Submitted:
26 April 2023
Posted:
27 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
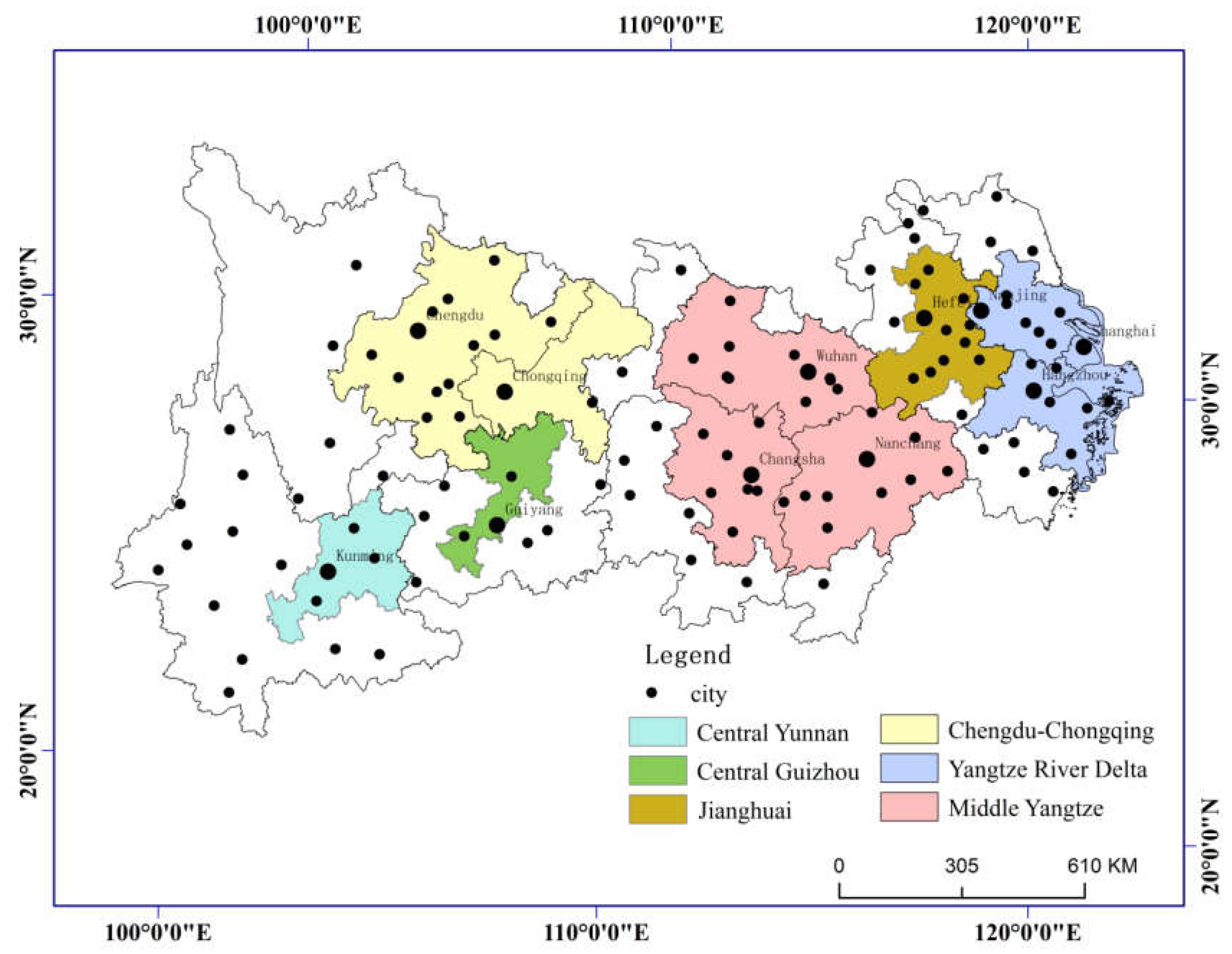
2. Overview of the study area
3. Research Methodology and Data Processing
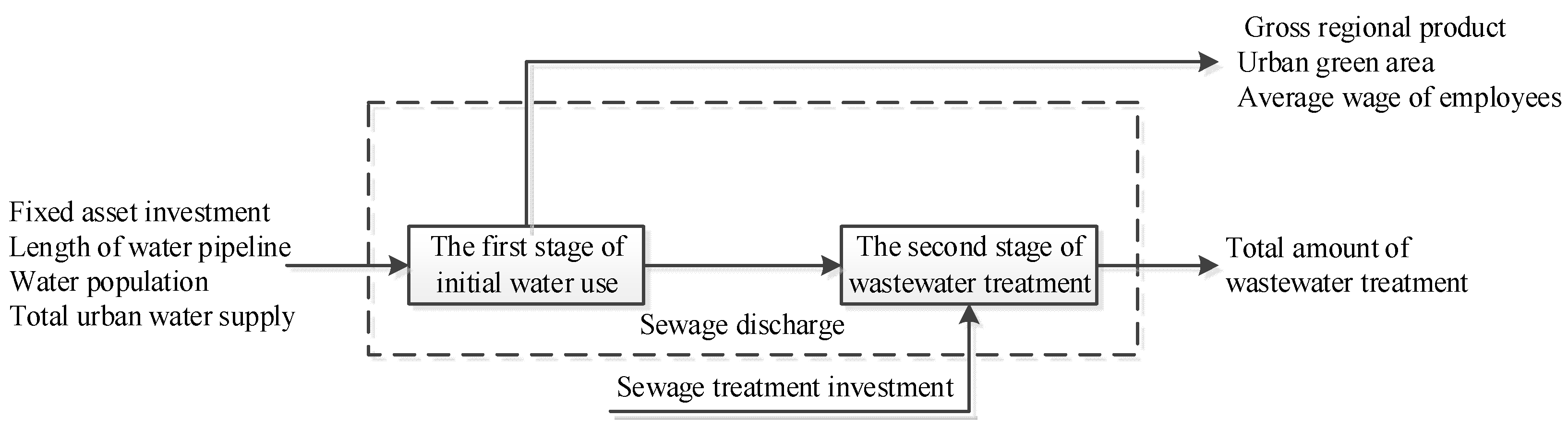
3.1. Two-stage network DEA model
3.2. Dagum's Gini coefficient and decomposition method
3.3. Convergence model
3.4. Data sources and processing
4. Results and Analysis
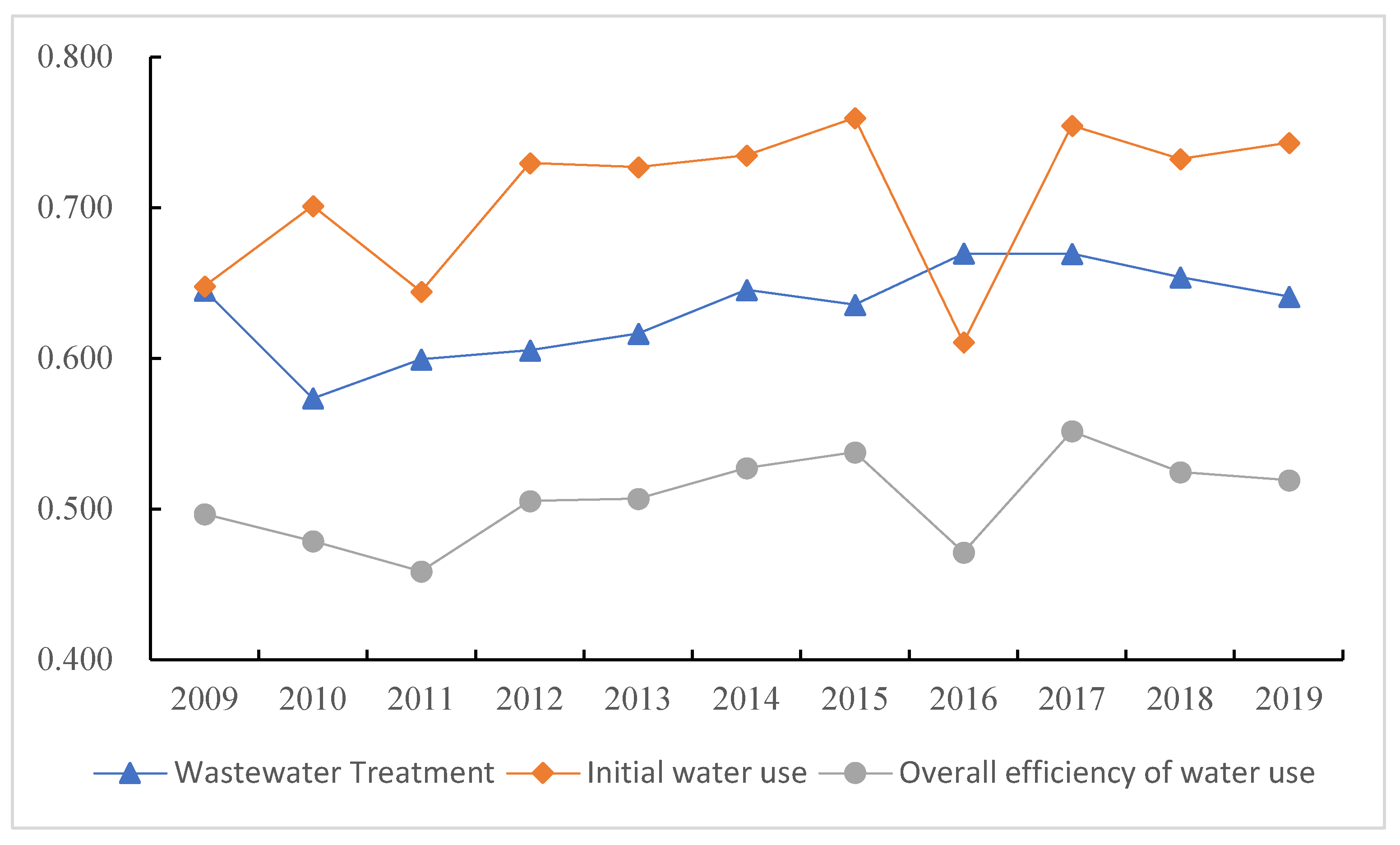
4.1. General characteristics of urban water use efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Zone
4.2. Classification of city types in the Yangtze River Economic Zone
4.3. Decomposition of water use efficiency differences among urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Zone
4.4. Convergence analysis of water use efficiency of urban clusters in the Yangtze River Economic Zone
4.4.1. Convergence analysis
4.4.2. β-absolute convergence analysis
4.4.3. β-conditional convergence analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaoxin Cai, Yin Songkui. Spatial and temporal evolution of urban water use efficiency in Northwest China and club convergence analysis. Economic Economics,2021,38(2),5-13.
- Xiang Y B, Wang S Y, Dai Z J.Green Development Efficiency Measurement and Influencing Factors of the Paper Industry in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Water ,2021, 13, 1286.
- Tian Guiliang, Li Jiaojiao, Li Lele. Study on the virtual water flow pattern of Yangtze River economic zone based on multi-regional input-output model. China Population-Resources and Environment,2019,29(3),81-88.
- An Hui, Wang Yonghao, An Min, Wang Lijie. Spatial and temporal evolution of water resources green efficiency and water conservation and emission reduction potential in cities along the Yangtze River Economic Belt [J/OL]. Yangtze River Basin Resources and Environment:1-18[2023-03-03]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1320.X.20220826.1526.002.html.
