Submitted:
14 April 2023
Posted:
24 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Database Construction
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis of Microbial 16S rRNA and ITS
2.5. Data Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Combined Pollution of GP and DQ on Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Community
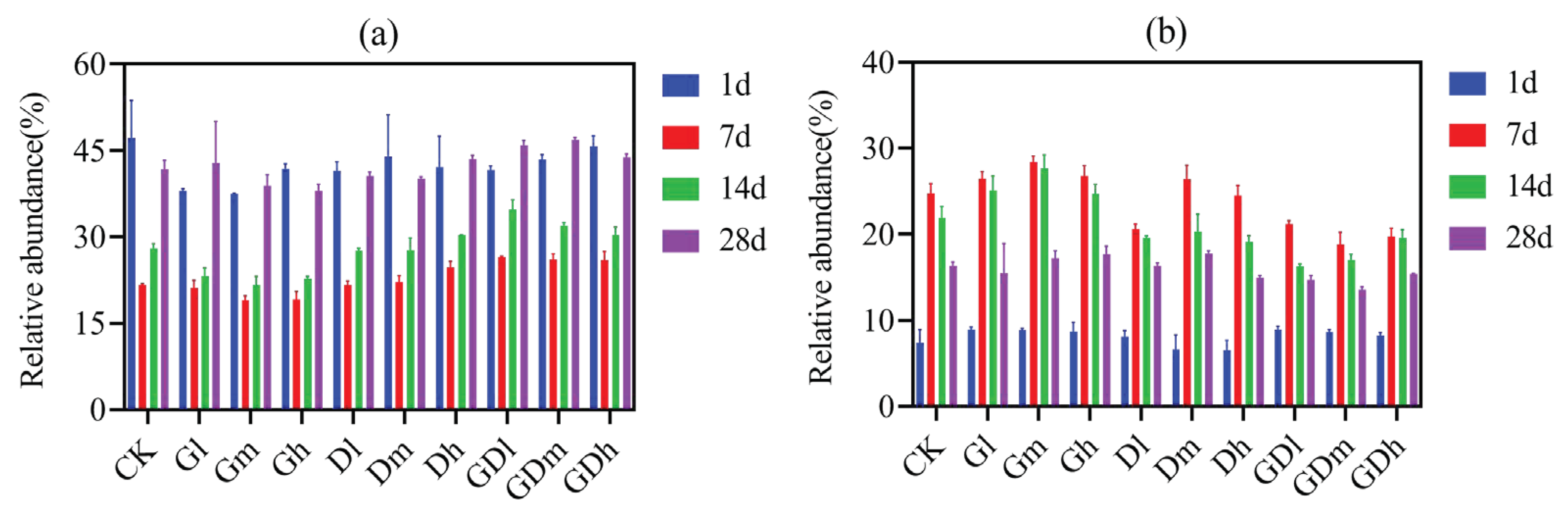
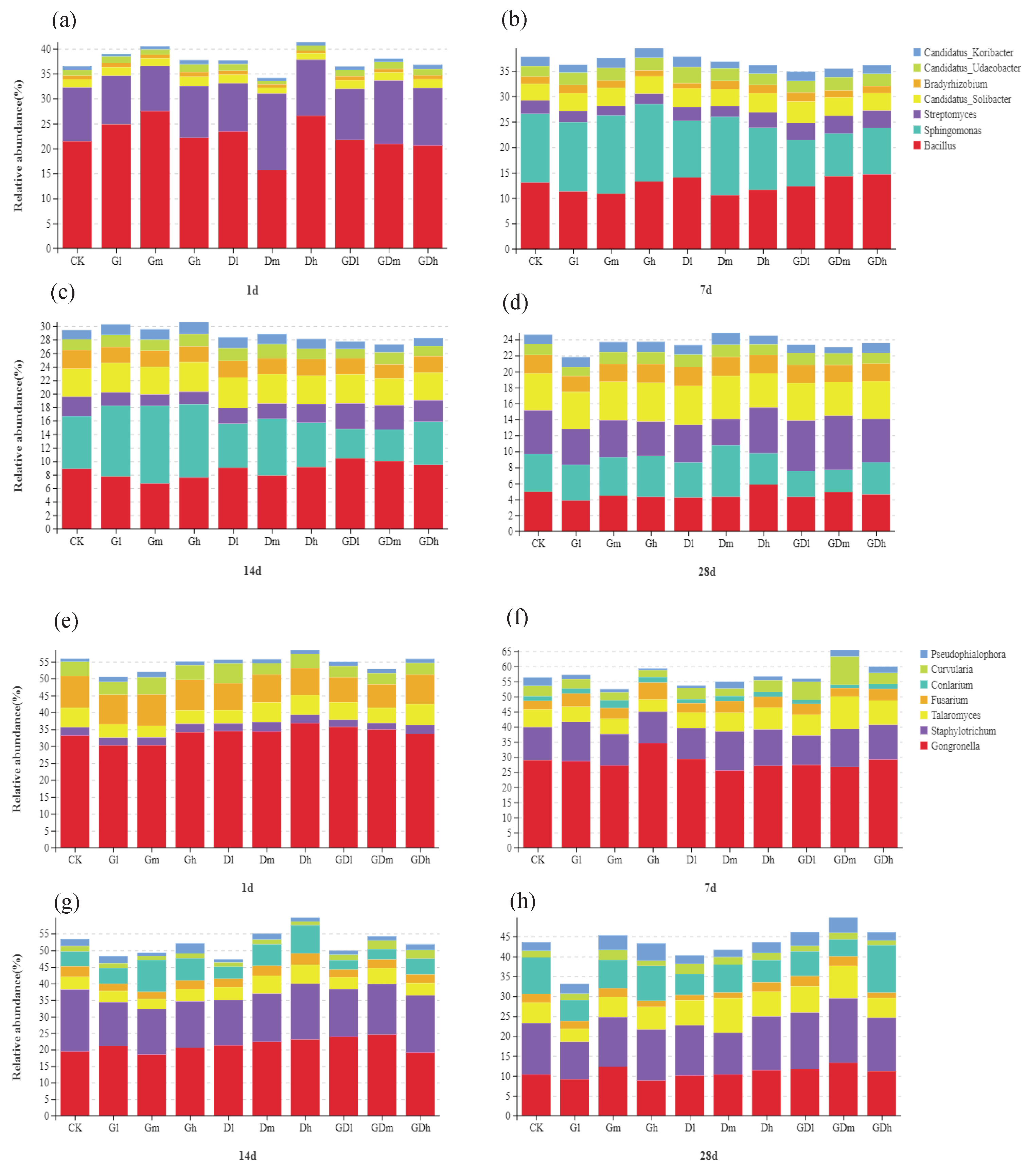
3.1.1. Bacterial Community Composition
3.1.2. Alpha Diversity of Bacterial Community
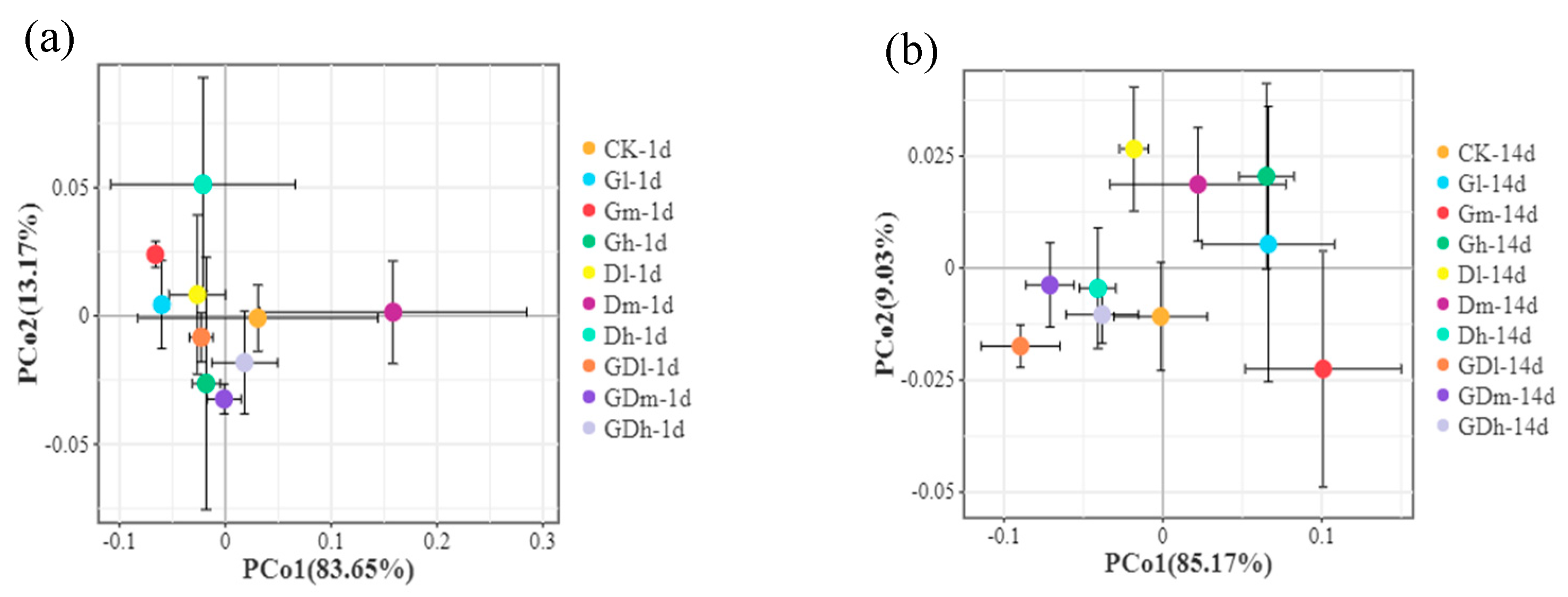
3.1.3. Beta Diversity of Bacterial Community
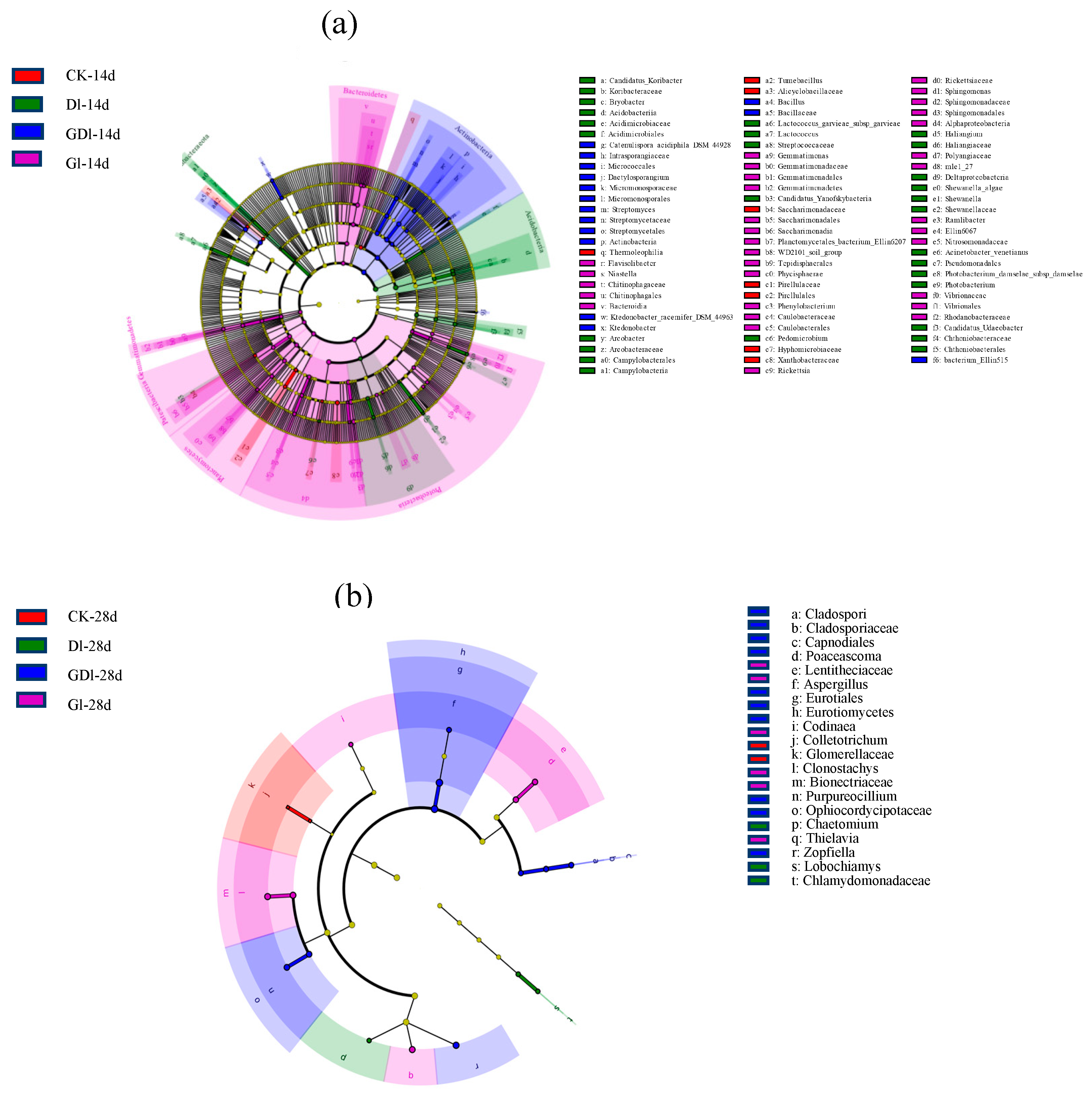
3.1.4. LEfse Analysis of Bacterial Community
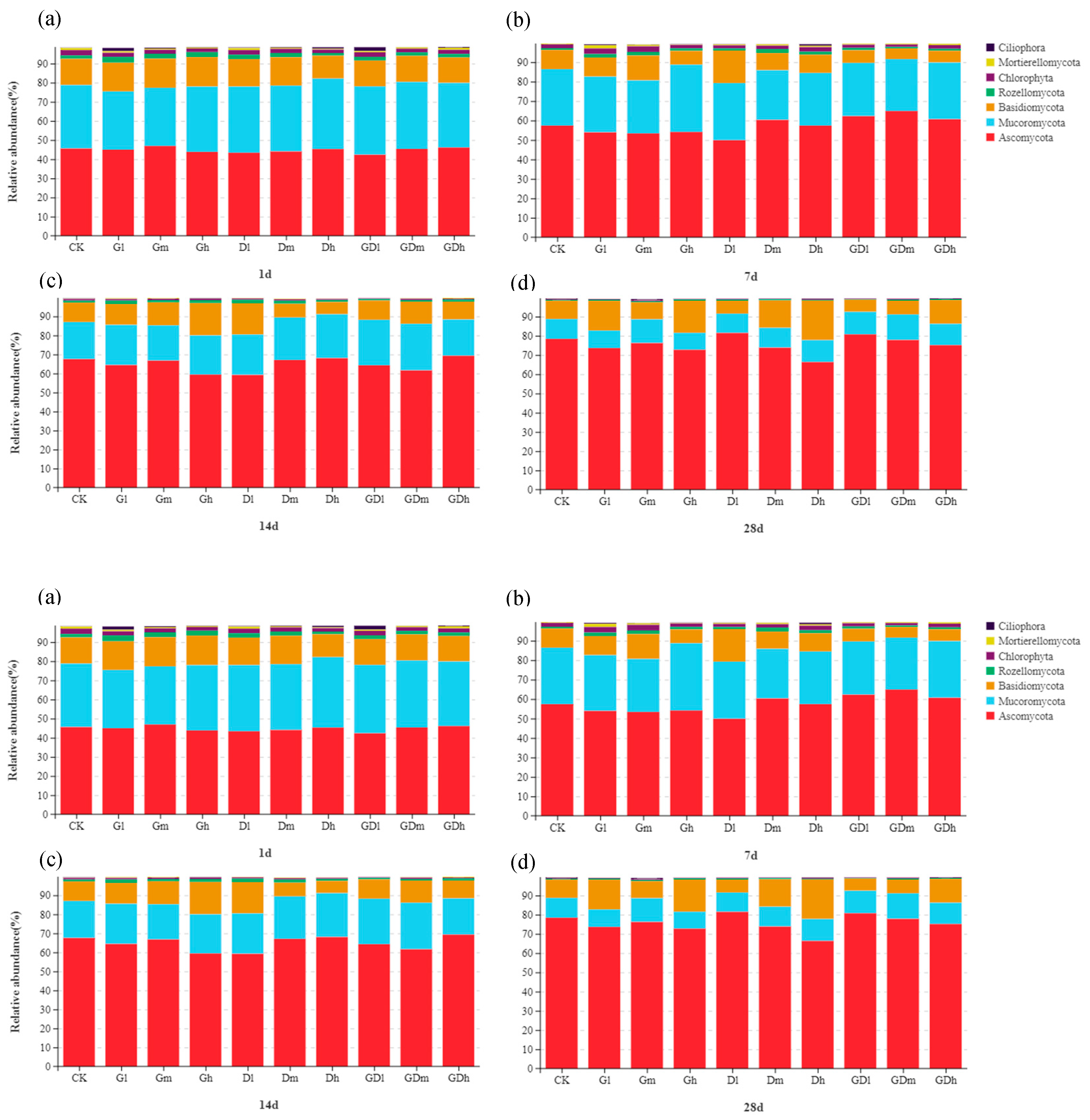
3.2. Effects of Combined Pollution of GP and DQ on Composition and Diversity of Soil Fungal Community
3.2.1. Fungal Community Composition
3.2.2. Alpha Diversity of Fungal Community
