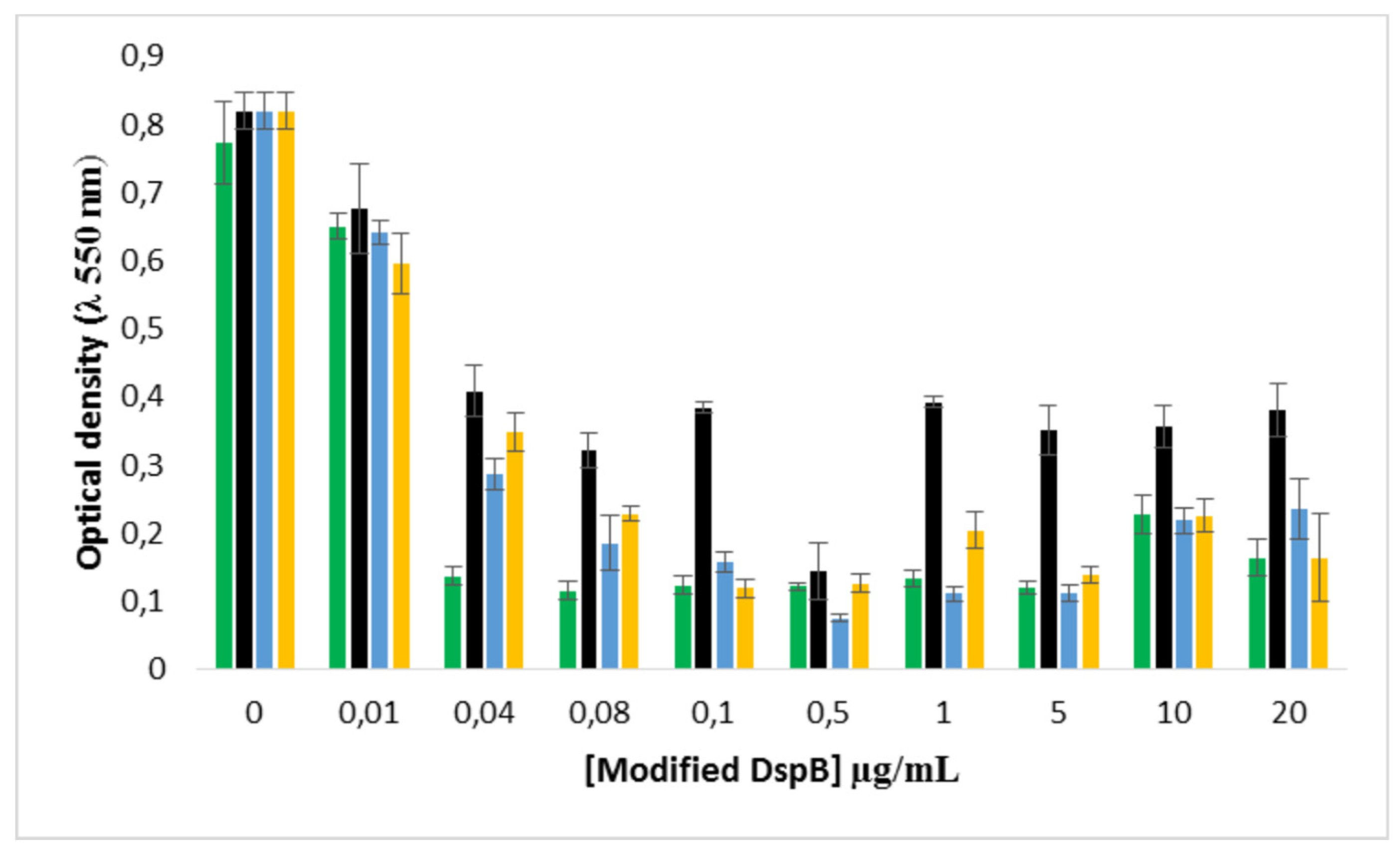
2.8. Effect of the DspB-β-CD3/CIP-Ad conjugate on biofilm of S. epidermidis
3. Discussion
Acknowledgment
References
- D. McKenney, J. Hübner, E. Muller, Y. Wang, D.A. Goldmann, G.B. Pier, The ica locus of Staphylococcus epidermidis encodes production of the capsular polysaccharide/adhesin, Infect. Immun. 66 (1998) 4711–4720. [CrossRef]
- M. Otto, Staphylococcal Infections: Mechanisms of Biofilm Maturation and Detachment as Critical Determinants of Pathogenicity, Annu. Rev. Med. 64 (2013) 175–188. [CrossRef]
- C. Von Eiff, G. Peters, C. Heilmann, Pathogenesis of infections due to coagulase-negative staphylococci, Lancet Infect. Dis. 2 (2002) 677–685. [CrossRef]
- J.W. Costerton, P.S. Stewart, E.P. Greenberg, Bacterial Biofilms: A Common Cause of Persistent Infections, Science (80-. ). 284 (1999) 1318–1322. [CrossRef]
- H.-C. Flemming, J. Wingender, The biofilm matrix, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8 (2010) 623–633. [CrossRef]
- C. Soumet, C. Ragimbeau, P. Maris, Screening of benzalkonium chloride resistance in Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated during cold smoked fish production, Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 41 (2005) 291–296. [CrossRef]
- K. Ganeshnarayan, S.M. Shah, M.R. Libera, A. Santostefano, J.B. Kaplan, Poly-Nacetylglucosamine matrix polysaccharide impedes fluid convection and transport of the cationic surfactant cetylpyridinium chloride through bacterial biofilms, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75 (2009) 1308–1314. [CrossRef]
- H. Nakamura, K.-I. Takakura, Y. Sone, Y. Itano, Y. Nishikawa, Biofilm Formation and Resistance to Benzalkonium Chloride in Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from a Fish Processing Plant, J. Food Prot. 76 (2013) 1179–1186. [CrossRef]
- E.A. Izano, M.A. Amarante, W.B. Kher, J.B. Kaplan, Differential roles of poly-Nacetylglucosamine surface polysaccharide and extracellular DNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74 (2008) 470–476. [CrossRef]
- M. Otto, Staphylococcus epidermidis - The “accidental” pathogen, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7 (2009) 555–567. [CrossRef]
- S. Jabbouri, I. Sadovskaya, Characteristics of the biofilm matrix and its role as a possible target for the detection and eradication of Staphylococcus epidermidis associated with medical implant infections, FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 60 (2010) 280–291. [CrossRef]
- G. Rf, R. Gk, G.B. Kostiner, Time-kill efficacy of antibiotics in combination with rifampin against Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms, Adv Perit Dial. 10 (1994) 189–92.
