1. Introduction
Urban forests and greenspaces are increasingly considered an important priority for improving the sustainability, resilience, and livability of the urban landscape [
1]. Trees in the urban forest provide many benefits such as air pollution reduction [
2], storm water runoff attenuation [
3], carbon sequestration [
4], and building energy conservation [
5]. Benefits generally increase as the size of trees increase [
6], but as trees mature they are more likely to develop decay that increases their likelihood of failure [
7]. In built environments, tree failures can result in fatalities [
8], power outages [
9], and catastrophic fires [
10]; and damage from failures is associated with higher costs [
11] and legal liability [
12].
Arborists have assessed tree risk for many years. Recent revisions have brought the process into better alignment with risk assessment practices used in other disciplines. The current U.S. standard considers 1) the likelihood of a tree failure, 2) the likelihood of impact of a tree or tree part on a target and 3) the severity of the consequence if impact were to occur. Arborists assign one of four ratings to likelihood of failure (
improbable,
possible,
probable,
imminent) that are defined as follows: [
13]:
Improbable: The tree or tree part is not likely to fail during normal weather conditions and may not fail in extreme weather conditions within the specified time frame.
Possible: Failure may be expected in extreme weather conditions, but it is unlikely during normal weather conditions within the specified time frame.
Probable: Failure may be expected under normal weather conditions within the specified time frame.
Imminent: Failure has started or is most likely to occur in the near future, even if there is no significant wind or increased load. This is a rare occurrence for a risk assessor to encounter and may require immediate action to protect people from harm. The imminent category overrides the stated time frame.
Decay is a common defect that is often associated with tree failure [
7,
14,
15]. Decay reduces load-bearing capacity by reducing wood strength and, if wood components are completely digested, by creating voids that reduce cross-sectional area. Many tools and techniques to detect and assess the extent of decay have been developed. Some are simple (e.g., sounding the stem with a mallet); others are sophisticated (e.g., resistance drills and tomography) [
16]. Many studies have investigated how well decay detection tools and techniques work [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24].
Despite advancements in decay detection tools and techniques, many aspects of risk assessment remain uncertain because of the lack of knowledge about how trees grow and fail. Uncertainty may also be exacerbated by assessor bias, including an assessor’s personal risk tolerance [
25]. Cognitive studies on human risk perception attribute an individual’s attitude towards risk to personal experiences [
26,
27], personal fears [
28], and biases shared by communities [
29]. An assessor’s training also influences ratings: trained professionals tended to return lower likelihood of failure ratings (LoFRs) than those without training [
25,
30].
Our objectives for this study were as follows:
to determine whether more detailed information about the extent of trunk decay influenced experienced assessors’ LoFRs and, if so,
to identify factors related to assessors and trees that explained the influence.
2. Materials and Methods
The study took place on the campus of the University of Massachusetts in Amherst, Mass., USA (USDA Hardiness Zone 5b). In July 2021, 18 experienced arborists who held the International Society of Arboriculture’s (ISA) Tree Risk Assessment Qualification (TRAQ) (among other credentials) assessed the likelihood of stem failure due to decay of 30 trees using 5 (basic and advanced) assessment techniques.
We selected trees for the field assessment based on practical considerations. The first was the availability of sonic and electrical resistance (ER) tomograms taken of the trunk taken within 2 m of the ground. Tomograms had been previously obtained using a PiCUS Sonic Tomograph 3, a TreeTronic 3 for ERT, and the Caliper 3 Geometry Measurement System (Argus Electronic GMBH, Rostock, Germany) following the methods of [
23]. A second consideration was variation in compartmentalization response: weak (
Pinus) and strong (
Quercus). Finally, only (i) larger individuals (> 50 cm stem diameter measured 1.4 m above ground—“DBH”) and (ii) individuals that were close enough to one another that they could be grouped by location were selected. In the latter case, we selected individuals in six discrete clusters around the campus. We selected clusters of individuals for two reasons: (i) it included a variety of landscape settings (open space or near infrastructure such as roads, buildings, and parking lots); and (ii) it limited travel time to maximize the number of individuals that could be assessed in the two days when assessors visited campus. Prior to conducting the study, we pre-tested the methods and determined an efficient route to assess as many trees as possible in two days.
We recruited assessors from our professional networks, inviting only experienced assessors who (i) held the TRAQ credential, (ii) regularly performed risk assessments as part of their professional practice, and (iii) were familiar with advanced decay detection techniques such as resistance drilling and tomography. We offered continuing education units to assessors, but neither financial compensation nor reimbursement of travel expenses.
Before assessors arrived on campus in July 2020 to participate in the study, we used a Resistograph® F500-S (IML North America, Moultonborough, N.H., USA) to determine the thickness of sound wood (
t) at between three and six locations spaced at approximately even intervals around the stem circumference and at the same height as the tomogram. For each location, we computed the
t/
R ratio, where
R is trunk radius [
31]. We attached flagging to the stem to indicate the locations of the tomography and Resistograph measurements (
Figure 1).
We provided each assessor a binder that included a sheet for each tree. The sheet contained the following information: genus and species, DBH, height, the Resistograph output (
Figure 2), and the sonic and ERT tomograms (
Figure 3). Output from the Resistograph included a scaled diagram of the cross-section of the stem and lines indicating where drillings were made, the height and stem diameter where the drillings were made, the mean
t value, and a table of all
t/
R values. The tomograms included the percentages of cross-sectional area that were sound or decayed. The decayed proportion of the cross-section was computed automatically from the combined areas of blue and purple in the sonic tomogram. Since we used the default settings (SoT1 calculation option and minimum velocity established at 50%), the resulting tomogram depicts the greatest possible area of decay in comparison to those generated using SoT2 and an expanded color space to view the minimum percent velocities. But the computed proportion of decayed wood indicated at the top of the tomogram assessors viewed during the study (e.g.,
Figure 3) did not include areas of intermediate velocities. We explained this to assessors prior to the field study. After the field study, we computed the loss in section modulus due to decay (
ZLOSS) from each sonic tomogram following the method of [
32].
We instructed assessors to assign a rating of the likelihood of stem failure due to decay (“LoFR”) within 2 m of the ground and reminded them not to assess likelihood of failure of other parts of the tree. We used LoFRs from [
13] and provided assessors with the definitions (listed in the Introduction). We instructed assessors to assign their LoFR based on a timeframe of three years.
Assessors performed five consecutive assessments of the LoFR. In order, assessments were as follows:
visual assessment of the tree and its surroundings;
sounding the trunk with a plastic mallet;
viewing the Resistograph output (
Figure 2);
consulting with a randomly assigned assessor.
Assessment techniques (a) and (b) are part of a Level 2 (“basic”) risk assessment [
13]. Assessment techniques (c) and (d) are more sophisticated techniques to assess the amount and location (i.e., the “extent”) of decay and part of a Level 3 (“advanced”) risk assessment [
13]. For odd-numbered trees, assessors viewed the resistance drilling output (c) before the viewing the tomogram (d); for even-numbered trees, assessors viewed the tomogram first. Consulting with a peer is not explicitly recommended in common professional guidelines [
13,
33]. Within each cluster of trees, assessors were randomly paired and inspected individual trees at their own pace.
After each of the five assessments [(a) – (e)] on a tree, assessors completed a survey to indicate their LoFR and describe the factor(s) (e.g., species, decay severity, tree size, exposure, lean, crown, etc.) that most influenced their LoFR, and if the additional information gained in the assessment technique changed their LoFR.
Assessors also self-reported the following information on the survey: years of experience performing tree risk assessments; number of trees assessed annually; relevant credentials in addition to TRAQ; and how frequently they used assessment techniques (b), (c), and (d) as part of their professional practice.
During the field study, not every assessor completed all five assessments of every tree. As a result, approximately 15% of the expected dataset was missing values. We used multivariate imputation by chained equations [
34,
35] to impute the most likely value for each missing value to obtain a full dataset prior to OLR analyses.
The university campus is well maintained, and no assessor assigned a LoFR of four (“imminent”) to any tree. Consequently, we coded LoFR ordinally as one (“improbable”), two (“possible”), or three (“probable”) and built ordinal logistic regression (OLR) models to investigate the effect of assessment technique on LoFR. All analyses were performed using the statistical language R, v4.1.2 [
36]. In the OLR models, we included covariates describing trees [genus; DBH; percent of cross-sectional area with decay (from tomograms); average sound wood thickness (
t) from the Resistograph output;
t/R, where
R is stem radius; Z
LOSS] and participants (years of experience; frequency of using a mallet, resistance drilling, and tomography when conducting risk assessments). We also included tree and assessor identification as random effects in each OLR model. We built models with the “clmm” function from the “Ordinal” package by iteratively adding covariates as single effects or interactions with the main effect of assessment technique [
37]. Since the order of assessments differed between even- (viewed tomogram before Resistograph output) and odd-numbered (viewed Resistograph output before tomogram) trees, the variable “assessment technique” contained ten levels that represented an interaction between the five assessment techniques and even- or odd-numbered trees. We then selected the best model using lowest AICc scores.
