Submitted:
24 April 2023
Posted:
24 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Patients
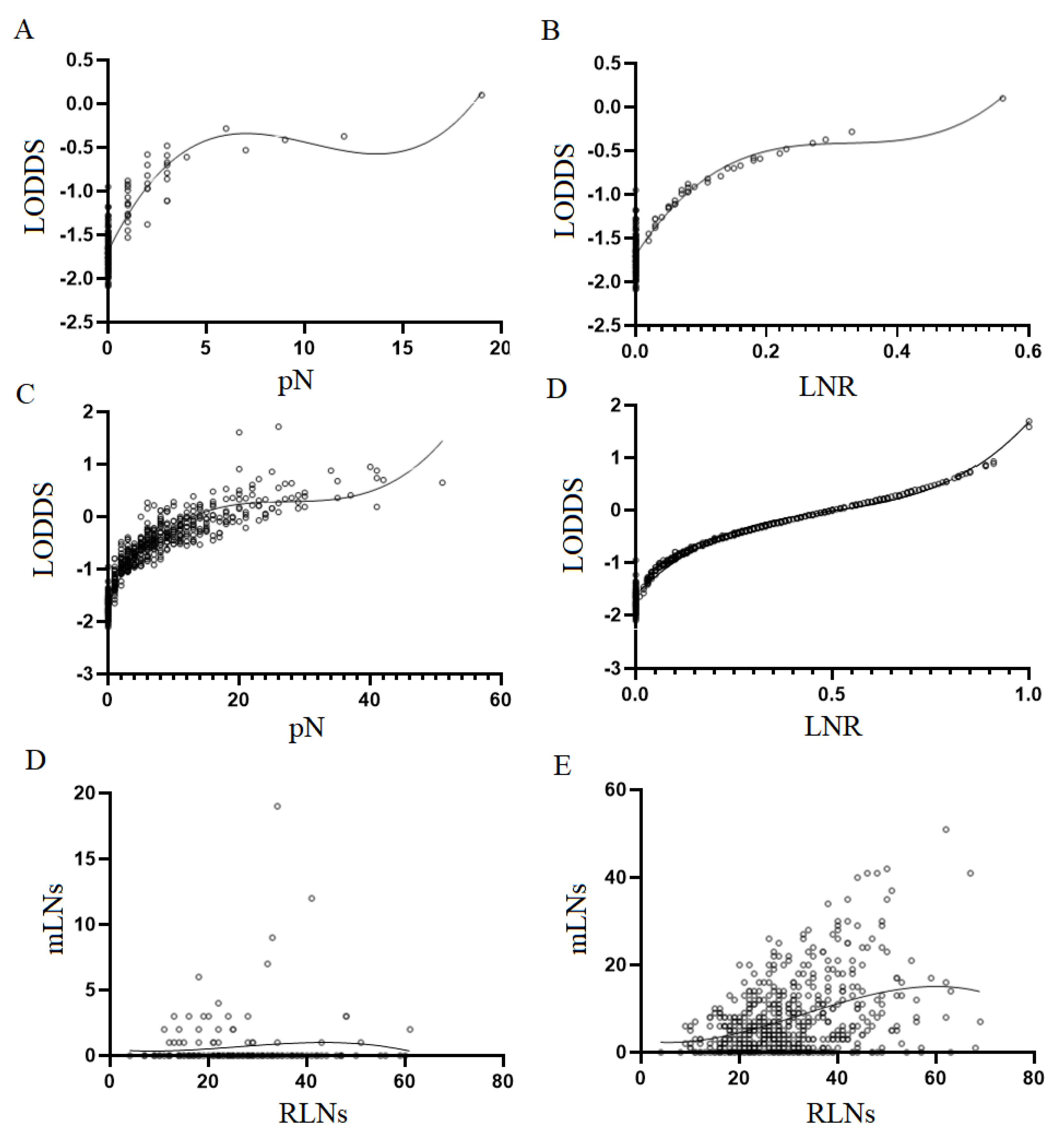
2.2. Lymph node staging system
2.3. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical characteristics
| Characteristics | pT1 (n=165) | pT2-pT4 (n=528) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.005 | ||
| Male | 90(54.5) | 352(66.7) | |
| Female | 75(45.5) | 176(33.3) | |
| Age, median, range | 55 (29-81) | 59 (23-82) | <0.001 |
| Tumor location | 0.001 | ||
| Upper | 8(4.8) | 58(11.0) | |
| Middle | 29(17.6) | 80(15.2) | |
| Lower | 128(77.6) | 358(67.8) | |
| Total | 0(0.0) | 32(6.1) | |
| Tumor size (mm) | <0.001 | ||
| ≤50 | 148(89.7) | 240(45.5) | |
| >50 | 17(10.3) | 288(54.5) | |
| pN | <0.001 | ||
| pN0 | 130(78.8) | 86(16.3) | |
| pN1 | 21(12.7) | 81(15.3) | |
| pN2 | 10(6.1) | 132(25.0) | |
| pN3 | 4(2.4) | 229(43.4) | |
| pTNM | <0.001 | ||
| Ⅰ | 151(91.2) | 27(5.1) | |
| Ⅱ | 13(7.9) | 144(27.3) | |
| Ⅲ | 1(0.6) | 357(67.6) | |
| Vascular invasion | <0.001 | ||
| No | 143(86.7) | 226(42.8) | |
| Yes | 22(13.3) | 302(57.2) | |
| Neural infiltration | <0.001 | ||
| No | 151(91.5) | 100(18.9) | |
| Yes | 14(8.5) | 428(81.1) | |