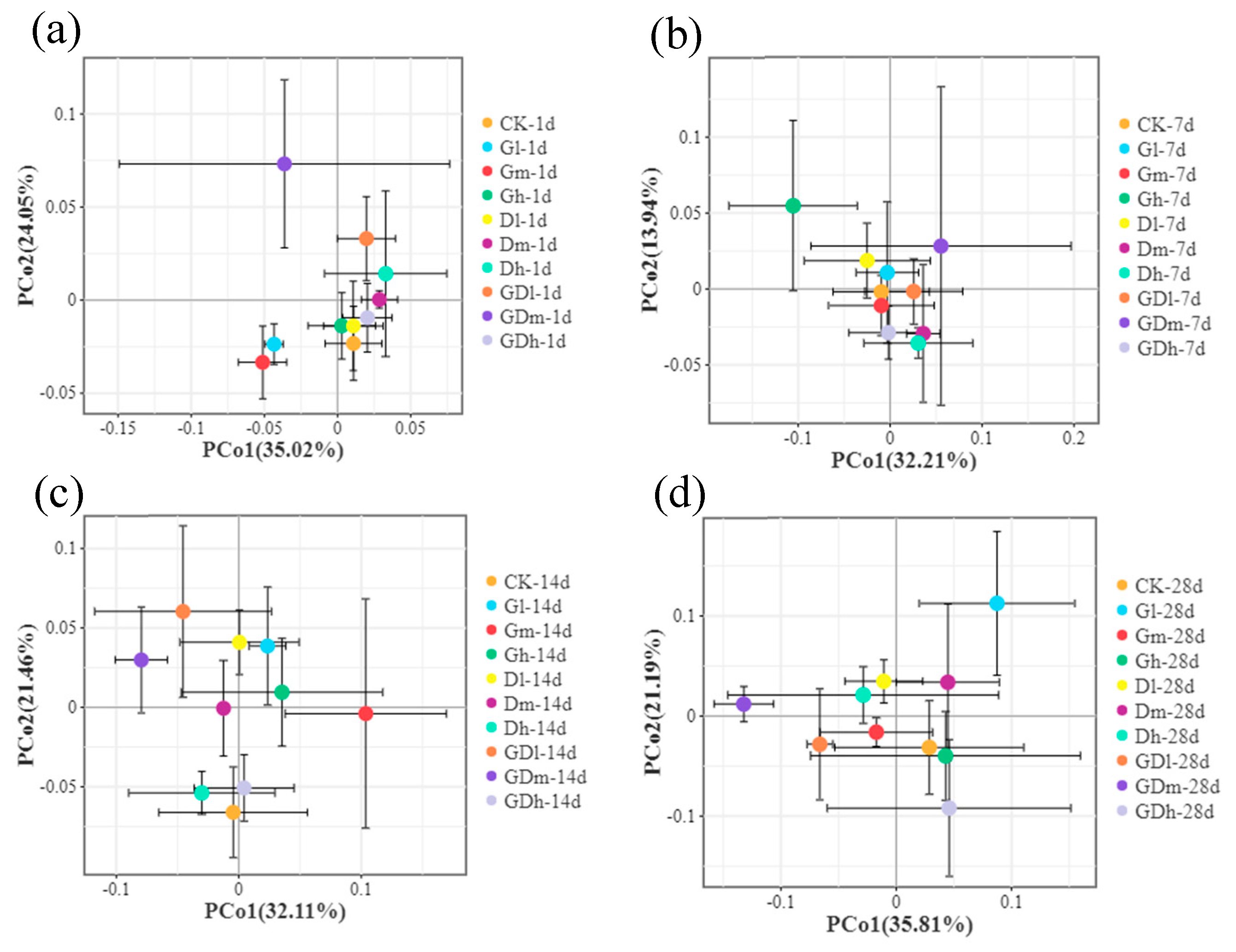
3.2.3. Beta Diversity of Fungal Community
3.2.4. LEfSe Analysis of Fungal Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grube, A.; Donaldson, D.; Kiely, T.; Wu, L. Pesticides Industry Sales and Usage. US EPA, Washington, DC, 2011.
- Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, B. Market forecast of China's pesticide industry in 2020. The world pesticide 2020, 42, 1–8. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O. The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, M.T.; Poulsen, H.D.; Katholm, C.L.; Højberg, O. Review: Feed residues of glyphosate – potential consequences for livestock health and productivity. Animal 2021, 15, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, G.; Atreya, K.; Scheepers, P.T.J.; Geissen, V. Concentration and distribution of pesticide residues in soil: Non-dietary human