In addition to the OLR analyses, we created a contingency table with four rows (one for each of the assessment techniques that followed the initial visual assessment) and two columns (to indicate whether the additional information gained for the assessment technique changed (“Yes”) or did not change (“No”) assessors’ LoFRs). We used a test to determine whether the proportion of affirmative and negative responses varied among assessment techniques.
Lastly, we investigated the influence of the random variables in the OLR model (assessor and tree) on LoFR. To investigate the influence of assessors, we evaluated if the consistency in assessor LoFRs changed among the five assessment techniques or four frequency-of-use categories of the tomogram or Resistograph. We quantified LoFR consistency with the “betadisper” function in the “vegan” package, which performed a multivariate test of homogeneity of variances on a Bray-Curtis (rank-based) dissimilarity matrix of the proportional distribution of LoFRs [
38]. A multivariate approach was needed to evaluate inconsistencies of LoFRs with a single test.
To investigate the influence of trees between the initial visual assessment and each subsequent assessment technique, we computed the ratio of the weighted mean change in LoFR to the proportion of unchanged LoFRs for each tree. The ratio illustrated the frequency, magnitude, and direction of changes in LoFR from the initial visual assessment. We computed the ratio () as follows:
Compute the difference in LoFR from the initial visual LoFR:
where
,
, and
, are indices for the 4 assessment techniques following the initial visual assessment (indicated by the subscript
), 30 trees, and 18 assessors, respectively.
Compute the proportion of unchanged LoFRs (i.e.,
) for each tree and assessment technique:
Compute the weighted mean change in LoFR:
where
is a weighting factor of 1 (for LoFRs that changed one level from the initial visual assessment, e.g., from probable to possible or improbable to possible) or 2 (for LoFRs that changed two levels, e.g., from probable to improbable).
For each tree and assessment technique,
We thus computed 30 values of for each of the 4 assessment techniques that followed the initial visual assessment. From the resulting distribution of 120 values of , we considered only values in the upper and lower quartiles as having increased and decreased LoFR, respectively. We considered values of within the interquartile range (IQR) as having the same LoFR as the initial visual assessment. In the rest of the paper, we refer to “increased”, “decreased”, or “unchanged” LoFRs rather than values of in upper quartile, lower quartile, and IQR, respectively.
We described the basic assessment techniques as “consistent” if the LoFR assigned in the mallet assessment was unchanged from the initial visual assessment, and “inconsistent” if the LoFR assigned in the mallet assessment was greater or less than the initial visual assessment. We described the advanced assessment techniques as consistent if the change in LoFR from the initial visual assessment was the same for both advanced assessment techniques. We described the advanced assessment techniques as inconsistent if the change in LoFR from the initial visual assessment was not the same for both advanced assessment techniques. With respect to changes in LoFR from the initial visual assessment, we described the effect of the consultation assessment as “confirming” (or not) the basic and advanced assessments. If the LoFR assigned in the mallet and consultation assessments was unchanged from the initial visual assessment, the consultation assessment confirmed the basic assessment techniques. Similarly, if the LoFR was greater than or less than the initial visual assessment for both advanced assessment techniques and the consultation assessment, the consultation confirmed the advanced assessment techniques.
4. Discussion
Our results demonstrate that detailed information about the extent of trunk decay influenced experienced TRAQ-credentialed assessors’ LoFRs, but neither consistently nor in a straightforward way. The effect was most noticeable in greater LoFRs assigned following the tomogram assessment. But covariates related to trees (percent decay and t) and assessors (frequency of using resistance drilling tools for risk assessments) led to significant interactions with assessment technique, indicating the need for a more nuanced interpretation. A larger sample of assessors may have improved our understanding of their effect on LoFRs.
Because the Resistograph output and tomogram helped assessors visualize the extent of decay, we expected that the advanced assessment techniques would influence LoFRs—particularly for assessors who used advanced techniques less frequently. The influence was obvious in the changing proportions of LoFRs as percent decay changed, but only after assessors viewed the Resistograph output and tomogram. The pattern persisted following the consultation assessment, further supporting the idea that visualizing decay affected assessors’ LoFRs. But the overall trend did not apply to every tree. Our observation that the consultation assessment confirmed the basic assessment nearly as often as the advanced assessment was the result of greater LoFRs assigned following the tomogram assessment.
We speculate that the significant increase in LoFR following the tomogram assessment was due in part to the visual presentation of tomograms themselves. Our choice of the default (and more liberal) SoT1 calculation with minimum velocity set at 50% created tomograms with the largest area of decay. Assessors who often used tomography for risk assessments would more likely have understood that the tomograms may have overestimated the extent of decay using the default calculation, whereas assessors who only rarely used tomography may have been more inclined to increase the LoFR they assigned, as our findings suggest. Especially on stems of larger diameter and less regular shape, it is imperative that assessors are familiar with the uncertainty associated with interpreting tomorgrams [
39].
It is also plausible that the complete and in-color view of decayed areas in tomograms may have been perceived as a more definitive depiction of decay, especially for assessors who used tomography less frequently. For instance, the number of holes drilled for the Resistograph may not have been adequate to precisely define the extent of decay, which could in turn result in assessors to experience greater uncertainty in how to interpret the Resistograph outputs. Resistograph outputs also were truncated and did not traverse the entire diameter. In contrast, tomograms presumably presented more visually compelling cross-sectional images than the black and white line drawings of the Resistograph output. For example, the extent of decay presented in Resistograph outputs and tomograms was similar for trees 22 and 27 (
Figure 8), but the change in LoFR from the visual assessment was only greater after viewing tomograms. Without comparing tomograms and the outputs from the Resistograph to pictures of the cross-sections themselves, it was not possible to know which portrayal of internal decay was more accurate. Many studies have demonstrated the accuracy and limitations of each technique [
18,
19,
21,
22,
23,
24], which is why using both techniques to investigate the extent of decay is helpful [
40].
For assessments that followed the initial visual assessment, the decreasing proportion of probable LoFRs assigned by assessors who more frequently used a resistance drilling tool in practice was intuitive. With visual assessments, however, the trend was inverted: the proportion of probable LoFRs increased with assessors who more frequently used a resistance drilling tool. It was not clear why this occurred. It may reflect assessors being accustomed to using simple and advanced tools to detect decay rather than focusing on a tree’s outward visual appearance. But previous studies have found for several species that visual assessment of a tree’s appearance often aligned with the extent of internal decay [
14,
15,
17].
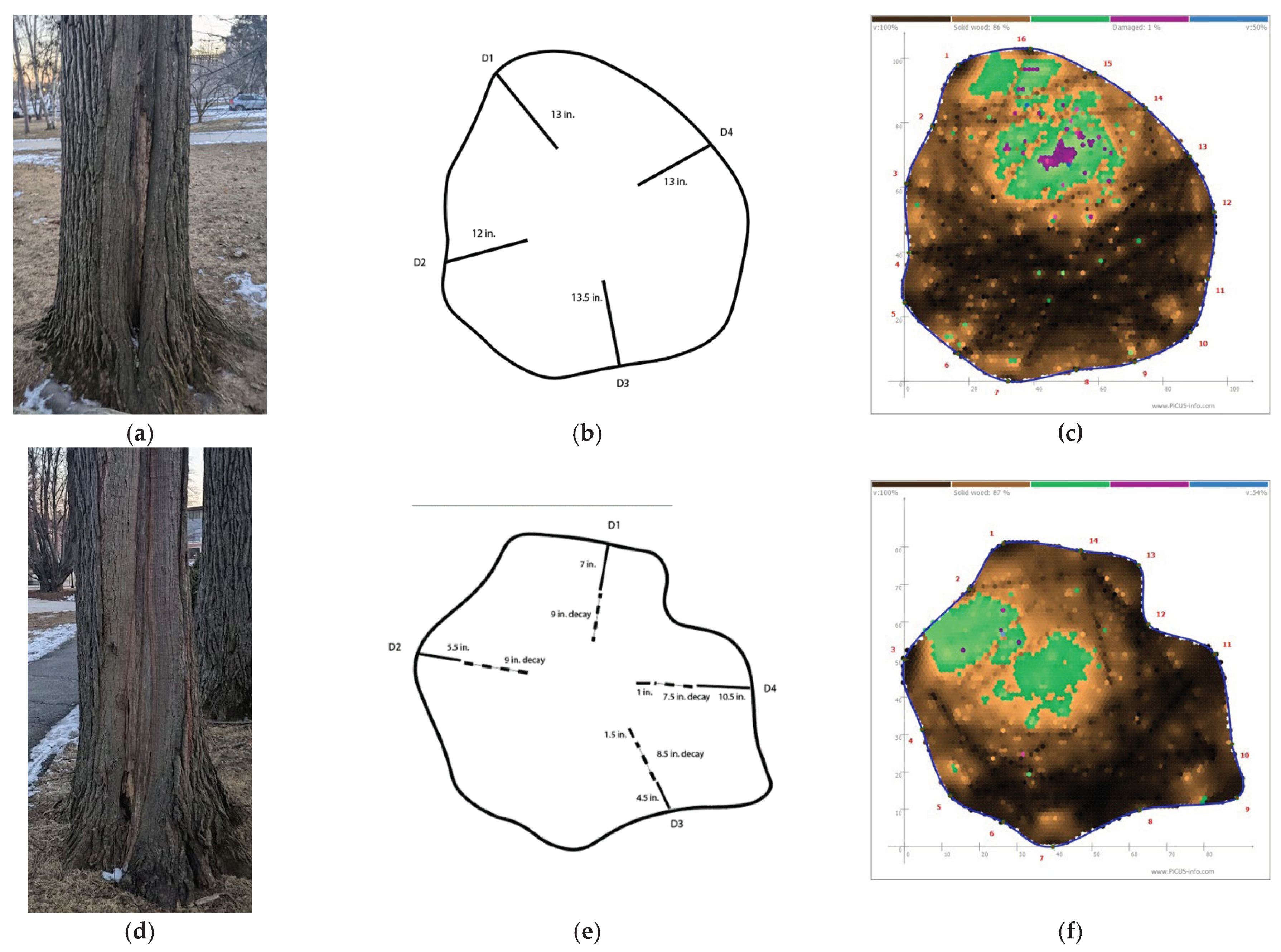
Statistically significant differences, however, do not imply that trends applied to all trees, assessors, and techniques. Trees 3 and 4 (
Figure 9) highlighted both the advantage of using more than one technique to assess likelihood of failure due to stem decay and the challenges of individual assessment techniques. Both trees were
Q.
