Submitted:
26 April 2023
Posted:
27 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background
1.1. Role of platelets and complement as prothrombotic factors in COVID-19 infection
1.2. Role of hypoxia, blood viscosity and vasoconstriction as prothrombotic factors in COVID-19 infection
1.3. Interlink between coagulation and inflammation in COVID-19 disease
1.4. Interlink between coagulopathy in viral infections and in COVID-19 disease
2. Thrombosis
2.1. Cytokine storm
2.2. Virus-specific mechanisms
3. Thrombocytopenia
3.1. Contribution of sepsis in coagulopathy during COVID-19 infection
3.2. Coagulation biomarkers in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a predictive method
| Study | Sample size | Thrombotic event reported | Confirmatory diagnostic test | Incidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Klok et al.8 | N = 184 ICU patients | Venous arterial thrombosis | CTPA or Ultrasound | 31% |
| Leonard-Lorant et al.103 | N = 106 (48 ICU and 58 non-ICU) | Acute PE | CTPA | 30% of all COVID-19 patients developed PE irrespective of ICU status |
| Helms et al.9 | N = 150 ICU patients | Clinically significant thrombosis | CTPA | 43% |
| Wichmann et al.104 | N = 12 (5 ICU and 7 non-ICU) | DVT | Autopsy | 58% of all COVID-19 patients autopsied had evidence of PE, irrespective of ICU status |
| Demelo-Rodríguez et al.105 | N = 156 non-ICU patients | DVT | Ultrasound | 15% |
| Nahum et al.106 | N = 34 ICU patients | DVT | Ultrasound | 79% |
| Middeldorp et al.107 | N = 198 (123 non-ICU and 75 ICU) | VTE in non-ICU vs ICU | Ultrasound | 9.2% in non-ICU vs 59% in ICU |
| Shah et al.108 | N = 187 (182no n-ICU and 5 ICU) | Acute PE | CTPA | 23% |
| Cui et al.109 | N = 81 non ICU | DVT | Ultrasound | 25% |
3.3. New clinical evidences of anticoagulant therapy in COVID-19
4. Closing Remarks
References
- Malerba M, Ragnoli B, Puca E, Pipero P. Supporting healthcare workers on front lines of the Covid-19 fight. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020157. [CrossRef]
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) – World Health Organization. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
- Harapan H, Itoh N, Yufika A, Winardi W, Keam S, Te H, Megawati D, Hayati Z, Wagner AL, Mudatsir M. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A literature review. J Infect Public Health. 2020, 13, 667-673. [CrossRef]
- Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, Guan L, Wei Y, Li H, Wu X, Xu J, Tu S, Zhang Y, Chen H, Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020, 395, 1054-1062. [CrossRef]
- Ragnoli B, Cena T, Radaeli A, Pochetti P, Conti L, Calareso A, Morjaria J, Malerba M. Pneumothorax in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure: Risk factors and outcome. Respir Med. 2023, 211:107194. [CrossRef]
- Obi AT, Tignanelli CJ, Jacobs BN, Arya S, Park PK, Wakefield TW, Henke PK, Napolitano LM. Empirical systemic anticoagulation is associated with decreased venous thromboembolism in critically ill influenza A H1N1 acute respiratory distress syndrome patients. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2019, 7, 317-324. [CrossRef]
- Fraissé M, Logre E, Pajot O, Mentec H, Plantefève G, Contou D. Thrombotic and hemorrhagic events in critically ill COVID-19 patients: A French monocenter retrospective study. Crit Care. 2020, 24, 275. [CrossRef]
- Klok FA, Kruip MJHA, van der Meer NJM, Arbous MS, Gommers D a. MPJ, Kant KM, Kaptein FHJ, van Paassen J, Stals M a. M, Huisman MV, Endeman H. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res. 2020, 191:145-147. [CrossRef]
- Helms J, Tacquard C, Severac F, Leonard-Lorant I, Ohana M, Delabranche X, Merdji H, Clere-Jehl R, Schenck M, Fagot Gandet F, Fafi-Kremer S, Castelain V, Schneider F, Grunebaum L, Anglés-Cano E, Sattler L, Mertes PM, Meziani F, CRICS TRIGGERSEP Group (Clinical Research in Intensive Care and Sepsis Trial Group for Global Evaluation and Research in Sepsis). High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1089-1098. [CrossRef]
- Lodigiani C, Iapichino G, Carenzo L, Cecconi M, Ferrazzi P, Sebastian T, Kucher N, Studt JD, Sacco C, Bertuzzi A, Sandri MT, Barco S, Humanitas COVID-19 Task Force. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb Res. 2020, 191:9-14. [CrossRef]
- Varga Z, Flammer AJ, Steiger P, Haberecker M, Andermatt R, Zinkernagel AS, Mehra MR, Schuepbach RA, Ruschitzka F, Moch H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet. 2020, 395, 1417-1418. [CrossRef]
- Danzi GB, Loffi M, Galeazzi G, Gherbesi E. Acute pulmonary embolism and COVID-19 pneumonia: A random association? Eur Heart J. 2020, 41, 1858. [CrossRef]
- Tang N, Li D, Wang X, Sun Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 844-847. [CrossRef]
- Tang N, Bai H, Chen X, Gong J, Li D, Sun Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 1094-1099. [CrossRef]
- Han H, Yang L, Liu R, Liu F, Wu KL, Li J, Liu XH, Zhu CL. Prominent changes in blood coagulation of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020, 58, 1116-1120. [CrossRef]
- Ren B, Yan F, Deng Z, Zhang S, Xiao L, Wu M, Cai L. Extremely High Incidence of Lower Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis in 48 Patients With Severe COVID-19 in Wuhan. Circulation. 2020, 142, 181-183. [CrossRef]
- Gralinski LE, Bankhead A, Jeng S, Menachery VD, Proll S, Belisle SE, Matzke M, Webb-Robertson BJM, Luna ML, Shukla AK, Ferris MT, Bolles M, Chang J, Aicher L, Waters KM, Smith RD, Metz TO, Law GL, Katze MG, McWeeney S, Baric RS. Mechanisms of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-induced acute lung injury. mBio. 2013, 4, e00271-13. [CrossRef]
