1. Introduction
Intergovernmental negotiations have been underway for nearly three decades to address climate change, in which India has been an active player. India’s announcement that it aims to reach net zero emissions by 2070 [
1,
2] and to meet 50% of its electricity requirements from renewable energy (RE) sources by 2030 [
3] is a hugely significant moment for the global fight against climate change [
4]. India’s first pledge, to the Paris Agreement also known as a Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC), had one of the targets to have 40% of installed electric power from non-fossil-based energy resources by 2030 [
5]. The country now stands committed to reducing the emissions intensity of its GDP by 45% by 2030, from the 2005 level, and achieving about 50% cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030 [
3]. In this context, the National Solar Mission has also been launched by the Government of India (GoI) in 2010 with an initial target of 20 GW for solar power by the end of the year 2022 [
6] which was revised and further raised to 100 GW in 2015 [
7]. Out of this 100 GW capacity, 60 GW capacity has been targeted through ground-mounted utility-scale solar projects and 40 GW is envisaged to meet through rooftop solar (RTS) projects [
8,
9].
To achieve these targets the Indian Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has also allocated specific capacity targets (see:
Table S1 of the supplementary information (SI)) to each state in India [
10]. The states have notified their policies and regulations to encourage end users to adopt RTS in order to achieve the targets [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. In addition to the federal government policies, almost every state in India through their respective State Nodal Agencies (SNAs) also launched RTS policies and regulations (see:
Table S2). Furthermore, MNRE has also set separate goals to boost the adoption of RTS in the residential sector and announced the phase-II scheme of grid-connected RTS implementation [
16]. Under this scheme, a 40 GW capacity of RTS installations by the end of 2022 has been targeted. The target of 40 GW has been divided and allocated to all states in the country (see:
Table S1).
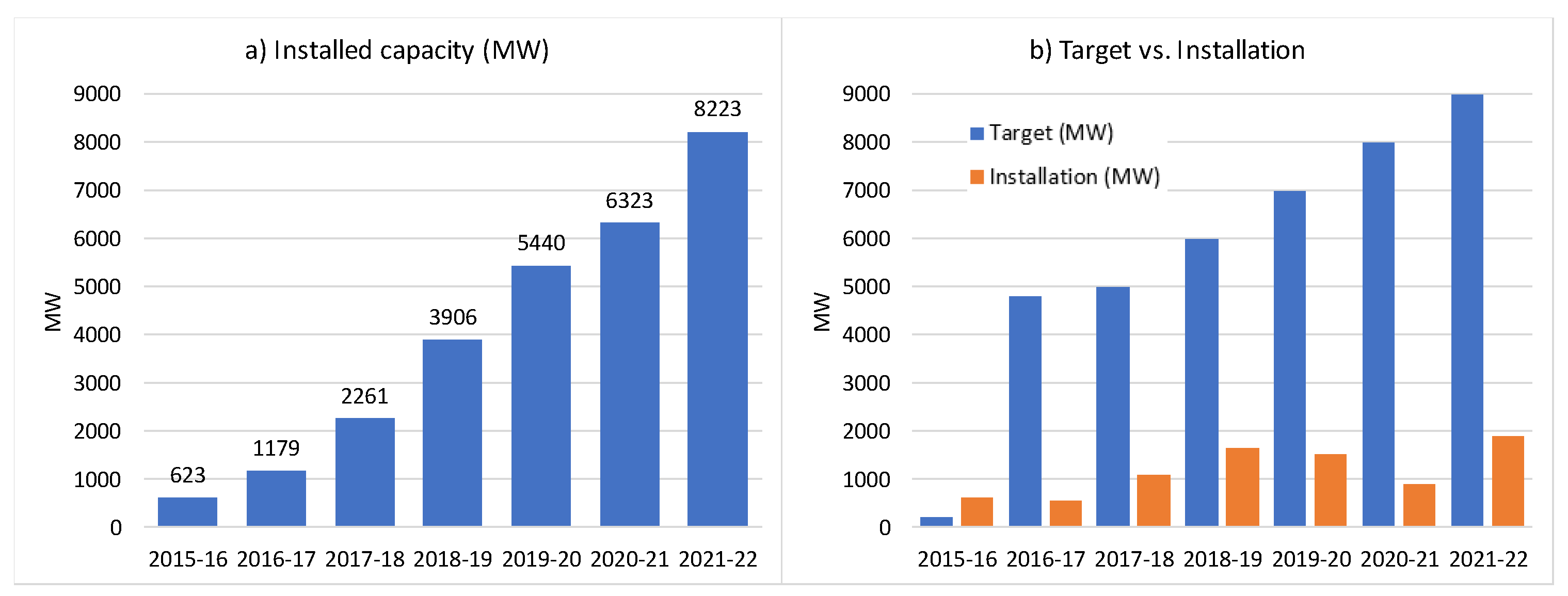
Figure 1 presents the year-wise implementation of RTS projects in India a) capacity and b) targets vs actual implementation [
17]. The RTS target of 40 GW does not seem to be approachable on a set timeframe by end of 2022 as country has only achieved approximately 8 GW of RTS installations. Since, target set by the GoI on RTS segment (cumulative 40 GW) has not been achieved even till 2022, the same has been extended up to 2026.
There exists a significant potential for RTS across the country as indicated by several studies [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. A study carried out by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) has estimated about 352 GW of technical potential and nearly 210 GW of economic potential in urban settlements of India [
20]. The total realistic market potential for rooftop solar PV in urban settlements of India is estimated to be around 124 GW [
20]. Joshi et al. [
21] assessed approximately 1815 TWh rooftop solar potential for India, based on a high-resolution global spatiotemporal assessment. As indicated in
Figure 1, the progress of the RTS sector is very slow compared to the anticipated targets. At the end of 2022, the total RTS installed capacity in India was approximately 8.2 GW which is about 20% of the total RTS target of 40 GW by 2022 in the country [
25]. Several authors [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31] analyzed various factors which affect the growth and development of both the utility and RTS markets in India. These studies emphasize analyzing RTS policies and various business models adopted for the growth of the RTS sector [
32] and highlighted the key challenges faced by the RTS segment in India [
27,
28,
29].
Several policy and regulatory initiatives have been undertaken to promote RTS in India, including the provision of subsidies for residential consumers and net metering regulations. About 20 states have introduced dedicated solar policies and net metering regulations to facilitate the scaling up and adoption of grid connected RTS across different consumer categories. However, there exist critical barriers to the growth and development of RTS in India, prevailing at the grass root level like lack of awareness about the technology, lack of transparency in implementing the policies, lack of coordination among different stakeholders or implementing agencies [
30,
31,
32,
33]. The information technology (IT) in RE brings with it a set of tools, expertise, insight and support that may prove invaluable [
34]. In fact, the combination of energy and IT innovations and renewable energy’s growing competitiveness are transforming the landscape of energy services [
35]. IT resources optimize the resources required to support the business and will reduce paper usage [
36,
37,
38]. Implementing agencies, SNAs, the distribution utilities can work towards demand aggregation as well and improve the deployment of the RTS through a systematic, non-tedious and least time-consuming approach through IT interventions that will facilitate execution of RTS programs in large range of consumers. In this context, the scope for IT interventions in the existing RTS implementation process of the Odisha Renewable Energy Development Agency (OREDA) has been assessed and a simplistic approach has been developed in this case study for the execution of the RTS projects in relatively lesser time with the least human interface as well as resources.
The paper is set out as follows:
Section 2 highlights the key barriers to the RTS implementation in India whereas
Section 3 focuses on key Stakeholders in Odisha state for rooftop implementation.
Section 4 discusses the current process for RTS implementation in Odisha state of India whereas
Section 5 summarizes the limitations of the existing approach to RTS implementation in Odisha. A novel approach highlighted in this study with the use of information technology in the implementation of RTS projects in Odisha state is highlighted in section 6.
Section 7 summarizes ongoing initiatives for RTS implementation at the Central and State level using IT interventions and finally,
Section 8 concludes.
2. Barriers to the RTS Implementation in India
As mentioned above, the RTS sector faces several barriers viz. rigidness for net-metering by the electricity distribution companies, bankability, smaller capacities to scale up, limited manpower/skill within the implementation agencies, and most prominently the conventional approach of project installation being adopted by the executive agencies [
39,
40,
41,
42]. The following sub-sections highlight key barriers those affected the progress of RTS installation in India:
2.1. Lack of awareness among end customers
The lack of awareness, information, and knowledge of solar energy among households in India is a major barrier to the growth and development of the RTS segment [
42,
43,
44]. Since the initial cost of RTS installation is comparatively high, therefore the central /state government is providing 30%
1 capital subsidies to the residential RTS systems [
44]. In 2020, the average cost of a residential RTS system in India was US
$658 per kilowatt (kW), declining by 73% from the 2013 level. In comparison, in 2020, the residential rooftop solar cost in leading residential markets, such as Japan, the United Kingdom, Switzerland and the U.S., was 3.3 to 6.4 times that of India [
23].