bicolor with nearly identical DBH; they were in the same location and presumably exposed to the same wind loads. Both trees also showed signs of past lightning strikes, with woundwood formed around the lightning damage, and superficial trunk decay. Their tomograms showed nearly identical percentages of sound wood (86% and 87%) but with areas of green indicating intermediate velocities and the possibility of decay. The Resistograph output for tree 3 (
t/
R ≥ 0.59, average
t = 30 cm) aligned neatly with the tomogram, confirming—at least for an assessor who appreciates the nuanced interpretation of green areas using the SoT1 setting—that the extent and severity of decay were minimal. But the Resistograph output for tree 4 (minimum
t/
R = 0.22, average
t = 18 cm) contradicted the tomogram: the extent and severity of decay presented more of a concern. The detailed description of each tree was reflected in the changes in LoFR: LoFRs assigned following the Resistograph and tomogram assessments decreased compared to the initial visual assessment of tree 3, but LoFR of tree 4 decreased compared to the initial visual assessment only following the tomogram assessment.
Individual trees also illustrated the limitations of using simple tools and techniques. Trees 14 and 26 (both P. strobus) thwarted assessors’ attempts to assess the extent of decay by sounding the trunk with a mallet, even though all but one assessor “often” sounded trunks in practice. Following the mallet assessment, the LoFR of each tree increased from the visual assessment. Assessors described the trunk as sounding hollow, but the advanced techniques revealed little decay. There were only five P. strobus in the study; that two were problematic suggests that sounding with a mallet may not be reliable for some species. Future studies should investigate this technique’s reliability.
Previous studies have shown that risk assessments are prone to bias related to an assessor’s training, experience, and perceptions of risk [
25,
41,
42,
43]. To manage subjectivity, clear definitions of categories in a risk matrix (e.g., the four LoFRs in [
13]) [
44] and sufficient training to calibrate assessors [
45] are imperative. Yet despite assessors (i) holding the TRAQ credential (which requires continual training to obtain and maintain), and (ii) receiving more information about the extent of decay through five successive assessments of stem decay, some variation among their LoFRs persisted. For most trees and all assessment techniques, assessors assigned two or three LoFRs, and the non-significant beta dispersion test demonstrated that obtaining more information about the extent of decay did not reduce assessors’ variation, aligning with the findings of [
42]. None of the covariates that described assessors’ experience adequately explained this finding. We speculate that this reflects the innate imprecision of assessing likelihood of failure. The persistent variation in LoFRs in our study and [
42] may not be as problematic as one might suppose because studies have shown that assigned LoFRs were broadly consistent with measured likelihood of failure following storms [
46,
47].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.K.; methodology, B.K., and N.B.; formal analysis, A.O., B.K., M.C-M., N.B., and D.B.; investigation, A.O., J.C., and B.K.; resources, B.K. N.B., D.B., and J.C.; data curation, B.K. and M.C-M.; writing—original draft preparation, B.K. and A.O.; writing—review and editing, B.K., N.B., J.C., M.C-M., and D.B.; visualization, B.K., M.C-M., N.B., and D.B.; supervision, B.K.; project administration, A.O. and B.K.; funding acquisition, B.K. and N.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
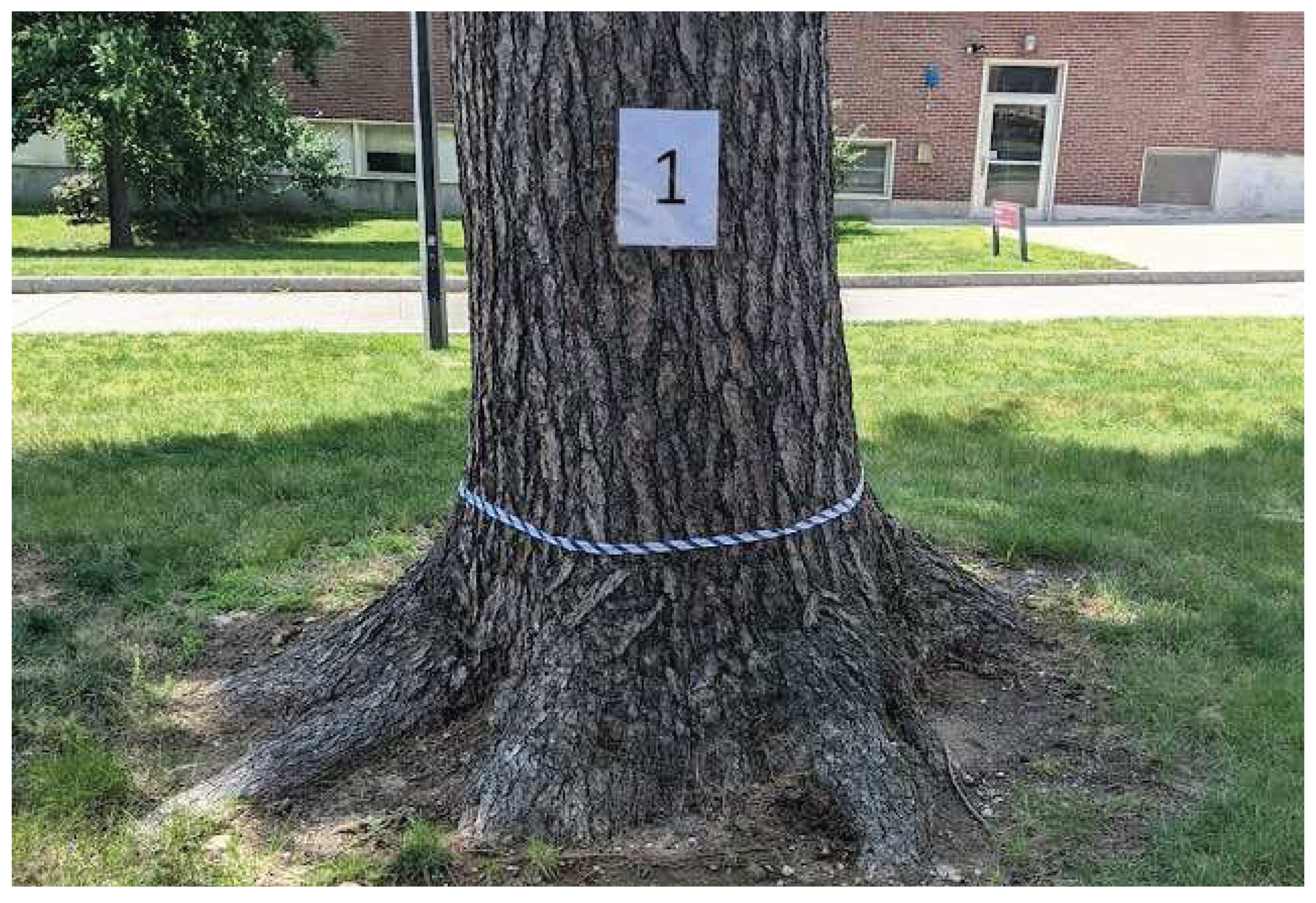
Figure 1.
lower trunk of tree 1 (Pinus strobus) with flagging to indicate the height at which the Resistograph drillings and tomograms were taken.