- P.M. Bales, E.M. Renke, S.L. May, Y. Shen, D.C. Nelson, Purification and Characterization of Biofilm-Associated EPS Exopolysaccharides from ESKAPE Organisms and Other Pathogens, PLoS One. 8 (2013) e67950. [CrossRef]
- M.C. Walters, F. Roe, A. Bugnicourt, M.J. Franklin, P.S. Stewart, Contributions of antibiotic penetration, oxygen limitation, and low metabolic activity to tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to ciprofloxacin and tobramycin, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47 (2003) 317–323. [CrossRef]
- J.N. Anderl, M.J. Franklin, P.S. Stewart, Role of Antibiotic Penetration Limitation in Klebsiella pneumoniae Biofilm Resistance to Ampicillin and Ciprofloxacin, 44 (2000) 1818–1824. [CrossRef]
- R. Singh, P. Ray, A. Das, M. Sharma, Penetration of antibiotics through Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65 (2010) 1955–1958. [CrossRef]
- W.L. Jones, M.P. Sutton, L. Mckittrick, P.S. Stewart, Chemical and antimicrobial treatments change the viscoelastic properties of bacterial biofilms, Biofouling. 27 (2011) 207–215. [CrossRef]
- N.M. Abraham, S. Lamlertthon, V.G. Fowler, K.K. Jefferson, Chelating agents exert distinct effects on biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus depending on strain background: Role for clumping factor B, J. Med. Microbiol. 61 (2012) 1062–1070. [CrossRef]
- Y. Itoh, X. Wang, B. Joseph Hinnebusch, J.F. Preston, T. Romeo, Depolymerization of β- 1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine disrupts the integrity of diverse bacterial biofilms, J.Bacteriol. 187 (2005) 382–387. [CrossRef]
- P. Chaignon, I. Sadovskaya, C. Ragunah, N. Ramasubbu, J.B. Kaplan, S. Jabbouri, Susceptibility of staphylococcal biofilms to enzymatic treatments depends on their chemical composition, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 75 (2007) 125–132. [CrossRef]
- C.B. Whitchurch, T. Tolker-Nielsen, P.C. Ragas, J.S. Mattick, Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation, Science (80-. ). 295 (2002) 1487. [CrossRef]
- N. Ramasubbu, L.M. Thomas, C. Ragunath, J.B. Kaplan, Structural analysis of dispersin B, a biofilm-releasing glycoside hydrolase from the periodontopathogen Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, J. Mol. Biol. 349 (2005) 475–486. [CrossRef]
- J.B. Kaplan, C. Ragunath, K. Velliyagounder, D.H. Fine, N. Ramasubbu, Enzymatic detachment of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48 (2004) 2633–2636. [CrossRef]
- M. Jamal, W. Ahmad, S. Andleeb, F. Jalil, M. Imran, M.A. Nawaz, T. Hussain, M. Ali, M. Rafiq, M.A. Kamil, Bacterial biofilm and associated infections, J. Chinese Med. Assoc. 81 (2018) 7–11. [CrossRef]
- M.R. Parsek, P.K. Singh, Bacterial Biofilms: An Emerging Link to Disease Pathogenesis, Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57 (2003) 677–701. [CrossRef]
- R.M. Donlan, Biofilms and device-associated infections, Emerg. Infect. Dis. 7 (2001) 277–281. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chao, L.R. Marks, M.M. Pettigrew, A.P. Hakansson, Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilm formation and dispersion during colonization and disease, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 4 (2015) article 194. [CrossRef]
- G. Donelli, I. Francolini, D. Romoli, E. Guaglianone, A. Piozzi, C. Ragunath, J.B. Kaplan, Synergistic activity of dispersin B and cefamandole nafate in inhibition of staphylococcal biofilm growth on polyurethanes, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 (2007) 2733–2740. [CrossRef]
- J.H. Lee, J.B. Kaplan, W.Y. Lee, Microfluidic devices for studying growth and detachment of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms, Biomed. Microdevices. 10 (2008) 489–498. [CrossRef]
- R.O. Darouiche, M.D. Mansouri, P. V. Gawande, S. Madhyastha, Antimicrobial and antibiofilm efficacy of triclosan and DispersinB® combination, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 64 (2009) 88–93. [CrossRef]
- V. Venketaraman, A.K. Lin, A. Le, S.C. Kachlany, N.D. Connell, J.B. Kaplan, Both leukotoxin and poly-N-acetylglucosamine surface polysaccharide protect Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans cells from macrophage killing, Microb. Pathog. 45 (2008) 173–180. [CrossRef]
- P.C. Sharma, A. Jain, S. Jain, Fluoroquinolone antibacterials: A review on chemistry, microbiology and therapeutic prospects, Acta Pol. Pharm. - Drug Res. 66 (2009) 587–604.