- Charnes, A. , Cooper, W.W., Rhodes, E.Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 6, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao Win. A study on green development performance and its influencing factors in eight integrated economic zones in China. Research on Quantitative Economics and Technology Economy,2019,36(9),3-23.
- P. Andersen and N.C. Petersen. A procedure for ranking efficient units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Management Science ,1993,39,1261 -1264.
- Francisco J. André, Inés Herrero, Laura Riesgo.A modified DEA model to estimate the importance of objectives with an application to agricultural A modified DEA model to estimate the importance of objectives with an application to agricultural economics.Omega,2010, 38 (5),371-382.
- He Wei, Wang Yiling. Measurement of urban water use efficiency in the Yellow River basin and analysis of influencing factors. Journal of Environmental Science,2021,41(11),4760-4770.
- Yao Tingting., Liu Suxia. Comparison of change characteristics of multiple efficiency indicators of water resources use in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei. Advances in Geographical Sciences,2021,40(7),1195-1207.
- Pittman R.W. Multilateral Productivity Comparisons with Undesirable Outputs.Economic Journal,1983,93(372),883-891.
- Yang Jingwen, He Gang, Zhou Qinting, Bao Keyu. Study on the spatial spillover effect of water resources utilization efficiency in Huaihe eco-economic zone. Hydroelectricity,2020,46(11),29-33.
- Yue Li, Ren Wanyu, Yao Xiaoqiang. Spatial and temporal variation of green water resources efficiency in cities of the Yellow River basin and its influencing factors--based on the perspective of river ecohydrological zoning. Industrial Technology and Economics,2021,40(10),15-22.
- Färe R,Groskopf S. Productivity and intermediate products: A frontier approach.Computational Economics,1996,50 (1) ,65-70.
- Tone, K. , Tsutsui, M.Network DEA: a slacks-based measure approach. eur. j. Oper. Res. 2009, 1, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. , Chen, Y., Liang, L., Xie, J. DEA models for extended two-stage networkstructures. Omega Int. J. Manage. Sci. 2012, 5, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian Y., YanS. ,Xu H.Efficiency Evaluation for Regionalban Water Use and Waste water Decontamination Systems in China: A DEA Approach. Respurces,Conservation and Recycling, 2014, 83, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marien Morán-Valencia, Martin Flegl, David Güemes-Castorena. A state-level analysis of the water system management efficiency in Mexico: two- stage DEA approach,Water Resources and Industry, 2023, 29, 100200.
- Zhao, L. ,Sun C.,Liu F.Interprovincial two stage water resource utilization effificiency under environmental constraint and spatial spillover effects in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 164, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng Guangyao,Zhang Zhongjie.Research on industrial water use efficiency of Chinese provinces based on network SBM-DEA model and GML index. Journal of Natural Resources,2019,34(7),1457-1470.
- Zhang Guoji, Wu Huaqing, Liu Yezheng, Zhou Zhixiang. Measurement of comprehensive water resources utilization efficiency in China and its spatial interaction analysis. Quantitative Economic and Technical Economics Research,2020,37(8),123-139.
- Ren Junlin, Li Hao, Wu Xinmu, Li Xuesong. Analysis of water use efficiency of provincial capitals in Yangtze River economic belt. China Population-Resources and Environment,2016,26(5),101-107.
- Wang Keliang, Liu Yue, Shi Lijuan, Liu Lei, Meng Xiagrui, Yang Baochen. Spatial and temporal divergence and influencing factors of industrial green water resources efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Zone - a two-stage analysis based on EBM-Tobit model. Resource Science,2017,39(8),1522-1534.
- Yang Gaosheng,Xie Qiuhao. Study on the spatial and temporal variation of green water resources efficiency in Yangtze River economic zone - based on SE-SBM and ML index method. Yangtze River Basin Resources and Environment,2019,28(2),349-358.
- Fang Chuanglin, Zhou Chenghu, Wang Zhenbo. Strategic issues of sustainable development of urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the focus of graded gradient development. Advances in Geographical Sciences,2015,34(11),1398-1408.
- Li Yongqing. Research on regional industrial environmental efficiency evaluation and driving factors in China based on two-stage network DEA [D]. China University of Petroleum (East China), 2019. [CrossRef]
- Guo Ji, Wu Xianhua, Chen Yufeng. Construction and empirical evidence of a two-stage DEA model for haze emission efficiency assessment. China Soft Science,2020(10),184-192.
- Chuanming, L.; Huitong, W.; Xiaomin, W. Research on regional difference decomposition and convergence of Internet financial development in China 's eight urban agglomerations. quant. econ. tech. econ. res. 2017, 34, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, L. Regional differences and stochastic convergence of China's economic growth quality. res. Quant. Econ. Tech. Econ. 2019, 36, 24–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Mingdou, Weng Aihua.. Spatial correlation network and formation mechanism of urban water use efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Zone. Journal of Geography,2022,77(9),2353-2373.
- Cheng Fengyu. Study on the spatial differences and convergence of science and technology innovation in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area metropolitan area. Research on Quantitative Economics and Technology Economy,2020,37(12),89-107.
- Zhu Binhai. Study on the measurement and influencing factors of water use efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Belt under environmental constraints . Journal of Hebei University of Geosciences,2018,41(2),51-57.
- Zhang Xiyue, Sun Fangcheng, Wang Huaizu. Study on green efficiency of industrial water resources in Yangtze River Economic Zone based on two-stage evaluation of "production-governance". Journal of Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, 2020(2),26-36.
- Qian Lexiang, Xu Shuming, Qin Fen. Spatial analysis of basin economy and western development strategy. Advances in Geographical Sciences,2000,19(3) , 266-272.