Figure 1.
lower trunk of tree 1 (Pinus strobus) with flagging to indicate the height at which the Resistograph drillings and tomograms were taken.
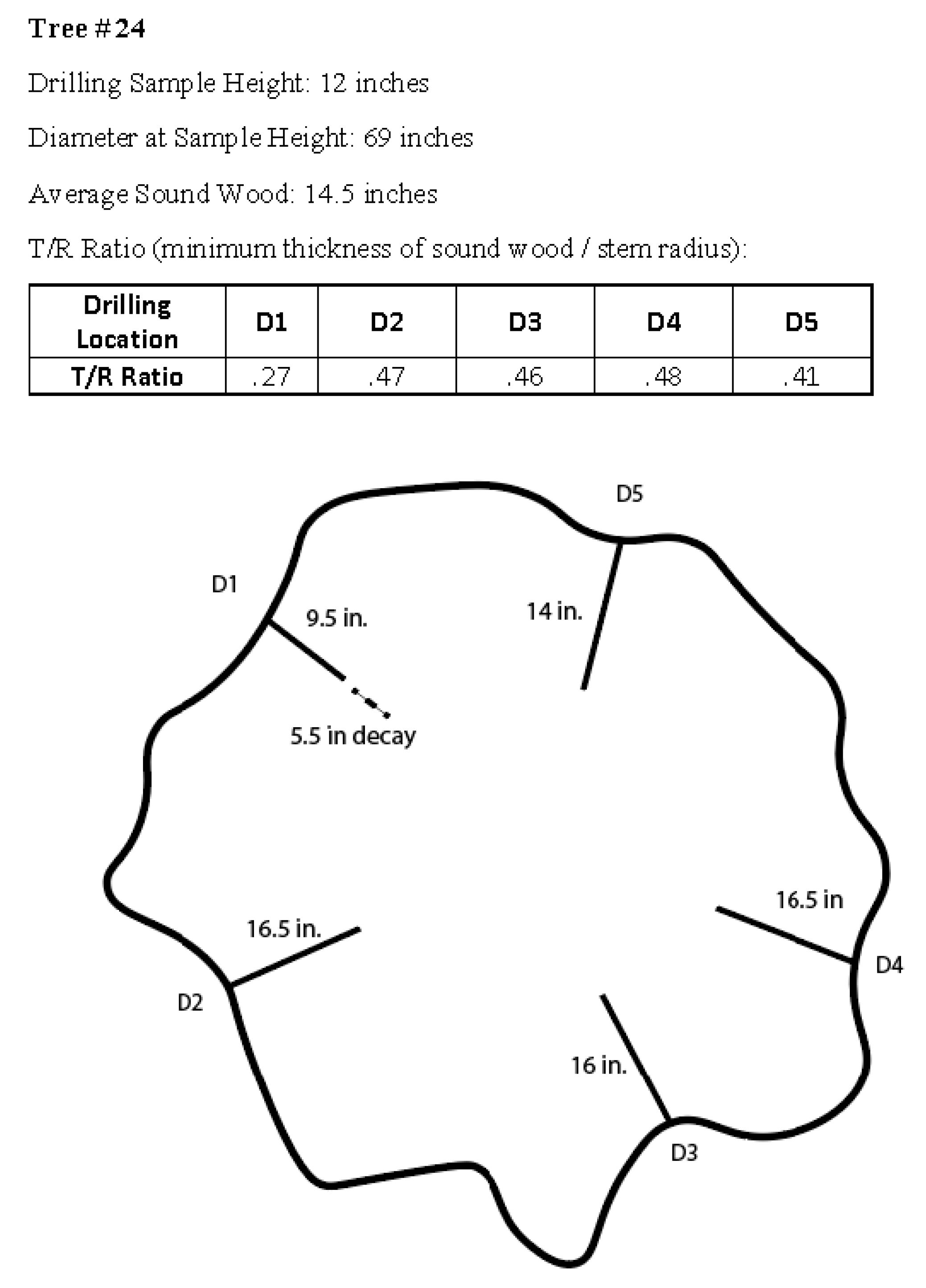
Figure 2.
Output of Resistograph for tree 24, including the height at which the trunk was drilled, the diameter at that height, the average sound wood thickness from five drillings, and the ratio of sound wood thickness (T) to trunk radius (R) at each drilling (D) location.
Figure 2.
Output of Resistograph for tree 24, including the height at which the trunk was drilled, the diameter at that height, the average sound wood thickness from five drillings, and the ratio of sound wood thickness (T) to trunk radius (R) at each drilling (D) location.
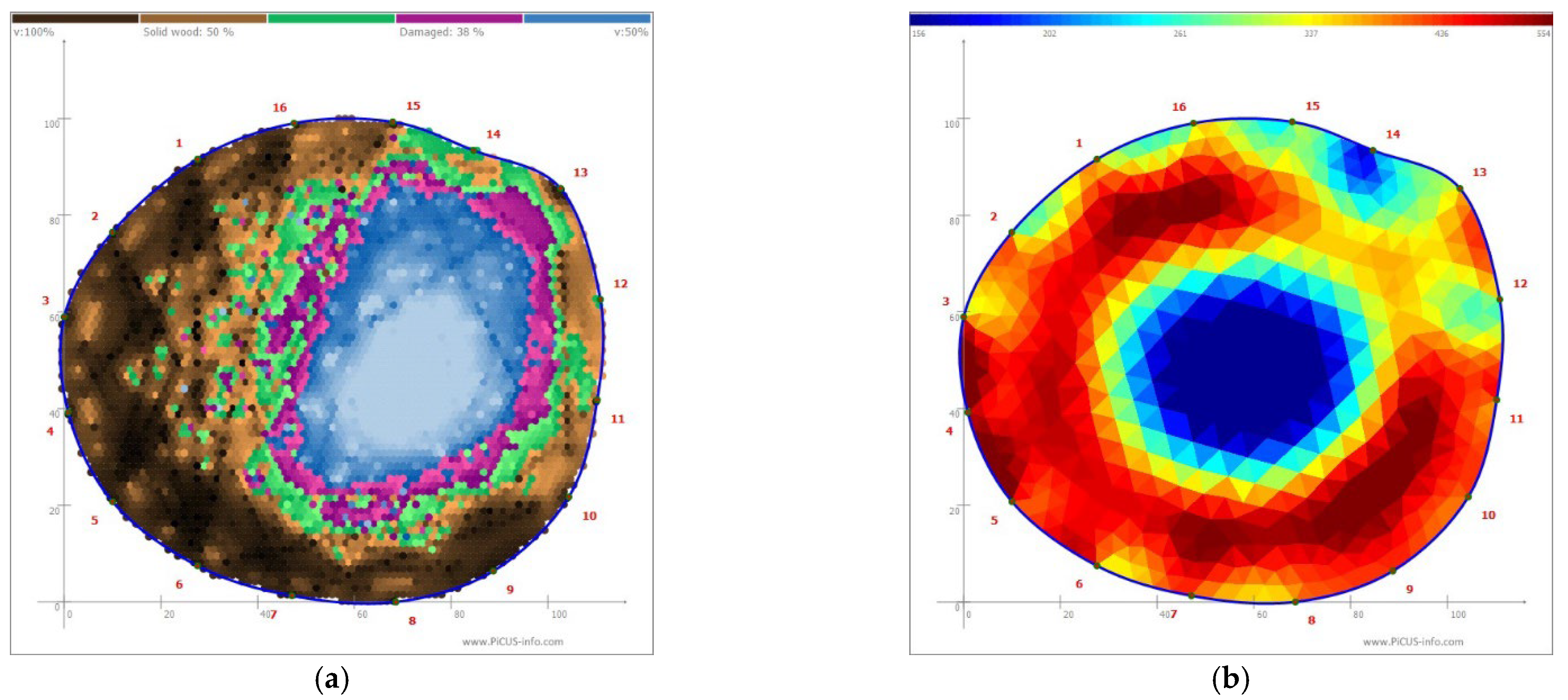
Figure 3.
(a) Sonic and (b) electrical resistance tomograms of a tree; color coding along the top margin of the sonic tomogram indicates the areas of sound (in brown) and damaged (in violet and blue) wood expressed as proportions of the total cross-sectional area. Areas of green in the sonic tomogram represent intermediate velocities that are not utilized by the software to report the “damaged” cross sectional area. In the ER tomogram, areas of relatively lower electrical resistance (higher relative conductivity) appear as blue, while relatively higher resistance appear as red.
Figure 3.
(a) Sonic and (b) electrical resistance tomograms of a tree; color coding along the top margin of the sonic tomogram indicates the areas of sound (in brown) and damaged (in violet and blue) wood expressed as proportions of the total cross-sectional area. Areas of green in the sonic tomogram represent intermediate velocities that are not utilized by the software to report the “damaged” cross sectional area. In the ER tomogram, areas of relatively lower electrical resistance (higher relative conductivity) appear as blue, while relatively higher resistance appear as red.