- Yao XH, Li TY, He ZC, Ping YF, Liu HW, Yu SC, Mou HM, Wang LH, Zhang HR, Fu WJ, Luo T, Liu F, Guo QN, Chen C, Xiao HL, Guo HT, Lin S, Xiang DF, Shi Y, Pan GQ, Li QR, Huang X, Cui Y, Liu XZ, Tang W, Pan PF, Huang XQ, Ding YQ, Bian XW. [A pathological report of three COVID-19 cases by minimal invasive autopsies]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020, 49, 411-417. [CrossRef]
- Wright FL, Vogler TO, Moore EE, Moore HB, Wohlauer MV, Urban S, Nydam TL, Moore PK, McIntyre RC. Fibrinolysis Shutdown Correlation with Thromboembolic Events in Severe COVID-19 Infection. J Am Coll Surg. 2020, 231, 193-203.e1. [CrossRef]
- Tay MZ, Poh CM, Rénia L, MacAry PA, Ng LFP. The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020, 20, 363-374. [CrossRef]
- Baldanzi G, Purghè B, Ragnoli B, Sainaghi PP, Rolla R, Chiocchetti A, Manfredi M, Malerba M. Circulating Peptidome Is Strongly Altered in COVID-19 Patients. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023, 20, 1564. [CrossRef]
- Purghè B, Manfredi M, Ragnoli B, Baldanzi G, Malerba M. Exosomes in chronic respiratory diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021, 144:112270. [CrossRef]
- Wool GD, Miller JL. The Impact of COVID-19 Disease on Platelets and Coagulation. Pathobiology. 2021, 88, 15-27. [CrossRef]
- Malerba M, Clini E, Malagola M, Avanzi GC. Platelet activation as a novel mechanism of atherothrombotic risk in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Review of Hematology. 2013, 6, 475-483. [CrossRef]
- Malerba M, Nardin M, Radaeli A, Montuschi P, Carpagnano GE, Clini E. The potential role of endothelial dysfunction and platelet activation in the development of thrombotic risk in COPD patients. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017, 10, 821-832. [CrossRef]
- Violi F, Cammisotto V, Pignatelli P. Thrombosis in Covid-19 and non-Covid-19 pneumonia: Role of platelets. Platelets. 2021, 32, 1009-1017. [CrossRef]
- Polosa R, Malerba M, Cacciola RR, Morjaria JB, Maugeri C, Prosperini G, Gullo R, Spicuzza L, Radaeli A, Di Maria GU. Effect of acute exacerbations on circulating endothelial, clotting and fibrinolytic markers in COPD patients. Intern Emerg Med. 2013, 8, 567-574. [CrossRef]
- Wiedmer T, Esmon CT, Sims PJ. Complement proteins C5b-9 stimulate procoagulant activity through platelet prothrombinase. Blood. 1986, 68, 875-880.
- JCI Insight - The complement system in COVID-19: Friend and foe? Accessed April 20, 2023. https://insight.jci.org/articles/view/140711.
- Gupta N, Zhao YY, Evans CE. The stimulation of thrombosis by hypoxia. Thromb Res. 2019, 181:77-83. [CrossRef]
- Leyfman Y, Erick TK, Reddy SS, Galwankar S, Nanayakkara PWB, Di Somma S, Sharma P, Stawicki SP, Chaudry IH. Potential Immunotherapeutic Targets for Hypoxia Due to COVI-Flu. Shock. 2020, 54, 438-450. [CrossRef]
- Kichloo A, Dettloff K, Aljadah M, Albosta M, Jamal S, Singh J, Wani F, Kumar A, Vallabhaneni S, Khan MZ. COVID-19 and Hypercoagulability: A Review. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020, 26:1076029620962853. [CrossRef]
- Harzallah I, Debliquis A, Drénou B. Lupus anticoagulant is frequent in patients with Covid-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 2064-2065. [CrossRef]
- Iba T, Connors JM, Levy JH. The coagulopathy, endotheliopathy, and vasculitis of COVID-19. Inflamm Res. 2020, 69, 1181-1189. [CrossRef]
- Levi M, van der Poll T, Schultz M. Infection and inflammation as risk factors for thrombosis and atherosclerosis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2012, 38, 506-514. [CrossRef]
- Ekholm M, Kahan T. The Impact of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System on Inflammation, Coagulation, and Atherothrombotic Complications, and to Aggravated COVID-19. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12:640185. [CrossRef]
- Goeijenbier M, van Wissen M, van de Weg C, Jong E, Gerdes VEA, Meijers JCM, Brandjes DPM, van Gorp ECM. Review: Viral infections and mechanisms of thrombosis and bleeding. J Med Virol. 2012, 84, 1680-1696. [CrossRef]
- Branchford BR, Carpenter SL. The Role of Inflammation in Venous Thromboembolism. Front Pediatr. 2018, 6:142. [CrossRef]
- Iba T, Levy JH, Levi M, Thachil J. Coagulopathy in COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 2103-2109. [CrossRef]
- Fuchs TA, Brill A, Wagner DD. Neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) impact on deep vein thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012, 32, 1777-1783. [CrossRef]
- Tsourouktsoglou TD, Warnatsch A, Ioannou M, Hoving D, Wang Q, Papayannopoulos V. Histones, DNA, and Citrullination Promote Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Inflammation by Regulating the Localization and Activation of TLR4. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107602. [CrossRef]
- Zuo Y, Yalavarthi S, Shi H, Gockman K, Zuo M, Madison JA, Blair C, Weber A, Barnes BJ, Egeblad M, Woods RJ, Kanthi Y, Knight JS. Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19. JCI Insight. 2020, 5, 138999. [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou C, Jourdi G, Adjambri E, Walborn A, Patel P, Fareed J, Elalamy I, Hoppensteadt D, Gerotziafas GT. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: An Update on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Strategies. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018, 24(9_suppl):8S-28S. [CrossRef]