- C. Florindo, A. Costa, C. Matos, S.L. Nunes, A.N. Matias, C.M.M. Duarte, L.P.N. Rebelo, L.C. Branco, I.M. Marrucho, Novel organic salts based on fluoroquinolone drugs: Synthesis, bioavailability and toxicological profiles, Int. J. Pharm. 469 (2014) 179–189. [CrossRef]
- J.M. Domagala, Structure-activity and structure-side-effect relationships for the quinolone antibacterials, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 33 (1994) 685–706. [CrossRef]
- E.A. Jefferson, E.E. Swayze, S.A. Osgood, A. Miyaji, L.M. Risen, L.B. Blyn, Antibacterial activity of quinolone-macrocycle conjugates, Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 13 (2003) 1635–1638. [CrossRef]
- G.M. Pacifici, G. Marchini, Review Article (Pages: 5023-5041) Effects and Pharmacokinetics, Int J Pediatr. 5 (2017) 5023–5041. [CrossRef]
- K. Matsuo, M. Azuma, M. Kasai, I. Hanji, I. Kimura, T. Kosugi, N. Suga, M. Satoh, Investigation of the clinical efficacy and dosage of intravenous ciprofloxacin in patients with respiratory infection, J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 11 (2008) 111s–117s. [CrossRef]
- E. Ohki, Y. Yamagishi, H. Mikamo, Relationship between the clinical efficacy and AUC/MIC of intravenous ciprofloxacin in Japanese patients with intraabdominal infections, J. Infect. Chemother. 19 (2013) 951–955. [CrossRef]
- M. V. Rekharsky, Y. Inoue, Complexation Thermodynamics of Cyclodextrins, Chem. Rev. 98 (1998) 1875–1917. [CrossRef]
- R. Villalonga, R. Cao, A. Fragoso, Supramolecular Chemistry of Cyclodextrins in Enzyme Technology, Chem. Rev. 107 (2007) 3088−3116. [CrossRef]
- M. Fernández, A. Fragoso, R. Cao, M. Baños, R. Villalonga, Chemical conjugation of trypsin with monoamine derivatives of cyclodextrins: Catalytic and stability properties, Enzyme Microb. Technol. 31 (2002) 543–548. [CrossRef]
- M. Fernández, M. de L. Villalonga, A. Fragoso, R. Cao, R. Villalonga, Stabilization of α- chymotrypsin by modification with β-cyclodextrin derivatives, Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 36 (2002) 235–239. [CrossRef]
- R. Villalonga, M. Fernández, A. Fragoso, R. Cao, L. Mariniello, R. Porta, Thermal stabilization of trypsin by enzymic modification with β-cyclodextrin derivatives, 2003. [CrossRef]
- M. Fernández, A. Fragoso, R. Cao, R. Villalonga, Stabilization of α-chymotrypsin by chemical modification with monoamine cyclodextrin, Process Biochem. 40 (2005) 2091–2094. [CrossRef]
- R. Villalonga, S. Tachibana, R. Cao, H.L. Ramirez, Y. Asano, Supramolecular-mediated thermostabilization of phenylalanine dehydrogenase modified with β-cyclodextrin derivatives, Biochem. Eng. J. 30 (2006) 26–35. [CrossRef]
- A. Štimac, M. Šekutor, K. Mlinarić-Majerski, L. Frkanec, R. Frkanec, Adamantane in drug delivery systems and surface recognition, Molecules. 22 (2017) 297. [CrossRef]
- M.E. Brewster, T. Loftsson, Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59 (2007) 645–666. [CrossRef]
- R.L. Carrier, L.A. Miller, I. Ahmed, The utility of cyclodextrins for enhancing oral bioavailability, J. Control. Release. 123 (2007) 78–99. [CrossRef]
- K.C. Nicolaou, T. Lister, R.M. Denton, A. Montero, D.J. Edmonds, Adamantaplatensimycin: A bioactive analogue of platensimycin, Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 46 (2007) 4712–4714. [CrossRef]
- H.-J. Schneider, F. Hacket, V. Rüdiger, H. Ikeda, NMR Studies of Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin Complexes, Chem. Rev. 98 (1998) 1755–1785. [CrossRef]
- R. Krishnan, A.M. Rakhi, K.R. Gopidas, Study of β-cyclodextrin-pyromellitic diimide complexation. Conformational analysis of binary and ternary complex structures by induced circular dichroism and 2D NMR spectroscopies, J. Phys. Chem. C. 116 (2012) 25004–25014. [CrossRef]
- M.W. Freyer, E.A. Lewis, Isothermal Titration Calorimetry: Experimental Design, Data Analysis, and Probing Macromolecule/Ligand Binding and Kinetic Interactions, Methods Cell Biol. 84 (2008) 79–113. [CrossRef]
- T. Wiseman, S. Williston, J.F. Brandts, N. Lint, Rapid Measurement of Binding Constants and Heats of Binding Using a New Titration Calorimeter, Anal. Biochem. 179 (1989) 131–137. [CrossRef]
- A. Velazquez-Campoy, Geometric features of the Wiseman isotherm in isothermal titration calorimetry, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 122 (2015) 1477–1483. [CrossRef]
- W.B. Turnbull, A.H. Daranas, On the Value of c: Can Low Affinity Systems Be Studied by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry?, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125 (2003) 14859–14866. [CrossRef]
- D.L. Cameron, J. Jakus, S.R. Pauleta, G.W. Pettigrew, A. Cooper, Pressure perturbation calorimetry and the thermodynamics of noncovalent interactions in water: Comparison of protein-protein, protein-ligand, and cyclodextrin-adamantane complexes, J. Phys. Chem. B. 114 (2010) 16228–16235. [CrossRef]
- J. Carrazana, A. Jover, F. Meijide, V.H. Soto, J.V. Tato, Complexation of adamantly compounds by β-cyclodextrin and monoaminoderivatives, J. Phys. Chem. B. 109 (2005) 9719–9726. [CrossRef]
- L. Liu, Q.X. Guo, The driving forces in the inclusion complexation of cyclodextrins, J. Incl. Phenom. 42 (2002) 1–14. [CrossRef]
- P.D. Ross, M. V. Rekharsky, Thermodynamics of hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interactions in cyclodextrin complexes, Biophys. J. 71 (1996) 2144–2154. [CrossRef]
- T. Higuchi, K.A. Connors, Phase Solubility Techniques, in: Reilly C.N. (Ed.), Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum., Interscience, New York, NY, 1965: pp. 117–212.