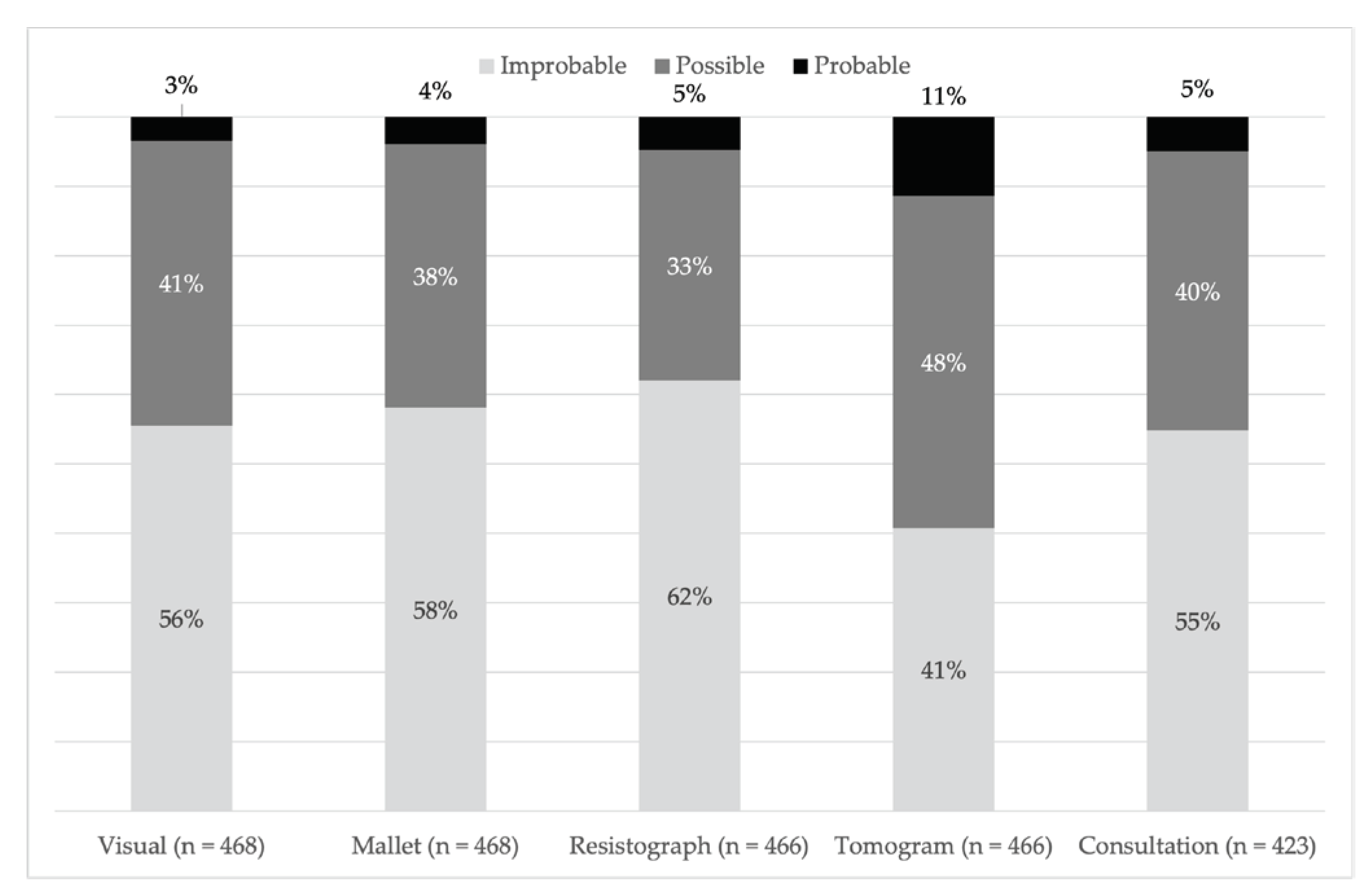
Figure 4.
Proportional likelihood of failure ratings assigned following each assessment technique, which are listed, from left to right, in the order they were conducted for odd-numbered trees. For even-numbered trees, the tomogram assessment was conducted before the resistance drill assessment.
Figure 4.
Proportional likelihood of failure ratings assigned following each assessment technique, which are listed, from left to right, in the order they were conducted for odd-numbered trees. For even-numbered trees, the tomogram assessment was conducted before the resistance drill assessment.
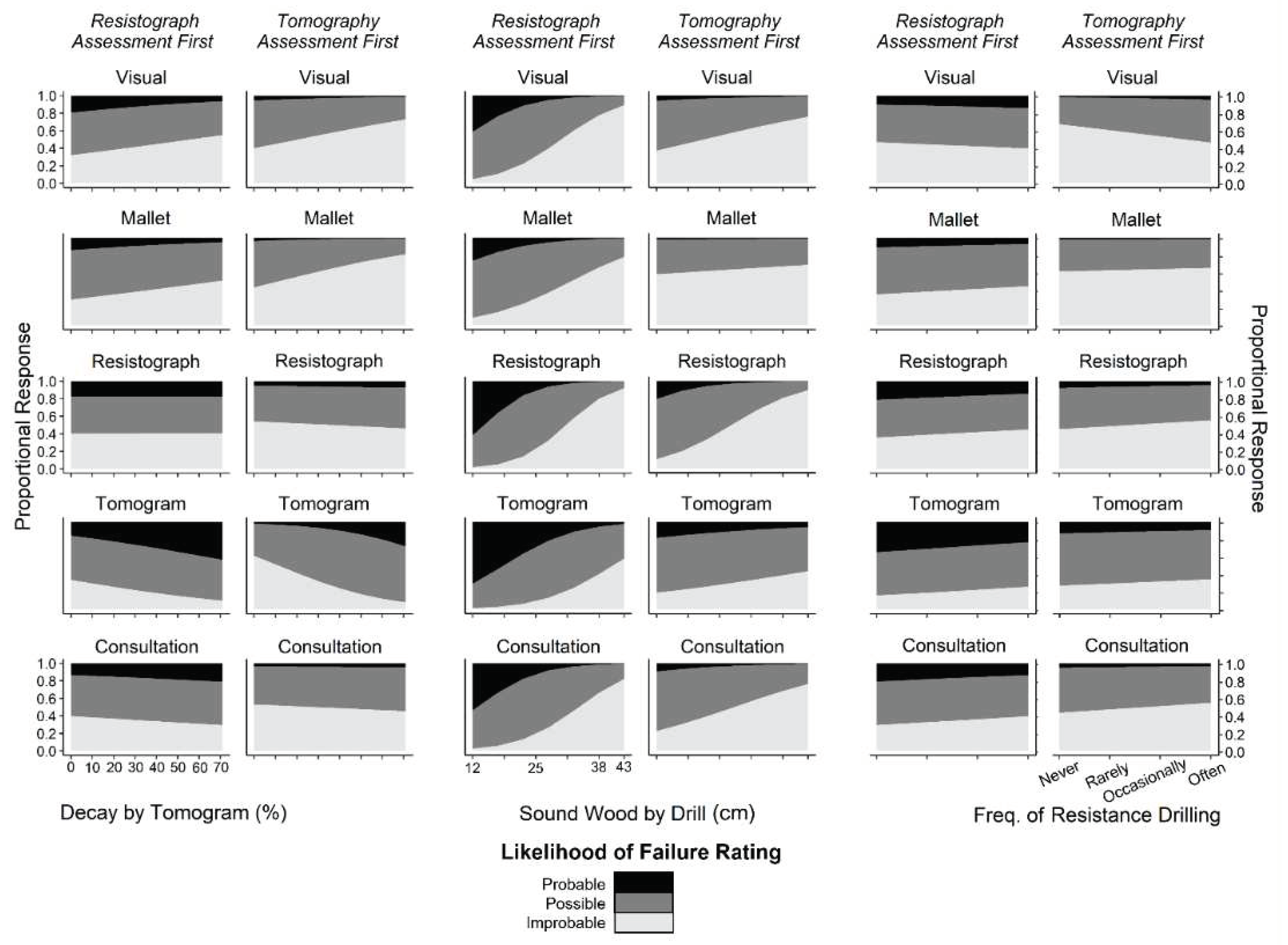
Figure 5.
Proportional response of likelihood of failure ratings—improbable (light shading), possible (gray shading), probable (black shading)—vs. continuous covariates (left-hand panels: percent of the cross-section with decay, assessed by tomography; middle panels: average thickness of sound wood, assessed by Resistograph; right-hand panels: frequency that assessors employed resistance drilling in risk assessments) for each assessment technique. The vertical ordering of plots in columns labeled “Resistograph Assessment First” indicates the order in which assessments were conducted. The order was the same for plots in columns labeled “Tomography Assessment First” except that the tomography assessment preceded the Resistograph assessment. The presentation facilitates comparison between techniques for each covariate.
