1. Introduction
1.1. Cell Heterogeneity
The transcriptome analysis, as a global profile of gene expression, is a key factor for the study of complex biological samples composed of multiple cell populations in heterogeneous mixtures. Specifically, transcriptomics enables identifying how genes change according to the regular processes happening in the human organism, or under specific pathological alterations that modify cellular function, such as tumorigenesis and cancer development. For example, increased infiltration of pro-inflammatory immune cells (primarily CD8+ cytotoxic T cells) in the tumor microenvironment (TME) is associated with a good prognosis in cancer patients [
1,
2,
3,
4], whereas the presence of immunosuppressive cells, such as myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), regulatory T cells, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and fibroblasts have an adverse effect, reducing the efficacy in oncological treatments [
5,
6,
7]. These studies are based on the quantitative analysis of gene expression, which is obtained using different techniques that measure the levels of total RNA (normally mRNA) in the biological samples. In our work, we used global gene expression data collected by microarrays technology and RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) signal expression data. The microarray techniques are cheaper and require less time to run the algorithms than RNA-Seq. However, this technology is limited to known genes or to sequences inserted in microarrays. On the other hand, RNA-Seq is computationally more complex but allows the identification of new genes by measuring any expressed sequence and detecting genes with low expression levels [
8].
On this topic, massive RNA data for millions of samples have been produced in thousands of transcriptomic studies over the last decades and include very relevant and accurate information on gene activity. Nevertheless, experimental techniques (in vivo), such as flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry, have some limitations because they are more expensive and time-consuming. In addition, they are limited to phenotypic markers, and, in the case of flow cytometry, its results may be altered by tissue disaggregation, losing or damaging cells [
9]. Hence, computational techniques (in silico) known as deconvolution methods have been developed, which propose algorithms to decompose a mixture of signals (bulk) and infer the relative frequencies of the cell types contained in the mixture or the expression of marker genes allowing the identification of new biomarkers [
9,
10].
1.2. Deconvolution to Decompose Mixtures
Global signals or numerical values are generally used to measure all elements present as a mixture in a complex sample (e.g., a biological sample compose of multiple cell types). These mixture samples are decomposed using a mathematical method to identify their elements and calculate the number of components and their relative composition or percentage. Deconvolution is the mathematical term for this type can of analytical approach. Usually, to explain this mathematical procedure, the phenomenon called `cocktail party problem´ is used [
11]. The experiment entails recording many people present at a party with many microphones, with the aim of disaggregating the voices and identifying a particular auditory stimulus by filtering and eliminating the rest of the voices [
11,
12]. Bringing this concept to biological omics data, and, to massive transcriptomics data from complex biological samples, when global gene expression profiling data is collected using full transcriptomics (either with high-density microarray technology or with deep sequencing RNA-Seq), an overall signal is obtained (bulk signal), that is made up of a mixture of signals and can be decomposed applying deconvolution methods. In this case, the expression signal of each gene would be a cocktail and the microphones that collect the signal would be represented by the samples present in the bulk [
13].
1.3. Formulation of Deconvolution
Peng Lu, Aleksey Nakorchevskiy, and Adward M. Macotte were the first to use such methodologies, estimating the quantity of distinct yeast cell types at various stages of the cell cycle [
14]. Since this time, many deconvolution methods have been developed [
10,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21], and probably the most practical and successful application has been in blood samples (which include many different cell types) and in tissue samples infiltrated with blood and immune cells. Deconvolution algorithms decompose a mixture of different cell types into their constituent elements and calculate their proportion or ratio and, in some cases, also calculate the overall expression signal of the factors or features (i.e., genes). Let n, m, and c be the number of genes, samples, and cell types, respectively. Global or bulk transcriptomic data can be defined as follow:
Where
is the mixture expression matrix (or bulk),
is the signature matrix (i.e., the matrix of genes that mark the expression of c cell types
), and
is the proportion matrix (i.e., the data matrix which contains the relative frequencies of cell types in the mixed samples m). For the deconvolution process to be successful, the P matrix must fulfill two properties: (i) the columns (samples) must sum 1 (
); (ii) each element of matrix must value between 0 and 1 (
This global data B can also be explained as a set of equations, one per gene for each of the samples (in total n x m) where the value b
ij is a linear combination of the expression level s
ik of gene
i (
i =1...
n) in cell type
k (
k =1...
c), weighted by the proportion p
kj of cell type k in sample j [
6]. Therefore, for each fixed sample j (j=1...m), the model is formulated as follows:
There are two types of deconvolution depending on the elements to be estimated. If the aim is only estimating one of the two matrices (S or P), it is known as partial deconvolution (supervised methods) and requires, in addition to a mixture matrix B, another remaining matrix (S or P) that provides the gene signatures or cell proportions. However, if the method can infer both matrices, so it only needs B matrix, then it is a complete deconvolution and the algorithm is defined as an unsupervised method [
22]. In our work, we implemented three supervised methods: CIBERSORT, FARDEEP and ABIS; and two unsupervised methods: LINSEED and DECONICA. Within this methodological framework, this study has two main goals: (i) first, perform a comparative analysis between different cell mixture deconvolution methods; (ii) second, apply these methods to a series of complex mixtures of blood and immune cells, but in which the proportions of cell types have been previously determined experimentally (in this way we know
a priori cell composition). Thus, the objective is not only to assess the accuracy in estimating cell proportions, but also to evaluate the identification of biological factors (i.e., gene signatures) that best separate the investigated cell mixtures, inferred by unsupervised methods (DECONICA and LINSEED).
