Submitted:
26 April 2023
Posted:
27 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Honey bees and N. ceranae
2.2. Entomopathogenic fungal culture extract
2.3. Purification of Nosema spores
2.4. In vitro germination assay
2.5. Safety test of fungal culture extract
2.6. Nosema inoculation and culture extract feeding assay
2.7. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inhibitory activity of entomopathogenic fungal culture extracts on Nosema germination
3.2. Nosema spore germination inhibitory activity according to the concentration of culture extract
3.3. Mechanism of spore germination inhibitory activity of culture extracts
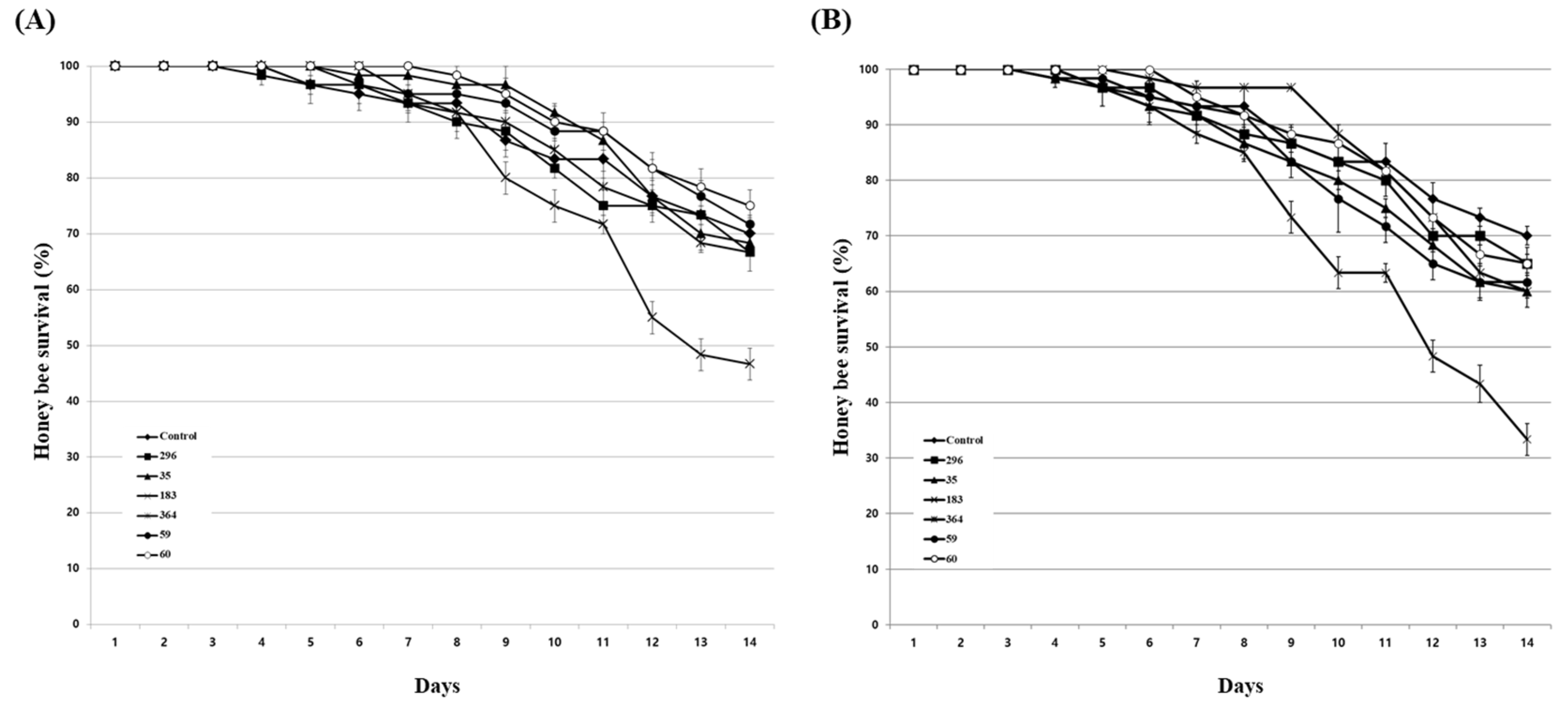
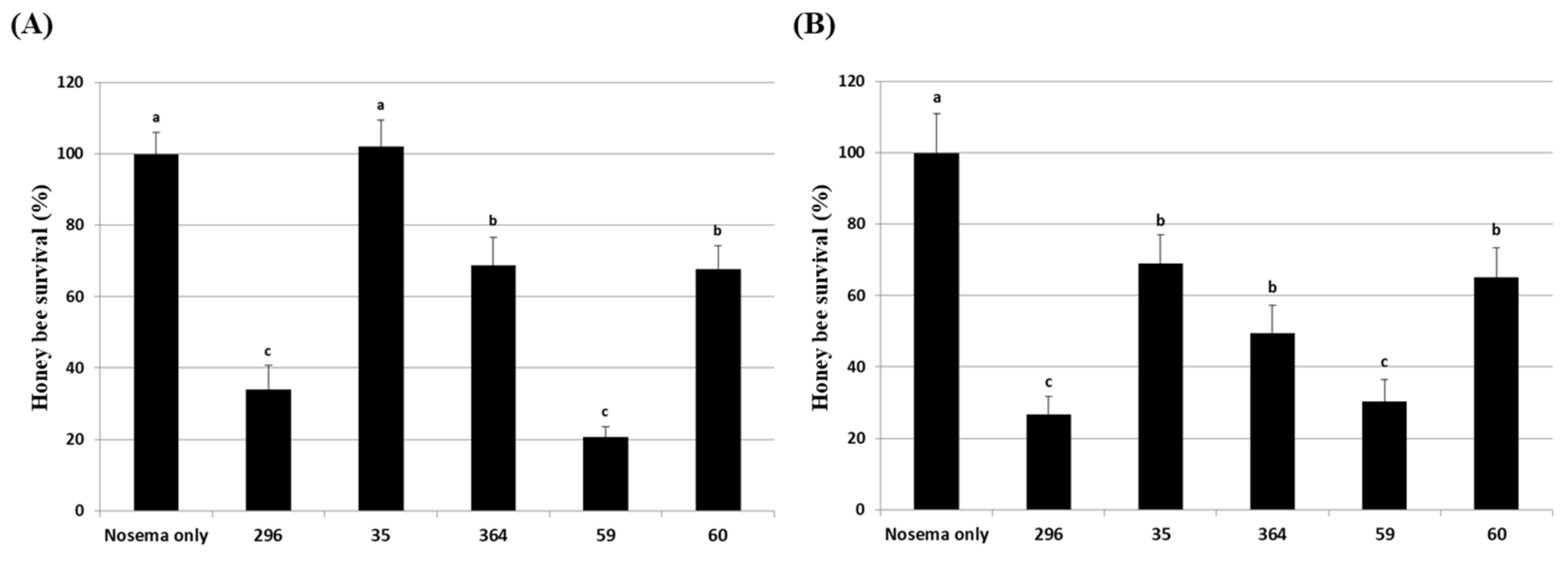
3.4. Effects of culture extracts on honey bees