| LNR | <0.001 | ||
| 0-0.2 | 159(96.4) | 272(51.5) | |
| 0.2-0.4 | 5(3.0) | 128(24.2) | |
| 0.4-0.6 | 1(0.6) | 72(13.6) | |
| >0.6 | 0(0.0) | 56(10.6) | |
| LODDS | <0.001 | ||
| LODDS 0 | 111(62.3) | 79(15.0) | |
| LODDS 1 | 31(18.8) | 71(13.4) | |
| LODDS 2 | 18(10.9) | 143(27.1) | |
| LODDS 3 | 4(2.4) | 154(29.2) | |
| LODDS 4 | 1(0.6) | 81(15.3) |
3.2. Comparison of predictive performance of lymph node staging systems
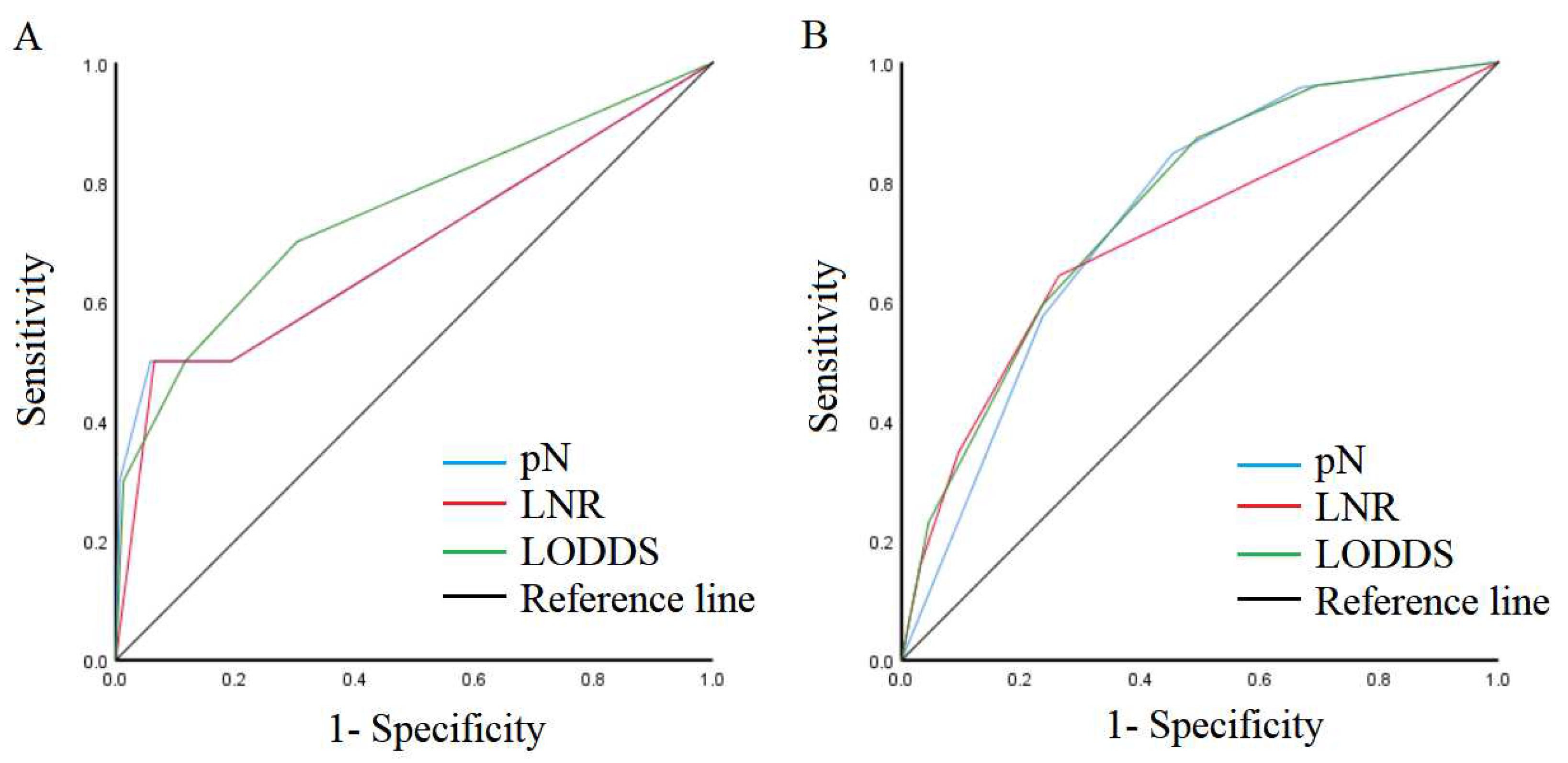
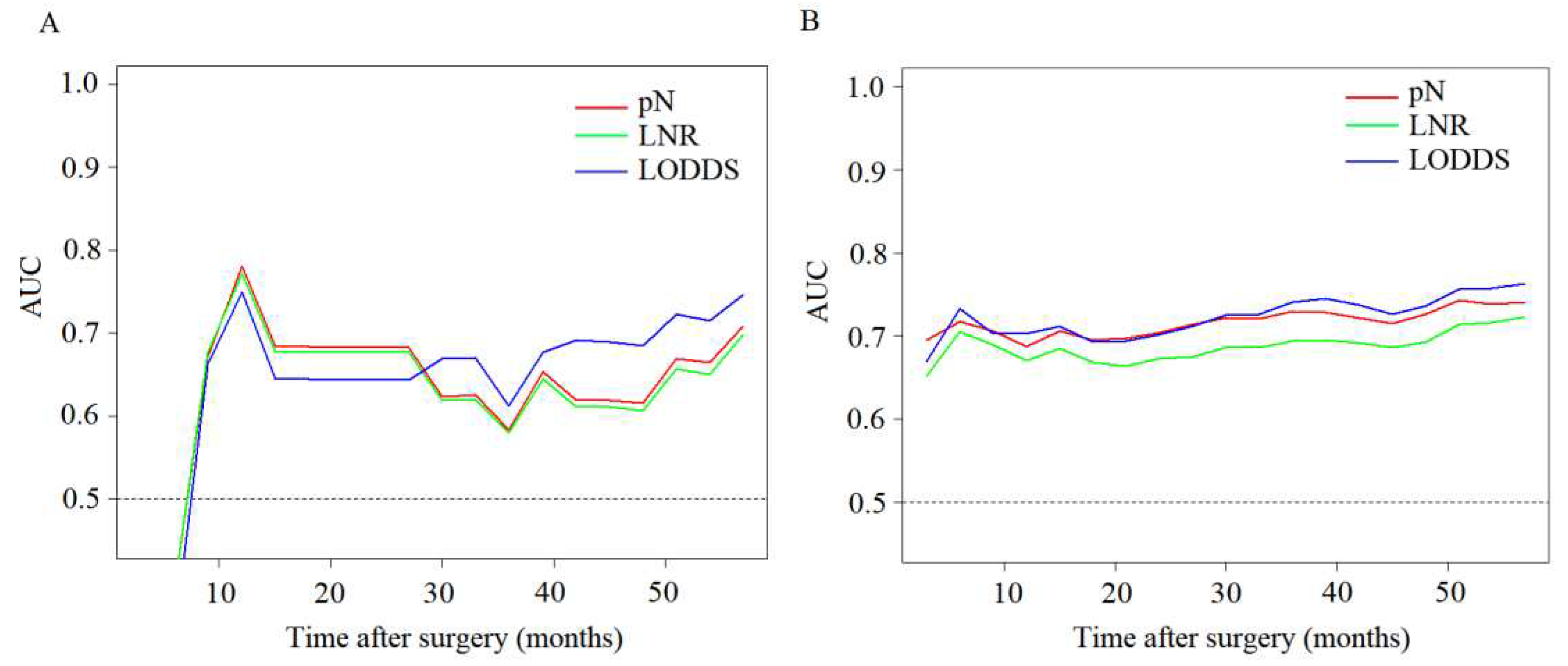
3.3. Effect of lymph node metastasis on patient outcomes
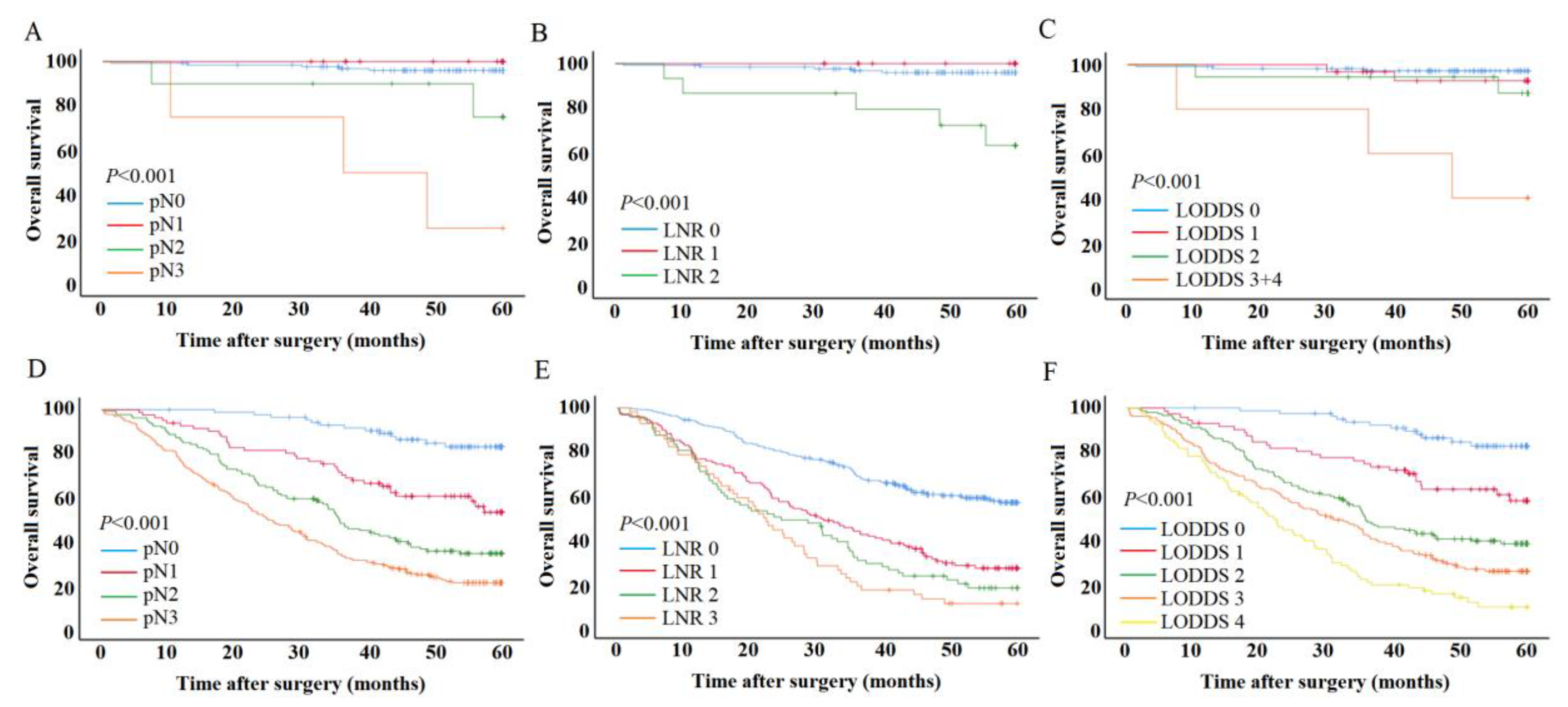
3.4. Univariate and multivariate analysis for patient outcomes
| Characteristics | Multivariate analysis for pN | Multivariate analysis for LNR | Multivariate analysis for LODDS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Vascular invasion | 0.091 | 0.074 | 0.045 | |||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 3.254(0.828-12.792) | 3.423(0.889-13.173) | 3.789(1.031-13.919) | |||
| pN | 0.003 | |||||
| pN0 | 1 | |||||
| pN1 | 0.000(0.000-inf) | 0.983 | ||||
| pN2 | 4.067(0.745-22.187) | 0.105 | ||||
| pN3 | 18.219(3.950-84.030) | <0.001 | ||||
| LNR | 0.017 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | |||||