- Zhang Kankan, Guo Wenjiong. A study of watershed economy based on spatial characteristics, processes and mechanisms. Economic Issues,2013(10),103-108.
- Chen Shu, Lv Wenfang, Wang Jianping. Analysis of the spatial and temporal evolution of water resource use efficiency in the Yangtze River basin. Water Resources Conservation,2022,38(4),80-86,94.
- Deng Qizhong,Zhang Ling. Spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of water resources green efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Zone and its influencing factors. Resource Science,2022,44(2),247-260.
- Chen Jie, He Wei, Chen Deliang. A study on performance assessment of urban wastewater management in the Yangtze River basin. Environmental Science and Management,2019,44(6),1-5.
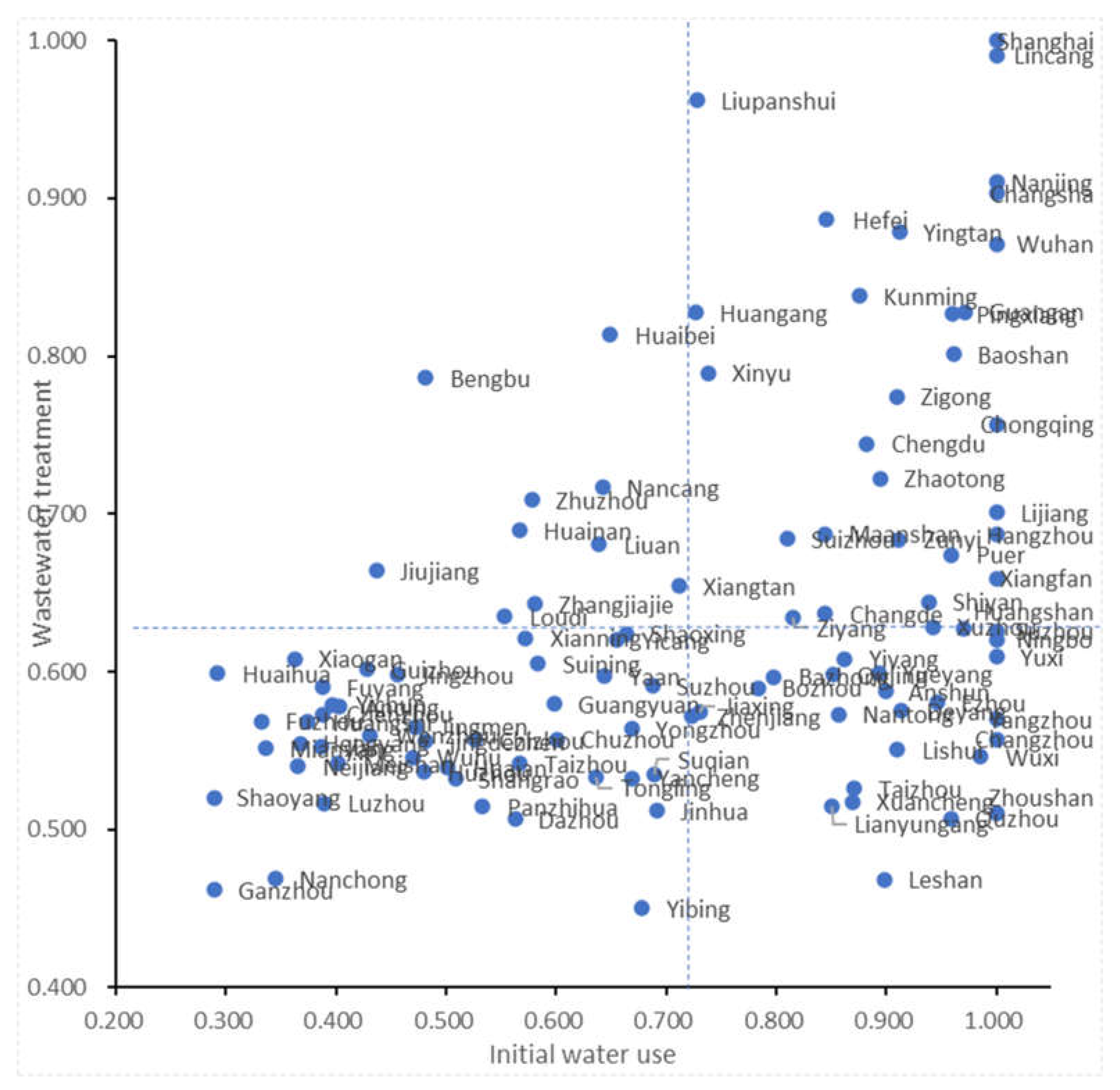
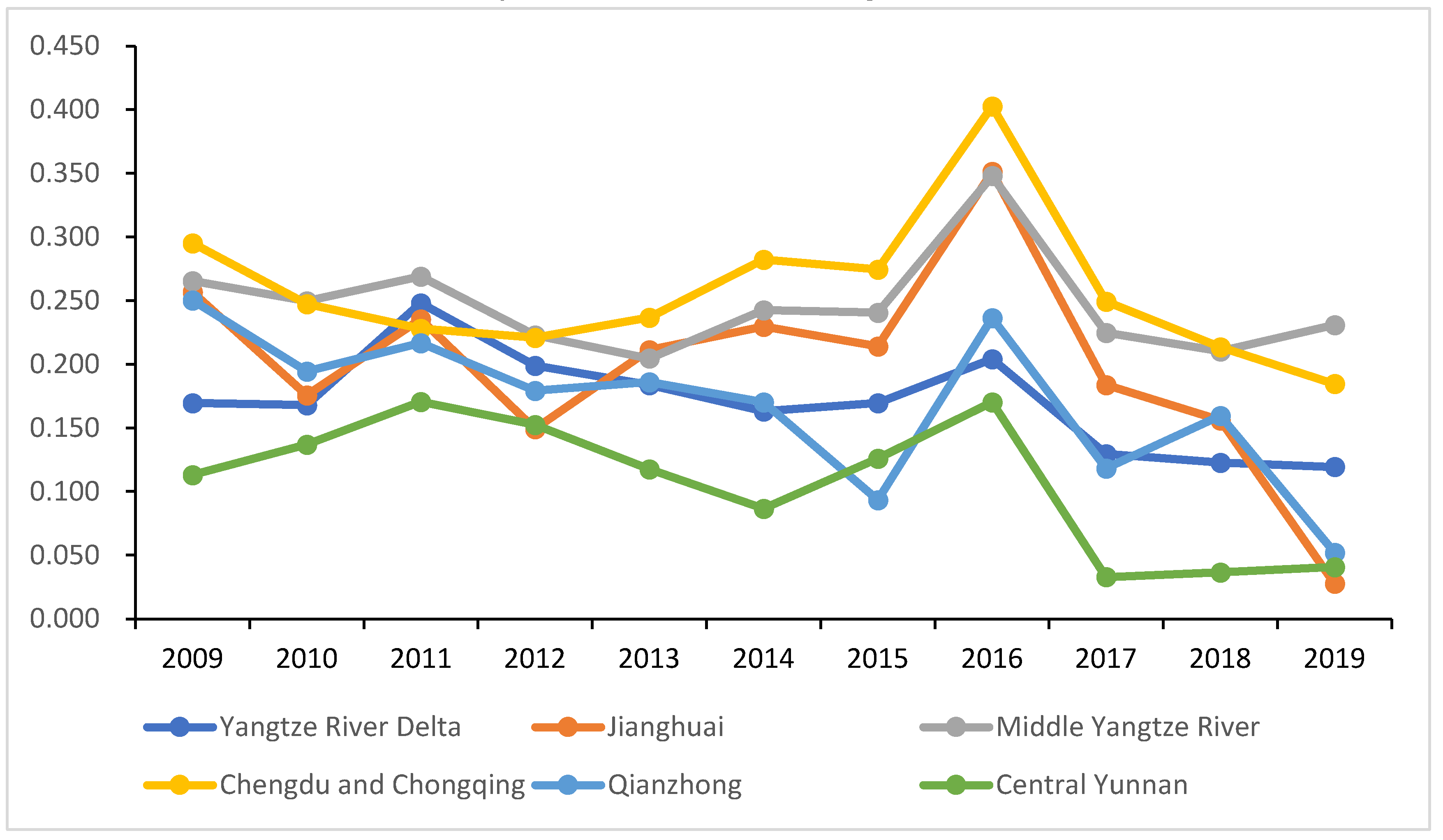
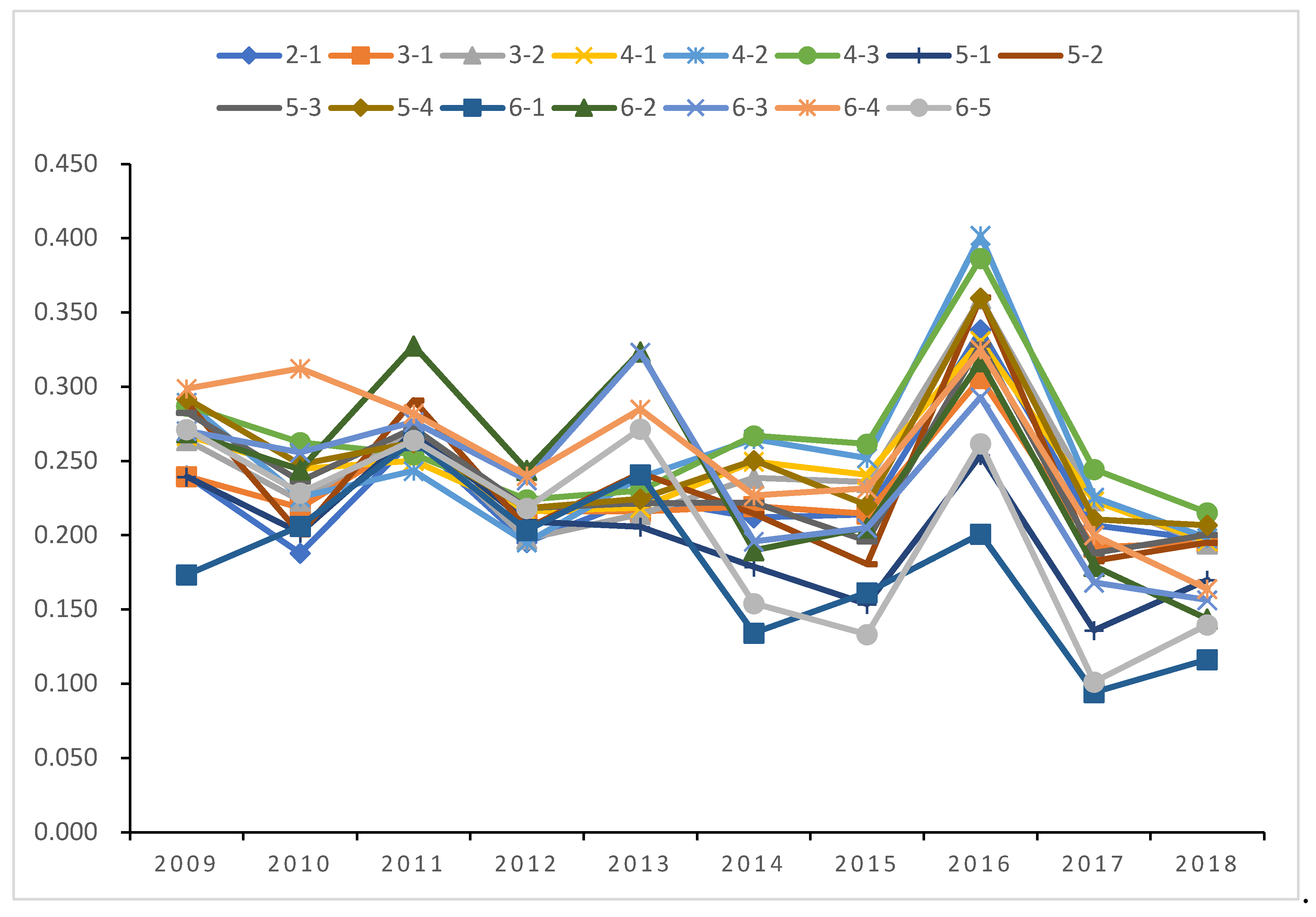
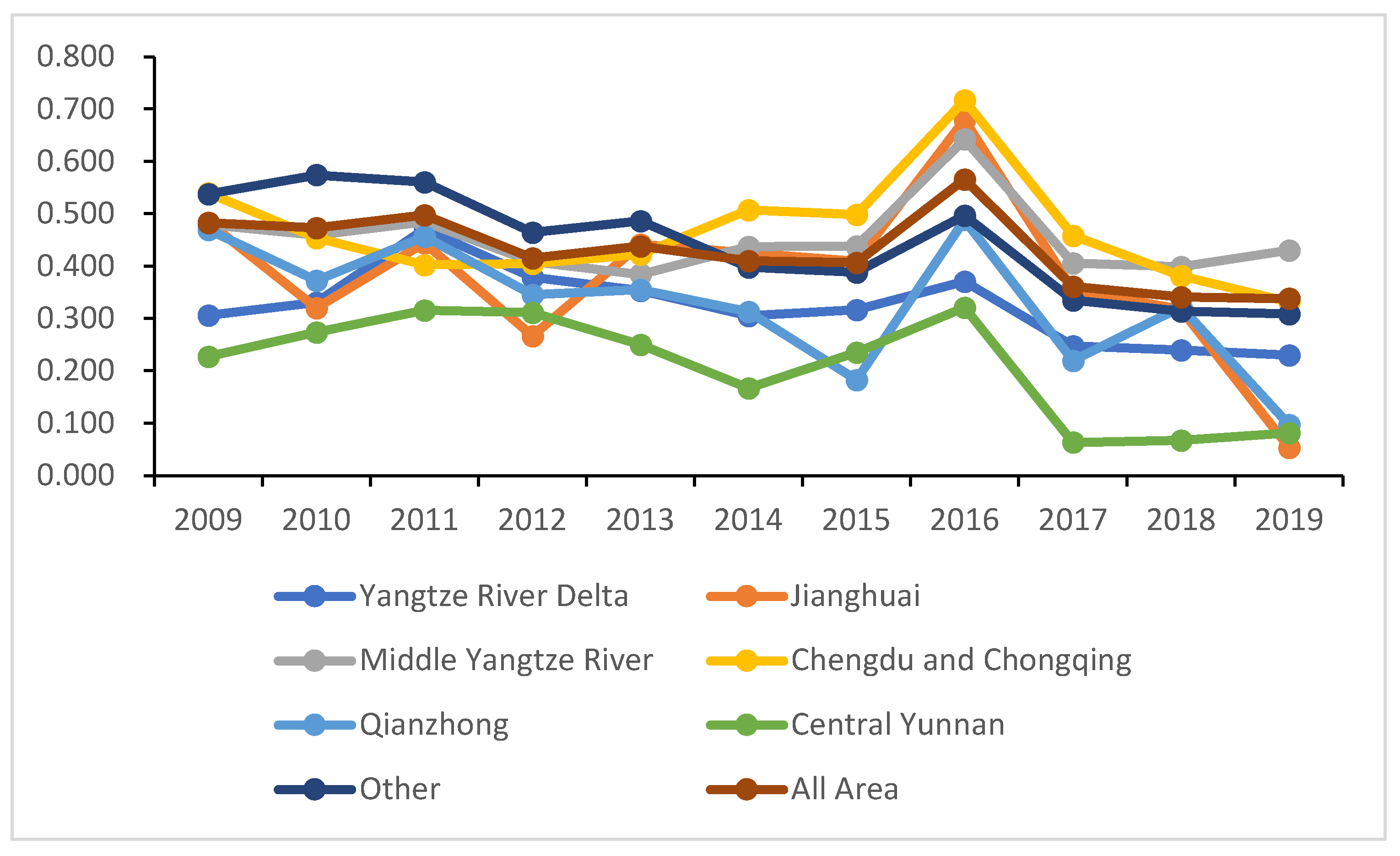
| Initial water use | Pollution control | Water use efficiency | Initial water use | Pollution control | Water use efficiency | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | Shanghai | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | Chengdu and Chongqing | Chongqing | 1.000 | 0.757 | 0.760 |
| Nanjing | 1.000 | 0.910 | 0.910 | Chengdu | 0.882 | 0.744 | 0.695 | ||
| Wuxi | 0.986 | 0.546 | 0.544 | Zigong | 0.909 | 0.774 | 0.741 | ||
| Changzhou | 1.000 | 0.557 | 0.565 | Luzhou | 0.389 | 0.517 | 0.267 | ||
| Suzhou | 1.000 | 0.626 | 0.635 | Deyang | 0.913 | 0.575 | 0.553 | ||
| Nantong | 0.856 | 0.573 | 0.520 | Mianyang | 0.336 | 0.552 | 0.239 | ||
| Yangzhou | 1.000 | 0.570 | 0.580 | Suining | 0.583 | 0.605 | 0.403 | ||
| Zhenjiang | 0.724 | 0.572 | 0.452 | Neijiang | 0.365 | 0.540 | 0.269 | ||