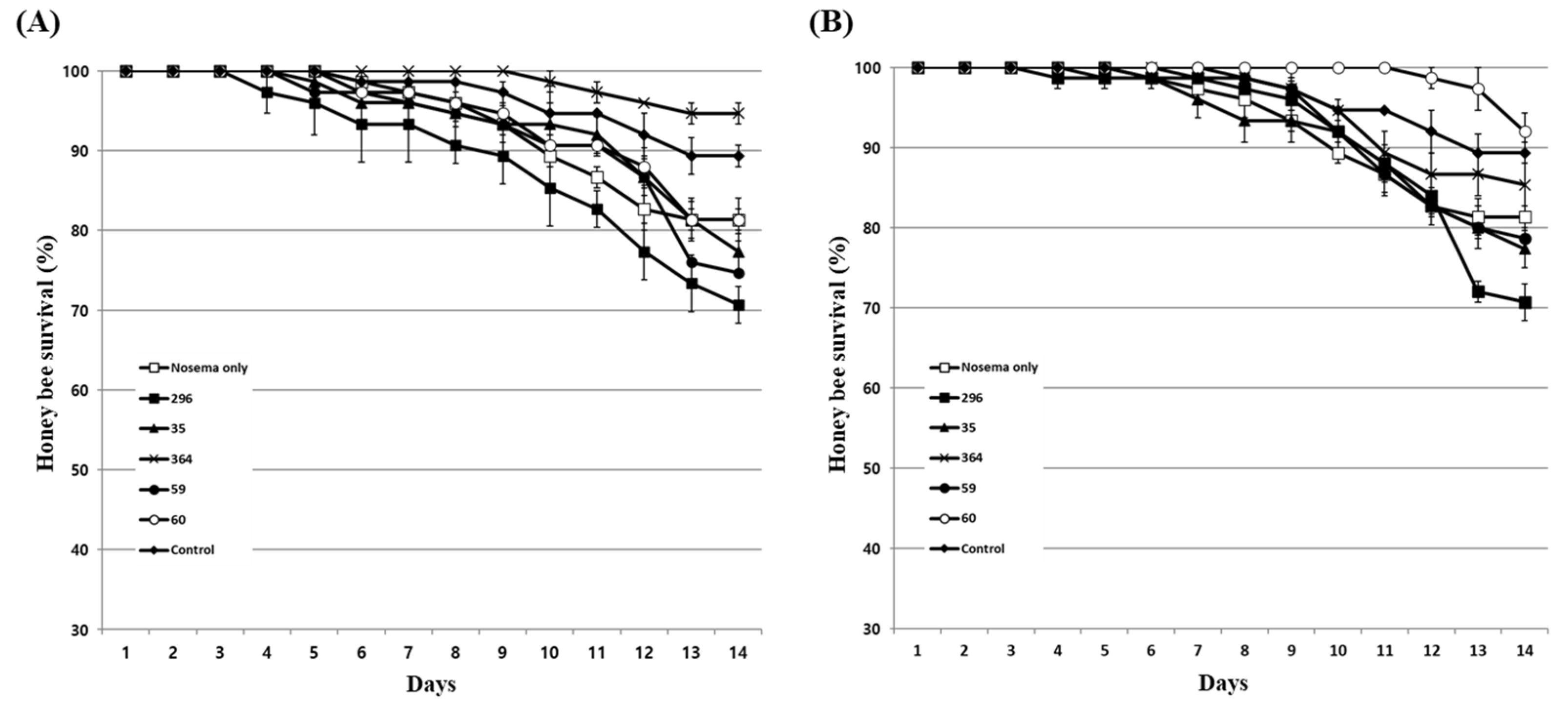
3.5. Inhibitory effect of culture extract on honey bee nosemosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallai, N.; Salles, J.M.; Settele, J.; Vaissière, B.E. Economic valuation of the vulnerability of world agriculture confronted with pollinator decline. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 810–821. [CrossRef]
- Breeze, T.D.; Bailey, A.P.; Balcombe, K.G.; Potts, S.G. Pollination services in the UK: How important are honeybees? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 142, 137-143. [CrossRef]
- Ollerton, J.; Winfree, R.; Tarrant, S. How many flowering plants are pollinated by animals? Oikos 2011, 120, 321-326. [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, L.A.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Winfree, R.; Aizen, M.A.; Bommarco, R.; Cunningham, S.A.; Kremen, C.; Carvalheiro, L.G.; Harder, L.D.; Afik, O.; et al. Wild pollinators enhance fruit set of crops regardless of honey bee abundance. Science 2013, 339, 1608–1611. [CrossRef]
- Papa, G.; Maier, R.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Karabagias, I.K.; Plutino, M.; Bianchetto, E.; Aromolo, R.; Pignatti, G.; Ambrogio, A.; Pellecchia, M.; Negri, I. The honey bee Apis mellifera: An insect at the interface between human and ecosystem health. Biology 2022, 11, 233. [CrossRef]
- Samarghandian, S.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samini, F. Honey and health: A review of recent clinical research. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, 121-127.