2. Results
2.1. Comparison of Cell Type Proportions Correlations Using 4 Deconvolution Methods
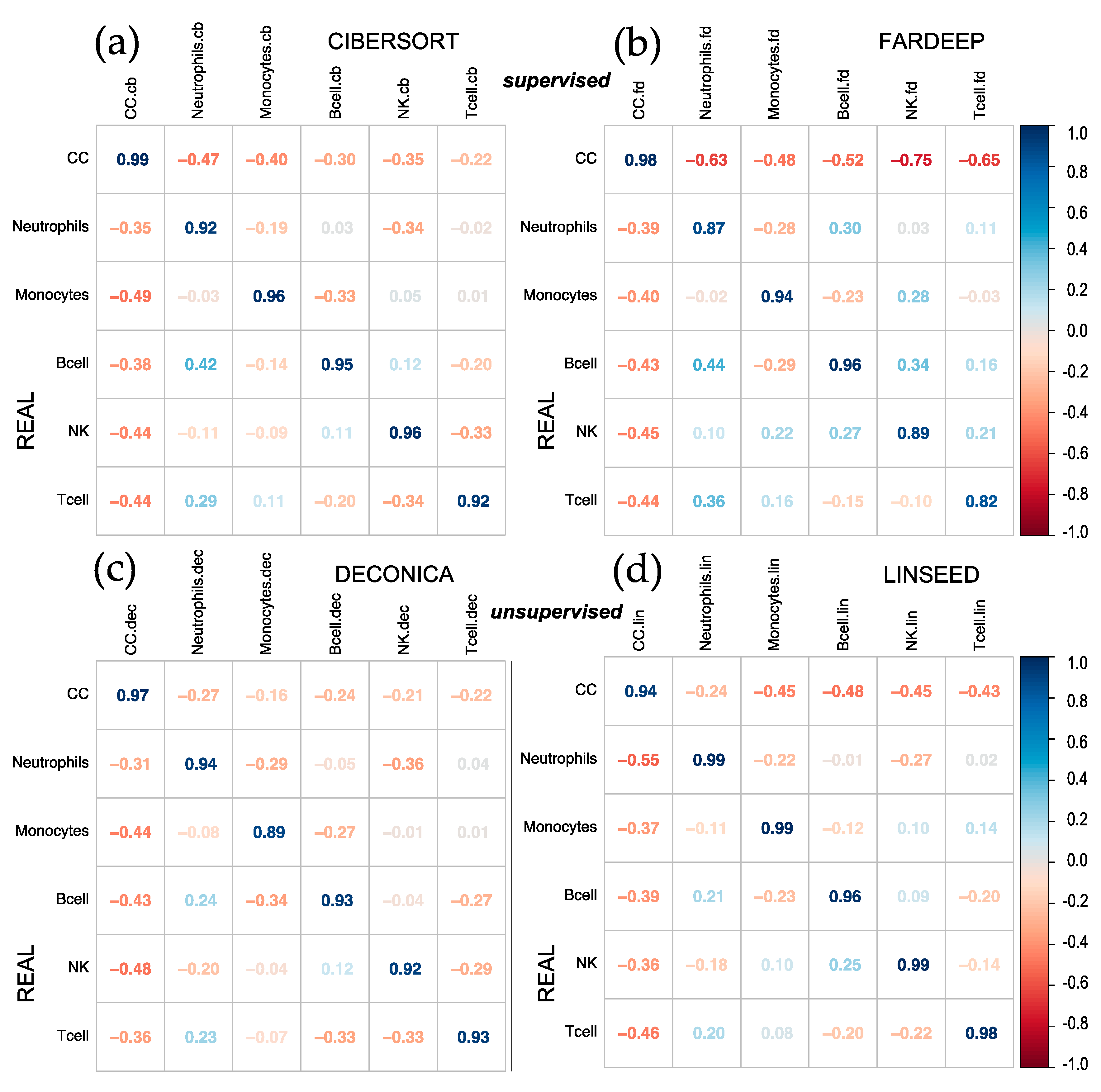
First, it was decided to analyze the results obtained after the implementation of CIBERSORT, FARDEEP, DECONICA and LINSEED, using two datasets of genome-wide gene expression data (GSE64385 and GSE20300). To evaluate the different algorithms, a correlation plot (corrplot) has been made for each method. In the first case, shown in
Figure 1, the proportions of tumor cells HTC116 (Cancer Cells, CC) and five immune cells were analyzed: Natural Killer cells (NKs), B lymphocytes (B cells), neutrophils, T lymphocytes (T cells) and monocytes. The highest correlation coefficients were obtained for the proportions calculated by CIBERSORT and FARDEEP. In addition, DECONICA also shows positive results and LINSEED was unable to recognize T cells. As a whole, the actual proportion values of each type of cell in the samples (real and estimated) are not revealed in the corrplots, so this way of analyzing and representing the data is not optimal since they do not present a critical information about the relative amount of different cells included in a mixture. Therefore, other plots (cell signature plots and bar mixture plots) were created. The cell signature plots for DECONICA results (
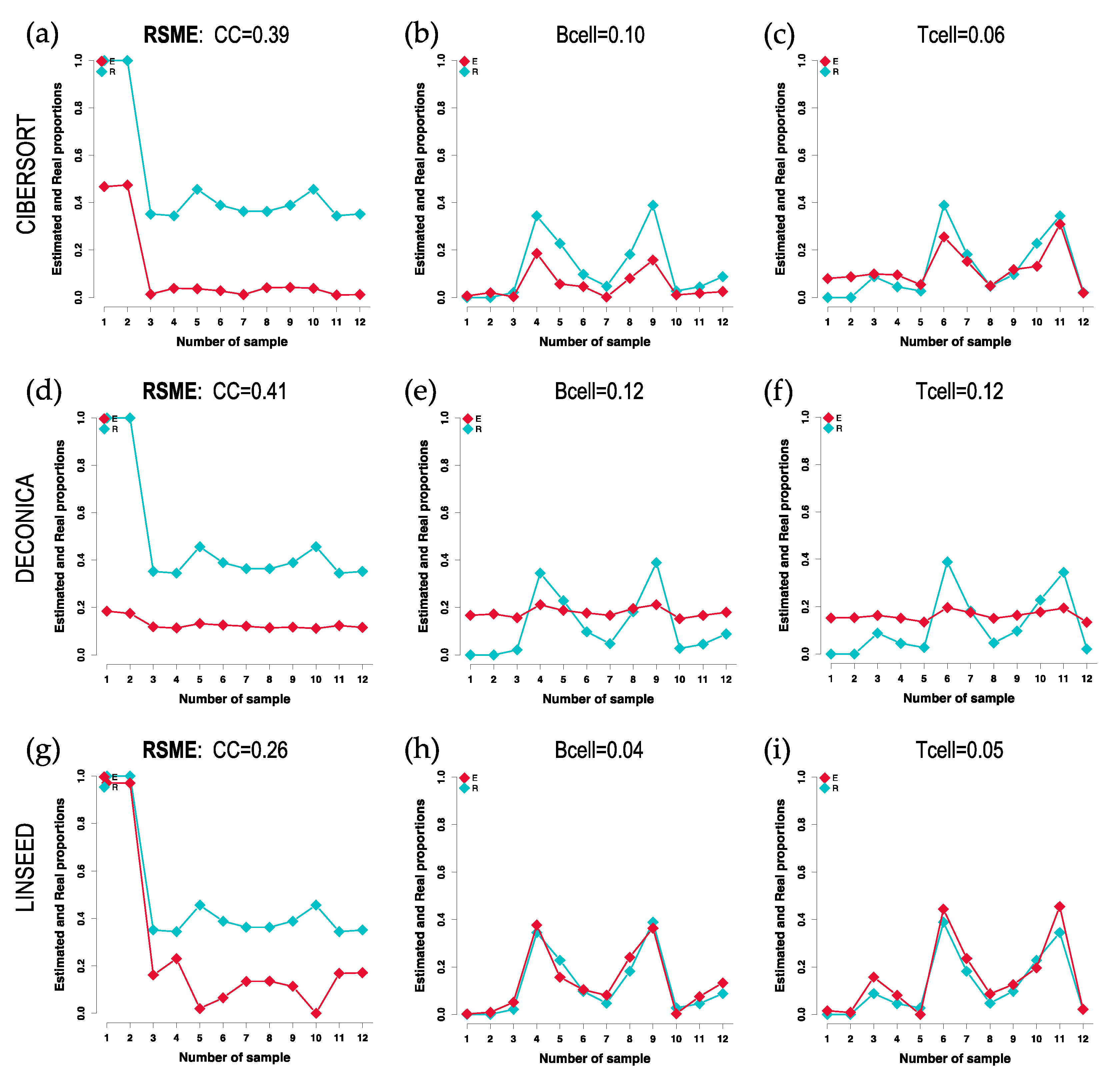
Figure 2), showed poor variability in the cellular composition of the different samples, i.e., all are distributed around a mean value. In contrast, the cell type distributions inferred by CIBERSORT and LINSEED had curves like the known cells. For all additional plots see supplementary data.