| 0.1 | 0.000 | 0.984 | ||||
| >0.1 | 6.823(1.831-25.427) | 0.004 | ||||
| LODDS | 0.002 | |||||
| LODDS 0 | 1 | |||||
| LODDS 1 | 2.207(0.367-13.278) | 0.387 | ||||
| LODDS 2 | 3.595(0.598-21.635) | 0.162 | ||||
| LODDS 3+4 | 21.966(4.293-112.394) | <0.001 | ||||
| Characteristics | Multivariate analysis for pN | Multivariate analysis for LMR | Multivariate analysis for LODDS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Age | 1.012(1.011-1.023) | 0.032 | 1.012(1.001-1.023) | 0.036 | 1.010(0.999-1.021) | 0.072 |
| Tumor location | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.006 | |||
| Upper | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Middle | 0.635(0.405-0.996) | 0.048 | 0.712(0.454-1.117) | 0.139 | 0.717(0.457-1.125) | 0.148 |
| Lower | 0.843(0.590-1.203) | 0.347 | 0.938(0.655-1.343) | 0.726 | 0.914(0.639-1.307) | 0.621 |
| Total | 1.785(1.085-2.937) | 0.023 | 1.878(1.125-3.133) | 0.016 | 1.734(1.039-2.893) | 0.035 |
| Vascular invasion | 0.381 | 0.189 | 0.314 | |||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.116(0.873-1.427) | 1.184(0.920-1.524) | 1.136(0.886-1.456) | |||