- Luo, X.; Dong, Y.; Gu, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Processing technologies for bee products: An overview of recent developments and perspectives. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 727181. [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, N.; Kulhanek, K.; Antúnez, K.; Human, H.; Chantawannakul, P.; Chauzat, M.P.; Vanengelsdorp, D. Drivers of colony losses. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 142-148. [CrossRef]
- Hristov, P.; Shumkova, R.; Palova, N.; Neov, B. Factors associated with honey bee colony losses: A mini-review. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 166. [CrossRef]
- Higes, M.; Martín-Hernández, R.; Garrido-Bailón, E.; González-Porto, A.V.; García-Palencia, P.; Meana, A.; et al. Honeybee colony collapse due to Nosema ceranae in professional apiaries. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 110-113. [CrossRef]
- Vanengelsdorp, D.; Evans, J.D.; Saegerman, C.; Mullin, C.; Haubruge, E.; Nguyen, B.K.; et al. Colony collapse disorder: A descriptive study. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6481. [CrossRef]
- Le Conte, Y.; Ellis, M.; Ritter, W. Varroa mites and honey bee health: Can Varroa explain part of the colony losses? Apidologie 2010, 41, 353-363.
- Cornman, R.S.; Tarpy, D.R.; Chen, Y.; Jeffreys, L.; Lopez, D.; Pettis, J.S.; et al. Pathogen webs in collapsing honey bee colonies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43562. [CrossRef]
- Adl, S.M.; Simpson, A.G.; Lane, C.E.; Lukeš, J.; Bass, D.; Bowser, S.S.; Brown, M.W.; Burki, F.; Dunthorn, M.; Hampl, V.; et al. The revised classification of Eukaryotes. J. Eukaryotic Microbiol. 2012, 59, 429-514. [CrossRef]
- Galajda, R.; Valenčáková, A.; Sučik, M.; Kandráčová, P. Nosema disease of European honey bees. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 714. [CrossRef]
- Fries, I. Nosema in European honey bees (Apis mellifera): An emerging threat to bee health. Insect Sci. 2010, 17, 418-424.
- Mayack, C.; Naug, D. Energetic stress in the honeybee Apis mellifera from Nosema ceranae infection. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 105, 20-27. [CrossRef]
- Goblirsch, M.J.; Spivak, M.; Kurtti, T.J. Nosema spp. infections in honey bees (Apis mellifera): Literature review and a survey of prevalence in North America. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 1-22.
- Huang, W.F.; Solter, L.F.; Yau, P.M. Nosema ceranae causes asynchronous emergence of honey bee workers and reduces colony productivity. Apidologie 2018, 49, 11-22.
- Higes, M.; Martín-Hernández, R.; Meana, A. Nosema ceranae in European honey bees (Apis mellifera): An emerging infectious disease threatening apiaries and beekeeping. Insects 2020, 11, 886.
- Klee, J.; Besana, A.M.; Genersch, E.; Gisder, S.; Nanetti, A.; Tam, D.Q.; Chin, T.X.; Puerta, F.; Ruz, J.M.; Kryger, P.; et al. Wide spread dispersal of the microsporidian Nosema ceranae, an emergent pathogen of the western honey bee, Apis mellifera. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2007, 96, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Evans, J.D.; Simith, I.B.; Pettis, J.S. Nosema ceranae is a long-present and wide-spread microsporidian infection of the European honey bee (Apis mellifera) in the United States. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 97, 186-188. [CrossRef]
- Emsen, B.; Guzman-Novoa, E.; Hamiduzzaman, M.M.; Eccles, L.; Lacey, B.; Ruiz-Perez, R.A.; Nasr, M. Higher prevalence and levels of Nosema ceranae than Nosema apis infections in Canadian honey bee colonies. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 175-181. [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D.; Nicholls, E.; Botías, C.; Rotheray, E.L. Bee declines driven by combined stress from parasites, pesticides, and lack of flowers. Science 2015, 347, 1255957. [CrossRef]
- Vanengelsdorp, D.; Evans, J.D.; Donovall, L.; Mullin, C.; Frazier, M.; Frazier, J.; Tarpy, D.R.; Hayes, J.; Pettis, J.S. Entombed pollen: A new condition in honey bee colonies associated with increased risk of colony mortality. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009. 101, 147-149. [CrossRef]
- Requier, F.; Garnery, L.; Kohl, P.L.; Njovu, H.K.; Pirk, C.W.W.; Crewe, R.M.; Steffan-Dewenter, I. The conservation of native honey bees is crucial. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 789-798. [CrossRef]
