Submitted:
26 April 2023
Posted:
27 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raindrop Size Distribution (RSD)
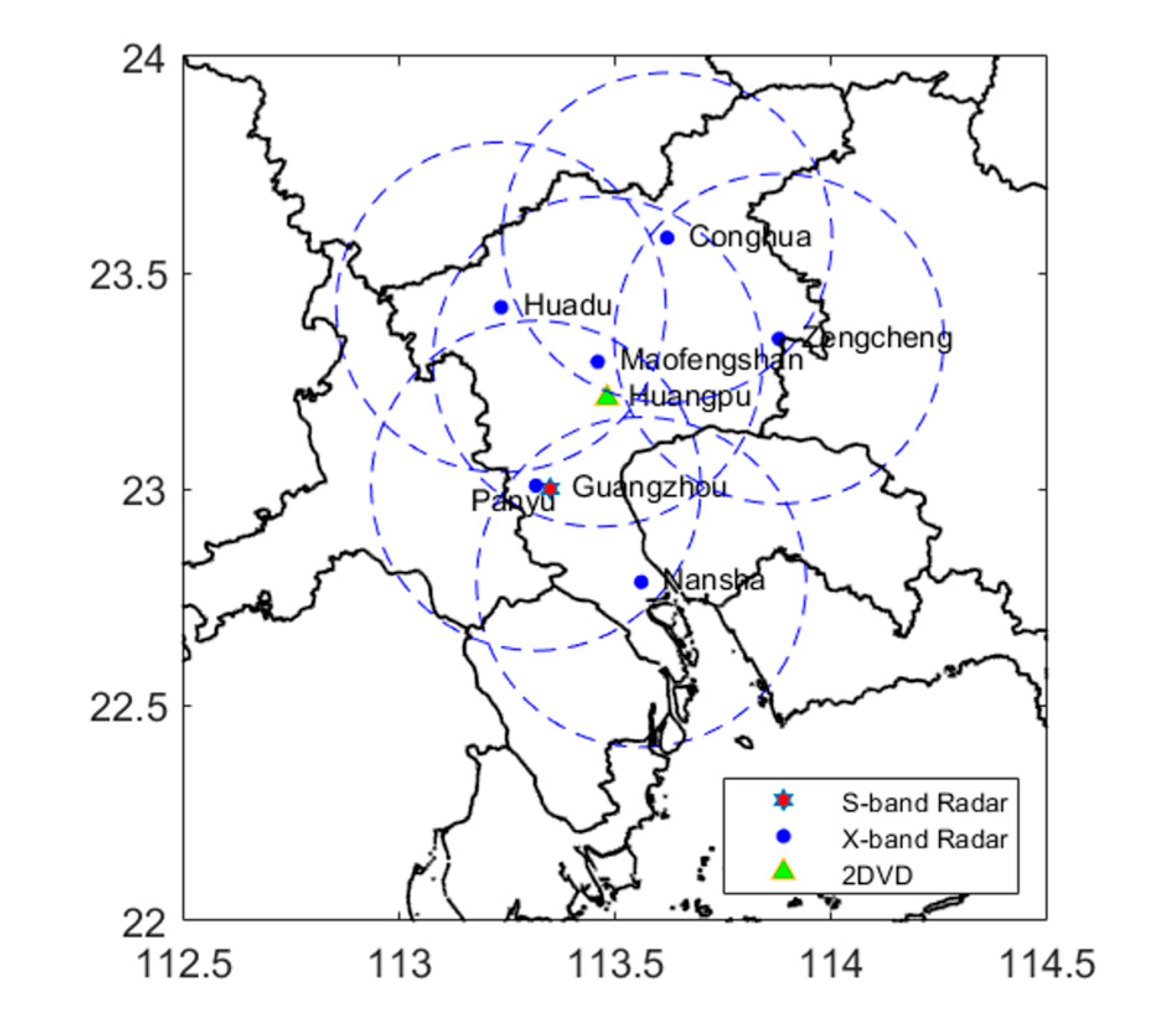
2.2. X-band dual-polarization phased array radar (XPAR-D)
2.3. S-band dual-polarization radar (SDPR)
2.4. Preprocessing of the X-band dual-polarization phased array radar data
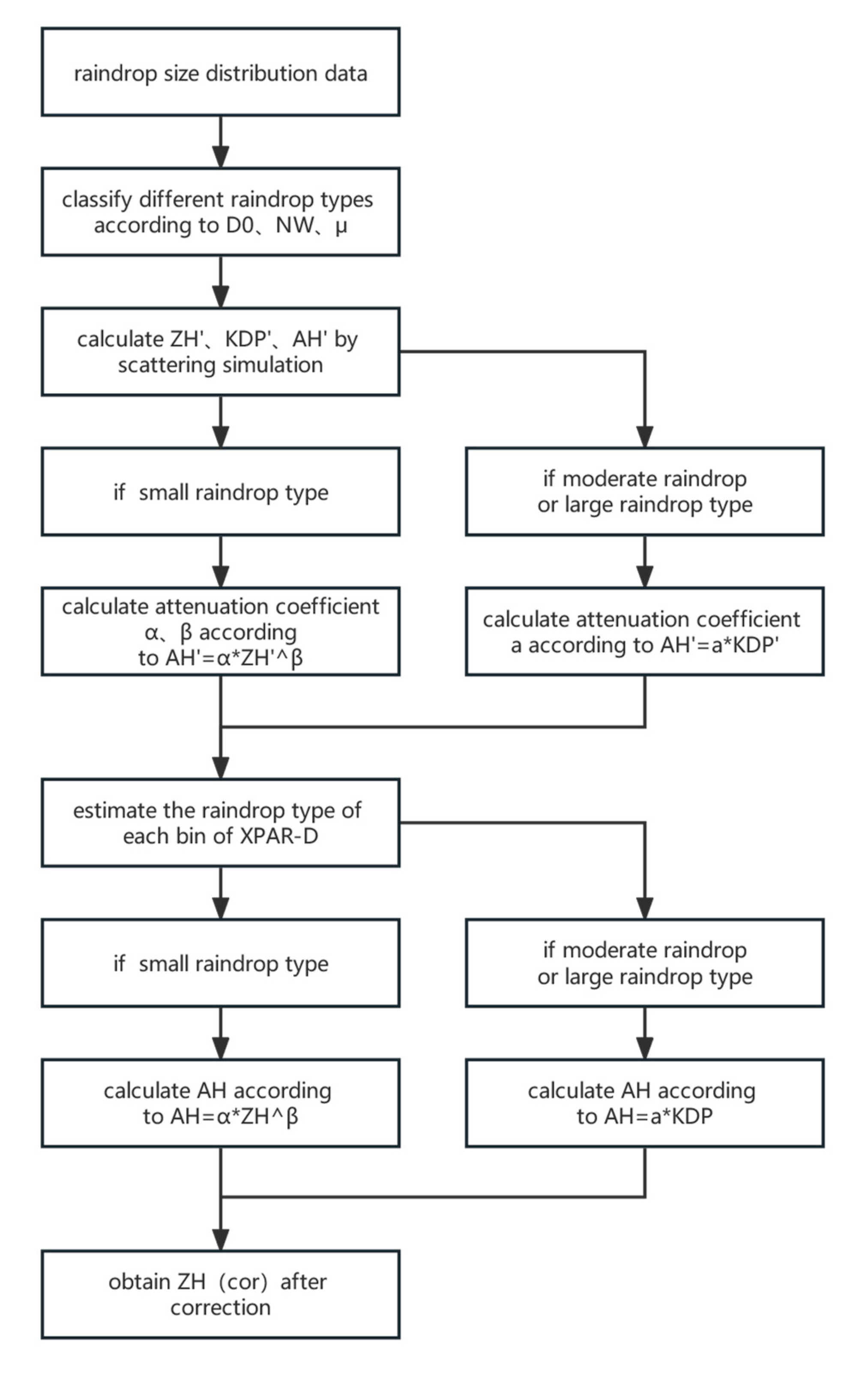
2.5. Attenuation correction method
2.5.1. ZH-KDP method
2.5.2. MZH-KDP method
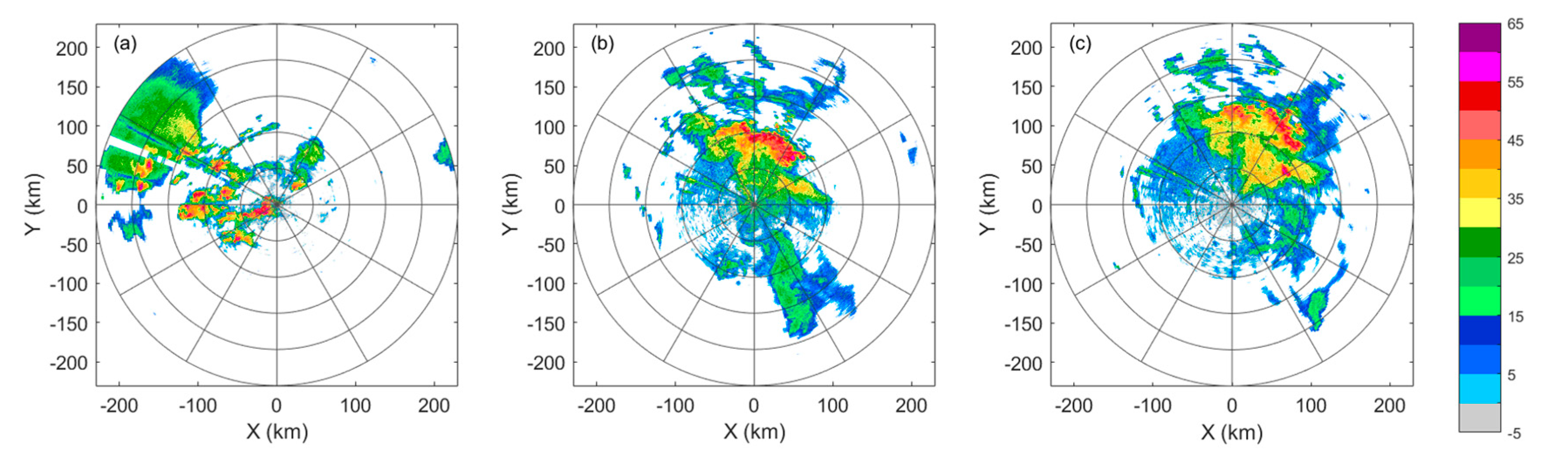
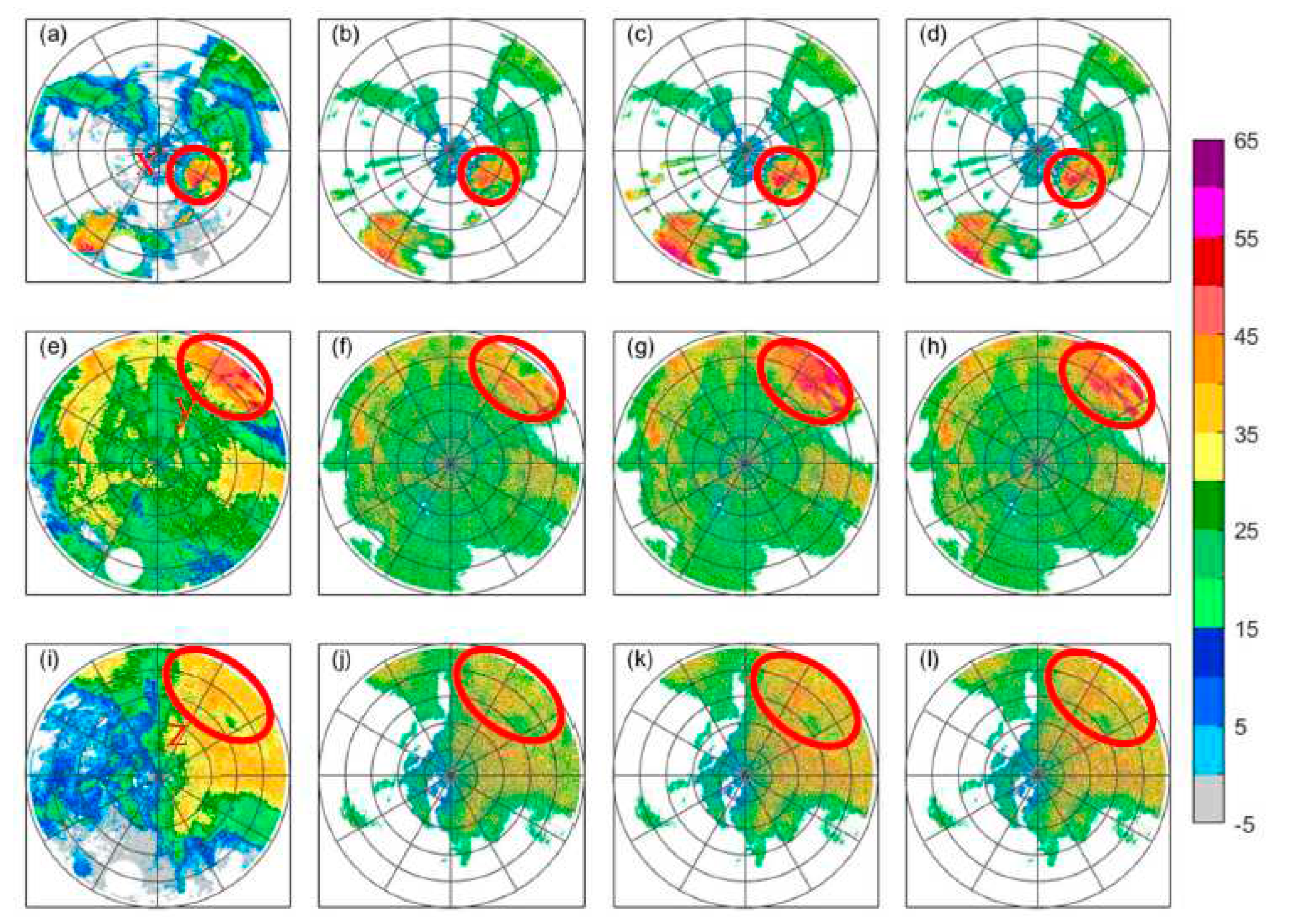
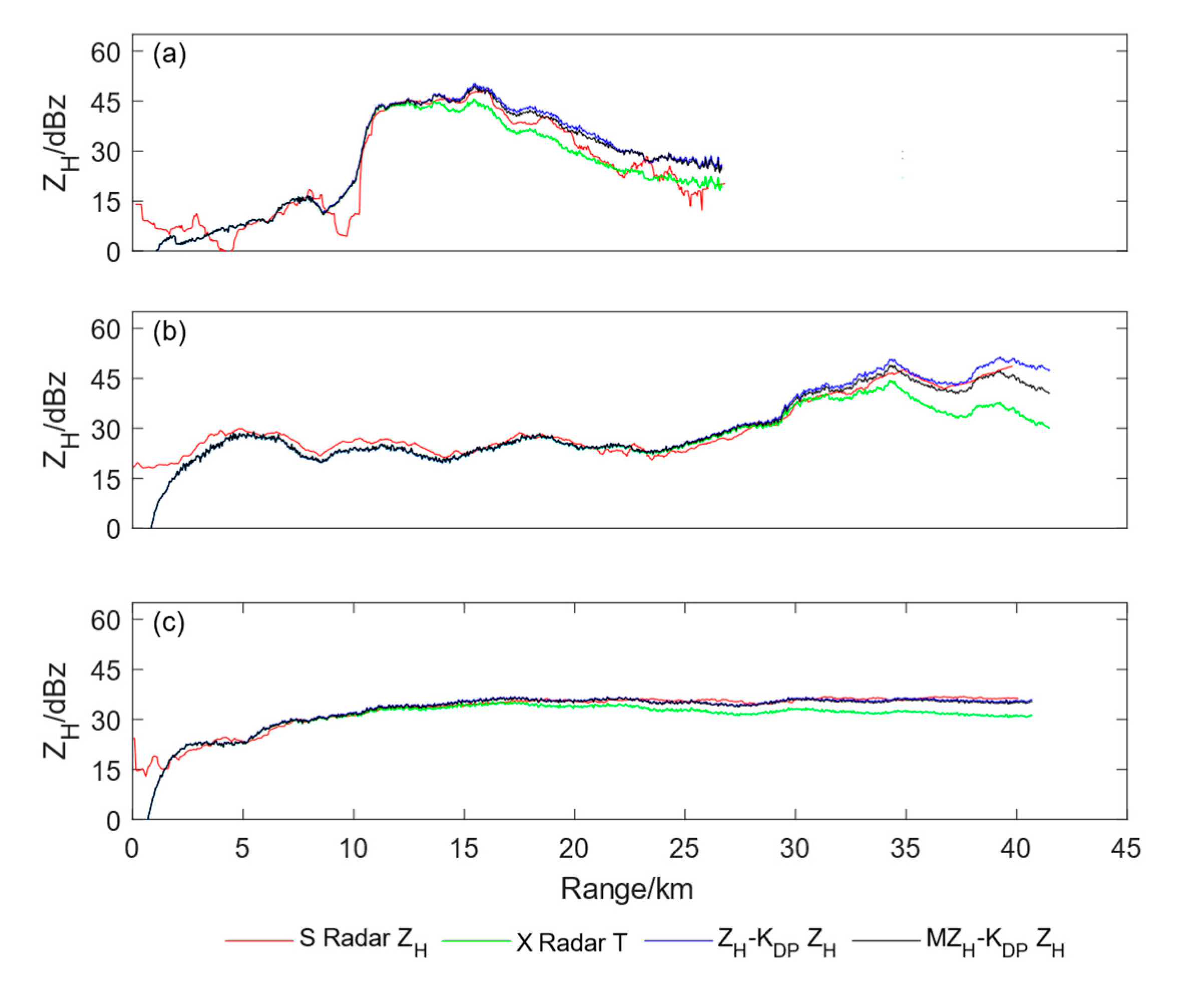
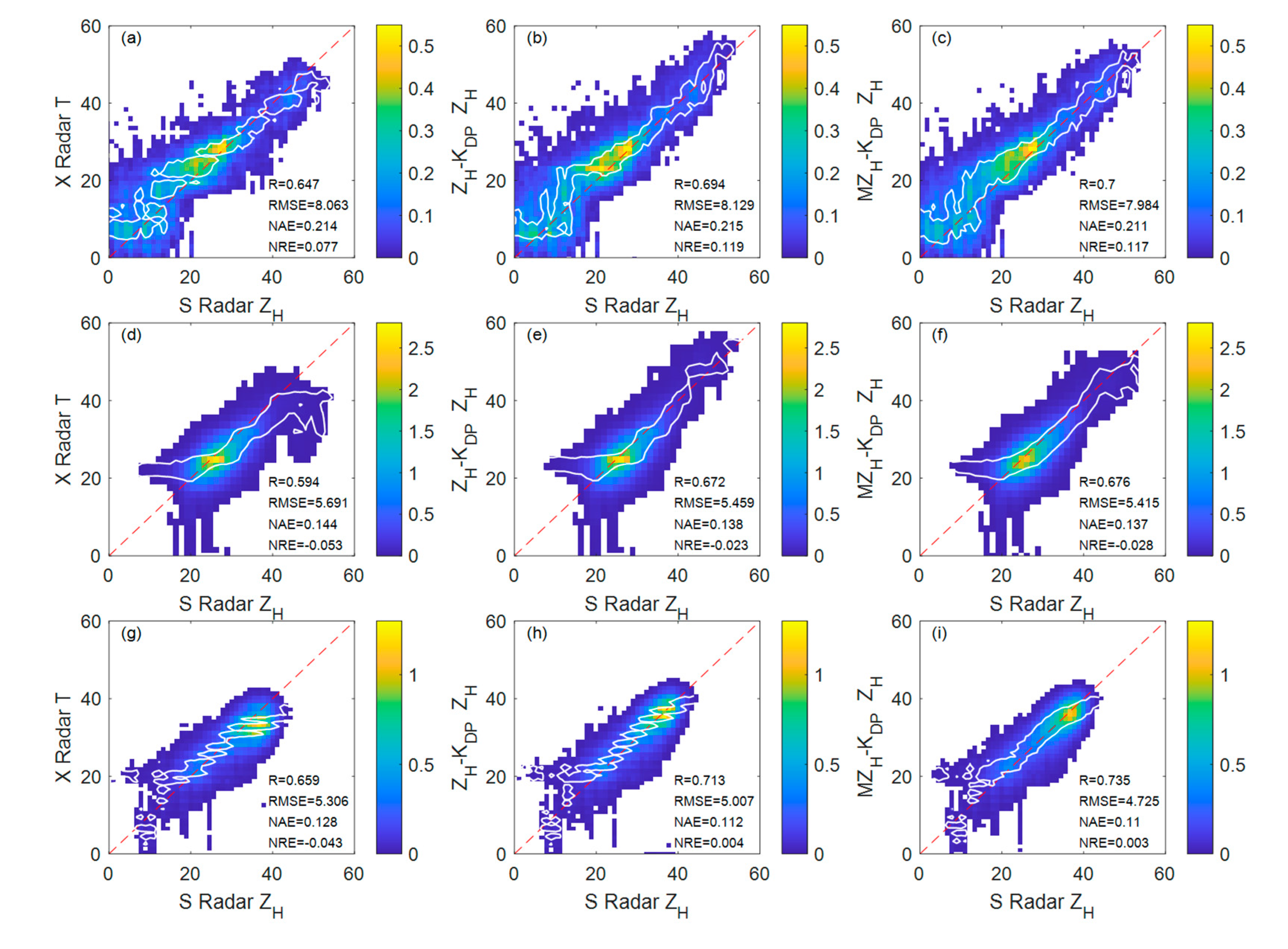
3. Results
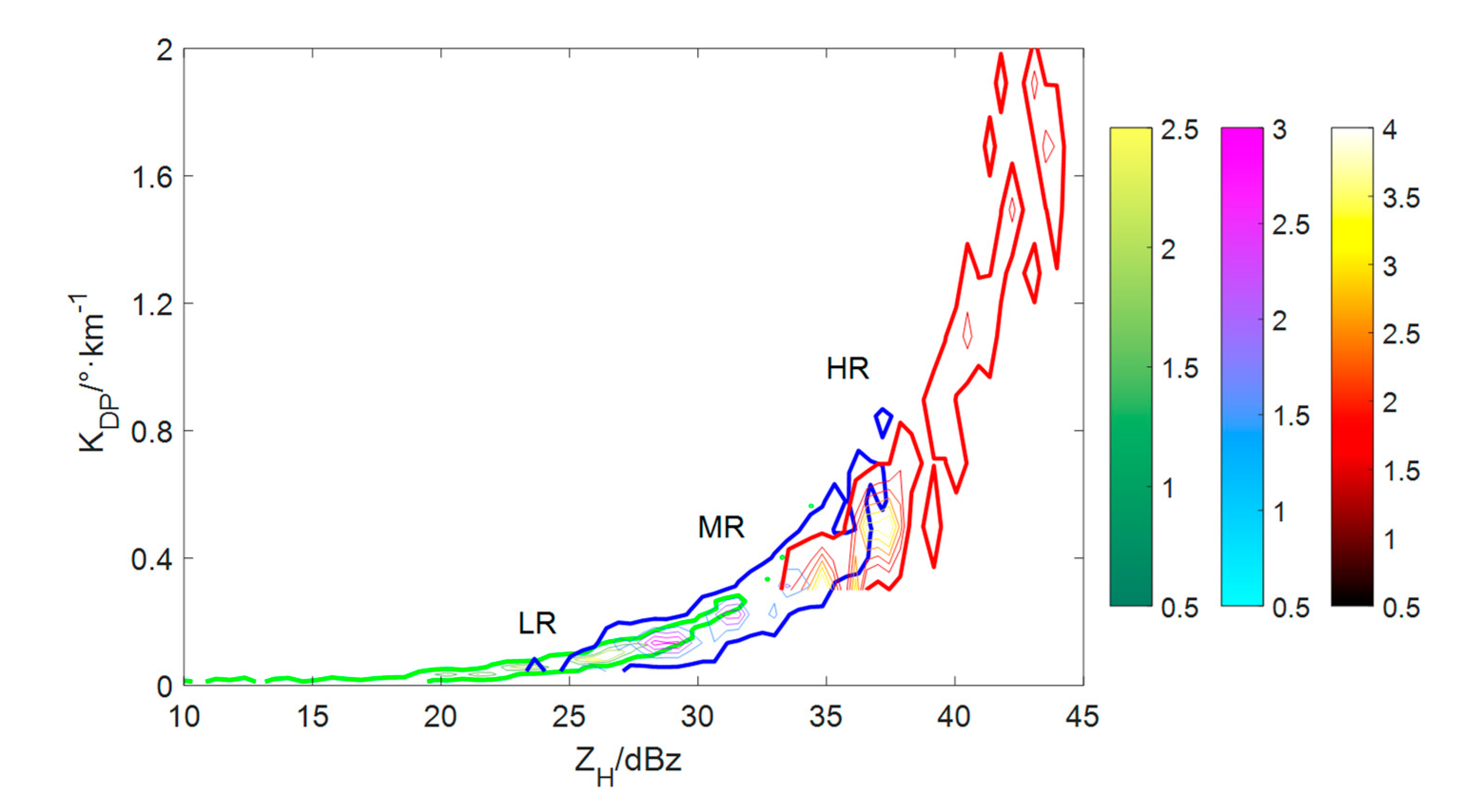