- van Gorp EC, Suharti C, ten Cate H, Dolmans WM, van der Meer JW, ten Cate JW, Brandjes DP. Review: Infectious diseases and coagulation disorders. J Infect Dis. 1999, 180, 176-186. [CrossRef]
- Caci G, Albini A, Malerba M, Noonan DM, Pochetti P, Polosa R. COVID-19 and Obesity: Dangerous Liaisons. J Clin Med. 2020, 9, 2511. [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Gomar F, Lavie CJ, Mehra MR, Henry BM, Lippi G. Obesity and Outcomes in COVID-19: When an Epidemic and Pandemic Collide. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020, 95, 1445-1453. [CrossRef]
- Lafontan M. Fat cells: Afferent and efferent messages define new approaches to treat obesity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005, 45:119-146. [CrossRef]
- Ragnoli B, Pochetti P, Raie A, Malerba M. Comorbid Insomnia and Obstructive Sleep Apnea (COMISA): Current Concepts of Patient Management. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021, 18, 9248. [CrossRef]
- Ragnoli B, Pochetti P, Pignatti P, Barbieri M, Mondini L, Ruggero L, Trotta L, Montuschi P, Malerba M. Sleep Deprivation, Immune Suppression and SARS-CoV-2 Infection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022, 19, 904. [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos AC, Levy JH, Ageno W, Connors JM, Hunt BJ, Iba T, Levi M, Samama CM, Thachil J, Giannis D, Douketis JD, Subcommittee on Perioperative, Critical Care Thrombosis, Haemostasis of the Scientific, Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Scientific and Standardization Committee communication: Clinical guidance on the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 1859-1865. [CrossRef]
- Giannis D, Ziogas IA, Gianni P. Coagulation disorders in coronavirus infected patients: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV and lessons from the past. J Clin Virol. 2020, 127:104362. [CrossRef]
- Avnon LS, Munteanu D, Smoliakov A, Jotkowitz A, Barski L. Thromboembolic events in patients with severe pandemic influenza A/H1N1. Eur J Intern Med. 2015, 26, 596-598. [CrossRef]
- Fridlender ZG, Khamaisi M, Leitersdorf E. Association between cytomegalovirus infection and venous thromboembolism. Am J Med Sci. 2007, 334, 111-114. [CrossRef]
- Kahn SR, Lim W, Dunn AS, Cushman M, Dentali F, Akl EA, Cook DJ, Balekian AA, Klein RC, Le H, Schulman S, Murad MH. Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012, 141(2 Suppl):e195S-e226S. [CrossRef]
- Connors JM, Levy JH. COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation. Blood. 2020, 135, 2033-2040. [CrossRef]
- Lazzaroni MG, Piantoni S, Masneri S, Garrafa E, Martini G, Tincani A, Andreoli L, Franceschini F. Coagulation dysfunction in COVID-19: The interplay between inflammation, viral infection and the coagulation system. Blood Rev. 2021, 46:100745. [CrossRef]
- Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ, HLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020, 395, 1033-1034. [CrossRef]
- Liu B, Li M, Zhou Z, Guan X, Xiang Y. Can we use interleukin-6 (IL-6) blockade for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)? J Autoimmun. 2020, 111:102452. [CrossRef]
- Moore JB, June CH. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19. Science. 2020, 368, 473-474. [CrossRef]
- Qin C, Zhou L, Hu Z, Zhang S, Yang S, Tao Y, Xie C, Ma K, Shang K, Wang W, Tian DS. Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020, 71, 762-768. [CrossRef]
- Ye Q, Wang B, Mao J. The pathogenesis and treatment of the `Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19. J Infect. 2020, 80, 607-613. [CrossRef]
- Zhang C, Wu Z, Li JW, Zhao H, Wang GQ. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: Interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020, 55, 105954. [CrossRef]
- Levi M, van der Poll T. Coagulation and sepsis. Thromb Res. 2017, 149:38-44. [CrossRef]
- Folman CC, Linthorst GE, van Mourik J, van Willigen G, de Jonge E, Levi M, de Haas M, von dem Borne AE. Platelets release thrombopoietin (Tpo) upon activation: Another regulatory loop in thrombocytopoiesis? Thromb Haemost. 2000, 83, 923-930.
- Levi M, van der Poll T, Schultz M. Systemic versus localized coagulation activation contributing to organ failure in critically ill patients. Semin Immunopathol 2012, 34:167–79 - Cerca con Google. Accessed April 5, 2023. https://www.google.com/search?q=Levi+M%2C+van+der+Poll+T%2C+Schultz+M.+Systemic+versus+localized+coagulation+activation+contributing+to+organ+failure+in+critically+ill+patients.+Semin+Immunopathol+2012%3B+34%3A167%E2%80%9379&oq=Levi+M%2C+van+der+Poll+T%2C+Schultz+M.+Systemic+versus+localized+coagulation+activation+contributing+to+organ+failure+in+critically+ill+patients.+Semin+Immunopathol+2012%3B+34%3A167%E2%80%9379&aqs=chrome..69i57.248j0j4&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8.
- Fox SE, Akmatbekov A, Harbert JL, Li G, Quincy Brown J, Vander Heide RS. Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in African American patients with COVID-19: An autopsy series from New Orleans. Lancet Respir Med. 2020, 8, 681-686. [CrossRef]
- Yang M, Ng MH, Li CK. Thrombocytopenia in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (review). Hematology. 2005, 10, 101-105. [CrossRef]
- Stouthard JM, Levi M, Hack CE, Veenhof CH, Romijn HA, Sauerwein HP, van der Poll T. Interleukin-6 stimulates coagulation, not fibrinolysis, in humans. Thromb Haemost. 1996, 76, 738-742.