| Neural infiltration | 0.026 | 0.023 | 0.023 | |||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.471(1.047-2.068) | 1.490(1.056-2.102) | 1.489(1.057-2.096) | |||
| pN | <0.001 | |||||
| pN1 | 1 | |||||
| pN2 | 2.917(1.532-5.551) | 0.001 | ||||
| pN3 | 5.440(3.012-9.825) | <0.001 | ||||
| LMR | <0.001 | |||||
| 0-0.2 | 1 | |||||
| 0.2-0.4 | 2.088(1.565-2.785) | <0.001 | ||||
| 0.4-0.6 | 2.663(1.892-3.748) | <0.001 | ||||
| >0.6 | 3.002(2.056-4.385) | <0.001 | ||||
| LODDS | <0.001 | |||||
| LODDS 0 | 1 | |||||
| LODDS 1 | 2.733(1.380-5.415) | 0.004 | ||||
| LODDS 2 | 5.055(2.751-9.289) | <0.001 | ||||
| LODDS 3 | 6.786(3.690-12.481) | <0.001 | ||||
| LODDS 4 | 9.565(5.040-18.155) | <0.001 | ||||
3.5. Nomogram in the patient outcomes
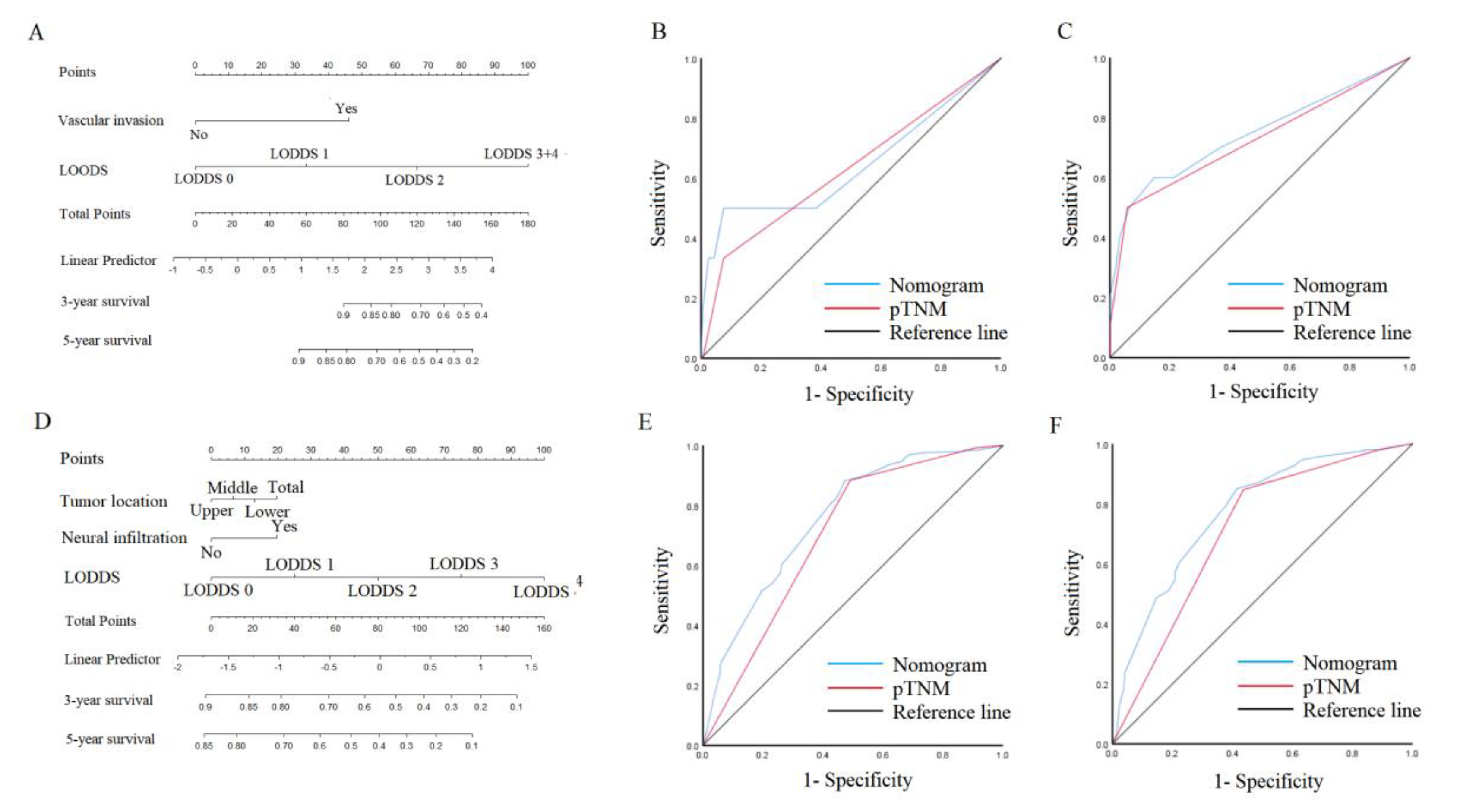
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding information
Ethical approval
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henson, D.E.; Dittus, C.; Younes, M.; Nguyen, H.; Albores-Saavedra, J. Differential trends in the intestinal and diffuse types of gastric carcinoma in the United States, 1973-2000: increase in the signet ring cell type. