1. Introduction
Yeast cells acquire a variety of stress-tolerant mechanisms, including the induction of stress proteins via stress-triggered signal-transduction pathways [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. The proteins of CYSTM superfamily were proposed to be a part of cellular protective mechanisms again stresses in yeast [
6]. Multiple sequence alignment revealed a cysteine-rich, transmembrane module, CYSTM, in a wide range of small molecular tail-anchored membrane proteins in eukaryotes, including humans [
6]. To date, the proteins of the family have not been fully annotated. The CYSTM1 gene has been identified in mammals; however, its function still unclear (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/InterPro/IPR043240/). It was identified as a biomarker of Huntington's disease [
7].
The functions of proteins belonging to CYSTM superfamily are best studied in plants. The significance of many CYSTM proteins in overcoming stress in plant cells has been demonstrated [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. A group of plant CYSTM proteins was demonstrated to confer tolerance to cadmium and copper in
Digitaria ciliaris and
Oryza sativa [
8]. Heterologous expression in yeast of plant
CDT1 belonging to this group conferred metal resistance by preventing uptake of the metal ions into the yeast cell [
8]. The Arabidopsis representative of the superfamily,
PCC1, was induced via the salicylic acid-dependent pathway upon pathogen exposure and its overexpression increased resistance to oomycetes [
9]. In
Arabidopsis thaliana, 13 CYSTM genes have been identified; they show different expression levels in various tissues, at different stages of development and under various stresses, which suggests the diversity of their functions [
10,
11]. For example, the transcription of
CYSTM4,
CYSTM5 and
CYSTM6 was suppressed in shoots, but induced in roots under heat stress. Their expression was also induced by cold, polyethylene glycol or salt in the root and shoot.
CYSTM2,
CYSTM3, and
CYSTM7 were upregulated by salt, cold or drought treatment [
10]. The involvement of
CYSTM3 in Na
+ homeostasis was proposed [
10]. The transcript of one gene (
At1g05340) of
A. thaliana encoding a CYSTM protein is induced mainly by heat and to a lesser extent by UV, but less by NaCl or sorbitol [
12]. A functional analysis of
At1g05340 and its paralog
At2g32210 using T-DNA insertional mutants revealed a decrease in seedlings root length, the increase of sensitivity to heat stress and to a lesser extent to UV stress, in comparison to the effect on wild-type plants [
12]. The sensitivity of these mutants to salt or osmotic stresses did not differ from wild type response, indicating a specific function for these genes in heat and UV stresses [
12]. Heat and UV increased reactive oxygen species levels in wild type; however, their levels were higher in the mutant line than in wild type due to heat treatment, but was similar in the mutant lines and wild type due to UV stress [
12]. The results suggest that these CYSTM proteins are necessary for thermotolerance and protection from UV exposure; the proteins, most likely, act in heat stress by reducing reactive oxygen species level by yet unknown mechanism [
12]. The overexpression of pathogen-induced cysteine-rich transmembrane proteins in
A. thaliana enhances resistance against pathogens and stimulates hypocotyl growth, suggesting their potential role in both processes [
13]. The CYSTM peptides in
A. thaliana displayed various subcellular localization, and most of them were detected in the plasma membrane [
10,
13] and in the cytoplasm [
10].
Due to the high conservative structure of the CYSTM module, it is assumed that a role in stress response and more specifically in providing of resistance to damaging substances might be a general function of the superfamily [
6]. The conserved acidic residue could allow tight association with certain types of lipids and alter the permeability of the plasma membrane to damaging substances [
6]. The changes in plasma membrane could explain the role of CYSTM proteins in plant pathogen resistance, probably by blocking invasion of intracellular pathogens. The peculiar arrangement of sulfhydryl groups within the membrane could also alter the redox potential of the membrane or potentially directly chelate metal ions [
6]. Data on the functions of CYSTM proteins in plants indicate that their various representatives may be involved in adaptation to different types of stress.
In
Saccharomyces cerevisiae several CYSTM proteins were revealed (
Table 1). In SGD data base (
https://www.yeastgenome.org/) the CYSTM proteins are mentioned mainly as unannotated ones. These proteins demonstrate similarity to the CYSTM proteins of other eukaryotes (
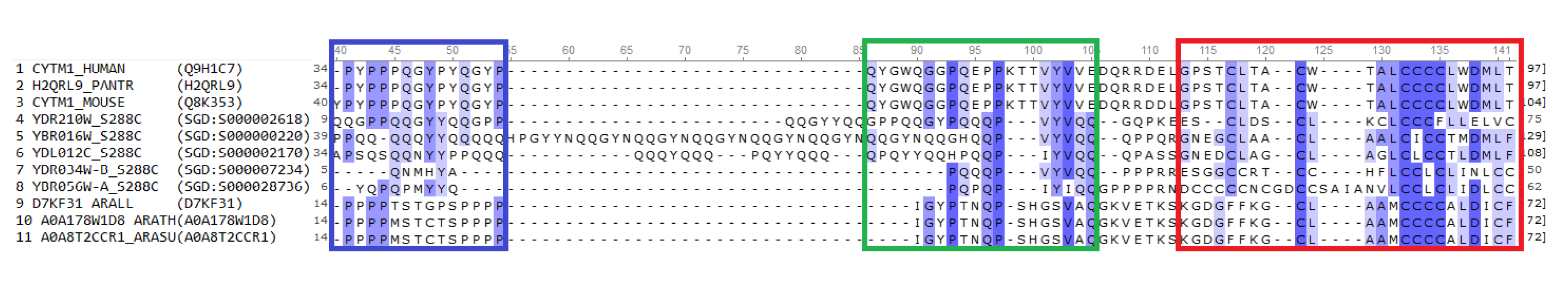
Figure 1). The features found in the structure of CYSTM yeast proteins are widely conserved throughout the family and found in no other membrane protein family. These features include an N-terminal cytoplasmic element that is predicted to adopt an β-strand connected by a highly variable linker to a C-terminal TM helix with 5-6 cysteine residue followed by an acidic residue [
6]. The 3–4 cysteine residues occur consecutively and constitute a conserved cysteine site that is characteristic of this superfamily [
6]. The article analyzing the structural features of CYSTM superfamily family describes four representatives revealed in yeast:
YDL012C,
YDR210W,
YBR016W and
YDR034W-B [
6]. The suggestion that they are tail-anchored membrane proteins was experimentally confirmed [
14,
15].