3.1. Dual-polarization parameter thresholds for raindrop classification
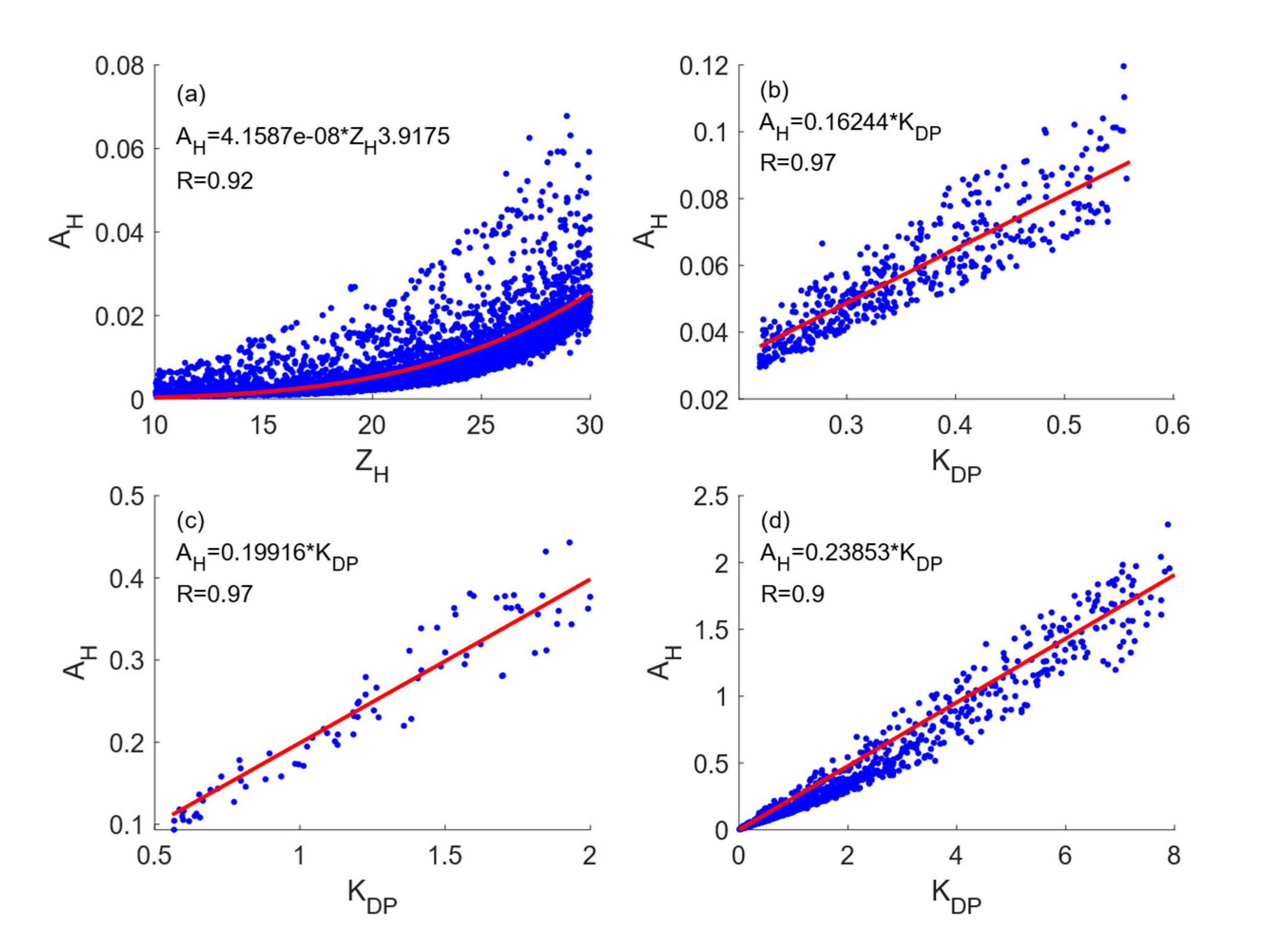
3.2. Attenuation Coefficients of different raindrop types
3.3. Verification of correction results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.-G.; Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Maki, M.; Iwanami, K. Correction of Radar Reflectivity and Differential Reflectivity for Rain Attenuation at X Band. Part I: Theoretical and Empirical Basis. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampe, H.J.A.; Weickmann, H.K. Errors Inherent in the Radar Measurement of Rainfall at Attenuating Wavelengths. J. Meteor. 