| Taizhou | 0.871 | 0.526 | 0.485 | Leshan | 0.898 | 0.468 | 0.467 | ||
| Hangzhou | 1.000 | 0.687 | 0.692 | Nanchong | 0.344 | 0.469 | 0.223 | ||
| Ningbo | 1.000 | 0.620 | 0.639 | Meishan | 0.402 | 0.542 | 0.277 | ||
| Jiaxing | 0.730 | 0.575 | 0.464 | Yibin | 0.678 | 0.450 | 0.377 | ||
| Huzhou | 0.479 | 0.536 | 0.299 | Guang'an | 0.971 | 0.828 | 0.813 | ||
| Introduction | 0.664 | 0.624 | 0.479 | Dazhou | 0.563 | 0.507 | 0.408 | ||
| Zhoushan | 1.000 | 0.511 | 0.533 | Ya'an | 0.644 | 0.597 | 0.471 | ||
| Taizhou | 0.567 | 0.542 | 0.356 | Ziyang | 0.815 | 0.634 | 0.552 | ||
| Average value | 0.867 | 0.623 | 0.572 | Average value | 0.668 | 0.597 | 0.470 | ||
| Jianghuai | Hefei | 0.846 | 0.887 | 0.798 | Central Guizhou | Guiyang | 0.428 | 0.602 | 0.330 |
| Wuhu | 0.469 | 0.546 | 0.309 | Zunyi | 0.911 | 0.684 | 0.673 | ||
| Bengbu | 0.481 | 0.786 | 0.482 | Anshun | 0.899 | 0.588 | 0.552 | ||
| Huainan | 0.566 | 0.690 | 0.452 | Average value | 0.746 | 0.625 | 0.518 | ||
| Ma On Shan | 0.844 | 0.687 | 0.612 | Central Yunnan | Kunming | 0.875 | 0.838 | 0.771 | |
| Tongling | 0.636 | 0.533 | 0.384 | Qujing | 0.852 | 0.598 | 0.544 | ||
| Anqing | 0.403 | 0.578 | 0.291 | Yuxi | 1.000 | 0.609 | 0.620 | ||
| Chuzhou | 0.600 | 0.557 | 0.378 | Average value | 0.909 | 0.682 | 0.645 | ||
| Chizhou | 0.526 | 0.557 | 0.347 | Non-urbancluster area | Baoshan | 0.961 | 0.801 | 0.796 | |
| Xuancheng | 0.869 | 0.518 | 0.472 | Zhaotong | 0.894 | 0.723 | 0.691 | ||
| Average value | 0.624 | 0.634 | 0.453 | Lijiang | 1.000 | 0.701 | 0.719 | ||
| Middle Yangtze River | Nanchang | 0.642 | 0.717 | 0.557 | Pu'er | 0.959 | 0.674 | 0.702 | |
| Jingdezhen | 0.481 | 0.556 | 0.349 | Lincang | 1.000 | 0.991 | 0.994 | ||
| Pingxiang | 0.960 | 0.826 | 0.814 | Xuzhou | 0.943 | 0.629 | 0.618 | ||