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004, 128, 765–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernot, S.; Voron, T.; Perkins, G.; Lagorce-Pages, C.; Berger, A.; Taieb, J. Signet-ring cell carcinoma of the stomach: Impact on prognosis and specific therapeutic challenge. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11428–11438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-C.; Fang, W.-L.; Wang, R.-F.; Li, A.F.-Y.; Yang, M.-H.; Wu, C.-W.; Shyr, Y.-M.; Huang, K.-H. Clinicopathological differences in signet ring cell adenocarcinoma between early and advanced gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2018, 22, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Lv, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B.; Lin, J. Different prognostic significance of signet ring cell histology for early and advanced gastric cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 14, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.J.; Kim, G.S. Prognostic significance of lymph node metastasis in advanced carcinoma of the stomach. Br. J. Surg. 1996, 83, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, S.; Byrd, D.; Compton, C.; Fritz, A.; Greene, F.; Trotti, A. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.K.; Yang, H.-K.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, K.U.; Choe, K.J.; Kim, J.-P. Influence of the number of lymph nodes examined on staging of gastric cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2001, 88, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian-Hui, C.; Shi-Rong, C.; Hui, W.; Si-Le, C.; Jian-Bo, X.; Er-Tao, Z.; Chuang-Qi, C.; Yu-Long, H. Prognostic value of three different lymph node staging systems in the survival of patients with gastric cancer following D2 lymphadenectomy. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 11105–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Appleby, D.; Zhang, X.; Gan, L.; Wang, J.; Wan, F. Comparison of three lymph node staging schemes for predicting outcome in patients with gastric cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2013, 100, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolverato, G.; Ejaz, A.; Kim, Y.; Squires, M.H.; Poultsides, G.; Fields, R.C.; Bloomston, M.; Weber, S.M.; Votanopoulos, K.; Acher, A.W.; et al. Prognostic Performance of Different Lymph Node Staging Systems After Curative Intent Resection for Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018 (5th edition). Gastric Cancer, 2021. 24(1): p. 1-21.