The yeast coexpression network analysis suggests that the proteins YDL012C, YDR210W and YBR016W are together involved in resistance against the DNA-damaging agents mitomycin C, the replication inhibitor methotrexate, the oxidizing agent hydrogen peroxide and the membrane destabilizing agent 1,8-nonadiene [
6].
YDL012C and
YDR210W were shown to be overlap in the chemicals against they provide resistance, suggesting that these proteins might function together as a complex [
6].
YDL012C and
YBR016W target GFP to the plasma membrane [
15]. Both YDL012C and YBR016W encoded proteins are localized mostly in regions of new membrane synthesis, toward the emergent buds of dividing cells [
15].
YDR034W-B has a paralog,
YBR056W-A. DNA microarray analysis made it possible to reveal a global set of yeast genes induced and repressed in response to various stresses, including variations in temperature, oxidation, nutrients, pH, and osmolarity, which indicates that nearly half of the genome is involved in the responses to environmental changes [
5]. Among these genes, the so-called Common Environmental Response (CER) genes were identified; their expression changed under variety of stresses, including temperature shift, peroxide, osmotic and pH stresses [
5]. One of the CER genes with its expression increasing under the above stress conditions was
YBR056W-A [
5]. The enhanced expression of
YBR056W-A (MNC1) in
S. cerevisiae cells adapted to growth in the presence of 2 mM Mn
2+ and the lytic phenotype of the ∆ybr056w-a strain in the presence of excess manganese have been shown, suggesting the possible role of this protein in manganese stress overcoming [
16]. As for
YDR034W-B encoded protein, there is no information about its role in stress conditions. Under normal growth conditions, the expression of this protein is negligible similar to
YBR056W-A [
16].
So, the aim of this study was to compare the stress conditions in which the expression of YDR034W-B and YBR056W-A is manifested and to assess the localization of GFP-fused proteins in the cells of S. cerevisiae. The effect of knockout mutations in YDR034W-B and YBR056W-A on resistance to stress caused by heavy metal ions was also assessed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strains and Cultivation Conditions
The S. cerevisiae wild-type (WT) strain BY4742 (MATα his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 lys2Δ0 ura3Δ0) and BY4742-derived mutant strains (∆ydro34w-b and ∆ybro56w-a) were obtained from the Euroscarf collection.
The S. cerevisiae GFP fusion strains YDRO34W-B-GFP and YBR056W-A-GFP derived from the BY4741 (MATa his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 lys2Δ0 ura3Δ0) strain were obtained from the Dharmacon collection. The strains were maintained on solid YPD medium containing 2% glucose, 2% peptone (Pronadisa, Madrid, Spain), and 1% yeast extract (Pronadisa, Madrid, Spain) supplemented with 2% agar (Sigma-Aldrich, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The start cultures were cultivated in 100 mL of the same YPD medium in Erlenmeyer flasks at 28 °C and 145 rpm for 24 h.
2.2. Fluorescence Microscopy
To test the effect stress factors on the expression of GFP fusion proteins, the cells of GFP fusion strains were cultivated in the control YPD medium and in YPD media supplemented with one of the following components: 40 mM KOH, 0.2 mM Cd(CH3COO)2·2 H2O, 2 mM MnSO4·4Н2O, 2 mM CoSO4·7H2O, 2 mM NiSO4·7H2O, 2 mM ZnSO4·7H2O, 2 mM CuSO4·5H2O, or 2 mM H2O2. The cultivation was performed in Erlenmeyer flasks in 100 mL of YPD at 28 °C and 145 rpm for 24 h.
To test the effect of 2,4-dinitrophenol, manganese and peroxide on GFP fusion proteins expression during a short incubation time, the cells of the YDRO34W-B-GFP and YBR056W-A-GFP strains were cultivated in 2 mL of YPD with stirring for 24 h to a culture absorption of 20 (measured in a 1-cm cuvette at 600 nm). After cultivation, the medium was supplemented with one of the following components: 0.2 mM 2,4-dinitrophenol (Sigma, USA), or 5 mM MnSO4·4Н2O, or 2 mM H2O2, and the cultivation was continued for 0.5, 1 and 1.5 h. The control cultivation was performed for both strains under the same conditions in YPD.
After cultivation, the cells were examined in an AXIO Imager A1 fluorescent microscope (Zeiss, Germany) with a 56HE filter set (Zeiss) at a wavelength of 480 nm (maximum excitation) and 512-630 (emission). Images were obtained with Axiocam 506 (Zeiss).
2.3. Staining with Nile Red
The cells of
YDRO34W-B-GFP and
YBR056W-A-GFP strains were cultivated in YPD supplemented with 4 mM Mn
2+ for 24 h. For visualization of lipids, the living cells were stained with Nile red (N1142, Thermo Scientific) [
17]. The cell were washed once in 0.025 M Hepes-KOH, pH 7.0, then incubated for 10 min at room temperature in the same buffer supplemented with the Nile Red (the stock solution containing 1 mg/mL of in ethanol was diluted l:100 with Hepes-KOH, pH 7.0).