Due to the lack of awareness about RTS systems [
24], lack of education, and poor training and development mechanisms, people cannot take benefits of capital subsidies and other State support. As per a survey conducted by Mercom Capital Group, 64% of interviewed households in rural areas and about 39.5% of the households in urban areas have no idea about renewable energy and government support [
45]. Several authors [
28,
46,
47] highlighted that the government has to prepare a robust mechanism to educate, aware, and train people about the State support and benefits of RTS technology.
2.2. Lack of clarity in rooftop solar policies
Some states have announced policies for the RTS systems [
13,
48], but there is a significant lack of clarity in these policies. There is very slow progress on net metering
2 policy across the country. It has been found that the average time to take an RTS connection is as high as 120 to 150 days in some states [
49]. The local implementing authorities or SNAs are facing a lack of appropriate training and process protocol as a result, they are unable to deliver proper services for installing RTS systems to the customers. There is no clear roadmap of permit mechanisms, commercial agreements, and technical requirements and therefore the RTS segment is still largely unexploited. International examples show that effective net-metering implementation can increase RTS adoption by as much as 50% [
49,
50]. The solar rooftop policies need an urgent overhaul to make them more user-friendly and this will be only possible when there is proper coordination between SNAs, State Electricity Regulatory Commission (SERC), and the DISCOM. In addition, policy and regulatory uncertainties still remain major barriers to faster penetration of RTS systems [
28,
51]. For example, initially the RTS sector was driven by the capital subsidy which was later made sector specific by the respective central/state governments. Moreover, several changes took place in the RTS segment, especially for commercial and industrial consumers (gross metering, net metering, FiT, open access etc.) that creates a lot of communication gaps at the ground level [
52,
53,
54,
55]. In fact, the SNAs are unable to update their processes in short time spans.
2.3. Poor technical or commercial skills
In order to achieve the 40 GW rooftop solar target India requires 210,800 skilled plant design and site engineers and approximately 624,600 semi-skilled and low-skilled technicians for construction [
56]. The lack of access to education, training, and availability of a skilled workforce for the development of RTS is because of limited institutional capacities for workforce training [
57].
2.4. Challenges to implementation agencies and other stakeholders
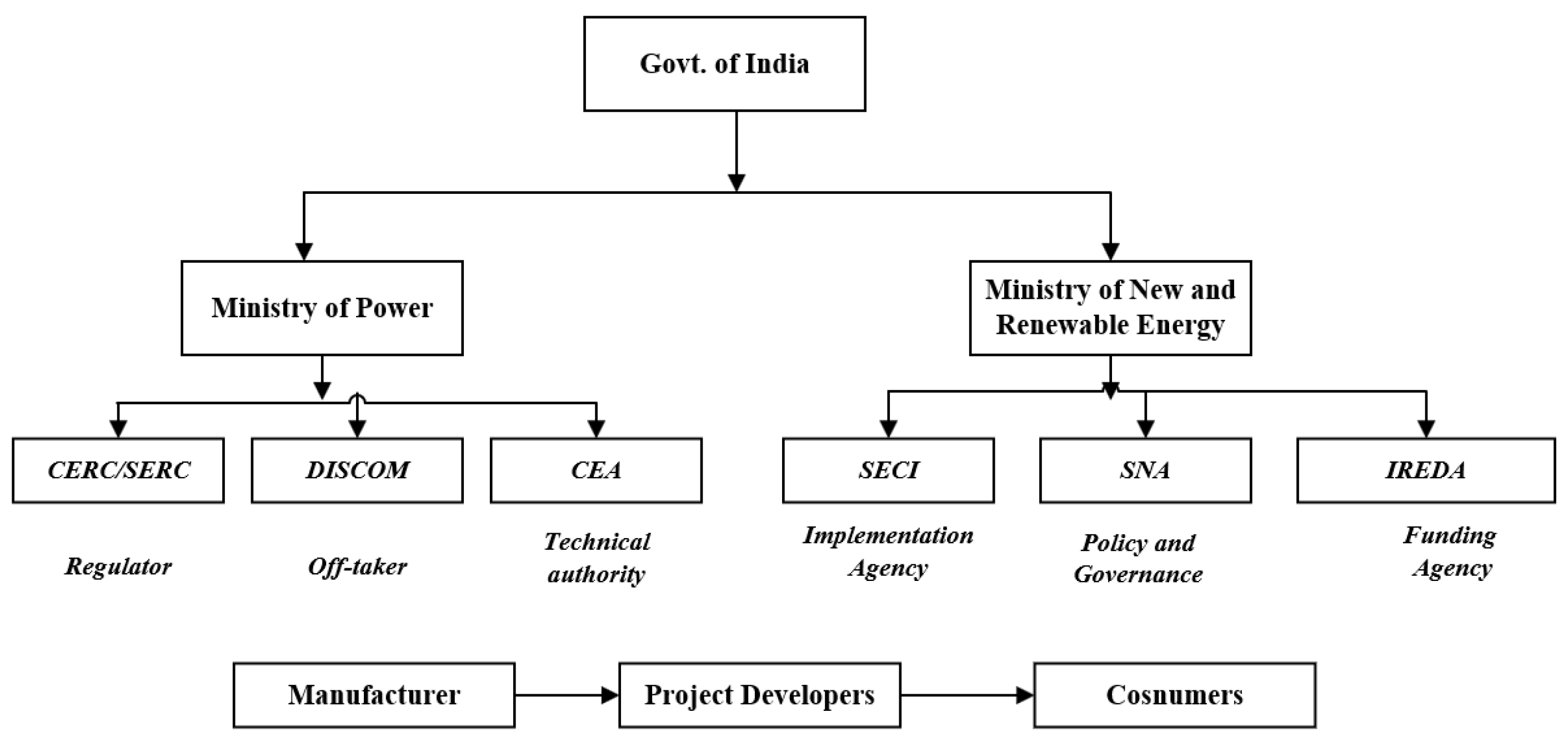
Figure 2 presents different agencies and stakeholders and their roles in RTS implementation in India. It’s worth mentioning that institutional mechanism is well established in India where every agency has assigned specific roles and responsibilities as shown in
Figure 2, to execute the RTS projects. Implementation of RTS projects requires mutual coordination of all these agencies such as the regulatory commissions, DISCOMS (on metering and approvals), SNAs (release of subsidy), financial institutions (banks for loan), urban/municipal local bodies (building byelaws), the rooftop owner (access to roofs), Developers/ Aggregators / EPC contractors (project implementation and maintenance), etc. which mostly delayed the overall process. DISCOMS/Utility also faced challenges in terms of revenue loss as electricity bills were reduced from paying customers mainly in the commercial and industrial sectors. There are also Challenges to SNAs and DISCOMS to handle RTS projects of smaller and medium capacities (residential and institutional sectors), due to lack of awareness, manual and conventional ways to handle the projects, limited technical manpower, managing the subsidy disbursement through minimum technical due diligence, etc. Demand aggregation is challenging on behalf of project developers as it is difficult to identify enthusiastic and financially capable customers.
2.5. Miscellaneous constraints at potential locations
Apart from the reason mentioned above, location specific miscellaneous constraints (i.e., technical or non-technical) also affect the adoption of RTS. As an example, most of the potential locations for RTS in India are the cities with high population density and with huge electricity demand. In 2008, GoI introduced a city specific programme “Development of Solar Cities” [
58]. Under this programme 60 cities in India have been identified for the rapid implementation of rooftop solar. However, this programme does not attain popularity and success. For example, out of the 532,000 properties with RTS potential in Nagpur (a city with adequate solar insolation), only 2,528 (0.47%) have actually installed RTS system, 2,187 residential and 341 non-residential, commercial or mixed use [
59]. As an incentive, the city's municipal corporation offers a 5% discount on property tax for those using RTS systems but even that has not helped much. Again, the reasons reported for poor implementation were high costs, tedious application and installation procedures, and tardy delivery of services. Another constraint is somehow non-technical though well justified. A large share of the population resides in multi-story buildings in these cities. In these buildings, although each resident has an identical electricity meter, most of them have limited or no access to rooftop area. As a result, potential aspirants may not adopt RTS systems due to non-technical reasons.
There is a lag in capacity addition even though most Indian states have comprehensive net and gross metering regulations (see:
Table S2). This could be because these regulations vary across states and most states not only restrict the maximum capacity of RTS systems [
12], but also have a cap on the amount of power that can be fed back into the grid, which affects the project economics.
3. Key Stakeholders in Odisha for rooftop implementation
As mentioned in the previous section, the implementation of RTS in India is executed through multiple agencies in an inclusive mode and this is similar in the case of Odisha as well. The multiple agencies (
Table 1) and their role in the implementation of RTS projects in Odisha are described in the following subsections.
3.1. The State Nodal Agency: Odisha Renewable Energy Development Agency (OREDA)
The SNAs (i.e., OREDA for the state of Odisha) are the state-owned bodies, primarily responsible for the implementation of MNRE policies, targets on the RE mix, and its overall promotion including RE projects. SNAs implement RE projects in the states by providing policy framework, identifying and providing monitorial support or incentive to individuals/groups for development and achieving the Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) targets set by GoI [
60,
61,
62]. Thus, in general, SNAs are the primary organizations that are leading the RTS program in the states along with the joint contribution and role of other local agencies such as DISCOMS, SERC, etc.