- T. Loftsson, D. Hreinsdóttir, M. Másson, Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs, Int. J. Pharm. 302 (2005) 18–28. [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of antibacterial agents by broth dilution, Clin.Microbiol.Infect. 9 (2003) 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Y. Nait Chabane, M. Ben Mlouka, S. Alexandre, M. Nicol, S. Marti, M. Pestel-Caron, J.Vila, T. Jouenne, E. Dé, Virstatin inhibits biofilm formation and motility of Acinetobacter baumannii, BMC Microbiol. 14 (2014) 62. [CrossRef]
- D. Mack, W. Fischer, A. Krokotsch, K. Leopold, R. Hartmann, H. Egge, R. Laufs, The intercellular adhesin involved in biofilm accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis is a linear β-1,6-linked glucosaminoglycan: Purification and structural analysis, J. Bacteriol. 178 (1996) 175–183. [CrossRef]
- I. Sadovskaya, E. Vinogradov, S. Flahaut, G. Kogan, S. Jabbouri, Extracellular carbohydrate-containing polymers of a model biofilm-produring strain, Staphylococcus epidermidis RP62A, Infect. Immun. 73 (2005) 3007–3017. [CrossRef]
- G. Kogan, I. Sadovskaya, P. Chaignon, A. Chokr, S. Jabbouri, Biofilms of clinical strains of Staphylococcus that do not contain polysaccharide intercellular adhesin, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 255 (2006) 11–16. [CrossRef]