- Conti P, Caraffa A, Gallenga CE, Ross R, Kritas SK, Frydas I, Younes A, Ronconi G. Coronavirus-19 (SARS-CoV-2) induces acute severe lung inflammation via IL-1 causing cytokine storm in COVID-19: A promising inhibitory strategy. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020, 34, 1971-1975. [CrossRef]
- Magro G. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: Is interleukin-6 (IL-6) the “culprit lesion” of ARDS onset? What is there besides Tocilizumab? SGP130Fc. Cytokine X. 2020, 2, 100029. [CrossRef]
- van de Veerdonk FL, Netea MG. Blocking IL-1 to prevent respiratory failure in COVID-19. Crit Care. 2020, 24:445. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Y, Qin L, Zhang P, Li K, Liang L, Sun J, Xu B, Dai Y, Li X, Zhang C, Peng Y, Feng Y, Li A, Hu Z, Xiang H, Ogg G, Ho LP, McMichael A, Jin R, Knight JC, Dong T, Zhang Y. Longitudinal COVID-19 profiling associates IL-1RA and IL-10 with disease severity and RANTES with mild disease. JCI Insight. 2020, 5, e139834, 139834. [CrossRef]
- Satış H, Özger HS, Aysert Yıldız P, Hızel K, Gulbahar Ö, Erbaş G, Aygencel G, Guzel Tunccan O, Öztürk MA, Dizbay M, Tufan A. Prognostic value of interleukin-18 and its association with other inflammatory markers and disease severity in COVID-19. Cytokine. 2021, 137:155302. [CrossRef]
- Teuwen LA, Geldhof V, Pasut A, Carmeliet P. COVID-19: The vasculature unleashed. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020, 20, 389-391. [CrossRef]
- Martini R. The compelling arguments for the need of microvascular investigation in COVID-19 critical patients. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2020, 75, 27-34. [CrossRef]
- Monteil V, Kwon H, Prado P, Hagelkrüys A, Wimmer RA, Stahl M, Leopoldi A, Garreta E, Hurtado Del Pozo C, Prosper F, Romero JP, Wirnsberger G, Zhang H, Slutsky AS, Conder R, Montserrat N, Mirazimi A, Penninger JM. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Engineered Human Tissues Using Clinical-Grade Soluble Human ACE2. Cell. 2020, 181, 905-913.e7. [CrossRef]
- Stern D, Nawroth P, Handley D, Kisiel W. An endothelial cell-dependent pathway of coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985, 82, 2523-2527. [CrossRef]
- Guang C, Phillips RD, Jiang B, Milani F. Three key proteases – angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE), ACE2 and renin – within and beyond the renin-angiotensin system. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2012, 105, 373-385. [CrossRef]
- Scialo F, Daniele A, Amato F, Pastore L, Matera MG, Cazzola M, Castaldo G, Bianco A. ACE2: The Major Cell Entry Receptor for SARS-CoV-2. Lung. 2020, 198, 867-877. [CrossRef]
- Marshall RP. The Pulmonary Renin-Angiotensin System. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 9, 715-722. [CrossRef]
- Wu YP, Wei R, Liu ZH, Chen B, Lisman T, Ren DL, Han JJ, Xia ZL, Zhang FS, Xu WB, Preissner KT, de Groot PG. Analysis of thrombotic factors in severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) patients. Thromb Haemost. 2006, 96, 100-101. [CrossRef]
- Reheman A, Gross P, Yang H, Chen P, Allen D, Leytin V, Freedman J, Ni H. Vitronectin stabilizes thrombi and vessel occlusion but plays a dual role in platelet aggregation. J Thromb Haemost. 2005, 3, 875-883. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Xiao M, Zhang S, Xia P, Cao W, Jiang W, Chen H, Ding X, Zhao H, Zhang H, Wang C, Zhao J, Sun X, Tian R, Wu W, Wu D, Ma J, Chen Y, Zhang D, Xie J, Yan X, Zhou X, Liu Z, Wang J, Du B, Qin Y, Gao P, Qin X, Xu Y, Zhang W, Li T, Zhang F, Zhao Y, Li Y, Zhang S. Coagulopathy and Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382, e38. [CrossRef]
- Borghi MO, Beltagy A, Garrafa E, Curreli D, Cecchini G, Bodio C, Grossi C, Blengino S, Tincani A, Franceschini F, Andreoli L, Lazzaroni MG, Piantoni S, Masneri S, Crisafulli F, Brugnoni D, Muiesan ML, Salvetti M, Parati G, Torresani E, Mahler M, Heilbron F, Pregnolato F, Pengo M, Tedesco F, Pozzi N, Meroni PL. Anti-Phospholipid Antibodies in COVID-19 Are Different From Those Detectable in the Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome. Front Immunol. 2020, 11:584241. [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Mesa JE, Galindo-Coral S, Montes MC, Muñoz Martin AJ. Thrombosis and Coagulopathy in COVID-19. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100742. [CrossRef]
- Li Q, Cao Y, Chen L, Wu D, Yu J, Wang H, He W, Chen L, Dong F, Chen W, Chen W, Li L, Ran Q, Liu Q, Ren W, Gao F, Chen Z, Gale RP, Hu Y. Hematological features of persons with COVID-19. Leukemia. 2020, 34, 2163-2172. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Sun W, Guo Y, Chen L, Zhang L, Zhao S, Long D, Yu L. Association between platelet parameters and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019: Retrospective cohort study. Platelets. 2020, 31, 490-496. [CrossRef]
- Chabert A, Hamzeh-Cognasse H, Pozzetto B, Cognasse F, Schattner M, Gomez RM, Garraud O. Human platelets and their capacity of binding viruses: Meaning and challenges? BMC Immunol. 2015, 16:26. [CrossRef]
- Assinger A. Platelets and infection - an emerging role of platelets in viral infection. Front Immunol. 2014, 5:649. [CrossRef]
- Seyoum M, Enawgaw B, Melku M. Human blood platelets and viruses: Defense mechanism and role in the removal of viral pathogens. Thromb J. 2018, 16:16. [CrossRef]
- Aleem A, Nadeem AJ. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed April 20, 2023. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570605/.