On the other hand, the
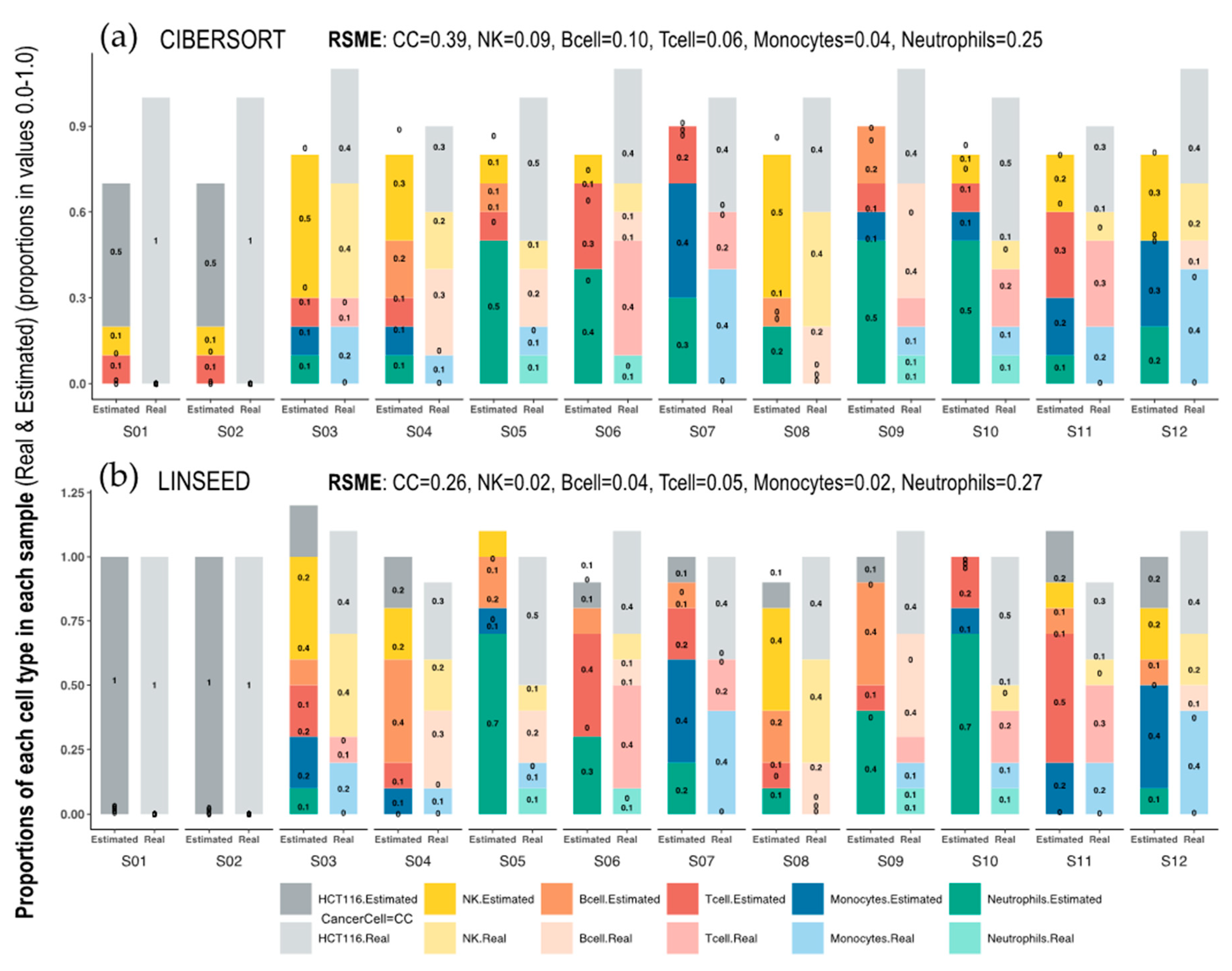
Figure 3 shows the dissimilarity between CIBERSORT and LINSEED regarding the cell prediction when noise is present in the data. In this case, the noise is represented by tumor cells, which are found in the first two samples (pure cancer cell samples), of which we had no marker genes in the immune signature matrix used by CIBERSORT. The abundance of immune cells inferred by the methods for the first and second samples would be zero, because these are composed exclusively of malignant cells and, consequently, the fractions of immune cells obtained by flow cytometry are zero. Despite this, CIBERSORT overestimated the values of some cell populations (monocytes and B and T lymphocytes) and did not estimate any CC in the remaining samples, which were composed of a mixture of tumor and immune cells.
2.2. Comparison of Proportions of 17 Cell Types, Identified in PBMCs, Calculated Using Different Deconvolution Methods against the Proportions Experimentally Determined
In this section, three supervised deconvolution methods (CIBERSORT, FARDEEP and ABIS) have been applied to calculate a large collection of cell-types and subtypes identified in PBMCs. The analyses were performed using 13 PBMC samples, obtained from dataset GSE107011. For these samples we had global gene expression data (i.e., the full transcriptomic profiling determined by RNA-Seq), plus the proportions of each cell-type in each sample determined experimentally.
Figure 4 presents the Pearson correlations between the cell proportions calculated by each method and the real proportion of each cell type. The data show that CIBERSORT is the best method with an average correlation of 0.78; presenting the worse correlation for: B-cells Memory (0.58), T-cells CD4+ Memory (0.23) and myeloid Dendritic Cells (0.39). The other methods are not better than this. In fact, not considering these 3 very specific cell-types, CIBERSORT shows the best average correlation of 0.86, revealing a quite correct adjustment to the real cellular concentrations.