The cells were examined by phase-contrast and fluorescent microscopy in an AXIO Imager A1 (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) with a filter set of 56HE (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) at a wavelength of 450–500 nm for excitation and 512 + 630 nm for emission. An Axiocam 506 camera (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) was used to acquire images.
2.5. Determination of Effects of Different Concentrations of Heavy Metal Ions
The GFP strains YDRO34W-B-GFP and YBR056W-A-GFP strains were used for asses the effects of different concentrations of cadmium and manganese ions on GFP protein fluorescence intensity and fluorescence cells count.
The S. cerevisiae wild-type (WT) strain BY4742 and BY4742-derived mutant strains (∆ydro34w-b and ∆ybro56w-a) were used for asses the effects of different concentrations of cadmium and manganese ions on cell growth.
The yeast strains were cultivated in a liquid YPD medium in sterile multiwell plates at 28 °C and 400 rpm for 24 h in a thermoshaker. Yeast samples were added to the normalized initial cell concentration (0.1 ·108 cell/ mL) to the wells containing 0.2 mL of YPD medium supplemented with different concentrations of Cd(CH3COO)2·2H2O or MnSO4·4Н2O. After cultivation, the cell concentration in culture samples was measured with a NovoCyte Flow cytometer. The samples were also examined with an AXIO Imager A1 ZEISS microscope (Oberkochen, Germany).
2.5. Flow Cytometry
The cell concentration in the cultivation medium was determined by flow cytometry. After a series of dilutions of the cell suspension with water, the number of cells in 25 μl in each sample was counted on a NovoCyte Flow cytometer (Agilent, USA). Expression of GFP-tagged proteins was determined on a NovoCyte flow cytometer using 488 nm for excitation and 585 nm for emission. 100 000 cells were counted at each experimental point. All assays were repeated 4–5 times and the mean results are presented.
2.4. Statistics
The experiments were performed in triplicate and the results are presented as the mean with standard deviation (Excel). Statistical analyses were performed by Excel using the Student’s t-test. The typical and most representative micrographs selected from 10-20 images obtained in independent experiments are presented.
3. Results
The
S. cerevisiae strains
YDRO34W-B-GFP and
YBR056W-A-GFP carrying the
YDRO34W-B and
YBR056W-A (MNC1) genes fused with GFP were used to test the expression of above genes in the presence of heavy metal ions, alkali and H
2O
2 by fluorescence microscopy. The cells were cultivated for 24 h. Stress factor concentrations were chosen based on our previous work using a related strain BY4741 [
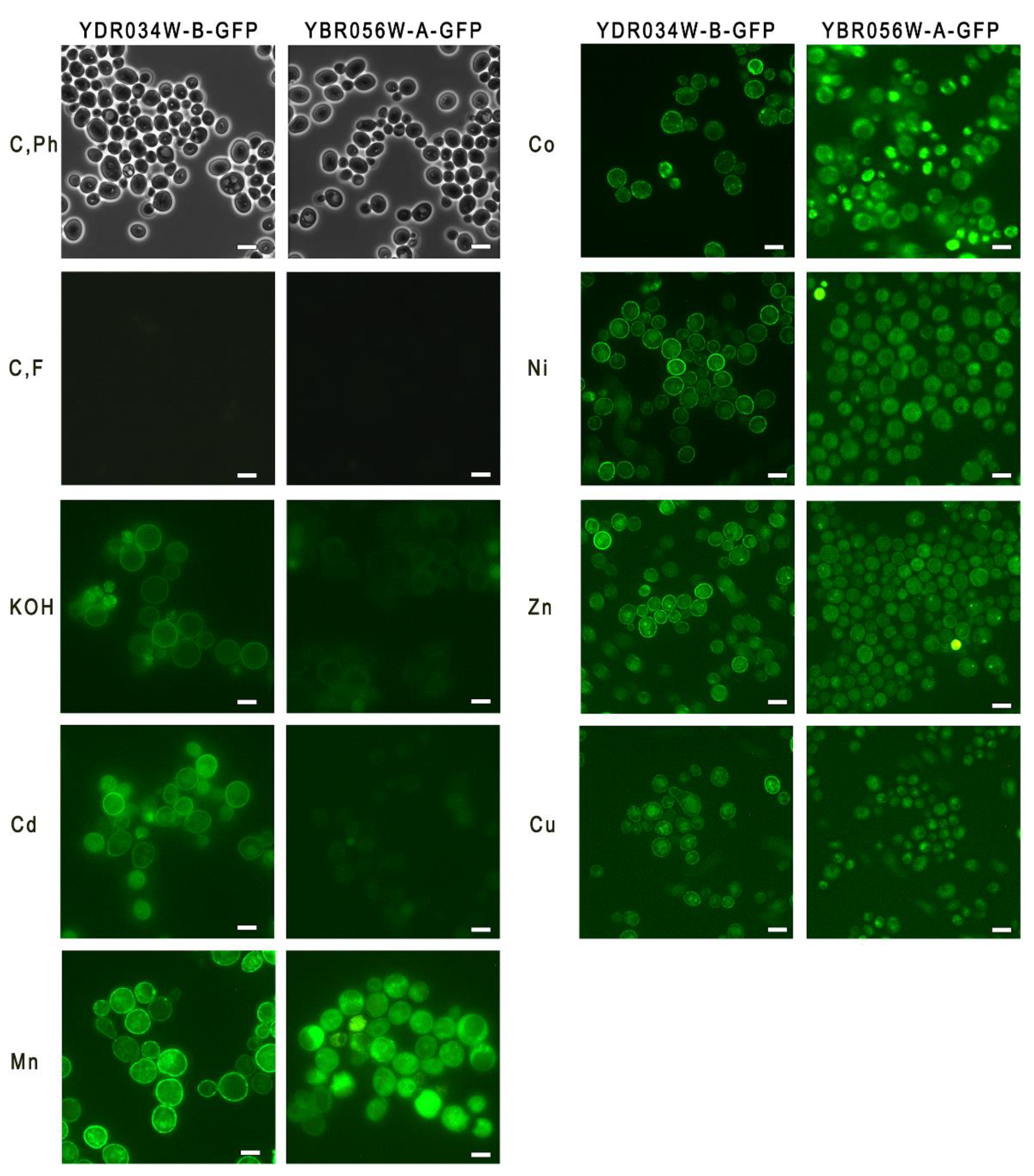
18]. The cells grown in the control YPD medium demonstrated negligible expression of both proteins (
Figure 2). No expression of these proteins was observed upon the addition of 2 mM H
2O
2 to the YPD medium (not shown). Green fluorescence of the cells indicating the enhanced expression of both
MNC1 and
YDRO34W-B was observed in the cells grown in YPD supplemented with Mn
2+, or Co
2+, or Ni
2+, or Zn
2+ and or Cu
2+ (
Figure 2). In the medium with KOH or Cd
2+, the fluorescence of
YDRO34W-B-GFP cells was much more pronounced than that of
YBR056W-A-GFP cells (
Figure 2).