| Jiujiang | 0.436 | 0.664 | 0.356 | Lianyungang | 0.850 | 0.515 | 0.472 | ||
| Xinyu | 0.738 | 0.789 | 0.649 | Huai'an | 0.501 | 0.539 | 0.331 | ||
| Yingtan | 0.912 | 0.879 | 0.841 | Yancheng | 0.669 | 0.532 | 0.395 | ||
| Ji'an | 0.386 | 0.552 | 0.273 | Suqian | 0.689 | 0.535 | 0.400 | ||
| Yichun | 0.396 | 0.579 | 0.285 | Wenzhou | 0.431 | 0.560 | 0.319 | ||
| Fuzhou | 0.332 | 0.569 | 0.248 | Jinhua | 0.691 | 0.512 | 0.395 | ||
| Shangrao | 0.508 | 0.532 | 0.325 | Quzhou | 0.959 | 0.507 | 0.512 | ||
| Wuhan | 1.000 | 0.871 | 0.874 | Lishui | 0.910 | 0.550 | 0.526 | ||
| Huangshi | 0.374 | 0.568 | 0.278 | Huaibei | 0.648 | 0.814 | 0.606 | ||
| Yichang | 0.655 | 0.620 | 0.457 | Huangshan | 0.970 | 0.628 | 0.619 | ||
| Xiangfan | 1.000 | 0.659 | 0.676 | Fuyang | 0.388 | 0.590 | 0.298 | ||
| Ezhou | 0.946 | 0.580 | 0.567 | Cebu | 0.688 | 0.591 | 0.484 | ||
| Jingmen | 0.473 | 0.565 | 0.331 | Lu'an | 0.639 | 0.681 | 0.498 | ||
| Xiaogan | 0.362 | 0.608 | 0.285 | Bozhou | 0.783 | 0.590 | 0.482 | ||
| Jingzhou | 0.455 | 0.598 | 0.348 | Ganzhou | 0.290 | 0.462 | 0.199 | ||
| Huanggang | 0.726 | 0.828 | 0.653 | Shiyan | 0.938 | 0.644 | 0.644 | ||
| Xianning | 0.572 | 0.621 | 0.435 | Suizhou | 0.810 | 0.684 | 0.591 | ||
| Changsha | 1.000 | 0.903 | 0.909 | Shaoyang | 0.289 | 0.520 | 0.230 | ||
| Zhuzhou | 0.578 | 0.709 | 0.498 | Zhangjiajie | 0.581 | 0.643 | 0.477 | ||
| Xiangtan | 0.712 | 0.654 | 0.538 | Chenzhou | 0.388 | 0.573 | 0.292 | ||
| Hengyang | 0.367 | 0.554 | 0.302 | Yongzhou | 0.669 | 0.564 | 0.468 | ||
| Yueyang | 0.893 | 0.599 | 0.573 | Huaihua | 0.292 | 0.599 | 0.251 | ||
| Changde | 0.845 | 0.637 | 0.578 | Panzhihua | 0.533 | 0.515 | 0.387 | ||
| Yiyang | 0.862 | 0.608 | 0.570 | Guangyuan | 0.598 | 0.580 | 0.413 | ||