2.3. Identification of Cell-Specific Gene Signatures Obtained by the Combination of two Deconvolution Methods
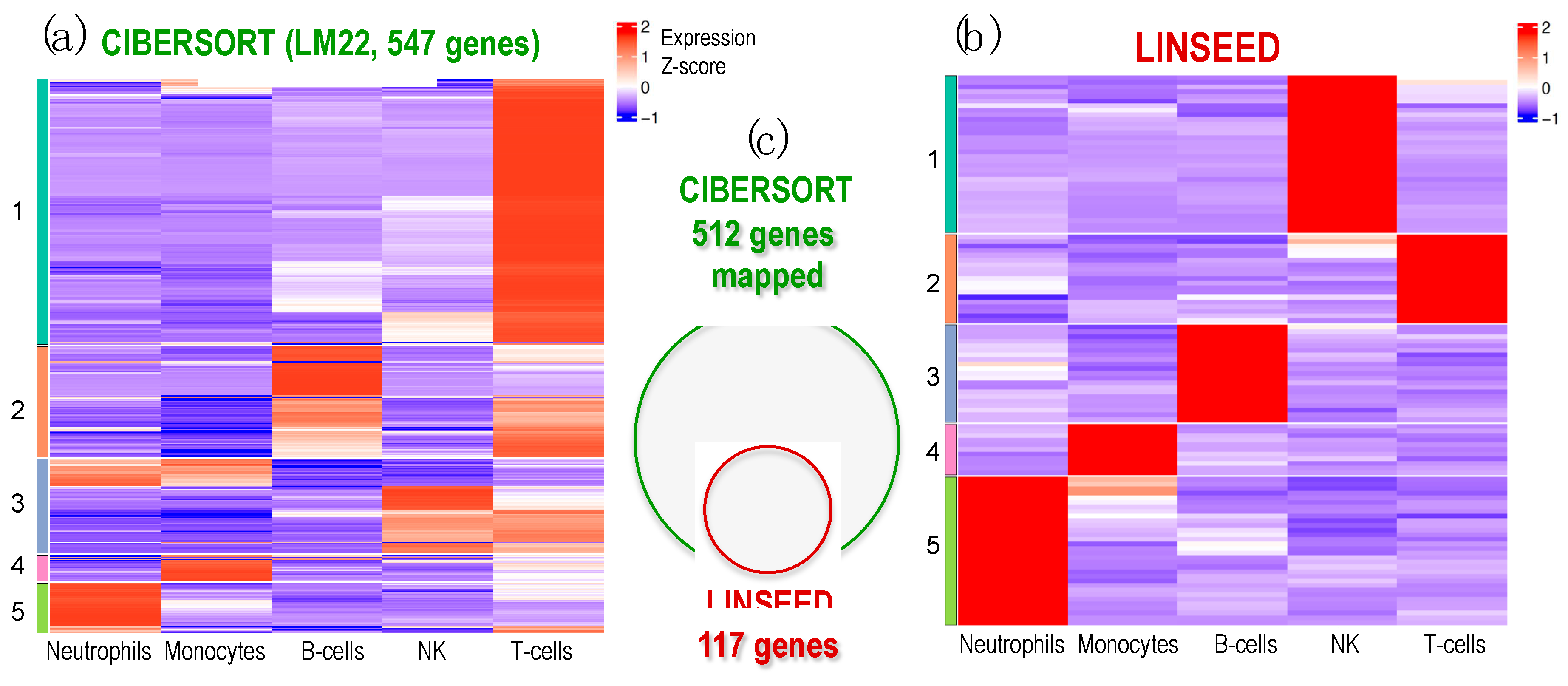
Finally, an analysis of cell signatures was performed to identify five immune cells (T and B lymphocytes, NKs, neutrophils and monocytes), provided by LM22 matrix (used in CIBERSORT and FARDEEP) and by those estimated by the unsupervised methods LINSEED, considering the matching genes between LM22 signature matrix and these ones present in the GSE64385 expression data (512 genes). For this purpose, we chose to apply a clustering analysis, whose results are shown in
Figure 5 through the expression level of the marker genes for each cell type.
The analysis in search for gene signatures for the cells carried out with LINSEED was quite specific, since using the LM22 cell data matrix provided by CIBERSORT, we were able to select with this unsupervised method 117 genes as cell markers for the 5 cells studied.
Supplementary Figure S1 presents the set of genes selected as gene signature for each cell type, which are: 21 genes for B-cells; 19 genes for T-cells; 34 genes for NK cells; 11 genes for Monocytes; and 32 genes for Neutrophils. These gene signatures are much more specific that the ones included in LM22. In this way, LINSEED is an unsupervised method that can optimize the biomarkers proposed by the authors of CIBERSORT (
https://cibersortx.stanford.edu/), decreasing the number of genes contained in the signature matrix while maintaining the most important genes, that are well reported in the literature. All the data corresponding to these two heatmaps are included in Supplementary material: Supplementary Table S1S (includes the genes presented in the heatmap in
Figure 5a produced using CIBERSORT with 547 genes arranged in order as in the heatmap clusters); Supplementary Table S2 (includes the normalized expression signal of the 547 genes presented in the heatmap of
Figure 5a); Supplementary Table S3 (includes the genes presented in the heatmap in
Figure 5b produced using LINSEED with 117 genes arranged in order as in the heatmap clusters); Supplementary Table S4 (includes the normalized expression signal of the 117 genes presented in the heatmap of
Figure 5b).
3. Discussion
Cellular heterogeneity research allows us to know and identify marker genes, determine changes in the organism because of biological processes, as well as to analyze the initiation and development of diseases, including cancer. Previous studies have demonstrated the clinical impact of the infiltration of certain immune cells, especially T lymphocytes [
23,
24], and the influence of the relative abundance of stromal cells, particularly adipocytes or fibroblasts, which can be related to tumor progression, invasion, metastasis, or drug resistance [
25,
26,
27,
28]. However, experimental (in vitro) techniques, such as flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry, are limited to known phenotypic markers. Therefore, computational (in silico) approaches known as deconvolution methods, able to decompose complex signal mixtures (bulk) into cellular proportions, as well as to identify known biomarkers, have been emerging.
In our work, we implemented five deconvolution methods: three supervised (CIBERSORT, FARDEEP, and ABIS) and two unsupervised (DECONICA and LINSEED) using global expression expression signal (bulk) data (GSE64385, GSE20300, GSE106898 and GSE107011). In general, the most accurate methods were CIBERSORT and FARDEEP, with high correlations, low RMSE values, and cell distributions like those known. Both methods were run using the LM22 matrix as the signature matrix, which as mentioned above was designed by the creators of CIBERSORT. Given that the calculation of cell proportions is directly related to the signatures considered and most of the methods use mathematical regression models, they are expected to have similar results. However, for the supervised methods to be accurate in their computations, the signature matrix and the bulk must have been collected by the same expression platform, as Binbin Chen mentions in his article [
29]. In addition, CIBERSORT is one of the most widely used deconvolution methods nowadays [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34], providing good results in predicting cell abundance. Nevertheless, FARDEEP was more robust in the presence of noise in the data (such as tumor cells), removing outliers before deconvolution and avoiding the alteration of the results, as demonstrated in the original article of the method [
35]. Despite this, genes should be well-defined as cell markers in the signature matrix.
On the other hand, the frequencies calculated by DECONICA may create confusion about its accuracy. The correlation coefficients were high and, moreover, the RMSE values were not significantly different from the errors calculated for CIBERSORT and FARDEEP results. However, DECONICA cell proportions are distributed around a mean value, so there is no variability between the calculated proportions for the samples. Based on this fact, it is recommended to use LINSEED, instead of DECONICA, when the signature array is not available. Nevertheless, if the bulk has a high number of genes, the calculation of correlations by gene pairs can be very expensive, reducing the accuracy of LINSEED. According to the application of ABIS, it is necessary to know the actual proportions, which are used to calculate the scale factor before running the algorithm. Thus, if the aim is only using the method to estimate cell abundance, it is not recommended to use it, because of an experimental technique would have to be applied previously.
Furthermore, the RMSE values obtained for the deconvoluted expression data used in section 2.2 were lower than those calculated for the signal expression data used in the first part (section 2.1). This could overestimate the precision of the method, since obtaining lower values in RMSE may be related to the presence of smaller proportions and, therefore, mathematically this value will decrease. The clearest example is the case of eosinophils, whose actual proportions are normally distributed in the 1-3% range. However, the correlations calculated for these cell types by CIBERSORT, FARDEEP and DECONICA had a value of 0.3 for eosinophils, approximately, while the RMSE is lower than for other cell types with correlations higher than 0.7 (e.g., neutrophils, whose actual relative frequencies take values between 55% and 70%), so the RMSE measurement cannot always be compared between different datasets or cells.
Regarding cell signatures, LINSEED was a powerful tool to optimize marker genes provided by CIBERSORT authors, selecting the most important genes contained in the LM22 reference matrix and summarizing immune cell markers.