3.2. Urban local bodies
Urban local bodies have the responsibility of urban planning, framing regulations of land use and construction of buildings, planning for economic and social development, and ensuring services like public health, sanitation conservancy, solid waste management, etc. As a part of urban planning and ensuring public health, reducing GHG emissions and promoting RE is also a focus area of ULBs. Under the building byelaws, regulation of land use, etc. the ULBs have the authority to mandate consumers for installing RE projects and provide incentives (if required) to encourage more participation. GoI has also designed the Solar City program to support/encourage ULBs to prepare a roadmap to guide their cities in becoming ‘renewable energy cities’ or ‘solar cities’ [
63]. For RTS, the main challenges that ULBs face were identified as a) lack of ULB-focused policies, programs, and targets; b) lack of consumer awareness; c) lack of amendment, adaption, and enforcement of existing building byelaws; d) limited PV installations at ULB establishments; e) coordination gap among ULBs, SNAs and smart cities; and f) lack of financing mechanism.
3.3. Odisha Electricity Regulatory Commission (OERC)
OERC plays the role of state electricity regulator, by laying rules and framing regulations in line with the Electricity Act, of 2003 [
64]. With regards to RTS, the role of OERC is to provide clarity on the implementation framework, metering mechanism, commercial settlement, technical limitations, safety standards, fees, timelines, etc. through Regulations/Orders. OERC sets the framework which is to be followed by other key stakeholders toward the implementation of RTS in Odisha.
3.4. Distribution utility (DISCOM)
The role of distribution utilities is to provide connectivity of the RTS system with the utility grid and to carry out metering/billing activities post-installation. During the process of installation, DISCOMs also play a crucial role through site inspection, safety approvals, synchronization/commissioning approvals, etc. The role of DISCOM becomes more crucial as it is directly interacting with consumers. Hence, DISCOM also has to ensure connectivity with consumers through proper communication channels.
3.5. Consumer/applicant
At the end of the process chain, the end consumer/applicant uses the electricity generated by the RTS system. The role of the applicant is also very crucial, it has to ensure the feasibility of the RTS system based on its consumption and availability of roof space. The consumer must also be aware of the key business models, application process, applicable incentive/subsidy from State or Central government, cost economics, competent vendors, etc. The consumer must also be conversant with operations and periodic maintenance of the RTS project. Implementation of RTS involves multiple steps and approval, and coordination from the above-mentioned agencies and stakeholders. A detailed description of the typical process being adopted by OREDA for RTS implementation is mentioned in the next section.
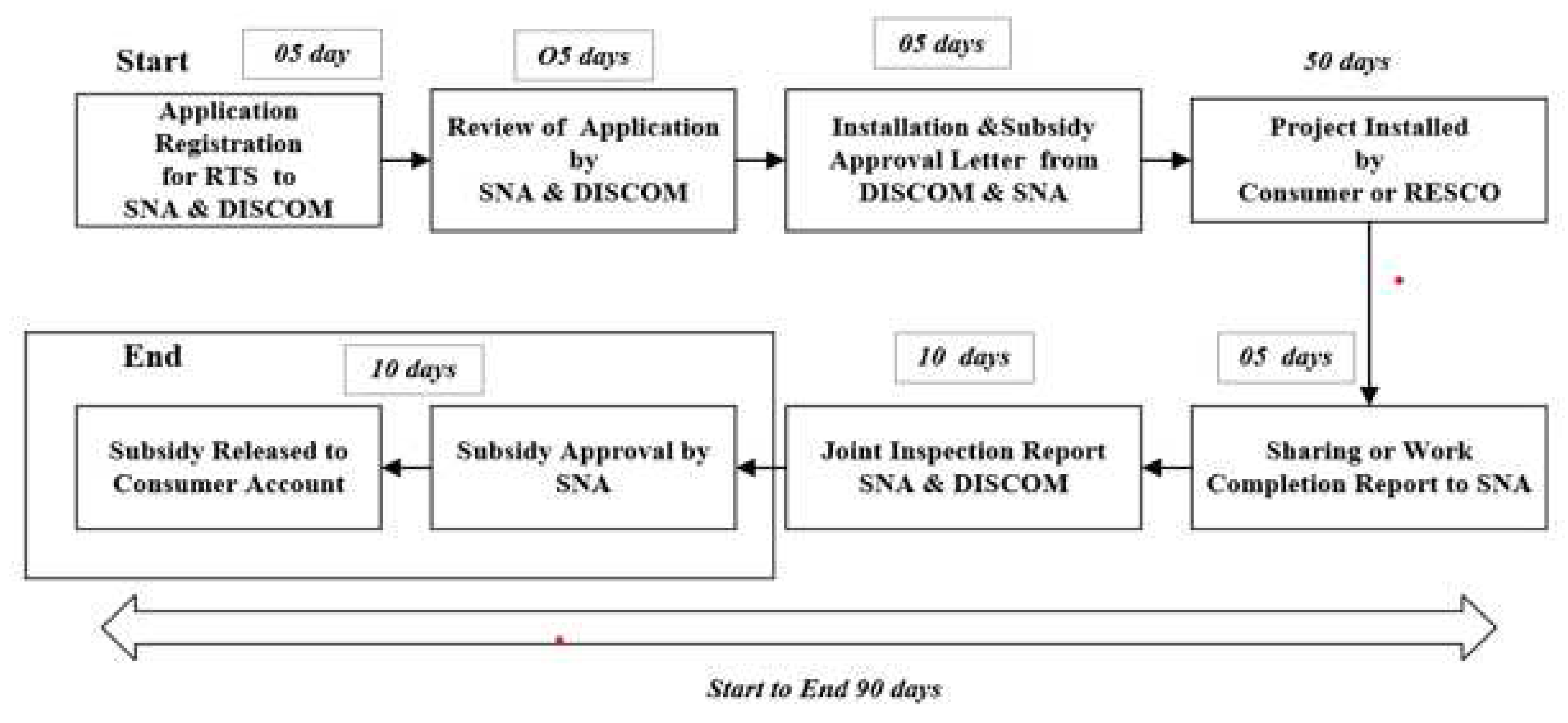
4. The existing process for the implementation of RTS in Odisha
The installation of grid-connected RE projects in India typically follows a step-by-step approach, which is initiated from information collection to project installation and subsidy disbursement [
65,
66], if applicable. It is worth mentioning that, only residential consumers of RTS are eligible for the provision of subsidies in India. The approach is almost similar in each state of the country. In this section, the existing process in the state of Odisha has been reviewed and considered as a representative case.
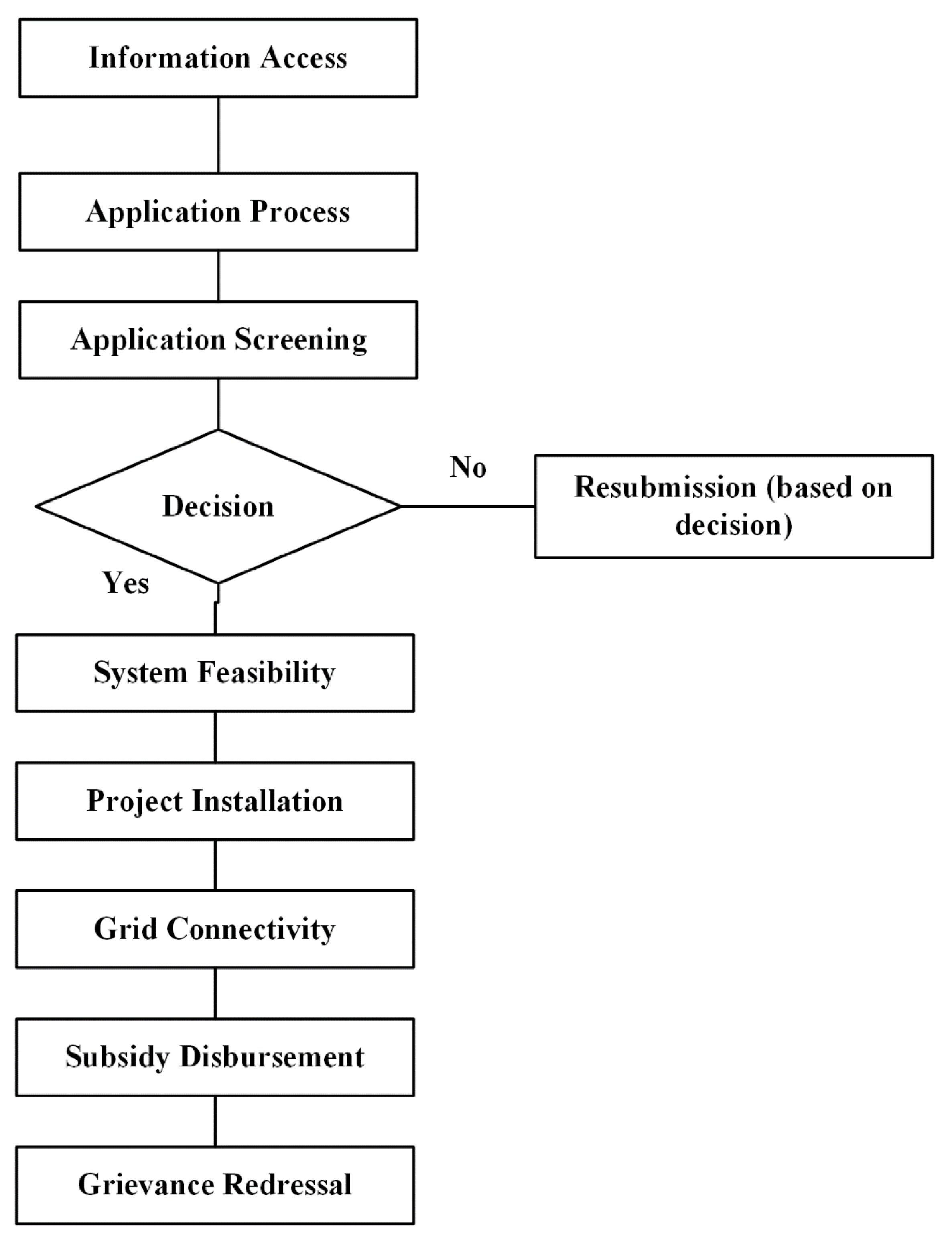
Figure 3 presents the steps involved in the implementation of RTS projects in Odisha.
