Submitted:
22 April 2023
Posted:
23 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
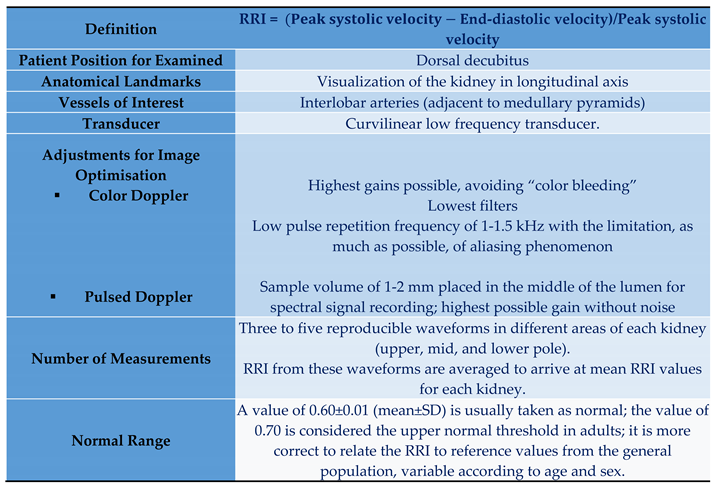
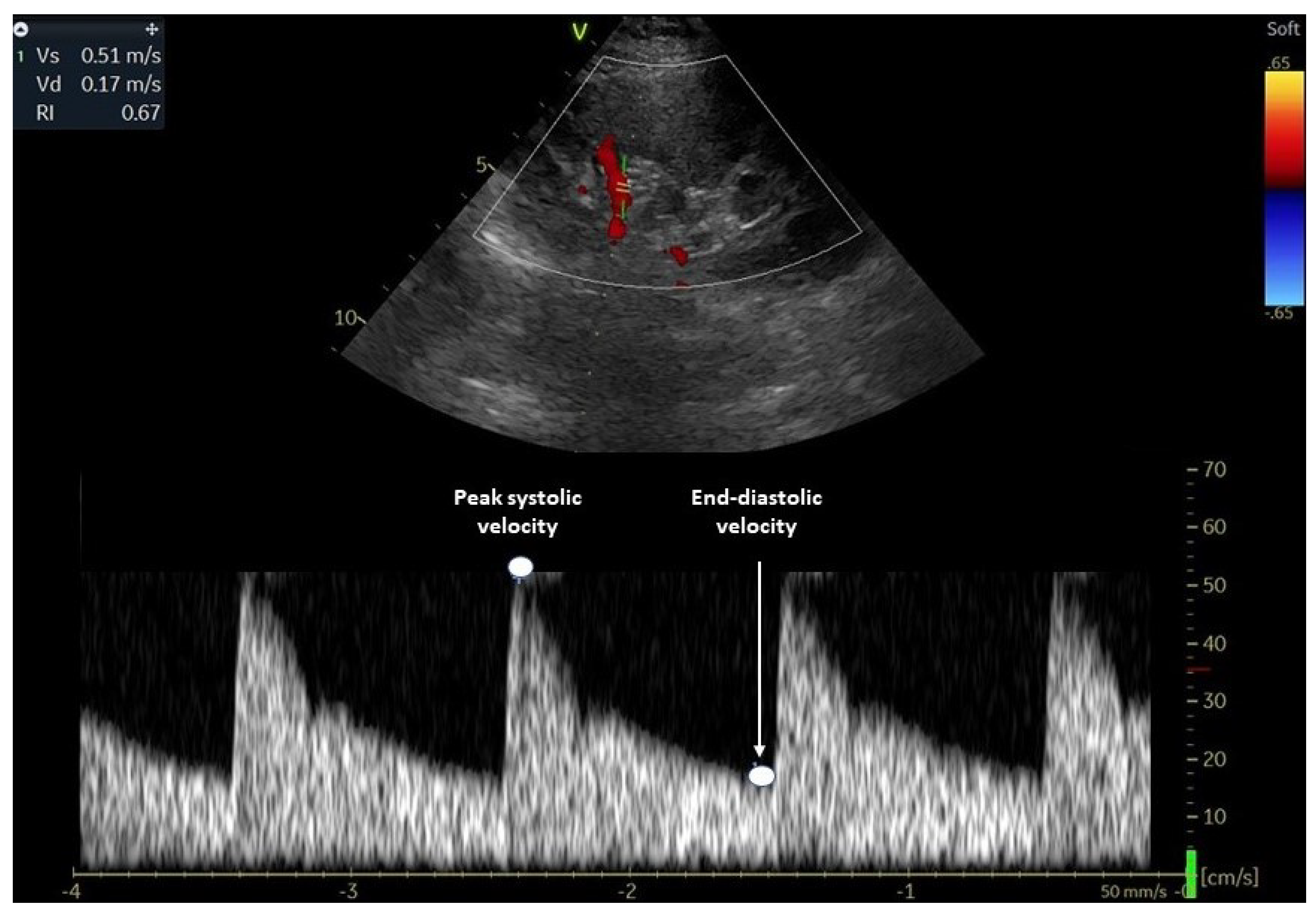
2. Evaluation of Renal Resistive Index
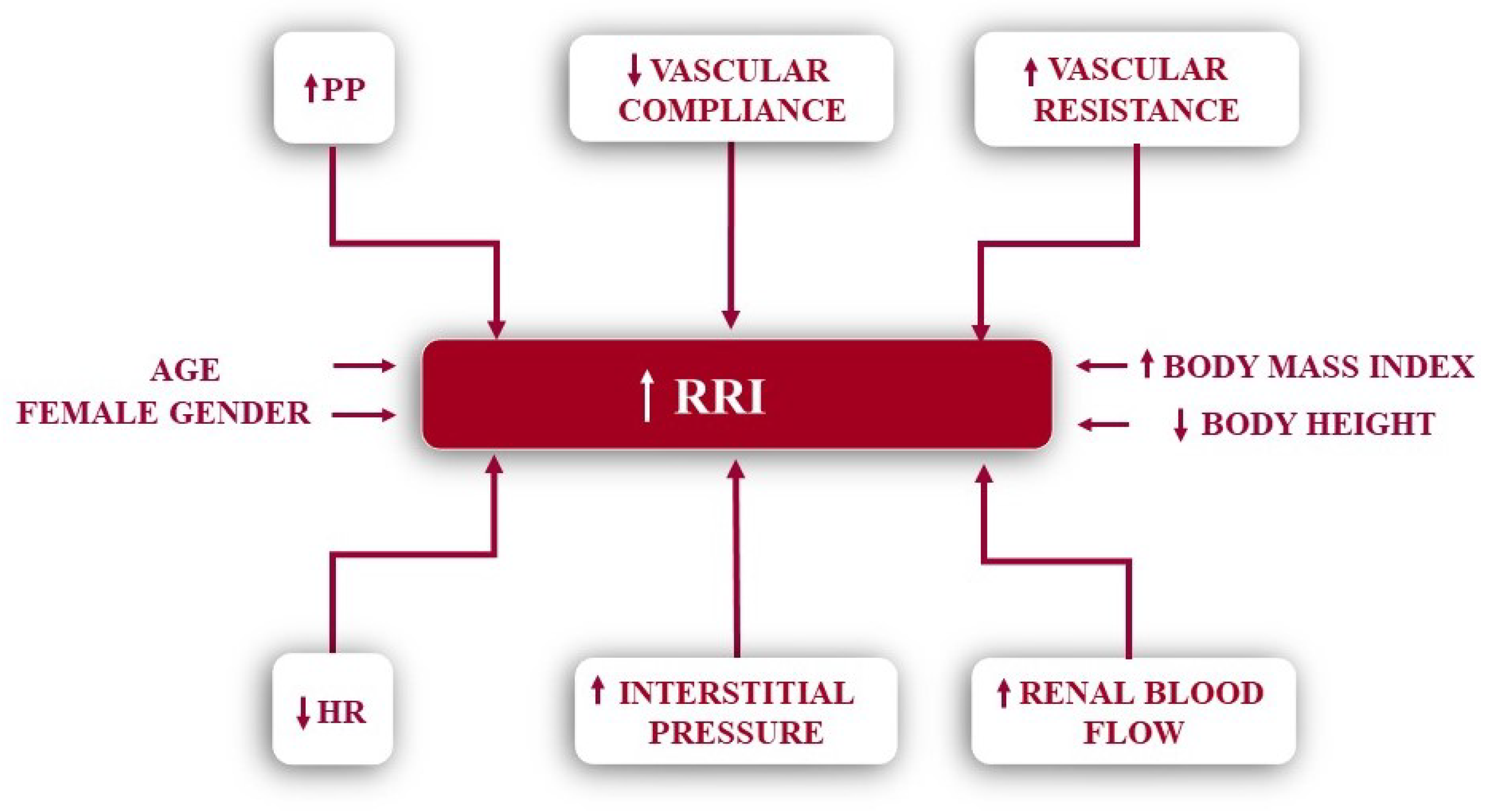
3. Determinants of Renal Resistive Index
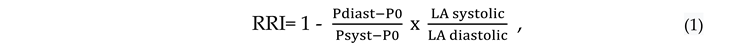
3.1. Renal Resistive Index in Kidney Disease
3.2. Renal Resistive Index and the Cardiovascular System
3.3. RRI Interaction with Other Diseases
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pourcelot, L. Applications clinique de 1'examen Doppler transcutané . In: Velocimetric Ultrasonore Doppler, Pourcelot, L (Eds), 1974, 34, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, R.H.; Luhmann, K.; Ruggenenti, P. Doppler ultrasound evaluation of normal native kidneys and native kidneys with urinary tract obstructions. J Ultrasound Med. 1989, 8, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warshauer, D.M.; Taylor, K.J.; Bia, M.J.; Marks, W.; Weltin, G.; Rigsby, C.; True, L.; Lorber, M.I. Unusual causes of increased vascular impedance in renal transplants: duplex Doppler evaluation. Radiology. 1988, 169, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, W.C. Sonographic evaluation of renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, 1021–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tublin, M.E.; Bude, R.O.; Platt, J.F. The resistive index in renal Doppler sonography: where do we stand? AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2003, 180, 885–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, A.; Zanoli, L.; Clementi, S.; DiNicolo, P.; Fiorini, F. Resistive renal index: myth or reality. Br J Radiol. 2014, 87, 20140004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, B.; Pruijm, M.; Ackermannn, D.; Vuistiner, P.; Eisenberger, U.; Guessous, I.; Rousson, V.; Mohaupt, M.G.; Alwan, H.; Ehret, G.; Pechere-Bertschi, A.; Paccaud, F.; Staessen, J.A.; Vogt, B.; Burnier, M.; Martin, P.Y.; Bochud, M. Reference values and factors associated with renal resistive index in a family-based population study. Hypertension. 2014, 63, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikou, I.; Tsioufis, C.; Konstantinidis, D.; Kasiakogias, A.; Dimitriadis, K.; Leontsinis, I.; Andrikou, E.; Sanidas, E.; Kallikazaros, I.; Tousoulis, D. Renal resistive index in hypertensive patients. J Clin Hypertens. 2018, 20, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, F.; Barozzi, L. The role of ultrasonography in the study of medical nephropathy. J Ultrasound. 2007, 10, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.W. Renal resistive index. A case of mistaken identity. Hypertension, 2014, 64, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bude, R.O.; Rubin, J.M. Relationship between the resistive index and vascular compliance associated with renal transplants. Radiology. 1999, 211, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tublin, M.E.; Tessler, F.N.; Murphy, M.E. Correlation between renal vascular resistance, pulse pressure, and resistive index in isolated perfused rabbit kidneys. Radiology. 1999, 213, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.E.; Tublin, M.E. Understanding the Doppler RI: impact of renal arterial distensibility on the RI in a hydronephrotic ex vivo rabbit kidney model. J Ultrasound Med. 2000, 19, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudon, M.; Barnewolt, C.E.; Taylor, G.A.; Dunning, P.S.; Boget, R.; Badwy, A.B. Renal blood flow in pigs: changes depicted with contrast-enhanced harmonic US imaging during acute urinary obstruction. Radiology. 1999, 212, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumme, B.; Grotz, W.; Kirste, G.; Schollmeyer, P.; Rump, L.C. Determination of intrarenal Doppler indices in stable renal allografts. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997, 8, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesens, M.; Heylen, L.; Lerut, E.; Claes, K.; De Wever, L.; Claus, F.; Oyen, R.; Kuypers, D.; Evenepoel, P.; Bammens, B.; Sprangers, B.; Meijers, B.; Pirenne, J.; Monbaliu, D.; de Jonge, H.; Metalidis, C.; De Vusser, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y. Intrarenal resistive index after renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2013, 369, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.F.; Safar, M. E; Relationship between aortic stiffness and microvascular disease in brain and kidney: cause and logic of therapy. Hypertension. 2005, 46, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikee, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Hemmi, N.; Imakiire, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Moriya, H.; Suzuki, S.; Miura, S. Correlation between the resistive index by Doppler ultrasound and kidney function and histology. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, G.; Florescu, C.; Sabo, A.A.; Stancu, S.; Mircescu, G. Intrarenal resistive index conundrum: systemic atherosclerosis versus renal arteriosclerosis. Ren Fail. 2019, 41, 930–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmon, M.; Schnell, D.; Zeni, F. Doppler-based renal resistive index: a comprehensive review; In: Vincent, J-L (ed): Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. Springer, Heidelberg. 2010, 331-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mostbeck, G.H.; Gössinger, H.D.; Mallek, R.; Siostrzonek, P.; Schneider, P.; Tscholakoff, D. Effect of heart rate on Doppler measurements of resistive index in renal arteries. Radiology. 1990, 175, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, J.; Ito, S. Central pulse pressure and aortic stiffness determine renal hemodynamics: pathophysiological implication for microalbuminuria in hypertension. Hypertension. 2011, 58, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, T.; Cauwenberghs, N.; Knez, J.; Thijs, L.; Liu, Y.P.; Gu, Y.M.; Staessen, J.A. Doppler indexes of left ventricular systolic and diastolic flow and central pulse pressure in relation to renal resistive index. Am J Hypertens. 2015, 28, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, C.; Thomas, G.; Schold, J.D.; Arrigain, S.; Gornik, H.L.; Nally, J.V.; Navaneethan, D. Reanal resistive index and mortality in chronic kidney disease. Hypertension. 2015, 66, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Yu, M.L.; Dai, C.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Chuang, W.L.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Tsai, J.F.; Chang, W.Y. Influence of age in intrarenal resistive index measurement in normal subjects. Abdom Imaging. 2003, 28, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedesco, M.A.; Natale, F.; Mocerino, R.; Tassinario, G.; Calabrò, E. Renal resistive index and cardiovascular organ damage in a large population of hypertensive pts. J Hum Hypertens. 2007, 21, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stea, F.; Sgrò, M.; Faita, F.; Bruno, R.M.; Cartoni, G.; Armenia, S.; Taddei, S.; Ghiadoni, L. Relationship between wave reflection and renal damage in hypertensive patients: a retrospective analysis. J Hypertens. 2013, 31, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabia, J.; Torguet, P.; Garcia, I.; Martin, N.; Mate, G.; Marin, A.; Molina, C.; Valles, M. The relationship between renal resistive index, arterial stiffness, and atherosclerotic burden: the link between macrocirculation and microcirculation. J Clin Hypertens. 2014, 16, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaques, D.A.; Pruijm, M.; Ackermann, D.; Vogt, B.; Guessous, I.; Burnier, M.; Pechere-Bertschi, A.; Bochud, M.; Ponte, B. Sodium intake is associated with renal resistive index in an adult population-based study. Hypertension. 2020, 76, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, P.M.; Bates, J.A.; Irving, H.C. Intrarenal Doppler ultrasound studies in normal and acutely obstructed kidneys. Br J Radiol. 1992, 65, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroun, A. Duplex Doppler sonography in patients with acute renal colic: prospective study and literature review. Int Urol Nephrol. 2003, 35, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, J.F.; Ellis, J.H.; Rubin, J.M. Intrarenal arterial Doppler sonography in the detection of renal vein thrombosis of the native kidney. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994, 162, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, J.F.; Ellis, J.H.; Rubin, J.M.; DiPietro, M.A.; Sedman, A.B. Intrarenal arterial Doppler sonography in patients with non-obstructive renal disease: correlation of resistive index with biopsy findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990, 154, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostbeck, G.H.; Kain, R.; Mallek, R.; Derfler, K.; Walter, R.; Havelek, L.; Tscholakoff, D. Duplex Doppler sonography in renal parenchymal disease. Histopathologic correlation. J Ultrasound Med. 1991, 10, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddi, M.; Cecioni, I.; Poggesi, L.; Fiorentino, F.; Olianti, K.; Berardino, S.; La Cava, G.; Gensini, G. Renal resistive index early detects chronic tubulointerstitial in normo-and hypertensive pts. Am J Nephrol. 2006, 26, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikee, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Hemmi, N.; Imakiire, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Moriya, H.; Suzuki, S.; Miura, S. Correlation between the resistive index by Doppler ultrasound and kidney function and histology. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Splendiani, G.; Parolini, C.; Fortunato, L.; Sturniolo, A.; Costanzi, S. Resistive index in chronic nephropathies: predictive value of renal outcome. Clin Nephrol. 