1954, 11, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Liu, X.; Pu, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, F.; Xu, B. Contrasts in the Evolution and Microphysical Features of Two Convective Systems during a Heavy Rainfall Event along the Coast of South China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.; Keenan, T.; Chandrasekar, V. Correcting C-band radar reflectivity and differential reflectivity data for rain attenuation: a self-consistent method with constraints. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2001, 39, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Rao, X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, G.; Chen, S. Detailed Evolution Characteristics of an Inclined Structure Hailstorm Observed by Polarimetric Radar over the South China Coast. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrnić, D.S.; Ryzhkov, A. Advantages of Rain Measurements Using Specific Differential Phase. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Feng, L.; Wan, Q.; Ou, G.; Zhang, X. Correction of Rainfall Attenuation and Partial Terrainblockage for C-band Dual Polarization Weather Radar. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2021, 37, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.-Y.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zhang, P.; Neilley, P.; Knight, M.; Wolf, B.; Lee, D.-I. Polarimetric Attenuation Correction in Heavy Rain at C Band. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2011, 50, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bouar, E.; Testud, J.; Keenan, T.D. Validation of the Rain Profiling Algorithm “ZPHI” from the C-Band Polarimetric Weather Radar in Darwin. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 1819–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Le Bouar, E.; Obligis, E.; Ali-Mehenni, M. The Rain Profiling Algorithm Applied to Polarimetric Weather Radar. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 332–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Chu, R.; Jin, R. Comparison of Different Attenuation Correction Methods and Theireffects on Estimated Rainfall Using X-band Dual Linear Polarimetric Radar. Acta. Meteorol. Sin. 2008, 66, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, K.; Zhao, Y. A Computational Study Of Polarimetric Radar Observables In Hail. T-GRS. 1990, 28, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Balakrishnan, N.; Zrnić, D.S. An Examination of Propagation Effects in Rainfall on Radar Measurements at Microwave Frequencies. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 1990, 7, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, A.R. A Comparison of Microwave Techniques for Measuring Rainfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1991, 30, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.D. Hydrometeor Classification with a C-band Polarimetric Radar. Aust. Met. Mag. 2003, 52, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zrnić, D.S.; Keenan, T.D.; Carey, L.D.; May, P. Sensitivity Analysis of Polarimetric Variables at a 5-cm Wavelength in Rain. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1514–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L. Application Study of Mobile C-Band Dual-Polarization Radar Quality Control and QPE Using Raindrop Size Distribution. Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2014.