For quantification, fluorescence levels at a wavelength of 585 nm were compared using flow cytometry of cells grown in the presence of manganese and cadmium ions as an example. The data obtained (Supplementary
Figure 1) confirmed that the fluorescence of the cells of both strains grown in the presence of 4 mM Mn
2+ was at a similar level. When the cells were grown in the presence of 0.2 mM Cd
2+, the fluorescence level of cells of
YDRO34W-B-GFP strain was significantly higher than that of the
YBR056W-A-GFP strain (Supplementary
Figure 1).
We also assessed the dependence of the proportion of fluorescing cells on concentrations of cadmium and manganese by flow cytometry. In the case of Cd
2+, the proportion of fluorescing cells was higher for the
YDRO34W-B-GFP strain, and in the case of Mn
2+, this proportion was higher for the cells of the
YBR056W-A-GFP strain (
Figure 3). This was observed over the entire range of used concentrations of metal ions.
Thus, we have observed differences in the expression of Ydro34w-b protein and Mnc1 depending on the type of stress.
The localization of CYSTM proteins in membranes, including the cytoplasmic membrane, was predicted due to the analysis of their structure [
6] and was experimentally confirmed for some yeast proteins belonging to this family [
14,
15]. Our microscopic data do not contradict this view (
Figure 2).
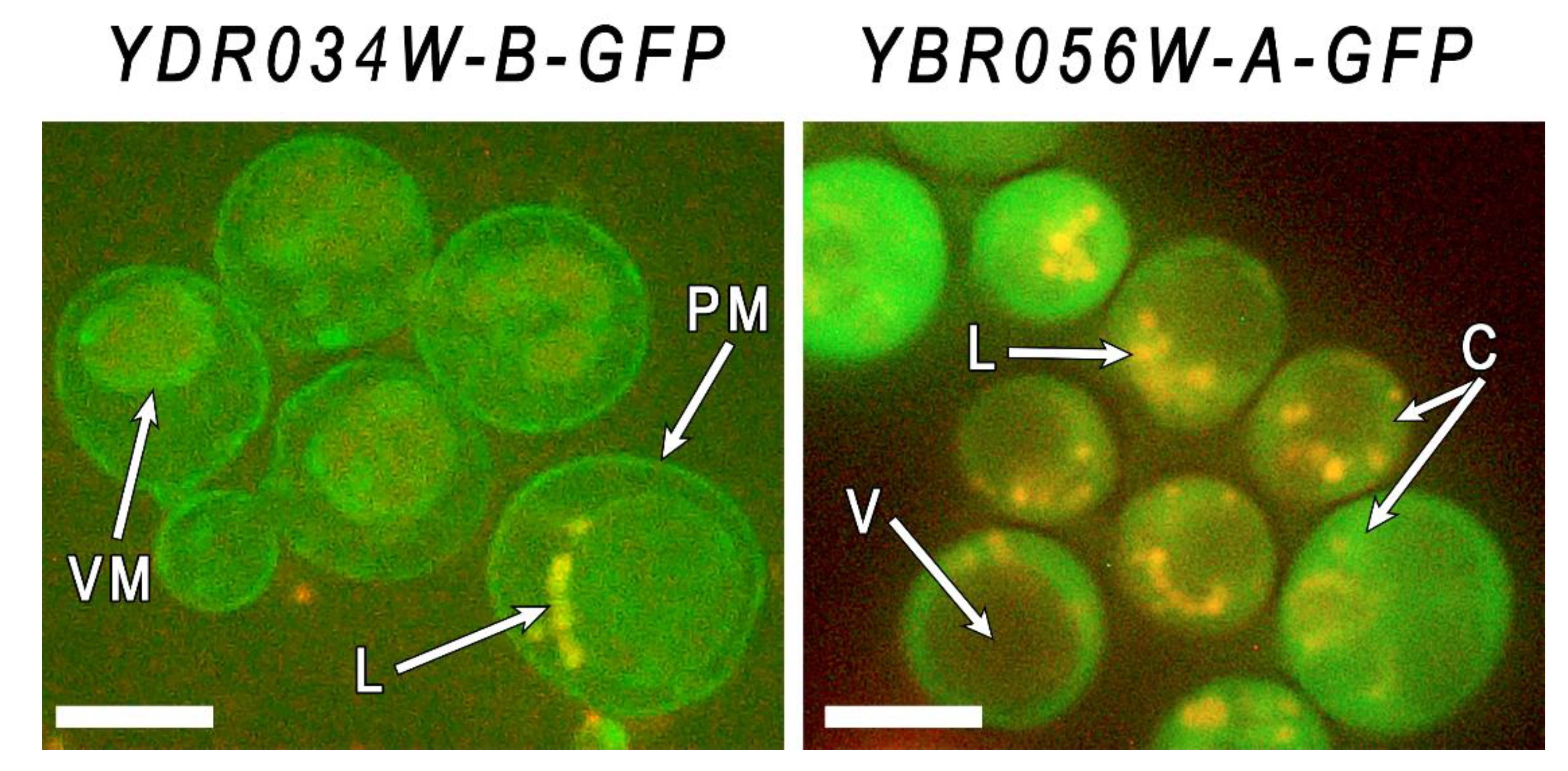
To improve visualization of membrane structures, we stained the cells grown in the presence of 4 mM Mn
2+ with Nile red (
Figure 4).