- Oldenburg J, Klamroth R, Langer F, Albisetti M, von Auer C, Ay C, Korte W, Scharf RE, Pötzsch B, Greinacher A. Diagnosis and Management of Vaccine-Related Thrombosis following AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccination: Guidance Statement from the GTH. Hamostaseologie. 2021, 41, 184-189. [CrossRef]
- Miller E. Rapid evaluation of the safety of COVID-19 vaccines: How well have we done? Clin Microbiol Infect. 2022, 28, 477-478. [CrossRef]
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016, 315, 801-810. [CrossRef]
- McGonagle D, O’Donnell JS, Sharif K, Emery P, Bridgewood C. Immune mechanisms of pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy in COVID-19 pneumonia. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e437-e445. [CrossRef]
- Asakura H, Ogawa H. COVID-19-associated coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Int J Hematol. 2021, 113, 45-57. [CrossRef]
- Rahman S, Montero MTV, Rowe K, Kirton R, Kunik F. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentations, diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19: A review of current evidence. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 601-621. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Yang X, Jiao H, Liu X. Coagulopathy in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020, 12, 24535-24551. [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino G, Benincasa G, Coppola A, Franzese M, Annunziata A, Affinito O, Viglietti M, Napoli C. Targeted genetic analysis unveils novel associations between ACE I/D and APO T158C polymorphisms with D-dimer levels in severe COVID-19 patients with pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2023, 55, 51-59. [CrossRef]
- Xiang G, Hao S, Fu C, Hu W, Xie L, Wu Q, Li S, Liu X. The effect of coagulation factors in 2019 novel coronavirus patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021, 100, e24537. [CrossRef]
- Xiong M, Liang X, Wei YD. Changes in blood coagulation in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. Br J Haematol. 2020, 189, 1050-1052. [CrossRef]
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020, 323, 1239-1242. [CrossRef]
- Léonard-Lorant I, Delabranche X, Séverac F, Helms J, Pauzet C, Collange O, Schneider F, Labani A, Bilbault P, Molière S, Leyendecker P, Roy C, Ohana M. Acute Pulmonary Embolism in Patients with COVID-19 at CT Angiography and Relationship to d-Dimer Levels. Radiology. 2020, 296, E189-E191. [CrossRef]
- Wichmann D, Sperhake JP, Lütgehetmann M, Steurer S, Edler C, Heinemann A, Heinrich F, Mushumba H, Kniep I, Schröder AS, Burdelski C, de Heer G, Nierhaus A, Frings D, Pfefferle S, Becker H, Bredereke-Wiedling H, de Weerth A, Paschen HR, Sheikhzadeh-Eggers S, Stang A, Schmiedel S, Bokemeyer C, Addo MM, Aepfelbacher M, Püschel K, Kluge S. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann Intern Med. 2020, 173, 268-277. [CrossRef]