2002, 57, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radermacher, J.; Ellis, S.; Haller, H. Renal resistive index and progression of renal disease. Hypertension. 2002, 39, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Wada, A. Resitive index predicts renal prognosis in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009, 24, 2780–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Wada, A. Resistive index predicts renal prognosis in chronic kidney disease: results of a 4-year follow-up. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011, 15, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigé, N.; Lévy, P.P.; Callard, P.; Faintuch, J.M.; Chigot, V.; Jousselin, V.; Ronco, P.; Boffa, J.J. Renal arterial resistive index is associated with severe histological changes and poor renal outcome during chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2012, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Son, Y.K.; Kim, S.E.; An, W.S. Resistive index as predictor of renal progression in patients with moderate renal dysfunction regardless of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor antagonist medication. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2017, 36, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanamura, K.; Tojo, A.; Kinugasa, S.; Asaba, K.; Fujita, T. The RRI is a marker of renal function, pathology, prognosis and responsiveness to steroid therapy in chronic kidney disease patients. Int J Nephrol, 2012; 2012, 139565. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, G.; Mioni, R.; Danieli, N.; Bertoni, M.; Croatto, E.; Merla, L.; Alcaro, L.; Peduzza, A.; Metcalf, X.; Rigamonti, A.; Catena, C.; Sechi, A.L.; Colussi, G. Elevated intrarenal resistive index predicted faster renal function decline and long-term mortality in non-proteinuric chronic kidney Dis. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangri, N.; Stevens, L.A.; Griffith, J.; Tighiouart, H.; Djurdjev, O.; Naimark, D.; Levin, A.; Levey, A.S. A predictive model for progression of chronic kidney disease to kidney failure. JAMA. 2011; 305, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Lennartz, C.S.; Pickering, J.W.; Seiler-Mußler, S.; Bauer, L; Untersteller, K; Insa, E. E; Zawada, A.M.; Radermacher, J.; Tangri, N.; Fliser, D. External validation of the kidney failure risk equation and re-calibration with addition of ultrasound parameters. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016, 11, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, Y.; Fujii, K.; Arima, H.; Matsumara, K.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Tokumoto, M.; Tsuruya, K.; Kanai, H.; Iwase, M.; Hirakata, H.; Iida, M. Increased renal resistive index in atherosclerosis and diabetic nephropathy assessed by Doppler sonography. J Hypertens. 2005, 23, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, J.F.; Rubin, J.M.; Ellis, J.H. Diabetic nephropathy: evaluation with renal duplex Doppler US. Radiology, 1994, 190, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, V.; Malik, A. Role of intrarenal resistive index and ElastPQ® renal shear modulus in early diagnosis and follow-up of diabetic nephropathy: A prospective study. Ultrasound. 2020, 28, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimura, E; Nishizawa, Y; Kawagishi, T; Okuno, Y; Kogawa, K; Fukumoto, S, Maekawa, K. ; Hosoi, M.; Inaba, M.; Emoto, M.; Morii, H. Intrarenal hemodynamic abnormalities in diabetic nephropathy measured by duplex Doppler sonography. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Ishimura, E.; Taniwaki, H.; Emoto, M.; Shoji, T.; Kawaguchi, T. , Inaba, M.; Nishizawa, Y. Diabetes mellitus worsens intrarenal hemodynamic abnormalities in nondialysed patients with chronic renal failure. Nephron. 2000, 86, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamano, K.; Nitta, A.; Ohtake, T.; Kobayashi, S. Association of renal vascular resistive index with albuminuria and other macroangiopathy I type 2 diabetic patients. Diabtes Care. 2008, 31, 1853–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masulli, M.; Mancini, M.; Liuzzi, R.; Daniele, S.; Mainenti, P.P.; Vergara, E.; Genovese, S.; Salvatore, M.; Vaccaro, O. Measurement of the intrarenal arterial resistance index for the identification and prediction of diabetic nephropathy. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009, 19, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, G.; Lin, Y.; Wei, C.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y. Ultrasonography combined with blood biochemistry on the early diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease. Dis Markers. 