- Park, J.; Jeon, C.H.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, H.S.; Song, K.Y.; Lee, H.H. A Novel Approach for Gastric Cancer Staging in Elderly Patients Based on the Lymph Node Ratio. J. Gastric Cancer 2021, 21, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.C.; Kil Lee, S.; Shin, S.K.; Park, J.C.; Chung, H.S.; Park, J.J.; et al. Is the recent WHO histological classification for gastric cancer helpful for application to endoscopic resection? Gastric Cancer 2015, 19, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Jing, J.; Ma, G. Development and validation of prognostic nomogram based on log odds of positive lymph nodes for patients with gastric signet ring cell carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 32, 778–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hao, X.; Liang, H. Superiority of the Ratio Between Negative and Positive Lymph Nodes for Predicting the Prognosis for Patients With Gastric Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 22, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzon, L.; Mercantini, P.; Ferri, M.; La Torre, M.; Sparagna, A.; Balducci, G.; Cavallini, M.; Ziparo, V. Lymph-Node Ratio Classification Strongly Correlates with Cancer Survivals of Patients Who Underwent R0 Resection for Gastric Cancer with More than 15 Nodes Harvested. Eur. Surg. Res. 2014, 53, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinh-Hung, V.; Verschraegen, C.; I Promish, D.; Cserni, G.; Van de Steene, J.; Tai, P.; Vlastos, G.; Voordeckers, M.; Storme, G.; Royce, M. Ratios of involved nodes in early breast cancer. 2004, 6, R680–R688. [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, A.R., D.M. Sosin, and C.K. Wells, The Will Rogers phenomenon. Stage migration and new diagnostic techniques as a source of misleading statistics for survival in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985. 312, 1604–1608.
- Sun, Z.; Zhu, G.-L.; Lu, C.; Guo, P.-T.; Huang, B.-J.; Li, K.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.-M.; Wang, Z.-N.; Xu, H.-M. The impact of N-ratio in minimizing stage migration phenomenon in gastric cancer patients with insufficient number or level of lymph node retrieved: results from a Chinese mono-institutional study in 2159 patients. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, I.J.; Kook, M.C.; Nam, B.-H.; Kim, Y.-W.; Ryu, K.W. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with early gastric cancer and signet ring cell histology. Br. J. Surg. 2010, 97, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunisaki, C.; Shimada, H.; Nomura, M.; Matsuda, G.; Otsuka, Y.; Akiyama, H. Therapeutic strategy for signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach. Br. J. Surg. 2004, 91, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Deng, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Liang, H.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Z. Superiority of log odds of positive lymph nodes (LODDS) for prognostic prediction after gastric cancer surgery: a multi-institutional analysis of 7620 patients in China. Surg. Today 2020, 51, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.F.K.P.; Pereira, M.A.; Dias, A.R.; Yagi, O.K.; Zaidan, E.P.; Ribeiro-Júnior, U.; Zilberstein, B.; Cecconello, I. Surgical outcomes of gastrectomy with D1 lymph node dissection performed for patients with unfavorable clinical conditions. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2018, 45, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.D.; Schwarz, R.R.; Schwarz, R.E. Impact of total lymph node count on staging and survival after gastrectomy for gastric cancer: data from a large US-population database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7114–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Desiderio, J.; Li, Z.; Tozzi, F.; Ji, J.; Parisi, A. The development and external validation of a nomogram predicting overall survival of gastric cancer patients with inadequate lymph nodes based on an international database. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