Overall, none of the methods studied is adaptable to any circumstance, depending on the data state. As a future perspective, the design of a method that improves the decomposition of cell mixtures is proposed. First, using new generation sequencing data, such as expression RNA-Seq, or even previously isolated single cells (Single-Cell RNA-Seq), is much more powerful in identifying cell populations. For deconvolution, we propose the application of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, specifically Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), to improve cell composition prediction. In addition, it would be convenient to consider other cell types, more than immune cells, because, as mentioned in previous paragraphs, it has been shown that they can affect the tumor development or drug resistance. Thus, knowing cell abundance could be a good diagnostic and prognostic factor for patients.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Datasets
We used for the analyses three cell mixture datasets, two of them including genome-wide expression data obtained using high-density microarrays technology: GSE64385 [
10], GSE20300 [
36] and GSE106898 [
37]; and another one obtained using RNA-Seq technology: GSE107011 [
37]. These samples are composed of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs), and one of them also includes human colon cancer cell line HTC116 [
10] in the mixture. Specifically, the first two samples are pure tumor samples, which have been used as control data. As for the GSE107011 dataset, 13 PBMC samples were selected for analysis from 127 total samples (these samples were: GSM2859500, CYFZ_PBMC_rep9; GSM2859501, FY2H_PBMC_rep8; GSM2859502, FLWA_PBMC_rep10; GSM2859503, 453W_PBMC_rep5; GSM2859504, 684C_PBMC_rep6; GSM2859505, CZJE_PBMC_rep7; GSM2859531, DZQV_PBMC_rep4; GSM2859532, 925L_PBMC_rep2; GSM2859533, 9JD4_PBMC_rep1; GSM2859534, G4YW_PBMC_rep3; GSM2859535, 4DUY_PBMC_rep11; GSM2859536, 36TS_PBMC_rep12; GSM2859537, CR3L_PBMC_rep13). All information regarding the cell types that compose the cell mixtures can be found in
Supplementary Figure S2. For summary information, see
Table 1 of this document.
Moreover, supervised methods require a gene signature matrix, which must contain the expression profiles of the gene markers used to identify the different cell types (i.e., the unique gene signature for each cell type interrogated in the sample mixture). These gene signature matrices must be generated using the same platform as the analyzed samples. In our analysis, we used three gene signatures matrices, all of which present genes as rows and cell populations as columns matrix:
(i) LM22: Signature matrix composed of 22 immune cell types and 547 gene signatures (rows), designed by CIBERSORT authors [
10]. We used it to decompose the mixtures (bulk) GSE64385 and GSE20300, with Affymetrix microarray signal expression data.
(ii) ‘sigmatrixMicro.txt’: Matrix consisting of 819 genes (rows) characterizing 11 immune cell types in complex cell mixtures with Illumina microarray signal expression [
37]. In our work, it was used to decompose the bulk GSE106898.
(iii) ‘sigmatrixRNAseq.txt’: Signature matrix composed of 1296 biomarkers to identify 17 immune cell populations in datasets with Illumina RNA-Seq expression profiles [
37]. We applied this matrix to deconvolute GSE107011.
4.2. Brief Description of the Cell Mixture Deconvolution Methods Used
4.2.1. DECONICA: Deconvolution of Transcriptome through Immune Component Analysis
This is an unsupervised deconvolution method and therefore only requires the mixture expression matrix or bulk [
13]. For the estimation of cell types, it is based on the algorithm FastICA [
38], which uses a multivariate technique (ICA: Independent Component Analysis) whose objective is to find uncorrelated latent variables, which present a non-Gaussian distribution (with skewness and kurtosis coefficients maximized far from zero). The aim is to obtain a matrix
A (representing absolute frequencies of the cell types in the samples) whose numbers maximize the skewness and kurtosis statistics of the distribution. Therefore, being n the number of observable variables (genes), m the number of samples, and c the components into which to decompose the data; the mixture expression matrix (B) can be formulated as the product of matrix A and the signature matrix S, as shown by equation (3).
4.2.2. LINSEED: Linear Subspace Identification for gene Expression
This method, like the previous one, solves a complete deconvolution since it is also an unsupervised method. In this case, cell type-specific genes are defined by their exclusive expression in only one component within a mixture. In an ideal scenario, the gene markers expression behaves exactly linearly with the proportions of the corresponding mixture component. Therefore, expression levels of the biomarkers to the same mixture component are also mutually linear with each other. Subsequently, to deconvolute a mixture of signals, LINSEED identifies the marker genes (the specific genes) for each cell type, by calculating the mutual linearity between pairs of genes [
39]. Mutual linearity of cell type-specific genes suggests that the space of the mixed gene expression profiles might have a distinct underlying structure. Thus, the method systematically investigates the topological properties of a common space that can be generated from two related space matrices: matrix X defines an
expression space with genes as dimensions and samples as data points; and matrix H, defines a
proportions space with cell types as dimension and samples as data points [
15]. The rows of both matrices, H and X, have the same dimensionality (equal to the number of samples in the dataset, m). This means that the vectors that make up the transposed matrices H
T and X
T have the same dimensionality and can be mapped as points within the common m-dimensional space. This mapping and transformation are done using the algorithm
Simplex [
40] which allows the convergence of row-normalized vectors of expression and cell proportion visualized in this m-dimensional space, in which the vertices (i.e., the corners of a multi-dimensional hyperplane representing the optimal points) are the cell types, and the closest points to each vertex their specific gene markers. In mathematical terms, the problem is formulated as follows:
Where is the mixture expression matrix (like in previous methods, row-normalized per gene), is the cell type proportions matrix (like P matrix, row-normalized per cell type), and α is a non-negative coefficient, which must sum to one per sample.
4.2.3. ABIS: ABsolute Inmune Signal Deconvolution
It is a supervised method, that can be applied to decompose the whole gene expression data [
37]. Before deconvolution, this method requires normalization by mRNA abundance, providing an optimal α coefficient for each cell type, that allows the difference between estimated and actual values to be calculated. The mathematical formula for α is defined as:
Subsequently, the expression of the signature matrix (per cell type) is multiplied by this coefficient, and the deconvolution is performed. For deconvolution, ABIS is based on a robust linear model (RLM), which for each gene and sample is described by equation (6).
Considering n the total gene number and c the cell types to be estimated. For any gene i (∀ i∈[1,...,n]) and any cell type k (∀ k∈[1,...,c]), is the expression of the gene in the bulk, is the cell type proportion, is the mRNA abundance and represents the expression of the gene i into the corresponding cell type k.
4.1.4. FARDEEP: Fast And Robust Deconvolution of Expression Profiles
Supervised method designed to solve partial deconvolution problems, previously eliminating outliers that may disrupt the results. For this purpose, FARDEEP is based on the aLTS (Adaptive Least Trimmed Squares) algorithm [
41], which incorporates outliers:
Where 𝜏 = (𝜏
1 + 𝜏
2 + ⋯ + 𝜏
n)
T indicates that the i-th gene (𝑖 𝜖 [1, ... , 𝑛]) is an outlier. For more information regarding the outliers estimation, see the original article [
35].
4.1.5. CIBERSORT: Estimation of Cell Types Abundances in a Mixed Cell Population Using Gene Expression Data
Supervised method that solves a partial deconvolution, so mixture and signature matrices are needed as parameters. To perform deconvolution, it is based on the machine learning algorithm known as Support Vector Regression (SVR) [
8], which is a feature of Support Vector Machine (SVM). This algorithm represents the regression model that best fits the data on a hyperplane, selecting support vectors (in our case the support vectors are the marker genes) that define the limits of the error (ɛ) that the model can tolerate [
26]. The hyperplane is defined by equation (9):
Where represents the proportions of the cell types to be estimated, is a positive constant that allows controlling the error, so if this value increases, then the tolerance for points outside ɛ will also increase. Finally, is the parameter that controls the error determined by the support bands (defined by the support vectors), calculating the distance between the points represented outside them and the limits of the acceptance region.