2022, 4231535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosadini, R.; Velussi, M.; Brocco, E.; Abaterusso, C.; Carraro, A.; Piarulli, F.; Morgia, G.; Satta, A.; Faedda, R.; Abhyankar, A.; Luthman, H.; Tonolo, G. Increased renal arterial resistance predicts the course of renal function in type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria. Diabetes. 2006, 55, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Y.; He, T.; Xiao, T.; Li, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, J. Potential role of the renal arterial resistance index in the differential diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022, 12, 731187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insalaco, M.; Zamboli, P.; Floccari, F.; Marrocco, F.; Andrulli, S.; Logias, F.; Di Lullo, L.; Fiorini, F.; Granata, A. Indication to renal biopsy in DM2 patients: potential role of intrarenal resistive index. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2012, 84, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeller, T. Renal artery stenosis: epidemiology, clinical manifestation, and percutaneous endovascular therapy. J Interv Cardiol. 2005, 18, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutchley, T.A.; Pearce, J.D.; Craven, T.E.; Stafford, J.M.; Edwards, M.S.; Hansen, K.J. Clinical utility of the resistive index in atherosclerotic renovascular disease. J Vasc Surg. 2009, 49, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grupp, C.; Koziolek, M.J.; Wallbach, M.; Hoxhold, K.; Müller, G.A.; Bramlage, C. Difference between renal and splenic resistive index as a novel criterion in Doppler evaluation of renal artery stenosis. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018, 20, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radermacher, J.; Chavan, A.; Bleck, J.; Vitzhum, A.; Stoess, B.; Gebel, M.J. , Galanski, M.; Koch, K.M.; Haller, H. Use of Doppler ultrasonography to predict the outcome of therapy for renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2001, 344, 4104–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulez, G.; Therasse, E.; Qanadli, S.D.; Froment, D.; Léveillé, M.; Nicolet, V.; Turpin, S.; Giroux, M.F.; Guertin, M.C.; Oliva, V.L. Prediction of clinical response after renal angioplasty: respective value of renal Doppler sonography and scintigraphy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumme, B.; Hollenbeck, M. Doppler sonography in renal artery stenosis--does the resistive index predict the success of intervention? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007, 22, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.M.; Daghini, E.; Versari, D.; Sgrò, M.; Sanna, M.; Venturini, L.; Romanini, C.; Di Paco, I.; Sudano, I.; Cioni, R, Lerman, O. L.; Ghiadoni, L.; Taddei, S.; Pinto, S. Predictive role of renal resistive index for clinical outcome after revascularization in hypertensive patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis: a monocentric observational study. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2014, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radermacher, J.; Mengel, M.; Ellis, S.; Stuht, S.; Hiss, M.; Schwarz, A.; Eisenberger, U.; Burg, M.; Luft, F.C.; Gwinner, W.; Haller, H. The renal arterial resistance index and renal allograft survival. N Engl J Med. 2003, 349, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saracino, A.; Santarsia, G.; Latorraca, A.; Gaudiano, V. Early assessment of renal resistance index after kidney transplant can help predict long-term renal function. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006, 21, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, C.; Geddes, C.C.; Baxter, G.M. Early measurement of pulsatility and resistive indexes: correlation with long-term renal transplant function. Radiology. 2011, 259, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Rubin, J.M.; Xiang, D.Y.; He, W.; Auh, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Ng, A.; Min, R. Doppler parameters in renal transplant dysfunction: correlations with histopathologic changes. J Ultrasound Med. 2011, 30, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, S.; Colbus, S.M.; Lucisano, G.; Rogacev, K.S.; Gerhart, M.K.; Ziegler, M.; Fliser, D.; Heine, G.H. Ultrasound resistive index is not an organ-specific predictor of allograft outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012, 27, 3315–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesens, M.; Heylen, L.; Lerut, E.; Claes, K.; De Wever, L.; Claus, F.; Oyen, R.; Kuypers, D.; Evenepoel, P.; Bammens, B.; Sprangers, B.; Meijers, B.; Pirenne, J.; Monbaliu, D.; de Jonge, H.; Metalidis, C.; De Vusser, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y. Intrarenal resistive index after renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2013, 369, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.S.; He, W.J.; Shin, M.H.; Choi, N.K. Resistive index as a predictor of early failure of kidney transplantation. Korean J Transplant, 2019, 33, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freminville, J.B.; Vernier, L.M.; Roumy, J.; Patat, F.; Gatault, P.; Sautenet, B.; Barbet, C.; Longuet, H.; Merieau, E.; Buchler, M. Early changes in renal resistive index and mortality in diabetic and nondiabetic kidney transplant recipients: a cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumme, B.; Grotz, W.; Kirste, G.; Schollmeyer, P.; Rump, L.C. Determination of intrarenal Doppler indices in stable renal allografts. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997, 8, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, G.H.; Gerhart, M.K.; Ulrich, C.; Köhler, H.; Girndt, M. Renal Doppler resistance indices are associated with systemic atherosclerosis in kidney transplant recipients. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faubel, S.; Patel, N.U.; Lockhart, M.E.; Cadnapaphornchai, M.A. Renal relevant radiology: use of ultrasonography in patients with AKI. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014, 9, 382–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, J.F.; Rubin, J.M.; Ellis, J.H. Acute renal failure: possible role of duplex Doppler US in distinction between acute prerenal failure and acute tubular necrosis. Radiology, 1991, 179, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, M.; Sugiura, T.; Nakamura, H.; Nagatoya, K.; Imai, E.; Hori, M. Differential diagnosis of prerenal azotemia from acute tubular necrosis and prediction of recovery by Doppler ultrasound. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmon, M.; Schortgen, F.; Vargas, F.; Liazydi, A.; Schlemmer, B.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Brochard, L. Diagnostic accuracy of Doppler renal resistive index for reversibility of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninet, S.; Schnell, D.; Dewitte, A.; Zeni, F.; Meziani, F.; Darmonm, M. Doppler-based renal resistive index for prediction of renal dysfunction reversibility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crit Care. 2015, 30, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; He, C.; Jia, L.; Ge, C.; Long, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, N.; Du, K.; Q; Shen, L. ; Zhao, H. Performance of the renal resistive index and usual clinical indicators in predicting persistent AKI. Ren Fail, 2022, 44, 2038–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haitsma Mulier, J.L.G.; Rozemeijer, S.; Roèttgering, J.G.; Spoelstra-de Man, A.M.E.; Elbers, P.W.G.; Tuinman, P.R.; de Waard, M.; Oudemans-van Straaten, H.M. Renal resistive index as an early predictor and discriminator of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients; A prospective observational cohort study. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13, e0197967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerolle, N.; Guérot, E.; Faisy, C.; Bornstain, C.; Diehl, J.L.; Fagon, J.Y. Renal failure in septic shock: predictive value of Doppler-based renal arterial resistive index. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, D.; Deruddre, S.; Harrois, A.; Pottecher, J.; Cosson, C; Adoui, N. ; Benhamou, D.; Vicaut, E.; Azoulay, E.; Duranteau, J. Renal resistive index better predicts the occurrence of acute kidney injury than cystatin C. Shock, 2012, 38, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossard, G.; Bourgoin, P.; Corbeau, J.J.; Huntzinger, J.; Beydon, L. Early detection of postoperative acute kidney injury by Doppler renal resistive index in cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Br J Anaesth. 2011, 107, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peillex, M.; Marchandot, B.; Bayer, S.; Prinz, E.; Matsushita, K.; Carmona, A.; Heger, J.; Trimaille, A.; Petit-Eisenmann, H.; Jesel, L. Bedside renal doppler ultrasonography and acute kidney injury after TAVR. J Clin Med. 2020, 9, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoncini, G.; Martinoli, C.; Viazzi, F.; Ravera, M.; Parodi, D.; Ratto, E.; Vettoretti, S.; Tomolillo, C.; Derchi, L.E.; Deferrari, G.; Pontremoli, R. Changes in renal resistive index and urinary albumin excretion in hypertensive patients under long-term treatment with lisinopril or nifedipine GITS. Nephron. 2002, 90, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solini, A.; Gianinni, L.; Segheri, M.; Vitolo, E.; Taddei, S.; Ghiadoni, S.; Bruno, R.M. Dapagliflozin acutely improves endothelial dysfunction, reduces aortic stiffness and renal resistive index in type 2 diabetic patients: a pilot study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoud, F.; Cremers, B.; Janker, J.; Link, B.; Vonend, O.; Ukena, C.; Linz, D.; Schmieder, R.; Rump, L.C.; Kindermann, I.; Sobotka, P.A. ; Krum. H.; Scheller, B.; Schlaich, M.; Laufs, U.; Böhm, M. Renal hemodynamics and renal function after catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation in patients with resistant hypertension, Hypertension, 2012, 60, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Sveceny, J.; Charvat, J.; Hrach, K.; Horackova, M.; Schuck, O. In essential hypertension, a change in the renal resistive index is associated with a change in the ratio of 24-hour diastolic to systolic blood pressure. Physiol Res. 2022, 71, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddi, M. Renal ultrasound (and doppler sonography) in hypertension: an update. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017, 956, 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Woodard, T.; Sigurdsson, S.; Gotal, J.D.; Torjesen, A.A.; Inker, L.A.; Aspelund, T.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Gudnason, V.; Harris, T.B.; Launer, L.J.; Levey, A.S.; Mitchell, G.F. Mediation analysis of aortic stiffness and renal microvascular function. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitsumoto, T. Correlation between the cardio-ankle index and renal resistive index in patients with essential hypertension. Cardiol Res. 2020, 11, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.H.; Lee, M.C.; Kong, A.P.S.; Chen, L.; Chan, J.C.N.; Wing, Chu, W. C. Associations of renal augmented velocity index with arterial stiffness, carotid intima-media thickness and blood pressure, in comparison with renal resistive index. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021, 47, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chowienczyk, P.J.; Spector, T.D.; Jiang, B. Relation of arterial stiffness to left ventricular structure and function in healthy women. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2018, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quisi, A.; Harbalıoğlu, H.; Özel, M.A.; Alıcı, G.; Genç, Ö.; Kurt, I.H. The association between the renal resistive index and the myocardial performance index in the general population. Echocardiography. 2020, 37, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotruchin, P.; Hoshide, S.; Ueno, H.; Shimizu, H.; Komori, T.; Kario, K. Differential impact of the renal resistive index on future cardiovascular events in hospitalized atherosclerotic cardiovascular patients according to left ventricular ejection fraction - The Jichi vascular hemodynamics in hospitalized cardiovascular patients (J-VAS) study. Circ J. 2020, 84, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wybraniec, M.T.; Bożentowicz-Wikarek, M.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Chudek, J.; Mizia-Stec, K. Renal resistive index and long-term outcome in patients with coronary artery disease. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020, 20, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quisi, A.; Kurt, I.H.; Şahin, D.Y.; Kaypaklı, O.; Söker, G.; Kaya, Ö.; Allahverdiyev, S.; Genç, Ö.; Alıcı, G.; Koç, M. Evaluation of the relationship between renal resistive index and extent and complexity of coronary artery disease in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Kardiol Pol. 2017, 75, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, R.; Goffredo, G.; Di Terlizzi, V.; Alcidi, G.; Tabella, E.; Centola, A.; Campanale, G.; Ruggiero, A.; Cuculo, A.; Di Biase, M.; Brunetti, N.D.; Iacoviello, M. Renal resistance index independently predicts worsening of renal function after coronary angiography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023, 39, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wybraniec, M.T.; Bożentowicz-Wikarek, M.; Chudek, J.; Mizia-Stec, K. Pre-procedural renal resistive index accurately predicts contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients with preserved renal function submitted to coronary angiography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017, 33, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajal, K.; Chauhan, R.; Negi, S.L.; Gourav, K.P.; Panda, P.; Mahajan, S.; Sarna, R. Intraoperative evaluation of renal resistive index with transesophageal echocardiography for the assessment of acute renal injury in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery: A prospective observational study. Ann Card Anaesth. 2022, 25, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Gosling, A.F.; Andrew, B.Y.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Nicoara, A.; Cherry, A.D. Renal resistive index for prediction of acute kidney injury in the setting of aortic insufficiency. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2021, 35, 3819–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Ren, A.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, J. The correlations between intraoperative renal resistive index and cardiac surgery associated acute kidney injury- a pilot, prospective, observational, single center study. J Clin Anesth. 2020, 67, 110066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, I.; Persona, P.; Pivetta, E.; De Rosa, S.; Cescon, R.; Petranzan, E.; Antonello, M.; Grego, F.; Navalesi, P. Renal-resistive index and acute kidney injury in aortic surgery: an observational pilot study. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2022, 36, 2968–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, N.; Liu, J. The predictive value of the intraoperative renal pulsatility index for acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery, Minerva Anestesiol. 2020, 86, 1161–1169. 86.