- Demelo-Rodríguez P, Cervilla-Muñoz E, Ordieres-Ortega L, Parra-Virto A, Toledano-Macías M, Toledo-Samaniego N, García-García A, García-Fernández-Bravo I, Ji Z, de-Miguel-Diez J, Álvarez-Sala-Walther LA, Del-Toro-Cervera J, Galeano-Valle F. Incidence of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and elevated D-dimer levels. Thromb Res. 2020, 192:23-26. [CrossRef]
- Nahum J, Morichau-Beauchant T, Daviaud F, Echegut P, Fichet J, Maillet JM, Thierry S. Venous Thrombosis Among Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Netw Open. 2020, 3, e2010478. [CrossRef]
- Middeldorp S, Coppens M, van Haaps TF, Foppen M, Vlaar AP, Müller MCA, Bouman CCS, Beenen LFM, Kootte RS, Heijmans J, Smits LP, Bonta PI, van Es N. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 1995-2002. [CrossRef]
- Shah A, Donovan K, McHugh A, Pandey M, Aaron L, Bradbury CA, Stanworth SJ, Alikhan R, Von Kier S, Maher K, Curry N, Shapiro S, Rowland MJ, Thomas M, Mason R, Holland M, Holmes T, Ware M, Gurney S, McKechnie SR. Thrombotic and haemorrhagic complications in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A multicentre observational study. Crit Care. 2020, 24, 561. [CrossRef]
- Cui S, Chen S, Li X, Liu S, Wang F. Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 1421-1424. [CrossRef]
- Carfora V, Spiniello G, Ricciolino R, Di Mauro M, Migliaccio MG, Mottola FF, Verde N, Coppola N, Coppola N, Sagnelli C, De Pascalis S, Stanzione M, Stornaiuolo G, Cascone A, Martini S, Macera M, Monari C, Calò F, Bianco A, Russo A, Gentile V, Camaioni C, De Angelis G, Marino G, Astorri R, De Sio I, Niosi M, Borrelli S, Celia B, Ceparano M, Cirillo S, De Luca M, Mazzeo G, Paoli G, Russo MG, Carfora V, Di Mauro M, Migliaccio MG, Mottola FF, Ricciolino R, Spiniello G, Verde N, Vanvitelli COVID-19 group. Anticoagulant treatment in COVID-19: A narrative review. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021, 51, 642-648. [CrossRef]
- Shi C, Wang C, Wang H, Yang C, Cai F, Zeng F, Cheng F, Liu Y, Zhou T, Deng B, Vlodavsky I, Li JP, Zhang Y. The potential of low molecular weight heparin to mitigate cytokine storm in severe COVID-19 patients: A retrospective clinical study. Published online April 15, 2020:2020.03.28.20046144. [CrossRef]
- Godino C, Scotti A, Maugeri N, Mancini N, Fominskiy E, Margonato A, Landoni G. Antithrombotic therapy in patients with COVID-19? -Rationale and Evidence-. International Journal of Cardiology. 2021, 324:261-266. [CrossRef]
- Mangana C, Lorigo M, Cairrao E. Implications of Endothelial Cell-Mediated Dysfunctions in Vasomotor Tone Regulation. Biologics. 2021, 1, 231-251. [CrossRef]