health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horth, H.; Blackmore, K. Survey of glyphosate and AMPA in groundwaters and surface waters in Europe. WRC report, 2009, no. UC8073, 2.
- Demonte, L.D.; Michlg,N. ; Gaggiotti, M. Determination of glyphosate, AMPA and glufosinate in dairy farm water from Argentina using a simplified UHPLC-MS/MS method. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, D. Glyphosate, aminomethyl-phosphonic acid, and glufosinate ammonium in agricultural groundwater and surface water in China from 2017 to 2018: Occurrence, main drivers, and environmental risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, V.C.; De Gerónimo, E.; Marino, D.; Primost, J.; Carriquiriborde, P.; Costa, J.L. Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, J. Monitoring and risk assessment of pesticide residue in plant soil-groundwater system about medlar planting in Golmud. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2021, 28, 26413–26426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Rosee, M.; Van Zwieten, L. Direct determination of glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA in soil using mixed-mode solid-phase purification and LC-MS/MS determination on a hypercarb column. J AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.Y.; Peng, Z.R.; He, W.H.; Feng, M.J.; Dai, X.L. Assessment of glyphosate residues and ecological risk in P. rosii cultured ponds. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University 2021, 5, 821–827. [Google Scholar]
- Botero-coy, A M. ; Ibáñez, M,; Sancho, J.V.; Hernandez, F. Improvements in the analytical methodology for the residue determination of the herbicide glyphosate in soils by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1292, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primost, J.E.; Marino, D.J.; Aparicio, V.C.; Costa, J.L; Carriquiriborde, P. Glyphosate and AMPA, "pseudo-persistent" pollutants under real-world agricultural management practices in the mesopotamic pampas agroecosystem, Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunarathna, S.; Gunawardana, B.; Jayaweera, M. Glyphosate and AMPA of agricultural soil, surface water, groundwater and sediments in areas prevalent with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology, Sri Lanka. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. B 2018, 53, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasali, H.; Pavlidis, G. Marousopoulou A. Investigation of the presence of glyphosate and its major metabolite AMPA in Greek soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2019, 26, 36308–36321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roede, J.R.; Miller, G.W. Diquat. Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 2014, 202–204.