Figure 5.
Proportional response of likelihood of failure ratings—improbable (light shading), possible (gray shading), probable (black shading)—vs. continuous covariates (left-hand panels: percent of the cross-section with decay, assessed by tomography; middle panels: average thickness of sound wood, assessed by Resistograph; right-hand panels: frequency that assessors employed resistance drilling in risk assessments) for each assessment technique. The vertical ordering of plots in columns labeled “Resistograph Assessment First” indicates the order in which assessments were conducted. The order was the same for plots in columns labeled “Tomography Assessment First” except that the tomography assessment preceded the Resistograph assessment. The presentation facilitates comparison between techniques for each covariate.
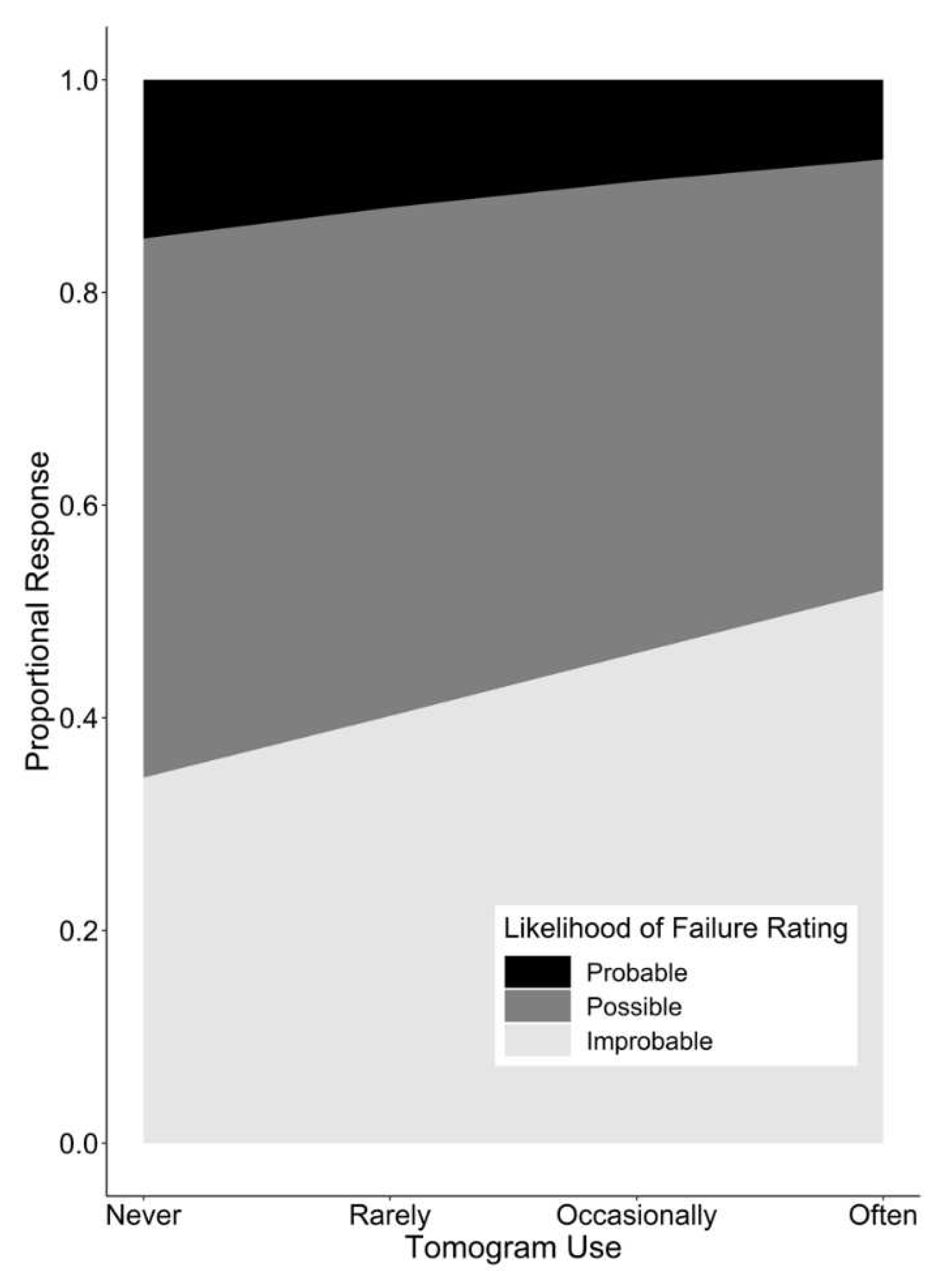
Figure 6.
Proportional response of likelihood of failure ratings as related to how frequently assessors used tomography for risk assessments.
Figure 6.
Proportional response of likelihood of failure ratings as related to how frequently assessors used tomography for risk assessments.
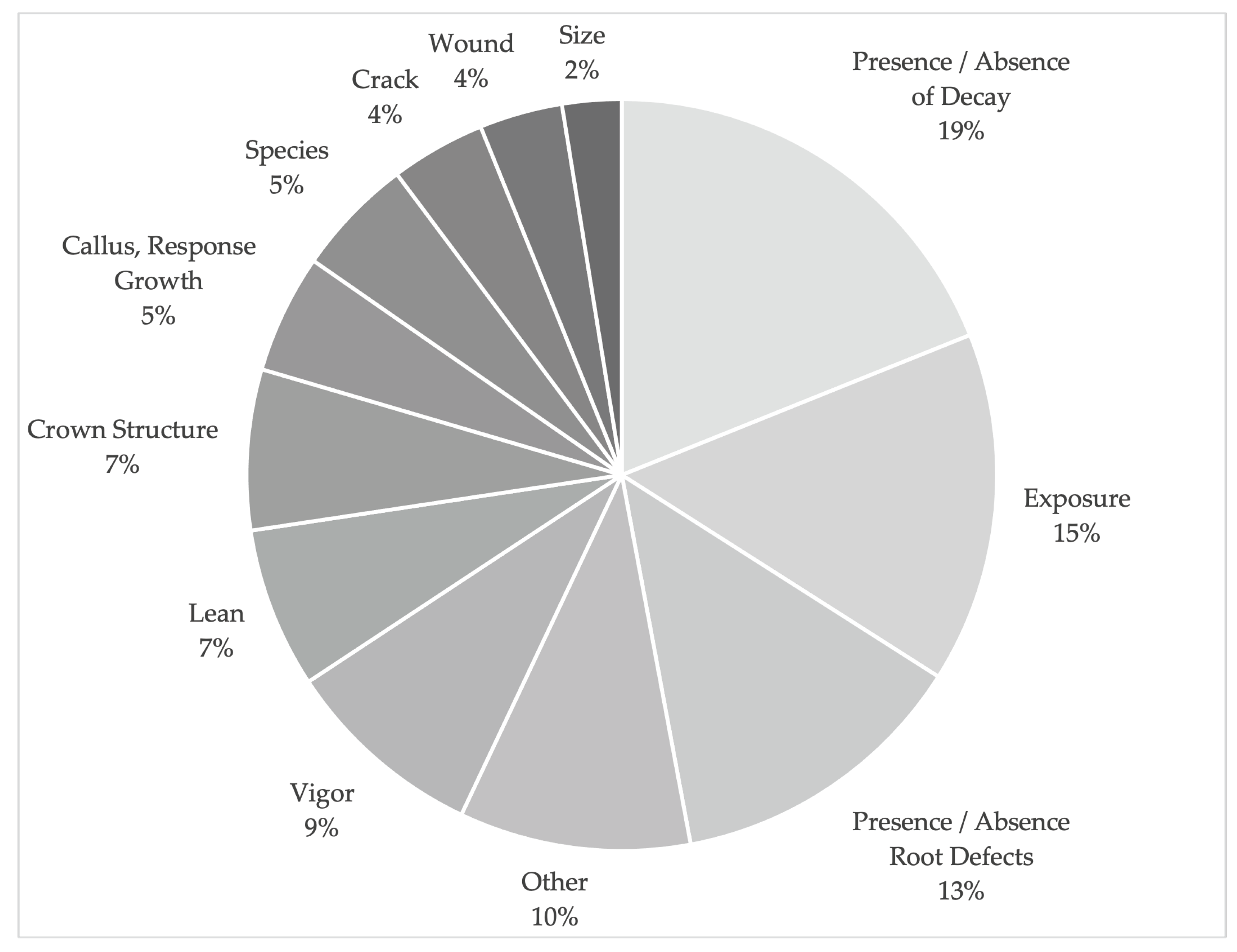
Figure 7.
Factors that assessors reported as influencing their likelihood of failure ratings.