- Xu J, Zhang X, Pelayo R, Monestier M, Ammollo CT, Semeraro F, Taylor FB, Esmon NL, Lupu F, Esmon CT. Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nat Med. 2009, 15, 1318-1321. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Li X. The Role of Histones and Heparin in Sepsis: A Review. J Intensive Care Med. 2022, 37, 319-326. [CrossRef]
- Mangiafico M, Caff A, Costanzo L. The Role of Heparin in COVID-19: An Update after Two Years of Pandemics. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 3099. [CrossRef]
- Mousavi S, Moradi M, Khorshidahmad T, Motamedi M. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Heparin and Its Derivatives: A Systematic Review. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2015, 2015:507151. [CrossRef]
- Thachil J. The versatile heparin in COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 1020-1022. [CrossRef]
- Oduah EI, Linhardt RJ, Sharfstein ST. Heparin: Past, Present, and Future. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2016, 9, 38. [CrossRef]
- Shukla D, Spear PG. Herpesviruses and heparan sulfate: An intimate relationship in aid of viral entry. J Clin Invest. 2001, 108, 503-510. [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi S, Cooper L, Rubio A, Pagani I, Capobianchi MR, Ippolito G, Pelletier J, Meneghetti MCZ, Lima MA, Skidmore MA, Broccoli V, Yates EA, Vicenzi E. Heparin prevents Zika virus induced-cytopathic effects in human neural progenitor cells. Antiviral Res. 2017, 140:13-17. [CrossRef]
- Mycroft-West C, Su D, Elli S, Guimond S, Miller G, Turnbull J, Yates E, Guerrini M, Fernig D, Lima M, Skidmore M. The 2019 coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) surface protein (Spike) S1 Receptor Binding Domain undergoes conformational change upon heparin binding. Published online March 2, 2020:2020.02.29.971093. [CrossRef]
- REMAP-CAP Investigators, ACTIV-4a Investigators, ATTACC Investigators, Goligher EC, Bradbury CA, McVerry BJ, Lawler PR, Berger JS, Gong MN, Carrier M, Reynolds HR, Kumar A, Turgeon AF, Kornblith LZ, Kahn SR, Marshall JC, Kim KS, Houston BL, Derde LPG, Cushman M, Tritschler T, Angus DC, Godoy LC, McQuilten Z, Kirwan BA, Farkouh ME, Brooks MM, Lewis RJ, Berry LR, Lorenzi E, Gordon AC, Ahuja T, Al-Beidh F, Annane D, Arabi YM, Aryal D, Baumann Kreuziger L, Beane A, Bhimani Z, Bihari S, Billett HH, Bond L, Bonten M, Brunkhorst F, Buxton M, Buzgau A, Castellucci LA, Chekuri S, Chen JT, Cheng AC, Chkhikvadze T, Coiffard B, Contreras A, Costantini TW, de Brouwer S, Detry MA, Duggal A, Džavík V, Effron MB, Eng HF, Escobedo J, Estcourt LJ, Everett BM, Fergusson DA, Fitzgerald M, Fowler RA, Froess JD, Fu Z, Galanaud JP, Galen BT, Gandotra S, Girard TD, Goodman AL, Goossens H, Green C, Greenstein YY, Gross PL, Haniffa R, Hegde SM, Hendrickson CM, Higgins AM, Hindenburg AA, Hope AA, Horowitz JM, Horvat CM, Huang DT, Hudock K, Hunt BJ, Husain M, Hyzy RC, Jacobson JR, Jayakumar D, Keller NM, Khan A, Kim Y, Kindzelski A, King AJ, Knudson MM; et al. Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021, 385, 777-789. [CrossRef]