- Silva, V.; Mol, H. G. J.; Zomer, P.; Tienstra, M.; Ritsema, C. J.; Geissen, V. Pesticide residues in European agricultural soils – A hidden reality unfolded. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 653, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Heijden, M.G.; Bardgett, R.D.; Van Straalen, N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Bender, S.F.; Widmer, F.; van der Heijden, M.G. Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Lydon, J.; Koskinen, W.C.; Moorman, T.B.; Chaney, R.L.; Hammerschmidt, R. Glyphosate effects on plant mineral nutrition, crop rhizosphere microbiota, and plant disease in glyphosate-resistant crops. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10375–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.B.; Rose, M.T.; Rose, T.J.; Morris, S.G.; Zwieten, L.V. Impact of glyphosate on soil microbial biomass and respiration: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 92, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, J.T.; Selim, H.M. Environmental behavior of Glyphosate in soils. Adv. Agron. 2020, 159, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; Finckh, M.R.; He, M.; Ritsema, C.J.; Harkes, P.; Knuth, D.; Geissen, V. Indirect effects of the herbicide glyphosate on plant, animal and human health through its effects on microbial communities. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 763917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, M.A.; Krutz, L.J.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Reddy, K.N. Effects of glyphosate on soil microbial communities and its mineralization in a Mississippi soil. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepler, R.M.; Schmidt, D.J.E.; Yarwood, S.A.; Cavigelli, M.A.; Reddy, K.N.; Duke, S.O.; Bradley, C.A.; Williams, M.M., Jr.; Buyer, J.S.; Maul, J.E. Soil microbial communities in diverse agroecosystems exposed to the herbicide glyphosate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01744–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupwayi, N.Z.; Fernandez, M.R.; Kanashiro, D.A.; Petri, R.M. Profiles of wheat rhizobacterial communities in response to repeated glyphosate applications, crop rotation, and tillage. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 101, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accinelli, C.; Koskinen, W.C.; Seebinger, J.D.; Vicari, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Effects of incorporated corn residues on Glyphosate mineralization and sorption in soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4110–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, E.; Ferreras, L.; Lovotti, L.; Fernández, E. Impact of Glyphosate application on microbial biomass and metabolic activity in a Vertic Argiudoll from Argentina. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accinelli, C.; Koskinen, W.C.; Becker, J.M.; Sadowsky, M.J. . Environmental fate of two sulfonamide antimicrobial agents in soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2677–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, S.H.; Hollister, E.B.; Senseman, S.A.; Gentry, T.J. Effects of repeated glyphosate applications on soil microbial community composition and the mineralization of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, T.I.; Warner, D.J.; Davies, K.G.; Edmonds-Brown, V. Tillage, glyphosate and beneficial arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Optimising crop management for plantfungal symbiosis. Agric. For. 2020, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch'avez-Ortiz, P.; Tapia-Torres, Y.; Larsen, J.; García-Oliva, F. Glyphosate-based herbicides alter soil carbon and phosphorus dynamics and microbial activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobiole, L.; Kremer, R.; Oliveira, R.; Constantin, J. Glyphosate affects microorganisms in rhizospheres of glyphosate-resistant soybeans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carles, L.; Artigas, J. Interaction between glyphosate and dissolved phosphorus on bacterial and eukaryotic communities from river biofilms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annett, R.; Habibi, H.R.; Hontela, A. Impact of glyphosate and glyphosate-based her-bicides on the freshwater environment. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 458–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.M.; Hoilett, N.; Lorenz, N.; Dick, R.P.; Liles, M.R.; Ramsier, C.; Kloepper, J.W. Glyphosate effects on soil rhizosphere-associated bacterial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegrini, M.; Gomez, E.; Zabaloy, M.C. Repeated glyphosate exposure induces shifts in nitrifying communities and metabolism of phenylpropanoids. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 105, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druille, M.; Omacini, M.; Golluscio, R.A.; Cabello, M.N. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are directly and indirectly affected by glyphosate application. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 72, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Fernandes, B.; Paiva, C.; Nogueira, V.; Cachada, A.; Fidalgo, F.; Pereira, R. Ecotoxicological relevance of glyphosate and flazasulfuron to soil habitat and retention functions – Single vs combined exposures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.H. The toxic effects of glyphosate and cadmium on E. coli. Master's degree thesis, Hunan University of Science and Technology, China, 16 December 2019. 16 December.