Figure 7.
Factors that assessors reported as influencing their likelihood of failure ratings.
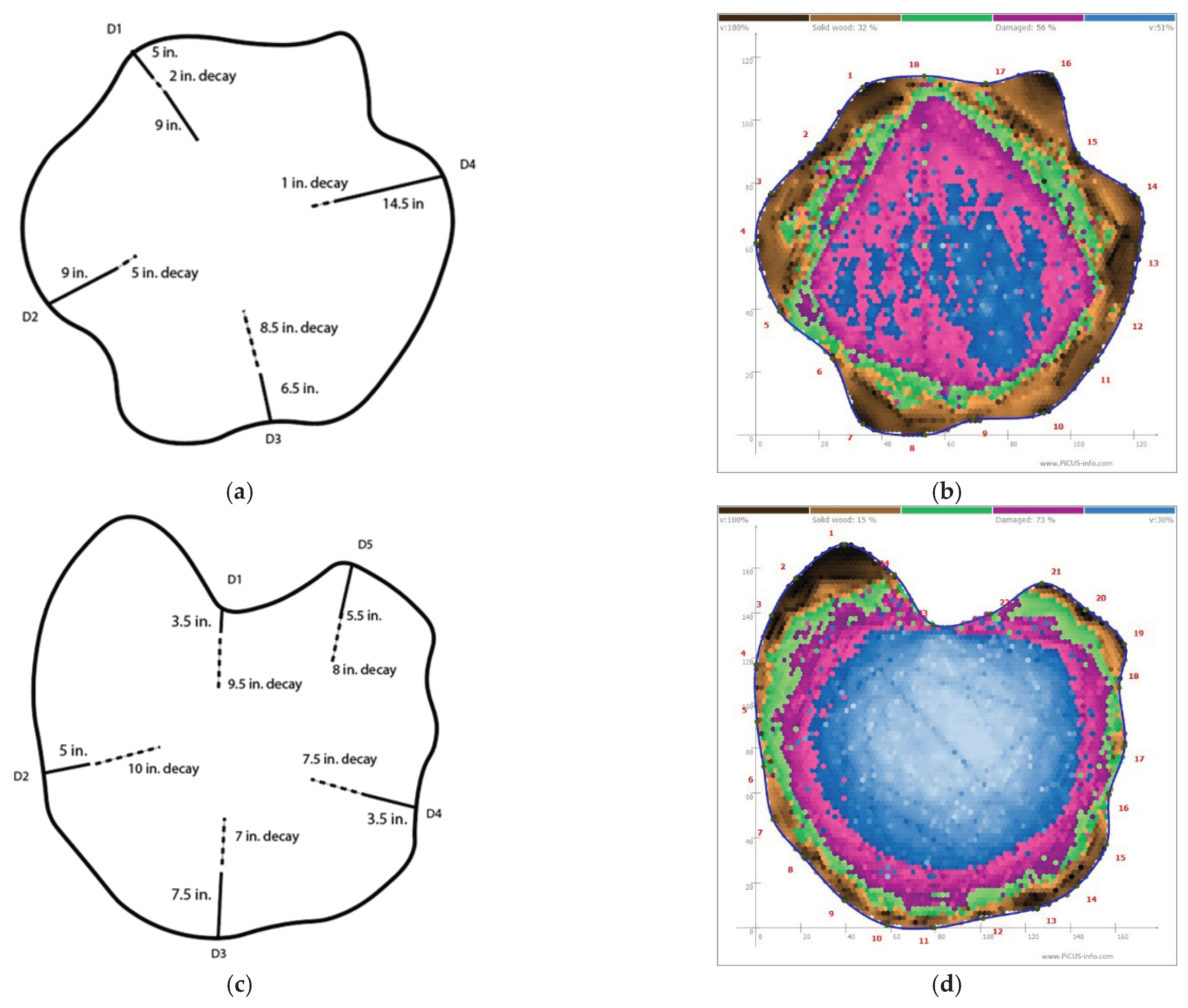
Figure 8.
(a) Resistograph output of tree 22; (b) tomogram of tree 22; (c) Resistograph output of tree 27; (d) tomogram of tree 27.
Figure 8.
(a) Resistograph output of tree 22; (b) tomogram of tree 22; (c) Resistograph output of tree 27; (d) tomogram of tree 27.
Figure 9.
(a) Tree 3 in situ; (b) Resistograph output of tree 3; (c) tomogram of tree 3; (d) Tree 4 in situ; (b) Resistograph output of tree 4; (c) tomogram of tree 4.
Figure 9.
(a) Tree 3 in situ; (b) Resistograph output of tree 3; (c) tomogram of tree 3; (d) Tree 4 in situ; (b) Resistograph output of tree 4; (c) tomogram of tree 4.
Table 1.
Assessors’ (n = 18) frequency of use with techniques and tools used in the study.
Table 1.
Assessors’ (n = 18) frequency of use with techniques and tools used in the study.
| Inquiry |
Never |
Rarely |
Occasionally |
Often |
| How frequently do you conduct basic visual risk assessments? |
0 |
0 |
1 |
17 |
| How frequently do you use a sounding mallet when conducting risk assessments? |
0 |
0 |
2 |
16 |
| How frequently do you use a resistance recording drill when conducting risk assessments? |
2 |
4 |
4 |
8 |
| How frequently do you use a sonic tomography system when conducting risk assessments? |
1 |
5 |
5 |
7 |
Table 2.
Morphological data for individuals of the two genera (Pinus and Quercus) in the study, including tree number, species, diameter 1.4 m above ground (DBH), tree height, crown width, height of tomography and Resistograph, mean thickness (t) of sound wood from Resistograph, minimum ratio of thickness of sound wood to stem radius (t/R), percentage of the stem cross-section with decay (% Decay) from the sonic tomogram, and percentage loss in section modulus (% ZLOSS) from Burcham et al. (2019).
Table 2.
Morphological data for individuals of the two genera (Pinus and Quercus) in the study, including tree number, species, diameter 1.4 m above ground (DBH), tree height, crown width, height of tomography and Resistograph, mean thickness (t) of sound wood from Resistograph, minimum ratio of thickness of sound wood to stem radius (t/R), percentage of the stem cross-section with decay (% Decay) from the sonic tomogram, and percentage loss in section modulus (% ZLOSS) from Burcham et al. (2019).
| Tree |
Species |
DBH (cm) |
Height (m) |
Width (m) |
Sample Height (cm) |
t (cm) |
t/R
|
% Decay |
% ZLOSS
|
| 1 |
P. strobus |
89 |
24 |
14 |
50 |
31 |
0.5 |
26 |
16 |
| 2 |
Q. bicolor |
84 |
20 |
28 |
30 |
25 |
0.5 |
0 |
0 |
| 3 |
Q. bicolor |
71 |
17 |
15 |
30 |
31 |
0.6 |
1 |
1 |
| 4 |
Q. bicolor |
69 |
17 |
13 |
30 |
18 |
0.2 |
13 |
0 |
| 5 |
Q. palustris |
122 |
23 |
24 |
30 |
34 |
0.3 |
36 |
47 |
| 6 |
Q. rubra |
76 |
17 |
9 |
30 |
29 |
0.2 |
18 |
21 |
| 7 |
Q. rubra |
152 |
23 |
26 |
30 |
23 |
0.0 |
32 |
14 |
| 8 |
Q. alba |
81 |
20 |
18 |
30 |
41 |
0.8 |
0 |
0 |
| 9 |
Q. alba |
84 |
18 |
17 |
30 |
37 |
0.6 |
26 |
19 |
| 10 |
P. strobus |
71 |
21 |
12 |
40 |
38 |
1.0 |
0 |
0 |
| 11 |
Q. palustris |
84 |
23 |
19 |
30 |
40 |
0.6 |
49 |
32 |
| 12 |
Q. bicolor |
91 |
20 |
14 |
30 |
36 |
0.1 |
40 |
77 |
| 13 |
Q. bicolor |
91 |
23 |
14 |
30 |
30 |
0.3 |
63 |
54 |
| 14 |
P. strobus |
97 |
24 |
16 |
100 |
45 |
0.9 |
0 |
0 |
| 15 |
P. strobus |
66 |
20 |
11 |
50 |
38 |
1.0 |
0 |
4 |
| 16 |
Q. alba |
61 |
19 |
8 |
30 |
34 |
0.7 |
0 |
0 |
| 17 |
Q. palustris |
91 |
23 |
19 |
40 |
33 |
0.0 |
44 |
23 |
| 18 |
Q. palustris |
97 |
25 |
23 |
40 |
20 |
0.0 |
53 |
65 |
| 19 |
Q. alba |
107 |
21 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
0.6 |
71 |
73 |
| 20 |
Q. velutina |
107 |
18 |
17 |
60 |
30 |
0.5 |
0 |
0 |
| 21 |
Q. velutina |
145 |
26 |
25 |
50 |
22 |
0.0 |
65 |
92 |
| 22 |
Q. velutina |
104 |
21 |
23 |
30 |
22 |
0.2 |
56 |
35 |
| 23 |
Q. bicolor |
155 |
27 |
30 |
30 |
38 |
0.3 |
44 |
65 |
| 24 |
Q. rubra |
124 |
21 |
27 |
30 |
37 |
0.3 |
66 |
88 |
| 25 |
Q. palustris |
102 |
23 |
19 |
30 |
41 |
0.5 |
51 |
85 |
| 26 |
P. strobus |
86 |
21 |
16 |
100 |
31 |
0.0 |
6 |
n/a 1
|
| 27 |
Q. rubra |
132 |
24 |
17 |
40 |
13 |
0.1 |
73 |
85 |
| 28 |
Q. velutina |
74 |
20 |
10 |
30 |
33 |
0.2 |
12 |
20 |
| 29 |
Q. velutina |
84 |
21 |
15 |
40 |
41 |
0.8 |
33 |
22 |
| 30 |
Q. velutina |
94 |
24 |
17 |
40 |
30 |
0.0 |
37 |
81 |
| Overall Mean |
96 |
21 |
18 |
40 |
32 |
0.39 |
31 |
35 |
| Odd-numbered trees 2
|
105 |
22 |
19 |
36 |
33 |
0.41 |
41 |
42 |
| Even-numbered trees 3
|
88 |
21 |
17 |
43 |
31 |
0.37 |
20 |
28 |
Table 3.