- Gigante, A.; Perrotta, A.M.; De Marco, O.; Rosato, E.; Lai, S.; Cianci, R. Sonographic evaluation of hypertension: role of atrophic index and renal resistive index. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022, 24, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.; Coca, A.; De Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; Kahan, T.; Mahfoud, F.; Redon, J.; Ruilope, L.; Zanchetti, A.; Kerins, M.; Kjeldsen, S.; Kreutz, R.; Laurent, S.; Lip, G.Y.H.; McManus, R.; Narkiewicz, K.; Ruschitzka, F.; Schmieder, R.; Shlyakhto, E.; Tsioufis, K.; Aboyans, V.; Desormais, I. 2018 practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. Blood Press. 2018, 27, 314–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafori, M.; Rashedi,,A. ; Montazeri, M.; Amirkhanlou, S. The relationship between renal arterial resistive index (RRI) and renal outcomes in patients with resistant hypertension. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2020, 14, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lubas, A.; Kade, G.; Niemczyk, S. Renal resistive index as a marker of vascular damage in cardiovascular diseases. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014, 46, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusunoki, H.; Iwashima, Y.; Kawano, Y.; Ohta, Y.; Hayashi, S.I.; Horio, T.; Shinmura, K.; Ishimitsu, T.; Yoshihara, F. Associations between arterial stiffness indices and chronic kidney disease categories in essential hypertensive patients. Am J Hypertens. 2021, 34, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettehad, D.; Emdin, C.A.; Kiran, A.; Anderson, S.G.; Callender, T.; Emberson, J.; Chalmers, J.; Rodgers, A.; Rahimi, K. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016, 387, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, F.; Ranieri, A.; Siciliano, A.; Casillo, B.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Granato, C.; Cirillo, C.; Concilio, C.; Tedesco, M.A.; Calabrò, P.; Golino, P.; Russo, M.G.; Calabrò, R. Rapid ultrasound score as an indicator of atherosclerosis’ clinical manifestations in a population of hypertensive: the interrelationship between flow-mediated dilatation of brachial artery, carotid intima thickness, renal resistive index and retina resistive index of central artery. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2014, 14, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cilsal, E.; Koc, A.S. Renal resistive index significantly increased in hypertensive children and it is independently related to the pulse pressure and left ventricular mass index. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2019, 41, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Iwashima, Y.; Yoshihara, F.; Kamide, K.; Takata, H.; Fujii, T.; Kubota, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Horio, T.; Kawano, Y. Association of renal resistive index with target organ damage in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2012, 25, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvvula, A.; Jamthikar, A.D.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, N.N.; Porcu, M.; Saba, L.; Viskovic, K.; Ajuluchukwu, J.N.A.; Gupta, A.; Mavrogeni, S.; Turk, M.; Laird, J.R.; Pareek, G.; Miner, M.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Protogerou, A.; Kitas, G.D.; Nicolaides, A.; Viswanathan, V.; Suri, J.S. Morphological carotid plaque area is associated with glomerular filtration rate: a study of south asian indian patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Angiology. 2020, 71, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akal, A.; Ulas, T.; Goncu, T.; Karakas, E.; Karakas, O.; Kurnaz, F.; Boyaci, F.N.; Yilmaz, O.F.; Bata, A.; Yildiz, S. Evaluation of resistive index using color Doppler imaging of orbital arteries in geriatric patients with hypertension. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2014, 62, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomii, D.; Horiuchi, Y.; Gonda, Y.; Yoshiura, D.; Nakajima, M.; Sekiguchi, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Setoguchi, N.; Nakase, M.; Kikushima, H.; Ninomiya, K.; Tanaka, T.; Asami, M.; Yahagi, K.; Yuzawa, H.; Komiyama, K.; Tanaka, J.; Aoki, J.; Tanabe, K. The role of the renal resistance index in patients with heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction. J Cardiol. 