- V.J. Stella, V.M. Rao, E.A. Zannou, V. Zia, Mechanisms of drug release from cyclodextrin complexes, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 36 (1999) 3–16. [CrossRef]
- V.J. Stella, R.A. Rajewski, Cyclodextrins: Their Future in Drug Formulation and Delivery, Pharm. Res. 14 (1997) 556–567. [CrossRef]
- T. Loftsson, M.D. Moya-Ortega, C. Alvarez-Lorenzo, A. Concheiro, Pharmacokinetics of cyclodextrins and drugs after oral and parenteral administration of drug/cyclodextrin complexes, J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 68 (2016) 544–555. [CrossRef]
- T. Carofiglio, M. Cordioli, R. Fornasier, L. Jicsinszky, U. Tonellato, Synthesis of 6Iamino-6I-deoxy-2I-VII, 3I-VII-tetradeca-O-methyl-cyclomaltoheptaose, Carbohydr. Res. 339 (2004) 1361–1366. [CrossRef]
- A. Angelova, C. Fajolles, C. Hocquelet, F. Djedaïni-Pilard, S. Lesieur, V. Bonnet, B. Perly, G. Lebas, L. Mauclaire, Physico-chemical investigation of asymmetrical peptidolipidylcyclodextrins, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 322 (2008) 304–314. [CrossRef]
- G.A. O’Toole, R. Kolter, Flagellar and twitching motility are necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development, Mol. Microbiol. 30 (1998) 295–304. [CrossRef]