Due to the fact that excitation of the Nile red starts at a wavelength of 410 nm, we can immediately observe both lipids and GFP proteins in yeast cells using Zeiss 56HE filter kit (a wavelength of 450–500 nm for excitation and 512 + 630 nm for emission). The fluorochrome stained vacuoles, but plasma membrane was not visualized because of high level of GFP fluorescence. Nevertheless, the obtained microphotographs show that in the cells of YDRO34W-B-GFP strain the GFP fused protein is localized in the periphery of the cell and in the vacuolar membrane, while in the cells of YBR056W-A-GFP strain the GFP fused protein is localized in the cytoplasm, without focusing in the cell periphery or vacuole. This method did not allow to precisely determine the localization of Mnc1. Taking into account the presence of a membrane domain, we speculate that Mnc1 can be localized in the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum. The data obtained confirm the idea of membrane localization of these members CYSTM family and indicate differences in their localization.
Many types of stress lead to a decrease in the electrochemical gradient on the yeast plasma membrane, and this disturbance may be the primary step of stress response [
19,
20]. In this regard, we have checked how the known uncoupler 2,4-dinitrophenol [
21] affects the expression of
MNC1 and
YDRO34W-B. The short-term incubation of the
YDRO34W-B-GFP and
YBR056W-A-GFP strains with 2,4-dinitrophenol, Mn
2+ and H
2O
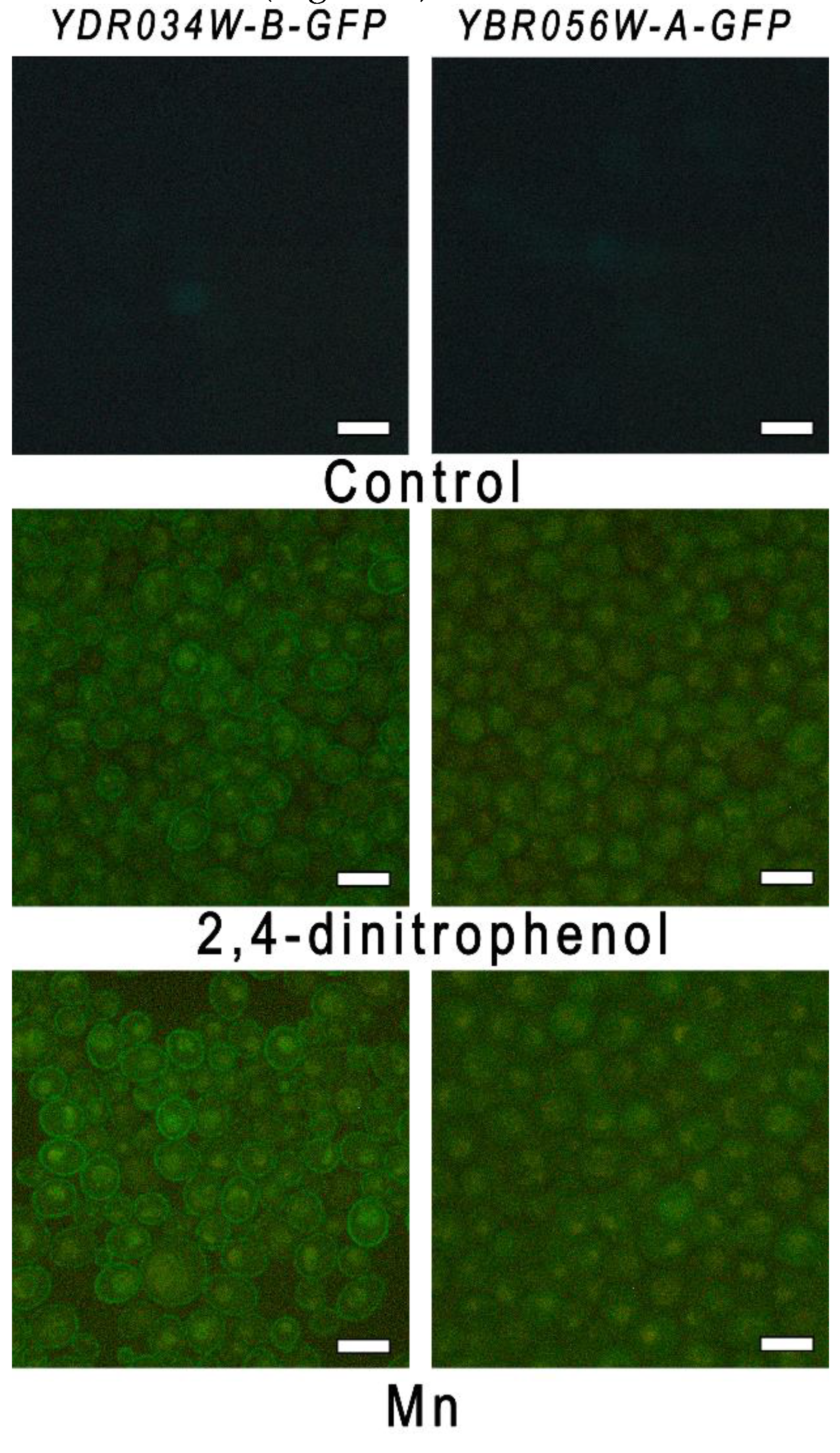
2 was used for this purpose. No green fluorescence of the cells of both strains was observed in the control cells (
Figure 5).