4.1. Information access
This is the first step of the RTS installation process in which the consumer/applicant collects all the required information about the RTS, policy (of native state), regulation, application procedure, information about vendors/installers in the market, tentative investment, subsidy provisions, annual energy yield, and financial benefits, etc. In most cases, the above information is delivered by the Customer Relationship Centre (CRC) established by the SNA of Odisha state (i.e., OREDA) to facilitate the potential applicants on the same. Such information is delivered through the websites of OREDA or helpline numbers. Sometimes, the applicant also gets the details of empaneled vendors and channel partners who could be approached for the installations of the RTS projects that were authorized by OREDA. In addition to this, applicants require to make tedious efforts in collecting relevant information, forms/formats required for installation of RTS projects from DISCOMS or OREDA offices.
4.2. Application process
After getting all the essential information mentioned in the first step, the applicant decides to apply for the RTS project and submit an application to implementing agencies. The application along with other documents goes through the screening process usually at the Division Office of local utility and DISCOMS. In addition to grid connectivity, if the RTS project lies under the provision of a subsidy scheme then the applicant has to submit a separate form to avail of subsidy benefits to SNA. The submission of both the above-mentioned forms for grid connectivity and the subsidy was offline in Odisha.
4.3. Application screening and system feasibility
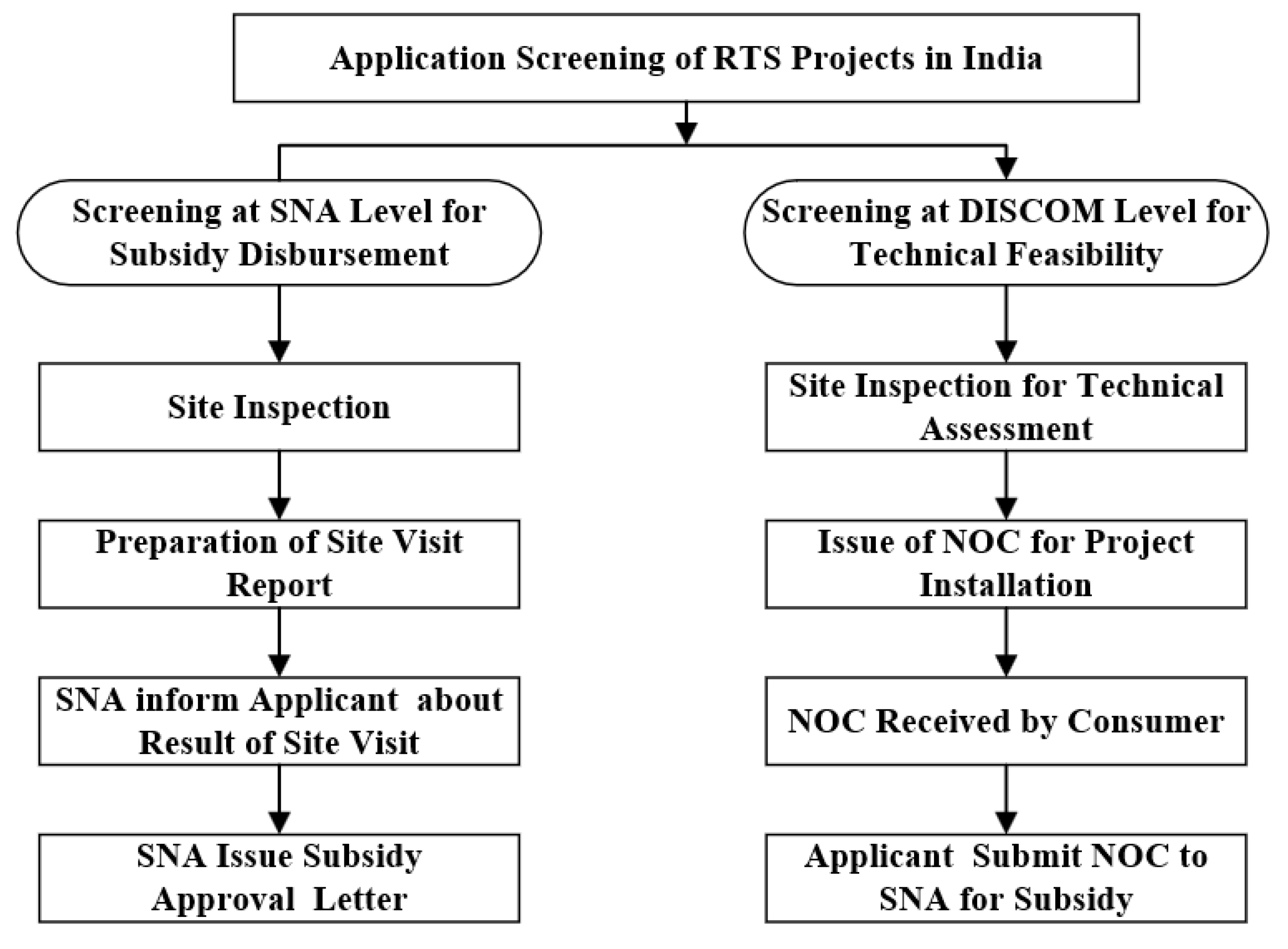
The third step after submission of the application is the review by concerned authorities as per the regulations meant for the installation of RTS projects. Such as applicant name, site/ location, the capacity of the project, sanctioned load, eligibility of the applicant for subsidy disbursement, etc. Once the general screening of the application is over, then the application is processed for technical screening at utility or DISCOMS offices. DISCOMS reviewed the technical parameters such as connected and contracted load, transformer interconnection, feeder capacity, metering details, etc. based on the specific regulations of the state where the RTS project is applied. In most of the states in India, application screening is being carried out by both the SNAs and DISCOMS. While the SNA performs general screening for subsidy disbursement the DISCOMS performs both general as well as technical screening. Under general screening, SNA officials verify the roof size, shadow-free area, proposed capacity, etc. filled in the application form.
On the other hand, generic screening on behalf of DISCOMS includes, completeness and correctness of application, and technical screening includes onsite feasibility assessment of the RTS project. Onsite feasibility assessment ensures the correctness of the application based on technical parameters such as contracted load, transformer loading, metering details, etc. As per the regulations, an onsite feasibility assessment must be carried out by the officials of DISCOMS within seven days of receiving the application. After the completion of the feasibility check a technical feasibility report is prepared and if it is found sufficient then the applicant gets a no objection certificate (NOC) to install the RTS project. The entire process of screening is illustrated in
Figure 4.
4.4. Project installation
After the completion of application screening and feasibility, the next phase is the installation of the RTS project. In Odisha, regulators provide a period of 90-180 days for project installation. The applicant procures project equipment/material directly or empaneled vendors procure the same on behalf of the applicant and install the project. After completing the project installation, a work completion certificate is issued by the vendor.
4.5. Grid connectivity
After project installation the most important “grid connectivity” step initiates. Grid connection ensures safety and quality of power. After receiving the work completion report from the applicant/ project owner, the concerned person from DISCOM conducts the site visit. During the site visit testing, commissioning, and synchronization of the RTS project are ensured. Further, after successful commissioning, a letter of synchronization is issued to the applicant.