- Stanimirovic, Z.; Stevanovic, J.; Bajic, V.; Radovic, I. Evaluation of genotoxic effects of fumagillin (dicyclohexylamine) by citogenetic tests in vivo. Mutat. Res. 2006, 628, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Pajuelo, A.G.; Torres, C.; Bermejo, F.J.O. Colony losses: A double blind trial on the influence of supplementary protein nutrition and preventative treatment with fumagillin against Nosema ceranae. J. Apic. Res. 2008, 47, 84-86. [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Shutler, D.; Little, C.M.; Burgher-MacLellan, K.L.; Rogers, R.E.L. The microsporidian Nosema ceranae, the antibiotic Fumagilin-B®, and western honey bee (Apis mellifera) colony strength. Apidologie 2011, 42, 15-22. [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Sampson, M.A.; Shutler, D.; Rogers, R.E. Does fumagillin control the recently detected invasive parasite Nosema ceranae in western honey bees (Apis mellifera)? J. Apic. Res. 2018, 57, 714-721. [CrossRef]
- Sabaté, D.C.; Cruz, M.S.; Benítez-Ahrendts, M.R.; Audisio, M.C. Beneficial effects of Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis Mori2, a honey-associated strain, on honeybee colony performance. Probiot. Antimicrob. Proteins 2012, 4, 39-46. [CrossRef]
- Glavinic, U.; Blagojevic, J.; Ristanic, M.; Stevanovic, J.; Lakic, N.; Mirilovic, M.; Stanimirovic, Z. Use of thymol in Nosema ceranae control and health improvement of infected honey bees. Insects 2022, 13, 574. [CrossRef]
- Klassen, S.S.; VanBlyderveen, W.; Eccles, L.; Kelly, P.G.; Borges, D.; Goodwin, P.H.; Petukhova, T.; Wang, Q.; Guzman-Novoa, E. Nosema ceranae infections in honey bees (Apis mellifera) treated with pre/probiotics and impacts on colonies in the field. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 107. [CrossRef]
- Kunat-Budzyńska, M.; Budzyński, M.; Schulz, M.; Strachecka, A.; Gancarz, M.; Rusinek, R.; Ptaszyńska, A.A. Natural substances, probiotics, and synthetic agents in the treatment and prevention of honeybee nosemosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1269. [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.A.; Frutos, R.; Kaya, H.K.; Vail, P. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Do they have a future? Biol. Control 2001, 21, 230-248. [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, G. Review on safety of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 879-920. [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.E.; Goettel, M.S.; Blackwell, M.; Chandler, D.; Jackson, M.A.; Keller, S.; Koike, M.; Maniania, N.K.; Monzon, A.; Ownley, B.H.; et al. Fungal entomopathogens: New insights on their ecology. Fungal Ecol. 2009, 2, 149-159. [CrossRef]
- Butt, T.M.; Coates, C.J.; Dubovskiy, I.M.; Ratcliffe, N.A. Entomopathogenic fungi: New insights into host-pathogen interactions. Adv. Genet. 2016, 94, 307-364. [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Kittakoop, P.; Kirtikara, K.; Hywel-Jones, N.L.; Thebtaranonth, Y. Bioactive substances from insect pathogenic fungi. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 813-823. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, L. Beauvericin, a bioactive compound produced by fungi: A short review. Molecules 2012, 17, 2367-2377. [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.Y.; Bae, S.M.; Kim, D.J.; Yun, H.G.; Woo, S.D. Evaluation of virulence, tolerance to environmental factors and antimicrobial activities of entomopathogenic fungi against two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae. Mycoscience 2017, 58, 204-212. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fasoyin, O.E.; Molnár, I.; Xu, Y. Secondary metabolites from hypocrealean entomopathogenic fungi: Novel bioactive compounds. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 1181-1206. [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.Y.; Lee, W.W.; Ko, S.H.; Choi, J.B.; Bae, S.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Je, Y.H.; Jin, B.R.; Woo, S.D. Distribution and characterisation of entomopathogenic fungi from Korean soils. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 288-304. [CrossRef]
- Gisder, S.; Hedtke, K.; Möckel, N.; Frielitz, M.C.; Linde, A.; Genersch, E. Five-year cohort study of Nosema spp. in Germany: Does climate shape virulence and assertiveness of Nosema ceranae? Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3032-3038. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Yun, H.G.; Kim, I.H.; Gwak, W.S.; Woo, S.D. Efficient method for the rapid purification of Nosema ceranae spores. Mycobiology 2017, 45, 204-208. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Evans, J.D.; Murphy, C.; Gutell, R.; Zuker, M.; Gundensen-Rindal, D.; Pettis, J.S. Morphological, molecular, and phylogenetic characterization of Nosema ceranae, a microsporidian parasite isolated from the European honey bee, Apis mellifera. J. Eukaryotic Microbiol. 2009, 56, 142-147. [CrossRef]
- Shimanuki, H.; Knox, D.A. Diagnosis of honey bee diseases. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook No. AH-690. Washington, DC, USA, 2000; p.61.