The fluorescence was low after 30 and 60 min of incubation with 2,4-dinitrophenol or Mn
2+ (not shown). Green fluorescence of the cells of both strains appeared in case of cultivation for 1.5 h in the presence of 2,4-dinitrophenol and Mn
2+ (
Figure 5), but not H
2O
2 (not shown). Hence, 2,4-dinitrophenol stimulated the expression of both genes similar to Mn
2+, and we suggest that the disturbance of the electrochemical gradient on plasma membrane may serve as a signal of this stimulation.
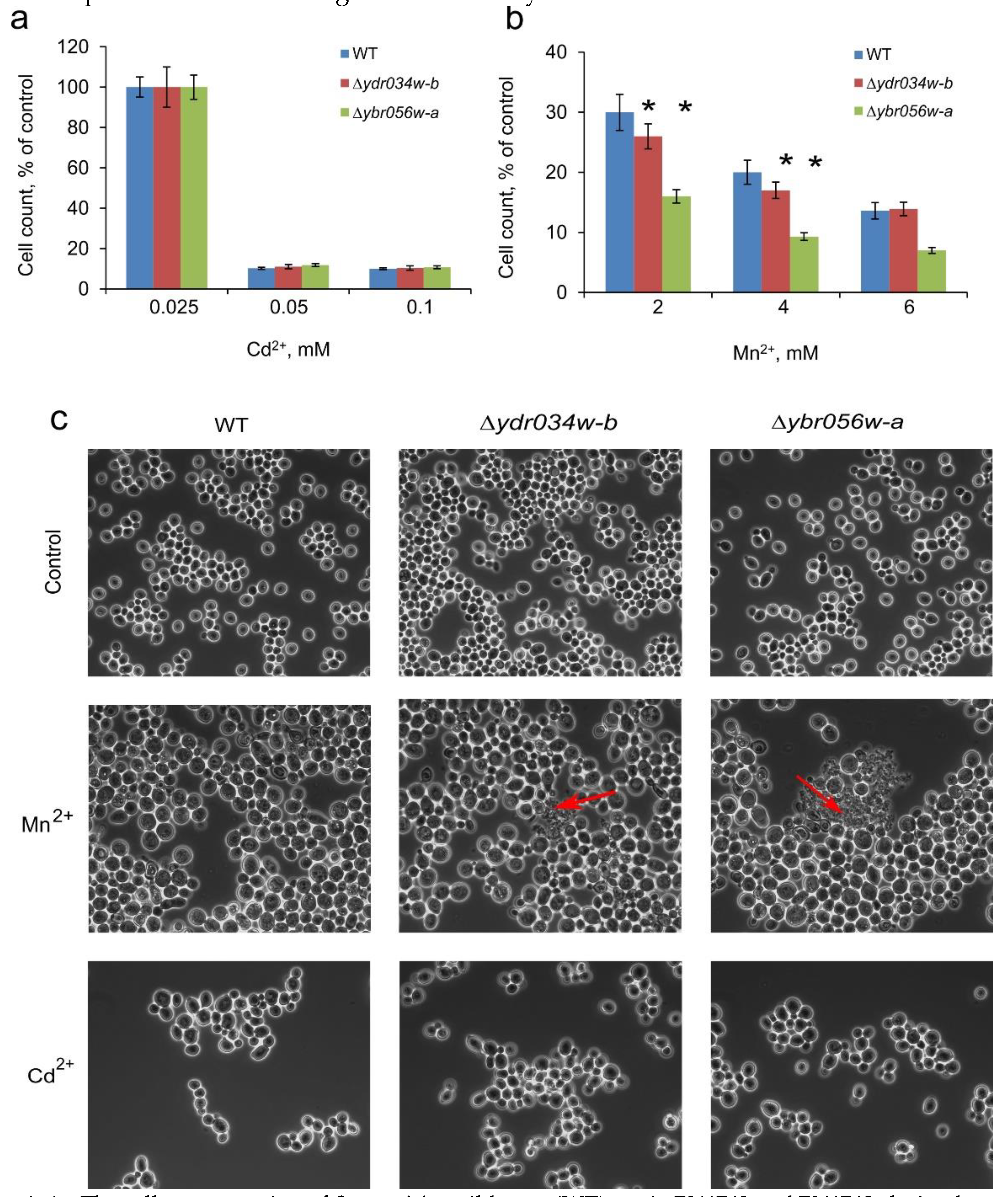
We have also checked the effects of the knockout mutations in
MNC1 and
YDRO34W-B on the growth and cell morphology under Cd
2+- and Mn
2+-induced stresses. The changes in cell concentrations (
Figure 6a) and cellular morphology (
Figure 6c) in WT-type strain and
∆mnc1 and
∆ydro34w-b strains under Cd
2+ stress were similar. In the presence of Mn
2+ (2-4 mM), cell concentration decreased for the
∆mnc1 and
∆ydro34w-b strains (
Figure 6b). Besides, cell lysis was observed by light microscopy (
Figure 6c). The effect of knockout mutations was not significant, however, it suggest the possibility of the participation of the studied proteins in overcoming stress caused by a toxic Mn
2+ concentration.