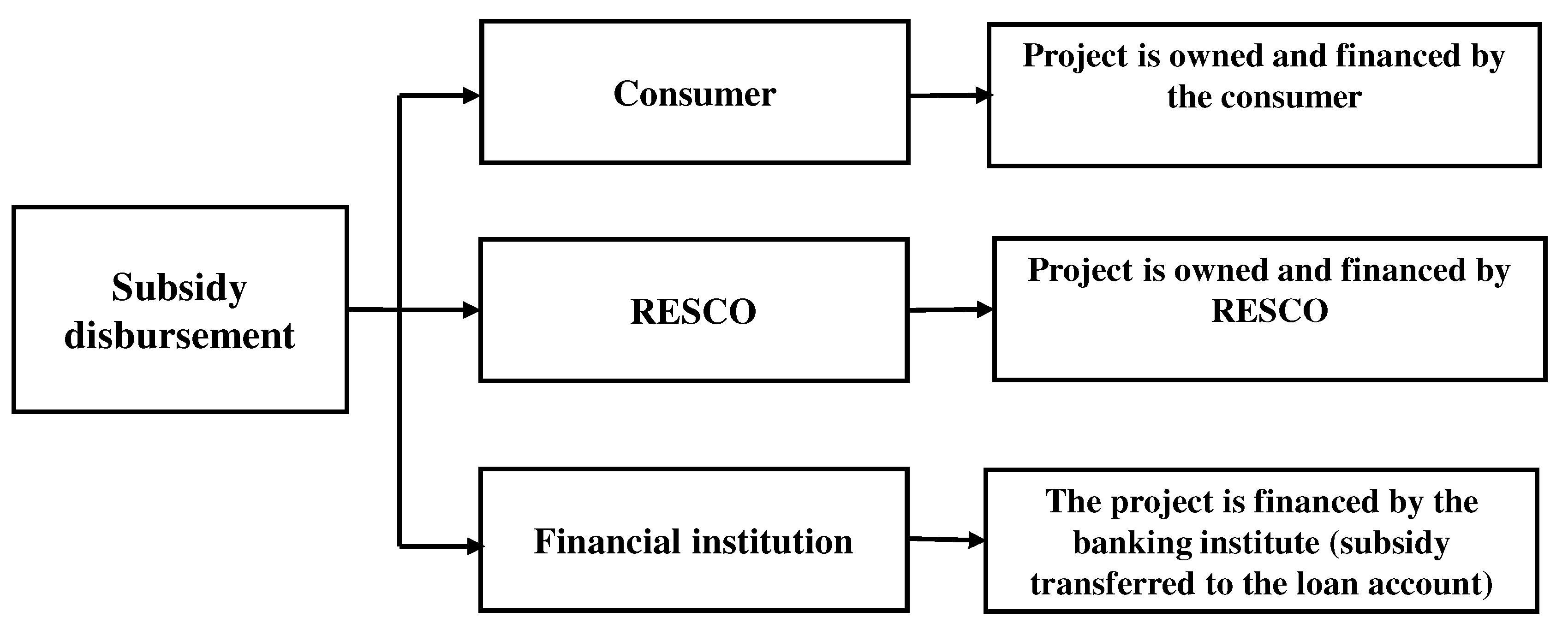
4.6. Subsidy disbursement
The disbursement of subsidies require prior approval of concerned agencies responsible for the project implementation which are SNA and DISCOMS in most cases. For the subsidy disbursement, the MNRE allocates the funds to SNAs, and SNAs further disburse the subsidy to the end consumer. Subsidy disbursement also depends on the policy of the state. The disbursement of subsidies under different scenarios of project implementation such as to consumer RESCO
4 or Financing institutions is also illustrated in
Figure 5.
In order to avail of the benefits of subsidy, after post-installation of the RTS project applicant, submits a copy of the work completion report to SNA and requests for site inspection. On a satisfactory result of the site inspection, SNA releases the subsidy to the applicant’s account. The steps involved in the overall process along with the time consumed are illustrated in
Figure 6.
4.7. Grievance redressal
This is the final step of RTS installation that incorporates the entire steps and provides support to the applicant concerning any grievance arising in the whole execution process. SNA’s established customer relationship centers, helpline numbers, etc. to help the applicant in order to resolve their grievance. In most of the states in India, consumer grievances are addressed through helpline numbers. However, if the consumer is not satisfied then he/she may approach the nodal person at local SNA offices.
5. Limitations of the Existing Approach of RTS Implementation in Odisha
The steps involved in the above
Section 4 seem to be very simple and systematic however these are very chaotic and time-consuming requiring the involvement of different agencies even for a single project installation. Moreover, the subsidy scheme seems to reduce the financial burden on the potential customers of RTS projects and make these projects financially attractive, however, availing the subsidy is quite a tedious task by itself. As it again involves the role of several government agencies such as MNRE, SNA (i.e., OREDA), local DISCOM, etc. Therefore, subsidy disbursement into the account of the applicant usually takes approximately six months to a year. The key gaps in the existing process of RTS implementation in India and recommendations provided to improve/replace the same are summarized in
Table 2.
It is evident from
Table 2, that the complex and repetitive process of RTS implementation results in a delayed response from distribution utilities, SNAs, and other concerned agencies and impacting as a huge gap in the envisaged targets and present status of RTS implementation. To overcome these gaps, there is a strong need for the adoption of an effective framework that could be well designed by analyzing the overall process of RTS implementation. The proposed framework in the next Section (i.e.,
Section 6) integrates all key stakeholders involved in the implementation of RTS projects under a single platform. However, such intervention would first require defining the role, and responsibilities of each stakeholder and finally standardizing the existing process. Thus, IT interventions could be well applied to resolve the above-mentioned challenges and to develop a novel framework for RTS implementation in Odisha, which could be further replicated in the other states of India as well.
6. IT-based RTS Implementation Approach
As mentioned in the previous sections, to boost the implementation of RTS projects and to achieve clean energy goals, especially the RPOs, stakeholders involved in the execution need to adopt state-of-the-art, and least time-consuming practices. In addition, consumers also need awareness and enhanced technical knowledge about the sector, along with cost-benefit assessment which may help them in decision-making further on the implementation of the project without hassle. These statements are well strengthened, from the barriers quoted for RTS implementation in India in the section above and concluded from the assessment carried out for the state of Odisha. Thus, to bring more efficiency to the system, it is envisaged to introduce IT interventions in the sector and to integrate all the implementing agencies in a web platform so that the whole process of applying for a project, getting approvals, connectivity, and finally disbursement of subsidy would be completed with lesser timelines and human resource.
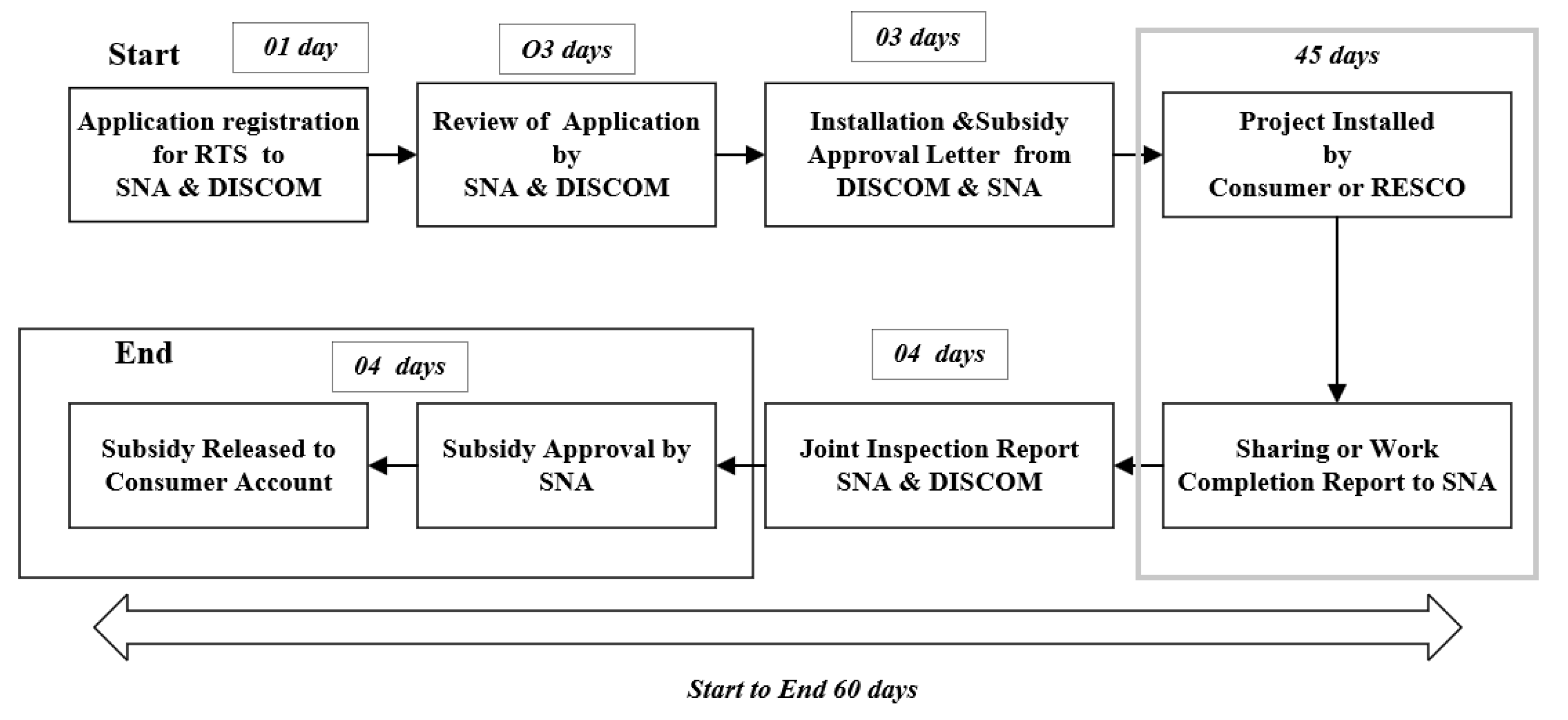
In view of the above, this section provides an IT-based approach that will optimize the time, and the role of individual agencies and makes the process/steps of RTS implementation more efficient. The proposed approach will be a combined process of all required approval and subsidy availing through a single window and several processes described in the previous sections will run in parallel. In brief, the IT-based approach will be multi-ended allowing access to different parts of project information to different stakeholders integrated into one master platform. The proposed, IT-based approach to RTS implementation in OREDA is presented in the following subsections.