| Loudi | 0.553 | 0.635 | 0.429 | Bazhong | 0.798 | 0.597 | 0.534 | ||
| Average value | 0.649 | 0.660 | 0.500 | Liupanshui | 0.727 | 0.962 | 0.731 | ||
| Overall mean value | 0.708 | 0.632 | 0.507 |
| Years | Overall differences | Intra-regional variation | Inter-regional differences | Super variable density | Contribution rates (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In the region | Inter-regional | Super variable density | |||||
| 2009 | 0.271 | 0.054 | 0.059 | 0.158 | 19.89 | 21.96 | 58.15 |
| 2010 | 0.259 | 0.055 | 0.049 | 0.156 | 21.06 | 18.89 | 60.05 |
| 2011 | 0.276 | 0.057 | 0.047 | 0.172 | 20.72 | 17.01 | 62.27 |
| 2012 | 0.228 | 0.048 | 0.035 | 0.145 | 21.10 | 15.45 | 63.45 |
| 2013 | 0.238 | 0.047 | 0.055 | 0.136 | 19.80 | 23.21 | 56.99 |
| 2014 | 0.230 | 0.047 | 0.039 | 0.144 | 20.23 | 16.98 | 62.78 |
| 2015 | 0.224 | 0.046 | 0.033 | 0.145 | 20.64 | 14.58 | 64.78 |
| 2016 | 0.320 | 0.063 | 0.060 | 0.197 | 19.83 | 18.70 | 61.48 |
| 2017 | 0.203 | 0.042 | 0.038 | 0.123 | 20.63 | 18.96 | 60.41 |
| 2018 | 0.188 | 0.038 | 0.044 | 0.106 | 20.25 | 23.40 | 56.35 |
| 2019 | 0.184 | 0.038 | 0.057 | 0.089 | 20.50 | 30.92 | 48.58 |
| Average value | 0.238 | 0.049 | 0.047 | 0.143 | 20.42 | 20.01 | 59.57 |
| Variables | All Areas | Yangtze River Delta | Jianghuai | Middle Yangtze River | Chengdu–Chongqing | Central Guizhou | Central Yunnan | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | −0.736*** (−21.560) |
−0.607*** (−4.790) |
−0.846*** (−4.840) |
−0.769*** (−13.330) |
−0.862*** (−12.420) |
−0.450 (−1.570) |
−0.872*** (−15.780) |
−0.673*** (−10.850) |
| Constant term | −0.630*** (−19.690) |
−0.476*** (−7.900) |
−0.728*** (−4.510) |
−0.638*** (−9.790) |
−0.880*** (−13.420) |
−0.296 (−1.050) |
−0.321 (−2.690) |
−0.597*** (−9.220) |