Analysis of variance table for the ordinal logistic regression model used to predict likelihood of stem failure rating from the main effect of assessment technique, covariates that quantified the random effects of trees and assessors, and their interactions; the table includes the χ2 value of the likelihood ratio (LR) and the degrees of freedom (Df) and p-value of the effect or interaction.
Table 3.
Analysis of variance table for the ordinal logistic regression model used to predict likelihood of stem failure rating from the main effect of assessment technique, covariates that quantified the random effects of trees and assessors, and their interactions; the table includes the χ2 value of the likelihood ratio (LR) and the degrees of freedom (Df) and p-value of the effect or interaction.
| Effect |
LR χ2
|
Df |
p-value |
| Technique |
93.87 |
9 |
<0.0001 |
| % Decay in cross-section |
0.005 |
1 |
0.9419 |
| Mean sound wood thickness |
0.006 |
1 |
0.9404 |
| Frequency of using a resistance drill |
0.001 |
1 |
0.9780 |
| Frequency of using tomography |
4.279 |
1 |
0.0386 |
| Genus |
2.474 |
1 |
0.1157 |
| Technique * % decay in cross-section |
167.3 |
9 |
<0.0001 |
| Technique * mean sound wood thickness |
42.70 |
9 |
<0.0001 |
| Technique * frequency of using a resistance drill |
27.47 |
9 |
0.0012 |
Table 4.
Analysis of variance table for beta dispersion tests for homogeneity of variance among (a) assessors’ self-reported frequency of sonic tomography use for tree risk assessment and (b) assessment techniques.
Table 4.
Analysis of variance table for beta dispersion tests for homogeneity of variance among (a) assessors’ self-reported frequency of sonic tomography use for tree risk assessment and (b) assessment techniques.
| |
Parameter |
Df |
Sum Sq |
Mean Sq |
F-value |
p-value |
| (a) |
Groups |
17 |
0.07237 |
0.004257 |
1.1438 |
0.3173 |
| |
Residuals |
162 |
0.60294 |
0.003722 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (b) |
Groups |
3 |
0.00041 |
0.000135 |
0.0393 |
0.9896 |
| |
Residuals |
176 |
0.60547 |
0.003440 |
|
|
Table 5.
Distribution of the number of different likelihood of failure ratings (LoFRs) within each assessment technique.
Table 5.
Distribution of the number of different likelihood of failure ratings (LoFRs) within each assessment technique.
| |
Assessment Technique 1
|
| Number of LoFRs |
Visual |
Mallet |
Resistograph |
Tomogram |
Consultation |
| 1 |
0 |
5 |
5 |
2 |
4 |
| 2 |
23 |
14 |
20 |
15 |
23 |
| 3 |
7 |
11 |
5 |
13 |
3 |
Table 6.
For each assessment technique, the distribution of assessors’ responses to the question Did the technique change your likelihood of failure rating?
Table 6.
For each assessment technique, the distribution of assessors’ responses to the question Did the technique change your likelihood of failure rating?
| |
Assessment Techniques After Visual Assessment 1
|
| Response |
Mallet |
Resistograph |
Tomogram |
Consultation |
| Yes |
210 |
252 |
270 |
170 |
| No |
223 |
165 |
153 |
178 |
Table 7.
For each tree and the four assessment techniques that followed the initial visual assessment (n = 120), the ratio () of the weighted mean change in likelihood of failure rating (LoFR) from the initial visual rating to the proportion of unchanged ratings for the tree and technique. Values in the upper quartile (underlined) indicate higher LoFRs than the initial visual assessment; values in the lower quartile (bolded) indicate lower LoFRs. Interquartile values in plain text indicate unchanged LoFRs.
Table 7.
For each tree and the four assessment techniques that followed the initial visual assessment (n = 120), the ratio () of the weighted mean change in likelihood of failure rating (LoFR) from the initial visual rating to the proportion of unchanged ratings for the tree and technique. Values in the upper quartile (underlined) indicate higher LoFRs than the initial visual assessment; values in the lower quartile (bolded) indicate lower LoFRs. Interquartile values in plain text indicate unchanged LoFRs.
| Tree |
Consistent Basic Assessment 1
|
Consistent Advanced Assessment 2
|
Consultation Confirmed 3
|
Mallet |
Drill |
Tomogram |
Consultation |
| 1 |
No |
Yes |
Neither |
0.60 |
0.46 |
1.11 |
0.42 |
| 2 |
No |
Yes |
Advanced |
-0.29 |
-0.38 |
-0.29 |
-0.31 |
| 3 |
Yes |
Yes |
Advanced |
0.00 |
-0.70 |
-0.42 |
-0.78 |
| 4 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
-0.20 |
0.31 |
-0.30 |
-0.08 |
| 5 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
-0.13 |
-0.13 |
0.78 |
0.18 |
| 6 |
No |
Yes |
Advanced |
-0.45 |
0.20 |
0.20 |
-0.11 |
| 7 |
No |
No |
Neither |
-0.38 |
0.27 |
0.56 |
0.00 |
| 8 |
Yes |
Yes |
n/a |
-0.14 |
-0.20 |
-0.14 |
-0.23 |
| 9 |
Yes |
No |
Neither |
-0.17 |
-0.29 |
2.60 |
0.50 |
| 10 |
Yes |
Yes |
Advanced |
-0.09 |
-0.80 |
-0.80 |
-0.36 |
| 11 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
0.33 |
0.08 |
0.89 |
0.44 |
| 12 |
No |
No |
Neither |
-0.27 |
-0.27 |
0.83 |
-0.14 |
| 13 |
Yes |
Yes |
Advanced |
0.25 |
0.78 |
6.00 |
0.60 |
| 14 |
No |
No |
Neither |
1.50 |
-0.30 |
0.00 |
0.09 |
| 15 |
Yes |
Yes |
n/a |
0.22 |
-0.25 |
-0.25 |
-0.20 |
| 16 |
Yes |
Yes |
n/a |
-0.07 |
-0.07 |
-0.07 |
-0.07 |
| 17 |
Yes |
Yes |
Advanced |
-0.15 |
0.50 |
2.20 |
0.75 |
| 18 |
Yes |
Yes |
Advanced |
0.00 |
3.67 |
6.00 |
3.33 |
| 19 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
-0.18 |
-0.18 |
4.00 |
0.00 |
| 20 |
No |
Yes |
Advanced |
-0.86 |
-6.00 |
-6.00 |
-3.67 |
| 21 |
Yes |
Yes |
Advanced |
0.29 |
0.63 |
2.50 |
0.50 |
| 22 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
-0.08 |
0.44 |
13.00 |
0.20 |
| 23 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
0.30 |
-0.38 |
0.57 |
0.40 |
| 24 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
-0.17 |
0.08 |
2.20 |
0.18 |
| 25 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
0.33 |
0.09 |
1.00 |
0.25 |
| 26 |
No |
Yes |
Advanced |
0.75 |
-0.67 |
-0.43 |
-0.80 |
| 27 |
No |
No |
Neither |
-0.50 |
0.43 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
| 28 |
No |
Yes |
Advanced |
-0.40 |
-3.67 |
-2.50 |
-2.25 |
| 29 |
Yes |
No |
Basic |
0.27 |
-0.27 |
0.09 |
-0.20 |
| 30 |
Yes |
Yes |
n/a |
-0.17 |
-0.11 |
0.40 |
0.25 |