6.1. Registration and application process, support on decision making
Under the proposed approach, interested customers are required to register themselves under the specified category in which they are applying for registration. In order to make an initial level of techno-commercial due diligence the IT platform may contain a solar calculator which gives the minimum technical requirements viz. annual solar irradiance, energy generation, shadow aspects, sun path, financial parameters (payback period, internal rate of return, etc.), greenhouse gas emission reduction, project cost estimates and recommendations of the key products (modules, inverters, cables, etc.) along with a high-level bill of quantity, based on few input parameters from consumer viz. geographical location, roof area, orientation, tariff, connected load, etc. This is also linked with a mobile application that consumers can directly use to make decisions.
Further, the applicant will assess the relevant information corresponding to the site, technology, sanctioned load, key equipment, solar resource at the proposed site, cost economics, business models that prevailed in the market, project developers/empaneled vendors, etc. After assessing the above information, the applicant may fill out the form. Further applicants may deposit the essential fee of SNAs online mode as a preferred option. An acknowledgment receipt of fee deposition could be downloaded from an online web platform. Further, after uploading the payment receipt, to the DISCOMS window in the web platform applicant will receive an application form for the official work of DISCOMS. In the same way, the applicant will get a subsidy application form from SNA.
6.2. Application screening and system feasibility assessment
After completion of the registration process, the application will get forwarded for technical screening. An e-mail, as well as SMS notification, could also be sent to the authorities to inform them of the same. During the screening process, both DISCOMS and SNA will screen the application to evaluate the feasibility of the RTS project. In the application screening, the implementing agencies has to review the duly filled application forms as per general requirements for RTS such as applicant name, address, site location, project capacity etc. Whereas, for technical screening, application will be examined on the basis of technical parameters such as inter-connection study, rooftop area availability, anticipated capacity, high level performance assessment (i.e., energy generation), system impact studies etc. Technical screening has been performed by distribution utilities with an objective specifically check whether the proposed RTS system is technically feasible and safe for the utility grid and connected load limits for connectivity and the scope of the subsidy respective to the information provided in the application. It is worth mentioning that the screening of applications on behalf of DISCOM, as well as SNA, will run in parallel.
After completing the screening, the applicant will get the go-ahead to sign an interconnection agreement with local DISCOMS and a feasibility report will be prepared by the authorities. On the completion and submission of the feasibility report, an online “No Objection Certificate” for grid connectivity will be forwarded to the applicant on its registered e-mail address or mobile number. The applicant will submit the same NOC to SNA and accordingly SNA will approve the subsidy and release the sanction letter. The subsidy sanction letter will also be forwarded to the applicant at his/her registered e-mail address and mobile number.
6.3. Project installation
After getting grid connectivity and subsidy approval the next step is the installation of the project. Meanwhile, the applicant may have limited knowledge of project vendors and channel partners empaneled by the SNA. Therefore, the online web platform will contain detailed information about the channel partners/vendors authorized with the SNAs along with the standards and regulations described for the equipment of the RTS system. The web platform will also be made available for such vendors so that they can even quote the price of installations which may create competition in the market. By selecting the appropriate vendor applicant can start the project installation. After the installation of the project, a work completion report has to be uploaded on the web platform. The overall time recommended for the entire process of project installation will be 45 days as compared to 55 days in the absence of the IT-based system.
6.4. Site inspection and commissioning of the project
As mentioned in the previous section, the applicant will submit the work completion report and request officers of DISCOMS for site inspection so that project will be commissioned. Working on the same, DISCOM authorities will conduct the site inspection where they will examine the project as per their regulation and requirements. To be satisfactory, the finding of the same officials from DISCOM will prepare a site inspection report which will again be uploaded on the web platform. Based on this report higher authorities will issue a project commissioning certificate and the same will be forwarded to the applicant on his registered e-mail address and SNA for their reference. On receiving the information about the commissioning of the project SNA officer will also schedule a site visit. The objective of this site visit is to ensure the compliance and standards set by the MNRE standards for subsidy disbursement. On satisfactory findings, the same SNA will issue a certificate to the applicant as well as the system installer.
6.5. Subsidy disbursement
The inspection report of SNA and certificate issued to the installer and applicant will then be forwarded to the higher authorities for final approval of the report. Further, the accounts department will be informed to release the subsidy on the satisfactory outcomes of the report. Finally, the accounts department of SNA will release the subsidy to the applicant or project installer based on the regulation of the state. In brief, the time will be targeted to complete these for the above administrative approvals will be 15 days only. The entire proposed process is illustrated in
Figure 7.
7. Consumer Proliferation
To date, most of the states in India have been following the conventional approach to RTS proliferation as described in
Section 4 above. A few initiatives for IT interventions have been reported at the central level by MNRE and in the states summarized below:
MNRE has launched an online platform - Solar Photovoltaic Installation (SPIN) to monitor the progress of the RTS sector in India [
65]. The platform is available for all executive agencies and the public. The platform incorporates several features to ensure the transparent implementation of RTS in India. Some of these features include (i) empanelment of stakeholders of RTS such as channel partners, project developers, etc.; (ii) managing and ensuring timebound achievement of targets of RTS with involvement of empaneled agencies; (iii) monitoring of installed RTS projects; (iv) awareness raising for the public; and (v) creation of a Geo-referenced database of all RTS projects [
66].
The MNRE, World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB), German Corporation for International Cooperation (GIZ), European Union (EU), and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) have also jointly worked on a program envisioning to provide technical assistance and support for RTS implementation in India [
66]. A PV Rooftop Cell has been established at MNRE under technical cooperation with the EU to expedite RTS implementation and to support stakeholders. Under the PV Rooftop Cell, the provision of technical support has been meant for DISCOMs and SNAs for faster deployment of grid-connected RTS projects in the country. This support will cover; the following aspects of the RTS project:
Gap assessment and action plan to boost the RTS installations in the country.
Establishing a dedicated RTS program that will act as a platform for technical experts and will also assist in the handholding of technologies as well as in training/capacity building.
Development of dedicated web portals at the national and state levels which will aware, assist and support potential customers on RTS installations.
A brief description of activities conducted by these organizations is summarized in the following subsections.
7.1. IFC Interventions on Web-based Consumer Proliferation
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) has supported the SNA of Odisha state - OREDA, on the development and launching of an IT-based consumer proliferation platform to accelerate the penetration of RTS in the residential sector of the state under the Eco-Cities initiative of EU [
67]. After reviewing the existing mechanism of RTS proliferation in the state, an optimized approach has been recommended that internalizes the use of IT in the overall process of RTS implementation at small (residential sector) to large capacity ranges (commercial and industrial sectors). A web platform and mobile application “OREDA Solar” has been created and made available in the public domain [
68]. In the absence of the web portal, the applicant has to apply differently for both connectivity approval from DISCOM and subsidy approval from SNA. With the new IT-based arrangement several modifications have been made and repetitive steps have also been eliminated. The whole process of application submission to subsidy disbursement reduces approximately 60 days (based on the RTS model) compared to the earlier process which used to take 90 days to avail the connectivity as well as subsidy. After the launch of this IT platform around 5 MW of the RTS, implementations have been reported in the state. Under the same program of eco-cities, IFC has also assisted the Maharashtra Energy Development Agency (MEDA) and SNA of the state of Maharashtra in developing such an IT-based consumer proliferation platform [
67].
7.2. IGEN- GIZ Initiative
A dedicated program, the Indo-German Energy Program (IGEN) to support the growth of the RTS sector in India through skill transfer and capacity development is running since 2015 [
69]. The program focuses on the capacity building of the various stakeholders of the RTS sector on policy and regulations drafting, ground implementation, and accelerated diffusion of RTS projects. To achieve the above objectives, IT-based consumer proliferation platforms have been developed for the selected SNAs of a few states/UTs in India viz. Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand and Daman, and Diu. As an example, a web platform for online submission of applications and subsidy disbursement has been developed for the state of Jharkhand, India which is hosted on the website of the respective State Nodal Agency of Jharkhand.