- F. Costa, I.F. Carvalho, R.C. Montelaro, P. Gomes, M.C.L. Martins, Covalent immobilization of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) onto biomaterial surfaces, Acta Biomater. 7 (2011) 1431–1440. [CrossRef]
- D. Campoccia, L. Montanaro, C.R. Arciola, A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces, Biomaterials. 34 (2013) 8533–8554. [CrossRef]
- K. Glinel, P. Thebault, V. Humblot, C.M. Pradier, T. Jouenne, Antibacterial surfaces developed from bio-inspired approaches, Acta Biomater. 8 (2012) 1670–1684. [CrossRef]
- P.L. Shah, S.F. Scott, R.A. Knight, C. Marriott, C. Ranasinha, M.E. Hodson, In vivo effects of recombinant human DNase I on sputum in patients with cystic fibrosis, Thorax. 51 (1996) 119–125. [CrossRef]
- J.N. Zitter, P. Maldjian, M. Brimacombe, K.P. Fennelly, Inhaled Dornase alfa (Pulmozyme) as a noninvasive treatment of atelectasis in mechanically ventilated patients, J. Crit. Care. 28 (2013) 218.e1–218.e7. [CrossRef]
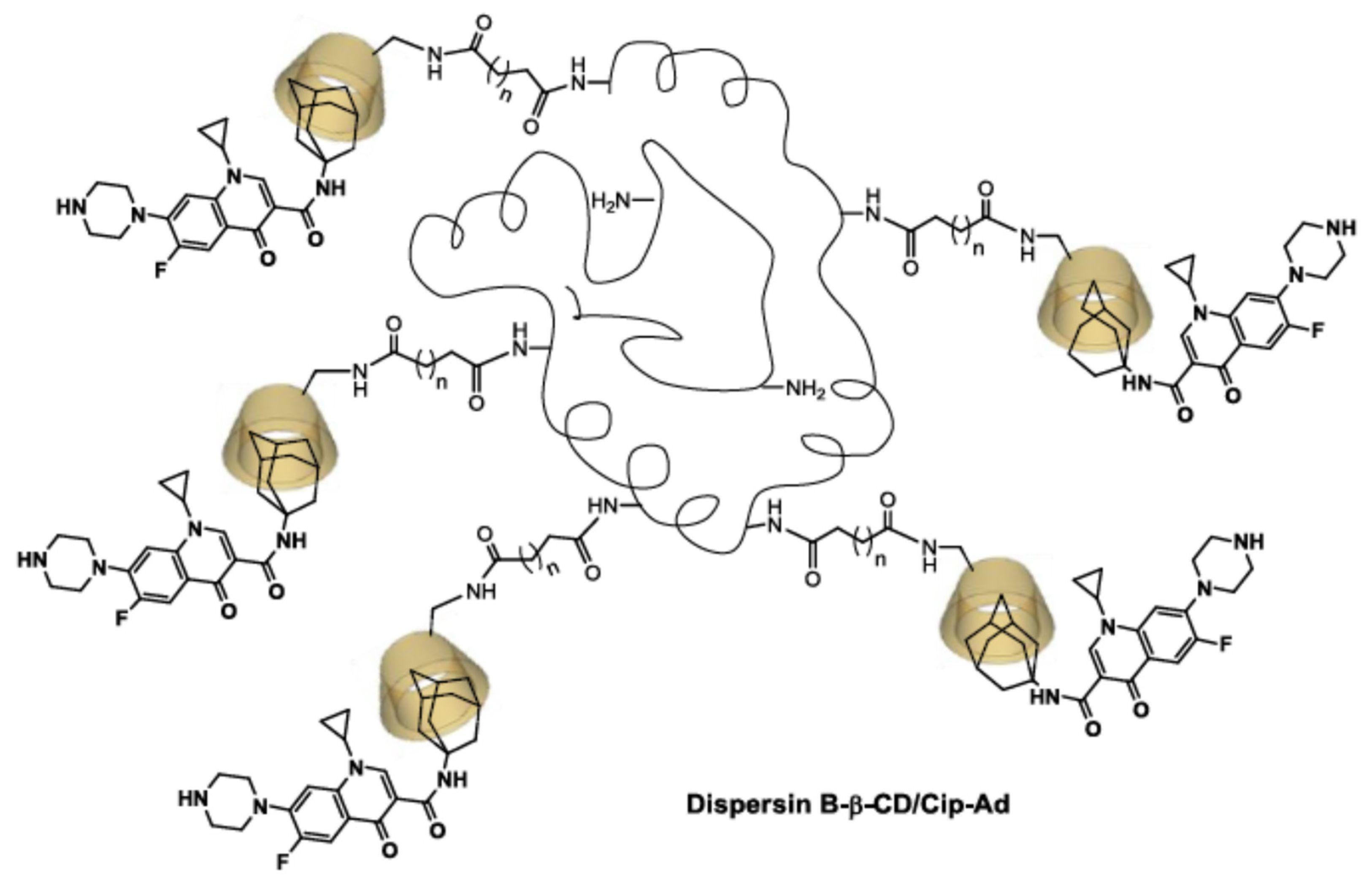
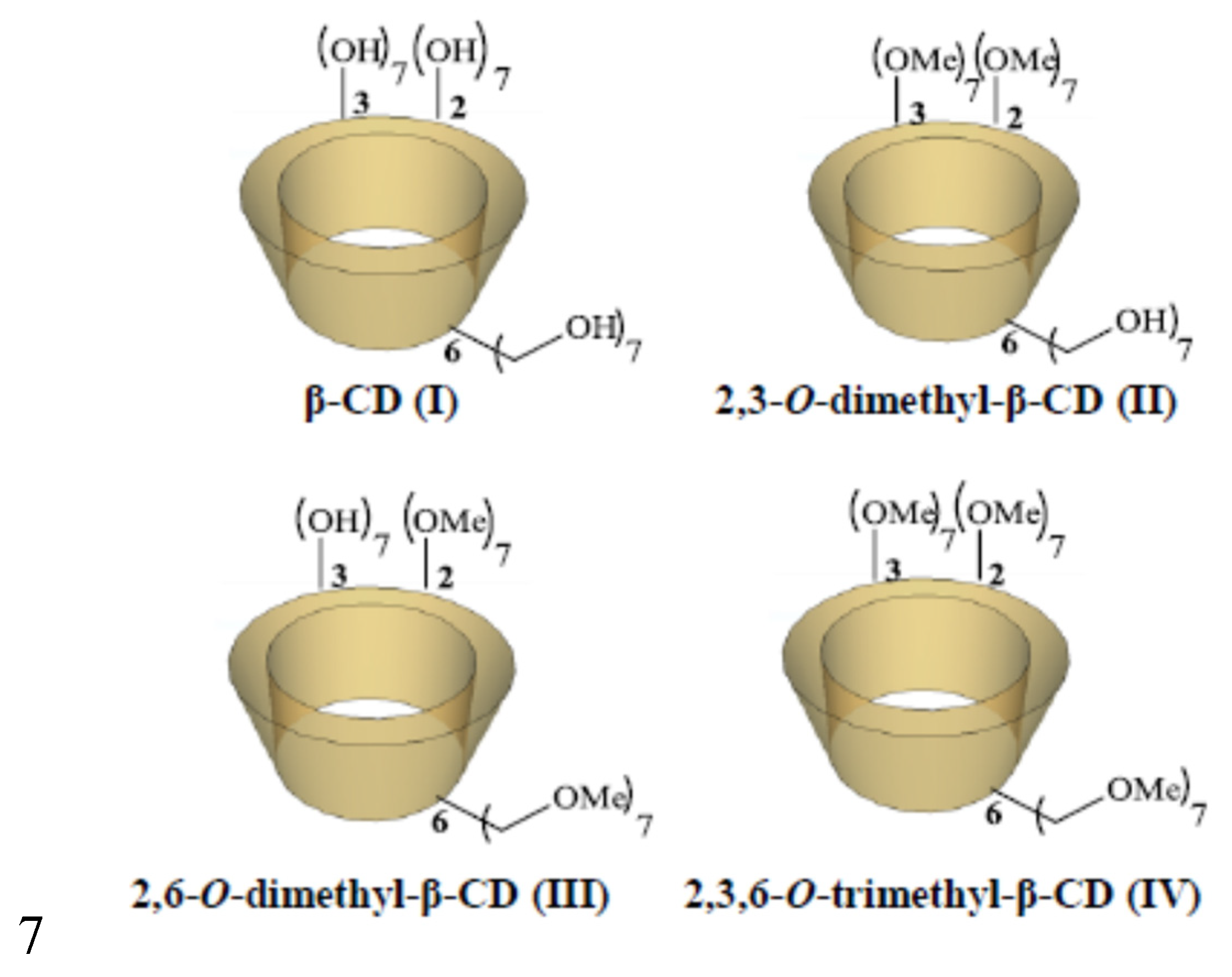
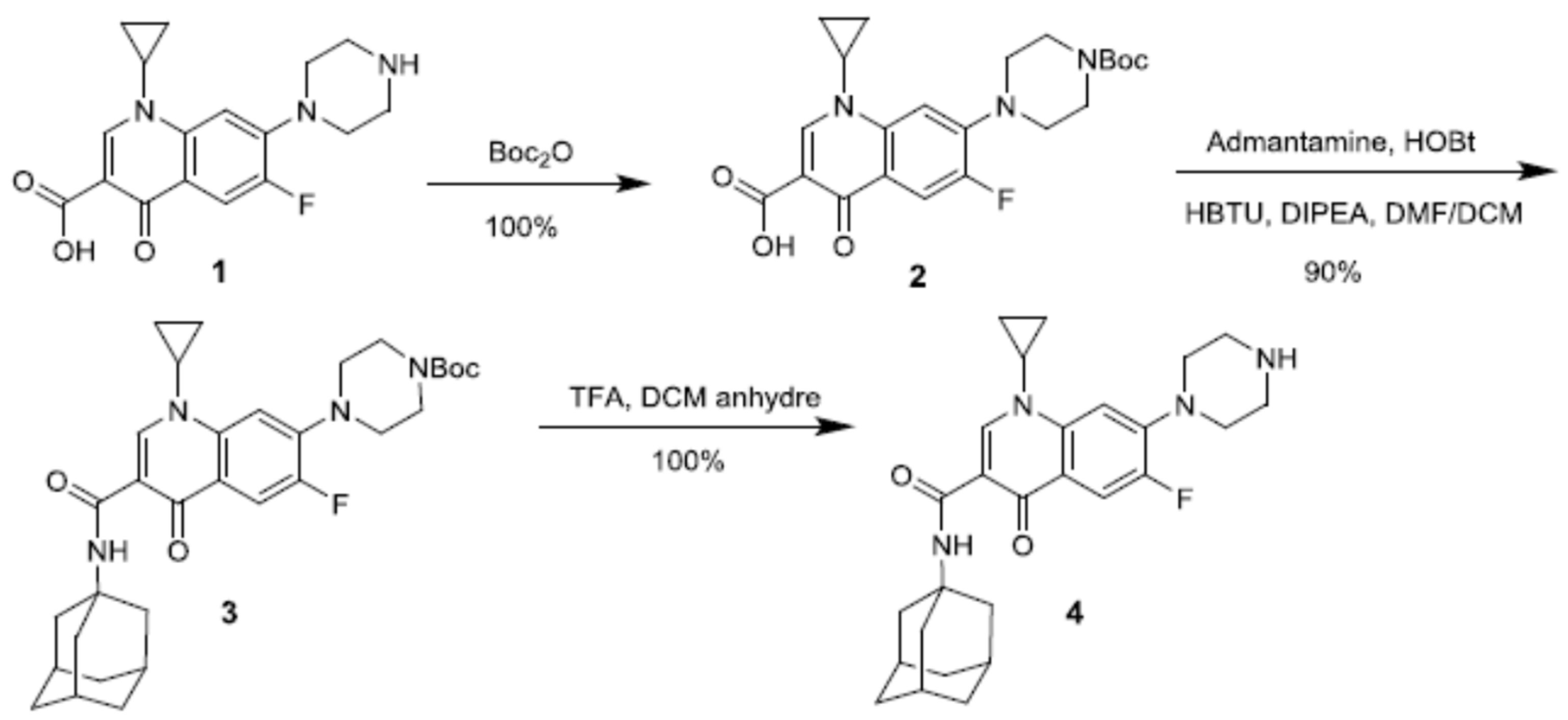
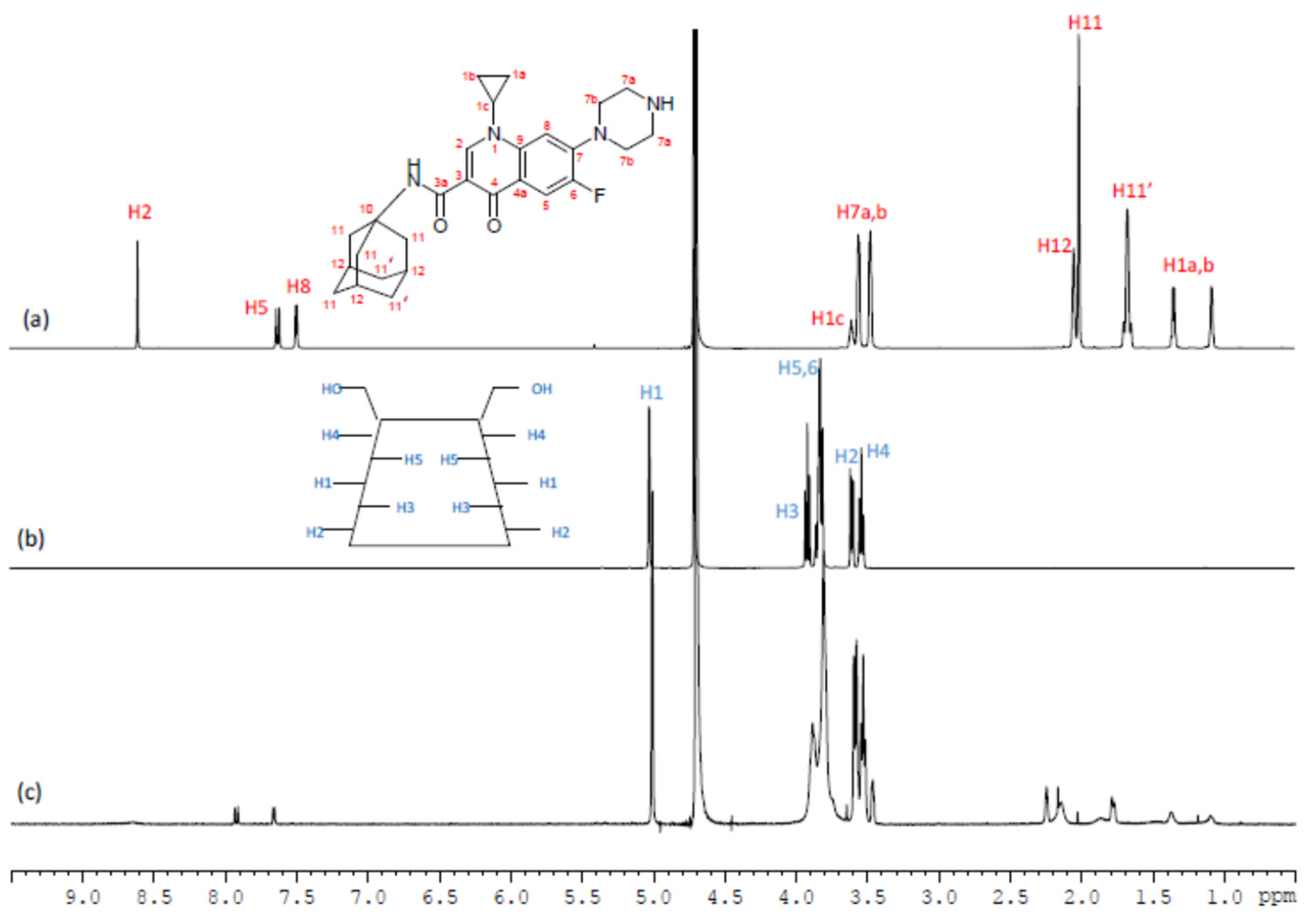
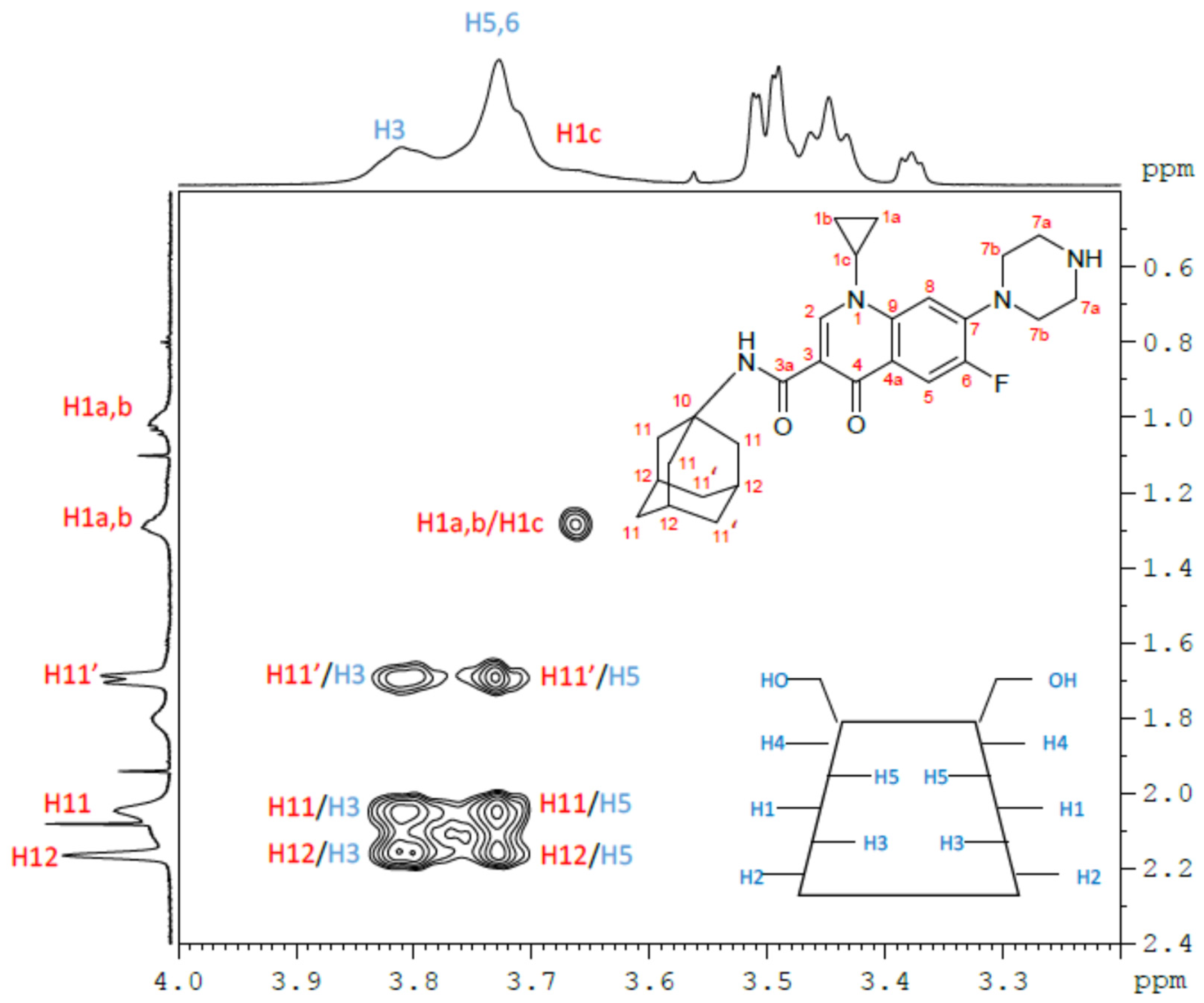
| β-CD protons | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5, H6 | ||||||||
| Free β-CD(*) | 5.02 | 3.60 | 3.91 | 3.53 | 3.82 | ||||||||
| β-CD/CIP-Ad Complex | 5.02 | 3.60 | 3.89 | 3.54 | 3.81 | ||||||||