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, C.; Fu, P.; Huang, H. Progress of Observation Experiment for X-band Dual-Polarization Phased Array Radars in Guangzhou. Adv. MeteorSci. Technol. 2020, 010, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, L.; Meng, Z.; Chen, B.; Tian, C.; Fu, P. Rapid-Scan and Polarimetric Phased-Array Radar Observations of a Tornado in the Pearl River Estuary. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2021, 27, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, H.; Hu, D.; Huang, H.; Fu, P.; Tian, C. Data Quality Analysis and Application of Guangzhou X-band Dual-Polarization Phased Array Radars. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2022, 38, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Xia, F.; Wan, Q.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, H. Characteristics of the Raindrop Size Distribution in Two Squall Lines Measured by Two-Dimensional Video Disdrometer at Guangdong. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2019, 35, 812–821. [Google Scholar]
- Xian-Tong, L.; Zheng, R.; Sheng, H.; Qi-Lin, W.; Li-Ping, L.; Ya-Li, L.; Zhi-Qun, H.; Hui-Qi, L.; Hui, X.; Wei-Yan, L.; et al. The Longmen Cloud Physics Field Experiment Base, China Meteorological Administration. 热带气象学报(英文版) 2023, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, H.; Hu, S.; Wan, Q.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, T.; Li, M.; Ye, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. A High-precision and Fast Solution Method of Gamma Raindrop Size Distribution based on 0-Moment and 3-Moment in South China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y. Preliminary Analysis of Data Quality of Guangzhou S-band Polarimetric Weather Radar. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2018, 34, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z. Quantitative Comparison Algorithm between the S-band Phased Array Radar and the CINRAD/SA and Its Preliminary Application. Acta. Meteorol. Sin. 2014, 72, 390–401. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W. Quantitative Precipitation Estimation by Dual Linear Polarization Radar Combined with Raindrop Spectrometer. Chengdu University of Information Technology, 2020.
- Feng, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Xiao, H.; Pan, X.; Xia, F.; Ou, G.; Zhang, C. Precipitation Microphysical Characteristics of Typhoon Mangkhut in Southern China Using 2D Video Disdrometers. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Qi, T.; Zeng, G. Improving S-Band Polarimetric Radar Monsoon Rainfall Estimation with Two-Dimensional Video Disdrometer Observations in South China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Liu, X.; Hu, S.; Xiao, H.; Xia, F.; Feng, L.; Li, H. Raindrop size distribution characteristic differences during the dry and wet seasons in South China. Atmospheric Res. 2022, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, K.; Zhao, Y.; Seliga, T. Rain-induced attenuation effects on C-band dual-polarization meteorological radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 1989, 27, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Guo, C.; Feng, L. Characteristics of the raindrop size distributions and their retrieved polarimetric radar parameters in northern and southern China. Atmospheric Res. 2014, 135-136, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wan, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Xia, F.; Feng, L. Raindrop Size Distribution Parameters Retrieved from Xinfeng C-Band Polarimetric Radar Observations. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2020, 26, 275–285. [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Experiments in Rainfall Estimation with a Polarimetric Radar in a Subtropical Environment. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yin, J.; Ma, L.; Huang, Z. Comprehensive Statistical Analysis of Rain Drop Size Distribution Parameters and Their Application to Weather Radar Measurement in Nanjing. Chinese J. Atmospheric Sci. 2019, 43, 691–704. [Google Scholar]

| Item | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Antenna type | One-dimensional array antenna |
| Peak power | 256 W |
| Operating frequency | 9.4 GHz |
| Polarization | Dual-pol/double-transmission and double receiving |
| Beam width (horizontal/vertical) | 3.6°/1.8° |
| Volume-scanning period | 90 s |
| Detection range | 42 km |
| Resolution | 30 m |
| Elevation range | 0.9°–20.7° |
| Cut number | 11 |
| Peak power | 256 W |
| Raindrop types | D0 (mm) | NW (mm−1 mm−3) | μ |
| Small Raindrop | |||
| Moderate Raindrop | |||
| Large Raindrop |
| Raindrop types | ZH | KDP |
|---|---|---|
| Small Raindrop | ||
| Moderate Raindrop | ||
| Large Raindrop |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