- Deng, M.C. Response of lead, cadmium and glyphosate to pollution stress and HSPs in C. elegans. Master's Thesis, Northeast Normal University, China, 16 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.F. Ecological toxicicology of heavy metals and glyphosate. Doctoral dissertation, Nanjing Forestry University, China, 16 February 2014. 16 February.
- Han, B.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.F. , Luo, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Tian, M. Microbial ecological effects of soil contaminated with Zn, Pb and glyphosate. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 32, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B.; Li, R.Q.; Deng, M.C.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, J.B. Combined toxicity of arsenic with the pesticide glyphosate, and dichlorvos against C. elegans. Journal of Ecological Toxicology, 2013, 8, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.J.; Rao, C.Y.; Yuan, R.J.; Sun, D.D.; Guo, S.Q.; Li, L.L.; Yang, S.; Qian, D.D.; Lu, R.H.; Cao, X.L. Long-term exposure to polyethylene microplastics and glyphosate interferes with the behavior, intestinal microbial homeostasis, and metabolites of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Sci. Total Environ 2022, 814, 152681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, M. A method to assess glyphosate, glufosinate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in soil and earthworms. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzutti, I.R.; Vela, G.M.E.; De Kok, A.; Scholten, J.M.; Dias, J.V.; Cardoso, C.D.; Vivian, R. Determination of paraquat and diquat: LC-MS method optimization and validation. Food Chemistry 2016, 209, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA. Soil survey manual. In: Soil Survey Division Staff; Soil Conservation Service Volume Handbook 18. U.S. Department of Agriculture (chapter 3), 2017.
- China Pesticide Information Network. http://www.chinapesticide.org.cn/. (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Wołejko, E.; Jabłonska-Trypuc, A.; Wydro, U.; Butarewicz, A.; Łozowicka, B. Soil biological activity as an indicator of soil pollution with pesticides–a review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widenfalk, A.; Bertilsson, S.; Sundh, I.; Goedkoop, W. Effects of pesticides on community composition and activity of sediment microbes–responses at various levels of microbial community organization. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, H.; Vera, M.S.; Vinocur, A.; P´erez, G.; Ferraro, M.; Helman, R.M.; Santos, D.; Afonso, M. Glyphosate input modifies microbial community structure in clear and turbid freshwater systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5143–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, M.; Lorenz, N.; Saxena, J.; Ramsier, C.; Dick, R.P. The effect of glyphosate on soil microbial activity, microbial community structure, and soil potassium. Pedobiol. 2012, 55, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.; Bakker, P.A. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ka, J.O.; Cho, J.C. Members of the phylum Acidobacteria are dominant and metabolically active in rhizosphere soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 285, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Lemanceau, P.; van der Putten, W.H. Going back to the roots: The microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Long, M.X.; Yin, Y.J.; Si, M.R.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.Q.; Shen, X.H. Physiological roles of mycothiol in detoxification and tolerance to multiple poisonous chemicals in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Arch. Microbiol. 2013, 195, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, M.B.; Moreno, M.V.; Amodeo, M.R.; Bianchinotti, M.V. Effects of Glyphosate on soil fungal communities: A field study. Revista Argentina de Microbiología, 2021, 53, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romdhane, S.; Devers-Lamrani, M.; Beguet, J.; Bertrand, C.; Calvayrac, C.; Salvia, M.V.; Jrad, A.B.; Dayan, F.E.; Spor, A.; Barthelmebs, L.; Martin-Laurent, F. Assessment of the ecotoxicological impact of natural and synthetic β-triketone herbicides on the diversity and activity of the soil bacterial community using omic approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashar, P.; Shah, S. Impact of fertilizers and pesticides on soil microflora in agriculture. In: Sustainable Agriculture Reviews. Springer, Cham 2016, 331–36.