5. Conclusions
In summary, one of the main conclusions is that we need multiple analytical tools to perform a fair evaluation of different cell mixture deconvolution methods, and our plots (implemented in R: corrplots, cell-signature plots and bar-mixture plots), facilitate such comparative analysis. Moreover, the study shows that CIBERSORT provides robust and consistent results in the deconvolution analyses of mixtures of immune cells; with high correlations in cell proportions, low RMSE values, as well as high similarity between the estimated and known cell type distributions. CIBERSORT is supervised, always using a predefined signature matrix (LM22), which includes genes that characterize each cell-type. Thus, the investigated cell-types need to be defined and if a sample mix includes cells that have not been pre-defined (e.g., cancer cells), the method does not work accurately. Other methods, like FARDEEP (supervised) performs fairly well, but again it needs a well predefined gene signature for the cell-types studied. ABIS (also supervised) needs to know the true proportions in the samples, which requires prior analysis using precise experimental techniques (such as flow cytometry). For this reason, we do not recommend this deconvolution method to predict cell ratios. DECONICA (unsupervised) presents good correlations between real and estimated cell proportions, but with much higher RMSE values, indicating that it can find the trend o relative values in cellular concentrations but is not good at estimating the real proportions. Regarding LINSEED, is the most successful unsupervised method, very robust in the presence of noise in the data (due, for example, to the presence of unidentified cell types or contamination). Furthermore, it was also the most accurate method for optimizing the cell-specific gene signatures provided by CIBERSORT, as it was able to select more specific genes for five main types of immune cells: neutrophils, monocytes, B-cells, NK cells and T-cells. The specific gene signatures obtained in this way for each of these cell-types are provided in the Supplementary Material.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
References
- Harlin, H.; Meng, Y.; Peterson, A.C.; Zha, Y.; Tretiakova, M.; Slingluff, C.; McKee, M.; Gajewski, T.F. Chemokine Expression in Melanoma Metastases Associated with CD8+ T-Cell Recruitment. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.F.; Wei, W.; Smithy, J.W.; Acs, B.; Toki, M.I.; Blenman, K.R.M.; Zelterman, D.; Kluger, H.M.; Rimm, D.L. Multiplex Quantitative Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Immunotherapy Outcome in Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uryvaev, A.; Passhak, M.; Hershkovits, D.; Sabo, E.; Bar-Sela, G. The role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) as a predictive biomarker of response to anti-PD1 therapy in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer or metastatic melanoma. Med Oncol. 2018, 35, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mami-Chouaib, F.; Blanc, C.; Corgnac, S.; Hans, S.; Malenica, I.; Granier, C.; Tihy, I.; Tartour, E. Resident memory T cells, critical components in tumor immunology. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerby-Arnon, L.; Shah, P.; Cuoco, M.S.; Rodman, C.; Su, M.-J.; Melms, J.C.; Leeson, R.; Kanodia, A.; Mei, S.; Lin, J.-R.; et al. A Cancer Cell Program Promotes T Cell Exclusion and Resistance to Checkpoint Blockade. Cell 2018, 175, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-García, M.; Bonfill-Teixidor, E.; Planas-Rigol, E.; Rubio-Perez, C.; Iurlaro, R.; Arias, A.; Cuartas, I.; Sala-Hojman, A.; Escudero, L.; Martinez-Ricarte, F.; et al. LIF regulates CXCL9 in tumor-associated macrophages and prevents CD8+ T cell tumor-infiltration impairing anti-PD1 therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraman, M.; Bambrough, P.J.; Arnold, J.N.; Roberts, E.W.; Magiera, L.; Jones, J.O.; Gopinathan, A.; Tuveson, D.A.; Fearon, D.T. Suppression of Antitumor Immunity by Stromal Cells Expressing Fibroblast Activation Protein–α. Science 2010, 330, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen-Orr, S.S.; Gaujoux, R. Computational deconvolution: extracting cell type-specific information from heterogeneous samples. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, E.C. Some Experiments on the Recognition of Speech, with One and with Two Ears. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1953, 25, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn-Cunningham, B.G. Object-based auditory and visual attention. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2008, 12, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerwińska, U. “Unsupervised deconvolution of bulk omics profiles: Methodology and application to characterize the immune landscape in tumors,”, Doctoral dissertation, Sorbonne University, París, 2018. Available online (accessed on June, 2021): https://urszulaczerwinska.github.io/UCzPhDThesis/.
- Lu, P.; Nakorchevskiy, A.; Marcotte, E.M. Expression deconvolution: A reinterpretation of DNA microarray data reveals dynamic changes in cell populations. 2003, 100, 10370–10375. [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.; Quon, G.; Rosenberg, A.M.; Yeung, R.S.M.; Morris, Q. ; BBOP Study Consortium Gene Expression Deconvolution for Uncovering Molecular Signatures in Response to Therapy in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0156055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, A.; Thu, D.; Waldvogel, H.J.; Faull, R.L.M.; Luthi-Carter, R. Population-specific expression analysis (PSEA) reveals molecular changes in diseased brain. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, W.; Quon, G.; Csaszar, E.; Yu, M.; Morris, Q.; Zandstra, P.W. PERT: A Method for Expression Deconvolution of Human Blood Samples from Varied Microenvironmental and Developmental Conditions. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, S.; Zuckerman, N.; Goldsmith, A.; Grama, A. A Critical Survey of Deconvolution Methods for Separating Cell Types in Complex Tissues. 2017, 105, 340–366. [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Szustakowski, J.D. DeconRNASeq: a statistical framework for deconvolution of heterogeneous tissue samples based on mRNA-Seq data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappello, V.; Marchetti, L.; Parlanti, P.; Landi, S.; Tonazzini, I.; Cecchini, M.; Piazza, V.; Gemmi, M. Ultrastructural Characterization of the Lower Motor System in a Mouse Model of Krabbe Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaujoux, R.; Seoighe, C. Semi-supervised Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for gene expression deconvolution: A case study. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, F.A.; Alquicira-Hernandez, J.; Powell, J.E.; Mestdagh, P.; De Preter, K. Benchmarking of cell type deconvolution pipelines for transcriptomics data. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Costes, A.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Kirilovsky, A.; Mlecnik, B.; Lagorce-Pagès, C.; Tosolini, M.; Camus, M.; Berger, A.; Wind, P.; et al. Type, Density, and Location of Immune Cells Within Human Colorectal Tumors Predict Clinical Outcome. Science 2006, 313, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liotta, L.A.; Kohn, E.C. The microenvironment of the tumour–host interface. Nature 2001, 411, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straussman, R.; Morikawa, T.; Shee, K.; Barzily-Rokni, M.; Qian, Z.R.; Du, J.; Davis, A.; Mongare, M.M.; Gould, J.; Frederick, D.T.; et al. Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature 2012, 487, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y. Adipocyte and lipid metabolism in cancer drug resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3006–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, S.; Zhou, H. Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts and targeted therapy for cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Liu, C.L.; Newman, A.M.; Alizadeh, A.A. “Profiling tumor infiltrating immune cells with CIBERSORT,” in Methods in Molecular Biology, 2018, 1711, Humana Press Inc., pp. 243–259. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Steen, C.B.; Newman, A.M. Computational approaches for characterizing the tumor immune microenvironment. Immunology 2019, 158, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, K.E.; Gökmen-Polar, Y.; Badve, S.S. CIBERSORT analysis of TCGA and METABRIC identifies subgroups with better outcomes in triple negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, J.-I.; Takeuchi, S.; Imai, H.; Okumura, T.; Horiba, K.; Suzuki, T.; Torii, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Ito, Y. Immune cell infiltration landscapes in pediatric acute myocarditis analyzed by CIBERSORT. J. Cardiol. 2020, 77, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Hua, W.; Xu, B.; Chen, H.; Xie, M.; Sun, X.; Ge, X. Robust rank aggregation and cibersort algorithm applied to the identification of key genes in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 4491–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; An, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Sun, X.; Sun, M. Potential Impact of ALKBH5 and YTHDF1 on Tumor Immunity in Colon Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yan, M.; Heath, B.R.; Lei, Y.L.; Xie, Y. Fast and robust deconvolution of tumor infiltrating lymphocyte from expression profiles using least trimmed squares. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen-Orr, S.S.; Tibshirani, R.; Khatri, P.; Bodian, D.L.; Staedtler, F.; Perry, N.M.; Hastie, T.; Sarwal, M.M.; Davis, M.M.; Butte, A.J. Cell type–specific gene expression differences in complex tissues. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, G.; Lee, B.; Xu, W.; Mustafah, S.; Hwang, Y.Y.; Carré, C.; Burdin, N.; Visan, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; Poidinger, M.; et al. RNA-Seq Signatures Normalized by mRNA Abundance Allow Absolute Deconvolution of Human Immune Cell Types. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyvarinen, A. “Fast ICA for noisy data using gaussian moments,” Proceedings - IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 1999, 5.