- Olsen, P.E.; Rice, W.A.; Liu, T.P. In vitro germination of Nosema apis spores under conditions favorable for the generation and maintenance of sporoplasms. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1986, 47, 65-73. [CrossRef]
- Klarić, M.S.; Pepeljnjak, S. Bovericin: Kemizam, bioloski aspekti i rasirenost [Beauvericin: Chemical and biological aspects and occurrence]. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2005, 56, 343-350.
- Liu, B.L.; Tzeng, Y.M. Development and applications of destruxins: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1242-1254. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Li, P.; Lai, D.; Zhou, L. Structural diversity and biological activities of cyclic depsipeptides from fungi. Molecules 2018, 23, 169. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, H.; Li, W.; Cheng, P.; Gong, M. The toxins of Beauveria bassiana and the strategies to improve their virulence to insects. Fron. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 705343. [CrossRef]
- Houard, J.; Aumelas, A.; Noël, T.; Pages, S.; Givaudan, A.; Fitton-Ouhabi, V.; Villain-Guillot, P.; Gualtieri, M. Cabanillasin, a new antifungal metabolite, produced by entomopathogenic Xenorhabdus cabanillasii JM26. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 617-620. [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.A.; Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Patel, M.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; Snoussi, M.; Ashraf, M.S.; Adnan, M.; Hadi, S. Cordycepin for health and wellbeing: A potent bioactive metabolite of an entomopathogenic Cordyceps medicinal fungus and Its nutraceutical and therapeutic potential. Molecules 2020, 25, 2735. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fasoyin, O.E.; Molnár, I.; Xu, Y. Secondary metabolites from hypocrealean entomopathogenic fungi: Novel bioactive compounds. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 1181-1206. [CrossRef]
- Lacatena, F.; Marra, R.; Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A.; Digilio, M.C.; Giorgini, M.; Woo, S.L.; Cavallo, P.; Lorito, M.; Vinale, F. Chlamyphilone, a novel Pochonia chlamydosporia metabolite with insecticidal activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 750. [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Li, Y.; Lin, R.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Z.; Ling, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Du, S.; Cheng, X.; Xie, B. Antibacterial radicicol analogues from Pochonia chlamydosporia and their biosynthetic gene cluster. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7266-7273. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.B.; Wang, X.; Li, G.H. Secondary metabolites and their bioactivities produced by Paecilomyces. Molecules 2020, 25, 5077. [CrossRef]
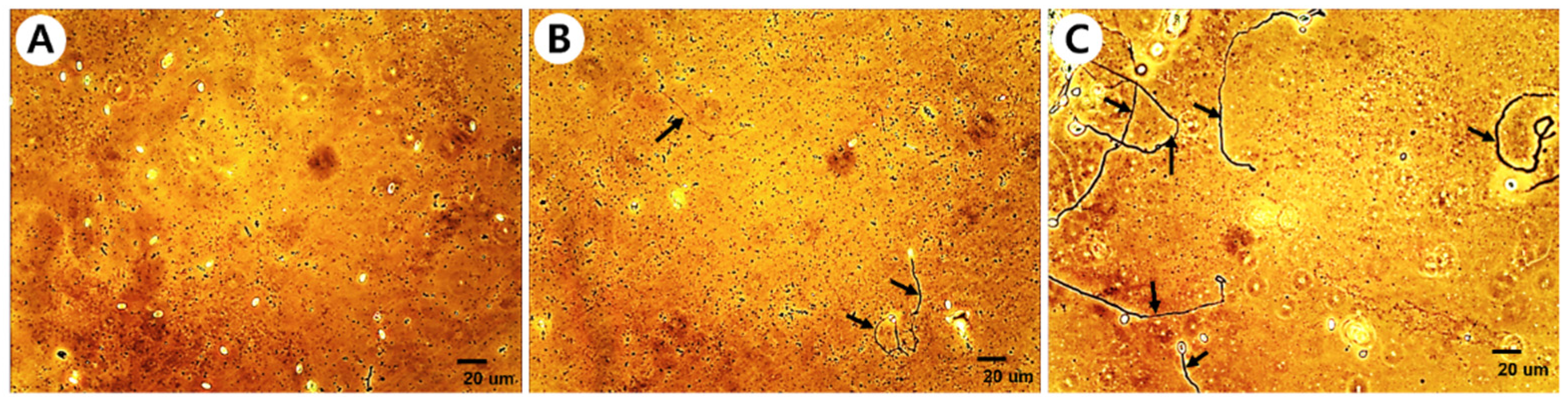
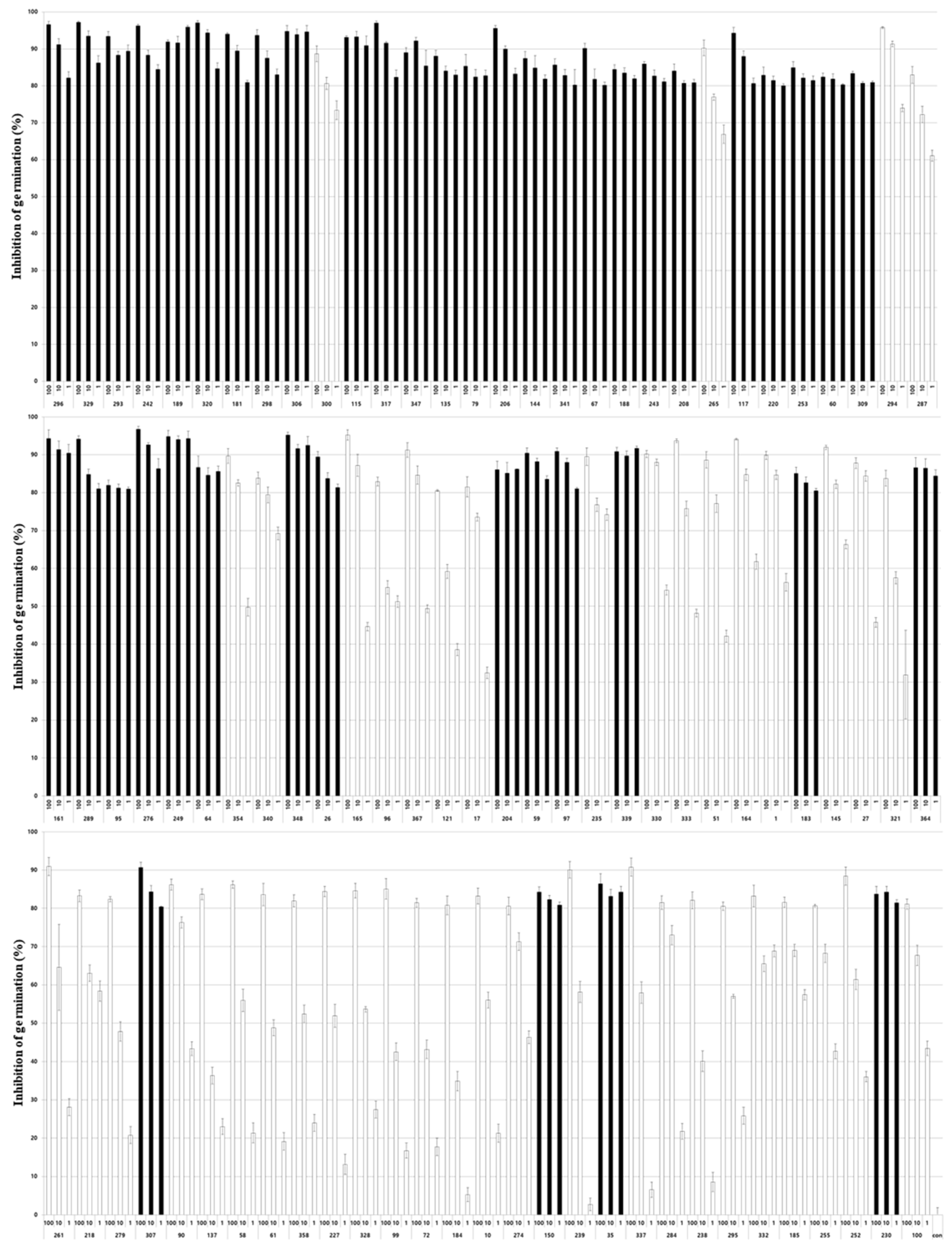

| Fungus | No. of tested isolates | No. of isolates showing the inhibition of spore germination |
| All fungal isolates | 342 | 89 (26%)* |
| Acremonium strictum | 1 | 0 (0%) |
| Aspergilluslentulus. | 5 | 0 (0%) |
| Aspergillus versicolor | 3 | 1 (33.3%) |