4. Discussion
The role of CYSTM proteins in metal homeostasis was proposed long ago: the arrangement of sulfhydryl groups of the protein within the membrane could alter the redox potential of the membrane or directly chelate metal ions [
6]. The enhanced expression of
MNC1 but not
YDR034W-B was observed in
S. cerevisiae cells adapted to the growth at toxic manganese concentrations [
16]. In this article, the transcriptome of cells of the stationary growth stage have been analyzed (120-h cultivation in the presence of 2.5 mM manganese salt); in the present work, we have analyzed the cells of the early active growth stage (24-h cultivation in the presence of 2.5 mM manganese salt). Possibly, the observed difference in the
YDR034W-B expression is associated with the growth stage. Previously we suggested the plasma membrane localization of Mnc1 [
16] based on data on structure and localization of other CYSTM proteins [
6,
15]. The data obtained for the strains containing GFP-fusion gene in the present work indicate that Mnc1 is localized mainly in cytoplasm, probably in intracellular membranes.
The expression of
YDR034W-B and
MNC1 in the cells grown in control YPD medium was very low [
16]. In this work we have identified first the stress conditions in which
YDR034W-B expression increased. This expression increased in yeast cells cultivated in the presence of toxic concentrations of Mn
2+, Co
2+, Ni
2+, Cu
2+, Zn
2+, Cd
2+ or KOH. The
MNC1 is expressed in the presence of toxic concentrations of Mn
2+, Co
2+, Ni
2+, Cu
2+, or Zn
2+, while its expression shows lower level in the presence of Cd
2+ or KOH.
To our surprise, we did not find the expression of these proteins under peroxide stress, although an increase in expression of
YBR056W-A under this type of stress has been previously reported [
6]. Perhaps this is due to differences in cultivation conditions and stress exposure. We did not find any effect on resistance to cadmium ions of knockout mutations in both genes studied. At the same time, we noted a decrease in the resistance of knockout mutant cells to manganese ions. Ions of cadmium [
22,
23] and manganese [
24,
25,
26] significantly differ in the mechanism of toxic action, the range of toxic concentrations, and the biological role. Cadmium does not participate in metabolic processes in yeast, while manganese is an essential trace element for yeast, being a cofactor for numerous metalloenzymes [
25] and a necessary component of the antioxidant system [
26]. In this regard, the system of manganese homeostasis in yeast includes a number of membrane proteins that differ in the mechanism of action and cellular localization. We speculate that Mnc1 and Ydro34w-b may be components of the manganese homeostasis system in yeast cells. We propose
MNC2 (manganese-chelating protein 2) as a possible gene name for
YDRO34W-B.
The significance of studying the yeast manganese homeostasis system is summarized in the review, where the authors indicate the functional conservation of proteins involved in manganese homeostasis from yeast to humans [
25]. This fact makes yeast a relevant model to find out new aspects of human neurodegenerative diseases and to propose new therapeutic approaches to their treatment [
25]. It is noteworthy that one of the markers of Hadington's disease is a protein of the CYSTM family [
7]. Thus, the study of CYSTM proteins are of interest for further research of stress adaptation in eukaryotes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.K.; methodology, A.Z.; software, V.F.; validation, A.Z.; formal analysis, L.L., L.R., A.V.; investigation, A.Z., L.L., L.R., A.V., V.F.; data curation, A.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, A.Z., T.K.; writing—review and editing, T.K.; visualization, A.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
The sequence alignment of the some proteins of CYSTM domain superfamily The alignment of protein sequences was performed by UGENE (
http://ugene.net/ru/) using ClustalW algorithm. The columns are colored according to the similarities, and the CYSTM domain is indicated with red. The sequences are labeled using the gene names and species abbreviations, the data base sequence codes are indicated in parentheses. The sequences 1-3 and 9-11 were from UniProt (
https://www.uniprot.org/), and the sequences 4-8 were from SGD (
https://www.yeastgenome.org/). The species abbreviations are — HUMAN:
Homo sapiens; PANTR:
Pan troglodytes; MOUSE:
Mus musculus; S288C:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S288C strain); ARALL:
Arabidopsis lyrata; ARATH:
Arabidopsis thaliana; ARASU:
Arabidopsis suecica.
Figure 1.
The sequence alignment of the some proteins of CYSTM domain superfamily The alignment of protein sequences was performed by UGENE (
http://ugene.net/ru/) using ClustalW algorithm. The columns are colored according to the similarities, and the CYSTM domain is indicated with red. The sequences are labeled using the gene names and species abbreviations, the data base sequence codes are indicated in parentheses. The sequences 1-3 and 9-11 were from UniProt (
https://www.uniprot.org/), and the sequences 4-8 were from SGD (
https://www.yeastgenome.org/). The species abbreviations are — HUMAN:
Homo sapiens; PANTR:
Pan troglodytes; MOUSE:
Mus musculus; S288C:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S288C strain); ARALL:
Arabidopsis lyrata; ARATH:
Arabidopsis thaliana; ARASU:
Arabidopsis suecica.
Figure 2.
Micrographs of cells of strains YBR056W-A-GFP and YDR034W-B-GFP. The cells were cultivated in YPD medium for 24 h. C, Ph - phase contrast microscopy, control cultivation; C, F - fluorescence microscopy, control cultivation; KOH - fluorescence microscopy, cultivation in the presence of 40 mM KOH, Cd – fluorescence microscopy, cultivation in the presence of 0.2 mM Cd2+; Mn, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu – fluorescence microscopy, cultivation in the presence of 2 mM of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, respectively. The bar line is 5 μm.