| R2 | 0.214 | 0.178 | 0.373 | 0.234 | 0.232 | 0.322 | 0.481 | 0.220 |
| Convergence speed | 12.12% | 8.49% | 17.01% | 13.32% | 17.99% | / | 18.71% | 10.16% |
| Variables | All Areas | Yangtze River Delta | Jianghuai | Middle Yangtze River | Chengdu–Chongqing | Central Guizhou | Central Yunnan | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | −0.775***(−25.710) | -0.745***(−9.890) | −0.946***(−8.750) | -0.863***(−13.940) | -0.939***(−12.310) | -0.851***(−3.920) | -1.065***(−4.020) | -0.699***(−12.790) |
| Industry Structure | −0.005***(-3.070) | -0.012***(−3.060) | 0.008(1.310) | -0.013***(−3.660) | 0.000(−0.030) | 0.070**(2.190) | 0.019(1.600) | −0.004(−1.030) |
| Level of financial development | −0.054***(-6.410) | -0.135***(−5.160) | −0.022(−0.210) | −0.025(−0.510) | -0.064***(−6.410) | 0.067(0.820) | −0.056(−1.110) | −0.014(−0.480) |
| Environmental regulation | −0.003(0.004) | −0.002(−0.270) | −0.005(−0.370) | 0.021***(3.090) | −0.014(−1.160) | 0.071*(1.930) | −0.078*(−1.820) | −0.009(−1.370) |
| Population density | 0.000(−0.260) | 0.000(1.090) | 0.000(−0.900) | 0.000(−0.060) | 0.000(−0.820) | 0.000(−0.730) | 0.000(−0.720) | 0.000(0.350) |
| Economic development level | 0.000(−0.070) | 0.000(−1.030) | 0.000(−0.130) | 0.000(−0.620) | 0.000(1.410) | 0.001**(2.100) | 0.000(−0.080) | 0.000(1.280) |
| Science and education development level | 0.556*(1.930) | −0.938(−1.240) | 1.063(1.070) | 0.948*(1.660) | 0.982(1.250) | 3.607(1.130) | 1.488(0.640) | 0.350(0.680) |
| Constant term | −0.268**(−2.450) | 0.778***(2.930) | −1.316**(−2.170) | −0.145(−0.500) | −0.745**(−2.540) | -4.703**(−2.650) | −1.311*(−1.740) | −0.435(−1.570) |
| R2 | 0.169 | 0.090 | 0.250 | 0.145 | 0.240 | 0.310 | 0.059 | 0.161 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