| Beauveria bassiana | 110 | 48 (43.6%) |
| Beauveria brongniartii | 8 | 1 (12.5%) |
| Beauveria pseudobassiana | 8 | 1 (12.5%) |
| Bionectria ochroleuca | 7 | 0 (0%) |
| Clonostachys rosea | 1 | 0 (0%) |
| Cordyceps farinosa | 12 | 5 (41.7%) |
| Cordyceps fumosorosea | 6 | 1 (16.7%) |
| Cordyceps javanica | 22 | 5 (22.7%) |
| Fusarium oxysporum | 2 | 0 (0%) |
| Lecanicillium spp. | 8 | 1 (12.5%) |
| Metarhizium anisopliae | 64 | 15 (23.4%) |
| Metarhizium lepidiotae | 1 | 0 (0%) |
| Metarhizium pemphigus | 16 | 3 (18.8%) |
| Mucoromycotina spp. | 1 | 0 (0%) |
| Myrothecium spp. | 5 | 0 (0%) |
| Paecilomyces lilacinus | 7 | 1 (14.3%) |
| Paecilomyces marquandii | 5 | 1 (20%) |
| Paraconiothyrium sporulosum | 2 | 1 (50%) |
| Phialocephala spp. | 1 | 0 (0%) |
| Pochonia bulbillosa | 16 | 3 (18.8%) |
| Pochonia rubescens | 1 | 0 (0%) |
| Simplicillium aogashimaense | 1 | 1 (100%) |
| Simplicillium sp. | 2 | 0 (0%) |
| Tolypocladium album | 23 | 1 (4.3%) |
| Tolypocladium cylindrosporum | 3 | 0 (0%) |
| Verticillium insectorum | 1 | 0 (0%) |
| Fungus | No. of isolate (%) |
| Aspergillus versicolor | 1 (2.3) * |
| Beauveria bassiana | 24 (54.5) |
| Beauveria brongniartii | 1 (2.3) |
| Cordyceps farinosa | 4 (9.1) |
| Cordyceps fumosorosea | 1 (2.3) |
| Cordyceps javanica | 1 (2.3) |
| Lecanicillium spp. | 1 (2.3) |
| Metarhizium anisopliae | 6 (13.6) |
| Paecilomyces lilacinus | 1 (2.3) |
| Paecilomyces marquandii | 1 (2.3) |
| Pochonia bulbillosa | 2 (4.5) |
| Tolypocladium album | 1 (2.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