7.3. EU- MNRE Initiative
The EU-India Technical Cooperation Program is operational since September 2014 [
66]. The program provides beneficiaries and participants with the opportunity to enhance their technical and institutional capacity. In line with the objectives, a project team is closely working with the rooftop cell of MNRE and assisting the SNAs of different states in India on the development of an IT-based consumer proliferation approach for RTS implementation. Under this program, a web-based platform for consumer proliferation has been successfully developed for the SNAs of Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Delhi states of India. Mobile applications for facilitating consumer proliferation and RTS installations have also been developed for these states. In addition to IFC work in Maharashtra, the EU team has also assisted MEDA in the development of the Mobile application for RTS consumer proliferation.
7.4. World Bank Initiative
The World Bank is supporting the MNRE’s mandate on the widespread installation of grid-connected RTS installations by lending US
$ 625 million to the State Bank of India (SBI) [
70]. The MNRE and the World Bank have also launched a joint special program named SUPRABHA (Sustainable Partnership for Rooftop Solar Acceleration in Bharat) to address the barriers to the RTS sector [
71]. It is a solar technical assistance five-year program. The activities under SUPRABHA are structured within the five thematic areas - policy and regulations, capacity building, raising consumer awareness through media outreach campaigns, process streamlining, and aggregation of demand for RTS. IT support is provided to the state nodal agencies for developing digital portals for streamlining the rooftop application process. The state governments are supported with the necessary support to update the policy and regulations for facilitating RTS growth. Finally, there is a comprehensive capacity-building program implemented for bankers, distribution utility officials, project developers, and entrepreneurs. These IT Interventions broadly involve streamlining the RTS application process through unified web portals (UWP). It is a common integrated platform at a state level, for consumers to apply for the RTS system, track the progress of their application, and access subsidies if any.
So far, 17 states of India, have been identified to receive technical assistance as per this program. The program envisaged supporting the faster adoption of grid-connected RTS. Meghalaya and Sikkim governments have already engaged in formulating their RTS policies. The scheme has been successful in stirring demand aggregation support for bidding by partner states such as Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh for more than 120 MW [
72]. The SUPRABHA scheme covers a wide range of stakeholders including consumers, regulators, distribution companies, financial institutions, and entrepreneurs. Under the same program, the SBI had also imparted solar training to its employees recently, to better understand the concepts and approve solar loans. Overall, 150 SBI officers have been trained so far. It is expected that in the next three-four months, all 17 states under the technical assistance program will have these portals operational. Several hundred applications have been processed through the operational portals.
8. Conclusions
Rooftop solar power is a key tool in the fight against climate change. India missed the 100 GW solar target of 2022 and RTS is the biggest reason for that. This study critically analyzed the conventional approach to RTS project installation and reviewed the existing practices of RTS installation adopted by the executive agencies. The scope for IT interventions in the existing RTS implementation process of the OREDA has been assessed and a simplistic approach has been developed which focuses on the execution of the RTS projects in relatively lesser time with the least human interface as well as resources.
The intervention of IT in the RE sector for enhancing the implementation process is a unique solution with multiple benefits. From the hands-on experience of Odisha states in India, it has been observed that the conventional approach to consumer proliferation and implementation of RTS projects in India is tedious and time-consuming for consumers as well as for implementing agencies. It has been noticed and identified that multiple agencies responsible for the implementation of projects were engaged in the repetitive process of issuing clearance and approvals which unnecessarily consumes their effort in terms of manpower and time. Therefore, even with vast potential and policy-supportive measures, most of the states in India are lacking far behind the assigned targets of RTS installations. It is observed that the case study of Odisha state can effectively reduce the time of execution and enhance the process.
Within the existing practices, potential consumers do not have access to a single platform that may guide or aware them of the potential benefits of RTS implementation based on cost-benefit assessment. Moreover, they don’t have awareness as well as access to the technical information of RTS systems, especially on the quality of products, equipment standards set by the implementing agencies, etc. IT platform of consumer proliferation incorporated with site-specific energy yield assessment and financial calculator may provide information access. Detailed information on vendors empaneled channel partners under such platforms may also assist the consumer in choosing EPC contractors as well.
It has been noticed that most of the State nodal Agencies (SNAs) do not follow competitive bidding as only benchmark cost is followed for project installation and subsidy disbursement. IT interventions may help empaneled vendors to quote their prices in the platform which could further be well evaluated by the potential consumers thus competitiveness among several vendors may reduce the cost of installations and further subsidy load on the Central/State government, and finally the cost of energy generation through solar implementation. In brief, IT intervention may provide a single platform for such mutual interaction between project developers and consumers.
In the example of Odisha State, it has been explicitly reported that the use of IT-based interventions only after 6-8 months of launching facilitated the installations of around 5 MW of RTS projects in the state out of the envisaged 8 MW through the same in a residential segment where system size is of 1-2 kW only. The platform is managing the data processing for more than 2000 consumers. Thus, necessitating and strongly supporting the adoption of an IT-based consumer proliferation approach to meet the desired targets and boost the diffusion of RE technologies/systems in the country.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, almost all the economies of the world are facing difficulties sustaining their growth. In addition, the pandemic has even restricted human interaction. Therefore, it becomes highly desirable to adopt such an IT-based mechanism, which is robust, secure, interactive, and required the least man-to-man interactions. The approach described as the outcome of this study thus will integrate key stakeholders such as SNAs, DISCOMS, applicants, project developers, vendors, etc. on a common platform and will facilitate them on the entire process of RTS implementation even by ensuring the least physical interface. Moreover, the adoption of an IT-based approach will also reduce the administrative burden on implementing agencies and will boost the proliferation of RTS projects across the states of India and achieve the envisaged targets of the updated nationally determined contributions. This approach of RTS implementation may be replicated in other developing countries in order to accelerate the penetration of RTS systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org., Table S1: Capacity allocated to states for rooftop solar implementation in India; Table S2: Rooftop solar policy and regulations in India.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.P. and A.K.S.; methodology, I.P., A.K.S., and P.P.; formal analysis, I.P., A.K.S., and P.P.; data curation, I.P., and A.K.S.; writing—original draft preparation, I.P., and A.K.S.; writing—review and editing, P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
I.P. and A.K.S. gratefully acknowledge the encouragement provided by the International Finance Corporation (IFC), The World Bank Group, New Delhi. The authors also thank the six anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, which helped to improve this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Notes
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
Net metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the grid. |
| 3 |
CERC: Central Electricity Regulatory Commission; SERC: State Electricity Regulatory Commission; CEA: Central Electricity Authority; SECI: Solar Energy Corporation of India; SNAs: State Nodal Agencies; IREDA: Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency. |
| 4 |
A Renewable Energy Service Company (RESCO) provides energy to consumers from renewable energy sources, usually solar photovoltaics, wind power, or micro hydro. RESCOs include investor-owned, publicly owned, cooperatives, and community organizations. |
References
- ASPI. Getting India to Net Zero: A report of the high-level policy commission on getting Asia to net zero. Asia Society Policy Institute (ASPI), New York, 22. 20 May.
- Das, A.; Saini, V.; Parikh, K.; Parikh, J.; Ghosh, P.; Tot, M. Pathways to net zero emissions for the Indian power sector. Energy Strategy Rev 2023, 45, 101042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC. India’s updated first Nationally Determined Contribution under Paris Agreement (2021-2030). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), Bonn, 22. 20 August.
- IEA. World Energy Outlook 2022. International Energy Agency (IEA), Paris, 22. 20 October.
- UNFCCC. India’s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution: Working Towards Climate Justice. United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), Bonn, 15. 20 October.
- MNRE. Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, New Delhi, 10. 20 January.
- MNRE. Scaling up of Grid Connected Solar Power Projects from 20,000 MW by the year 2021-22 to 1,00,000 MW by the year 2021-22 under the National Solar Mission. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, New Delhi, 15. 20 July.
- Purohit, I.; Purohit, P. 2018. Performance assessment of grid-interactive solar photovoltaic projects under India’s national solar mission. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 25-41.
- MNRE. Annual Report: 2019-20. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, New Delhi. Available online: https://mnre.gov.in/img/documents/uploads/file_f-1597797108502.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2022).
- MNRE. Solar RPO for States in India. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, New Delhi. Available online: https://mnre.gov.in/solar/rpo / (accessed on 27 November 2022).
- MNRE. Solar Policies and Guidelines. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, New Delhi. Available online: https://mnre.gov.in/Solar/policy-and-guidelines (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Sarangi, G.K.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Rooftop solar development in India: Measuring policies and mapping business models. ADBI Working Paper Series, No. 1256, Asian Development Bank Institute (ADBI), Tokyo, 21. 20 April.
- Chandel, R.; Chandel, S.S.; Malik, P. Perspective of new distributed grid-connected roof top solar photovoltaic power generation policy interventions in India. Energy Policy 2022, 168, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Garg, T.; Jain, R.; Kuldeep, N. Demystifying India’s rooftop solar policies: A state-level analysis. Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW), New Delhi, 19. 20 November.