| ∆δ (free-complex) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | -0.01 | 0.01 | ||||||||
| CIP-Ad protons | H1a,H1b | H1c | H2 | H5 | H7a,H7b | H8 | H11,H11′ | H12 | |||||
| Free CIP-Ad | 1.35; 1.08 | 3.60 | 8.60 | 7.62 | 3.55; 3.47 | 7.49 | 2.01, 1.67 | 2.04 | |||||
| β-CD/ CIP-Ad Complex | 1.38; 1.10 | 3.75 | 8.6 | 7.93 | 3.57; 3.47 | 7.67 | 2.15, 1.78 | 2.25 | |||||
| ∆δ (free-complex) | 0.03; 0.02 | -0.15 | 0.06 | -0.31 | (0.02); 0.00 | -0.18 | -0.14,-0.11 | -0.21 | |||||
| Host | T (°C) |
Ka/104 (M-1) |
∆H (kJ/mol) |
∆S (J/mol.K) |
∆G (kJ/mol) |
∆Cp (J/mol.K) |
C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-CD I | 15 | 44.5 ± 4.6 | -17.8 ± 0.1 | 46.2 | -31.1 |
-201 (r2= 0.996) |
134 |
| 25 | 33.5 ± 3.2 | -19.9 ± 0.1 | 38.9 | -31.5 | 101 | ||
| 37 | 21.3 ± 1.4 | -21.9 ± 0.1 | 31.4 | -31.6 | 64 | ||
| 45 | 17.9 ± 1,3 | -23.8 ± 0.2 | 25.7 | -31.9 | 54 | ||
| 55 | 15.1 ± 1.1 | -25.7 ± 0.2 | 20.8 | -32.5 | 45 | ||
| 60 | 10.7 ± 0.7 | -27.1 ± 0.2 | 15.1 | -32.0 | 32 | ||
| 2,3-O- dimethyl- β-CD II |
25 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | -5.7 ± 0.1 | 58.5 | -23.1 |
-320 (r2= 0.962) |
3 |
| 37 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | -10.1 ± 0.3 | 43.8 | -23.7 | 3 | ||
| 45 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | -13.7 ± 0.6 | 32.5 | -24.1 | 3 | ||