- Zaitsev, K.; Bambouskova, M.; Swain, A.; Artyomov, M.N. Complete deconvolution of cellular mixtures based on linearity of transcriptional signatures. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzig, G.B. Origins of the simplex method. In A history of scientific computing; ACM, 1990; pp. 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Yan, M.; Huang, C.; Xiong, J.; Huang, Q.; Yao, Y. Exploring Outliers in Crowdsourced Ranking for QoE, in Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia, 2017, 17. Accessed: Jun. 07, 2021.
Figure 1.
Corrplots comparing real versus estimated cell proportions. Pearson correlations where calculated with the 12 samples of the dataset (GSE64385), between the real proportions (rows) and the estimated proportions (columns) obtained with 4 methods: (a) CIBERSORT, (b) FARDEEP, (c) DECONICA and (d) LINSEED. The samples included 6 cell types mixed in known proportions: Cancer Cells (CC), Neutrophils, Monocytes, B cells, NK cells and T cells. GSE64385 includes the bulk gene expression data used in the deconvolution analyses.
Figure 1.
Corrplots comparing real versus estimated cell proportions. Pearson correlations where calculated with the 12 samples of the dataset (GSE64385), between the real proportions (rows) and the estimated proportions (columns) obtained with 4 methods: (a) CIBERSORT, (b) FARDEEP, (c) DECONICA and (d) LINSEED. The samples included 6 cell types mixed in known proportions: Cancer Cells (CC), Neutrophils, Monocytes, B cells, NK cells and T cells. GSE64385 includes the bulk gene expression data used in the deconvolution analyses.
Figure 2.
Cell-signature plots obtained for 3 cell types: Cancer Cells (CC), B cells and T cells; using GSE64385 dataset. The plots include in blue (R) the real proportions of each cell type in each of the 12 samples (proportions marked with squared dots) and in red (E) the estimated proportions. The cellular profiles or signatures obtained with 3 different methods are presented: (a), (b), (c) CIBERSORT; (d), (e), (f) DECONICA; and (g), (h), (i) LINSEED. The RSME (Root Mean Square Error) calculated between the real data (blue) and the estimated data (red) is presented at the top of each graph.
Figure 2.
Cell-signature plots obtained for 3 cell types: Cancer Cells (CC), B cells and T cells; using GSE64385 dataset. The plots include in blue (R) the real proportions of each cell type in each of the 12 samples (proportions marked with squared dots) and in red (E) the estimated proportions. The cellular profiles or signatures obtained with 3 different methods are presented: (a), (b), (c) CIBERSORT; (d), (e), (f) DECONICA; and (g), (h), (i) LINSEED. The RSME (Root Mean Square Error) calculated between the real data (blue) and the estimated data (red) is presented at the top of each graph.
Figure 3.
Bar-mixture plots. Bar plots presenting the cell mixtures in each sample as proportional sections of each cell type, which are marked with the colors presented in the color panel at the bottom of the figure. The estimated proportions in each sample were calculated with (a) CIBERSORT and (b) LINSEED. The real proportions in each sample (determined experimentally by flow cytometry) are presented as bars on the right in pale colors. The first sample (S01) only includes Cancer Cells (100% HTC116 cells). The RMSEs (Root Mean Square Errors) calculated between the real data and the estimated data for each cell type, are presented at the top of each graph.
Figure 3.
Bar-mixture plots. Bar plots presenting the cell mixtures in each sample as proportional sections of each cell type, which are marked with the colors presented in the color panel at the bottom of the figure. The estimated proportions in each sample were calculated with (a) CIBERSORT and (b) LINSEED. The real proportions in each sample (determined experimentally by flow cytometry) are presented as bars on the right in pale colors. The first sample (S01) only includes Cancer Cells (100% HTC116 cells). The RMSEs (Root Mean Square Errors) calculated between the real data and the estimated data for each cell type, are presented at the top of each graph.
Figure 4.
Corrplots obtained with the geneexpression profiles from 13 PBMC samples (taken from dataset GSE107011), calculated using three deconvolution methods. Pearson correlations were calculated between the real proportions (rows) and the estimated proportions (columns) for 17 cell types and subtypes (12 from the lymphoid lineage and 5 from the myeloid lineage). The correlations were calculated using: (a) CIBERSORT (corrplot) and (b) FARDEEP and ABIS (table; in this case only including the diagonal values of real versus estimated for each cell type). (Labels of the cells: B.Naive = B Cells Naïve; B.Memory = B Cells Memory; Plasmablasts; T.CD4.Naive = CD4+ T Cells Naive; T.CD8.Naive = CD8+ T cells Naive; T.CD4.Memory = CD4+ T Cells Memory; T.CD8.Naive = CD8+ T cells Naive; T.gd.Vd2 = γδ2+ T Cells; T.gd.non.Vd2 = γδ2- T Cells; MAIT = Mucosal Associated Invariant T Cells; NK = Natural Killer Cells; pDCs = Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells ; mDCs = Myeloid Dendritic Cells; Monocytes.C = Classical Monocytes; Monocytes.NC.I = Non-Classical Intermediate Monocytes; Neutrophils.LD = Low-Density Neutrophils; Basophils.LD = Los-Density Basophils). The real mean proportions of the cells in the 13 PBMC samples, determined experimentally, are indicated (in %) in the table (b) second column.
Figure 4.