- Stasi C, Fallani S, Voller F, Silvestri C. Treatment for COVID-19: An overview. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020, 889:173644. [CrossRef]
- Mennuni MG, Renda G, Grisafi L, Rognoni A, Colombo C, Lio V, Foglietta M, Petrilli I, Pirisi M, Spinoni E, Azzolina D, Hayden E, Aimaretti G, Avanzi GC, Bellan M, Cantaluppi V, Capponi A, Castello LM, D’Ardes D, Corte FD, Gallina S, Krengli M, Malerba M, Pierdomenico SD, Savoia P, Zeppegno P, Sainaghi PP, Cipollone F, Patti G, COVID-UPO Clinical Team. Clinical outcome with different doses of low-molecular-weight heparin in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021, 52, 782-790. [CrossRef]
- Rentsch CT, Beckman JA, Tomlinson L, Gellad WF, Alcorn C, Kidwai-Khan F, Skanderson M, Brittain E, King JT, Ho YL, Eden S, Kundu S, Lann MF, Greevy RA, Ho PM, Heidenreich PA, Jacobson DA, Douglas IJ, Tate JP, Evans SJW, Atkins D, Justice AC, Freiberg MS. Early initiation of prophylactic anticoagulation for prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 mortality in patients admitted to hospital in the United States: Cohort study. BMJ. 2021, 372:n311. [CrossRef]
- ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19 - Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Accessed April 24, 2023. https://www.jthjournal.org/article/S1538-7836(22)00324-5/fulltext.
- Hasan SS, Radford S, Kow CS, Zaidi STR. Venous thromboembolism in critically ill COVID-19 patients receiving prophylactic or therapeutic anticoagulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020, 50, 814-821. [CrossRef]
- Thachil J, Tang N, Gando S, Falanga A, Cattaneo M, Levi M, Clark C, Iba T. ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2020, 18, 1023-1026. [CrossRef]
- Sayed Ahmed HA, Merrell E, Ismail M, Joudeh AI, Riley JB, Shawkat A, Habeb H, Darling E, Goweda RA, Shehata MH, Amin H, Nieman GF, Aiash H. Rationales and uncertainties for aspirin use in COVID-19: A narrative review. Fam Med Community Health. 2021, 9, e000741. [CrossRef]
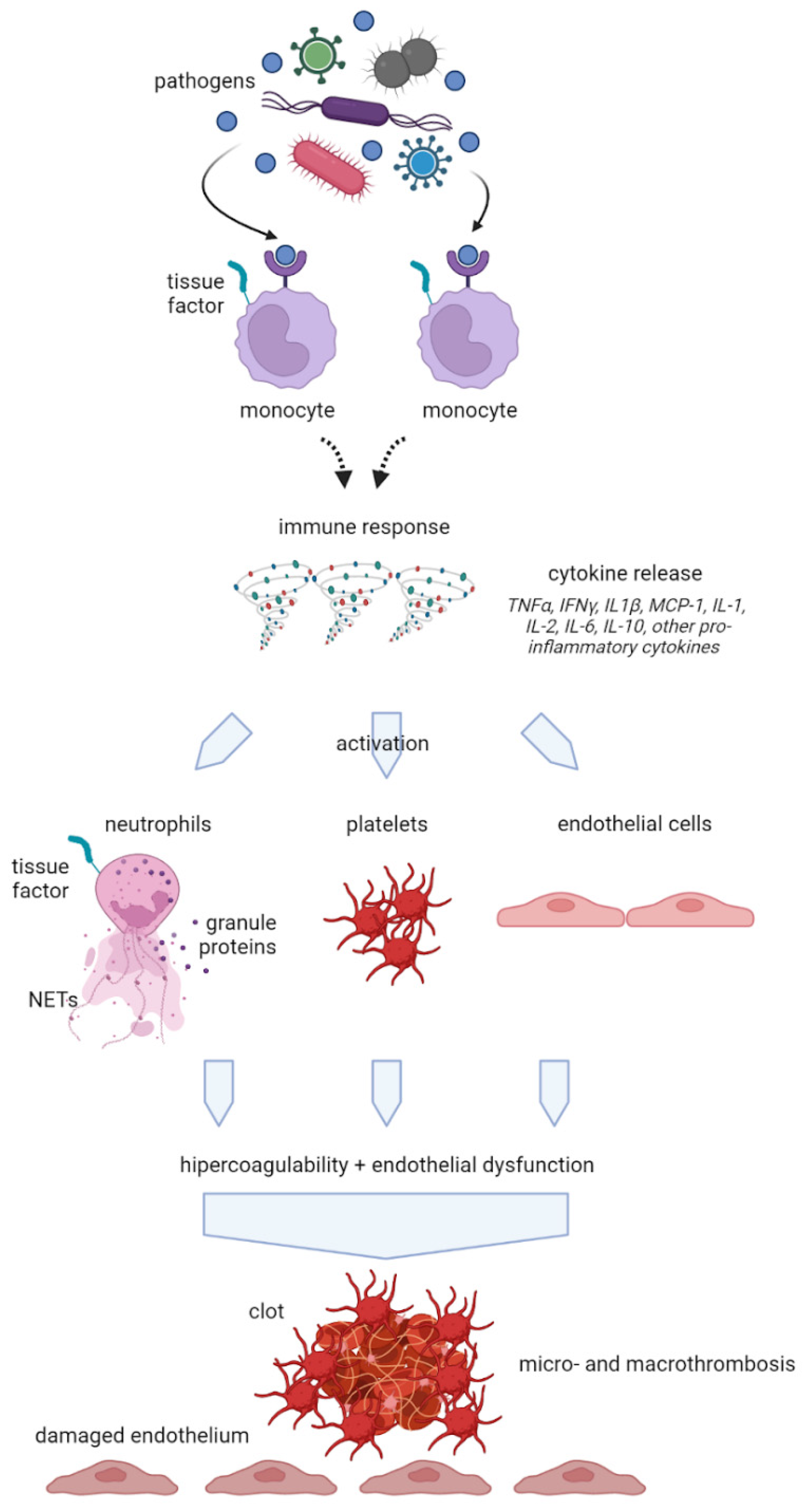
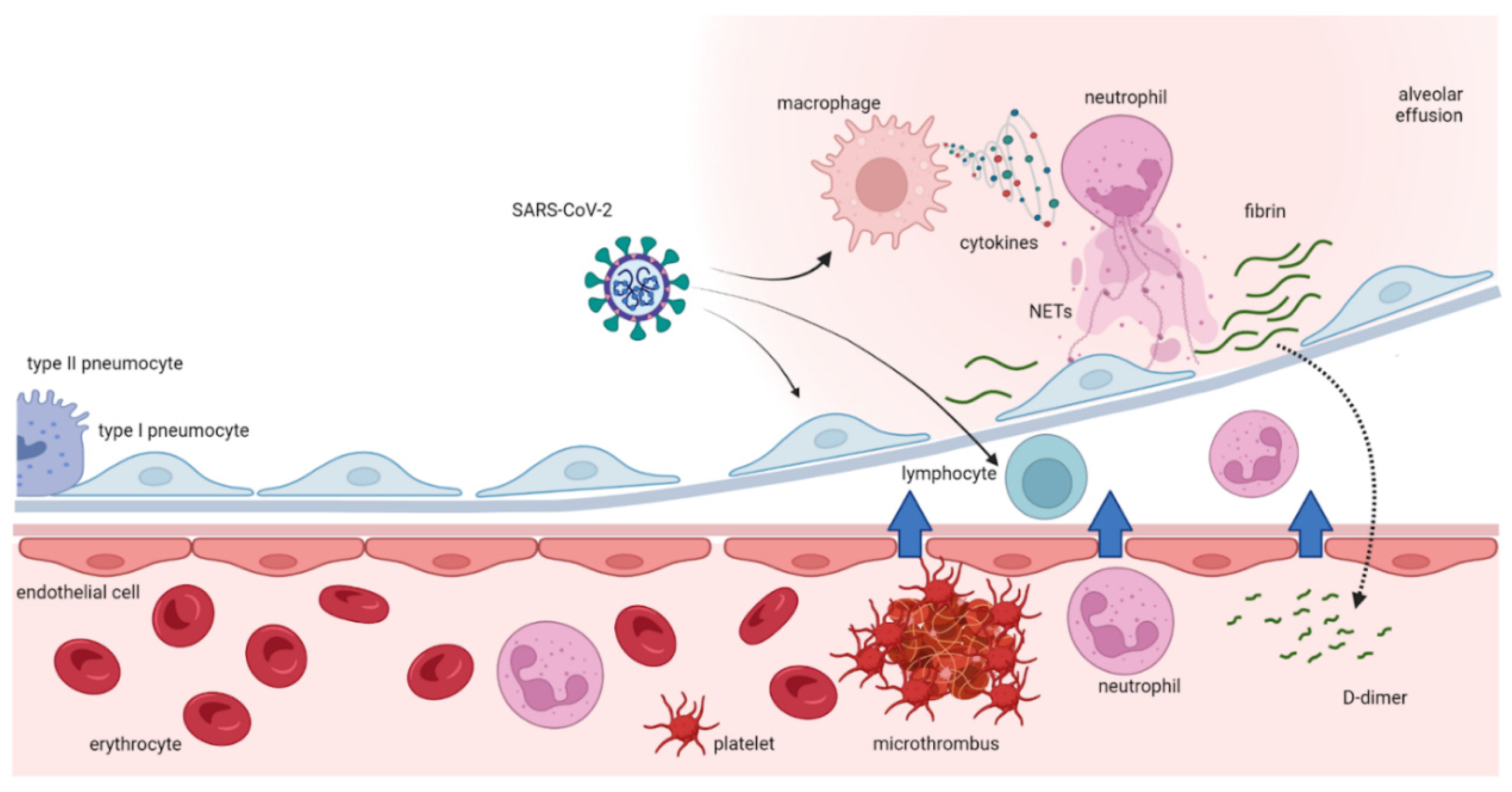
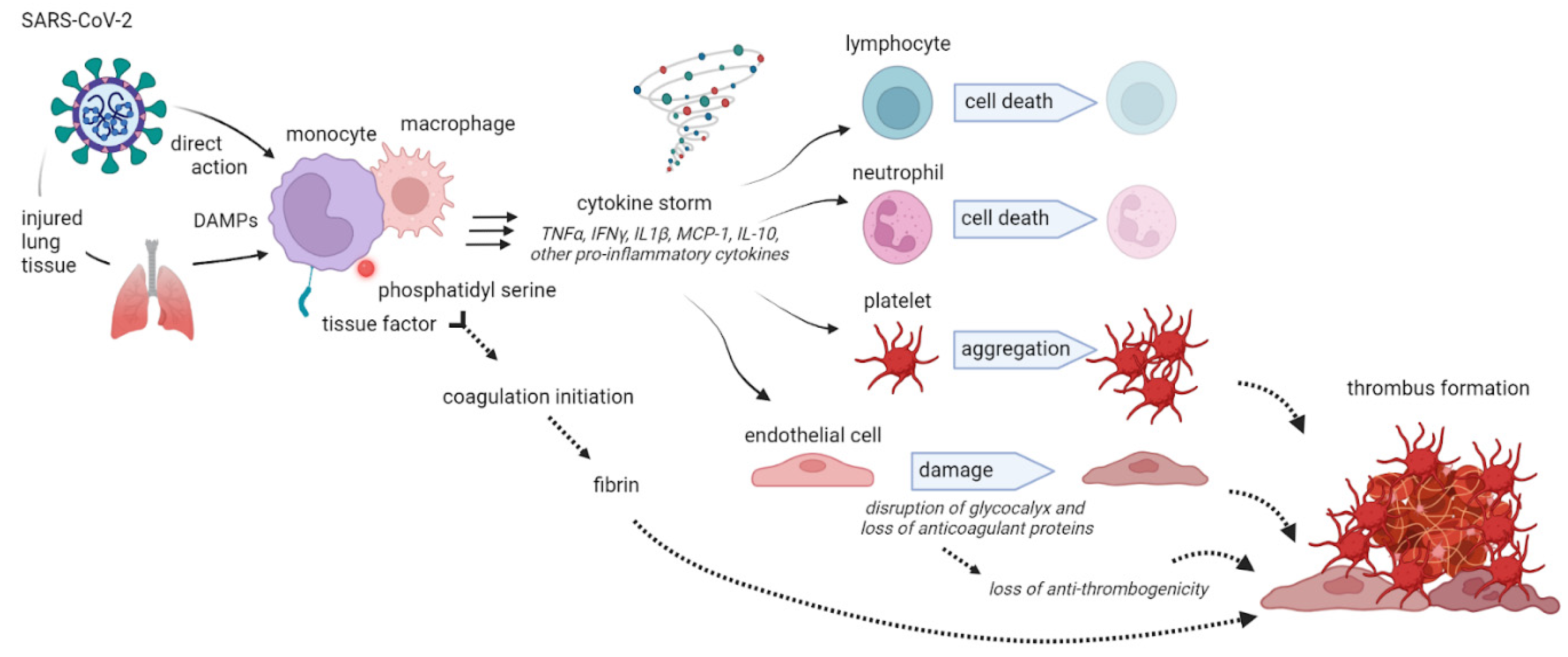
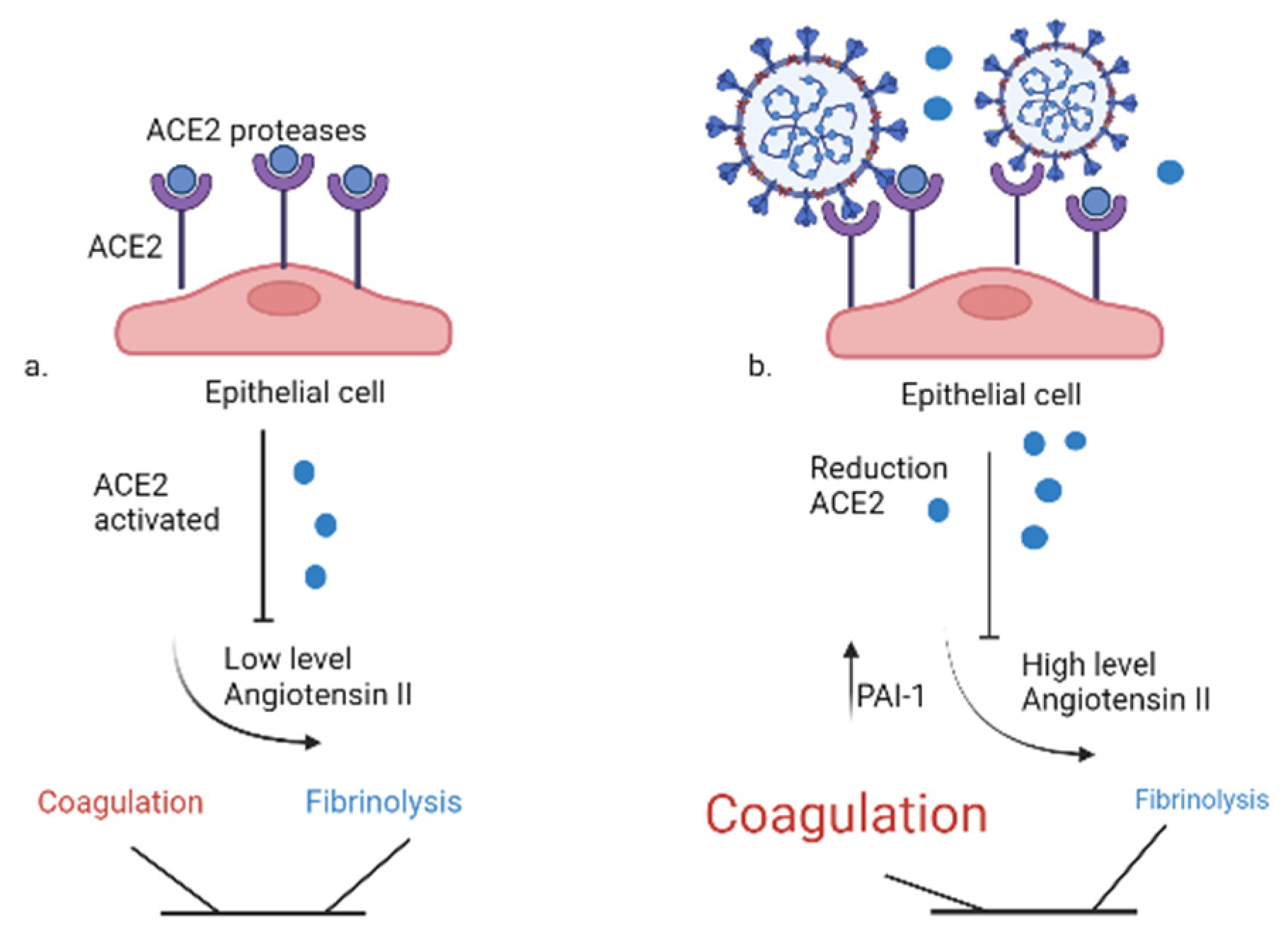
| Item | Value | Score |
|---|---|---|
| SOFA score | 1 ≥2 |
1 2 ≥4 |
| PT-INR | 1.2-1.4 >1.4 |
1 2 |
| Platelet count (x mm3) | 100.000-150.000 < 100.000 |
1 2 |
| Coagulation biomarkers | D-di D-dimer, PLT, PT, APTT, FIB |
| Inflammatory biomarkers | ES ESR, CRP, Serum ferritin, PCT, IL-2, IL-6, IL8, IL10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