- Dutta, A.; Das, S. Adoption of grid-connected solar rooftop systems in the state of Jammu and Kashmir: A stakeholder analysis. Energy Policy 2020, 140, 111382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MNRE. Operational guidelines for implementation of Phase-II of grid-connected Rooftop Solar Programme for achieving a cumulative capacity of 40,000 MW from Rooftop Solar (RTS) Projects by the year 2022. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, New Delhi, August 2019. Available online: https://www.itsmysun.com/solar-state-wise-polic/ (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- BTI. Indian Solar Compass. Bridge to India (BTI) Reports. Available online: https://bridgetoindia.com/report/india-solar-compass-q1-2022/ (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Singh, R. Approximate rooftop solar PV potential of Indian cities for high-level renewable power scenario planning. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 42, 100850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Jain, G.; Mishra, S.; Bhattacharya, B. Assessment of roof-top solar energy potential in proposed smart cities of India. Proceedings of the 39th Asian Conference of Remote Sensing, Kuala Lumpur, 15-19th 18. 20 October.
- Sudhakar, S.; Lovedeep, M.; Bhattacharjee, U.; Graud, S.; Tripathi, A.K. Reaching the Sun with Rooftop Solar. The Energy and Resource Institute (TERI), New Delhi, 2014.
- Joshi, S.; Mittal, S.; Holloway, P.; Shukla, P.R.; Gallachóir, B.O.; Glynn, J. High-resolution global spatiotemporal assessment of rooftop solar photovoltaics potential for renewable electricity generation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.K.; Tiwari, P.K.; Sood, Y.R. Solar energy in India: strategies, policies, perspectives and future potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, J.; Thayillam, A.; Sharma, P.; Garg, V. Indian Residential Rooftops: A Vast Trove of Solar Energy Potential. Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), Ohio, 22. 20 October.
- IEA. Unlocking the Economic Potential of Rooftop Solar PV in India. International Energy Agency (IEA), Paris, 21. 20 April.
- MNRE. Current Status Solar capacity. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, New Delhi. Available online: https://mnre.gov.in/solar/current-status/ (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Beck F; Martinot, E. Renewable energy policies and barriers. Encycl. Energy 2004, 5.
- Singh R; Banerjee, R. Estimation of rooftop solar photovoltaic potential of a city. Solar Energy 2015, 115, 589–602. [CrossRef]
- Rathore, P.K.S.; Rathore, S.; Singh, R.P.; Agnihotri, S. Solar power utility sector in India: challenges and opportunities, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2703–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adithya, S.N. Large-scale implementation of grid-connected rooftop solar photovoltaic system in India — potential, challenges, outlook, and technical impact. 14 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Sudhakar, K.; Baredar, P.; Mamat, R. Solar PV and BIPV system: Barrier, challenges and policy recommendation in India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 3314–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Sharma, A. Knowledge politics, vulnerability and recognition-based justice: public participation in renewable energy transitions in India. Energy Res. Social Sci. 2021, 71, 101824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, M.; Meeks, R.; Yamano, T. Reducing information barriers to solar adoption: Experimental evidence from India. Energy Economics 2023, 120, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra T; Sengar A.; Sajith, S. Identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing barriers in the Indian industrial and commercial rooftop solar sector. Solar Energy 2023, 254, 15–26. [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M. Focus on low carbon technologies: The positive solution. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2331–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRENA. Climate Change and Renewable Energy: National policies and the role of communities, cities and regions. Report to the G20 Climate Sustainability Working Group (CSWG), International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Abu Dhabi, 19. 20 June.
- Vallecha, H.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Osiri, J.K.; Bhola, P. Evaluation of barriers and enablers through integrative multicriteria decision mapping: Developing sustainable community energy in Indian context. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Haleem, A. Barriers to implement green supply chain management in automobile industry using interpretive structural modeling technique – an Indian perspective. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2011, 4, 231–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañales, S. The enabling impact of digital technologies on distributed energy resources integration. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2020, 12, 045301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRENA. Future of Solar Photovoltaic: Deployment, investment, technology, grid integration and socio-economic aspects. International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Abu Dhabi, 19. 20 November.
- Dhankhar, H.; Anwer, N. A critical analysis of present net metering regulatory framework and identification of potential barriers in the growth of rooftop market. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering 2019, 553, 825–835. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, J.; Chakraborty, B. Impact of compensation mechanisms for PV generation on residential consumers and shared net metering model for developing nations: A case study of India. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, D. Understanding the barriers to the diffusion of rooftop solar: A case study of Delhi (India). Energy Policy 2020, 144, 111674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappagantu, R.; Daniel, S.A.; Venkatesh, M. Analysis of Rooftop Solar PV System Implementation Barrier in Puducherry Smart Grid Pilot Project. Procedia Technology 2015, 21, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Buckley, T. Vast Potential of Rooftop Solar in India: Setting the Pace for Rapidly Increasing Rooftop Solar Installations in India. Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), Ohio, 19. 20 May.
- MERCOM. Survey of India Consumer Perceptions on Renewable Energy. Available online: https://mercomindia.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/Survey_MercomIndiaSurveyRenewables.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Painuly, J.P. Barriers to renewable energy penetration; a framework for analysis, Renew. Energy 2001, 24, 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yaqoot, M.; Diwan, P.; Kandpal, T.C. Review of barriers to the dissemination of decentralized renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.K.; Syed, A.A.; Garg, S. Diffusion of residential RT solar – is lack of funds the real issue? Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2020, 14, 316–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BTI. Poor Implementation of Net-metering Policies Poses a Major Challenge for Rooftop Solar. Bridge to India (BTI), November 2016. 7 November. Available online: http://www.bridgetoindia.com/poor-implementationnet-metering-policies-poses-major-challenge-rooftop-solar/ (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Rathore, P.K.S.; Chauhan, D.S.; Singh, R.P. Decentralized solar rooftop photovoltaic in India: On the path of sustainable energy security. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.G.; Sindhu, M.R.; Mohan, V.; Viswanathan, R.; Sudhakaran, A.V. An adaptive staggered investment strategy for promotion of residential rooftop solar PV installations in India. Int. J. Sustain. Energy Plan. 2023, 37, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PwC and CIF. Rooftop Solar in India: Looking back, Looking ahead. PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) Pvt Ltd, India and Climate Investment Funds, 18. 20 April.
- Deloitte. Scaling up of rooftop solar in the SME sector in India. April 2019.
- Das, B. Rooftop solar: Why India is now considered to be a laggard globally. Down to Earth, Centre for Science and Environment, New Delhi, 22. 20 January.
- Ernst & Young. Accelerating India’s clean energy transition. 22. 20 June.
- CEEW-NRDC. Filling the Skill Gap in India’s Clean Energy Market: Solar Energy Focus. Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) and the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), New Delhi, 16. 20 February.
- Timilsina, G.R.; Kurdgelashvili, L.; Narbel, P.A. Solar energy: markets, economics and policies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MNRE. Solar/Green Cities. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE). New Delhi. Available online: http://164.100.94.214/solar-cities (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Khandekar, N. How rooftop solar struggles even in India's most sunny cities, 27 July 2021. Available online: https://www.indiaspend.com/development/rooftop-solar-energy-inconsistent-regulatory-policies-high-costs-patchy-implementation-subsidy-scheme-763796 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Sharma, C.; Sharma, A.K.; Mullick, S.C.; Kandpal, T.C. Solar thermal power generation in India: effect of potential incentives on unit cost of electricity. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Purohit, P. Renewable energy certificate mechanism in India: A preliminary assessment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, I.; Purohit, P. Technical and economic potential of concentrating solar thermal power generation in India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 648–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, S.; Ray, I.; Vulturius, G. Scaling up Rooftop Solar Power in India: The Potential of Solar Municipal Bonds. Climate Policy Initiatives (CPI), 18. 20 February.
- The Electricity Act, 2003 [No.36 of 2003], Ministry of Law and Justice (MoLJ), Government of India, New Delhi. Available online: https://cercind.gov.in/Act-with-amendment.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- MNRE. National Portal of Rooftop Solar. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, New Delhi. Available online: https://solarrooftop.gov.in/ (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- MNRE. National Solar Mission - Grid connected solar rooftop programme in India. EU – India Technical Cooperation Project: Energy, Available online:. Available online: https://solarrooftop.gov.in/notification/Notification-24012017.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Eco-Cities India Program: Private sector solutions for sustainable urban development. Available online: https://www.ecocities.in (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- OREDA. Solar Rooftop PV Cell. Odisha Renewable Energy Development Agency (OREDA), Bhubaneswar. Available online: http://rts.odisha.gov.in/ (accessed on 14 November 222).
- Indo-German Energy Programme (PVRT). IGEN-GEC-Rooftop Solar PV component. Available online: https://www.giz.de/en/worldwide/70459.html (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- World Bank. World Bank Approves $625 Million to Support Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Program in India. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2016/05/13/world-bank-approves-625-million-to-support-grid-connected-rooftop-solar-program-in-india (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- SUPRABHA. The Sustainable Partnership for Rooftop Solar Acceleration in Bharat (SUPRABHA) Programme. Available online: http://www.nbirt.org.in/suprabha-programme (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Shah, S. All You Wanted To Know About The SUPRABHA Solar Scheme. 15 November 2018. Available online: https://www.greenworldinvestor.com/2018/11/15/all-you-wanted-to-know-about-the-suprabha-solar-scheme/ (accessed on 23 January 2023).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).