| Treatment | Concentration (mg kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (l) | Middle (m) | High (h) | |
| Blank (CK) | 0 | ||
| Glyphosate (G) | 0.6 (Gl) | 6 (Gm) | 60 (Gh) |
| Diquat (D) | 0.4 (Dl) | 4 (Dm) | 40 (Dh) |
| Glyphosate+diquat (GD) | 0.6+0.4 (GDl) | 6+4 (GDm) | 60+40 (GDh) |
| Index | Treatment | Days after application | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 14 | 28 | ||
| Shannon | CK | 5.918±0.311ab | 7.264±0.027bc | 7.556±0.023cd | 7.315±0.093abc |
| Gl | 6.390±0.071a | 7.458±0.009a | 7.650±0.017abc | 7.254±0.320bc | |
| Gm | 6.249±0.063a | 7.405±0.032ab | 7.736±0.022a | 7.497±0.090ab | |
| Gh | 6.266±0.161a | 7.145±0.051c | 7.671±0.018ab | 7.453±0.067abc | |
| Dl | 6.131±0.140a | 7.407±0.033ab | 7.583±0.015bcd | 7.416±0.027abc | |
| Dm | 5.382±0.379b | 7.485±0.044a | 7.669±0.030ab | 7.629±0.006a | |
| Dh | 5.770±0.256ab | 7.416±0.038ab | 7.404±0.011e | 7.152±0.014bc | |
| GDl | 6.298±0.046a | 7.381±0.029ab | 7.284±0.078f | 7.100±0.034c | |
| GDm | 6.409±0.001a | 7.414±0.090ab | 7.505±0.015d | 7.090±0.023c | |
| GDh | 6.092±0.104a | 7.370±0.106ab | 7.499±0.038de | 7.238±0.039bc | |
| Chao1 | CK | 2188.649±150.191bcd | 2263.584±36.558ab | 2369.947±39.031a | 2303.254±45.996ab |
| Gl | 2536.324±75.475ab | 2377.208±3.108a | 2352.648±36.608a | 2219.027±135.281b | |
| Gm | 2602.062±60.436a | 2338.966±56.674a | 2386.601±49.563a | 2450.166±44.036aA | |
| Gh | 2508.073±91.128abc | 2184.617±30.267b | 2417.438±28.661a | 2285.848±30.396ab | |
| Dl | 2229.911±153.341bcd | 2406.547±28.774a | 2334.005±44.040a | 2352.122±40.203ab | |
| Dm | 1993.626±203.891d | 2417.230±8.741a | 2351.966±34.642a | 2254.606±47.180b | |
| Dh | 2154.460±98.706cd | 2329.326±48.987ab | 2249.354±70.180a | 2297.709±26.360ab | |
| GDl | 2372.901±44.448abc | 2332.078±103.682ab | 2305.535±69.564a | 2309.014±8.035ab | |
| GDm | 2488.896±9.119abc | 2363.224±52.350a | 2358.002±63.922a | 2366.971±23.944ab | |
| GDh | 2250.869±64.077abcd | 2380.824±14.352a | 2332.714±39.074a | 2250.471±9.346b | |
| Index | Treatment | Days after Application | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 14 | 28 | ||
| Shannon | CK | 4.780±0.083abc | 4.368±0.046cd | 4.614±0.015a | 4.727±0.044abc |
| Gl | 4.882±0.054a | 4.634±0.023ab | 4.363±0.029ab | 4.783±0.039ab | |
| Gm | 4.765±0.011ab | 4.635±0.086bc | 4.259±0.135ab | 4.980±0.057a | |
| Gh | 4.544±0.129d | 4.231±0.043d | 4.388±0.121ab | 4.684±0.023cd | |
| Dl | 4.686±0.072bcd | 4.371±0.020cd | 4.259±0.076ab | 4.708±0.007bcd | |
| Dm | 4.683±0.018abc | 4.652±0.044ab | 4.516±0.052ab | 4.661±0.028bcd | |
| Dh | 4.509±0.014cd | 4.800±0.053a | 4.488±0.043ab | 4.598±0.053cd | |
| GDl | 4.688±0.033abc | 4.405±0.049cd | 4.128±0.111b | 4.867±0.076bcd | |
| GDm | 4.452±0.014d | 4.325±0.028cd | 4.376±0.097ab | 4.821±0.134abcd | |
| GDh | 4.763±0.060abc | 4.490±0.069cd | 4.369±0.010ab | 4.547±0.053d | |
| Chao1 | CK | 673.214±21.296ab | 543.470±18.721bc | 462.809±3.810b | 455.377±60.937a |
| Gl | 773.434±39.275ab | 579.153±19.726abc | 464.205±2.574b | 479.181±56.792a | |
| Gm | 772.912±28.255a | 626.580±29.634a | 465.700±4.486b | 469.934±53.990a | |
| Gh | 717.335±44.500ab | 510.983±12.810c | 452.857±1.069b | 438.914±55.892a | |
| Dl | 733.530±38.877ab | 546.209±15.359bc | 461.212±6.469b | 438.962±53.068a | |
| Dm | 706.838±26.245ab | 595.042±19.484ab | 477.764±9.637b | 425.494±44.871a | |
| Dh | 641.645±17.447b | 578.217±19.415ab | 468.624±8.868b | 437.094±48.999a | |
| GDl | 697.382±28.165ab | 540.641±15.796bc | 452.803±0.858b | 455.715±39.099a | |
| GDm | 666.482±30.530b | 500.521±2.086bc | 496.728±3.212a | 491.149±35.763a | |
| GDh | 679.040±27.961ab | 541.952±8.107abc | 499.915±16.673b | 426.687±6.304a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