| 55 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | -16.5 ± 0.6 | 23.8 | -24.6 | 2 | ||
| 60 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | -16.3 ± 0.6 | 24.6 | -24.5 | 2 | ||
| 2,6-O- dimethyl- β-CD III |
15 | 114.0 ± 22.0 | -9.9 ± 0.1 | 81.7 | -33.3 |
-438 (r2= 0.989) |
342 |
| 25 | 94.5 ± 5.5 | -13.3 ± 0.1 | 69.8 | -34.0 | 284 | ||
| 37 | 72.7 ± 6.7 | -18.6 ± 0.1 | 52.3 | -34.7 | 218 | ||
| 45 | 60.1 ± 3.6 | -21.0 ± 0.1 | 44.7 | -35.1 | 180 | ||
| 55 | 39.9 ± 2.7 | -27.4 ± 0.4 | 23.7 | -35.1 | 120 | ||
| 60 | 37.5 ± 3.2 | -29.4 ± 0.2 | 18.4 | -35.5 | 113 | ||
| 2,3,6-O- trimethyl- β-CD IV |
15 | 13.4 ± 1.5 | -11.3 ± 0.1- | 58.7 | -28.2 |
-537 (r2= 0.982) |
40 |
| 25 | 12.1 ± 1.3 | -19.6 ± 0.2 | 31.4 | -29.0 | 36 | ||
| 37 | 8.4 ± 0.7 | -22.7 ± 0.2 | 21.2 | -29.2 | 25 | ||
| 45 | 6.5 ± 0.4 | -28.3 ± 0.2 | 3.2 | -29.3 | 20 | ||
| 55 | 4.6 ± 0.3 | -34.7 ± 0.4 | -16.6 | -29.2 | 14 | ||
| 60 | 3.6 ± 0.2 | -35.8 ± 0.4 | -20.2 | -29.0 | 11 |
| Strain | 5 | RP62A | 1457 | 9142 |
| MIC (µg/mL) | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 4.00 |
| Strain | 5 | RP62A | 1457 | 9142 |
| MIC (µg / mL) | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 8.0 |
|
Strain |
Complex | |
| β-CD II/CIP-Ad | β-CDIV/CIP-Ad | |
| 5 | 2 | 4 |
| RP62A | 4 | 8 |
| 1457 | 4 | 8 |
| 9142 | 8 | 16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