2021, 78, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, M.I.; Parisi, G.; Grande, D.; Albanese, M.; Alcidi, G.; Correale, M.; Brunetti, N.D.; Ciccone, M.M.; Iacoviello, M. Effects of sacubitril/valsartan on the renal resistance index. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Saito, Y.; Ikeya, Y.; Nakai, T.; Arima, K. Association of renal resistance index and arterial stiffness on clinical outcomes in patients with mild-to-moderate renal dysfunction and presence or absence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Heart Vessels. 2020, 35, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, A.; Said, K.; Ammar, W.; Eltawil, A.E.; Abdelhamid, M. New renal haemodynamic indices can predict worsening of renal function in acute decompensated heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 2581–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X. , Zhen J., Meng Q., Li L., Yan J. Intrarenal Doppler approaches in hemodynamics: a major application in critical care. Front Physiol. 2022, 13, 951307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallbach, M.; Valentova, M.; Schroeter, M.R.; Alkabariti, A.; Iraki, I.; Leha, A.; Tampe, D.; Hasenfuß, G.; Zeisberg, M.; Hellenkamp, K.; Koziolek, M.J. Intrarenal Doppler ultrasonography in patients with HFrEF and acute decompensated heart failure undergoing recompensation. Clin Res Cardiol. 2023 Mar 25. Online ahead of print. [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Farmakis, D.; Gilard, M.; Heymans, S.; Hoes, A.W.; Jaarsma, T.; Jankowska, E.A.; Lainscak, M.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lyon, A.R.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Mebazaa, A.; Mindham, R.; Muneretto, C.; Francesco Piepoli, M.; Price, S.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Ruschitzka, F.; Kathrine Skibelund, A.; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 4–131. [Google Scholar]
- Elkazzaz, S.K.; Khodeer, D.M.; El Fayoumi, H.M.; Moustafa, Y.M. Role of sodium glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors dapagliflozin on diabetic nephropathy in rats; Inflammation, angiogenesis and apoptosis. Life Sci. 2021, 280, 119018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Abeysekera, K.W.M.; Howe, L.D.; Hughes, A.D.; Fraser, A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver and fibrosis is associated with cardiovascular structure and function in young adults. Hepatol Commun. 2023, 7, e0087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Y.; Uslu, A.U.; Tarhan, G.; Tiryaki, Ş. Renal artery resistive index and estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Med Imaging. 2022, 18, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, D.; Sen Sarma, M.; Yachha, S.K.; Prasad, R.; Srivastava, A.; Poddar, U.; Kumar, A. Can we predict early renal impairment in pediatric cirrhosis? Indian J Gastroenterol. 2022, 41, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onwuka, C.C.; Ayoola, O.O.; Adekanle, O.; Famurewa, O.C.; Abidoye, I.A. Renal arterial resistance index among subjects with liver cirrhosis in a Nigerian population. J Clin Ultrasound. 2021, 49, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Jain, S.; Sharma, C.R.; Mishra, D.; Rathi, M.; Prakash, M.; Jain, S. Prognostic role of measurement of renal resistive index in systemic sclerosis. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2021, 32, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leodori, G.; Pellicano, C.; Gigante, A.; Rosato, E. Estimated glomerular filtration rate and renal resistive index as possible predictive markers of mortality in systemic sclerosis. Eur J Intern Med. 2021, 87, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cafarotti, A.; Marcovecchio, M.L.; Lapergola, G.; Di Battista, C.; Marsili, M.; Basilico, R.; Di Donato, G.; David, D.; Pelliccia, P.; Chiarelli, F.; Breda, L. Kidney function and renal resistive index in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Exp Med. 2022 Sep 21. Online ahead of print. [CrossRef]
- Märker-Hermann, E. Renal manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis and spondylarthritis. Z Rheumatol. 2022, 8, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalesso, F.; Rigato, M.; Cirella, I.; Protti, M.P.; Zanella, R.; Rossi, B.; Putti, M.C.; Martino, F.K.; Calò, L.A. The assessment of renal functional reserve in β-thalassemia major patients by an innovative ultrasound and Doppler technique: a pilot study. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basut, F.; Keşkek, Ş.Ö.; Gülek, B. better renal resistive index profile in subjects with beta thalassemia minor. Med Princ Pract. 2018, 27, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).