Corrplots obtained with the geneexpression profiles from 13 PBMC samples (taken from dataset GSE107011), calculated using three deconvolution methods. Pearson correlations were calculated between the real proportions (rows) and the estimated proportions (columns) for 17 cell types and subtypes (12 from the lymphoid lineage and 5 from the myeloid lineage). The correlations were calculated using: (a) CIBERSORT (corrplot) and (b) FARDEEP and ABIS (table; in this case only including the diagonal values of real versus estimated for each cell type). (Labels of the cells: B.Naive = B Cells Naïve; B.Memory = B Cells Memory; Plasmablasts; T.CD4.Naive = CD4+ T Cells Naive; T.CD8.Naive = CD8+ T cells Naive; T.CD4.Memory = CD4+ T Cells Memory; T.CD8.Naive = CD8+ T cells Naive; T.gd.Vd2 = γδ2+ T Cells; T.gd.non.Vd2 = γδ2- T Cells; MAIT = Mucosal Associated Invariant T Cells; NK = Natural Killer Cells; pDCs = Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells ; mDCs = Myeloid Dendritic Cells; Monocytes.C = Classical Monocytes; Monocytes.NC.I = Non-Classical Intermediate Monocytes; Neutrophils.LD = Low-Density Neutrophils; Basophils.LD = Los-Density Basophils). The real mean proportions of the cells in the 13 PBMC samples, determined experimentally, are indicated (in %) in the table (b) second column.
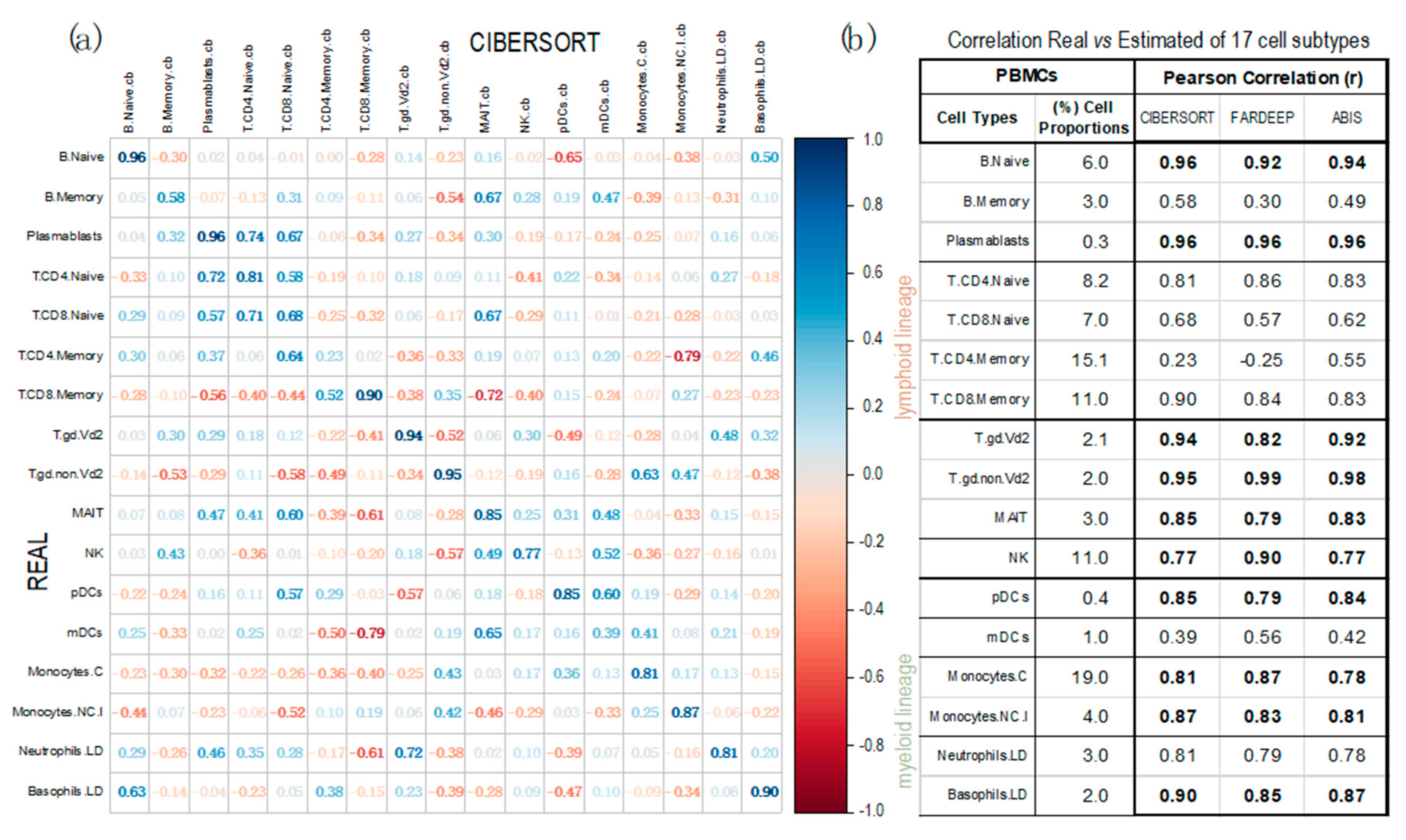
Figure 5.
Heatmap of expression profiles corresponding to the genes selected in the signature matrices provided by CIBERSORT and LINSEED for 5 major cell-types: Neutrophils, Monocytes, B-cells, NK cells and T-cells. The analysis is done using dataset GSE64385. (a) Heatmap presenting the expression profiles of the LM22 data matrix, provided by CIBERSORT platform, which includes 547 genes used to identify the 5 cell-types tested. (b) Heatmap presenting the expression profiles of the 117 genes selected by LINSEED (unsupervised method) from the gene list provided in the LM22 matrix (i.e., the same used by CIBERSORT). (c) Venn diagram presenting the genes that each method uses in the signatures to identify the 5 cell-types in dataset GSE64385. All the genes selected by LINSEED are included in the ones used by CIBERSORT. The set of 117 genes, selected by LINSEED, provides more precise and specific gene signatures for each of the 5 cell-types analyzed.
Figure 5.
Heatmap of expression profiles corresponding to the genes selected in the signature matrices provided by CIBERSORT and LINSEED for 5 major cell-types: Neutrophils, Monocytes, B-cells, NK cells and T-cells. The analysis is done using dataset GSE64385. (a) Heatmap presenting the expression profiles of the LM22 data matrix, provided by CIBERSORT platform, which includes 547 genes used to identify the 5 cell-types tested. (b) Heatmap presenting the expression profiles of the 117 genes selected by LINSEED (unsupervised method) from the gene list provided in the LM22 matrix (i.e., the same used by CIBERSORT). (c) Venn diagram presenting the genes that each method uses in the signatures to identify the 5 cell-types in dataset GSE64385. All the genes selected by LINSEED are included in the ones used by CIBERSORT. The set of 117 genes, selected by LINSEED, provides more precise and specific gene signatures for each of the 5 cell-types analyzed.
Table 1.
Summary of cell mixtures datasets used in this work.
Table 1.
Summary of cell mixtures datasets used in this work.
| Accession number |
Gene expression
Platform |
Samples |
Genes |
Biological
source |
Cell
types |
Reference |
| GSE64385 |
Microarray HGU133 Plus 2.0 – Affymetrix
|
12 |
54,675 |
PBMCs1, PMNs2, and Cancer Cells (HCT116) |
5 |
[10] |
| GSE107011 |
RNA-Seq HiSeq 2000 – Illumina
|
13 |
17,487 |
PBMCs |
17 |
[37] |
| GSE106898 |
Microarray Human HT-12 V4.0 – Illumina
|
13 |
17,487 |
PBMCs |
11 |
[37] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).