Figure 2.
Micrographs of cells of strains YBR056W-A-GFP and YDR034W-B-GFP. The cells were cultivated in YPD medium for 24 h. C, Ph - phase contrast microscopy, control cultivation; C, F - fluorescence microscopy, control cultivation; KOH - fluorescence microscopy, cultivation in the presence of 40 mM KOH, Cd – fluorescence microscopy, cultivation in the presence of 0.2 mM Cd2+; Mn, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu – fluorescence microscopy, cultivation in the presence of 2 mM of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, respectively. The bar line is 5 μm.
Figure 3.
The effects of different concentrations of Cd2+ (a) and Mn2+ (b) on the proportion of green fluorescence cells in cell populations of S. cerevisiae strains YBR056W-A-GFP and YDR034W-B-GFP. The yeast were cultivated for 24 h as described in Method section and counted by flow cytometer. The experiments were performed in triple, the values denote mean, the whiskers denote s.d. * p < 0.01, significance assessed with the two-tailed Student’s T-test (YDR034W-B-GFP vs YBR056W-A-GFP).
Figure 3.
The effects of different concentrations of Cd2+ (a) and Mn2+ (b) on the proportion of green fluorescence cells in cell populations of S. cerevisiae strains YBR056W-A-GFP and YDR034W-B-GFP. The yeast were cultivated for 24 h as described in Method section and counted by flow cytometer. The experiments were performed in triple, the values denote mean, the whiskers denote s.d. * p < 0.01, significance assessed with the two-tailed Student’s T-test (YDR034W-B-GFP vs YBR056W-A-GFP).
Figure 4.
Micrographs of cells of strains YBR056W-A-GFP and YDR034W-B-GFP grown in YPD the presence of 4 mM of Mn2+ for 24 h. Staining with Nil red. PM – plasma membrane, VM – vacuolar membrane, L – lipid inclusions, V – vacuole, C – cytoplasm, The bar line is 5 μm.
Figure 4.
Micrographs of cells of strains YBR056W-A-GFP and YDR034W-B-GFP grown in YPD the presence of 4 mM of Mn2+ for 24 h. Staining with Nil red. PM – plasma membrane, VM – vacuolar membrane, L – lipid inclusions, V – vacuole, C – cytoplasm, The bar line is 5 μm.
Figure 5.
Micrographs of cells of strains YBR056W-A-GFP and YDR034W-B-GFP, fluorescence microscopy. The cells were incubated in control YPD and in the presence of 0.2 mM dinitrophenol or 5 mM MnSO4 for 1.5 hours.
Figure 5.
Micrographs of cells of strains YBR056W-A-GFP and YDR034W-B-GFP, fluorescence microscopy. The cells were incubated in control YPD and in the presence of 0.2 mM dinitrophenol or 5 mM MnSO4 for 1.5 hours.
Figure 6.
A - The cell concentration of S. cerevisiae wild-type (WT) strain BY4742 and BY4742-derived mutant strains (∆ydr034w-b and ∆ybro56w-a); cultivation in control YPD and in YPD supplemented with various concentrations of Cd2 +(a) or Mn2+ (b). The cell concentration ~2.3 ·108 cell/mL in control cultivation corresponds to 100%. The cells were cultivated for 24 h in multiwel plates. The experiments were performed in triple, the values denote mean, the whiskers denote s.d. , * p < 0.05, in other cases he difference was insignificant, the significance assessed with the two-tailed Student’s T-test against WT. (c) - Phase-contrast micrographs of cells of wild-type (WT) strain BY4742 and BY4742-derived mutant strains (∆ydr034w-b and ∆ybro56w-a) grown in YPD control medium and in the presence of 2 mM Mn2+, or 0.075 mM Cd2+; red arrows indicate the agglomerates of lysed cells.
Figure 6.
A - The cell concentration of S. cerevisiae wild-type (WT) strain BY4742 and BY4742-derived mutant strains (∆ydr034w-b and ∆ybro56w-a); cultivation in control YPD and in YPD supplemented with various concentrations of Cd2 +(a) or Mn2+ (b). The cell concentration ~2.3 ·108 cell/mL in control cultivation corresponds to 100%. The cells were cultivated for 24 h in multiwel plates. The experiments were performed in triple, the values denote mean, the whiskers denote s.d. , * p < 0.05, in other cases he difference was insignificant, the significance assessed with the two-tailed Student’s T-test against WT. (c) - Phase-contrast micrographs of cells of wild-type (WT) strain BY4742 and BY4742-derived mutant strains (∆ydr034w-b and ∆ybro56w-a) grown in YPD control medium and in the presence of 2 mM Mn2+, or 0.075 mM Cd2+; red arrows indicate the agglomerates of lysed cells.
| Systematic Gene Name |
Molecular Mass of Protein, Da |
Description |
| YDR034W−B |
5968.2 |
Predicted tail-anchored plasma membrane protein; N- and C-terminal fusion proteins localize to the cell periphery; has a paralog, YBR056W-A, that arose from the whole genome duplication |
YBR056W-A
(MNC1)
|
7326.8 |
Putative membrane protein upregulated in toxic manganese levels |
| YDL012C |
12173.4 |
Tail-anchored plasma membrane protein, possibly involved in response to stress; has a paralog, YBR016W, that arose from the whole genome duplication |
| YBR016W |
14617.0 |
Tail-anchored plasma membrane protein; has similarity to hydrophilins, which are involved in the adaptive response to hyperosmotic conditions |
| YDR210W |
8567.7 |
Predicted tail-anchored plasma membrane protein |